Distribution Characteristics and Enrichment Mechanisms of Fluoride in Alluvial–Lacustrine Facies Clayey Sediments in the Land Subsidence Area of Cangzhou Plain, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.3.1. Sediment Samples
2.3.2. Clay Porewater and Groundwater Samples
3. Results
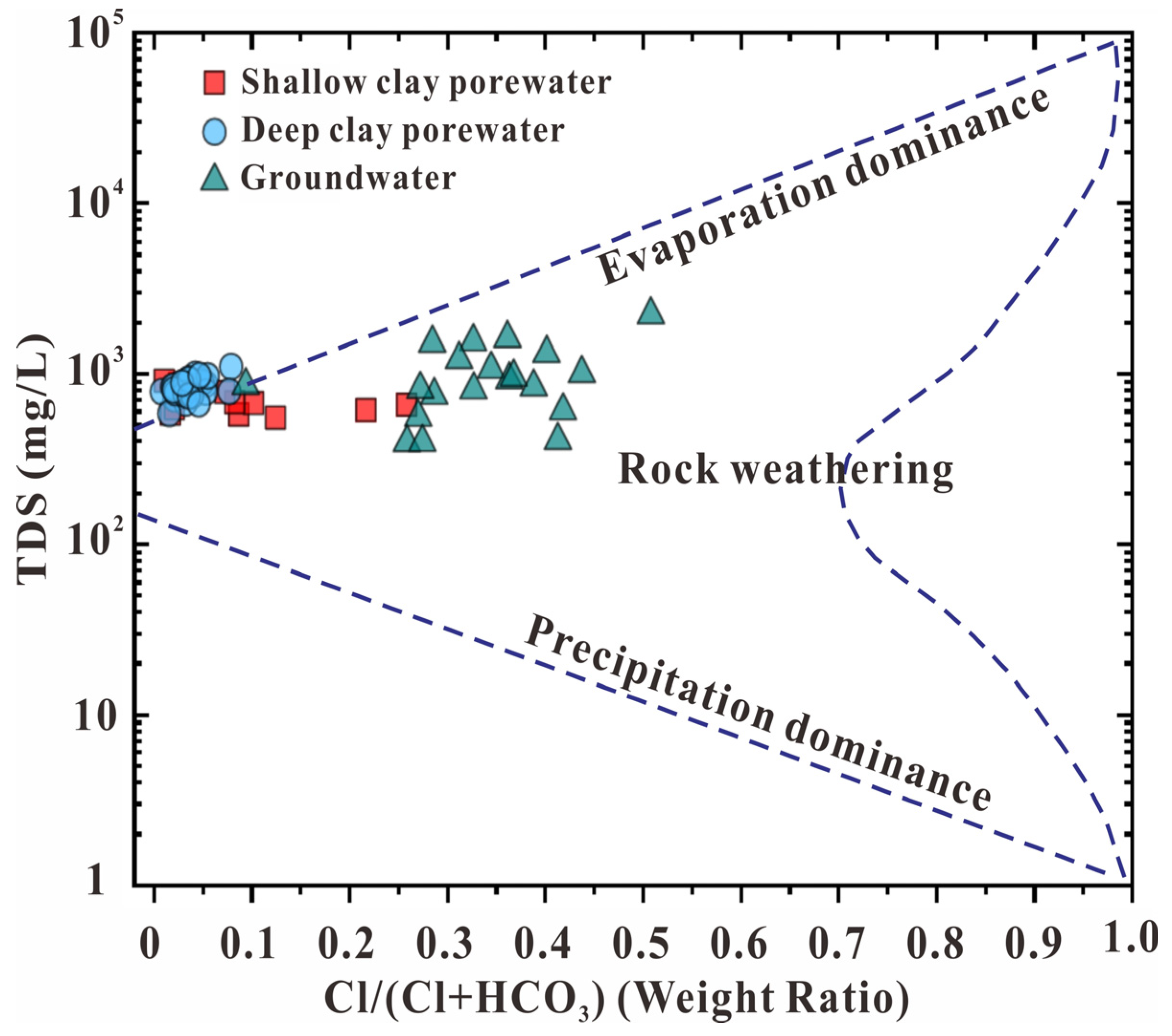
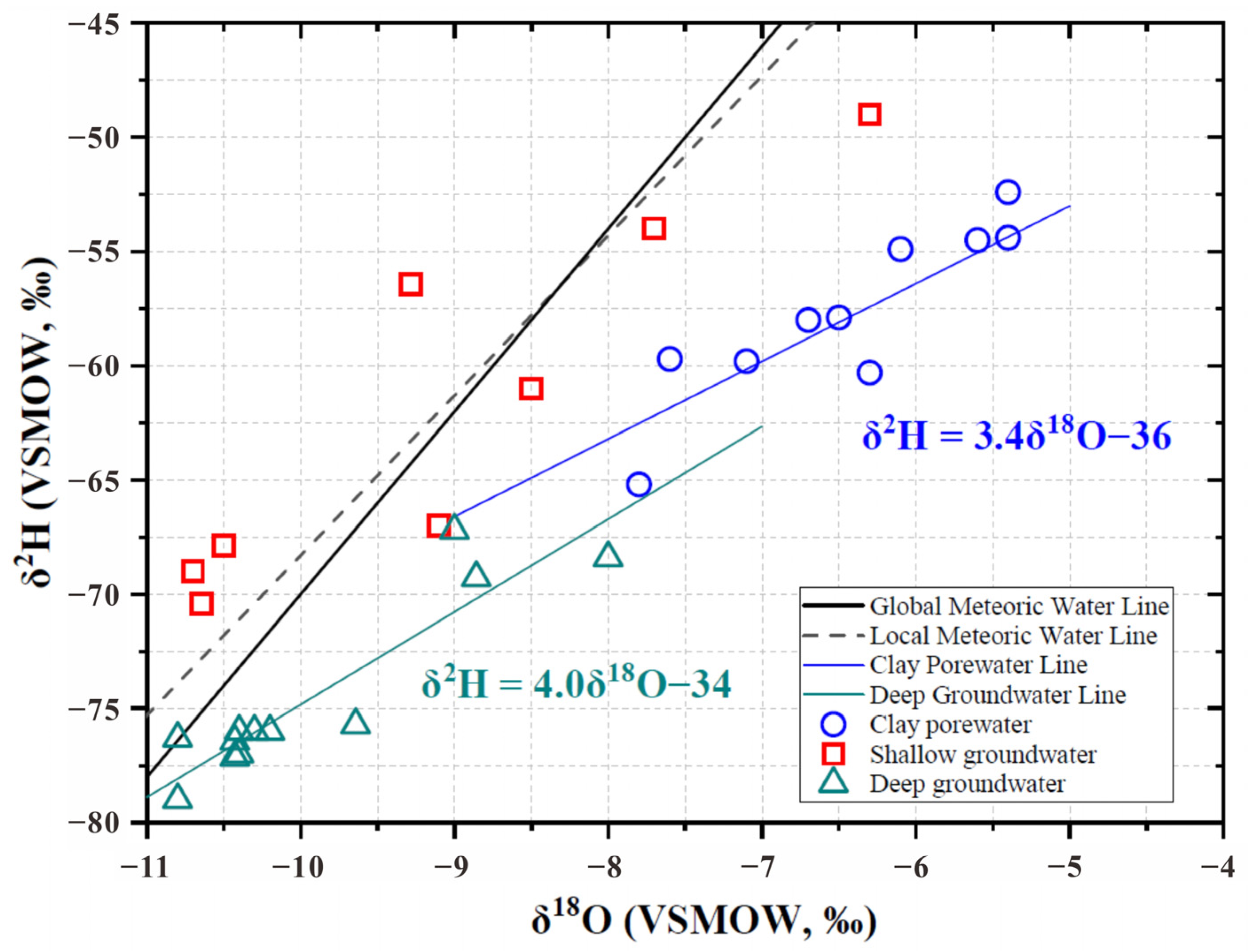
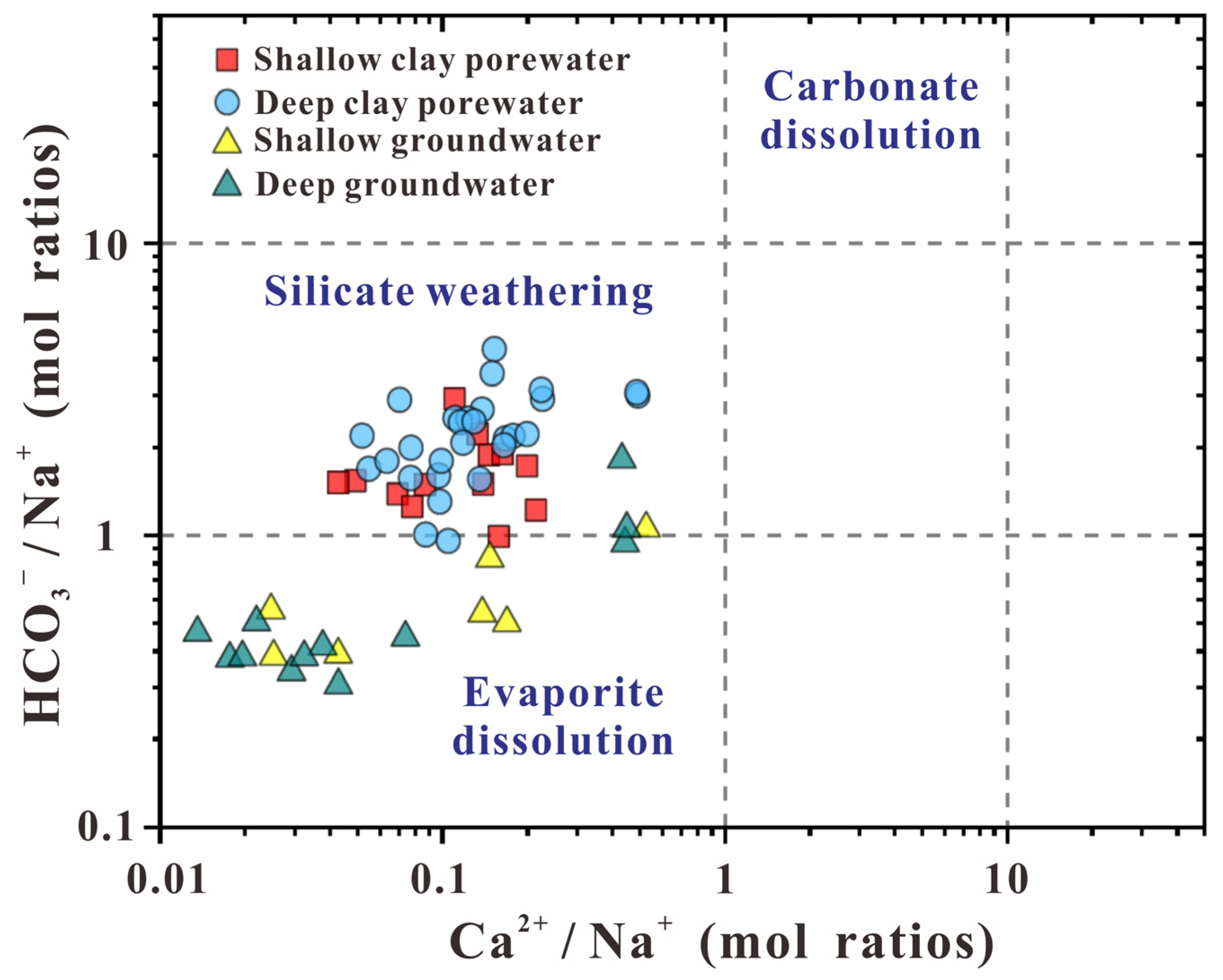
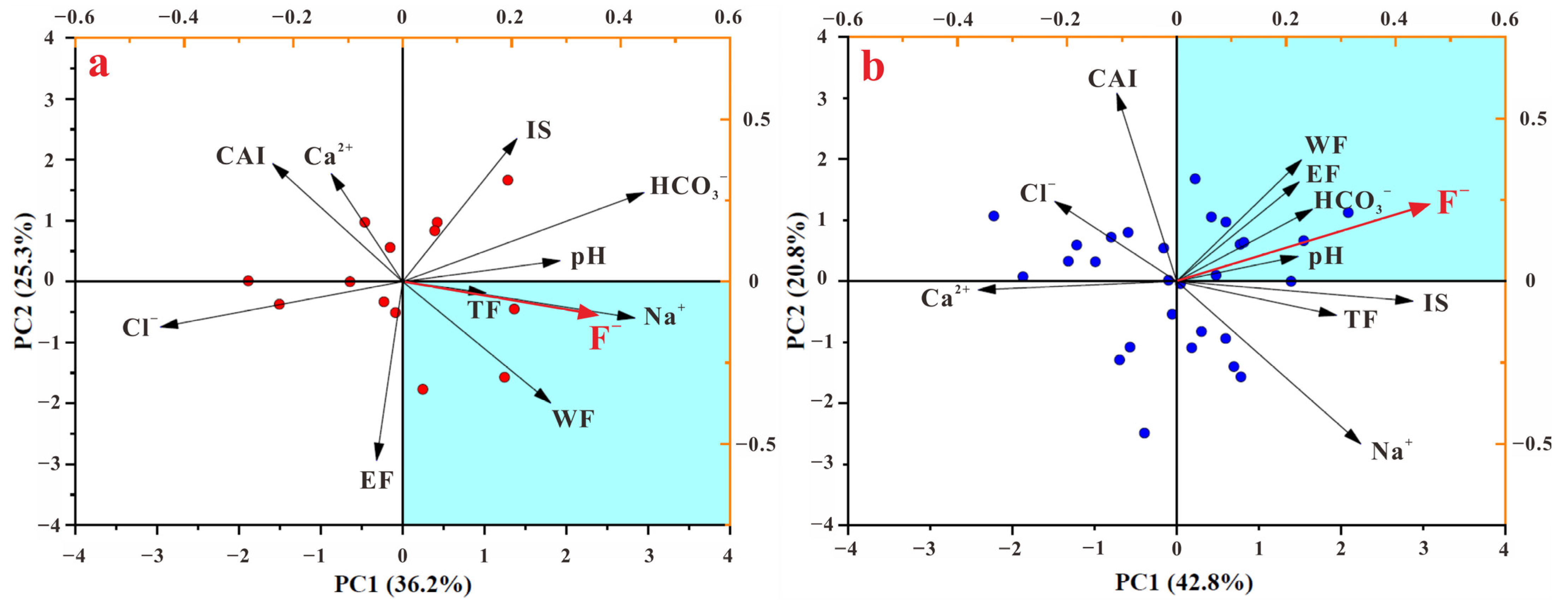
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Clay Porewater and Groundwater Samples
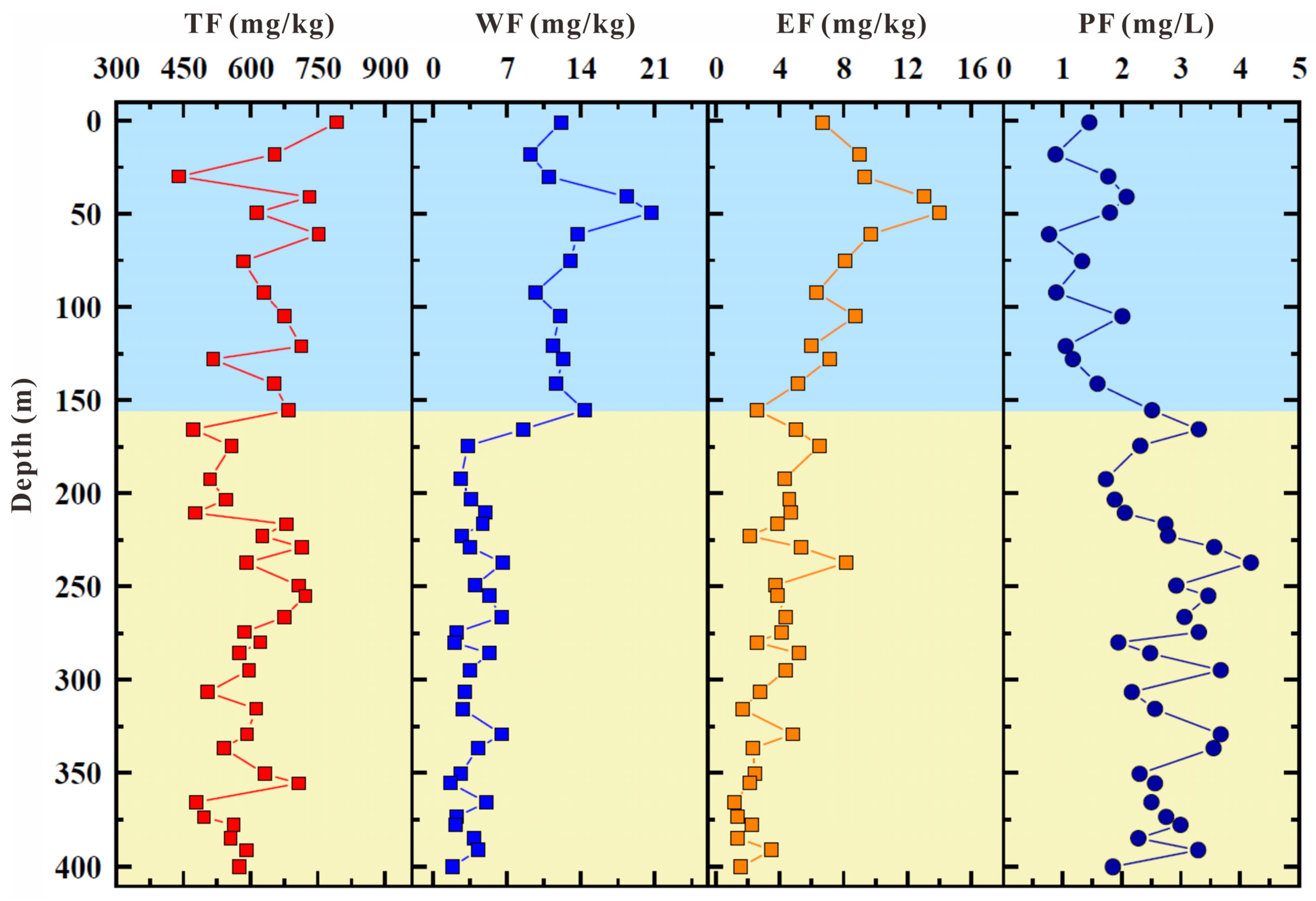
3.2. Variation in Clayey Sediment Fluoride Levels from Borehole
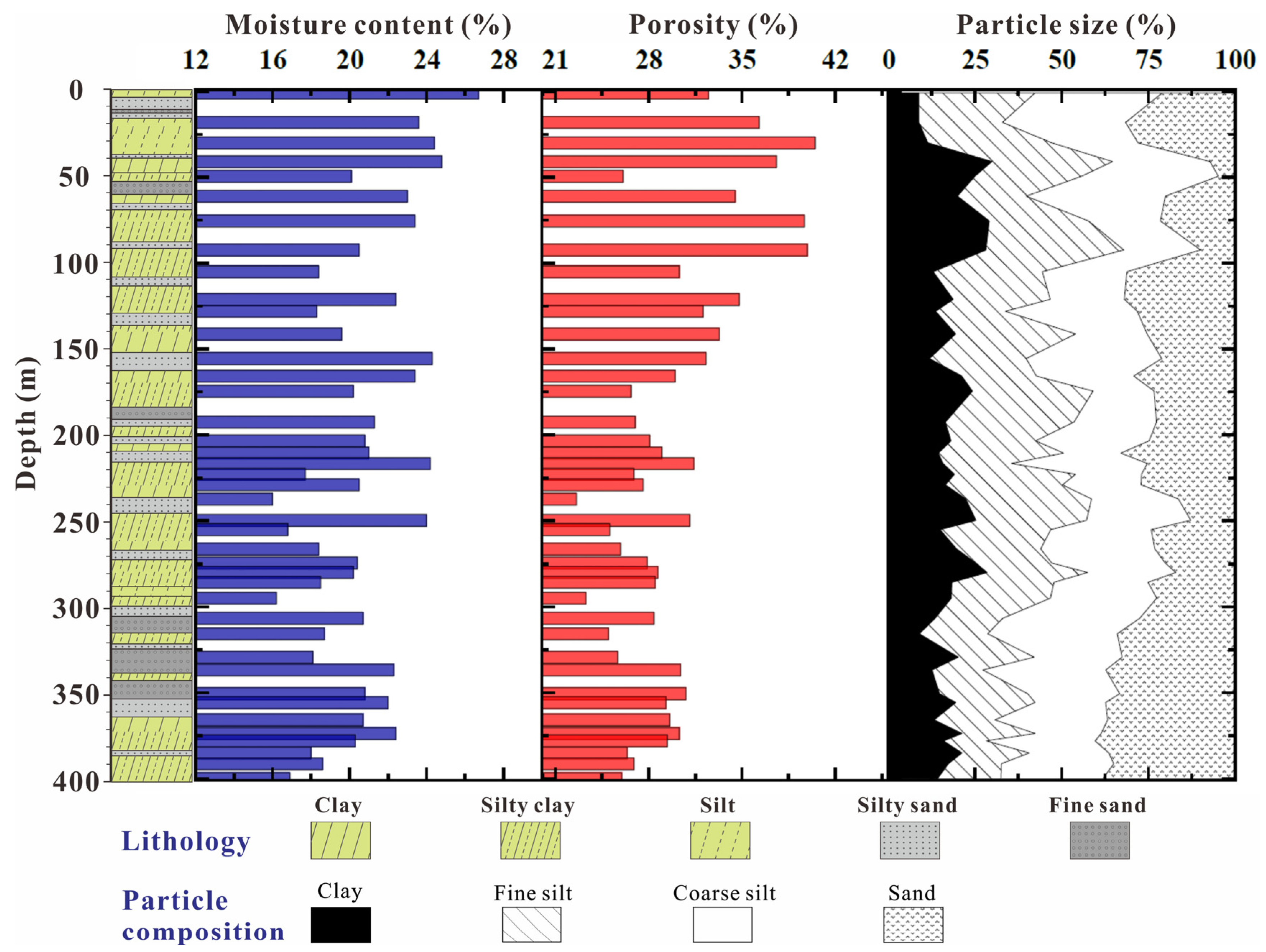
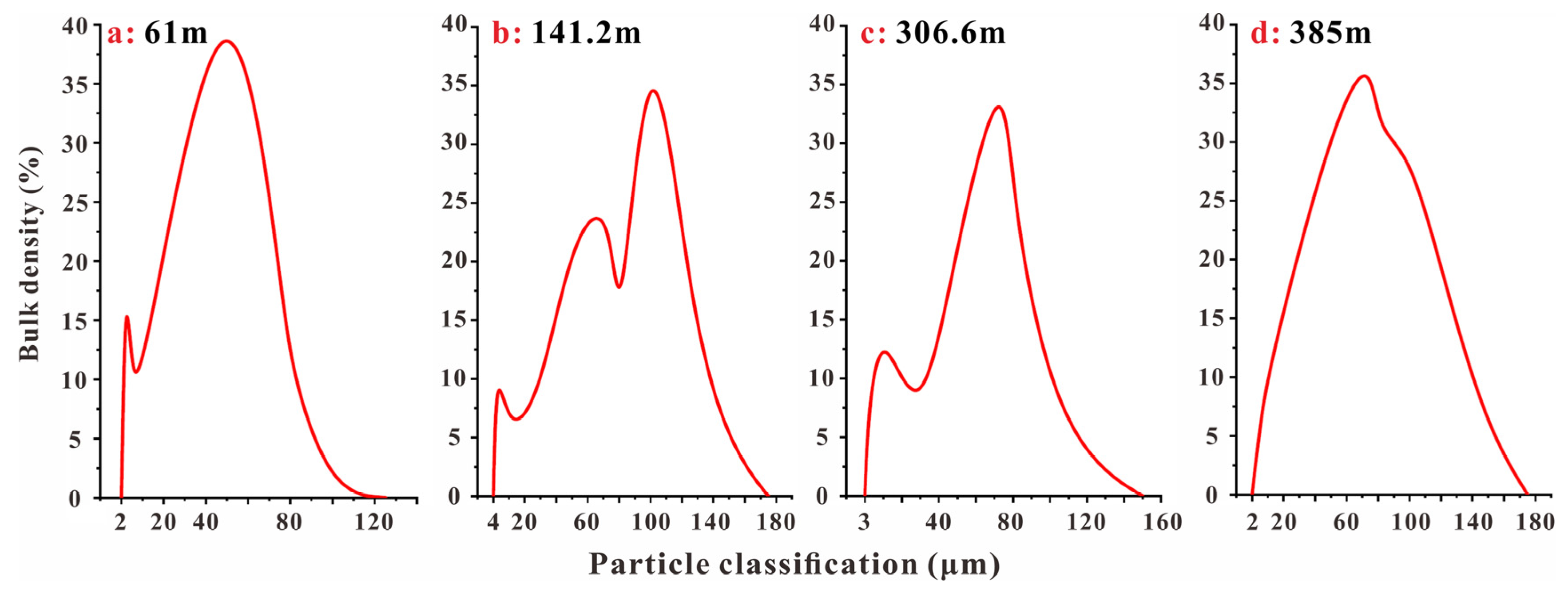
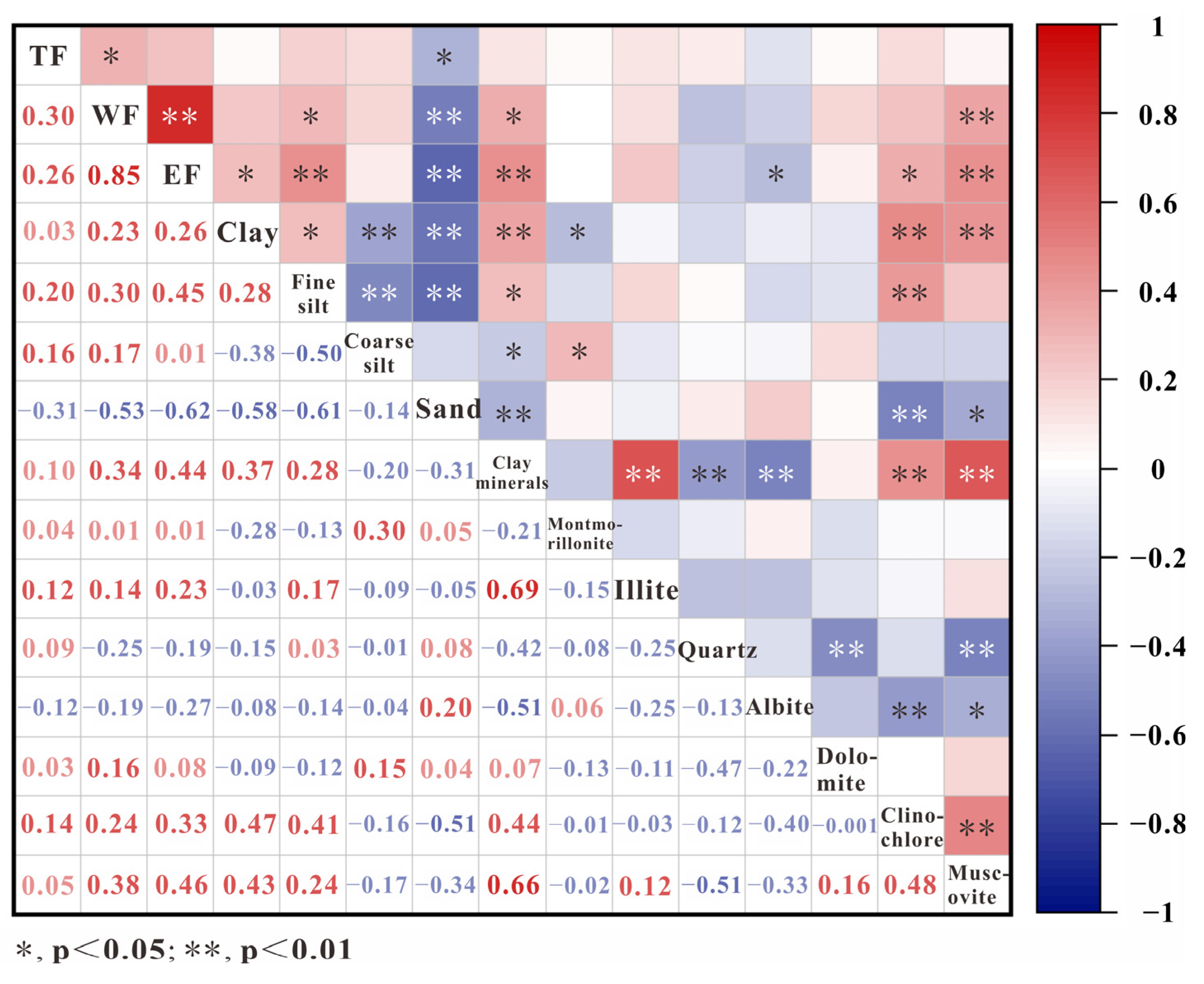
3.3. Physical and Chemical Composition of Borehole Samples
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydraulic Connection Between Clay Layer and Aquifer
4.2. Occurrence Forms of F in Sediments Under Different Sedimentary Environments
4.3. Transformation Mechanisms of Clayey Sediment F into Porewater
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukherjee, A.; Coomar, P.; Sarkar, S.; Johannesson, K.H.; Fryar, A.E.; Schreiber, M.E.; Ahmed, K.M.; Alam, M.A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Bundschuh, J.; et al. Arsenic and other geogenic contaminants in global groundwater. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iamandii, I.; De Pasquale, L.; Giannone, M.E.; Veneri, F.; Generali, L.; Consolo, U.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Castenmiller, J.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Filippini, T.; et al. Does fluoride exposure affect thyroid function? A systematic review and dose–response meta–analysis. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahman, K.D.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Naseem, S.; Arain, S.S.; Ullah, N. Evaluation of high levels of fluoride, arsenic species and other physicochemical parameters in underground water of two sub districts of Tharparkar, Pakistan, a multivariate study. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batabyal, A.K.; Gupta, S. Fluoride–contaminated groundwater of Birbhum district, West Bengal, India, Interpretation of drinking and irrigation suitability and major geochemical processes using principal component analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J.; Guo, H. Controls on distributions of sulphate, fluoride, and salinity in aquitard porewater from the North China Plain, Long–term implications for groundwater quality. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Bodrud–Doza, M.; Siddiqua, M.T.; Zahid, A.; Islam, A.R.M.T. Spatiotemporal distribution of fluoride in drinking water and associated probabilistic human health risk appraisal in the coastal region, Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yan, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Schmidt–Vogt, D.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J. Spatial distribution and temporal variation of high F contents in groundwater and prevalence of fluorosis in humans in Yuanmou County, Southwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, C.; Hu, B.; Chang, W.; Wu, G.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Q. Enrichment mechanism of fluoride and iodine in saline groundwater in the lower flood plain of the Yellow River, northern China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, D.; Donn, M.; Atteia, O.; Sun, J.; MacRae, C.; Raven, M.; Pejcic, B.; Prommer, H. Fluoride and phosphate release from carbonate–rich fluorapatite during managed aquifer recharge. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, C.; Zhao, W.; Han, Z. Characteristics and driving factors of fluoride in groundwater in different urban functional area of Lanzhou city. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2024, 51, 215–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, W.; Cao, W.; Gao, Z.; Pan, D.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. Contrasting behaviors of groundwater arsenic and fluoride in the lower reaches of the Yellow River basin, China, Geochemical and modeling evidences. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, K.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Su, C.; Ma, T.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Hydrogeochemistry of co–occurring geogenic arsenic, fluoride and iodine in groundwater at Datong Basin, northern China. J. Hazard Mater. 2015, 300, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, K.; Hao, Q.; Li, Y.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence, controlling factors and health hazards of fluoride–enriched groundwater in the lower flood plain of Yellow River, Northern China. Expos. Health 2022, 14, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Bhattacharya, P. Fluoride in the environment, sources, distribution and defluoridation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Xue, Y.; Wu, J.; Yan, X.; Yu, J. Progression and mitigation of land subsidence in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 24, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, H.; Li, W.; Tian, X. Relationship between land subsidence and deep groundwater yield in the North China Plain. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 165–169, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, R. Distribution Characteristics and Source of Fluoride in Groundwater in Lower Plain Area of North China Plain, A Case Study in Nanpi County. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 4051–4059, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xue, X.; Qian, K.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y. Hydrogeochemical processes controlling the mobilization and enrichment of fluoride in groundwater of the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bian, Y. Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2021, 48, 162–171. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Xie, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Hydrogeochemical analysis and paleo-hydrogeological modeling of shallow groundwater salinization processes in North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2025, 651, 132616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Peng, F.; Pang, Q.; He, F.; Xu, B. Distribution, occurrence mechanisms, and management of high F levels in the water, sediment, and soil of Shahu Lake. China Appl. Geochem. 2021, 126, 104869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Das, A.; Joardar, M.; Mridha, D.; Majumdar, A.; Das, J.; Roychowdhury, T. Investigating spatial distribution of fluoride in groundwater with respect to hydro–geochemical characteristics and associated probabilistic health risk in Baruipur block of West Bengal. India Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 886, 163877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Guo, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Zang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Effect of clayey sediment compaction on fluoride enrichment in the Quaternary groundwater system of Cangzhou Plain, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Ma, T.; Du, Y.; Yu, H.; Shen, S. Arsenic releasing characteristics during the compaction of muddy sediments. Environ. Sci.–Proc. Imp. 2016, 18, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, S.; Jia, Q.; Lu, W.; Huang, Y.; Ni, G. Accumulation of high concentration fluoride in the Ulungur Lake water through weathering of fluoride containing rocks in Xinjiang. China Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xie, X. Evolution of groundwater salinity and fluoride in the deep confined aquifers of Cangzhou in the North China plain after the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 147, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Qian, K.; Wang, Y. Impacts of sediment compaction on iodine enrichment in deep aquifers of the North China Plain. Water Res. 2019, 159, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, H.; Cui, D.; Ji, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Jing, H.; Lu, A. Mineralogical and hydrogeochemical insights into the distribution and source of groundwater fluoride in the southern Beijing plain. J. Hydrol. 2025, 652, 132660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Xue, Y.; Ren, F.; Shi, D.; Yin, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, C. Evolution of Groundwater Environment in North China Plain; China Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Devriendt, L.S.; Watkins, J.M.; McGregor, H.V. Oxygen isotope fractionation in the CaCO3-DIC-H2O system. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 214, 115–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Ni, P.; Liang, X. Occurrence and formation of high fluoride groundwater in the Hengshui area of the North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, T.; Zhang, D.; Lin, C.; Chen, J. Spatial distribution and factors influencing the different forms of ammonium in sediments and pore water of the aquitard along the Tongshun River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Wen, R. Spatial patterns of vegetation and climate in the North China Plain during the Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene climatic optimum. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qian, K.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X. Iodine speciation and its potential influence on iodine enrichment in groundwater from North China plain. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 17, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Han, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, D. Natural and anthropogenic factors regulating fluoride enrichment in groundwater of the Nansi Lake Basin. North. China Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Kumari, R.; Singh, N.; Mallick, J.; Mukherjee, S. Fluoride enrichment in aquifers of the Thar Desert, controlling factors and its geochemical modelling. Hydrol. Process 2013, 27, 2462–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global analysis and prediction of fluoride in groundwater. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Kang, W.; Kang, N.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Hydrogeochemistry and health hazards of fluoride-enriched groundwater in the Tarim Basin. China Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbandi, R.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B. Geochemical sources, hydrogeochemical behavior, and health risk assessment of fluoride in an endemic fluorosis area, central Iran. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garand, A.; Mucci, A. The solubility of fluorite as a function of ionic strength and solution composition at 25 degrees C and 1 atm total pressure. Mar. Chem. 2004, 91, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, T.; Chen, J. Releasing mechanism of ammonium during clayey sediments compaction and its impact on groundwater environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
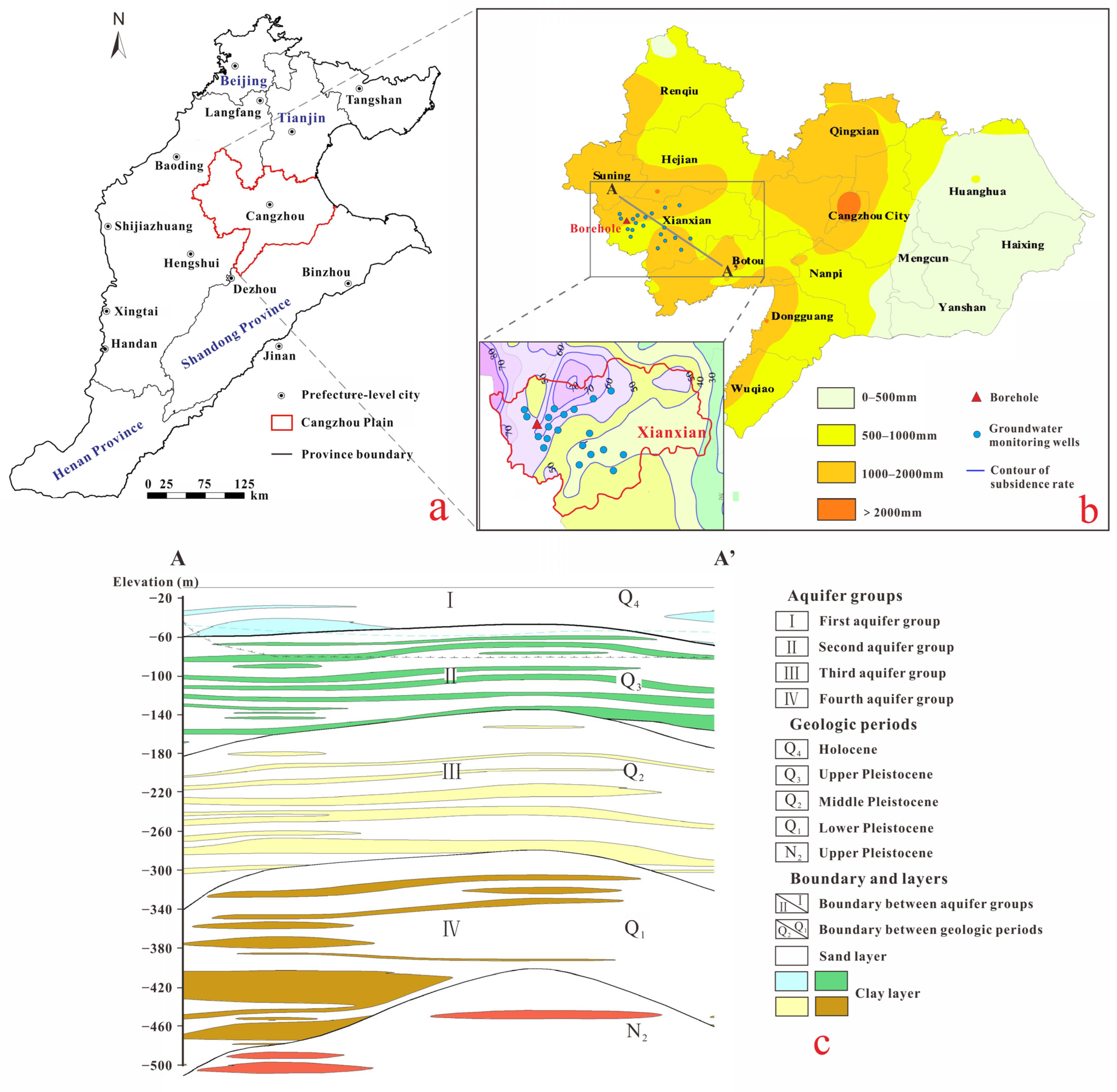
| Aquifer | Lower Boundary Depth | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Aquifer I | −20~−60 m | Composed of fluvial–deltaic deposits that span the Holocene lower boundary and the Late Pleistocene upper boundary. |
| Aquifer II | −120~−180 m | Formed during the Late Pleistocene and is primarily composed of fluvial deposits interspersed with marine sediments. |
| Aquifer III | −250~−350 m | Formed during the Middle Pleistocene and is primarily composed of alluvial–lacustrine deposits. |
| Aquifer IV | −350~−550 m | Formed during the Early Pleistocene, consisting primarily of terrestrial sediments originated from river bends and floodplains. |
| Shallow Groundwater Samples | Deep Groundwater Samples | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | |
| K+ (mg/L) | 0.19 | 2.6 | 0.77 | 0.15 | 12.2 | 1.5 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 96.2 | 517 | 329.8 | 41.8 | 359 | 210.9 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 3.13 | 149 | 62.02 | 6.51 | 202 | 37.92 |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 1.87 | 177 | 77.52 | 1.3 | 180 | 23.3 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 79.3 | 512 | 295.7 | 20.8 | 506 | 151.8 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 112 | 743 | 290.2 | 25 | 558 | 161.7 |
| HCO3− (mg/L) | 175 | 974 | 499.4 | 130 | 651 | 293.3 |
| CO32− (mg/L) | 0 | 30.4 | 4.6 | 0 | 18.2 | 5.9 |
| F− (mg/L) | 0.31 | 1.6 | 0.86 | 0.2 | 5.54 | 1.92 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 841 | 2220 | 1419 | 395 | 960 | 707 |
| pH | 7.18 | 9.36 | 7.87 | 6.93 | 8.57 | 8.04 |
| Eh (mV) | −84.3 | −11.5 | −44.2 | −82.8 | 2.4 | −36.6 |
| CAI | −0.69 | 0.08 | −0.35 | −0.35 | −0.35 | −0.35 |
| Shallow Clay Porewater Samples | Deep Clay Porewater Samples | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | |
| K+ (mg/L) | 2.39 | 15.6 | 7.6 | 1.6 | 8.7 | 4.0 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 44.6 | 89.4 | 63.9 | 34.8 | 102 | 66.2 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 5.08 | 21.6 | 13.35 | 7.08 | 33.16 | 15.02 |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 6.12 | 20.4 | 12.45 | 8.4 | 30.4 | 16.9 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 4.1 | 42 | 19.3 | 3.0 | 26.4 | 13.2 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 7.6 | 23.9 | 15.5 | 4.6 | 20.9 | 14.3 |
| HCO3− (mg/L) | 120.6 | 521 | 283.8 | 256 | 540 | 367.8 |
| CO32− (mg/L) | 0 | 10.6 | 4.5 | 9 | 88 | 33.8 |
| F− (mg/L) | 0.77 | 2.51 | 1.48 | 1.73 | 4.18 | 2.77 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 554 | 914 | 700 | 587 | 1104 | 836.3 |
| pH | 7.63 | 9.01 | 8.42 | 8.11 | 9.19 | 8.69 |
| Eh (mV) | −119.3 | −51.7 | −96.2 | −143.7 | −81.4 | −120 |
| CAI | −0.65 | −0.30 | −0.49 | −0.91 | −0.15 | −0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Liu, R.; Guo, H.; Chen, J.; Ning, D.; Zang, X. Distribution Characteristics and Enrichment Mechanisms of Fluoride in Alluvial–Lacustrine Facies Clayey Sediments in the Land Subsidence Area of Cangzhou Plain, China. Water 2025, 17, 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192887
Zhu J, Liu R, Guo H, Chen J, Ning D, Zang X. Distribution Characteristics and Enrichment Mechanisms of Fluoride in Alluvial–Lacustrine Facies Clayey Sediments in the Land Subsidence Area of Cangzhou Plain, China. Water. 2025; 17(19):2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192887
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Juyan, Rui Liu, Haipeng Guo, Juan Chen, Di Ning, and Xisheng Zang. 2025. "Distribution Characteristics and Enrichment Mechanisms of Fluoride in Alluvial–Lacustrine Facies Clayey Sediments in the Land Subsidence Area of Cangzhou Plain, China" Water 17, no. 19: 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192887
APA StyleZhu, J., Liu, R., Guo, H., Chen, J., Ning, D., & Zang, X. (2025). Distribution Characteristics and Enrichment Mechanisms of Fluoride in Alluvial–Lacustrine Facies Clayey Sediments in the Land Subsidence Area of Cangzhou Plain, China. Water, 17(19), 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192887







