Nutrient Distribution Characteristics and Eutrophication Evaluation of Coastal Water near the Yellow River Estuary, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
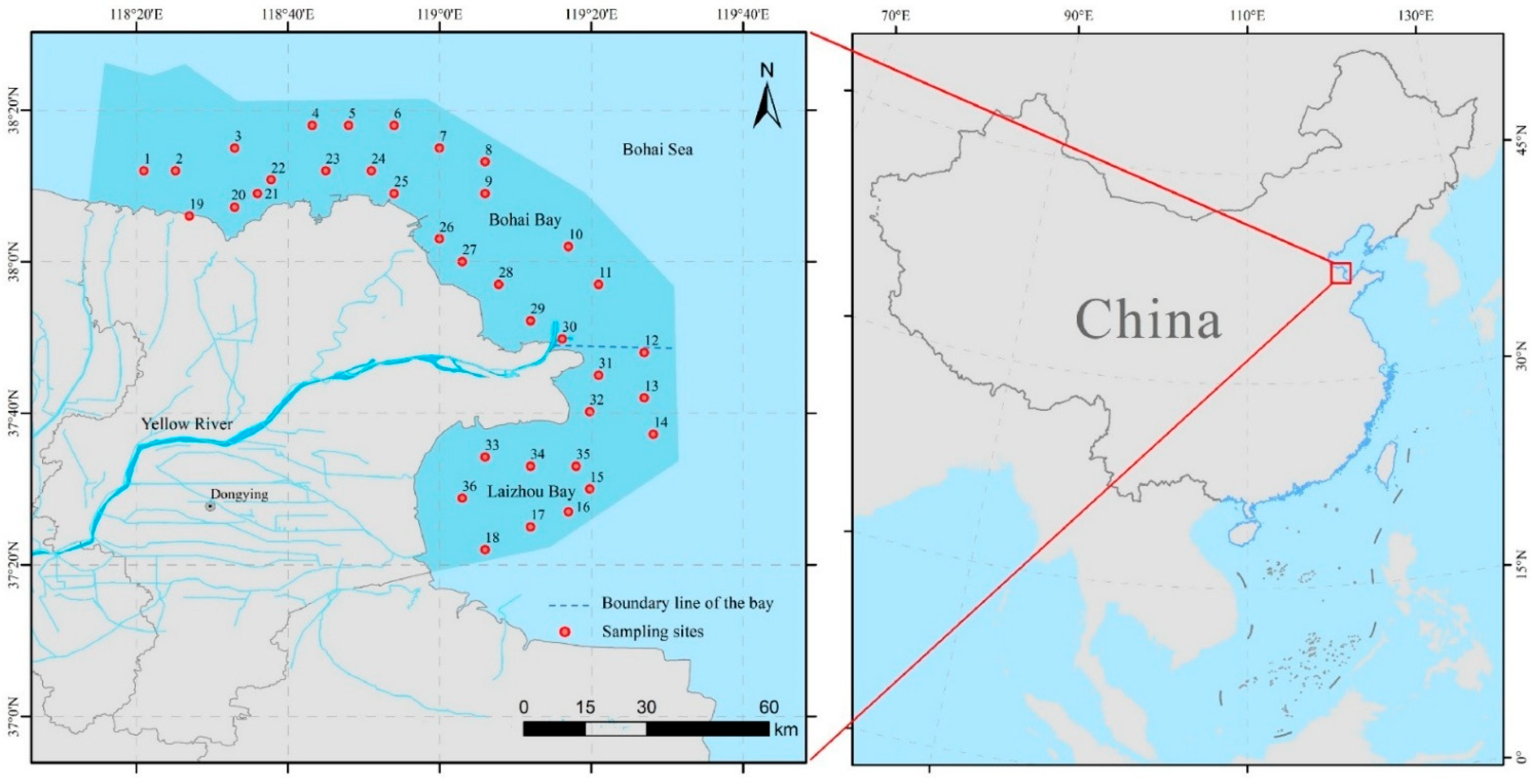
2.1. Study Area
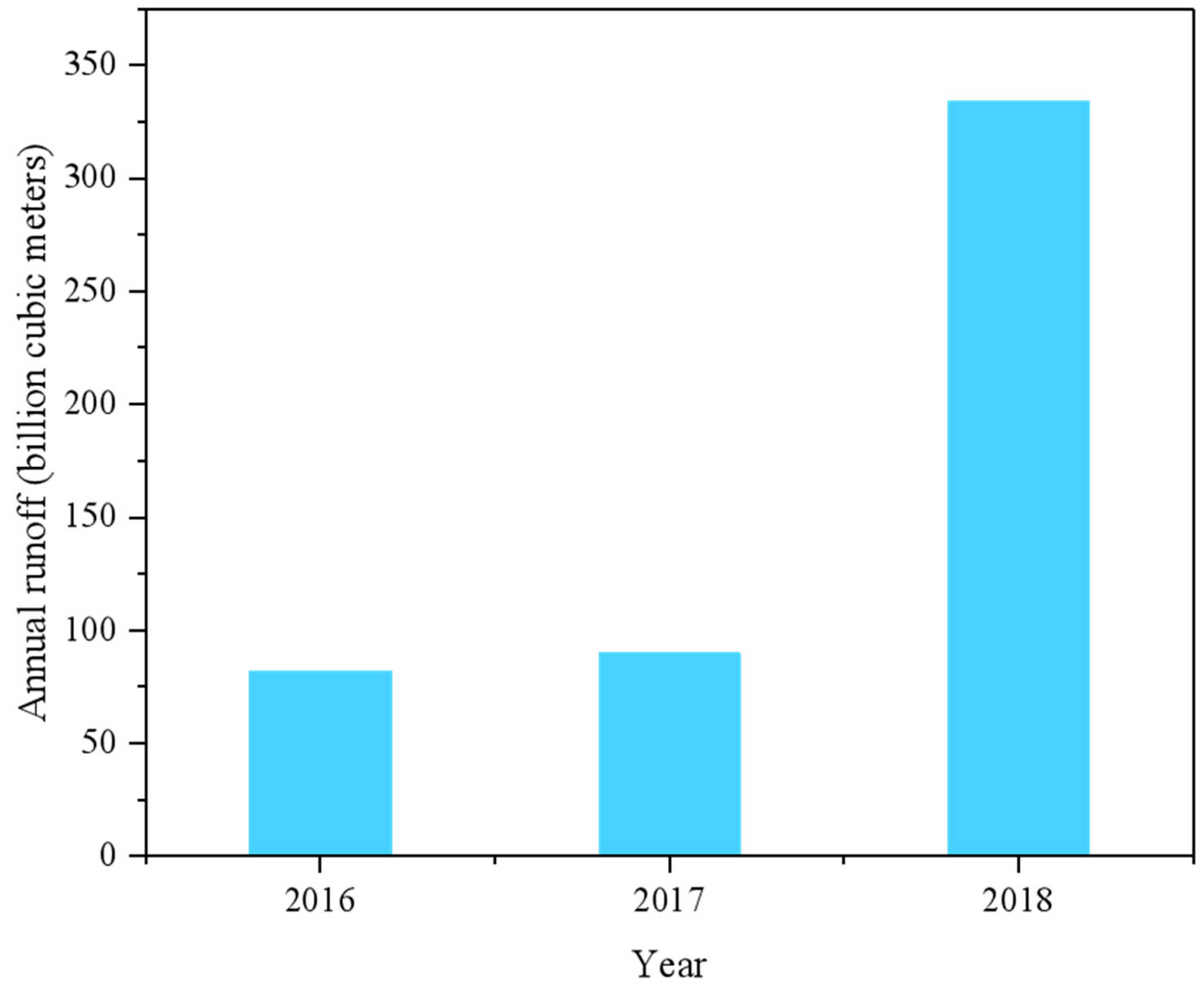
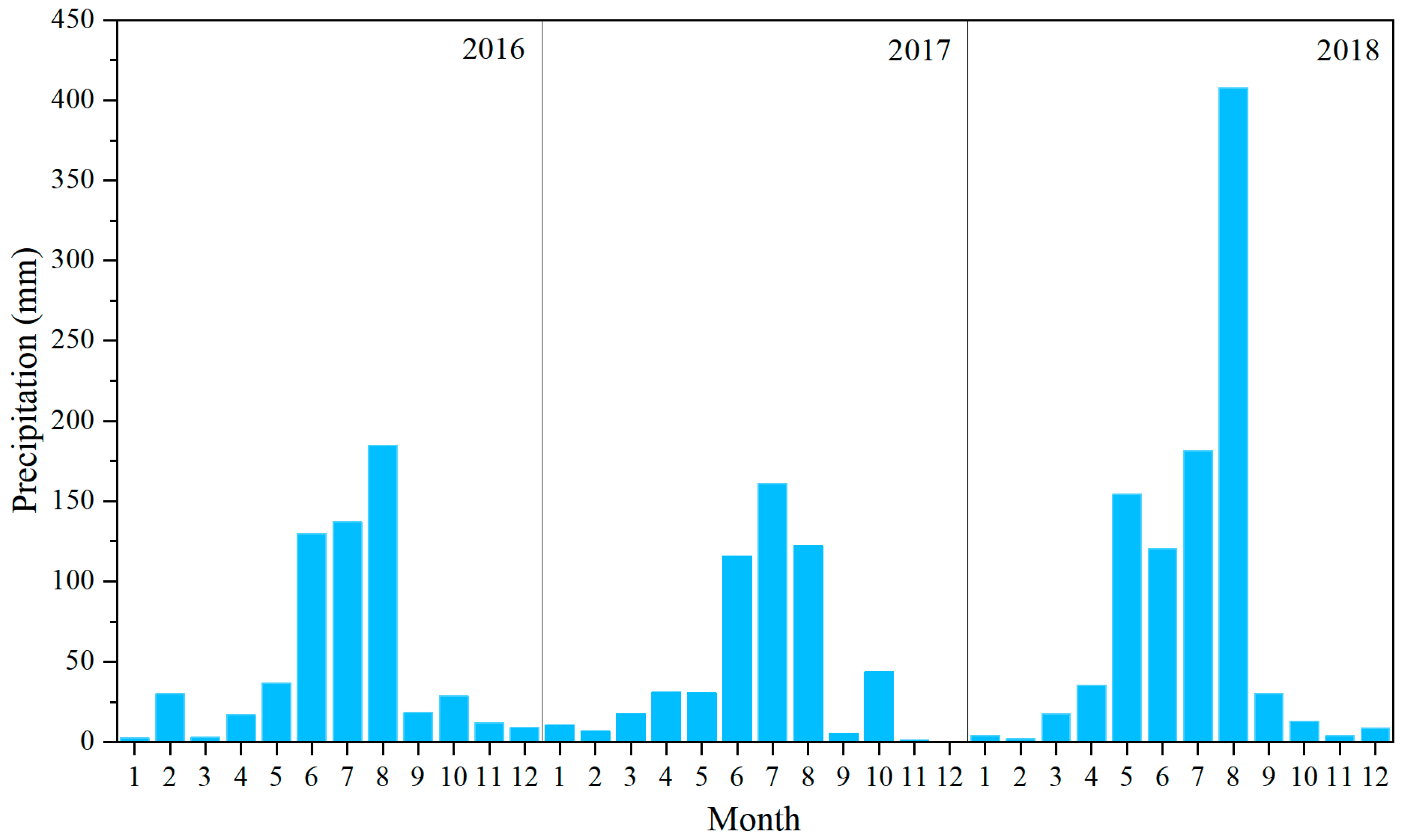
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Seawater Eutrophication Evaluation
2.3.1. Eutrophication Index Evaluation Method
2.3.2. Potential Eutrophication Evaluation Method
2.3.3. Identification of Nutrient-Limiting Factors
3. Results and Discussion
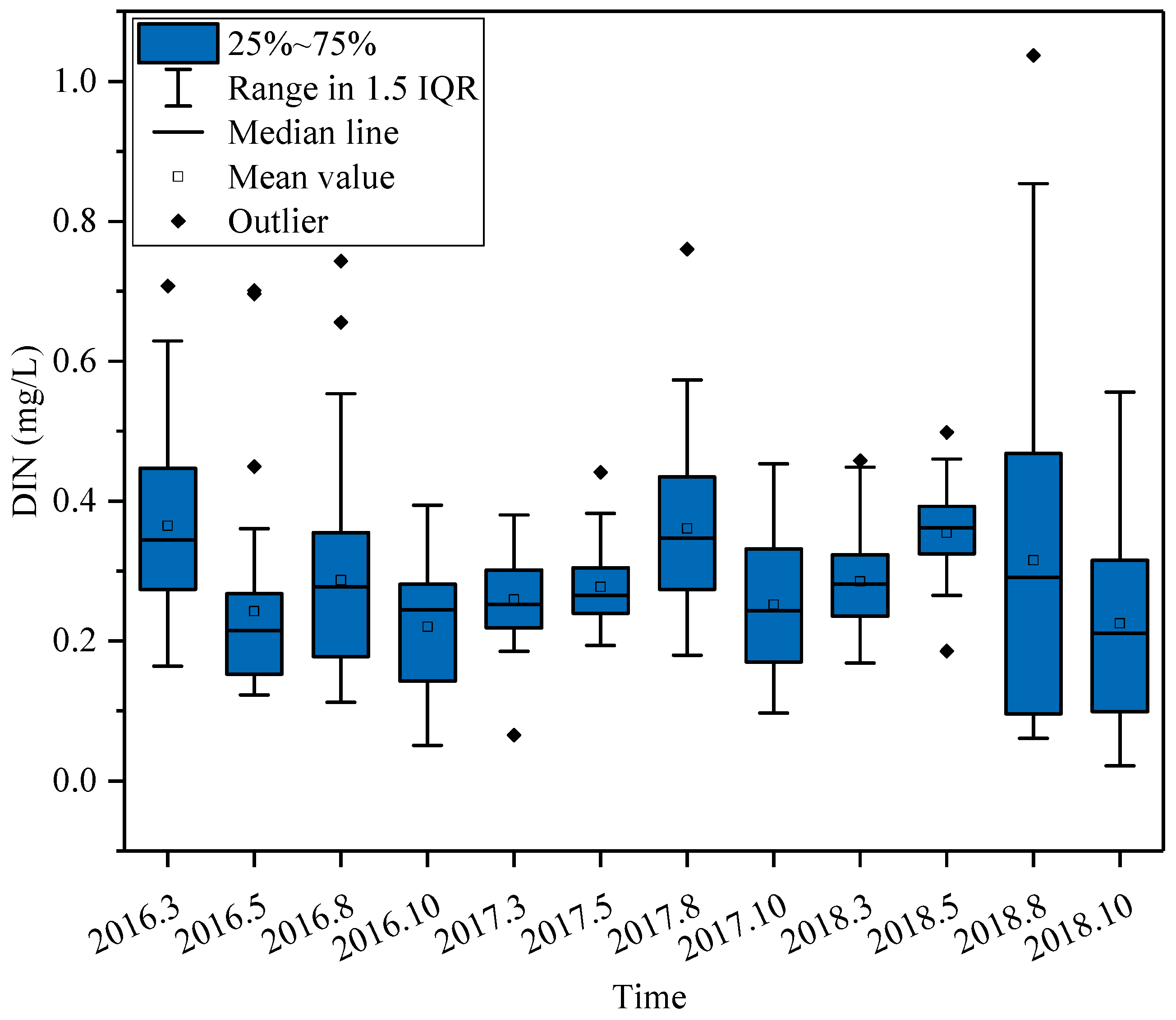
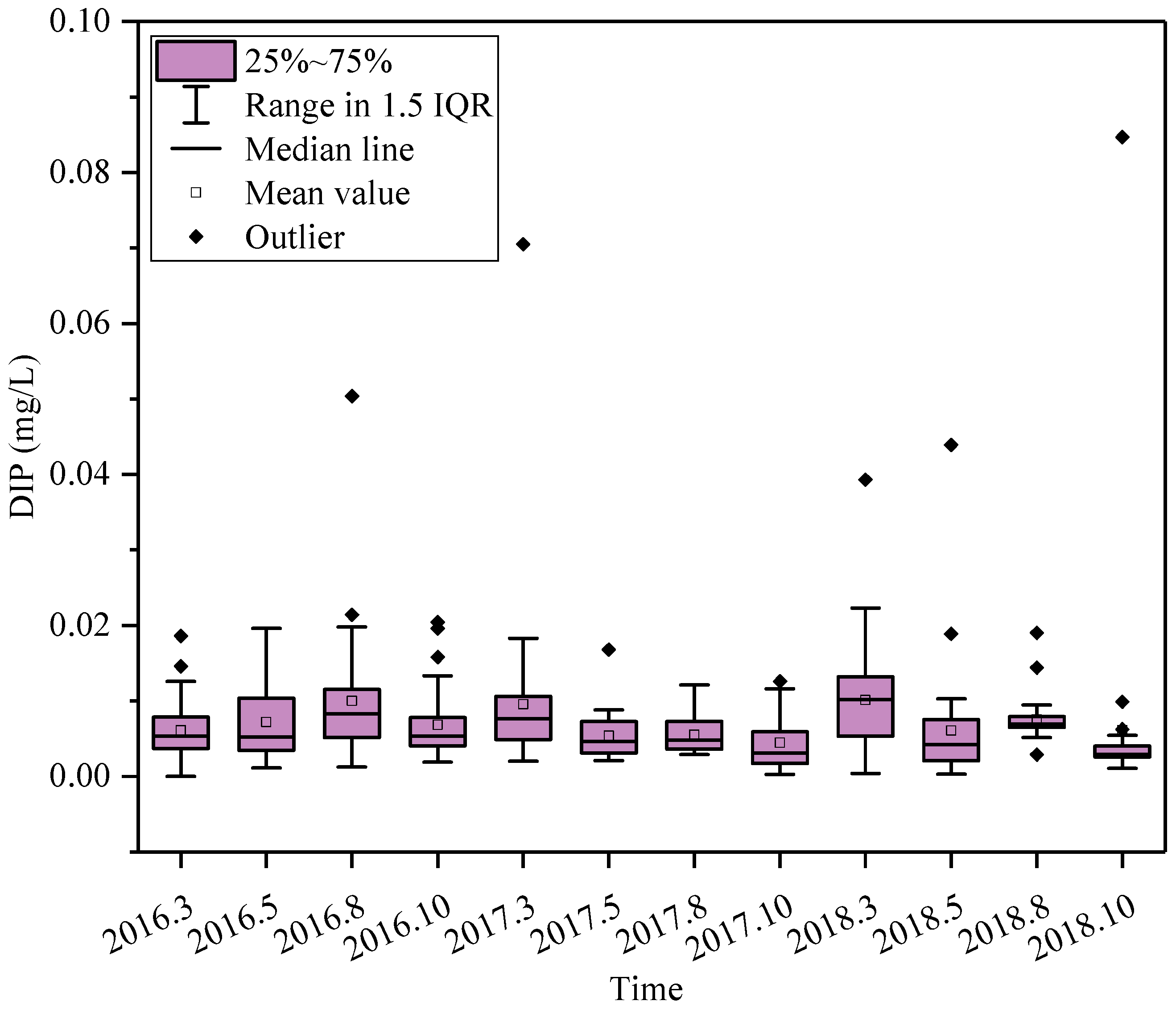
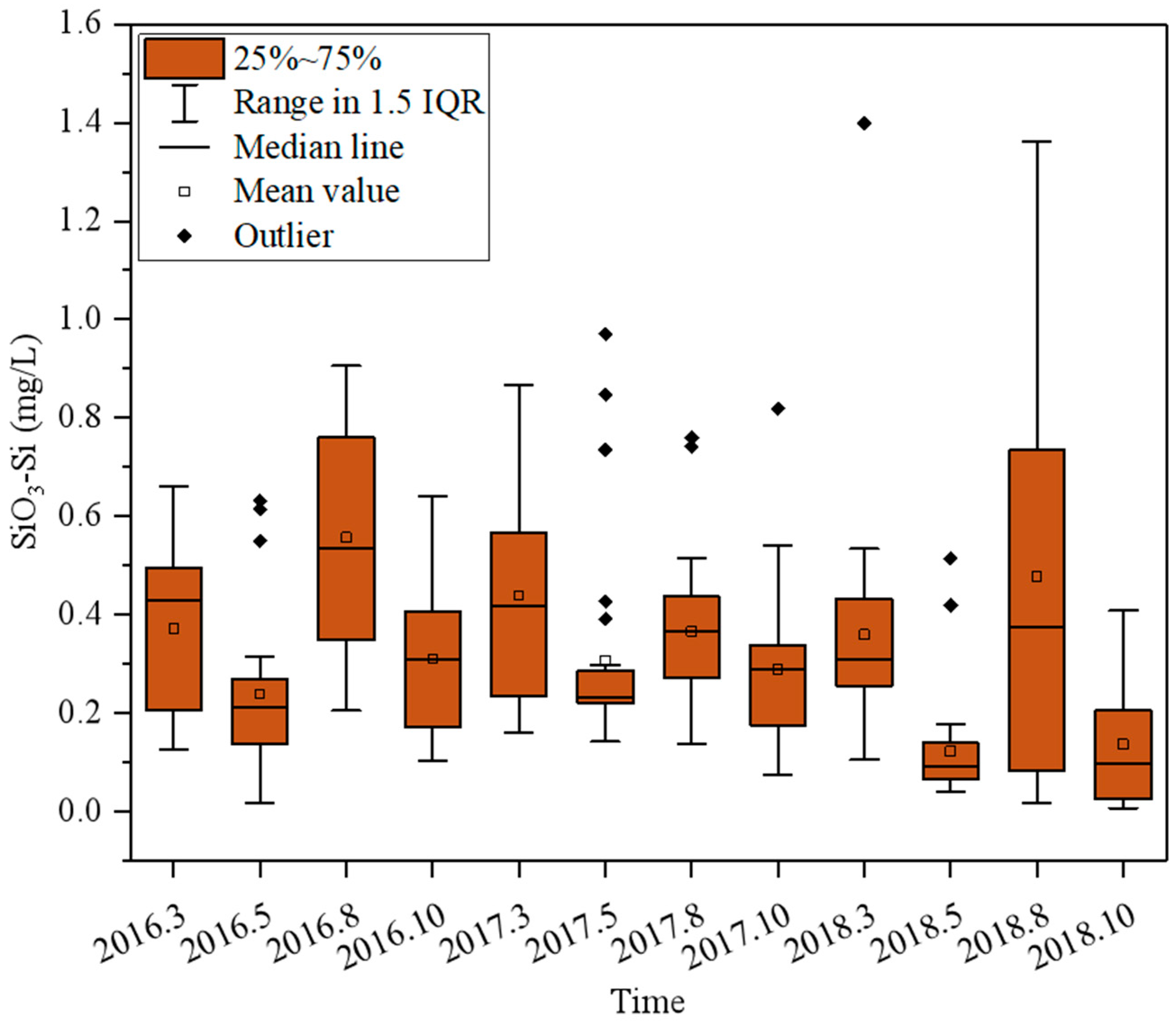
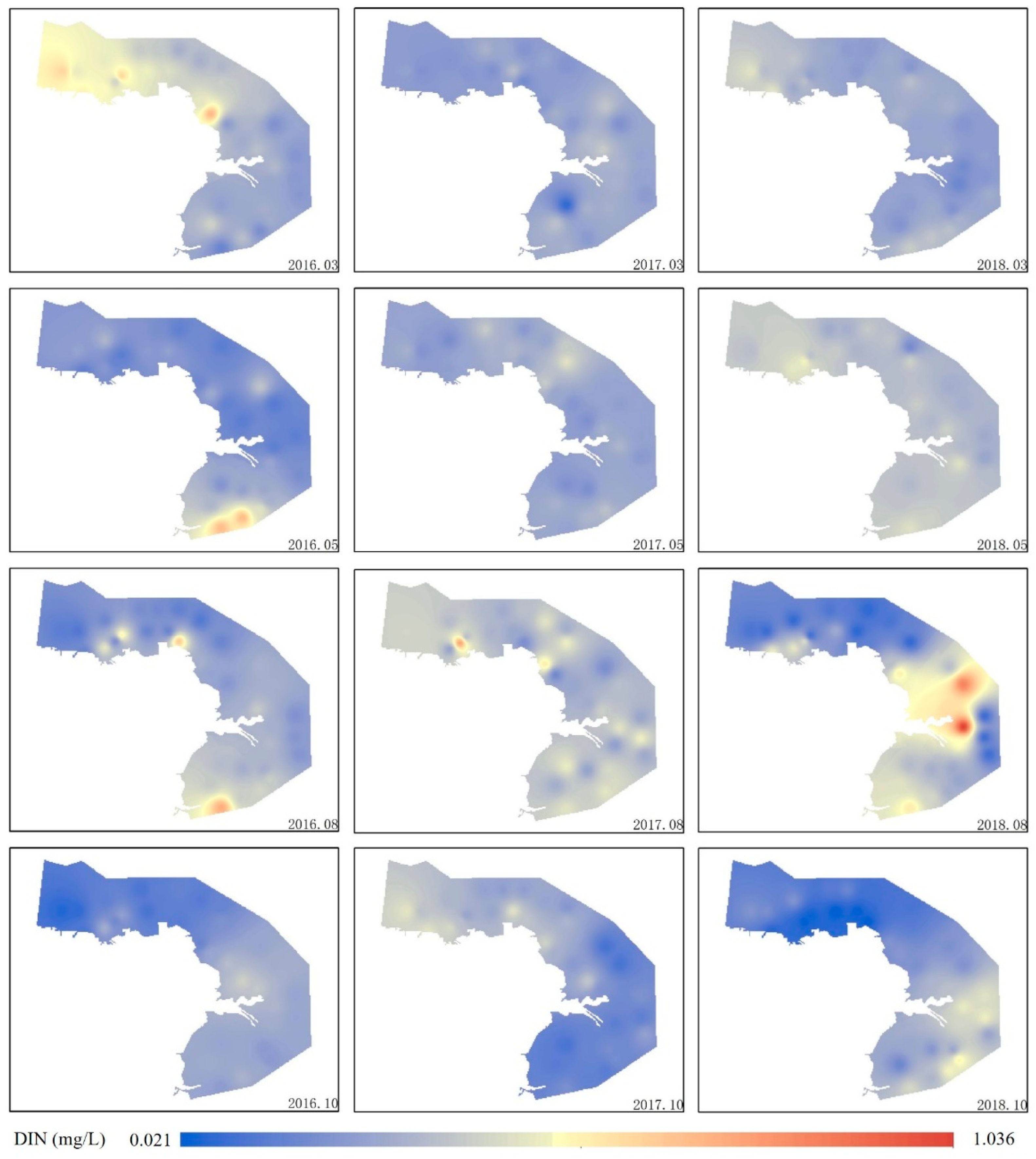
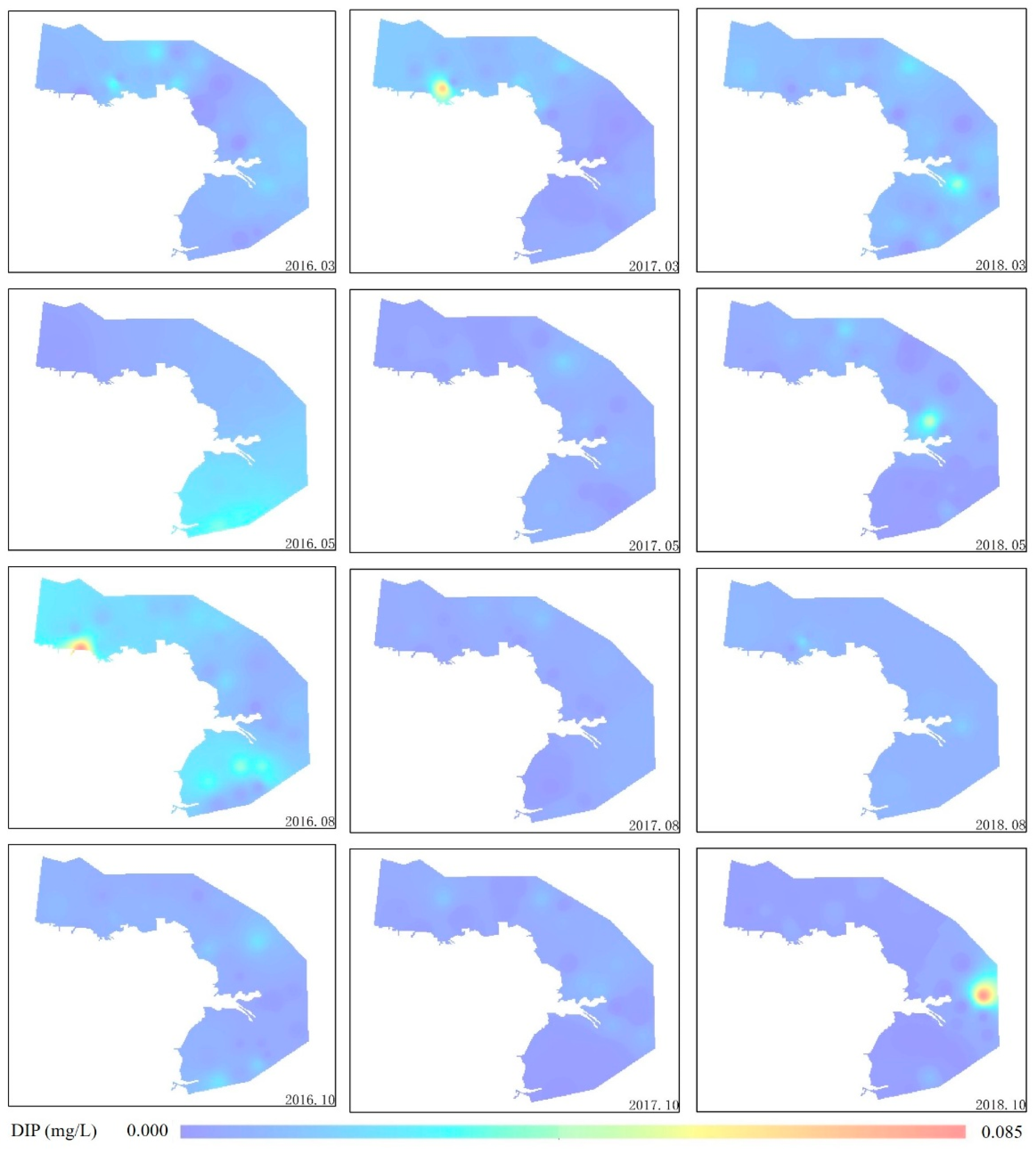
3.1. Seasonal Distributions of Nutrients
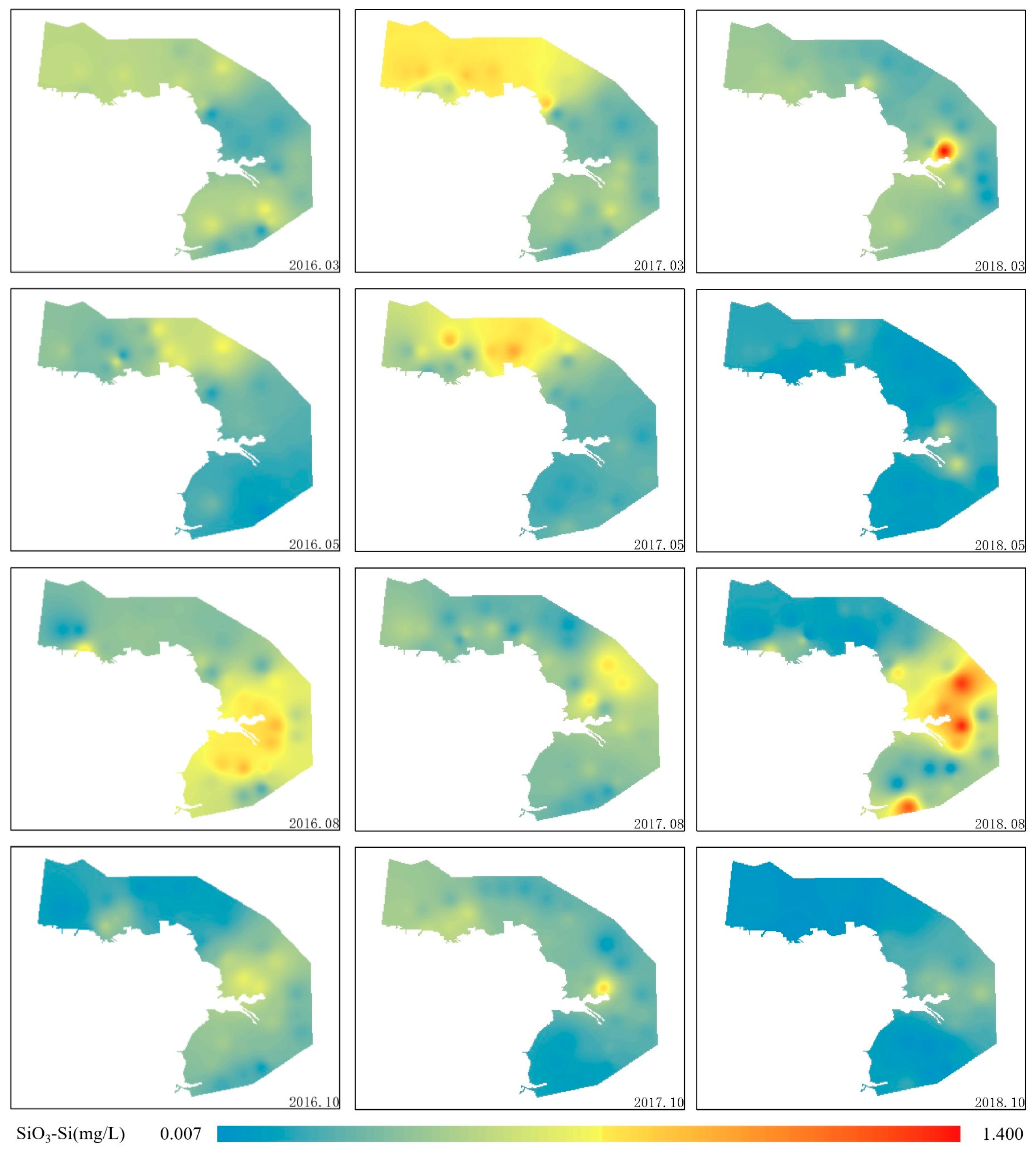
3.2. Spatial Distribution Patterns of Nutrients
3.3. Seawater Eutrophication Levels
3.3.1. Eutrophication Index
3.3.2. Potential Eutrophication
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G.; Li, J.; Luo, W. Spatial distribution, source apportionment, and assessment of marine water quality parameters in the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 195, 115526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Xu, X.; Qi, T.; Luo, J.; Lee, X.; Duan, H. Lakes shifted from a carbon dioxide source to a sink over past two decades in China. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Song, J.; Dai, J.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Yuan, H.; Duan, L.; Wang, Q. Nutrient characteristics driven by multiple factors in large estuaries during summer: A case study of the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ou, S.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhao, L.R.; Zhang, J.B. Categorizing numeric nutrients criteria and implications for water quality assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1004235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menesguen, A.; Lacroix, G. Modelling the marine eutrophication: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Xu, X.; Duan, H.; Qi, T.; Qin, B.; Lee, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, W.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M. Eutrophic Lake Taihu as a significant CO2 source during 2000–2015. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.D.; Xin, M.; Sun, X.; Wei, Q.S.; Zhang, X.L. Does reduced sediment load contribute to increased outbreaks of harmful algal blooms off the Changjiang Estuary? Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Y.; Sun, Z.G. Effects of exogenous nitrogen import on variations of nutrient in decomposing litters of Suaeda salsa in coastal marsh of the Yellow River estuary, China. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 33165–33180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Daler, D. Ocean pollution from land-based sources: East China Sea, China. Ambio 2004, 33, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, J.W.; Wu, J.W.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, J.W.; Gao, C.; Lin, Z.Y. Comprehensive Assessment of Eutrophication in Xiamen Bay and Its Implications for Management Strategy in Southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P. Oyster reef restoration in controlling coastal pollution around India: A viewpoint. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Feng, H.; Witherell, B.B.; Alebus, M.; Mahajan, M.D.; Zhang, W.G.; Yu, L.Z. Causes, Assessment, and Treatment of Nutrient (N and P) Pollution in Rivers, Estuaries, and Coastal Waters. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, A.; Östman, Ö.; Ask, J.; Bell, O.; Berggren, M.; Rulli, M.P.D.; Younes, H.; Huss, M. Coastal darkening exacerbates eutrophication symptoms through bottom-up and top-down control modification. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.J.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, X.J.; Cui, M.Y.; Huang, C. An Improved Eutrophication Assessment Algorithm of Estuaries and Coastal Waters in Liaodong Bay. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Fu, H.R.; Lou, H.W.; Sun, X.J.; Zhang, D.; Sun, P.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Li, Y.M.; Lu, J.R.; Bao, M.T. Assessment of eutrophication from Xiaoqing River estuary to Laizhou Bay: Further warning of ecosystem degradation in typically polluted estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Das Purkayastha, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Gogoi, N. Eco-bioengineering tools in ecohydrological assessment of eutrophic water bodies. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.B.H.; Atabay, H.; Evcen, A.; Kurt, G.; Taskin, E.; Beken, Ç. Integrated assessment of eutrophication in the southern Black Sea waters, using the Nested Environmental Status Assessment Tool. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 195, 115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njock, P.G.A.; Zhou, A.N.; Yin, Z.Y.; Shen, S.L. Integrated risk assessment approach for eutrophication in coastal waters: Case of Baltic Sea. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, U.; Sundblad, G.; Downie, A.L.; Snickars, M.; Boström, C.; Lindegarth, M. Evaluating eutrophication management scenarios in the Baltic Sea using species distribution modelling. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Wan, X.M.; Wang, S.; Xia, L.; Song, Y.W. Assessment of Eutrophication Characteristics and Evaluation of the First-Generation Eutrophication Model in the Nearshore Waters of Shantou City. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 442.10-2020; Technical Specification for Offshore Environmental Monitoring Part 10 Evaluation and Report. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Liu, J.Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, N.; Wu, H.L.; Liu, F.D. Allometric releases of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediments mediated by bacteria determines water eutrophication in coastal river basins of Bohai Bay. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 235, 113426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.L. Spatial and temporal distribution of nutrients and eutrophication evaluation in Dongying inshore. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 813–820, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ren, H.W.; Mou, L.; Hu, Y.B. Assessment on the water quality of coastal seawater in the Aoshan bay, Qingdao in spring. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.Z.; Dong, L.P.; Qin, B.P. A Preliminary Study on Eutrophication and Red Tide Problems in the Bohai Bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 1983, 2, 45–58, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.D.; Zhang, X.M.; Yang, Y.P.; Hu, M.H. Evaluation of potential eutrophication in coastal waters of China. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 1998, 1, 64–70, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.X.; Pan, D.W.; Yang, T.T.; Wang, C.C. Spatial and environmental characteristics of colloidal trace Cu in the surface water of the Yellow River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Han, M.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, M.; Du, H. An Analysis on the Trend of Sustainable Utilization of Water Resources in Dongying City, China. Water Resour. 2021, 48, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Qu, F.Z.; Bi, X.L.; Xia, J.B.; Li, Y.Z.; Wang, X.H.; Yu, J.B. Elemental stoichiometry (C, N, P) of soil in the Yellow River Delta nature reserve: Understanding N and P status of soil in the coastal estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.D.; Xin, M.; Wei, Q.S.; Xie, L.P. A historical overview of coastal eutrophication in the China Seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Q.; Cui, H.W.; Hu, Q.J.; Bai, Y.; Qu, K.M.; Sun, J.; Cui, Z.G. Eutrophication status assessment in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Further evidence for the ecosystem degradation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yu, M.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Guan, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lv, Z.; Qu, F.; Yang, J. Impacts of inland pollution input on coastal water quality of the Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Shen, Y.; Su, M.; Yu, C. Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic and water quality effects of shoreline changes in Bohai Bay. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S.; Mizuno, K. Long-term trends in eutrophication in the inner part of Tokyo Bay, Japan, from 1998 to 2023. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 85, 104153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-W.; Ju, Y.-R.; Chen, C.-F.; Dong, C.-D. Evaluation of organic pollution and eutrophication status of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.N.; Wu, M.M. Application of eutrophication index in the coastal waters of China. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 316–320. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gao, C. Application and Development of the Redfield Ratio in the Study of Eutrophication. Sichuan Environ. 2016, 35, 109–114, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.K.; Guo, X.Y.; Gao, H.W.; Gao, J.; Shi, J.; Yu, X.J.; Wu, Z.S. Seasonal variations of nutrient concentrations and their ratios in the central Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.M.; Cai, Y.Z.; Zhao, C.H.; Cao, B.Y.; Lu, W.P.; Liu, L.F. Temporal-spatial distribution of nutrients and potential eutrophication assessment in Shanwei coastal area. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 497–506, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Feng, J.; Cui, S.; Zhu, L. Long-term changes in nutrients, chlorophyll a and their relationships in a semi-enclosed eutrophic ecosystem, Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Sun, J.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xin, Y.; Guo, Y.; Gu, T. Seasonal Shift of a Phytoplankton (>5 µm) Community in Bohai Sea and the Adjacent Yellow Sea. Diversity 2021, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Q. Coupling effect of phytoplankton community structure and environmental factors in the Bohai Sea of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, S.; Xu, M.; Luo, X.; Peng, X.; Ren, C.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Nutrient Patterns, Stoichiometry, and Eutrophication Assessment in the Tieshan Bay Coastal Water, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.; Wu, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, S. Nutrient changes in the Bohai Sea over the past two decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.W.; Zhai, W.D.; Wang, L.F.; Huang, T. Improving the understanding of central Bohai Sea eutrophication based on wintertime dissolved inorganic nutrient budgets: Roles of north Yellow Sea water intrusion and atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Lv, X.; Zhao, J. Perpetual atmospheric dry deposition exacerbates the unbalance of dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus in coastal waters: A case study on a mariculture site in North China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maúre, E.D.; Terauchi, G.; Ishizaka, J.; Clinton, N.; DeWitt, M. Globally consistent assessment of coastal eutrophication. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L. Insighting into the Bohai Sea from the Phosphorus Dimension: A Study of Fluxes and Budget of Phosphorus from Land to Sea with Implication for the Environment Change; First Institute of Oceanology, Ministry of Natural Resources: Qingdao, China, 2021.
- Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Du, J. Fresh and saline groundwater nutrient inputs and their impacts on the nutrient budgets in a human-effected bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 116026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, R.; Liu, S.; Ning, Z.; Jiang, Z. The phosphorus cycle in the Sanggou Bay. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lu, Q.; Wang, D.; Ding, D.; Cui, Z.; Shi, H. Spatiotemporal evolution of nutrients and the influencing factors in Laizhou Bay over the past 40 years. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, G.; Li, H.L. Effect of submarine groundwater discharge on nutrient distribution and eutrophication in Liaodong Bay, China. Water Res. 2023, 247, 120732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Wei, X.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Li, C.C.; Tang, H.J. Comparative study on the influene factors of chlorophyll-a and nutrient structure betweenwinter and summer n the central Bohai Sea. Mar. Fish. 2021, 43, 473–484, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yu, Z.; Bouwman, A.F.; Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Yao, Q.; Gong, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Significant impacts of artificial regulation on nutrient concentrations and transport in Huanghe River. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, U.; Topcu, D.; Schütt, M.; Leujak, W. Eutrophication assessment in the transit area German Bight (North Sea) 2006-2014-Stagnation and limitations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Liu, D.Y.; Yang, S.M.; Guo, J.; Qian, S.B. A Preliminary Study on the Community Structure of Phytoplankton in the Central Bohai Sea, Bohai Strait and Adjacent Waters. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin./Haiyang Yu Huzhao 2002, 5, 11, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Bouwman, L.; Ran, X. Changes in the distribution and preservation of silica in the Bohai Sea due to changing terrestrial inputs. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 166, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Thangaraj, S.; Sun, J. Water quality shifts the dominant phytoplankton group from diatoms to dinoflagellates in the coastal ecosystem of the Bohai Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 183, 114078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Song, Z.; Bouwman, A.F.; Ran, X. Phosphorus depletion is exacerbated by increasing nitrogen loading in the Bohai sea. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 352, 124119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, K. Nutrients and heavy metals mediate the distribution of microbial community in the marine sediments of the Bohai Sea, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, W.; Zong, H.; Ding, P.; Hou, L. A modelling approach to assess the effects of atmospheric nitrogen deposition on the marine ecosystem in the Bohai Sea, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 208, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, P.J. Analysis and prediction of historical characteristics of temperature and precipitation in Dongying City. Shandong Water Resour. 2021, 3, 8–10, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Xian, W. Changjiang nutrient distribution and transportation and their impacts on the estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 165, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokal, M.; Kroeze, C.; Wang, M.; Ma, L. Reducing future river export of nutrients to coastal waters of China in optimistic scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.Q. Spatiotemporal Dissolved Silicate Variation, Sources, and Behavior in the Eutrophic Zhanjiang Bay, China. Water 2020, 12, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Song, Z.; Ran, X. Composition and transport of silicon in rivers of the Bohai rim with implications for the coastal environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.-M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.-H.; Yang, G.-P. Distribution and characteristics of inorganic nutrients in the surface microlayer and subsurface water of the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 168, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yao, Y.; Wu, Y. Silica supply and diatom blooms in the Jiaozhou Bay, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Bouwman, A.F.; Van Gils, J.; Vilmin, L.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, Z.; Ran, X. Hindcasting harmful algal bloom risk due to land-based nutrient pollution in the Eastern Chinese coastal seas. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, Z.X.; Zhang, G.T.; Wang, S.W.; Wan, A.Y.; Liu, Q. Distinguishing nutrient-depleting effects of scallop farming from natural variabilities in an offshore sea ranch. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlenstedt, D.; Bottcher, H.D.; Osmers, F. Endocrinologic-radiologic aspects of galactorrhea. Review and personal results. Med. Welt. 1983, 34, 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.M.; Li, L.W.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Ren, J.L. Impacts of human activities on nutrient transports in the Huanghe (Yellow River) estuary. J. Hydrol. 2012, 430–431, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, K.; Li, M.; Jiang, H.; Gao, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, K. Diatom-dinoflagellate succession in the Bohai Sea: The role of N/P ratios and dissolved organic nitrogen components. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. A Century-Long Phytoplankton Shift and Environmental Responses in the Adiacent Sea of the Yellow River Estuary. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, D.; Song, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, A.; Cheng, L.; He, J.; Sun, S. Response of phytoplankton assemblages to nitrogen reduction in the Laizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Kan, W.J.; Zhang, Y.N. Nutrient Variation and Eutrophication Assessment of Bohai Bay in Tianjin. J. Tianjin Univ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 30, 56–61, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B.; Zhang, J.J.; Wu, W.T.; Liu, J.; Ran, X.B.; Zhang, A.J.; Zang, J.Y. Variations in the marine seawater environment and the dominant factors in the Lianyungang coastal area. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 52, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhao, N.; Ni, Y.; Yi, J.; Wilson, J.P.; He, L.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; Zhou, C.; Song, C.; et al. China’s improving inland surface water quality since 2003. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaau3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, M.; Sun, X.; Xie, L.-P.; Wang, B.-D. A historical overview of water quality in the coastal seas of China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1203232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.P.; Zhao, Y.T.; Sun, S.; Su, B.; Ma, Y.Q.; Wang, L.M.; Qi, Y.M.; Li, J.H.; Dong, X.X. Characteristics of nutrient structures and limitations in Laizhou Bay in the spring and summer of 2018. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2021, 42, 15–24, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Liu, S.M. Advances in studies of phosphorus utilization by marine phytoplankton. Adv. Earth Sci. 2013, 28, 253–261, (In Chinese, with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J. The identification of nutrient limitations on eutrophication in Dianchi Lake, China. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

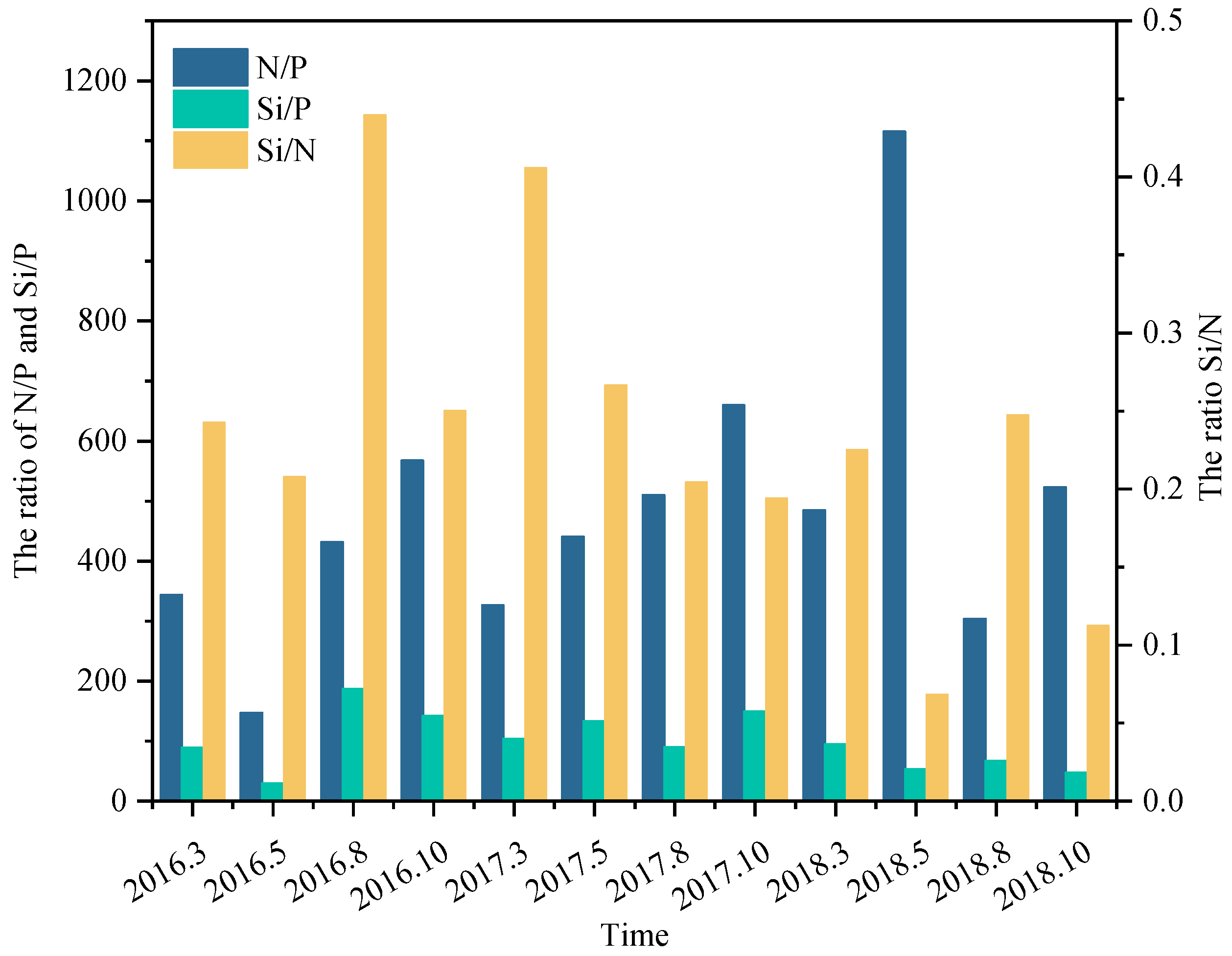
| Range of EI | Degree of Eutrophication |
|---|---|
| EI ≤ 3.0 | Mild eutrophication |
| 3.0 < EI ≤ 9.0 | Moderate eutrophication |
| EI > 9.0 | Severe eutrophication |
| Eutrophication Levels | Trophic Level | DIN/ μmol·L−1 | DIP/ μmol·L−1 | N/P (Molar Ratio) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Oligotrophy | <14.28 | <0.97 | 8~30 |
| II | Moderate nutrition | 14.28~21.41 | 0.97~1.45 | 8~30 |
| III | Eutrophy | >21.41 | >1.45 | 8~30 |
| IVP | Phosphorus limits moderate nutrition | 14.28~21.41 | - | >30 |
| VP | Phosphorus moderately limits potential eutrophication | >21.41 | - | 30~60 |
| VIP | Phosphorus limits potential eutrophication | >21.41 | - | >60 |
| IVN | Nitrogen-restricted moderate nutrition | - | 0.97~1.45 | <8 |
| VN | Nitrogen moderately limits potential eutrophication | - | >1.45 | 4~8 |
| VIN | Nitrogen-limiting potential eutrophication | - | >1.45 | <4 |
| Year | Month | EI | Station Proportion of Eutrophication Severity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Eutrophication | Moderate Eutrophication | Severe Eutrophication | |||
| 2016 | March | 0.055~2.308 | 16.67% | - | - |
| May | 0.054~4.429 | 11.11% | 5.56% | - | |
| August | 0.116~2.544 | 25.00% | - | - | |
| October | 0.055~2.192 | 11.11% | - | - | |
| 2017 | March | 0.028~3.059 | - | 2.78% | - |
| May | 0.125~1.450 | 2.78% | - | - | |
| August | 0.075~1.538 | 11.11% | - | - | |
| October | 0.009~1.048 | 2.78% | - | - | |
| 2018 | March | 0.120~3.761 | 33.33% | 5.56% | - |
| May | 0.023~3.788 | 8.33% | 2.78% | - | |
| August | 0.063~3.721 | 11.11% | 2.78% | - | |
| October | 0.017~6.004 | - | 2.78% | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Hang, X.; Chen, Y. Nutrient Distribution Characteristics and Eutrophication Evaluation of Coastal Water near the Yellow River Estuary, China. Water 2025, 17, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162469
Xiao J, Chen X, Zhou L, Zhang H, Hang X, Chen Y. Nutrient Distribution Characteristics and Eutrophication Evaluation of Coastal Water near the Yellow River Estuary, China. Water. 2025; 17(16):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162469
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Jing, Xiang Chen, Li Zhou, Haibo Zhang, Xiaoshuai Hang, and Yudong Chen. 2025. "Nutrient Distribution Characteristics and Eutrophication Evaluation of Coastal Water near the Yellow River Estuary, China" Water 17, no. 16: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162469
APA StyleXiao, J., Chen, X., Zhou, L., Zhang, H., Hang, X., & Chen, Y. (2025). Nutrient Distribution Characteristics and Eutrophication Evaluation of Coastal Water near the Yellow River Estuary, China. Water, 17(16), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162469







