Spatiotemporal Patterns of Algal Blooms in Lake Bosten Driven by Climate and Human Activities: A Multi-Source Remote-Sensing Perspective for Sustainable Water-Resource Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
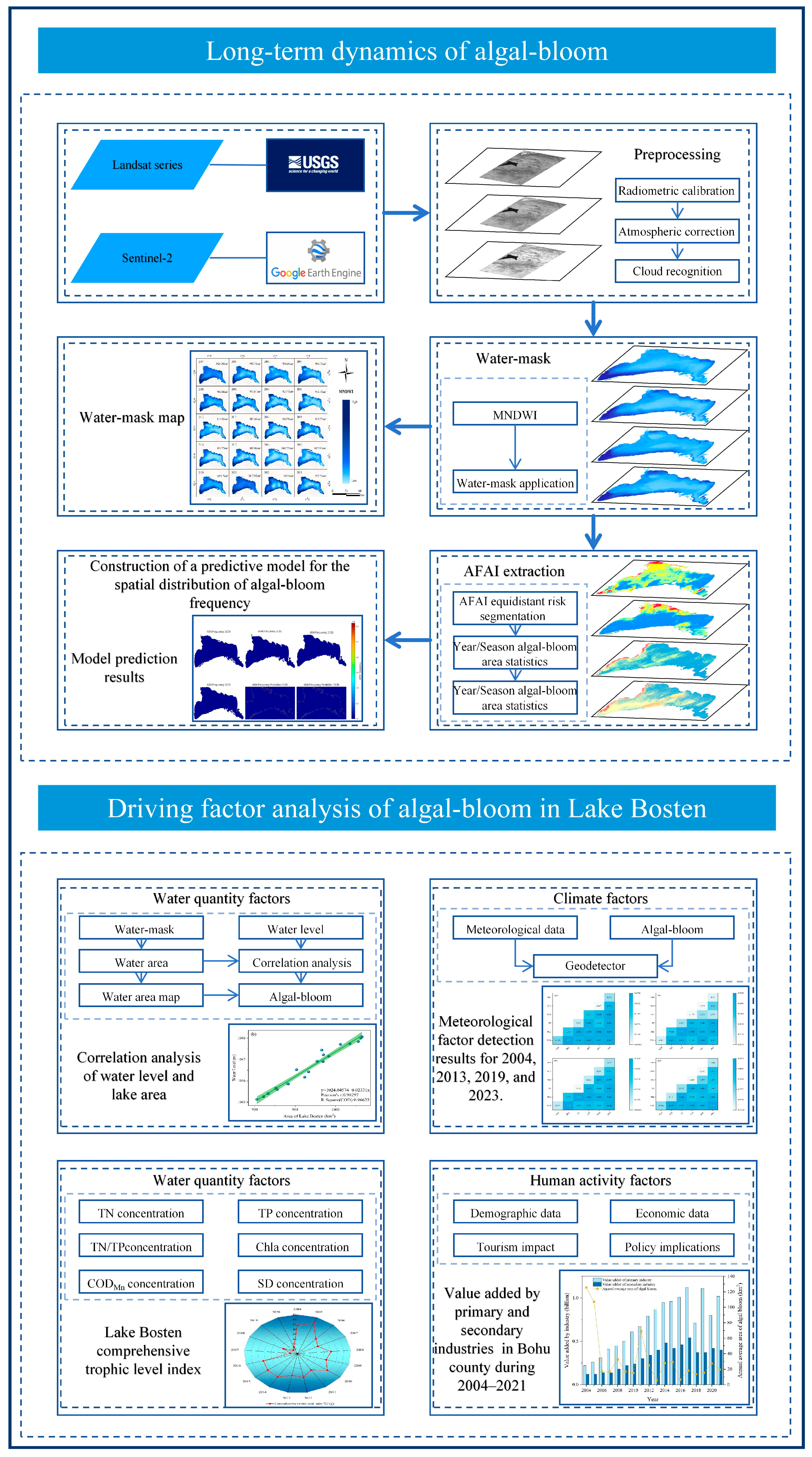
2. Materials and Methods
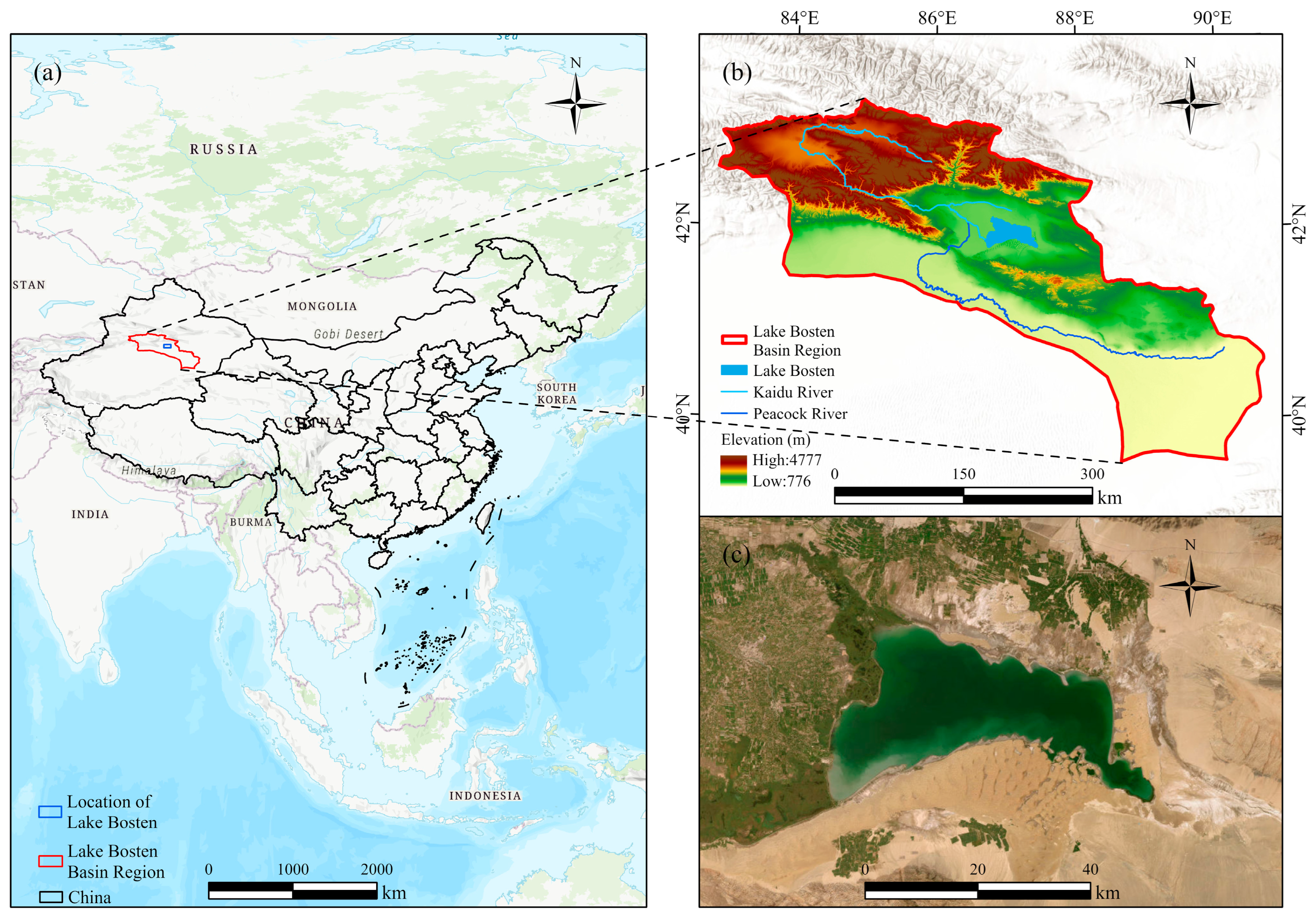
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Modified Normalized Difference Water Index
2.3.2. Adjusted Floating Algae Index
2.3.3. Extent of Lake-Area Dynamics
2.3.4. Pearson Correlation Analysis
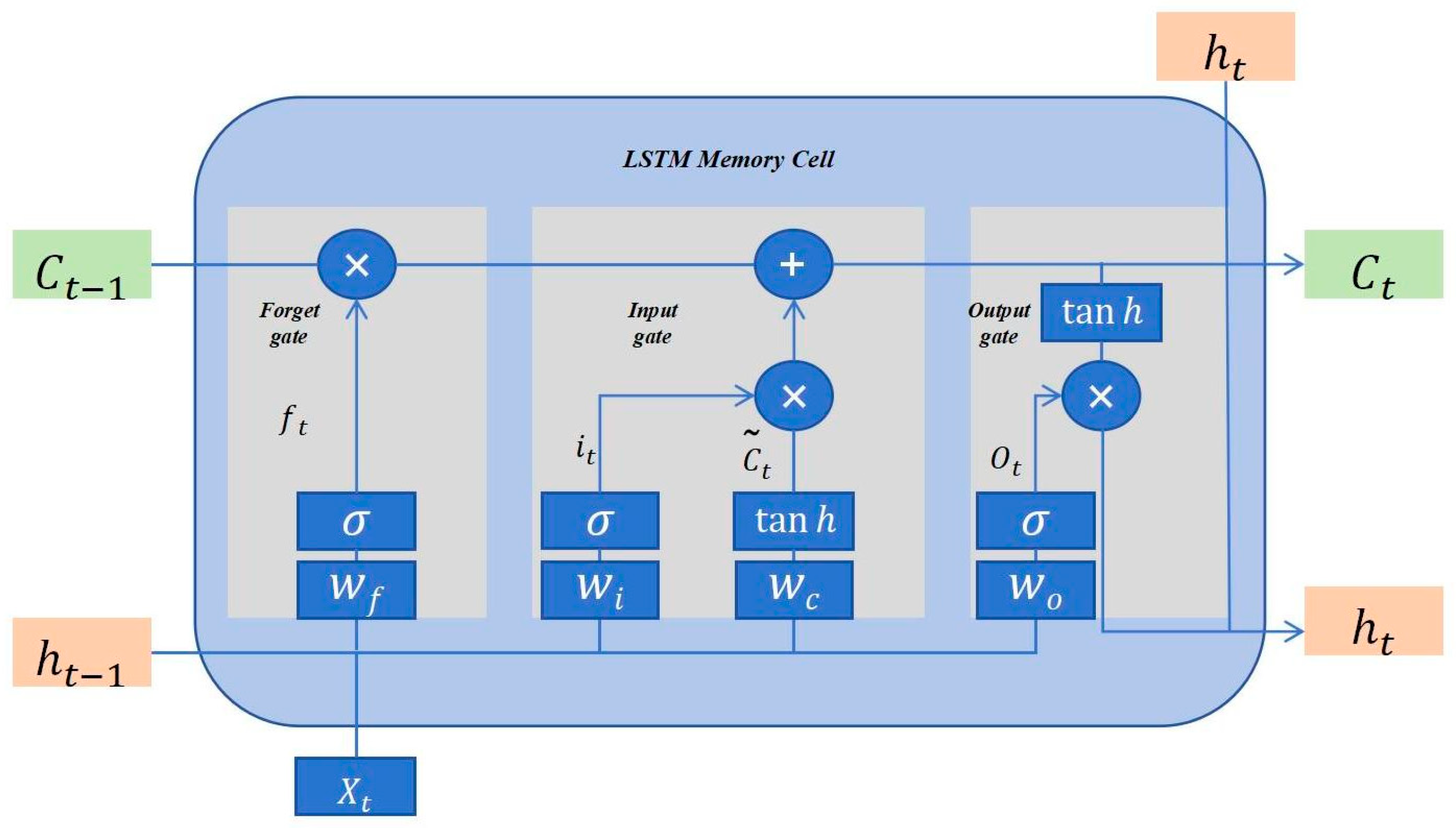
2.3.5. LSTM (Long Short Term Memory)
2.3.6. Geodetector
2.3.7. Comprehensive Trophic Level Index TLI(Σ)
3. Results
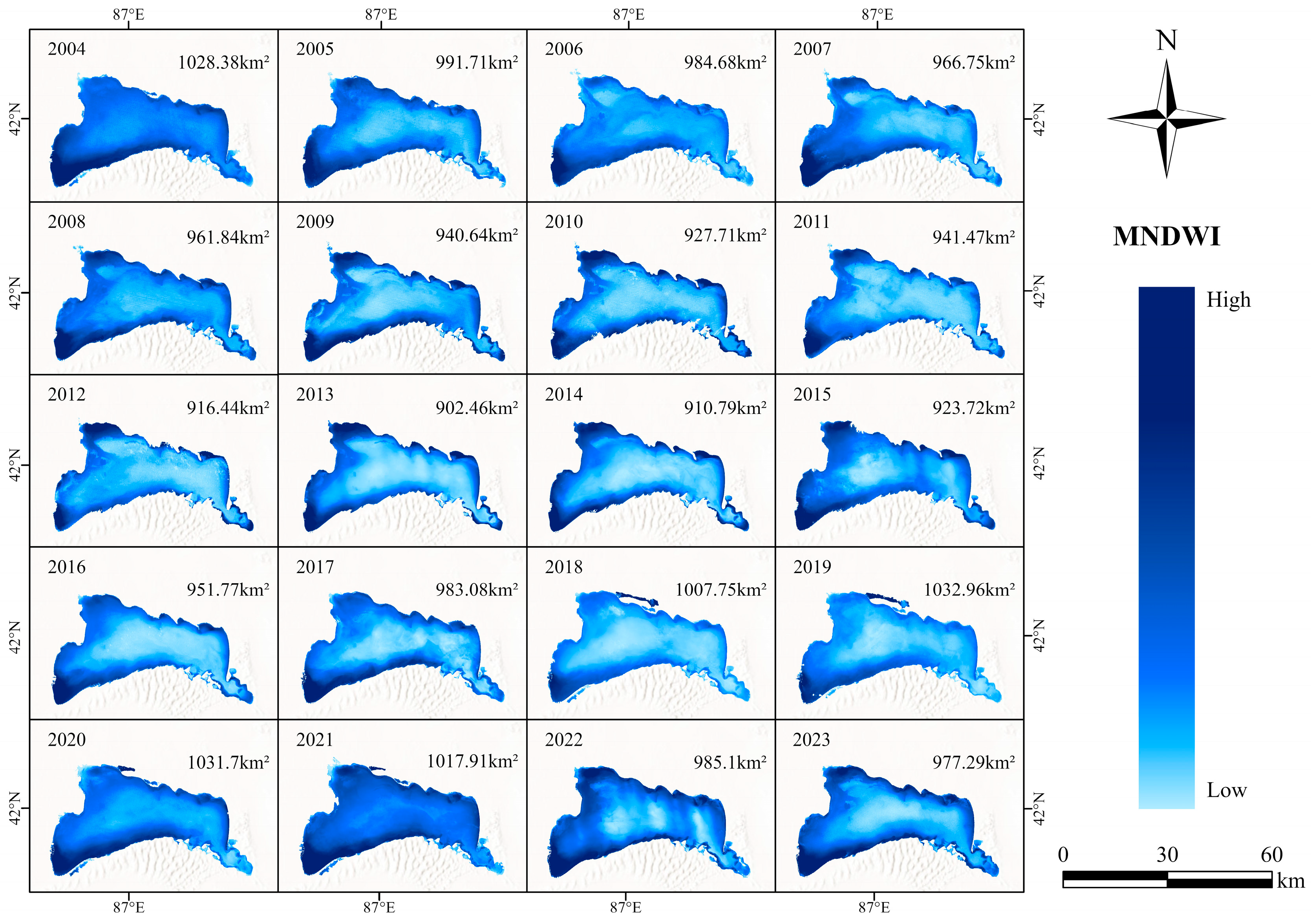
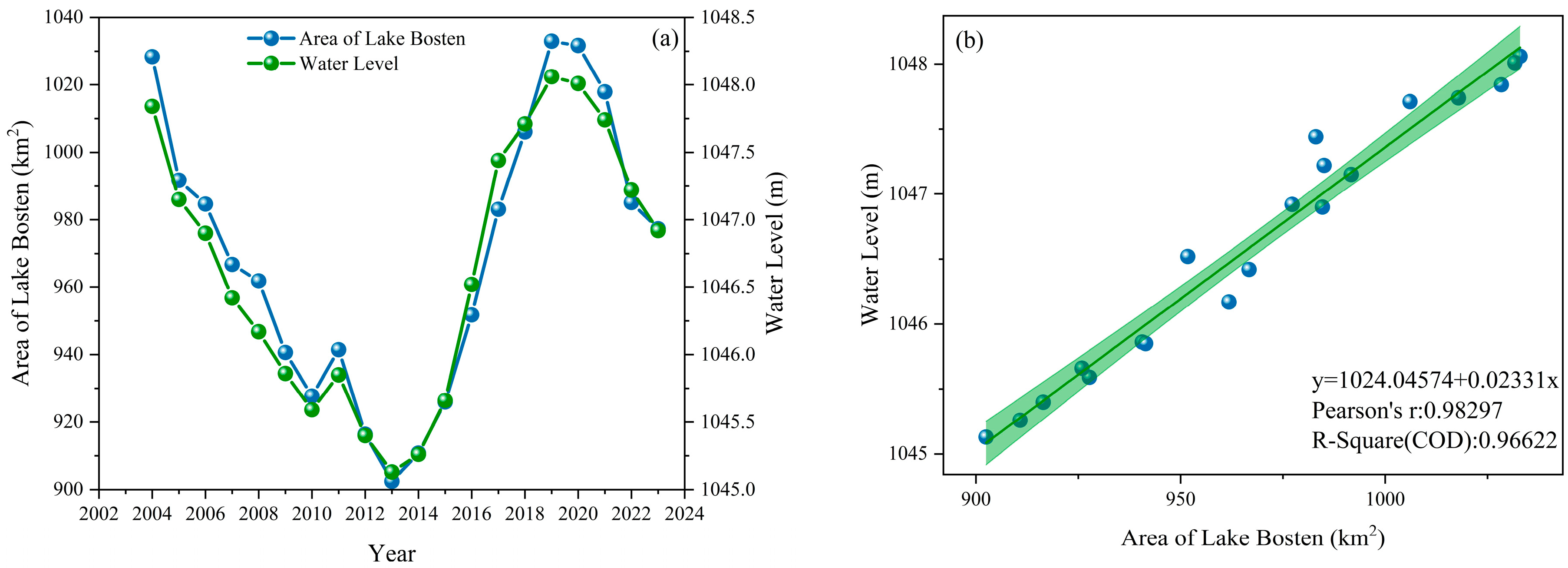
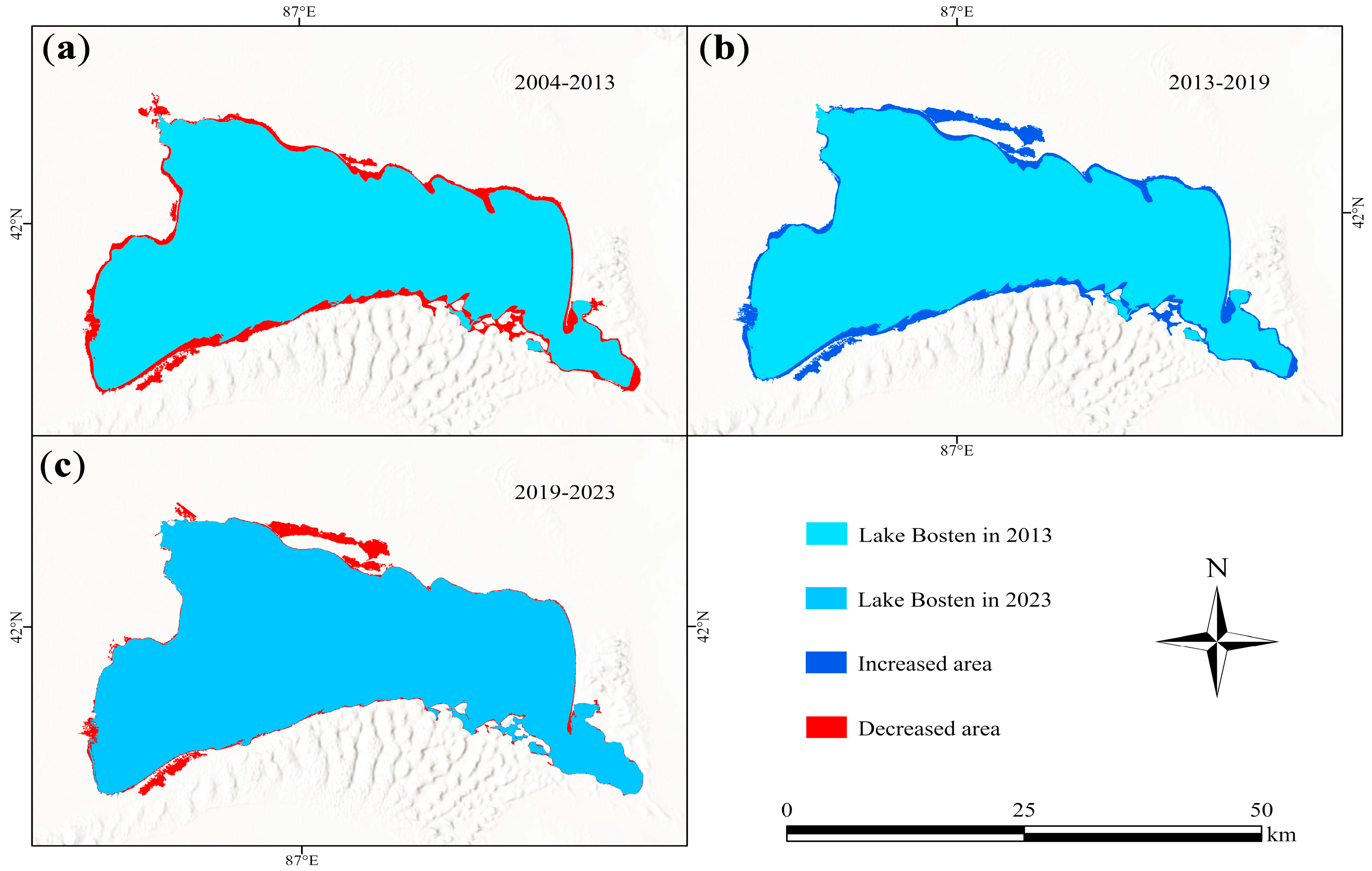
3.1. Analysis of Lake Bosten Area Extraction and Area Change
3.2. Characteristics of the Spatiotemporal Distribution of Algal Blooms in Lake Bosten
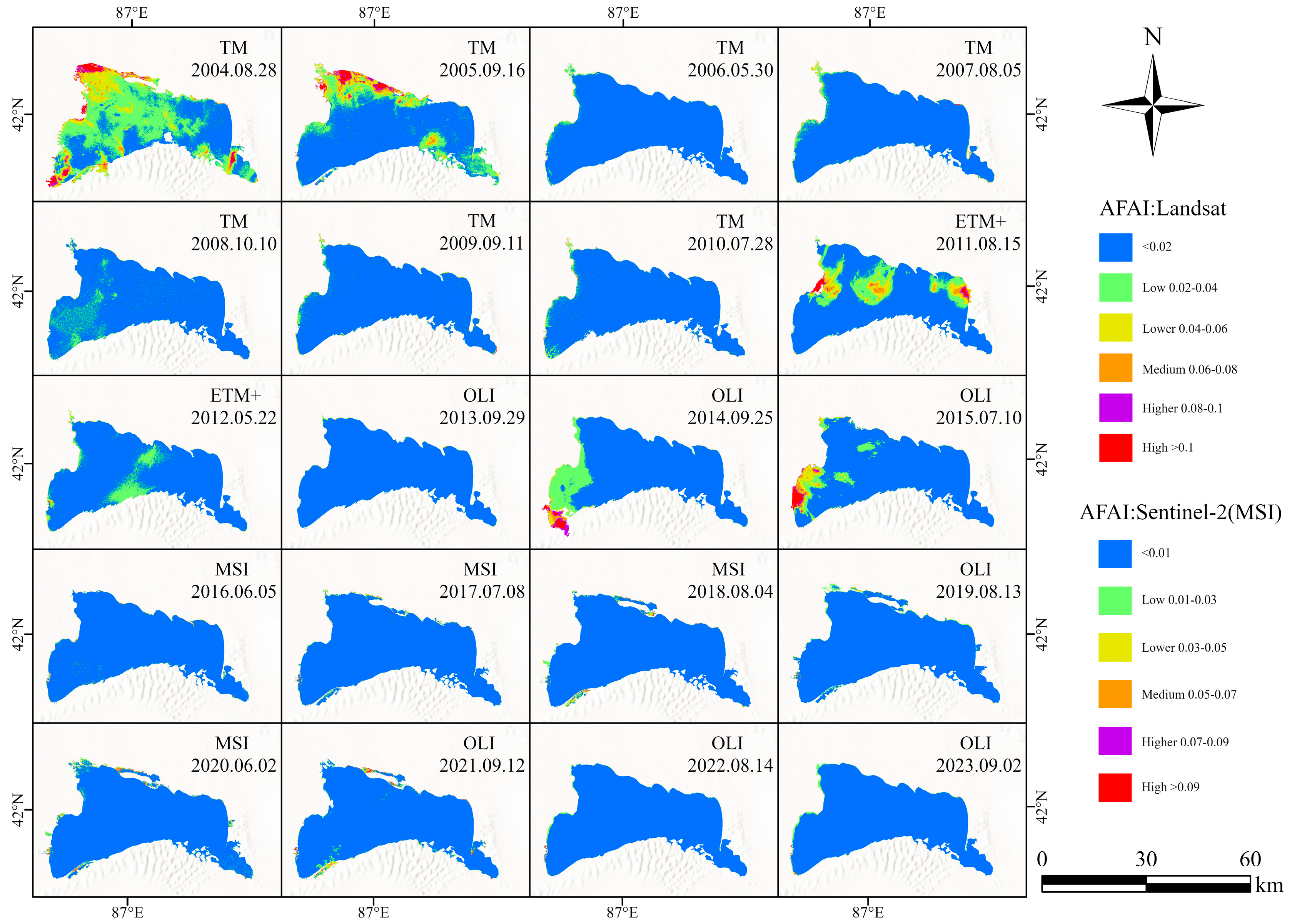
3.2.1. Spatiotemporal Variability of Algal Blooms
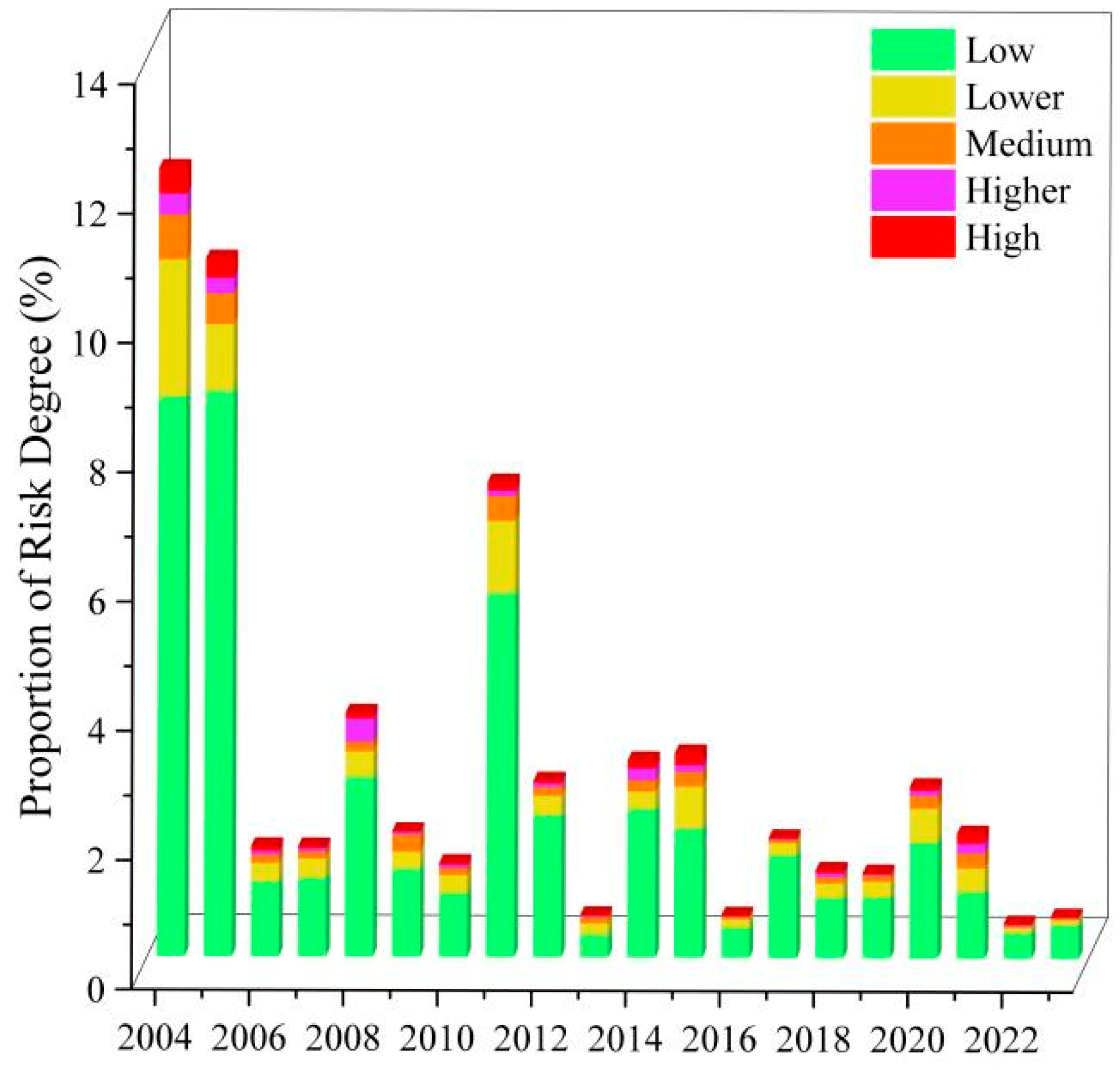
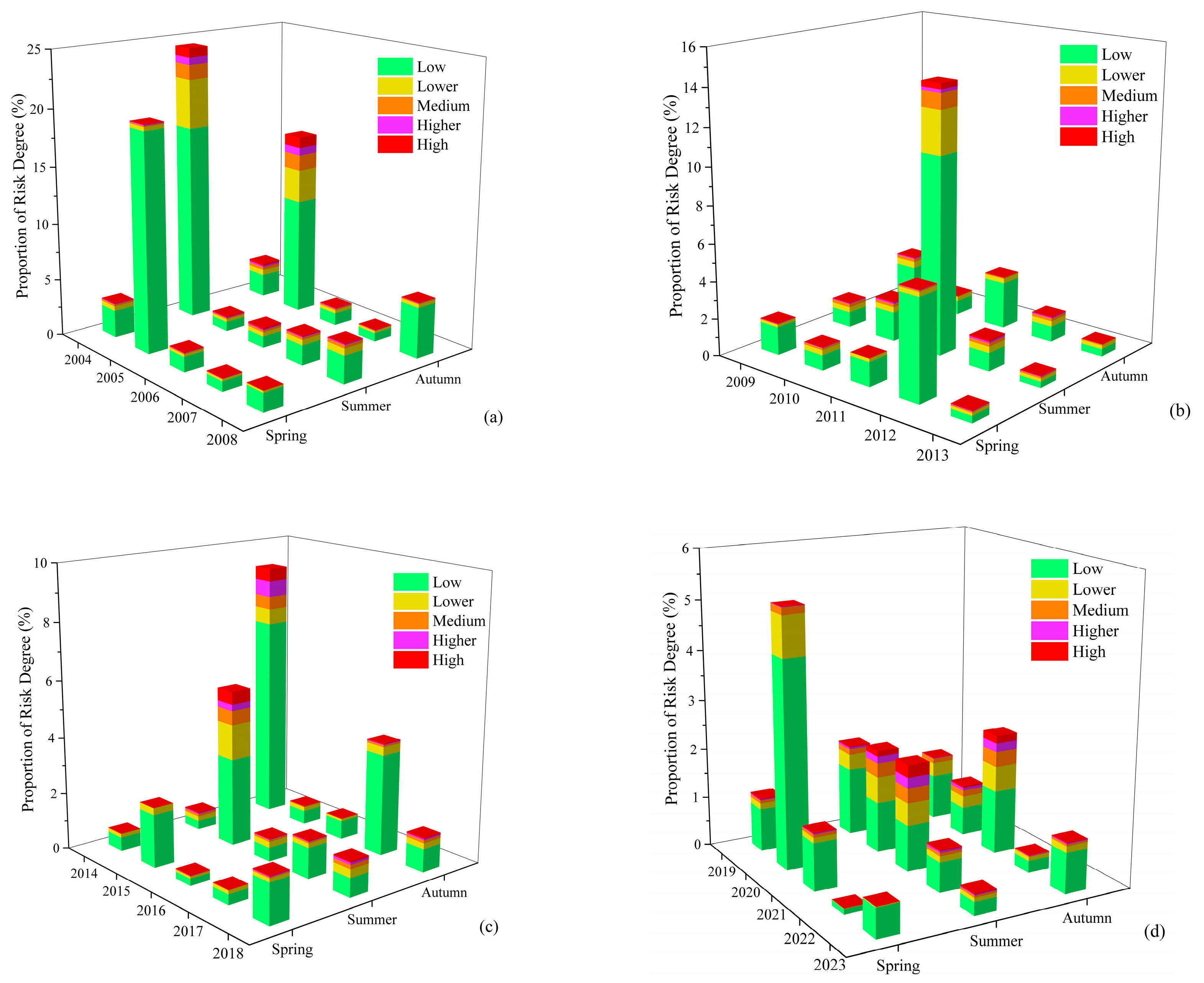
3.2.2. Trends in the Area Coverage of Algal Blooms at Different Levels of Risk
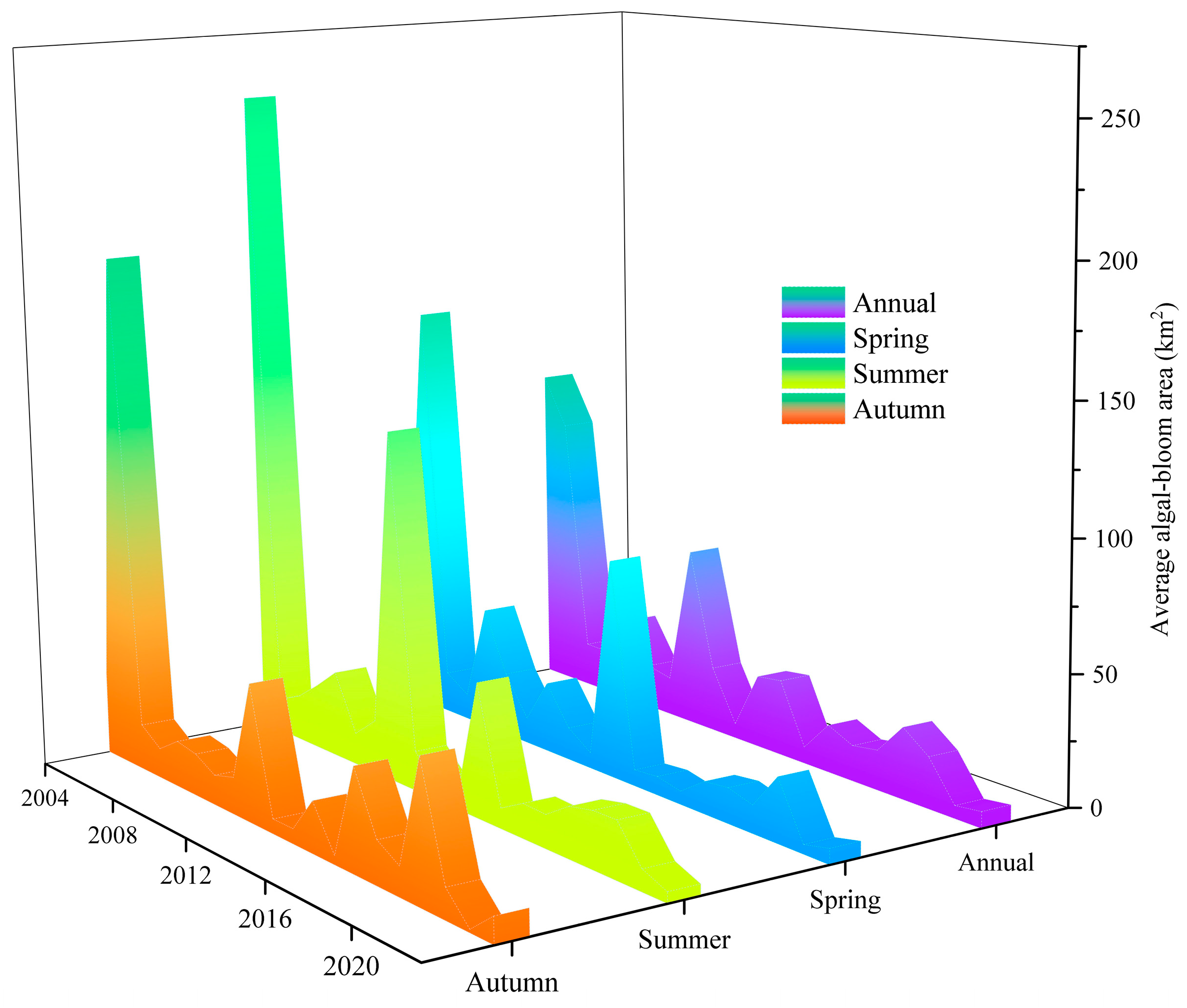
3.2.3. Average Area Covered by Algal Blooms
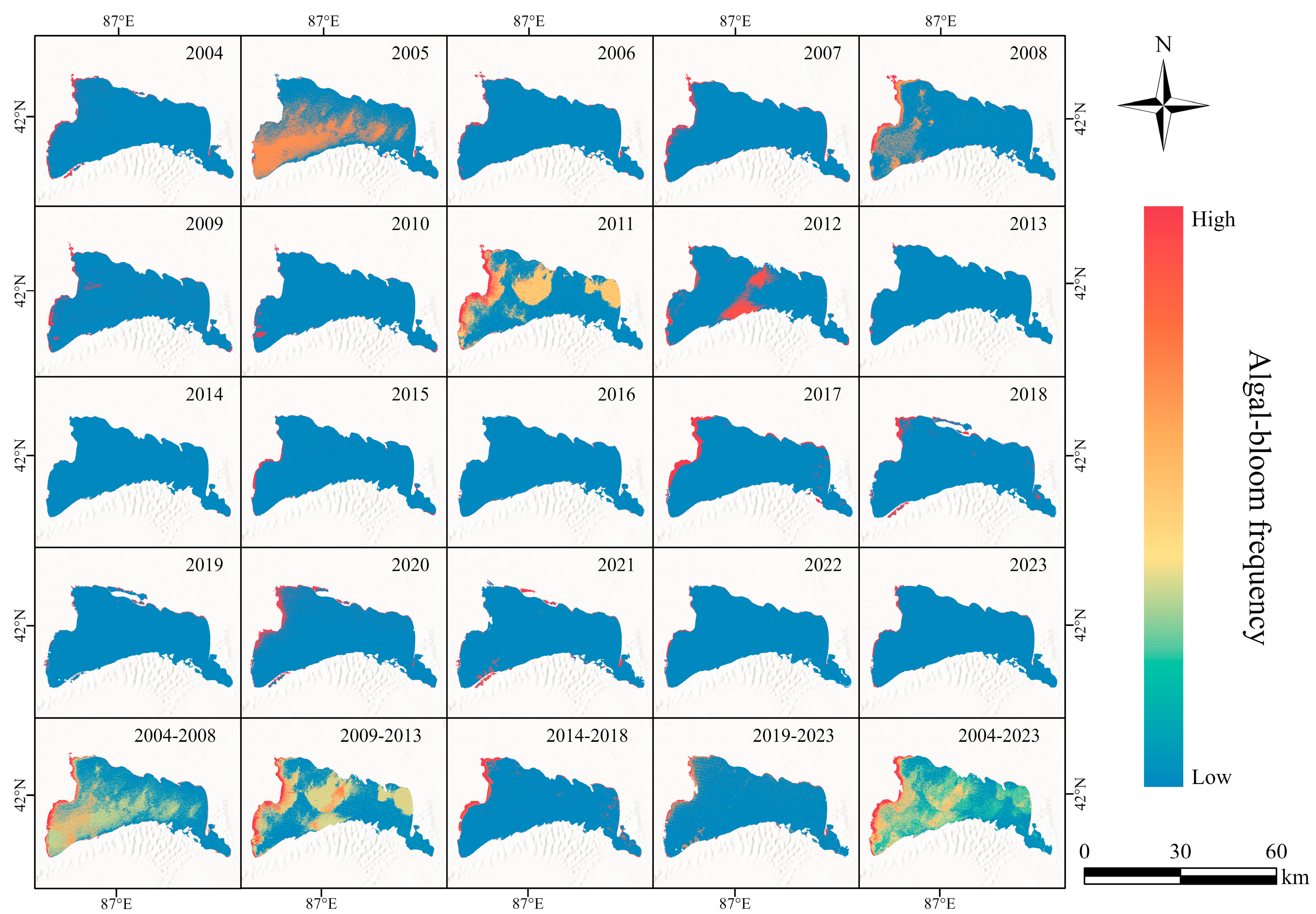
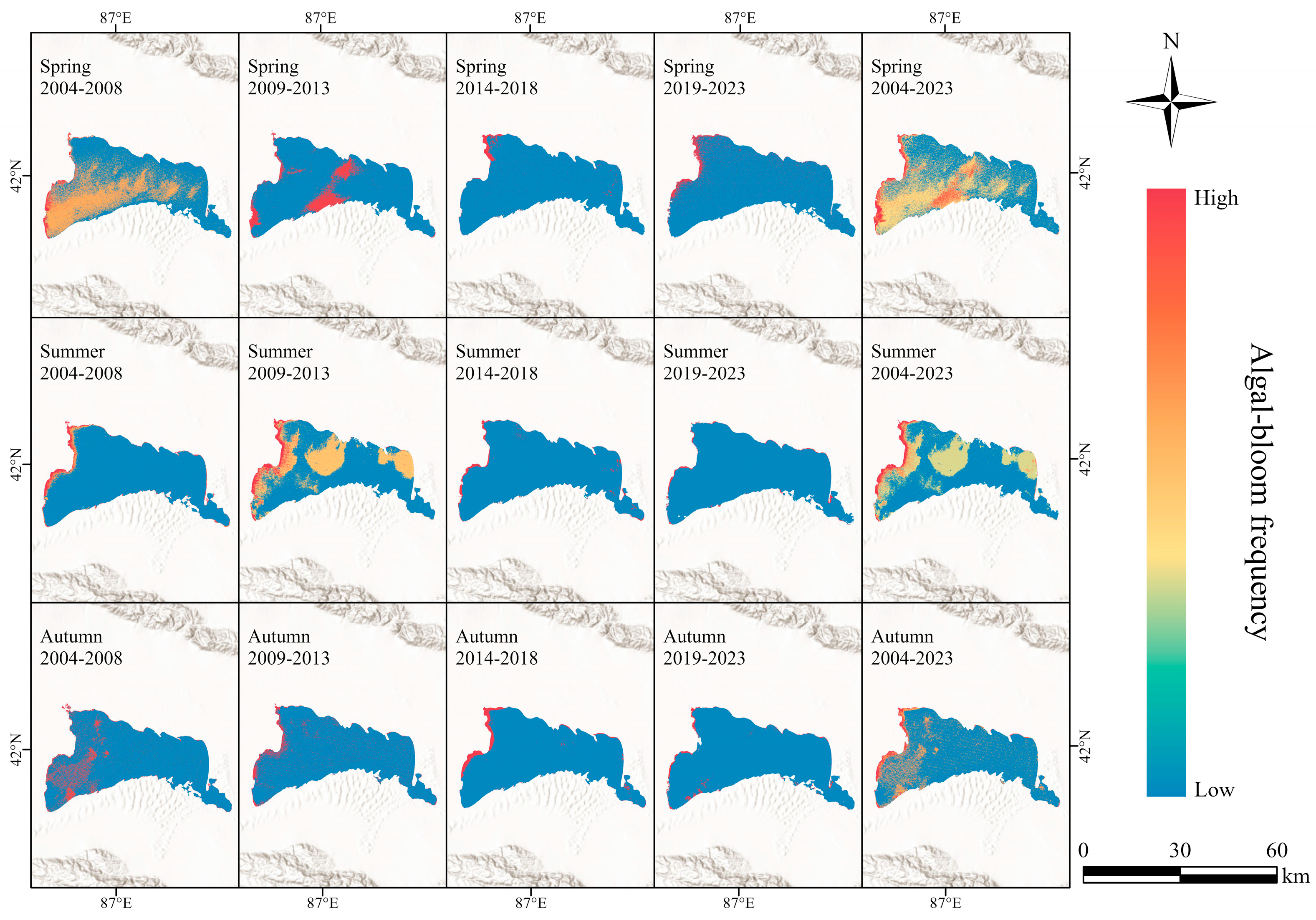
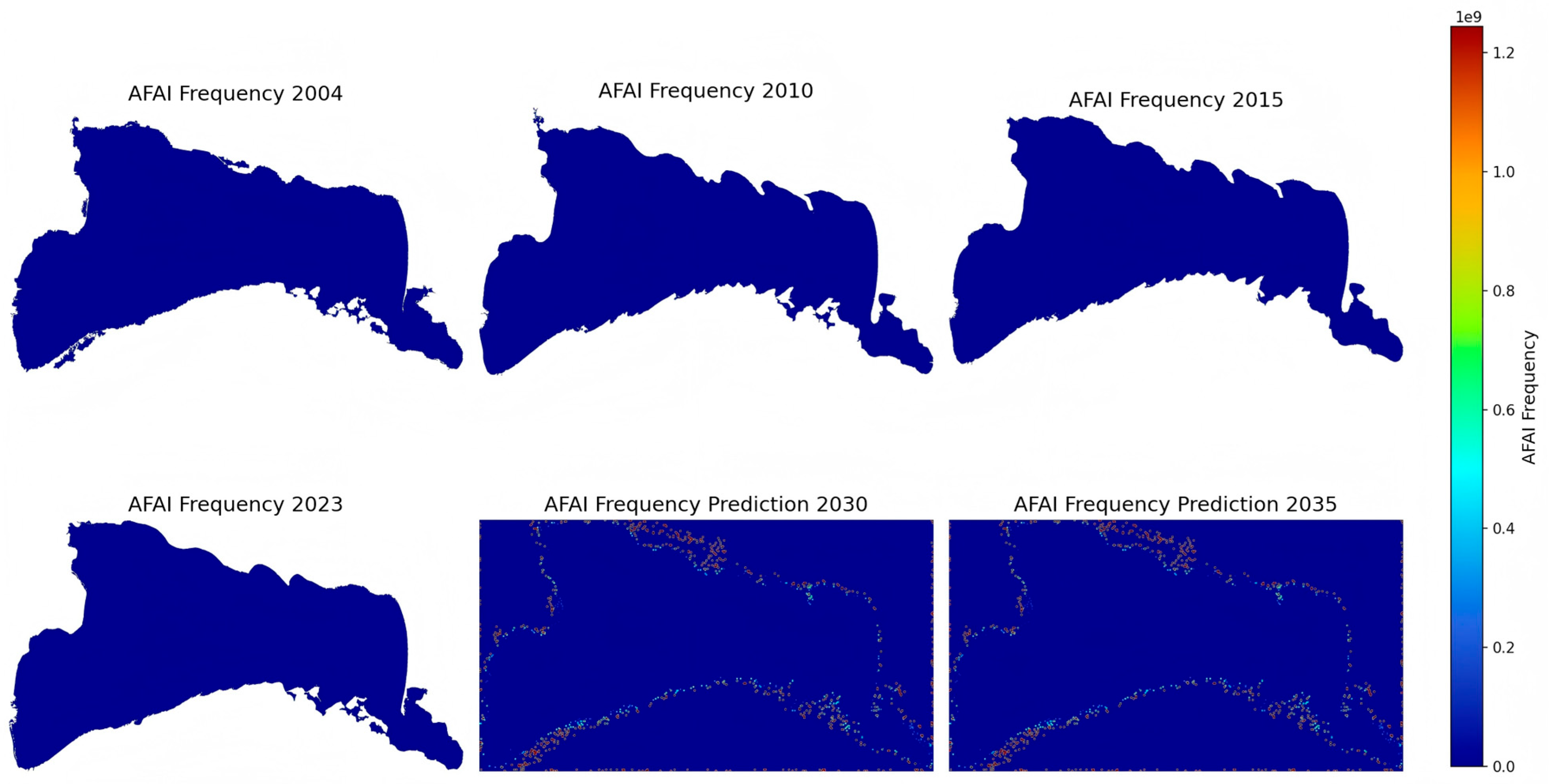
3.2.4. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Bloom Frequency
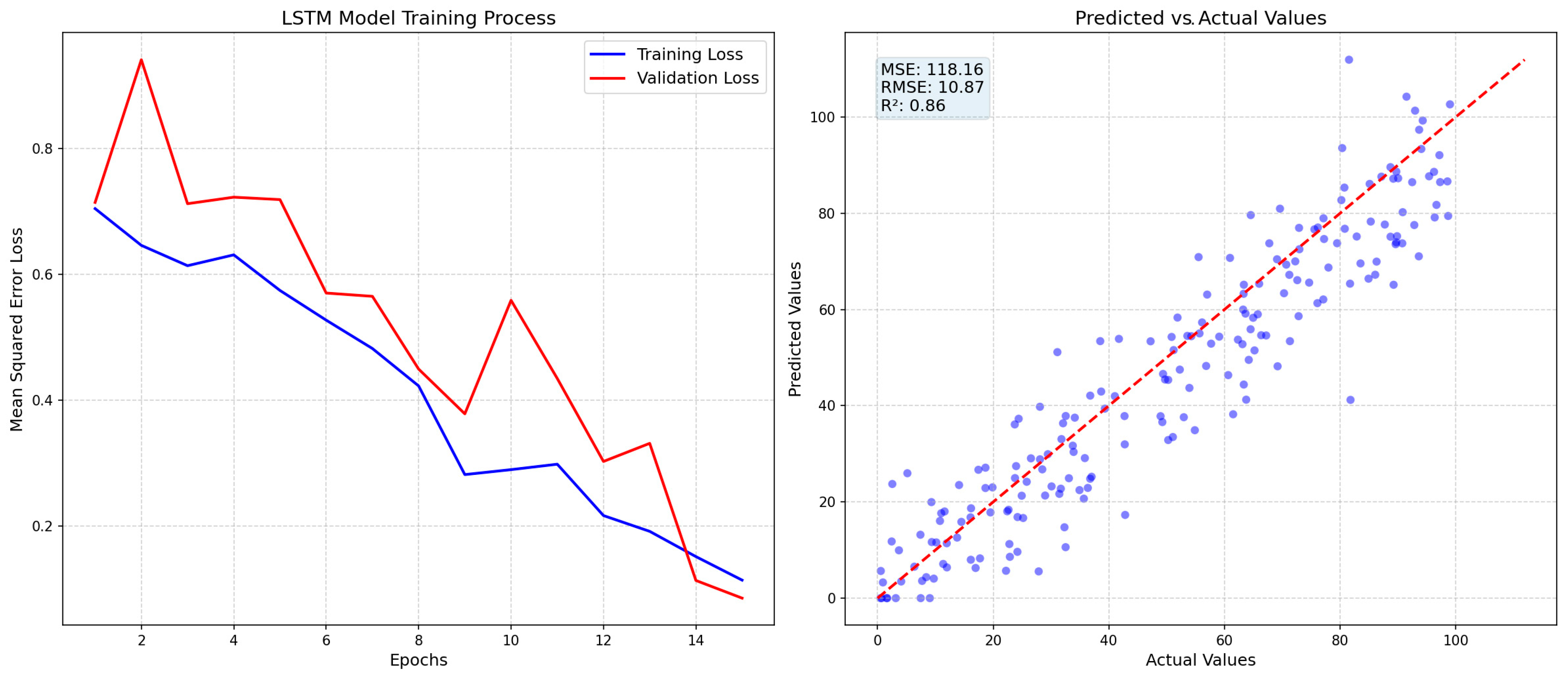
3.2.5. Construction of a Predictive Model for the Spatial Distribution of Algal-Bloom Frequency
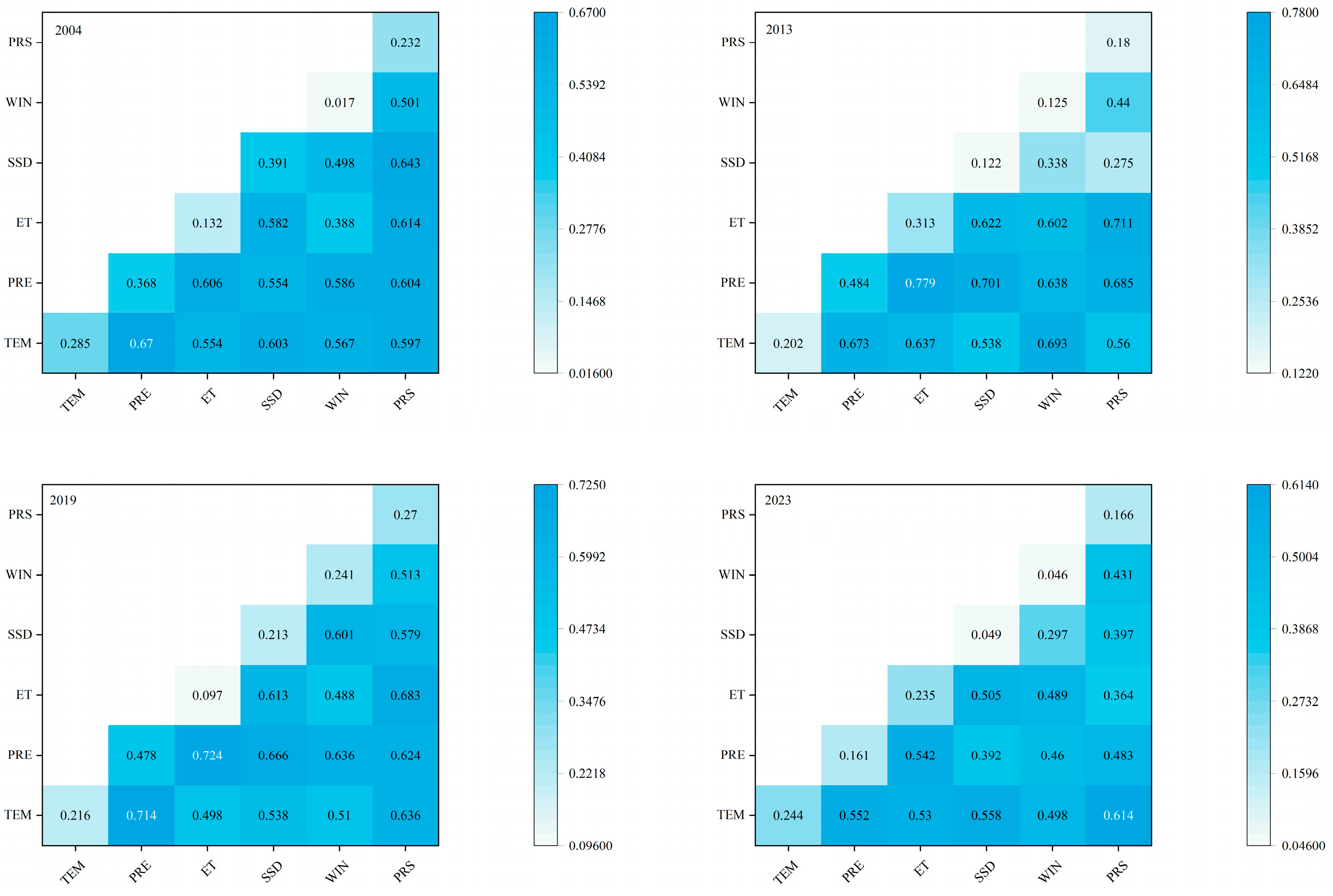
3.3. Analysis of Driving Factors
3.3.1. Analysis of the Impact of Changes in Water Area of Lake Bosten on Algal Blooms
3.3.2. Analysis of the Impact of Meteorological Factors on Algal Blooms
3.3.3. Analysis of the Impact of the Water Column Environment on Algal Blooms
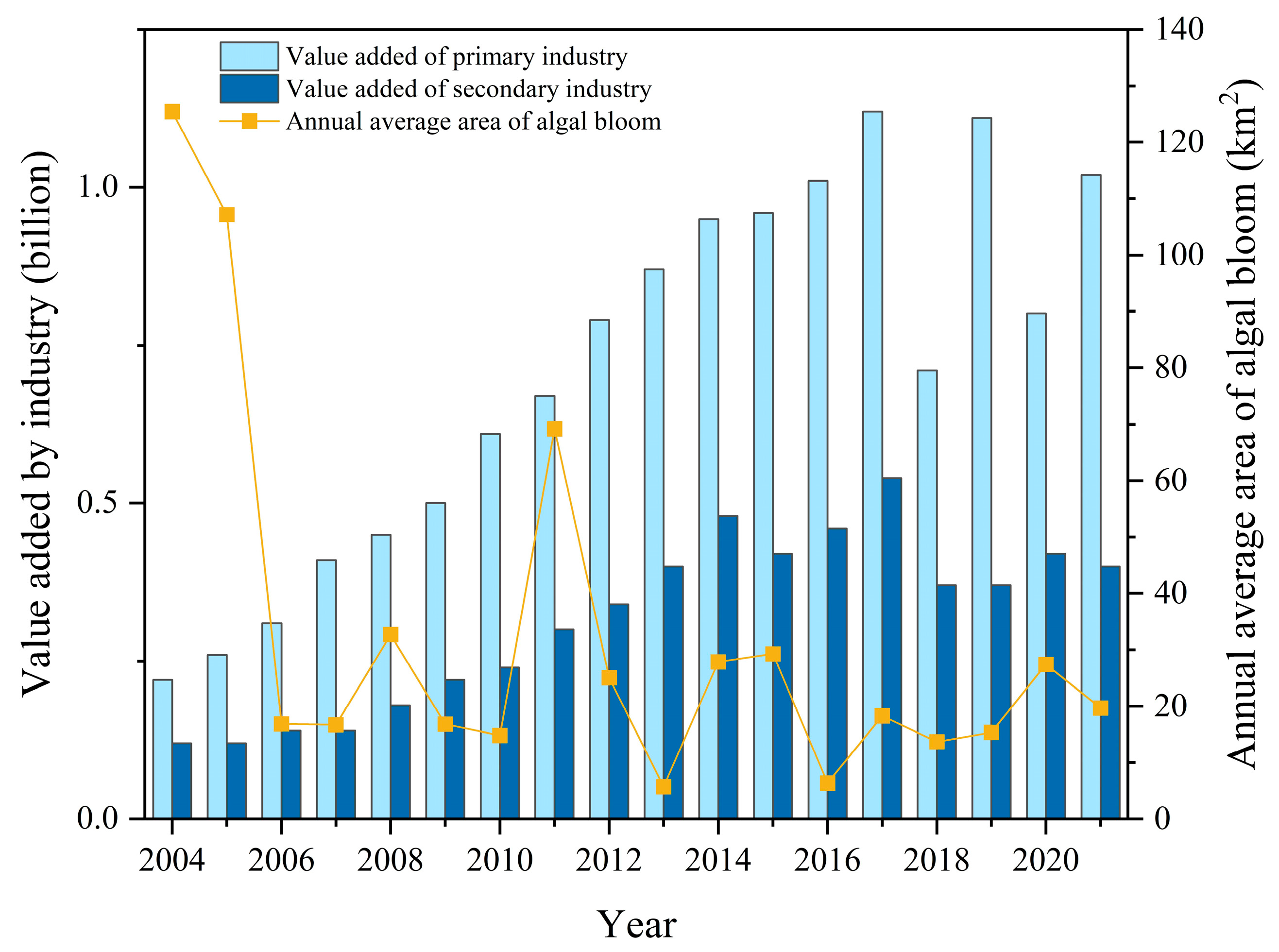
3.3.4. Analysis of the Impact of Human Activities on Algal Blooms
4. Discussion
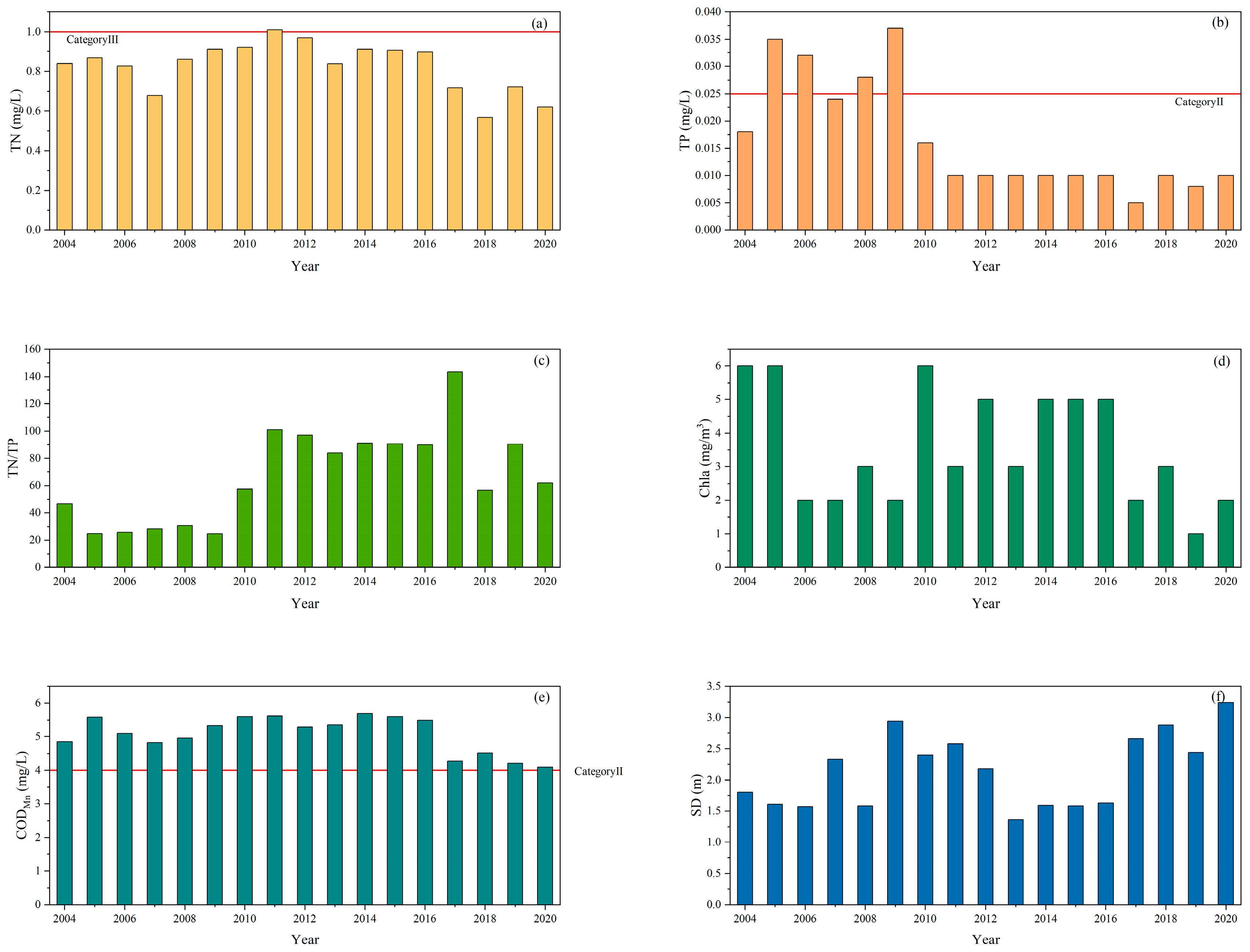
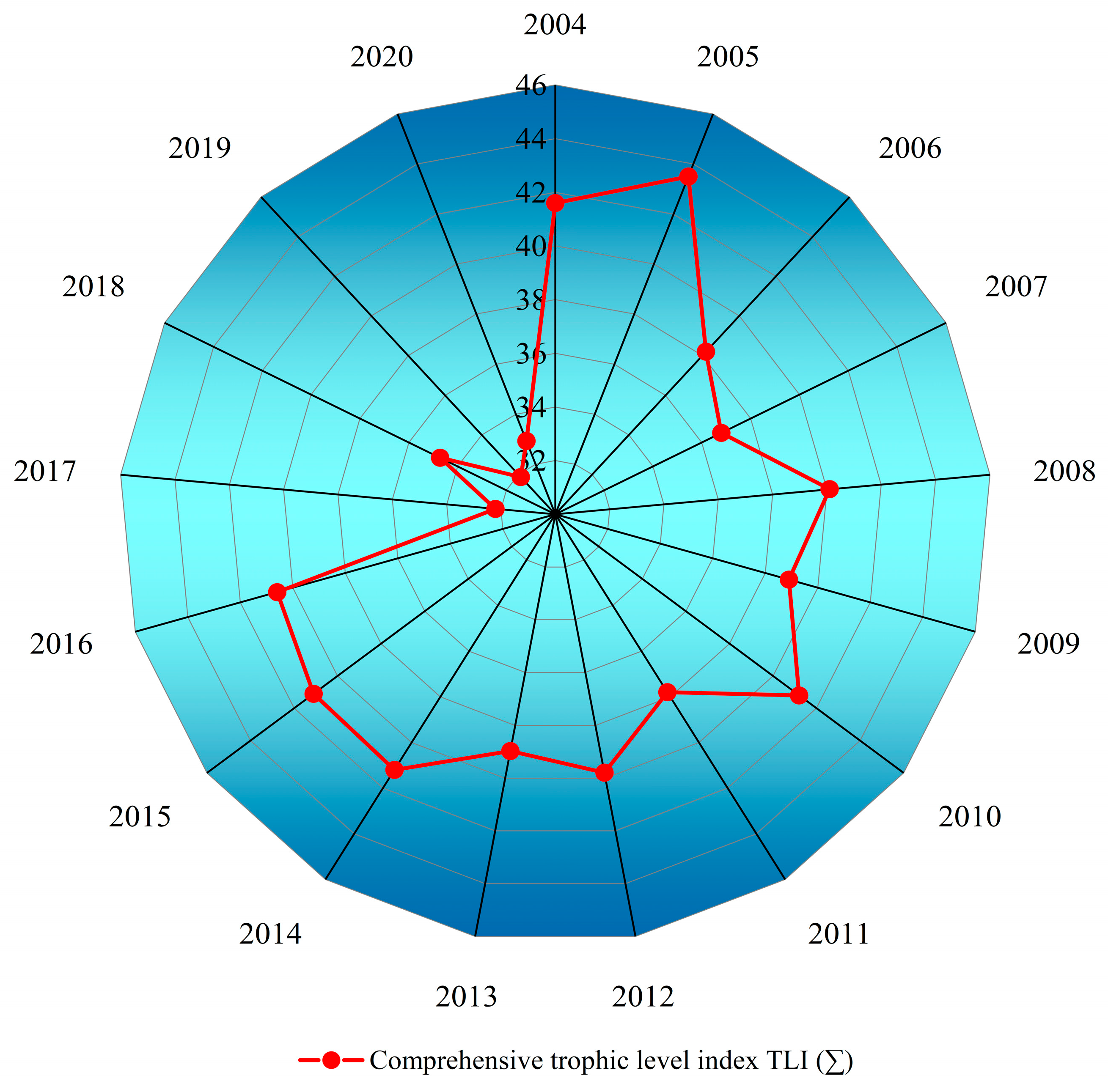
4.1. Water-Quality Trends in Lake Bosten
4.2. Implications for Enhancing Ecological Management of Lakes
4.3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Remote Sensing for Monitoring Algal Blooms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, J.; Jin, S.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Shang, W. Spatio-temporal variations and driving forces of harmful algal blooms in Chaohu Lake: A multi-source remote sensing approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ding, H.; Han, X.; Lang, Y.; Chen, W. Mapping algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems using long-term landsat data: A case study of Yuqiao reservoir from 1984–2022. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, D.; Jin, H.; Wei, Q. Long-term temporal and spatial monitoring of cladophora blooms in qinghai lake based on multi-source remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Pang, Y.; Bao, K. Spatiotemporal distribution of water environmental capacity—A case study on the western areas of Taihu Lake in Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5465–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.-J.; He, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Qin, N.; Ouyang, H.-L.; Wang, Q.-M.; Kong, X.-Z.; He, Q.-S.; Yang, C.; Yang, B. The seasonal and spatial variations of phytoplankton community and their correlation with environmental factors in a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Lv, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, N. Common fate of sister lakes in Hulunbuir Grassland: Long-term harmful algal bloom crisis from multi-source remote sensing insights. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Yan, Q. Improving spaceborne GNSS-R algal bloom detection with meteorological data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Xu, Q.J.; Gao, G.; Shen, J.H. Evaluating genotoxicity associated with microcystin-LR and its risk to source water safety in Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake. Environ. Toxicol. Int. J. 2006, 21, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Li, D.; Shang, S. Moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake, China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115, C04002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L. Spatiotemporal heterogeneities and driving factors of water quality and trophic state of a typical urban shallow lake (Taihu, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53831–53843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, H.; Cheng, B.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, B. A Study of the Effect of Lake Shape on Hydrodynamics and Eutrophication. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xie, M.; Lin, L.; He, S.; Luo, C.; Dong, H. A Study on Spatiotemporal Downscaling Methods for Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Taihu Lake Based on Remote Sensing Data from Sentinel-2 MSI and COMS-1 GOCI. Water 2025, 17, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Jin, S.; Lv, Y.; Yan, Q. Enhancing Algal Bloom Level Monitoring with CYGNSS and Sentinel-3 Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y. Long-term spatiotemporal variation and environmental driving forces analyses of algal blooms in Taihu Lake based on multi-source satellite and land observations. Water 2020, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Alatalo, J.M.; Li, C.; Ni, C. Tracking spatio-temporal dynamics of harmful algal blooms using long-term MODIS observations of Chaohu Lake in China from 2000 to 2021. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Song, K.; Shang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wen, Z.; Du, J. Remote sensing of harmful algal blooms variability for Lake Hulun using adjusted FAI (AFAI) algorithm. J. Environ. Inform. 2018, 34, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ye, Q.; Cai, J.; Wu, C.; Syed, A.K.; Li, J. Long-term remote sensing monitoring on LUCC around Chaohu Lake with new information of algal bloom and flood submerging. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, H.; Dong, H.; He, S. Predictive Modeling of Cyanobacterial Blooms and Diurnal Variation Analysis Based on GOCI. Water 2025, 17, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Xia, W.; Hu, X.; Shao, Z. Dynamic variations of cyanobacterial blooms and their response to urban development and climate change in Lake Chaohu based on Landsat observations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 33152–33166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, K.; Liu, X.; Yao, R.; Cao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Spatial and temporal distributions of microplastics and their macroscopic relationship with algal blooms in Chaohu Lake, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 248, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Loiselle, S.; Shi, K.; Han, T.; Zhang, M.; Hu, M.; Jing, Y.; Lai, L.; Zhan, P. Wind effects for floating algae dynamics in eutrophic lakes. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, T. An evolving marine environment and its driving forces of algal blooms in the Southern Yellow Sea of China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 178, 105635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.-X.; Yu, R.-C.; Zhou, M.-J. Evolution of harmful algal blooms in the East China Sea under eutrophication and warming scenarios. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Cao, Z.; Chu, Q.; Jing, Y. Optimized remote sensing estimation of the lake algal biomass by considering the vertically heterogeneous chlorophyll distribution: Study case in Lake Chaohu of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Shi, X.; Yang, G. Using hydrogen peroxide to control cyanobacterial blooms: A mesocosm study focused on the effects of algal density in Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Chu, Q.; Ma, R. MODIS-satellite-based analysis of long-term temporal-spatial dynamics and drivers of algal blooms in a plateau lake Dianchi, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shao, N.; Yang, S.; Ren, H.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, P.; Liu, W. Quantitative assessment of the effects of human activities on phytoplankton communities in lakes and reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Iqbal, M.; Turan, V.; Tauqeer, H.M.; Farhad, M.; Ahmed, A.; Yasin, S. Household chemicals and their impact. In Environmental Micropollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 201–232. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, M.; Hou, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Multi-factor identification and modelling analyses for managing large river algal blooms. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busico, G.; Kazakis, N.; Cuoco, E.; Colombani, N.; Tedesco, D.; Voudouris, K.; Mastrocicco, M. A novel hybrid method of specific vulnerability to anthropogenic pollution using multivariate statistical and regression analyses. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Zhang, X.; Dong, R. Long-term spatial and temporal monitoring of cyanobacteria blooms using MODIS on google earth engine: A case study in Taihu Lake. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, Q.; Chen, Y. Sustainable Water Use in the Bosten Lake Basin; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Zeng, H. Water quality and quantity characteristics and its evolution in Lake Bosten, Xinjiang over the past 50 years. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water bodies’ mapping from Sentinel-2 imagery with modified normalized difference water index at 10-m spatial resolution produced by sharpening the SWIR band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Yue, W.; Wang, H.; Tan, K.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, W. Research on the Method of Extracting Water Body Information in Central Asia Based on Google Earth Engine. Water 2025, 17, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Ma, Y.J.; Xu, H.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, D.S. Impact of land use and land cover change on environmental degradation in Lake Qinghai watershed, northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Li, G.; Liang, J.; Yu, D.; Aishan, T.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Abulimiti, A.; Liu, J. Dynamic detection of water surface area of Ebinur Lake using multi-source satellite data (Landsat and Sentinel-1A) and its responses to changing environment. Catena 2019, 177, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Xue, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Mechanism of Vegetation Greenness Change and Its Correlation with Terrestrial Water Storage in the Tarim River Basin. Land 2024, 13, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, W.; Chen, Y. High-Precision Prediction of Total Nitrogen Based on Distance Correlation and Machine Learning Models—A Case Study of Dongjiang River, China. Water 2025, 17, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing mechanisms of ecosystem service value in the Tarim River Basin, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Xue, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y. Characterization and Multi-Scenario Prediction of Habitat Quality Evolution in the Bosten Lake Watershed Based on the InVEST and PLUS Models. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, M.; Wang, Y. Contrasting eutrophication risks and countermeasures in different water bodies: Assessments to support targeted watershed management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yan, J.; Ma, J.; Li, F.; Liu, C.; Cai, Y.; Chen, S.; Zeng, J.; Qi, Y. A fuzzy comprehensive assessment and hierarchical management system for urban lake health: A case study on the lakes in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, N.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, F. Assessment of the Effects and Contributions of Natural and Human Factors on the Nutrient Status of Typical Lakes and Reservoirs in the Yangtze River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-L.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Zhan, W.; Zhao, S.-S.; Dawson, R.; Tao, S. An ecosystem health index methodology (EHIM) for lake ecosystem health assessment. Ecol. Model. 2005, 188, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.D.; Gordon, S.I.; Munawar, M.; Charlton, M.N.; Culver, D.A. The Planktonic Index of Biotic Integrity (P-IBI): An approach for assessing lake ecosystem health. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 1234–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooij, W.M.; Trolle, D.; Jeppesen, E.; Arhonditsis, G.; Belolipetsky, P.V.; Chitamwebwa, D.B.; Degermendzhy, A.G.; DeAngelis, D.L.; De Senerpont Domis, L.N.; Downing, A.S. Challenges and opportunities for integrating lake ecosystem modelling approaches. Aquat. Ecol. 2010, 44, 633–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.-m.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Zeng, J.; Miao, A.; Zhao, H. Effects of climatic changes and anthropogenic activities on lake eutrophication in different ecoregions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chislock, M.F.; Kaul, R.B.; Durham, K.A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E. Eutrophication mediates rapid clonal evolution in Daphnia pulicaria. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Peng, W.; Fan, J.; Zhang, T. Water balance of Lake Bosten using annual water-budget method for the past 50 years. Arid. Land Geogr. 2013, 36, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Fu, A. Water-salt succession patterns (1951–2011) and its response to climate change in Lake Bosten. J. Lake Sci. 2014, 26, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro, J.P.; Carder, K.L. Estimating chlorophyll a concentrations from remote-sensing reflectance in optically shallow waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Tang, R.; Sun, X.; Liu, D. Simple methods for satellite identification of algal blooms and species using 10-year time series data from the East China Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Source Name | Time Scale | Spatial Resolution/m | Temporal Resolution/Day | Number of Bands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat5 TM | 1982–2011 | 30 | 16 | 7 bands |
| Landsat7 ETM+ | 1999–present | 30 | 16 | 8 bands |
| Landsat8 OLI | 2013–present | 30 | 16 | 9 bands |
| Sentinel-2 | 2015–present | 20 | 5 | 12 bands |
| Chla | TP | TN | SD | CODMn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.7056 | 0.6724 | 0.6889 | 0.6889 | |
| 0.2663 | 0.1879 | 0.179 | 0.1834 | 0.1834 |
| TLI(Σ) < 30 | Oligotropher |
|---|---|
| 30 ≤ TLI(Σ) ≤ 50 | Mesotropher |
| 50 < TLI(Σ) ≤ 60 | Light eutropher |
| 60 < TLI(Σ) ≤ 70 | Middle eutropher |
| TLI(Σ) > 70 | Hyper eutropher |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xia, T. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Algal Blooms in Lake Bosten Driven by Climate and Human Activities: A Multi-Source Remote-Sensing Perspective for Sustainable Water-Resource Management. Water 2025, 17, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162394
Wang H, Li Z, Wang Y, Xia T. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Algal Blooms in Lake Bosten Driven by Climate and Human Activities: A Multi-Source Remote-Sensing Perspective for Sustainable Water-Resource Management. Water. 2025; 17(16):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162394
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haowei, Zhoukang Li, Yang Wang, and Tingting Xia. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Patterns of Algal Blooms in Lake Bosten Driven by Climate and Human Activities: A Multi-Source Remote-Sensing Perspective for Sustainable Water-Resource Management" Water 17, no. 16: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162394
APA StyleWang, H., Li, Z., Wang, Y., & Xia, T. (2025). Spatiotemporal Patterns of Algal Blooms in Lake Bosten Driven by Climate and Human Activities: A Multi-Source Remote-Sensing Perspective for Sustainable Water-Resource Management. Water, 17(16), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162394






