A Tombolo Alternating Between a Double Tombolo and a Salient on the West Coast of Honghai Bay, Guangdong, China, Driven by Dynamic Fluvial and Coastal Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
2.1. Location of the Study Site
2.2. Climate and Ocean Hydrology of the Study Site
2.3. Geological and Geomorphological Setting
2.4. MEPBAY Model
2.5. XBeach Simulation
2.6. Grain Size Analysis
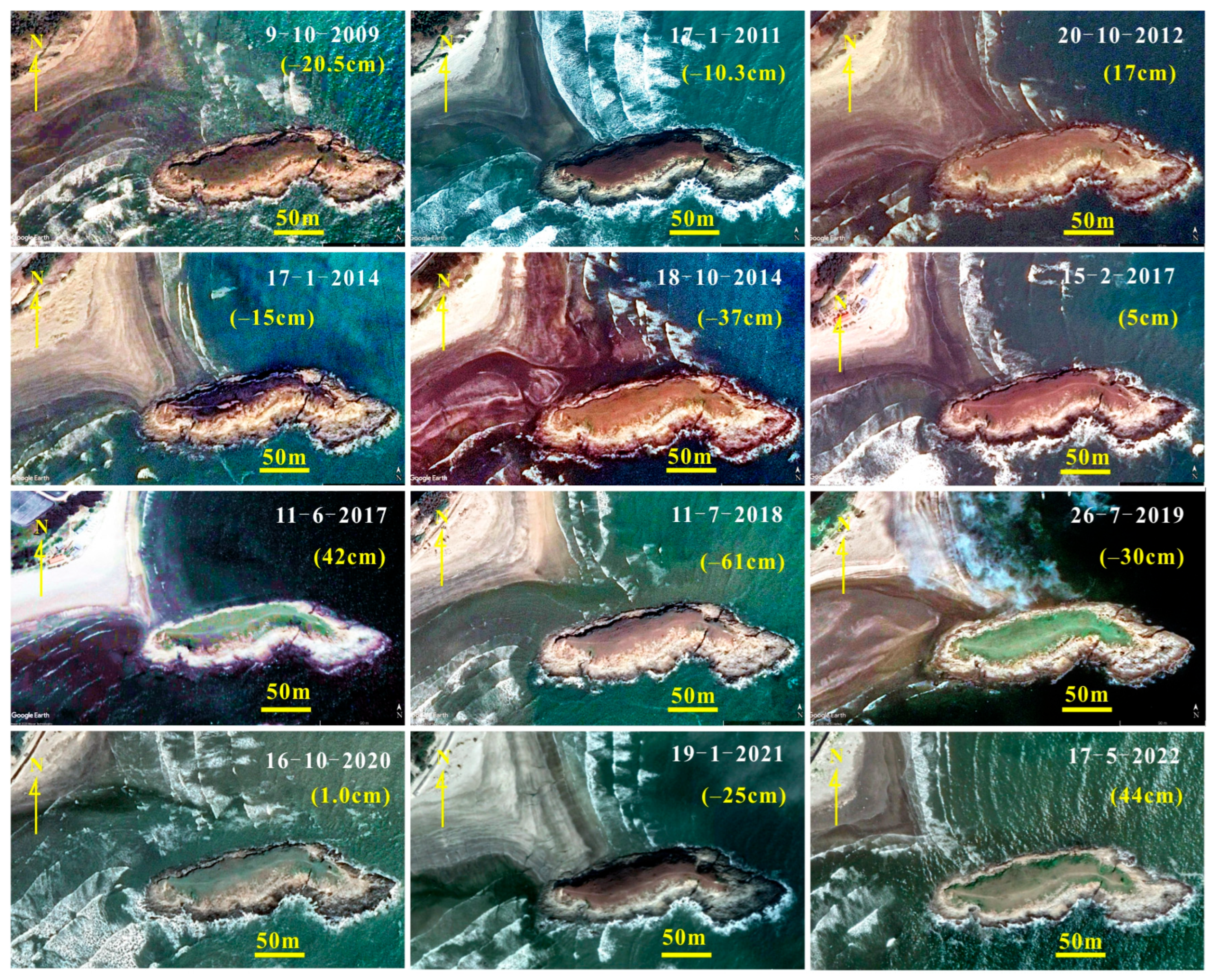
3. Results
4. Discussion
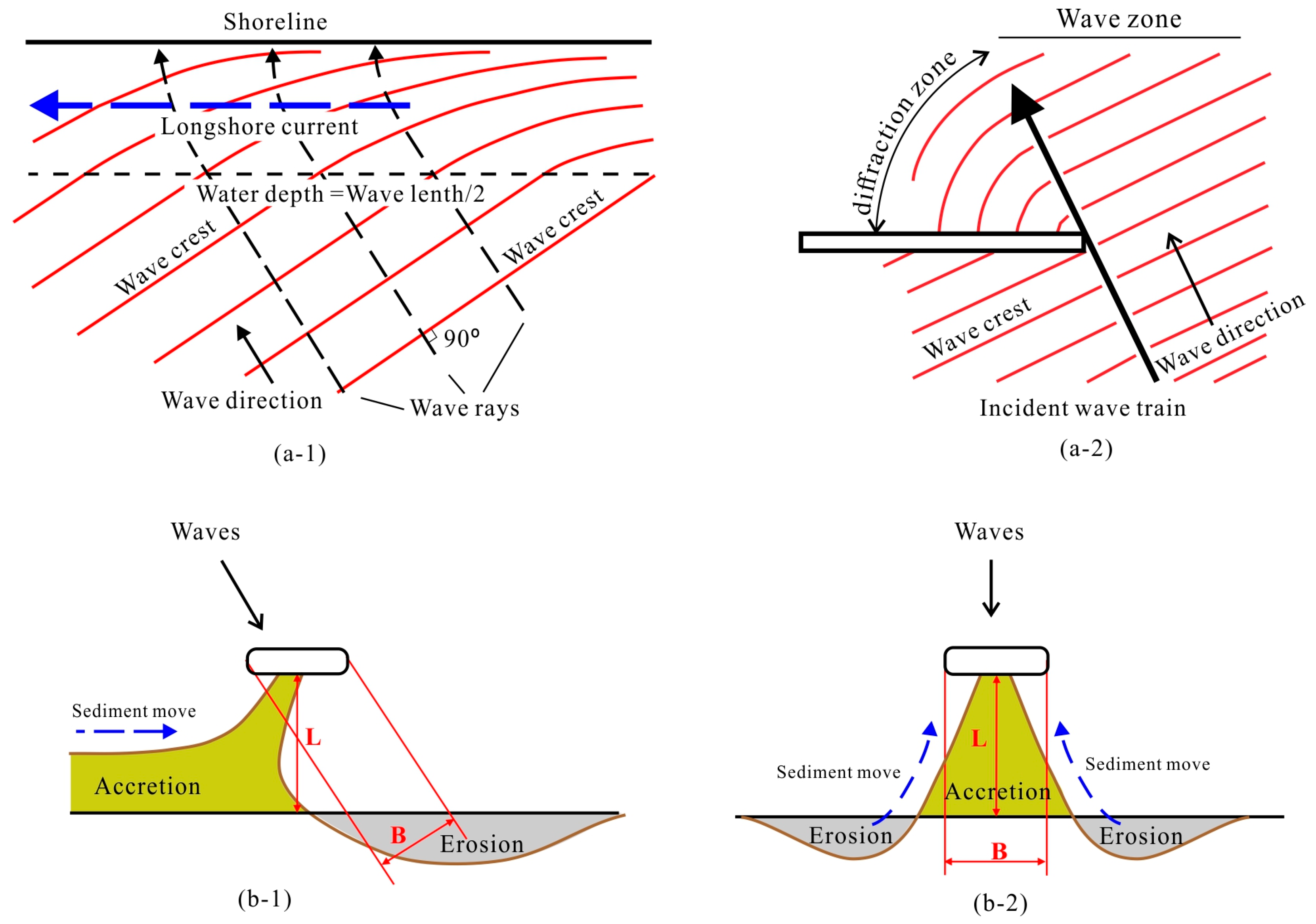
4.1. The Morphological Significance of the Value of LB
4.2. Sediment Sources for the Tombolo Interpreted with Equilibrium Shorelines
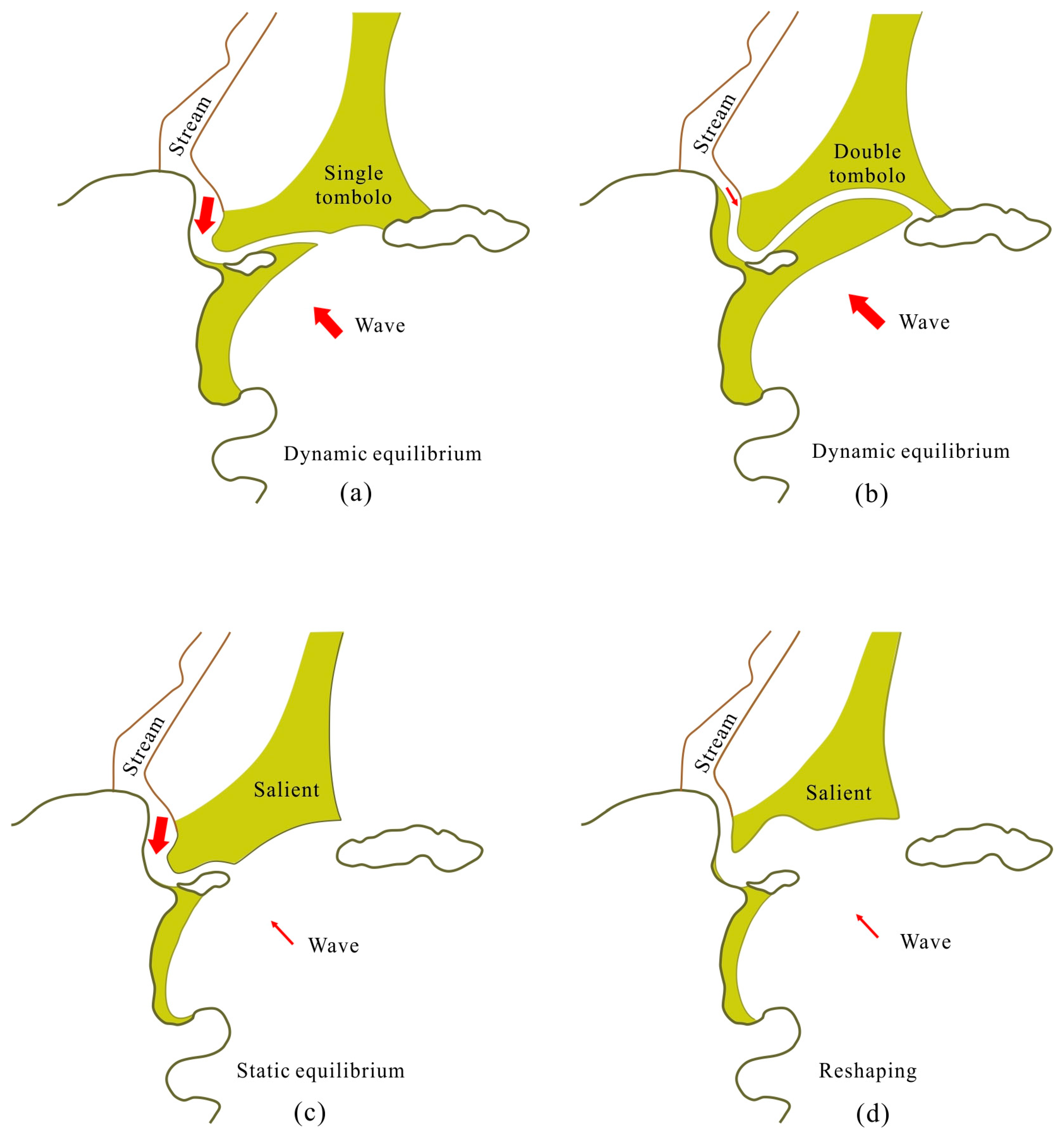
4.3. Formation of the Double Tombolo
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The tombolo behind Huarongshu Island demonstrates a transitional morphology between salient and tombolo formations, primarily influenced by local geological conditions that define the limiting parameter (LB).
- (2)
- A tombolo forms when the natural shoreline on the lee side of the island extends further seaward than the equilibrium shoreline. This occurs because refracted and/or diffracted onshore waves behind Huarongshu Island, along with sediment transported by a stream flowing into the lee side of the island, contribute additional sediment to the area. Longshore drift is not a necessary condition for the formation of the Huarongshu tombolo.
- (3)
- The existence of a stream originating from the hinterland of the Huizhou Peninsula and discharging into the sheltered region behind Huarongshu Island constitutes the primary factor enabling the formation of the double tombolo behind Huarongshu Island.
- (4)
- The formation of either a tombolo or a salient depends on the relative contributions of wave-transported sediment and inland river-derived sediment, and is independent of sea level fluctuations caused by tidal variations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maroukian, H.; Spyrou, E.; Tsiatoura, S.; Tzouxanioti, M.; Evelpidou, N. Sea Level Rise and the Future of Tombolos: The Case of Greece. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, P.G.; Eliot, I. Shoreline Salients, Cuspate Forelands and Tombolos on the Coast of Western Australia. J. Coast. Res. 1996, 12, 761–773. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.W. Shore Processes and Shoreline Development; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1919. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, J.A.; Pérez-Alberti, A. Introducing the Spanish Coast. In The Spanish Coastal Systems: Dynamic Processes, Sediments and Management; Morales, J.A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vidal, J.; Finlayson, G.; Finlayson, C.; Negro, J.J.; Cáceres, L.M.; Fa, D.A.; Carrión, J.S. Undrowning a Lost World—The Marine Isotope Stage 3 Landscape of Gibraltar. Geomorphology 2013, 203, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, F.J.; Del Río, L.; Aranda, M.; Anfuso, G.; Talavera, L.; Montes, J.B.; Benavente, J. Dunes in the Gibraltar Strait Realm. In The Spanish Coastal Systems; Morales, J.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 661–680. [Google Scholar]
- Courtaud, J. Dynamiques Géomorphologiques et Risques Littoraux. Cas Du Tombolo de Giens (Var, France Méridionale); Université deProvence: Aix-en-Provence, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Blanc, J.J. Recherches Sédimentologiques Littorales et Sous-Marines en Provence Occidentale. Ph.D. Thesis, Masson, Paris, France, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Gosseaume, E. Le Tombolo Triple d’Orbetello (Toscane). Bull. Soc. Languedoc. Geogr. 1973, 7, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, E.J.; Blivi, A.B. Morphosedimentary evolution of a delta-sourced, drift-aligned sand barrier-lagoon complex, western Bight of Benin. Mar. Geol. 1999, 158, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blivi, A.; Anthony, E.J.; Oyede, L.M. Sand barrier development in the bight of Benin, West Africa. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2002, 45, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriner, N.; Goiran, J.P.; Morhange, C. Alexander the Great’s tombolos at Tyre and Alexandria, eastern Mediterranean. Geomorphology 2008, 100, 377–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkovich, V.P. Processes of Coastal Development; Oliver and Boyd: Edinburgh, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Specht, C.; Lewicka, O.; Specht, M.; Zblewski, S. Impact of Hydrotechnical Structures on Forming the Tombolo Oceanographic Phenomenon in Kołobrzeg and Sopot. TransNav Int. J. Mar. Navig. Saf. Sea Transp. 2021, 15, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangor, K.; Dronen, N.K.; Kærgaard, K.H.; Kristensen, N. Shoreline Management Guide. Available online: https://www.dhigroup.com/marine-water/ebook-shoreline-management-guidelines (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Davies, J.L. Geographical Variation in Coastal Development; Longman: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Goiran, J.P. Recherches Géomorphologiques Dans la Région Littorale d’Alexandrie en Egypte; Université de Provence-Aix-Marseille: Marseille, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Flinn, D. The Role of Wave Diffraction in the Formation of St. Ninian’s Ayre (Tombolo) in Shetland, Scotland. J. Coast. Res 1997, 13, 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Brocard, G.; Jean-Philippe Goiran, J.P.; Conforti, A.; Preusser, F.; Vitale, Q.; Jouvee, G.; Darrasa, L.; Benecha, C.; Vittoria, C.; Oberlinf, C.; et al. Double tombolo formation by regressive barrier widening and landside submergence: The case of Orbetello, Italy. Mar. Geol. 2024, 477, 107415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S. Tombolo. In Encyclopedia of Geomorphology; Goudie, A.S., Ed.; Rutledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hansom, J.D. St Ninian’s Tombolo, Shetland. In Coastal Geomorphology of Great Britain; May, V.J., Hansom, J.D., Eds.; Geological Conservation Review Series No. 28; Joint Nature Conservation Committee: Peterborough, UK, 2003; pp. 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- Pirazzoli, P.A.; Stiros, S.C.; Arnold, M.; Laborel, J.; Laborel-Deguen, F.; Papageorgiou, S. Episodic uplift deduced from Holocene shorelines in the Perachora Peninsula, Corinth area, Greece. Tectonophysics 1994, 229, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malliouri, D.I.; Petrakis, S.; Vandarakis, D.; Kikaki, K.; Hatiris, G.-A.; Gad, F.-K.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P.; Kapsimalis, V. The Role of Sea State to the Morphological Changes of Prasonisi Tombolo, Rhodes Island, Greece. Water 2022, 14, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Fontoura Klein, A.H.; Junior, N.A.; De Menezes, J.T. Shoreline Salients and Tombolos on the Santa Catarina coast (Brazil): Description and analysis of the morphological relationships. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 36, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemura, T.; Takasugi, J.; Komiya, Y. Formation of tombolo at the west coast of Iwo-Jima. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Houston, TX, USA, 17–21 September 1984; pp. 1403–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, K.D.; Hardaway, C.S. Calculation of Tombolo in shoreline numerical model. Proc. Coast. Eng. 1995, 3, 2653–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyawan, W.B. Meulaboh Tombolo Response to Large Tsunami, West Coast of Sumatra Island, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 750, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntafloukas, C.; Savvidis, Y. Climate-DrivenWave Analysis Reveals Changes in Alongshore Sediment Transport: The Case of the Coastal Zone of a Harbor in Thermaikos Bay (NW Aegean Sea). Water 2024, 16, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykal, C.; Özsoy, C. Quasi-2DH Modeling of the Shoreline Evolution Around an Offshore Breakwater. J. ETA Mar. Sci. 2024, 12, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, F.; Lin, P. Formation law of tombolos and its application in port construction. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1984, 6, 117–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, A.; Cai, Y. Formation of Gongqian Tombolo in Dongshan Island. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 1990, 10, 81–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, E. The formation and evolution of the Chudao Island Tombolo. Period. Ocean Univ. China 1993, 23, 81–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.D. Morphological analysis of a tombolo associated with a wrecked ship. Port Eng. Technol 1989, 2, 31–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B. Hydrological characterization of Huizhou City. Guangdong Water Res. Hydropower 2004, 5, 73–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huizhou Mucipal Bureau of Statistics and National Bureau of Statistics Huizhou Survey Team. In Huizhou Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023.
- China Gulf Records Compilation Committee. China Gulf Records, V. 9; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Ye, C. Ocean Hydrology of Islands off the Coast of Guangdong; Guangdong Science and Technology Press: Guangzhou, 1995. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.Q.; Chen, P.Q. Geology of Islands off the Coast of Guangdong; Guangdong Science and Technology Press: Guangzhou, China, 1994. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ahd, K.; Vargas, A.; Ala, R.; Hsu, J.R.C. Visual assessment of bayed beach stability with computer software. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.G.; Sánchez, J.M.; Medina, R.; Beck, A.L.; Taji, M.A. On the use of satellite information to detect coastal change: Demonstration case on the coast of Spain. Coast. Eng. 2024, 191, 104517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasso, W.E. Plan geometry of headland-bay beaches. J. Geol. 1965, 73, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.R.C.; Evans, C. Parabolic bay shapes and applications. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1989, 87, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.J.; Kraus, N.C.; Equilibrium Shape of Headland-Bay Beaches for Engineering Design. Coastal Defense Program Madrid (Spain). 1999. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA483142.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Manakul, C.; Mohanasundaram, S.; Weesakul, S.; Shrestha, S.; Ninsawat, S.; Chonwattana, S. Classifying Headland-Bay Beaches and Dynamic Coastal Stabilization. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.L. MeePaSoL: MATLAB-GUI Based Software Package; SKKU Copyright No. C-2015-02461; Sungkyunkwan University: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, J.R.C.; Benedet, L.; Klein, A.H.F.; Raabe, A.L.A. Appreciation of static bay beach concept for coastal management and protection. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 24, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvester, R.; Hsu, J.R.C. Coastal Stabilization: Innovative Concepts; Prentice-Hall: Sudbury, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, J.R.C.; Yu, M.J.; Lee, F.C.; Benedet, L. Static bay beach concept for scientists and engineers: A review. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Razak, M.S.; Nor, N.A.Z.M. XBeach process-based modelling of coastal morphological features near breakwater. EDP Sci. 2018, 203, 01007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Konert, M.; Vandenberghe, J.E.F. Comparison of laser grain size analysis with pipette and sieve analysis—A solution for the underestimation of the clay fraction. Sedimentology 1997, 44, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier-Sowinski, J. Practical Handbook of Grain Size Analysis. Principles and Methods; Zenodo: Station Marine, France, 2024; p. 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumbein, W.C.; Pettijohn, F.J. Manual of Sedimentary Petrography; Appleton-Century: New York, NY, USA, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar [Texas]; a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Z. A Matlab method of graphical calculation for grain size parameters. Trop. Geogr. 2006, 26, 239–242. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Carmona, P.; Ruiz, J.M. Geomorphological and geoarchaeological evolution of the coastline of the Tyre tombolo: Preliminary results. Bull. Archéol. Archit. Libanaises Hors-Série 2004, 1, 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Coghlan, I.; Carley, J.T.; Harrison, A.J.; Vos, K.; Lenehan, N.; Wiecek, D. Broulee: An Island No More? In Proceedings of the 27th NSW Coastal Conference 2018, Merimbula, NSW, Australia, 7–9 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Engineering Field Handbook, Chapter 2—Estimating Runoff Volume and Peak Discharge. 2021. Available online: https://directives.nrcs.usda.gov/sites/default/files2/1712930818/31754.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Castelle, B.; Robinet, A.; Idier, D.; D’Anna, M. Modelling of embayed beach equilibrium planform and rotation signal. Geomorphology 2020, 369, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, N.G.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T.; Conley, D.; McCarroll, R.J. Role of waves and tides on depth of closure and potential for headland bypassing. Mar. Geol. 2019, 407, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
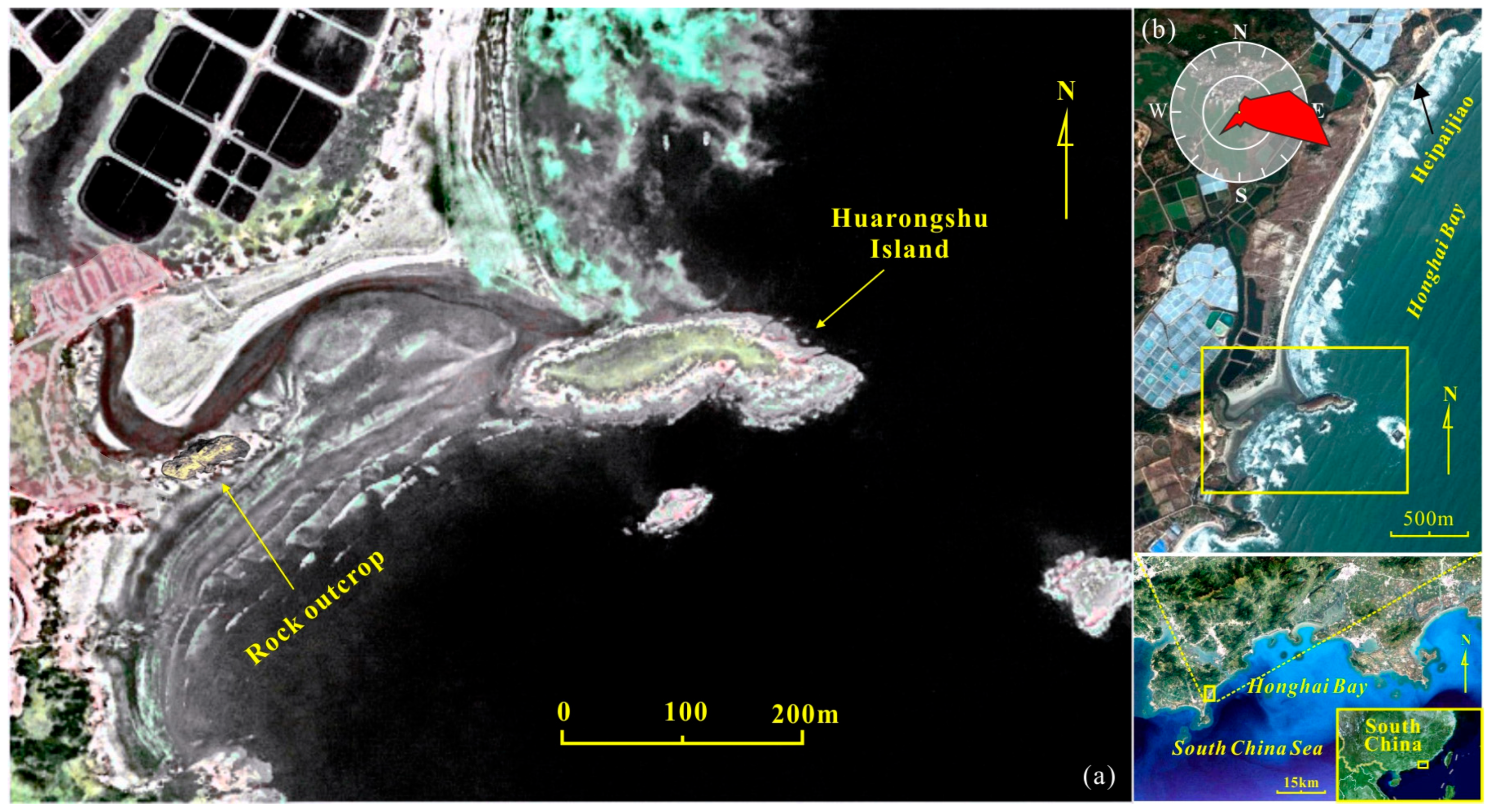
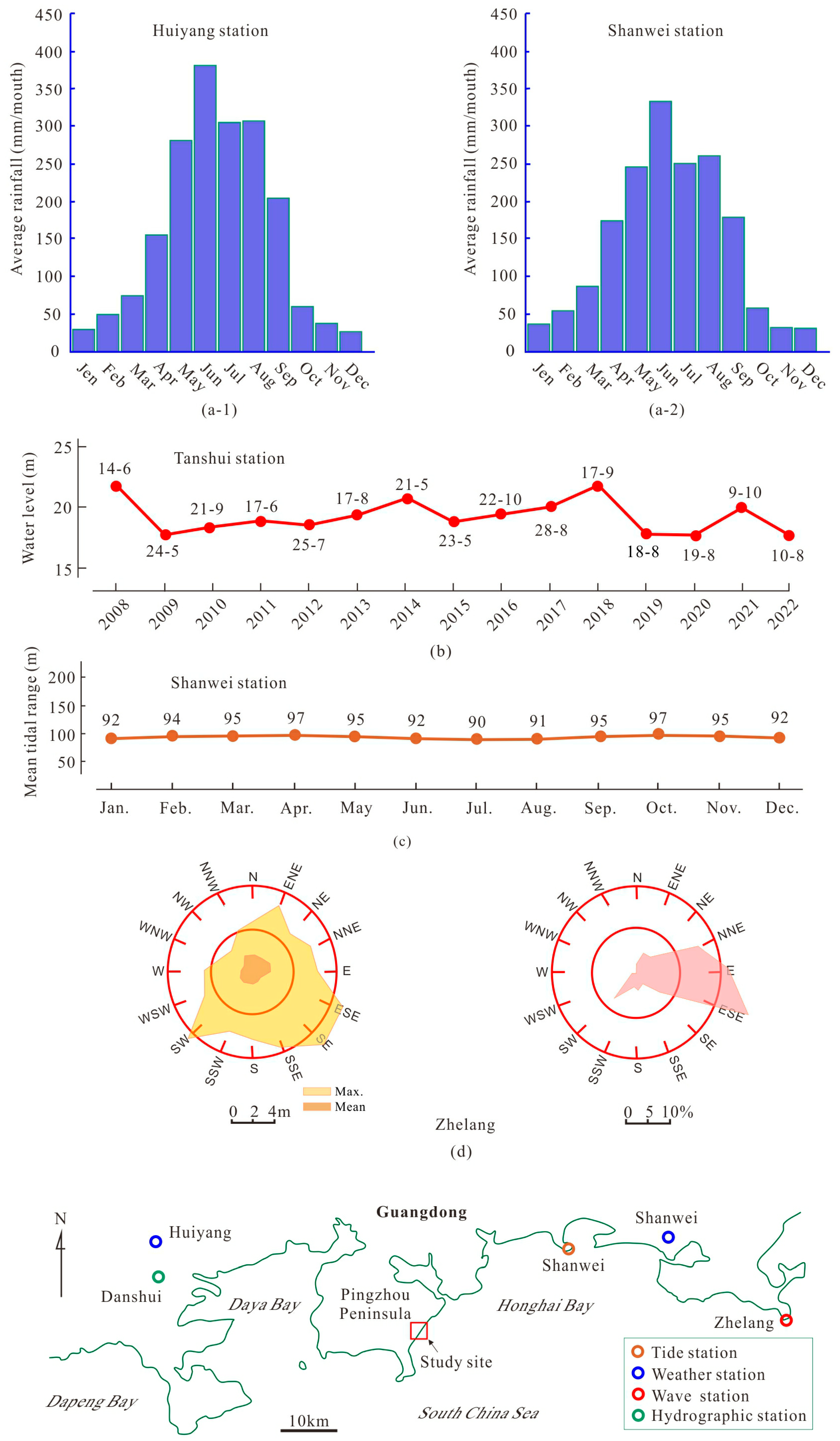
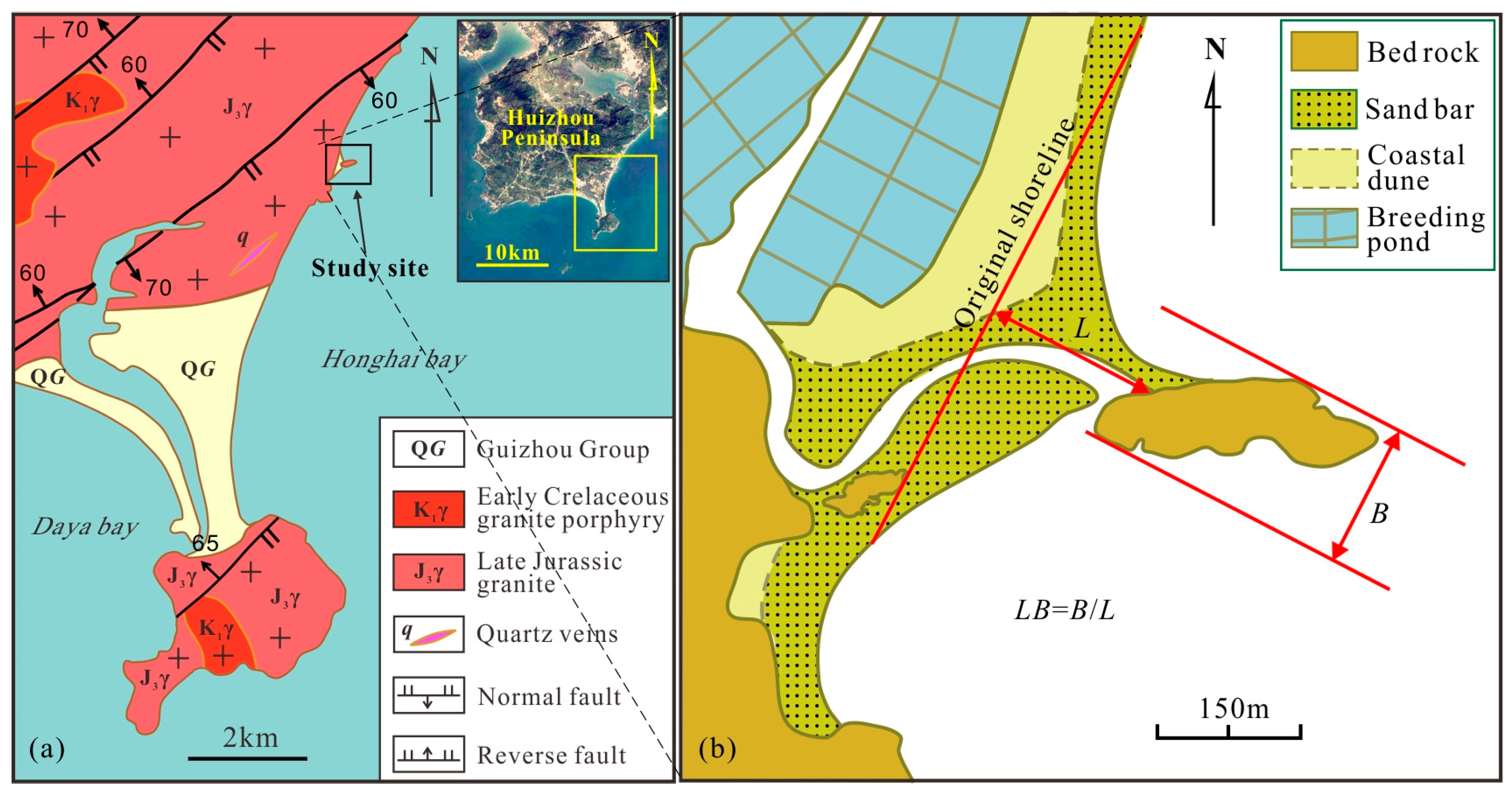

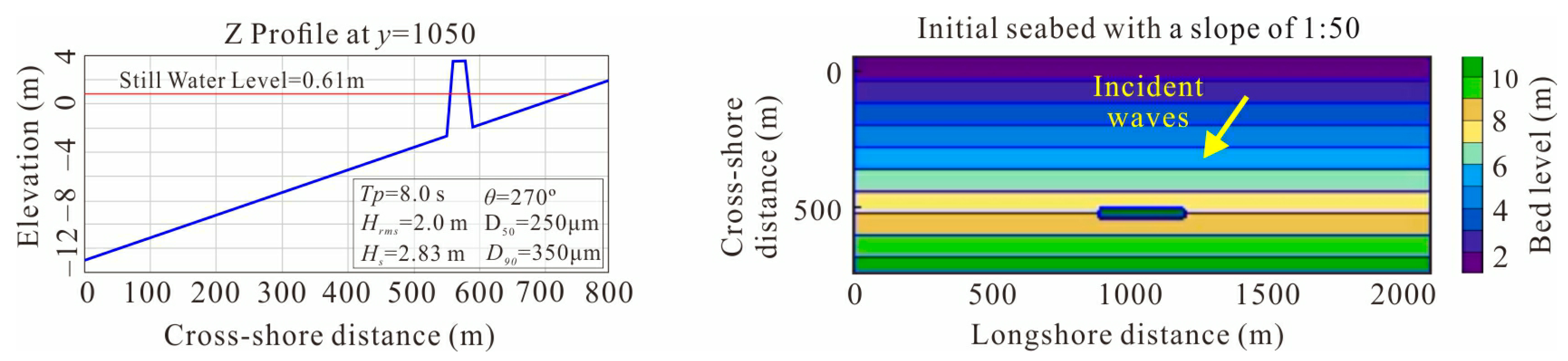
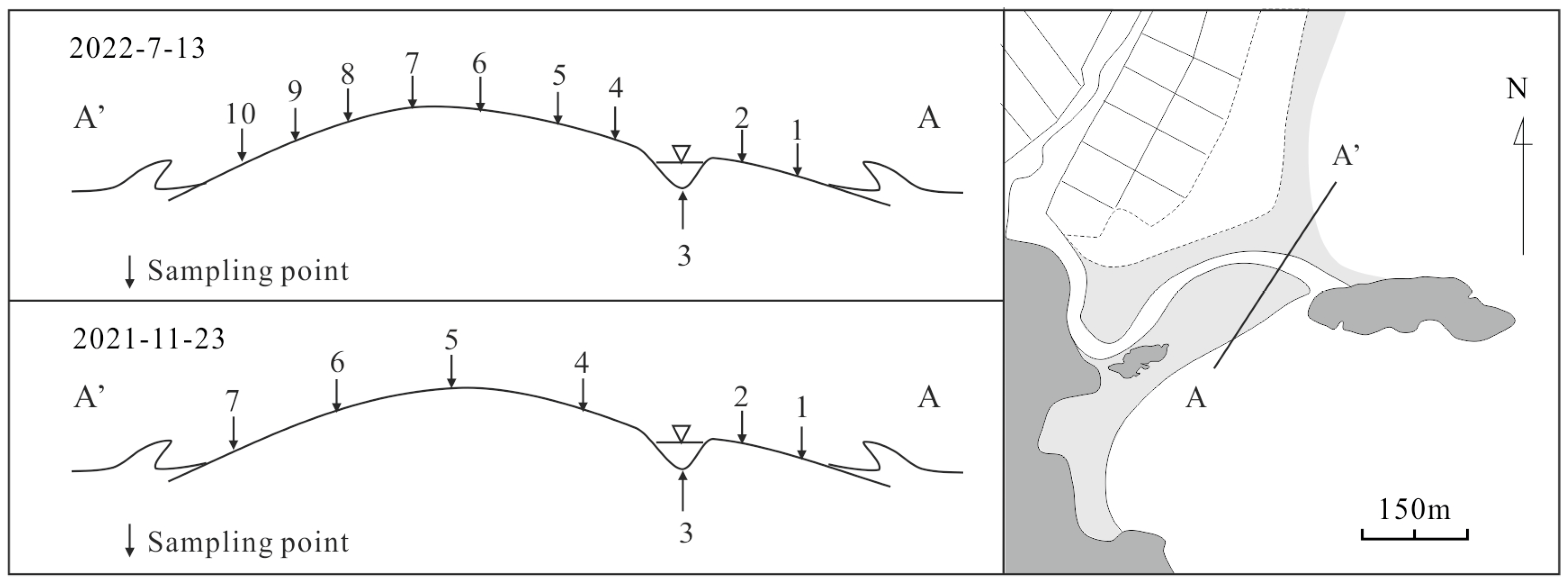



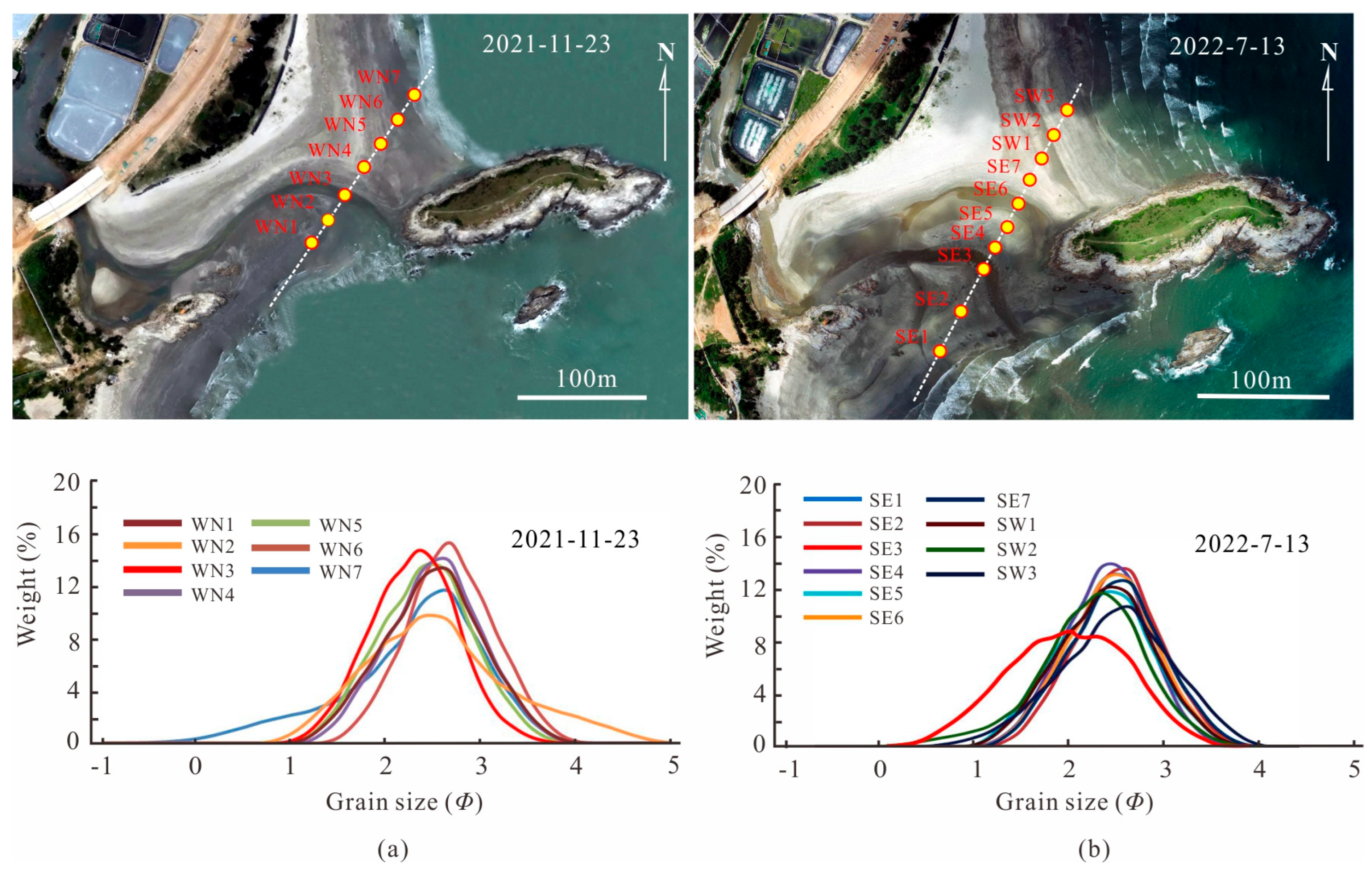
| Sample Location | Mean Size (Mz Φ) | Sorting (σ1) | Asymmetry (Sk1) | Kurtosis (KG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE-1 | 2.35 | 0.47 | −0.03 | 1.00 |
| SE-2 | 2.43 | 0.46 | −0.00 | 0.98 |
| SE-3 | 1.91 | 0.65 | −0.06 | 1.03 |
| SE-4 | 2.31 | 0.45 | −0.02 | 0.96 |
| SE-5 | 2.28 | 0.52 | −0.03 | 0.93 |
| SE-6 | 2.36 | 0.47 | −0.03 | 0.95 |
| SE-7 | 2.41 | 0.50 | −0.01 | 1.00 |
| SW-1 | 2.30 | 0.51 | −0.03 | 0.98 |
| SW-2 | 2.08 | 0.57 | −0.08 | 1.09 |
| SW-3 | 2.41 | 0.60 | −0.06 | 1.03 |
| WN-1 | 2.39 | 0.53 | −0.02 | 1.00 |
| WN-2 | 2.45 | 0.79 | 0.14 | 1.10 |
| WN-3 | 2.20 | 0.48 | −0.01 | 0.99 |
| WN-4 | 2.42 | 0.50 | −0.01 | 0.98 |
| WN-5 | 2.31 | 0.51 | −0.03 | 0.94 |
| WN-6 | 2.59 | 047 | −0.01 | 0.99 |
| WN-7 | 2.21 | 0.74 | −0.25 | 1.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, M.; Wang, W. A Tombolo Alternating Between a Double Tombolo and a Salient on the West Coast of Honghai Bay, Guangdong, China, Driven by Dynamic Fluvial and Coastal Interactions. Water 2025, 17, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101510
Qiu M, Wang W. A Tombolo Alternating Between a Double Tombolo and a Salient on the West Coast of Honghai Bay, Guangdong, China, Driven by Dynamic Fluvial and Coastal Interactions. Water. 2025; 17(10):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101510
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Mingkun, and Wei Wang. 2025. "A Tombolo Alternating Between a Double Tombolo and a Salient on the West Coast of Honghai Bay, Guangdong, China, Driven by Dynamic Fluvial and Coastal Interactions" Water 17, no. 10: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101510
APA StyleQiu, M., & Wang, W. (2025). A Tombolo Alternating Between a Double Tombolo and a Salient on the West Coast of Honghai Bay, Guangdong, China, Driven by Dynamic Fluvial and Coastal Interactions. Water, 17(10), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101510






