Abstract
Fifty-one surface sediment samples from Dongshan Bay, China, were analyzed for heavy metals to evaluate their distribution, pollution status, and controlling factors. The enrichment factor is suggestive of the potential pollution status, ranging from minimal to moderate enrichment, for Pb, As, Zn, and Hg, with one site showing significant enrichment in As. A principal component analysis and the geochemical characteristics indicate that heavy metal concentrations are mainly influenced by clay minerals and Fe oxides, while Pb and Hg levels are also closely linked to the absorption of Mn oxides. Potential pollution is primarily from aquaculture (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) and industrial and domestic discharges. Approximately 270 tons of heavy metals were estimated to have been deposited in Dongshan Bay in 2021, highlighting the potential impact of human activities on coastal sediment quality.
1. Introduction
Heavy metal contamination, known for its persistence, potent bioaccumulation, and diverse sources, has garnered significant worldwide attention due to its ecological and environmental impacts [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. These impacts are primarily summarized into two aspects: First, heavy metal elements readily traverse biological membranes and accumulate in the food chain, with accumulation coefficients reaching 104, thereby posing potential risks to the human central nervous system and certain organs [4,6]. These environmental hazards are epitomized by the Minamata disease incident (related to high concentrations of Hg and MeHg) in the 1950s in Japan [10] and the cadmium pollution events through rice consumption [11,12]. Second, some heavy metals, such as mercury (Hg) and lead (Pb), are globally transported, with their ability to infiltrate environmentally sensitive areas such as bays, lakes, reservoirs, marshes, and estuaries via atmospheric and riverine transportation and deposition [13]. Typical cases include the excessive presence of Pb in lake waters during the Flint Water Crisis in the USA [14] and the identification of the ‘Arctic mercury snow belt’ [15]. Furthermore, the behaviors of heavy metal elements in estuaries or bays have consistently been a critical aspect of the global metal element cycle, playing a pivotal role in studies of the “source to sink” and land–ocean interactions.
Estuary or bay sediments act as the sink where rivers flow into the sea [16]. Compared to water bodies, sediments have higher concentrations of heavy metals, which can be readily released back into the water, causing secondary pollution, especially during changes in the seabed environment [6,7]. Bays, crucial for human economic activities, are characterized by their semi-enclosed hydrodynamic environment due to being surrounded by land, leading to the easy accumulation of heavy metals along the coast from human activities [17,18,19,20,21,22]. With the advancement of economic development, urbanization, and population growth, a significant amount of pollutants from industrial and agricultural production, as well as human activities, were discharged into rivers and subsequently accumulate in estuaries or bays [23,24,25]. Therefore, conducting research on the content, existing forms, and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in bay sediments can reflect the current status of heavy metal enrichment under the influence of human activities in bays and reveal the impact of watershed human activities on the bay environment.
Dongshan Bay, located in the Southeast of China, is substantially impacted by aquacultural practices. This study aims to elucidate the distribution patterns and determinants of heavy metal concentrations within the seabed sediments of Dongshan Bay, with the objective of evaluating the sediment quality. To assess the impacts of recent anthropogenic activities, including the discharge of industrial and domestic wastewater, aquaculture practices, and marine pollution from shipping, surface sediments were sampled from Dongshan Bay in 2021. The analyses conducted on these sediments encompassed the determination of concentrations of major and trace elements, organic carbon, total carbon, and grain size. This investigation offers a comprehensive assessment of the environmental condition of Dongshan Bay, laying the groundwork for the formulation of effective conservation strategies and the sustainable utilization of its marine ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
Dongshan Bay (23°40′ N, 117°25′ E, Figure 1), located in the southeastern part of Fujian province, is a typical subtropical, tide-dominated semi-enclosed bay and is representative of bays along Southeast China’s coast affected by human activities [21]. The bay covers a total area of 275.6 km2, making it one of the three major bases for aquaculture production in Fujian province. The bay extends inland in an irregular pear shape, with the Zhangjiang River flowing into its northeastern part and the Bachimen strait connecting it to Zhao’an Bay on the west. The bay’s mouth opens southward to the East China Sea. The sediments in Dongshan Bay consist of mud, sandy mud, silt, sandy silt, and silty sand. Mud and sandy mud are mainly found in the northeastern part of the bay near the Zhangjiang River channel and the Bachimen strait. Silty sand is predominantly located at the junction between the bay and the East China Sea. Silt is chiefly distributed in nearshore areas, while sandy silt is mainly found in the central and southern parts of the bay (Figure 1).
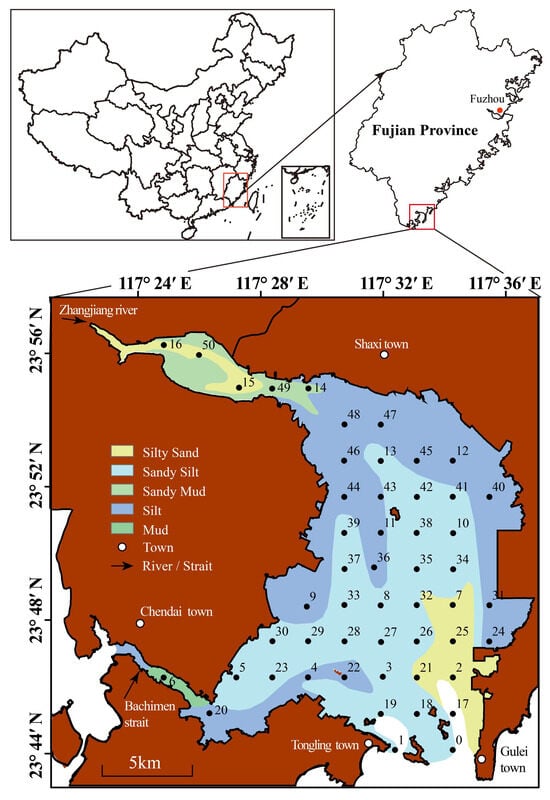
Figure 1.
Sediment type and sample stations of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China. The brown area represents the land.
A total of 51 sampling stations were established across Dongshan Bay for the collection of surface sediments in November 2021 (the sampling stations illustrated in Figure 1). The arrangement of these stations comprehensively covers most of the bay, including the Zhangjiang river channels and the Bachimen strait, representing one of the most systematic marine surveys to date. Surface sediments (0 to 5 cm) were collected using a gravity box corer, which had an opening area of approximately 50 × 50 cm and achieved a penetration depth of 60 cm. Samples designated for geochemical composition analysis, as well as for the identification of grain size, detritus, and clay content, were transferred into sealed plastic bags and stored in aluminum boxes, and subsequently preserved at 4 °C in a refrigerator. These collected samples were subjected to freeze-drying for a duration exceeding 48 h and then ground to a fineness of 200 mesh in preparation for elemental analyses.
2.2. Major and Trace Elements Analyses
The analyses of major and trace elements in surface sediment samples were completed at the Sanming Laboratory of the Fujian Institute of Geological Survey. An accurate weight of 0.7000 g of the sample was taken, then melted with anhydrous sodium tetraborate, using ammonium nitrate as an oxidant, lithium fluoride, and a small amount of lithium bromide as fluxing and mold releasing agents, at a temperature of 1150 °C on a fusion machine to form glass beads. Subsequently, the contents of SiO2, Al2O3, TFe2O3, TiO2, K2O, Na2O, CaO, MgO, MnO, and P2O5 were determined using the Axios max X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Almelo, The Netherlands), based on the fluorescence intensity. Based on the sediment and rocks standards, the errors in the measurement of the major elements were found to be less than 5%.
For trace element analyses, a 50 mg sample was weighed into a PTFE sealed digestion vessel. Then, 1 mL of concentrated HNO3 and 3 mL of concentrated HF were added, and the mixture was heated on a hot plate at 160 °C for 48 h. Subsequently, 0.2 mL concentrated HClO4, 2 mL of HCl, and 2 mL of HNO3 were added to ensure complete sample dissolution. After evaporation to dryness, the dissolved sample, along with 0.5 mL of rhodium internal standard solution, was volumed in a 50 mL volumetric flask using 3% HNO3. These solutions were then analyzed using iCAP Q ICP-MS (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) for trace elements concentrations. For As and Hg, freeze-dried sample (about 0.2 to 1 g) were dissolved with aqua regia in a water bath (about 100 °C). The extract supernatant underwent a mixture of iron salts and thiourea for the determination of As using AFS-9700 atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (Beijing Haiguang Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Another aliquot was used for the determination of Hg using cold-vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (Beijing Haiguang Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). According to the relevant sediments and rocks reference standards, the errors in the trace elements were found to be less than 10%.
2.3. Oragnic Carbon, Total Carbon, and Loss on Ignition
In a concentrated sulfuric acid medium, a certain amount of potassium dichromate is added, and the organic carbon in the sample is oxidized to carbon dioxide under heating conditions. The excess potassium dichromate is titrated back with a standard solution of ferrous sulfate. The content of organic carbon is calculated based on the consumption of potassium dichromate.
The total carbon was analyzed using the HCS-801 high frequency infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer (Sichuan Science Instrument Co., Ltd., Sichuan, China). Principally, the samples were heated and combusted in the oxygen stream of a high-frequency induction furnace, generating carbon dioxide, which is carried by oxygen to the detection chamber of an infrared analyzer. Carbon dioxide absorbs infrared energy at a specific wavelength, and its absorption energy is directly proportional to the concentration of carbon. The total carbon content was measured based on the change in energy received by the detector.
For the loss on ignition, a 1 g sample was weighted into a porcelain crucible, and heated in a furnace to 1000 °C in 1.5 h. Based on the weight changes, we calculate the content of loss on ignition [26].
2.4. Grain Size Analysis
The sample was mixed with 0.5 mol/L sodium hexametaphosphate and water, soaking the sample for 24 h to ensure full dispersion. The soaked sample was then transferred into the laser sample cell, subjected to ultrasonic vibration and high-speed stirring to achieve full dispersion again, and subsequently, the particle size was measured using a Malvern MS2000 laser particle size analyzer (Malvern Instrument Ltd., Malvern, UK).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The distribution of elements, and enrichment factors in the surface sediments of the study area was analyzed using the geostatistical analysis module of ArcGIS 10.8, with ordinary kriging employed for interpolation. Prior to interpolation analysis, spatial data analysis tools, including histograms, were used to analyze and process the data to conform to a normal distribution. A principal component analysis of the samples from the study area was conducted using SPSS 22.0. The correlation relationships of different parameters were also produced SPSS 22.0.
3. Results
3.1. Concentrations and Distribution Patterns of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments
Some major element concentrations (Al2O3, Fe2O3, MnO, SiO2, TOC and P2O5) observed in the surface sediment from Dongshan Bay are listed in the Supplementary Table S1. The concentrations of Al2O3, Fe2O3, MnO, SiO2, TOC, and P2O5 in sediments range from 3.73 to 18.70 wt. % (with an average value of 13.34 wt. %), 1.04 to 6.12 wt. % (with an average value of 4.45 wt. %), 0.03 to 0.12 wt. % (with an average value of 0.08 wt. %), 45.68 to 84.13 wt. % (with an average value of 63.68 wt. %), 0.12 to 1.01 wt. % (with an average value of 0.57 wt. %), 0.02 to 0.21 wt. % (with an average value of 0.11 wt. %), respectively.
The total heavy metal concentrations (Cu, Co, Ni, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg) observed in the surface sediment from Dongshan Bay were listed in the Supplementary Table S1. The concentrations of Cu, Co, Ni, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg in sediments range from 3.05 to 26.70 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 14.78 mg/kg), 2.5 to 16.8 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 11.23 mg/kg), 3.2 to 40.1 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 23.76 mg/kg), 20.30 to 68.00 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 36.78 mg/kg), 20.60 to 155.00 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 91.45 mg/kg), 8.65 to 92.90 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 54.35 mg/kg), 0.007 to 0.220 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 0.066 mg/kg), 3.65 to 19.60 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 8.03 mg/kg), 0.019 to 0.077 mg/kg (enveloping an average value of 0.043 mg/kg), respectively. These new heavy metals data in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay fall within the range of the data reported previously from the East China Sea [27,28,29], Yellow sea [30], Laizhou bay [31], Bohai bay [32], Liaodong bay [33], and Beibu bay [34]. More broadly, these data also approximate those reported from sediments derived from the Malaysian coast [35], the coast of the Gulf of Mexico [36], and the Arctic Ocean [37], but they are significant lower than those reported from highly contaminated sediments derived from the Iskar River of NW Bulgaria [38] and the Fal estuary system from southwest England [39] (More details in Table 1).

Table 1.
Heavy metal data from Dongshan Bay and other regions.
The distribution of major elements such as Al2O3, Fe2O3, MnO, TOC, and P2O5 as well as heavy metals such as Cu, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr, As, and Hg in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay exhibits a similar pattern (Figure 2a–c,e–f and Figure 3a,c–f,h,i). Generally, these metals show lower concentrations in the river channel of Zhangjiang, along the western and eastern coasts of the bay, while higher concentrations are observed in the northeast coast of the bay, the Bachimen Strait, and the nearby coastal areas. Overall, there is a trend of decreasing concentrations from the shore towards the sea. On the contrary, SiO2 shows an absolutely opposite tendency to these elements (Figure 2d). Additionally, high concentrations of mercury are observed along the southern coast of Dongshan Bay. However, unlike the distribution of Al2O3, Fe2O3, MnO, TOC, and P2O5, Cu, Zn, Co, Ni, and Cr, high concentrations of cadmium and lead are also found in the Zhangjiang river channel (Figure 3b,g). In summary, the data suggest that although river input dominates the heavy metal content in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, localized areas exhibit elevated concentrations of certain metals, including Zn, Pb, and As, likely attributable to specific human activities in those regions.
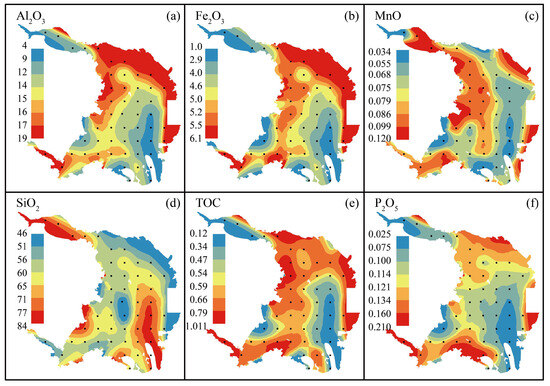
Figure 2.
Major elements and TOC distribution patterns of the surface sediments in Dongshan Bay, Southeast China. Al2O3, Fe2O3, MnO, SiO2, TOC, and P2O5 are presented in panel (a–f), respectively.
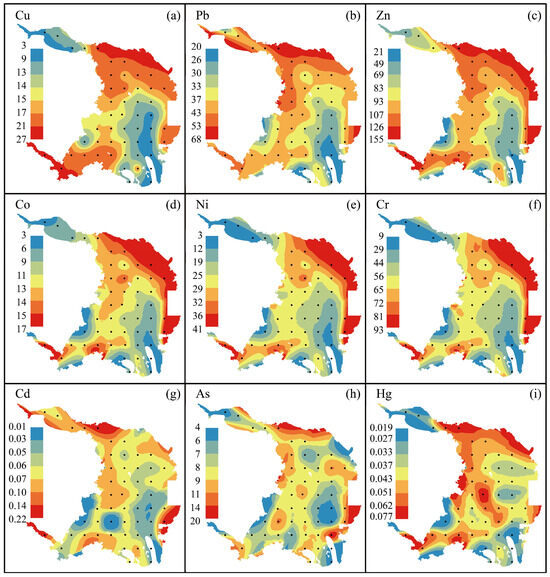
Figure 3.
Heavy metals distribution patterns of the surface sediments in Dongshan Bay, Southeast China. Cu, Pb, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr, Cd, As, Hg are presented in panel (a–i), respectively.
3.2. Principal Component Analysis
To further investigate the controlling factors of heavy metal element distribution in sediments, we conducted a principal component analysis (PCA) on the variations in the concentrations of nine heavy metals (Cr, Cu, Co, Ni, Pb, Zn, Cd, As, Hg) along with major elements and organic carbon (Table S1). The correlation matrix of major elements, TOC, and heavy metals in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay are also presented in Supplementary Table S2. The results revealed that three extracted factors (F1 to F3 in Table 2, Supplementary Table S3) accounted for a total variance contribution of 86.26%. Factor F1, accounting for 55.96% of the total variance, is characterized by Al, Fe, P2O5, and organic carbon, with Ni, Co, Cr, Cu, and Zn also showing high factor loadings. This primarily reflects terrigenous sediments associated with fine-grained clays, iron oxides, and organic carbon components, indicating that the mass ratios and distribution of these elements are predominantly controlled by the supply of terrigenous detrital particles. Factor F2, representing 20.29% of the total variance, is mainly reflected by variations in the mass of Mn, Pb, Hg, and Cd, likely influenced by adsorption on manganese oxides and changes in redox conditions. Factor F3, comprising 10.01% of the total variance, is primarily reflected by variations in As and Cd concentrations. Given the active exchange between dissolved and particulate forms of As and Cd, their distribution is likely closely related to the degree of water oxidation–reduction. Factor F3 should predominantly reflect the mechanism of transition between dissolved and particulate forms.

Table 2.
Rotated component matrix from major elements, trace elements, and TOC in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China. The extraction method is principal component analysis. Rotation converged in 5 iterations.
To further investigate the sources of heavy metal elements in sediments, the influence of terrigenous detritus was eliminated by comparing the ratios of heavy metals to Al. Subsequently, PCA was performed on the variations in Cr/Al, Ni/Al, Co/Al, Cu/Al, Pb/Al, Zn/Al, Cd/Al, As/Al, Hg/Al ratios, along with major elements and organic carbon content (Table 3). The correlation matrix of major elements, TOC, and the ratios of heavy metals to Al in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay were also presented in Supplementary Table S4. The four extracted factors (G1 to G4) contributed to a total variance of 83.80% (see Table 3, Supplementary Table S5). Factor G1, accounting for 40.14% of the total variance, is characterized by Al, Fe, Mg, Ti, P, and organic carbon, with Cu/Al, Ni/Al, Cr/Al, exhibiting high positive factor loading, primarily reflecting fine-grained clays, iron oxides, and organic carbon which absorb the heavy metals before precipitation. Factor G2, representing 19.61% of the total variance, is mainly reflected by variations in the mass ratios of Co/Al, Ni/Al, and Cr/Al, possibly indicating the impact of anthropogenic emissions. Factor G3, accounting for 12.81% of the total variance, is dominated by variations in Mn, unrelated to other factors, with lower loadings of other heavy metals. This factor might be related to Mn recycling in water. Factor G4, comprising 11.24% of the total variance, is primarily driven by variations in the ratios of Zn/Al, and Cd/Al, with less contribution from Cu/Al, and Pb/Al, possibly indicating impacts from human activities distinct from those associated with Factor G2.

Table 3.
Rotated component matrix from the ratio of heavy metals to Al, the major elements, and TOC in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China. The extraction method is principal component analysis. Rotation converged in 5 iterations.
3.3. Enrichment Factors
The enrichment factor method was applied to assess the contamination levels of nine heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr, Cd, As, Hg) in surface sediments of the study area [40]. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
In this analysis, Cn and CAl denote the concentration of the evaluated metal and Al within the sediment samples, respectively, and Bn and BAl correspond to the background concentration of the metal and Al, respectively, utilizing the upper crust as the benchmark for background values. The criteria for evaluating the enrichment levels are detailed in Figure 4.
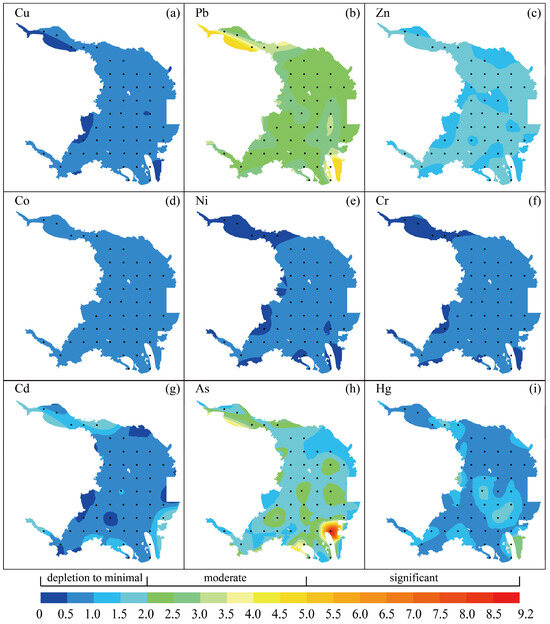
Figure 4.
Enrichment factors and distribution patterns of heavy metals from the surface sediments in Dongshan Bay, Southeast China. Cu, Pb, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr, Cd, As, Hg are presented in panel (a–i), respectively. The grading of the enrichment factors is presented below the figures.
The investigation reveals that the sequence of enrichment factors for various metals is as follows: Ni < Cu < Cr < Co < Cd < Hg < Zn < As < Pb, as detailed in Supplementary Table S6. Among the nine heavy metals examined, the enrichment factor indices for Cu, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr, and Cd are below 2.0, indicating depletion to minimal enrichment in the sediments for these metals. Conversely, except for one significant enrichment site in As, the enrichment factors of Pb, Hg, and As range from 2.0 to 5.0, signifying sediment conditions from minimal to moderate enrichment. The analysis of the potential pollution distribution of heavy metals across sampling sites (refer to Figure 4) demonstrates that for Pb, 4% of sites range from depletion to minimal enrichment, while 96% of sites show moderate enrichment. Regarding Hg, almost 98% of sites range from depletion to minimal enrichment, while the remaining sites exhibit enrichment of moderate levels. Concerning As, about 67% of sites exhibit depletion to minimal enrichment, with 31% showing moderate contamination, and 2% indicating significant enrichment. These findings underscore the observable influence of anthropogenic activities on the accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Dongshan Bay.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Role of Clay Minerals and Fe Oxides
A principal component factor analysis can effectively reduce the dimensionality of complex data, thereby categorizing the data into different controlling factors. Here, we combine statistical analysis with the geochemical behavior of elements to meticulously delineate the sources and factors of heavy metal enrichment in the sediment of Dongshan Bay. Previous studies have indicated that the main sources of elements in sediments nearshore or in bays were terrigenous debris, atmospheric deposition, and anthropogenic inputs [6,8,17,19,39,40]. Terrigenous debris inputs are primarily composed of clay minerals, iron oxides, organic carbon, manganese oxides, silicate minerals, carbonate minerals, quartz, and minor heavy minerals. Based on PCA of the tested elements and organic carbon (see Table 3), heavy metal elements (Cu, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr) show strong positive correlations with Al2O3 and Fe2O3, explaining approximately 56% of the total variance. These results clearly indicate that terrigenous input is the primary controlling factor for heavy metal elements (Cu, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr) in sediments. During the river input process, heavy metal elements couple with clay minerals (hydrated aluminosilicate minerals) through adsorption or direct lattice incorporation [41]. Iron oxides could capture heavy metal ions from the water column through adsorption; this feature was commonly observed not only in shallow seas but was also notably pronounced at deep-sea hydrothermal vents [42,43]. Unlike clay minerals and iron oxides, heavy metal ions primarily form organic matter–heavy metal complexes, then accumulate in sediments. For instance, the strong binding ability of natural organic matter to Cu(II) is observed in nature and experiments [44]. Chromium could form monomeric or polynuclear Cr–organic species with organic matter [45]. Upon entering the bay, the particles of clay minerals, iron oxides, and organic matter, enriched in heavy metals, undergo considerable precipitation due to decreased hydrodynamic forces [16,46]. This process leads to pronounced heavy metal accumulation at the bay’s mouth. Overall, the terrigenous inputs from rivers are a major source of heavy metal elements such as Cu, Zn, Co, Ni, and Cr in the sediments, contributing to approximately 50% of their content.
4.2. Mn Oxides Adsorption
The dominant processes for the deposition of heavy metals are river input and atmospheric precipitation. For example, environmentally sensitive areas like lakes, reservoirs, bays, and estuaries can receive mercury and lead through atmospheric and riverine transport [47,48]. Anthropogenic emissions of Hg, Pb, Cd, and Zn, following atmospheric and river transport, settle in bay areas and eventually deposit in sediments. This observation aligns with the PCA analysis (factor F2 in Table 3) suggesting that Hg, Pb, Cd, and Zn are governed by Mn oxides compared to other heavy metals. Given that Hg, Pb, Cd, and Zn readily adsorb to dust and other fine particles during mining and smelting processes [49], entering the river and atmospheric circulation system, it is reasonable to infer that the enrichment of Hg, Pb, Cd, and Zn in the sediments of Dongshan Bay is likely related to mining and smelting activities, primarily occurring through Mn oxides absorption. If the Mn oxides are reduced, these ions are then re-adsorbed by organic carbon, clay minerals, and iron oxides. Previous studies have indicated that Pb and Zn, in the suspended particulate matter and bottom sediments of the Yangtze River estuary, primarily exist in residual forms and are bound to iron-manganese oxides [50], highlighting the association with iron-manganese oxides as an important compositional form in the sediments of China’s coastal waters. It is important to note that although the content of manganese oxides is not abundant in modern seawater, their strong absorption ability and redox properties can significantly scavenge heavy metals ions introduced into seawater by human activities. This process leads to the enrichment of these anthropogenic heavy metals in the sediments.
4.3. Human Activity Effects
Considering that the ratio of heavy metals could help eliminate the influence from the terrigenous input, in Table 3, factor G2 is predominantly related to the variations in the ratios of Co/Al, Ni/Al, and Cr/Al. Conversely, Factor G4 (Table 3) is primarily dominated by changes in the ratios of Cd/Al, Zn/Al, Cu/Al, and Pb/Al. Previous research indicates that human activities contribute to the enrichment of heavy metals in sediments or soils in two main aspects: (1) the release of Cu, Zn, Cd, Cr, Ni, Hg, Pb, and As from industrial and domestic wastewater [51], mining and smelting operations [52], and fossil fuel combustion processes [53], with these metals being transported partly via rivers and partly through atmospheric deposition, and (2) the release of elements such as Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd during aquaculture processes [54], directly discharged into coastal bay waters. Thus, it is reasonable to speculate that the ratios of Zn/Al, Cd/Al, Cu/Al, and Pb/Al represented by Factor G4 may be associated with local aquaculture activities. This speculation is consistent with the observed enrichment of Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd along the northern coast of Dongshan Bay and the presence of numerous aquaculture farms in the area. Factor F2 (Table 3) is likely associated with human activities such as emissions from industrial and domestic wastewater, mining and smelting operations, and combustion processes, with these effluents primarily entering Dongshan Bay via river inputs. Overall, the sedimentary heavy metals in Dongshan Bay are influenced by human activities.
Based on the sediment types, grain size, and published sedimentary chronology data [21], Dongshan Bay can be roughly divided into two regions: the nearshore sedimentary area following the Zhangjiang River’s entry into the bay, characterized predominantly by silt or mud sediments, and the sandy sediment-dominated region. In the silt-dominated sedimentary region, the sedimentation rate, determined by 210Pb, is approximately 0.53 cm/year [21]. Utilizing this data as the average sedimentation rate for the entire region and considering the sediment dry density of about 1.06 g/cm3, a rough estimation for 2021 indicates the precipitations of Cu, Pb, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg were 12.6, 28.5, 75.1, 9.2, 20.5, 46.4, 0.1, 5.8, and 0.03 tons, respectively, with a total accumulation of 198 tons. Similarly, for the sandy sediment-dominated marine areas, with a sedimentation rate of about 0.22 cm/year and a sediment dry density of 1.12 g/cm3 [21], it is roughly estimated that in 2021, the precipitations of Cu, Pb, Zn, Co, Ni, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg in this region were 4.4, 11.8, 28.1, 3.5, 7.1, 16.5, 0.02, 2.7, and 0.01 tons, respectively, totaling 74 tons. Overall, Dongshan Bay has accumulated approximately 272 tons of heavy metals in 2021.
It is crucial to note that the sedimentation rates were calibrated based on only 1–2 sampling sites within each sedimentary region, which inevitably leads to inaccuracies in the estimated sedimentation rates and, consequently, significant discrepancies between the estimated sediment fluxes and their actual values. Nonetheless, these data can still provide valuable insights for the environmental management of Dongshan Bay.
5. Conclusions
We conducted a comprehensive field survey of Dongshan Bay, a typical coastal bay in southeastern China, and collected 51 surface sediment samples in 2021. In general, these metals exhibit lower concentrations in the Zhangjiang river channel, along the western and eastern coasts of the bay. Higher concentrations are observed on the northeast coast of the bay, the Bachimen Strait, and the nearby coastal areas. There is a general trend of decreasing concentrations from the shore towards the sea. The assessment based on the enrichment factor indicates that Pb, As, Zn, and Hg in the sediments may pose potential element enrichment. The heavy metal elements in the sediments are primarily influenced by clay minerals and Fe oxides, while Pb and Hg levels also closely linked to the absorption of Mn oxides. Human activity pollution impacts are mainly concentrated in two categories: heavy metal pollution related to aquaculture (e.g., Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) and heavy metal pollution associated with industrial production and domestic sewage discharge. Furthermore, based on the existing sedimentation rates and relevant parameters, we estimate that approximately 270 tons of heavy metals were deposited in Dongshan Bay in 2021.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16060905/s1. Table S1: Sampling depth (m), major (wt. %) and trace elements (mg/kg) concentrations in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China; Table S2: Correlation Matrix of major elements, trace elements and TOC in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China; Table S3: Total Variance Explained of major elements, trace elements and TOC in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China; Table S4: Correlation Matrix of major elements, TOC and the ratios of heavy metals to Al in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China; Table S5: Total Variance Explained of major elements, TOC and the ratios of heavy metals to Al in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China; Table S6: Average values of the enrichment factors (EF) of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Dongshan Bay, Southeast China.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Y., X.C. and A.D.; methodology, X.Y., W.Z. and G.Z.; investigation, X.C. and W.Z.; formal analysis, X.Y., X.C., W.Z. and A.D.; resources, X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Y. and A.D.; writing—review and editing, X.Y., X.C., W.Z., G.Z. and A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Geological Exploration Special Fund of Fujian Province, grant number GY20210302.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are publicly available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Feng, X.; Qiu, G. Mercury Pollution in Guizhou, Southwestern China-an Overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, K.A.; Amirbahman, A. Mercury Methylation Dynamics in Estuarine and Coastal Marine Environments—A Critical Review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 96, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wong, M.H. Environmental Mercury Contamination in China: Sources and Impacts. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M. Biological Effects of Heavy Metals: An Overview. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26 (Suppl. S2), 301–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiang, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Lei, K.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, D.; Fang, X.; Cao, Y. Heavy Metal Contamination Risk Assessment and Correlation Analysis of Heavy Metal Contents in Soil and Crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, G.W.; Langston, W.J. Bioavailability, Accumulation and Effects of Heavy Metals in Sediments with Special Reference to United Kingdom Estuaries: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 76, 89–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Wu, Q.; Liu, P.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Shi, B.; Zhou, Y.; Kwon, B.-O.; Choi, K.; Ryu, J.; et al. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments and Water from the Coastal Areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Yin, J.; Zhu, L. Risk Assessment for Sediment Associated Heavy Metals Using Sediment Quality Guidelines Modified by Sediment Properties. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 115844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, A. Heavy Metal Pollution from Listvenitization: In Case of Alakeçi (Bayramiç-Çanakkale/West Türkiye). Turk. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 4, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counter, S.A.; Buchanan, L.H. Mercury Exposure in Children: A Review. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Fang, W.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Z. Cadmium Accumulation in Different Rice Cultivars and Screening for Pollution-Safe Cultivars of Rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cadmium Pollution of Soil-Rice Ecosystems in Rice Cultivation Dominated Regions in China: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungur, A.; Vural, A.; Gundogdu, A.; Soylak, M. Effect of Antimonite Mineralization Area on Heavy Metal Contents and Geochemical Fractions of Agricultural Soils in Gümüşhane Province, Turkey. CATENA 2020, 184, 104255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, K.J.; Martin, R.; Tang, M.; Walters, L.; Parks, J.; Roy, S.; Devine, C.; Edwards, M.A. Evaluating Water Lead Levels During the Flint Water Crisis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8124–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Agnan, Y.; Jiskra, M.; Olson, C.L.; Colegrove, D.P.; Hueber, J.; Moore, C.W.; Sonke, J.E.; Helmig, D. Tundra Uptake of Atmospheric Elemental Mercury Drives Arctic Mercury Pollution. Nature 2017, 547, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milliman, J.D.; Shen, H.T.; Yang, Z.S.; Mead, R.H. Transport and Deposition of River Sediment in the Changjiang Estuary and Adjacent Continental Shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.A.; Feng, W.; Zhu, G.; Hossain, M.B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. Bioaccumulation and Potential Human Health Risks of Metals in Commercially Important Fishes and Shellfishes from Hangzhou Bay, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, G.; Tu, X. Heavy Metal Pollution in Intertidal Sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, X. Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of the Intertidal Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China: Distributions, Sources and Contamination Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Yin, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Distribution and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soils and Sediments of Yueqing Bay Basin, East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ye, X.; Yin, X.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, A.; Li, Y. Geochemical Analysis of Sediments from a Semi-Enclosed Bay (Dongshan Bay, Southeast China) to Determine the Anthropogenic Impact and Source. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.P.; Lawson, N.M.; Lawrence, A.L.; Leaner, J.J.; Lee, J.G.; Sheu, G.-R. Mercury in the Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Chem. 1999, 65, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Meng, F.; Fu, W.; Wang, Z. Distribution, Speciation and Bioaccumulation of Hg and As in Mariculture Sediments from Dongshan Bay, China. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2016, 25, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Lin, H. Microplastic Contamination in Seafood from Dongshan Bay in Southeastern China and Its Health Risk Implication for Human Consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 303, 119163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Luo, Y.; Wu, B.; Qi, S.; Lin, M.; Tian, J.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Seasonal Variation, Virulence Gene and Antibiotic Resistance of Vibrio in a Semi-Enclosed Bay with Mariculture (Dongshan Bay, Southern China). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, A.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Kendall, B.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, C. A Multi-Isotope Approach towards Constraining the Origin of Large-Scale Paleoproterozoic B-(Fe) Mineralization in NE China. Precambrian Res. 2017, 292, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, N. Fractionation, Sources and Budgets of Potential Harmful Elements in Surface Sediments of the East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 68, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Song, J.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Li, N. Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Environmental Risk of Arsenic in Sediments of the East China Sea. Chem. Geol. 2013, 340, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.-Q.; Song, J.-M.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, H.-M.; Li, X.-G.; Li, N. Spatial Variation, Fractionation and Sedimentary Records of Mercury in the East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Teng, A.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Lu, A. Occurrence, Speciation and Transportation of Heavy Metals in 9 Coastal Rivers from Watershed of Laizhou Bay, China. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Song, J.; Duan, L.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Qu, B.; Wang, Q.; Xing, J. Source Identification and Risk Assessment Based on Fractionation of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ma, M. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Heavy Metals in Marine Sediments from Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Hu, B.; Yang, S. Distribution, Enrichment and Source of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of the Eastern Beibu Bay, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoly Sany, S.B.; Salleh, A.; Rezayi, M.; Saadati, N.; Narimany, L.; Tehrani, G.M. Distribution and Contamination of Heavy Metal in the Coastal Sediments of Port Klang, Selangor, Malaysia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Pérez-Bernal, L.H.; Gracia, A. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Heavy Metal Concentrations and Enrichment in the Southern Gulf of Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3174–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, E.; Puchkov, A.; Malkov, A.; Bedrina, D. Assessment of Heavy Metals Distribution and Environmental Risk Parameters in Bottom Sediments of the Pechora River Estuary (Arctic Ocean Basin). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, Y.; Lincheva, S.; Yotinov, I.; Topalova, Y. Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Long-Term Polluted Sediments with Heavy Metals in Small Hydropower Cascade. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4171–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerfield, P.J.; Gee, J.M.; Warwick, R.M. Soft Sediment Meiofaunal Community Structure in Relation to a Long-Term Heavy Metal Gradient in the Fa1 Estuary System. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 105, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jia, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X. Distribution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of Coastal Mudflats on Leizhou Peninsula, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tian, R.; Yang, Q. Insight into Mechanisms of Heavy Metal-Induced Natural Clay Aggregation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 231, 106746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feely, R.A.; Lewison, M.; Massoth, G.J.; Robert-Baldo, G.; Lavelle, J.W.; Byrne, R.H.; Damm, K.L.V.; Curl, H.C. Composition and Dissolution of Black Smoker Particulates from Active Vents on the Juan de Fuca Ridge. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1987, 92, 11347–11363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feely, R.A.; Trefry, J.H.; Lebon, G.T.; German, C.R. The Relationship between P/Fe and V/Fe Ratios in Hydrothermal Precipitates and Dissolved Phosphate in Seawater. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 2253–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, A.; Matynia, A. The Nature of Cu Bonding to Natural Organic Matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 2556–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Luo, W.; Mo, Y.; Ding, K.; Zhang, M.; Jin, C.; Wang, S.; Chao, Y.; Tang, Y.-T.; Qiu, R. New Insights into the Role of Natural Organic Matter in Fe–Cr Coprecipitation: Importance of Molecular Selectivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 13991–14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Shao, X.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, F.; Li, G.; Matsumoto, E. Temporal Variation of Sedimentation Rates and Potential Factors Influencing Those Rates over the Last 100 Years in Bohai Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, S.W.; Moran, S.B. Stable Pb Isotope Ratios in Aerosols, Precipitation, and Size-Fractionated Particulate Matter in the Gulf of Maine, Scotian Shelf, and Labrador Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.-R.; Han, Y.-J.; Holsen, T.M.; Yi, S.-M. Atmospheric Particulate Mercury: Concentrations and Size Distributions. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csavina, J.; Field, J.; Taylor, M.P.; Gao, S.; Landázuri, A.; Betterton, E.A.; Sáez, A.E. A Review on the Importance of Metals and Metalloids in Atmospheric Dust and Aerosol from Mining Operations. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Zhai, S.; Zabel, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F. Heavy Metals in Changjiang Estuarine and Offshore Sediments: Responding to Human Activities. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M.K.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Arain, M.B.; Jalbani, N.; Memon, A.R. Speciation of Heavy Metals in Untreated Domestic Wastewater Sludge by Time Saving BCR Sequential Extraction Method. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2007, 42, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Van Der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A Review of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution from Mines in China: Pollution and Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, J.R.; Edwards, R. Coal Burning Leaves Toxic Heavy Metal Legacy in the Arctic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12140–12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendiguchía, C.; Moreno, C.; Mánuel-Vez, M.P.; García-Vargas, M. Preliminary Investigation on the Enrichment of Heavy Metals in Marine Sediments Originated from Intensive Aquaculture Effluents. Aquaculture 2006, 254, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).