Seasonal Freezing Drives Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) and Microbial Communities in Reclaimed Water-Recharged River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
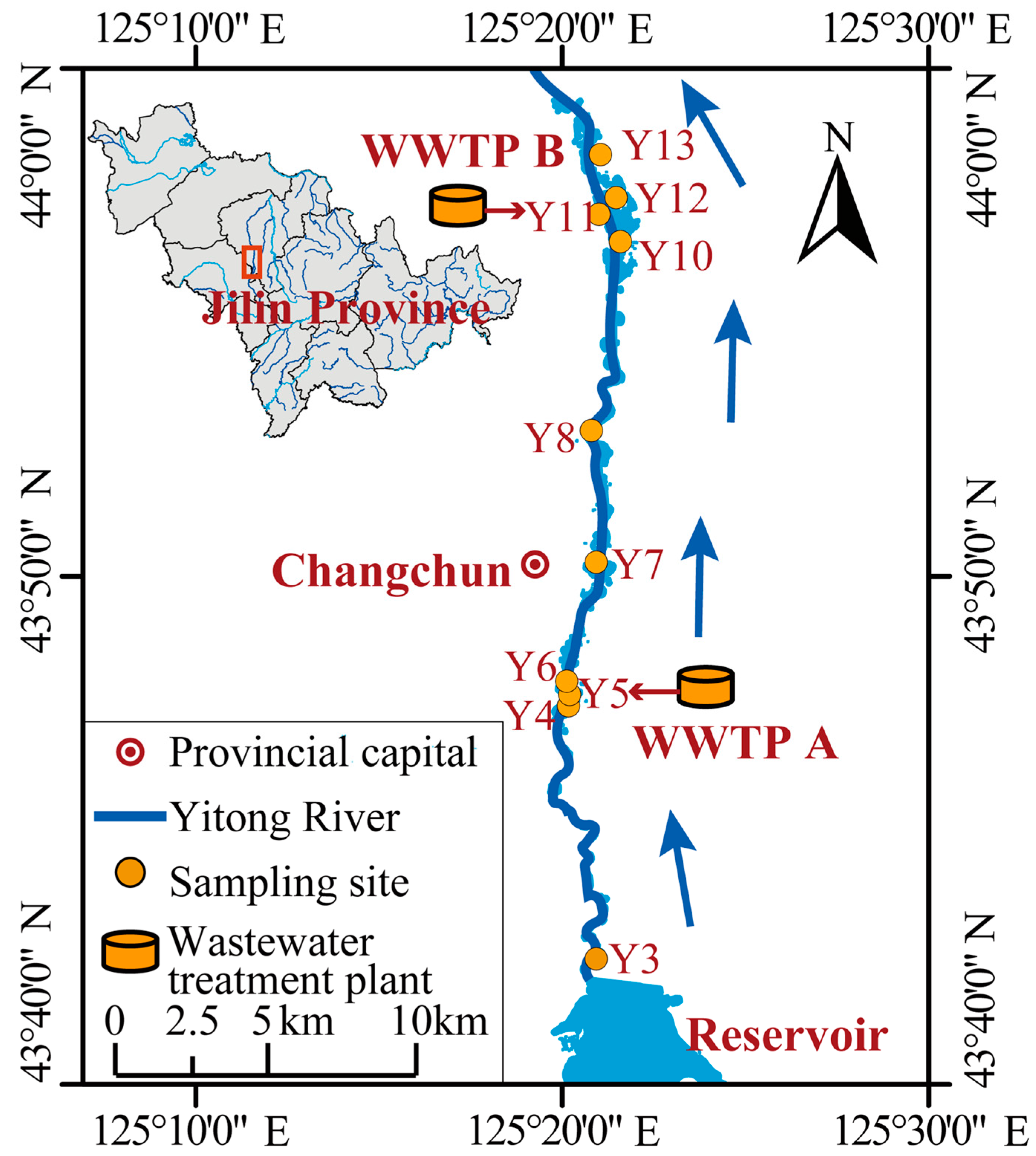
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Detection of Water Quality Parameters
2.3. Optical Spectroscopy Measurements and Analysis
2.4. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Pathogen Quantification Using High-Throughput Quantitative PCR (HT-qPCR)
2.6. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Variation in River Water Physicochemical Characteristics
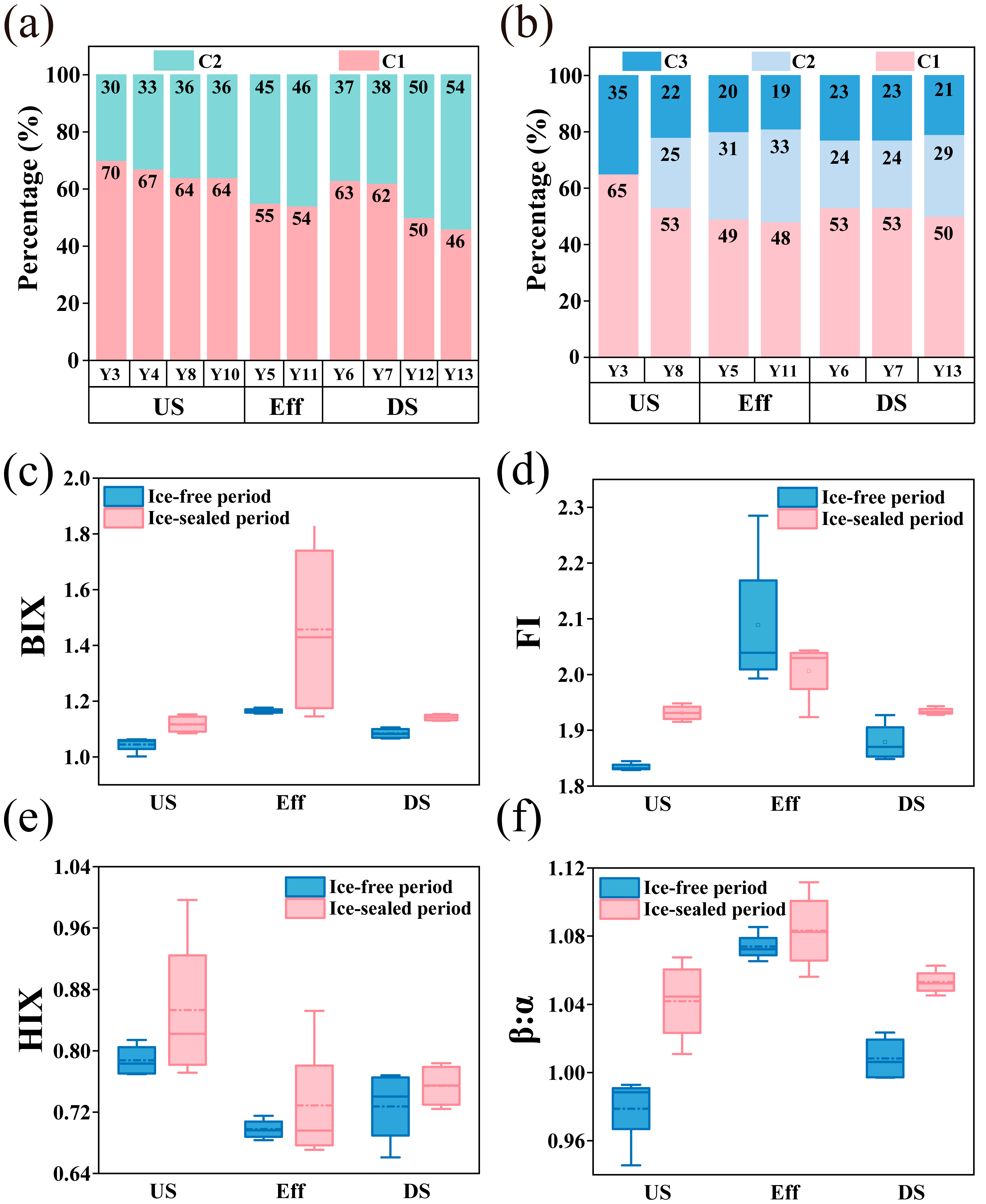
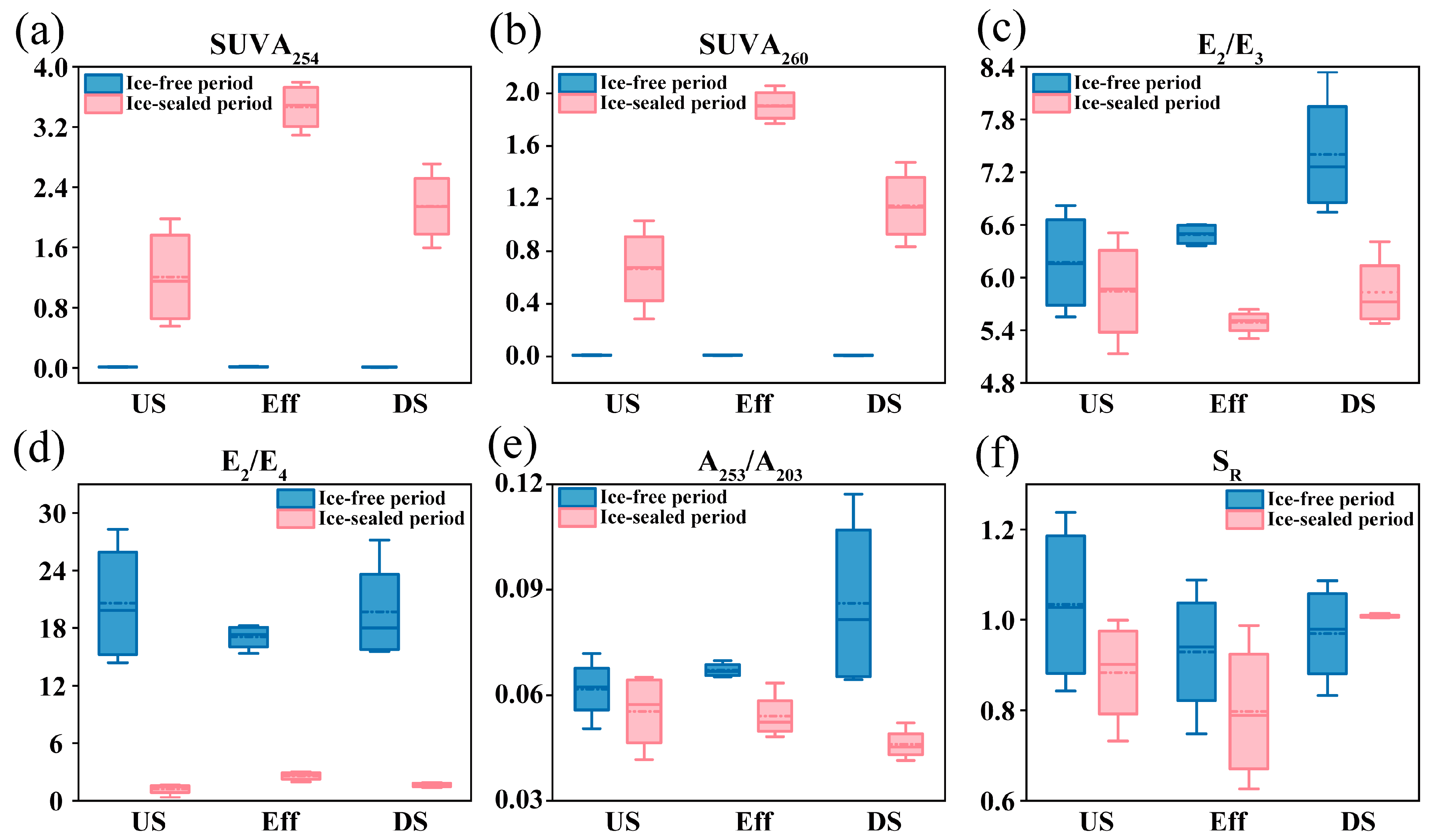
3.2. Spectral Characteristics and Source Identification of DOM
3.3. BC Composition and Distribution Characteristics
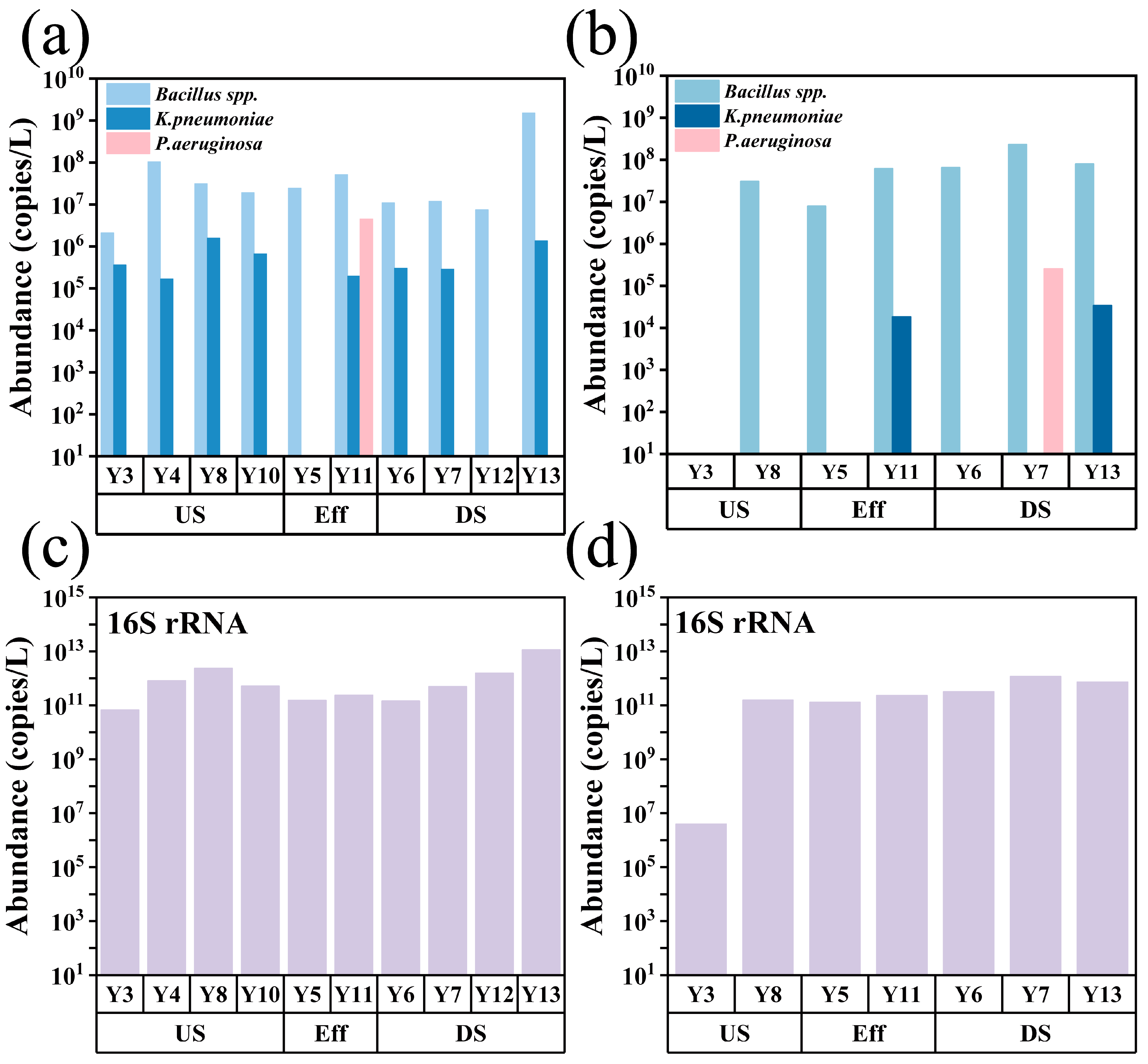
3.4. Distribution Characteristics of Pathogenic Bacteria
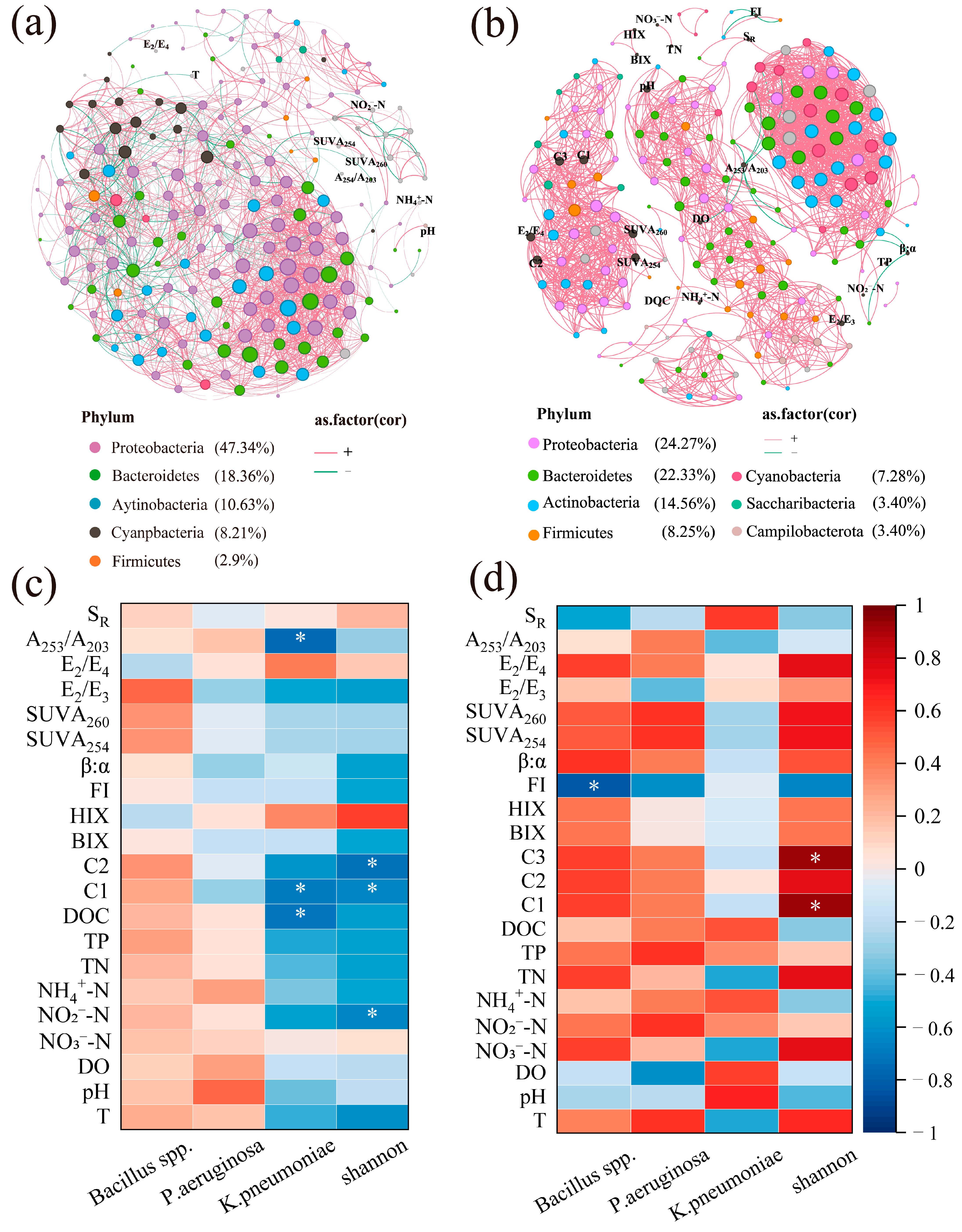
3.5. Co-Occurrence Patterns among Bacterial Community and Their Interactions with Environmental Factors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Cockburn, C.; Lamouroux, N.; Pella, H.; Snelder, T.; Tockner, K.; Trautmann, T.; Watt, C.; Datry, T. Global prevalence of non-perennial rivers and streams. Nature 2021, 594, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Thieme, M.; Geenen, B.; Tickner, D.; Antonelli, F.; Babu, S.; Borrelli, P.; Cheng, L.; Crochetiere, H.; et al. Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers. Nature 2019, 569, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Bond, N.; Tun, N.N.; Ding, C. Keep the Salween River free-flowing. Science 2023, 381, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.W.; He, J.T.; Li, B.H.; He, B.A.; Huang, J.X.; Guo, M.L.; Luo, D. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics and genesis of groundwater under long-term infiltration (2007–2018) of reclaimed water in Chaobai River, Beijing. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Zeng, S.Y.; Shi, L.; Dong, X. What the reclaimed water use can change: From a perspective of inter-provincial virtual water network. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munné, A.; Solà, C.; Ejarque, E.; Sanchís, J.; Serra, P.; Corbella, I.; Aceves, M.; Galofré, B.; Boleda, M.R.; Paraira, M.; et al. Indirect potable water reuse to face drought events in Barcelona city. Setting a monitoring procedure to protect aquatic ecosystems and to ensure a safe drinking water supply. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.Q.; Song, Y.; Fu, Q.; Qi, R.; Wu, Z.H.; Ge, F.Y.; Lu, X.Q.; An, W.; Han, W.X. Reclaimed water use improved polluted water’s self-purification capacity—Evidenced by water quality factors and bacterial community structure. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 386, 135736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Bai, Y.; Qu, J. Unravelling riverine microbial communities under wastewater treatment plant effluent discharge in large urban areas. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6755–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Huo, Y.; Liao, K.; Qu, J. Influence of microbial community diversity and function on pollutant removal in ecological wastewater treatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 7293–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Bai, Y.; Huo, Y.; Jian, Z.; Hu, W.; Zhao, C.; Qu, J. Integrating microbial biomass, composition and function to discern the level of anthropogenic activity in a river ecosystem. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CastellanoHinojosa, A.; GallardoAltamirano, M.J.; GonzálezLópez, J.; GonzálezMartínez, A. Anticancer drugs in wastewater and natural environments: A review on their occurrence, environmental persistence, treatment, and ecological risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Jian, S.L.; Li, K.M.; Wu, Z.B.; Guan, H.T.; Hao, J.W.; Wang, S.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Li, A.H. Community structure of bacterioplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the upper reaches of the Heihe River in Qinghai Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.X.; Zhang, B.; Ning, D.L.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, T.J.; Wu, L.; Li, T.L.; Liu, W.; Zhou, J.Z.; Wen, X.H. Seasonal dynamics of the microbial community in two full-scale wastewater treatment plants: Diversity, composition, phylogenetic group based assembly and co-occurrence pattern. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.W.; Yu, H.; Yu, Y.H.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zeng, J.X.; Chen, P.B.; Xiao, F.S.; He, Z.L.; Yan, Q.Y. Ecological stability of microbial communities in Lake Donghu regulated by keystone taxa. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Y.; Bu, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.X.; Huang, K.L.; He, X.W.; Ye, L.; Shan, Z.J.; Ren, H.Q. Metagenomic analysis of bacterial community composition and antibiotic resistance genes in a wastewater treatment plant and its receiving surface water. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2016, 132, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proia, L.; Osorio, V.; Soley, S.; Köck-Schulmeyer, M.; Perez, S.; Barcelo, D.; Romani, A.M.; Sabater, S. Effects of pesticides and pharmaceuticals on biofilms in a highly impacted river. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Chen, Y.; Cai, P.G.; Gao, Q.; Zhong, H.H.; Sun, W.L.; Chen, Q. Impacts of municipal wastewater treatment plant discharge on microbial community structure and function of the receiving river in Northwest Tibetan Plateau. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusiñol, M.; Hundesa, A.; Cárdenas-Youngs, Y.; Fernández-Bravo, A.; Pérez-Cataluña, A.; Moreno-Mesonero, L.; Moreno, Y.; Calvo, M.; Alonso, J.L.; Figueras, M.J.; et al. Microbiological contamination of conventional and reclaimed irrigation water: Evaluation and management measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.J.; Guan, Y.T.; Zhao, R.X.; Feng, J.; Huang, J.; Ma, L.P.; Li, B. Metagenomic and network analyses decipher profiles and co-occurrence patterns of antibiotic resistome and bacterial taxa in the reclaimed wastewater distribution system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artifon, V.; Zanardi-Lamardo, E.; Fillmann, G. Aquatic organic matter: Classification and interaction with organic microcontaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1620–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.D.; He, X.S.; Xi, B.D.; Gao, R.T.; Zhao, X.W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.H.; Tan, W.B. Investigating the composition characteristics of dissolved and particulate/colloidal organic matter in effluent-dominated stream using fluorescence spectroscopy combined with multivariable analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9132–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.R.; Qi, Y.L.; Han, Y.F.; Ge, J.F.; Dong, Y.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Yi, Y.B.; Volmer, D.A.; Li, S.L.; Fu, P.Q. Seasonal variation and dissolved organic matter influence on the distribution, transformation, and environmental risk of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in coastal zone: A case study of Tianjin, China. Water Res. 2023, 249, 120881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.W.; Li, H.; Liu, D.P.; Wang, L.T.; Dong, D.M.; Guo, Z.Y. Antibiotics in a seasonal ice-sealed reservoir: Occurrence, temporal variation, prioritization, and source apportionment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 857, 159469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.W.; Du, S.Y.; Zhang, X.; Lyu, G.Z.; Dong, D.M.; Hua, X.Y.; Zhang, W.M.; Guo, Z.Y. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk of pharmaceuticals in a seasonally ice-sealed river: From ice formation to melting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.W.; Lin, L.; Wang, L.F.; Niu, L.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C. Response of bacterial community in composition and function to the various DOM at river confluences in the urban area. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, A.; Choi, M.; Tanentzap, A.J.; Liu, J.F.; Jang, K.S.; Lennon, J.T.; Liu, Y.Q.; Soininen, J.; Lu, X.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Ecological networks of dissolved organic matter and microorganisms under global change. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellerman, A.M.; Dittmar, T.; Kothawala, D.N.; Tranvik, L.J. Chemodiversity of dissolved organic matter in lakes driven by climate and hydrology. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Ge, F.J.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhou, Q.H.; Wu, Z.B.; Liu, B.Y. Spatial characteristics of nitrogen forms in a large degenerating lake: Its relationship with dissolved organic matter and microbial community. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 371, 133617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Ji, Y.; Kuang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z. Changes in shale gas produced water DOM during its early storage period: Molecular composition correlated with microbial functions. Process Saf. Environ. 2022, 165, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, J.B.; Stedmon, C.A.; Kellerman, A.M.; Nielsen, N.J.; Andersson, A.F.; Laudon, H.; Lindstrom, E.S.; Kritzberg, E.S. Experimental insights into the importance of aquatic bacterial community composition to the degradation of dissolved organic matter. ISME J. 2016, 10, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xie, X.Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Wei, Z.M.; Yang, H.Y.; Zhang, S.B.; Song, C.H.; Jia, L.M. Photodegradation, bacterial metabolism, and photosynthesis drive the dissolved organic matter cycle in the Heilongjiang River. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.Q.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, X.B.; Wei, Q.G.; Ma, S.C.; Sun, G.L.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, L.D.; Dou, H.S.; Zhang, H.H. Factors affecting seasonal variation of microbial community structure in Hulun Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, Z.R.; Zhu, S.Y.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.Z.; Huo, M.X. Deciphering the influence of multiple anthropogenic inputs on taxonomic and functional profiles of the microbial communities in Yitong River, Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39973–39984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, W.; Zhao, J.; Hou, Z.; Wang, X. Wastewater Deterministically Impacts the Composition and Assembly of Planktonic Microorganisms in the River Ecosystem. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.R.; Stedmon, C.A.; Graeber, D.; Bro, R. Fluorescence spectroscopy and multi-way techniques. PARAFAC. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 6557–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Pu, Q.; Li, H.; Pan, T.; Li, H.Q.; Pan, F.X.; Su, J.Q. High-throughput diagnosis of human pathogens and fecal contamination in marine recreational water. Environ. Res. 2020, 190, 109982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, D.; Kuczynski, J.; Charlson, E.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Mozer, M.C.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Knight, R.; Kelley, S.T. Bayesian community-wide culture-independent microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.O.; Yang, T.J.; Bao, Y.Z.; He, P.P.; Yang, K.M.; Mei, X.L.; Wei, Z.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R.; Banerjee, S. Network analysis and subsequent culturing reveal keystone taxa involved in microbial litter decomposition dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Xiong, W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Nie, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Geisen, S. Temperature-induced annual variation in microbial community changes and resulting metabolome shifts in a controlled fermentation system. mSystems 2020, 5, e00555-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollinger, A.; Seneca, J.; Dahl, M.B.; Motleleng, L.L.; Prommer, J.; Verbruggen, E.; Sigurdsson, B.D.; Janssens, I.; Penuelas, J.; Urich, T.; et al. Down-regulation of the bacterial protein biosynthesis machinery in response to weeks, years, and decades of soil warming. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenheer, J.A.; Croué, J.P. Characterizing aquatic dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 18A–26A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Karl, B. Fluorescence excitation—Emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boodoo, K.S.; Fasching, C.; Battin, T.J. Sources, Transformation, and Fate of Dissolved Organic Matter in the Gravel Bar of a Prealpine Stream. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2020, 125, e2019JG005604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.M.; Boyer, E.W.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Doran, P.T.; Kulbe, T.; Andersen, D.T. Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, L.; Stedmon, C.A.; Granskog, M.A.; Middelboe, M. Tracing the long-term microbial production of recalcitrant fluorescent dissolved organic matter in seawater, Geophysical Research Letters. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 8, 593–599. [Google Scholar]
- Peuravuori, J.; Pihlaja, K. Molecular size distribution and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 337, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.L.; He, X.S.; Liu, J.; Bei, D.X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, M.Z.; Jiang, Y.H.; Su, J.; Hu, C.M. Study on the Characteristic UV Absorption Parameters of Dissolved Organic Matter Extracted from Chicken Manure during Composting. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2010, 30, 3081–3085. [Google Scholar]
- Praise, S.; Ito, H.; An, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, T. Dissolved organic matter characteristics along sabo dammed streams based on ultraviolet visible and fluorescence spectral properties. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, L. Prediction of dissolved organic nitrogen via spectroscopic fingerprint in the shallow riverbed sediments of effluent-dominated rivers: A case study in Xi’an, northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, K.; Hu, A.; Fu, Q.; He, H.; Wang, D.; Shi, J.; Zhang, W. The molecular characteristics of DOMs derived from bio-stabilized wastewater activated sludge and its effect on alleviating Cd-stress in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Wang, K.; Yang, F.; Zhuang, T. Antibiotic pollution of the Yellow River in China and its relationship with dissolved organic matter: Distribution and Source identification. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, H.; Wen, J.; Zhao, C.; Dong, L.; Liu, H. Underestimated humic acids release and influence on anaerobic digestion during sludge thermal hydrolysis. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, A.; Brozel, V.S. Phylogeny of Nitrogenase Structural and Assembly Components Reveals New Insights into the Origin and Distribution of Nitrogen Fixation across Bacteria and Archaea. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Dai, Q. Response of bacterial communities and nitrogen-cycling genes in newly reclaimed mudflat paddy soils to nitrogen fertilizer gradients. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 71113–71123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Mu, X.; Gan, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, Q.; Li, H. Temperature rise alters phosphorus pool in corpse polluted water by inhibiting organic phosphorus mineralization and phosphorus transports. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Sun, F.; Zhang, J.; Feng, L.; Tu, H.; Li, A. Low-temperature-resistance granulation of activated sludge and the microbial responses to the granular structural stabilization. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Xu, L.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, M.; Kong, H.; Huang, X.; Zheng, X. Domestic wastewater treatment for single household via novel subsurface wastewater infiltration systems (SWISs) with NiiMi process: Performance and microbial community. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Qi, R.; Zhong, H.; Chai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M. Analysis of seasonal variation characteristics of nitrogen transformation functional bacteria and functional genes in urban sewage treatment plants in cold regions. Water Wastewater Eng. 2023, 49, 38–43+52. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Yang, F.; Gao, X.; Ma, L. Effects of sewage treatment on microbial community structure of surface water in Xiantao wetland. Microbiol. China 2019, 46, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Wong, M.H.; Zaynab, M.; Wang, K.; Zhong, L.; Ouyang, L. Changes in the composition of bacterial communities and pathogen levels during wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Wan, P.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, R. Seasonal variability of the correlation network of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance determinants, and bacteria in a wastewater treatment plant and receiving water. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, I.; Tyagi, K.; Chandra, K.; Kumar, V. Characterization of bacterial diversity in wastewater of Indian paper industries with special reference to water quality. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 3669–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, S.; Amouroux, D.; Lanceleur, L.; Cagnon, C.; Monperrus, M.; Deborde, J.; Laureau, C.C.; Duran, R. Keystone microbial taxa organize micropollutant-related modules shaping the microbial community structure in estuarine sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Yang, X.; Xia, H.; Yang, S.; Yang, L. The association between ambient temperature and antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae in China: A difference-in-differences analysis. Front. Public. Health 2023, 11, 1158762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, C.; Ho, H.C.; Shi, L.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, Q.; Pei, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, L. Association between antibiotic resistance and increasing ambient temperature in China: An ecological study with nationwide panel data. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2023, 30, 100628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraiem, K.; Wahab, M.A.; Kallali, H.; Fra-vazquez, A.; Pedrouso, A.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Jedidi, N. Effects of short- and long-term exposures of humic acid on the Anammox activity and microbial community. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19012–19024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Siddique, M.S.; Liu, M.; Graham, N.; Yu, W. The migration and microbiological degradation of dissolved organic matter in riparian soils. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ye, T.; Hu, Y.; Yang, C. Dynamic variations of dissolved organic matter from treated wastewater effluent in the receiving water: Photo- and bio-degradation kinetics and its environmental implications. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, X.; Kang, W.; Qu, Q.; Feng, R.; Mu, L. Interactions between dissolved organic matter and the microbial community are modified by microplastics and heat waves. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Jang, K.-S.; Dolfing, J.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Jeppesen, E. Terrestrial dissolved organic matter inputs drive the temporal dynamics of riverine bacterial ecological networks and assembly processes. Water Res. 2023, 249, 120955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanentzap, A.J.; Fitch, A.; Orland, C.; Emilson, E.J.S.; Yakimovich, K.M.; Osterholz, H.; Dittmar, T. Chemical and microbial diversity covary in fresh water to influence ecosystem functioning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24689–24695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X. Comparison of optical properties of DOM and CDOM in lake Tianmuhu catchment. Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 998–1007. [Google Scholar]



| T (°C) | pH | DO (mg/L) | NO3−-N (mg/L) | NO2−-N (mg/L) | NH4+-N (mg/L) | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | DOC (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y3O | 5.2 | 5.47 | 6.66 | 1.22 | 0.021 | 0.02 | 1.23 | 0.05 | 6.078 |
| Y4O | 4.7 | 5.45 | 7.03 | 1.54 | 0.029 | 0.72 | 1.92 | 0.08 | 9.708 |
| Y5O | 13.3 | 5.51 | 6.08 | 3.76 | 0.052 | 2.96 | 3.95 | 0.17 | 11.57 |
| Y6O | 7.8 | 5.47 | 6.51 | 3.35 | 0.033 | 1.88 | 3.67 | 0.05 | 10.66 |
| Y7O | 8.8 | 5.48 | 6.19 | 3.12 | 0.05 | 0.66 | 3.37 | 0.13 | 8.92 |
| Y8O | 8.2 | 7.48 | 5.87 | 2.45 | 0.063 | 1.13 | 3.00 | 0.17 | 9.003 |
| Y10O | 12.2 | 8.11 | 5.44 | 2.14 | 0.115 | N | 2.53 | 0.28 | 8.086 |
| Y11O | 15.1 | 7.36 | 5.74 | 3.52 | 0.09 | 1.63 | 3.88 | 0.32 | 9.908 |
| Y12O | 13.9 | 7.89 | 5.84 | 2.96 | 0.167 | 3.25 | 3.43 | 0.10 | 12.61 |
| Y13O | 13.2 | 8.02 | 5.32 | 1.23 | 0.116 | 4.6 | 1.57 | 1.25 | 24.63 |
| Y3F | 3.4 | 7.47 | 6.16 | 1.54 | 0.008 | 0.01 | N | 0.08 | 8.629 |
| Y5F | 8.2 | 7.42 | 6.47 | 3.77 | 0.019 | 0.02 | 3.54 | 0 | 11.74 |
| Y6F | 3.5 | 7.57 | 6.79 | 3.46 | 0.014 | 0 | 3.62 | 0.03 | 10.78 |
| Y7F | 2.8 | 7.61 | 6.97 | 3.05 | 0.023 | 0.37 | 3.35 | 0.23 | 10.32 |
| Y8F | 1.9 | 7.67 | 6.83 | 2.33 | 0.031 | 0.52 | 2.66 | 0.32 | 10.04 |
| Y11F | 9.8 | 7.53 | 5.55 | 3.55 | 0.127 | 0.97 | 2.74 | 0.20 | 15.58 |
| Y13F | 2.7 | 7.69 | 6.81 | 2.14 | 0.055 | 1.64 | 2.37 | 0.15 | 12.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Fan, W.; Geng, Z.; Huo, M. Seasonal Freezing Drives Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) and Microbial Communities in Reclaimed Water-Recharged River. Water 2024, 16, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060906
Zhao J, Huo Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Hou Z, Fan W, Geng Z, Huo M. Seasonal Freezing Drives Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) and Microbial Communities in Reclaimed Water-Recharged River. Water. 2024; 16(6):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060906
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jiaqi, Yang Huo, Zhiruo Zhang, Ying Zhang, Zhenlai Hou, Wei Fan, Zhi Geng, and Mingxin Huo. 2024. "Seasonal Freezing Drives Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) and Microbial Communities in Reclaimed Water-Recharged River" Water 16, no. 6: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060906
APA StyleZhao, J., Huo, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., Hou, Z., Fan, W., Geng, Z., & Huo, M. (2024). Seasonal Freezing Drives Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) and Microbial Communities in Reclaimed Water-Recharged River. Water, 16(6), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060906








