Effect of Stocking Density, Multispecies Probiotics, and Biofloc on Metabolic and Physiological Responses of Puntius sophore in Laboratory Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Sampling and Experimental Site
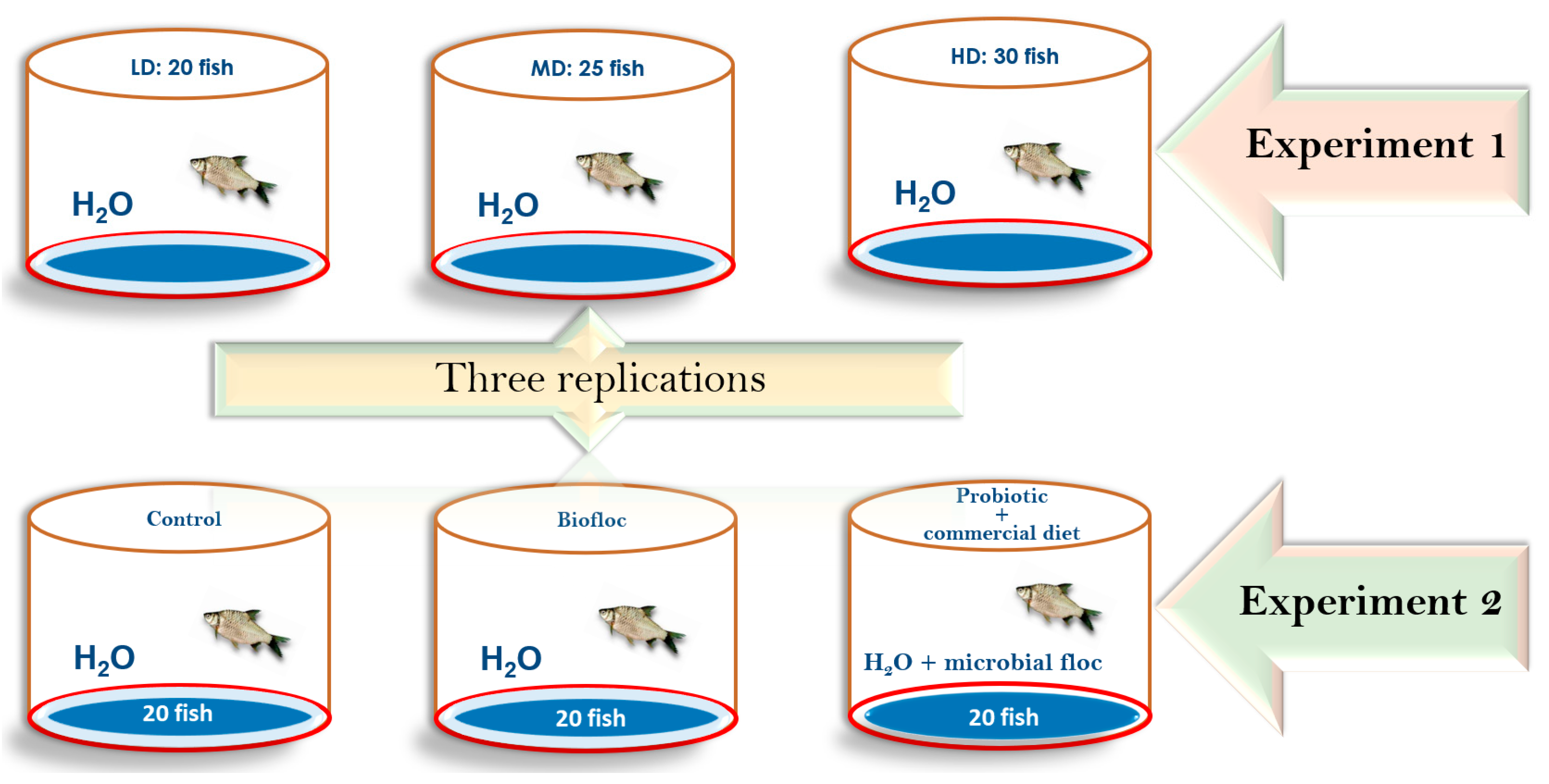
2.2. Experimental Design
- (1)
- Stocking density experiment (SD): P. sophore were subjected to three treatments and three replicates each (low-density LD: 20 fish per 400 L; medium-density MD: 25 fish per 400 L; and high-density HD: 30 fish per 400 L). A total of 225 fish were used in the first experiment.
- (2)
- Diet supplementation experiment (DS): Similarly, fish were subjected to three treatments with triplicates each (D1: control diet; D2: biofloc; and D3: probiotic + commercial diet). For each tank, 20 fish were used (Figure 2). A commercial diet was used as a control diet. In this experiment, a total of 180 fish were used.
2.3. Experimental Feeds and Biofloc
2.4. Experimental Feeds with Probiotic
2.5. Water Quality Parameters
2.6. Growth and Survival
2.7. Surgical Protocol and Haematological Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Parameters
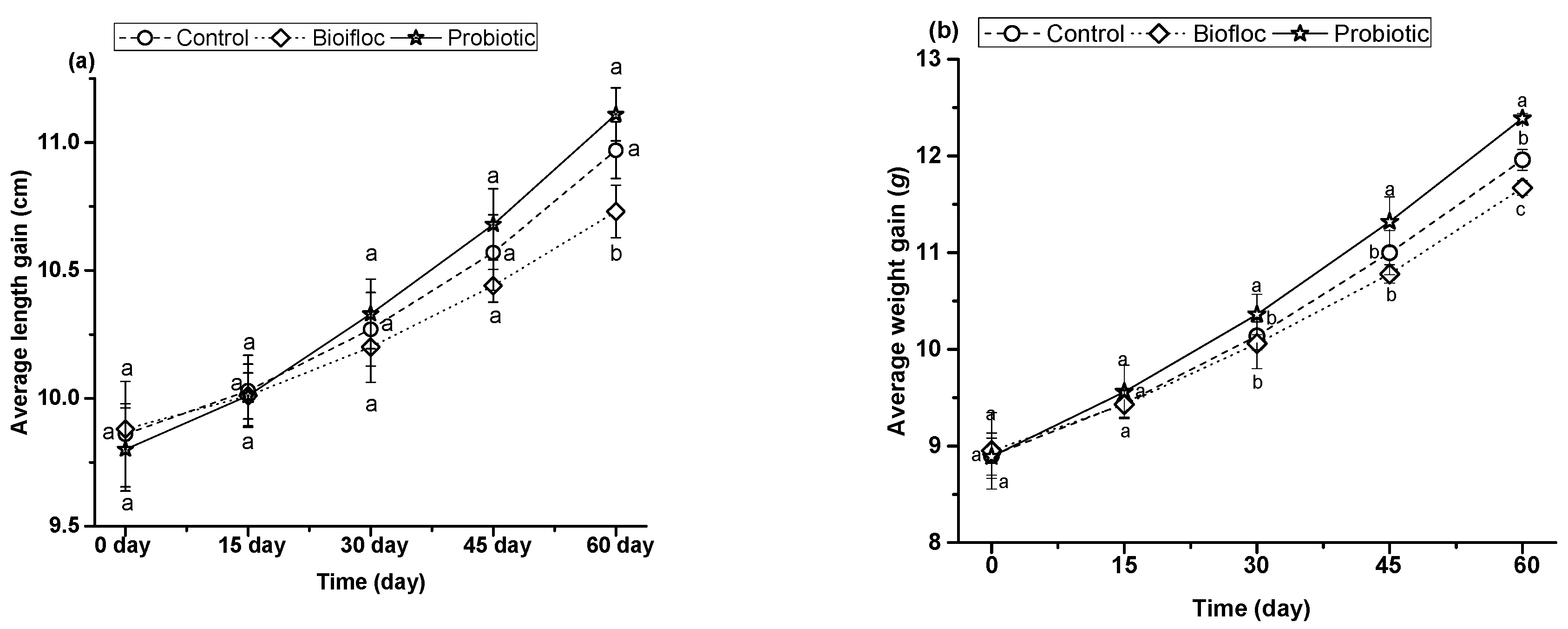
3.1.1. Growth Performances
3.1.2. Haematological Responses
3.1.3. Growth Performances
3.1.4. Haematological Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Froese, R.; Tsikliras, A.C.; Stergiou, K.I. Editorial note on weight–length relations of fishes. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2011, 41, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, U.K.; Roy, K.; Naskar, M.; Srivastava, P.K.; Bose, A.K.; Verma, V.K.; Gupta, S.; Nandy, S.K.; Sarkar, S.D.; Karnatak, G.; et al. Minnows may be more reproductively resilient to climatic variability than anticipated: Synthesis from a reproductive vulnerability assessment of Gangetic pool barbs (Puntius sophore). Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Y.; Rahman, M.M.; Miranda, R.; Leunda, P.M.; Oscoz, J.; Jewel, M.A.S.; Naif, A.; Ohtomi, J. Size at first sexual maturity, fecundity, length–weight and length–length relationships of Puntius sophore (Cyprinidae) in Bangladeshi waters. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Faruque, M.; Kabir, M.; Mustafa, M. Effects of stocking density on growth performance and profitability of Labeo bata fry reared in earthen ponds. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2019, 18, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Battisti, E.K.; Rabaioli, A.; Uczay, J.; Sutili, F.J.; Lazzari, R. Effect of stocking density on growth, hematological and biochemical parameters and antioxidant status of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) cultured in a biofloc system. Aquaculture 2020, 524, 735213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Pal, A.K.; Das, T.; Mohammed, M.S.; Sarma, K.; Venkateshwarlu, G.; Mukherjee, S.C. Secondary stress responses in Indian major carps Labeo rohita (Hamilton), Catla catla (Hamilton) and Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton) fry to increasing packing densities. Aquac. Res. 2006, 37, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Ahmed, M.U.; Parvez, M.S.; Karmokar, A.K.; Ahsan, M.N. Effect of stocking density on growth performance and body composition of climbing perch (Anabas testudineus) in biofloc system. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Shukry, M.; Zayed, M.M.; Omar, A.A.; Zaineldin, A.I.; El Basuini, M.F. Digestive enzymes, immunity and oxidative status of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared in intensive conditions. Slov. Vet. Res. 2019, 56 (Suppl. S22), 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahem, M.D. Evolution of probiotics in aquatic world: Potential effects, the current status in Egypt and recent prospectives. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Mamun, A.; Ahmad, I.; Rashid, I. Influence of probiotics on the growth performance of sex reversed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, Linnaeus, 1758) fry. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Dimitroglou, A.; Bradley, G.; Baker, R.T.M.; Davies, S.J. Probiotic applications for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) I. Effects on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal microbiota and related health criteria. Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 16, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon, H.L.; Dimitroglou, A.; Merrifield, D.L.; Ringø, E.; Davies, S.J. Probiotics and prebiotics: Concepts, definitions and history. In Aquaculture Nutrition: Gut Health, Probiotics and Prebiotics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaj-Fyzul, A.; Al-Harbi, A.H.; Austin, B. Developments in the use of probiotics for disease control in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telli, G.S.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T.; de Carla Dias, D.; Sussel, F.R.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Tachibana, L. Dietary administration of Bacillus subtilis on hematology and non-specific immunity of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus raised at different stocking densities. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wei, C.; et al. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Abdel-Rahman, A.M.; Ismael, N.E. Evaluation of commercial live bakers’ yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a growth and immunity promoter for Fry Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) challenged in situ with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Chaklader, M.R.; Shukry, M.; Ahmed, H.A.; Khallaf, M.A. A multispecies probiotic modulates growth, digestive enzymes, immunity, hepatic antioxidant activity, and disease resistance of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus fingerlings. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y. A review on the application of Bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaineldin, A.I.; Hegazi, S.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Bakr, A.; El-Keredy, A.M.; Dawood, M.A.; Dossou, S.; Wang, W.; Yukun, Z. Bacillus subtilis as probiotic candidate for red sea bream: Growth performance, oxidative status, and immune response traits. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 79, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Yilmaz, E.; Dawood, M.A.; Ringø, E.; Ahmadifar, E.; Yilmaz, S. Shrimp vibriosis and possible control measures using probiotics, postbiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics: A review. Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Sousa, N.; do Couto, M.V.S.; Abe, H.A.; Paixão, P.E.G.; Cordeiro, C.A.M.; Monteiro Lopes, E.; Ready, J.S.; Jesus, G.F.A.; Martins, M.L.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; et al. Effects of an Enterococcus faecium-based probiotic on growth performance and health of Pirarucu, Arapaima gigas. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 3720–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkhani, R.; Imani, A.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Moghanlou, K.S.; Manaffar, R. The effects of host-associated Enterococcus faecium CGMCC1. 2136 on serum immune parameters, digestive enzymes activity and growth performance of the Caspian roach (Rutilus rutilus caspicus) fingerlings. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvanasundram, P.; Chong, C.M.; Sabri, S.; Yusoff, M.S.; Karim, M. Multi-strain probiotics: Functions, effectiveness and formulations for aquaculture applications. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Hu, S.Y.; Chiu, C.S.; Liu, C.H. Multiple-strain probiotics appear to be more effective in improving the growth performance and health status of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, than single probiotic strains. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lara, A.R.; Castro, M.G.; Monroy, D.M.C.; Castro, M.J.; Davila, F.S. Growth and survival of Puntius conchonius (Hamilton, 1822) cultured in a Biofloc system. E-bios. Revis. Dig. Depart. Hombr. Amb. 2017, 1, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Aiyushirota, I. Heterotrophic bacteria system in shrimp culture with bioflocs. Biotech. Consult. Trad. Indo. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology: A Practical Guide Book; World Aquaculture Society: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco-Vega, J.M.; Cadena-Roa, M.A.; Leyva-Flores, J.A.; Zavala-Leal, O.I.; Pérez-Bravo, E.; Ruiz-Velazco, J.M. Effect of isolated bacteria and microalgae on the biofloc characteristics in the Pacific white shrimp culture. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 11, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesarcodi-Watson, A.; Kaspar, H.; Lategan, M.J.; Gibson, L. Probiotics in aquaculture: The need, principles and mechanisms of action and screening processes. Aquaculture 2008, 274, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.M. Status and Use of Biological Indicators for Evaluating the Effects of Stress on Fish; [Formerly used by DOE/TIC for titles for which valid CODEN was not available. Now invalid] 92-DEC-15; (Country unknown/Code not available); Office of Scientific and Technical Information, U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 8.
- Ayoola, S.O.; Kuton, M.P.; Idowu, A.A.; Adelekun, A.B. Acute toxicity of Nile Tilapia (Orechromis niloticus) juveniles exposed to aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Ipomoea aquatic leaf. Nat. Sci. 2011, 9, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Maceda-Veiga, A.; Monroy, M.; Viscor, G.; De Sostoa, A. Changes in non-specific biomarkers in the Mediterranean barbel (Barbus meridionalis) exposed to sewage effluents in a Mediterranean stream (Catalonia, NE Spain). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pedro, N.; Guijarro, A.I.; López-Patiño, M.A.; Martínez-Álvarez, R.; Delgado, M.J. Daily and seasonal variations in haematological and blood biochemical parameters in the tench, Tinca tinca Linnaeus, 1758. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percin, F.; Konyalioglu, S. Serum biochemical profiles of captive and wild northern bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus L. 1758) in the Eastern Mediterranean. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.; Ballester, E.L.; Cavalli, R.O.; Wasielesky, W. Effect of biofloc technology (BFT) on the early postlarval stage of pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus paulensis: Growth performance, floc composition and salinity stress tolerance. Aquac. Int. 2011, 19, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, N.; Islam, S.M.; Rohani, M.F.; Hossain, M.T.; Shahjahan, M. Probiotic yeast enhances growth performance of rohu (Labeo rohita) through upgrading hematology, and intestinal microbiota and morphology. Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.K.; Das, S.K.; Rahim, S.M.; Ghaffar, M. Temperature and diet effect on the pepsin enzyme activities, digestive somatic index and relative gut length of Malabar blood snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus). Aquac. Rep. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.K.; Fivelstad, S.; Ghaffar, M.A.; Das, S.K. Haematological and biochemical responses of juvenile Malabar blood snapper (Lutjanus molabaricus Bloch & Schneider, 1801) exposed to different rearing temperatures and diets. Sains Malays. 2019, 48, 1790–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, F.; Marafioti, S.; Arfuso, F.; Piccione, G.; Faggio, C. Influence of different salinity on haematological and biochemical parameters of the widely cultured mullet, Mugil cephalus. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2013, 46, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J.; Sokal, R.R. Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.; Park, J. Does Stocking Density Affect Growth Performance and Hematological Parameters of Juvenile Olive Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in a Recirculating Aquaculture System? Animals 2022, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohinoor, A.H.M.; Khan, M.M.; Yeasmine, S.; Mandol, P.; Islam, M.S. Effects of stocking density on growth and production performance of indigenous stinging catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Int. J. Agric. Res. Innov. Technol. 2012, 2, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narejo, N.T.; Salam, M.A.; Sabur, M.A.; Rahmatullah, S.M. Effect of stocking density on growth and survival of indigenous catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch) reared in cemented cistern fed on formulated feed. Pak. J. Zool. 2005, 37, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, B.K. Effect of stocking density on survival and growth of endangered elong, Bengala elonga (Hamilton) in nursery ponds. Int. J. Oceanogr. Aquac. 2017, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pouey, J.L.O.F.; Piedras, S.R.N.; Rocha, C.B.; Tavares, R.A.; Santos, J.D.M.; Britto, A.C.P. Productive performance of silver catfish, Rhamdia quelen, juveniles stocked at different densities/Desempenho produtivo de juvenis de Jundiá (Rhamdia quelen) submetidos a diferentes densidades de estocagem. Ars Vet. 2011, 27, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Barcellos, L.G.; Nicolaiewsky, S.; De Souza, S.G.; Lulhier, F. The effects of stocking density and social interaction on acute stress response in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.) fingerlings. Aquac. Res. 1999, 30, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R. Probiotics: An emerging food supplement with health benefits. Food Biotechnol. 2005, 19, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzer, C.; Çoban, D.; Kamaci, H.O.; Saka, Ş.; Firat, K.; Otgucuoğlu, Ö.; Küçüksari, H. Lactobacillus spp. bacteria as probiotics in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) larvae: Effects on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Soltan, M.A.; Jarmołowicz, S.; Abdo, H.S. Combined effects of dietary malic acid and Bacillus subtilis on growth, gut microbiota and blood parameters of Nile tilapia (O reochromis niloticus). Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanbo, W.; Zirong, X. Effect of probiotics for common carp (Cyprinus carpio) based on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2006, 127, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, M.; Lazado, C.C.; Safari, R.; Yeganeh, S.; Zorriehzahra, M.J. Aqualase®, a yeast-based in-feed probiotic, modulates intestinal microbiota, immunity and growth of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Yun, S.; Jun, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Han, S.J.; Sukumaran, V.; Park, S.C. Therapeutic effect of intestinal autochthonous Lactobacillus reuteri P16 against waterborne lead toxicity in Cyprinus carpio. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Feeding with microbial flocs by tilapia in minimal discharge bio-flocs technology ponds. Aquaculture 2007, 264, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Wahab, M.A.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Huque, S.; Salam, M.A.; Azim, M.E. C/N ratio control and substrate addition for periphyton development jointly enhance freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii production in ponds. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Pan, L.Q.; Sun, X.; Huang, J. Effects of bioflocs on water quality, and survival, growth and digestive enzyme activities of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) in zero-water exchange culture tanks. Aquac. Res. 2012, 44, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, V.; Cappello, T.; Costa, G.; Cannavà, C.; Sanfilippo, M.; Fazio, F.; Fasulo, S. Comparative study of haematology of two teleost fish (Mugil cephalus and Carassius auratus) from different environments and feeding habits. Eur. Zool. J. 2018, 85, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, S.P.; Zarejabad, A.M.; Nasrabadi, R.G.; Ahmadifar, E.; Molaee, M. Haematology, morphology and blood cells characteristics of male and female Siamese fighting fish (Betta splendens). Comp. Clin. Path. 2012, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, M.; Cristea, V.; Dediu, L.; Bocioc, E.; Grecu, R.I.; Ion, S.; Vasilean, I. The effect of probiotic diet on growth and hematology parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum 1792). Lucr. Stiintifice-Sera Zootheniie 2010, 59, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Montero, D.; Tort, L.; Robaina, L.; Vergara, J.M.; Izquierdo, M.S. Low vitamin E in diet reduces stress resistance of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2001, 11, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, C.F.; Iwama, G.K. Effect of handling and stocking density on hematocrit, plasma cortisol, and survival in wild and hatchery-reared chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Aquaculture 1993, 112, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, N. Blood performance: A new formula for fish growth and health. Biology 2021, 10, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.S.; Moustafa, M.M.; Mohamed, N.M. Evaluation of immunomodulatory effects of some probiotics on cultured Oreochromis niloticus. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Tilapia in Aquaculture, Cairo, Egypt, 12–14 October 2008; p. 1043. [Google Scholar]
- Jäger, R.; Zaragoza, J.; Purpura, M.; Iametti, S.; Marengo, M.; Tinsley, G.M.; Anzalone, A.J.; Oliver, J.M.; Fiore, W.; Biffi, A.; et al. Probiotic administration increases amino acid absorption from plant protein: A placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, crossover study. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sihag, R.C.; Gahlawat, S.K. Effect of probiotic on haematogical paramaters of diseased fish (Cirrihinus mrigal). J. Fish. Sci. 2013, 7, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpur, A.D.; Ikhwanuddin, M. Azadirachta indica (neem) leaf dietary effects on the immunity response and disease resistance of Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer challenged with Vibrio harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, Y.A.E.; Shalaby, A.M.E.; Sharaf, S.M.; El-Marakby, H.I.; Rizkalla, E.H. The physiological changes and growth performance of the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus after feeding with Biogen® as growth promoter. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2004, 8, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Long, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Guan, C.; Wu, F. Effect of biofloc technology on growth, digestive enzyme activity, hematology, and immune response of genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2015, 448, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.E.; Little, D.C. The biofloc technology (BFT) in indoor tanks: Water quality, biofloc composition, and growth and welfare of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2008, 283, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Proximate Composition | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 12.98 ± 0.41 |
| Protein | 31.20 ± 0.34 |
| Lipid | 6.72 ± 0.80 |
| Ash | 13.22 ± 0.61 |
| Fibre | 11.58 |
| NFE * | 24.30 |
| Parameters | D1 | D2 | D3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 26 ± 0.64 | 26 ± 0.14 | 27 ± 0.15 |
| DO (mg L−1) | 5.9 ± 0.20 | 5.8 ± 0.30 | 5.9 ± 0.30 |
| TH (mg L−1) | 119.33 ± 22.33 | 108.07 ± 18.41 | 125.4 ± 16.49 |
| NH3-N (mg L−1) | 0.25 ± 0.20 | 0.24 ± 0.34 | 0.33 ± 0.24 |
| pH | 7.47 ± 0.09 | 7.07 ± 0.31 | 7.27 ± 0.17 |
| Variables | Stocking Density | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LD | MD | HD | |
| L1 (cm) | 9.86 ± 0.22 a | 9.96 ± 0.41 a | 9.99 ± 0.31 a |
| L2 (cm) | 10.97 ± 0.30 a | 10.99 ± 0.52 a | 10.79 ± 0.48 a |
| W1 (g) | 8.90 ± 1.04 a | 8.91 ± 0.78 a | 8.90 ± 0.73 a |
| W2 (g) | 11.96 ± 1.49 a | 11.67 ± 0.93 a | 11.46 ± 0.83 a |
| TLG (cm) | 1.11 ± 0.10 a | 1.03 ± 0.14 a | 0.80 ± 0.27 b |
| BWG (g) | 3.06 ± 0.53 a | 2.76 ± 0.21 ab | 2.56 ± 0.32 b |
| FCR | 1.78 ± 0.04 b | 1.82 ± 0.05 b | 2.07 ± 0.07 a |
| FCE | 0.57 ± 0.10 a | 0.52 ± 0.04 ab | 0.49 ± 0.06 b |
| SGR (% day−1) | 0.49 ± 0.05 a | 0.45 ± 0.03 ab | 0.42 ± 0.05 b |
| RGR (%) | 34.34 ± 3.87 a | 31.07 ± 2.09 ab | 28.93 ± 4.15 b |
| DGR (% day−1) | 30.60 ± 5.33 a | 27.60 ± 2.06 ab | 25.60 ± 3.23 b |
| Survival (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Parameter | Treatments | Analysis of Variance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD | MD | HD | Adj SS | Adj MS | F | p | |
| WBC (×109 L−1) | 41.93 ± 1.21 b | 47.47 ± 4.41 b | 60.83 ± 3.94 a | 566.5 | 283.25 | 15.54 | 0.004 |
| LYM (%) | 65.20 ± 3.90 a | 69.67 ± 3.19 a | 73.37 ± 5.53 a | 100.3 | 50.17 | 1.79 | 0.245 |
| MON (%) | 4.47 ± 0.61 a | 4.30 ± 0.16 a | 4.93 ± 0.29 a | 0.6467 | 0.3233 | 1.33 | 0.331 |
| RBC (×106 mm−3) | 3.15 ± 0.54 a | 2.81 ± 0.93 a | 2.61 ± 0.51 a | 0.4482 | 0.2241 | 0.32 | 0.741 |
| Hb (g dL−1) | 13.00 ± 1.76 a | 11.62 ± 1.82 a | 11.50 ± 1.20 a | 4.177 | 2.089 | 0.53 | 0.613 |
| HCT (%) | 42.80 ± 5.92 a | 39.13 ± 1.16 a | 38.23 ± 2.02 a | 35.11 | 17.55 | 0.87 | 0.467 |
| MCV (pg) | 137.60 ± 14.8 a | 154.25 ± 44.77 a | 153.40 ± 36.16 a | 527.9 | 263.9 | 0.15 | 0.864 |
| MCH (fl) | 43.69 ± 14.10 a | 47.21 ± 18.02 a | 46.55 ± 13.39 a | 20.98 | 10.49 | 0.03 | 0.971 |
| MCHC (%) | 31.29 ± 7.88 a | 29.59 ± 3.98 a | 30.00 ± 1.82 a | 4.683 | 2.341 | 0.06 | 0.945 |
| PLT (×103 mm−3) | 37.40 ± 4.97 a | 27.45 ± 5.50 a | 32.13 ± 3.13 a | 148.8 | 74.39 | 2.30 | 0.182 |
| Variables | Diet | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | D3 | |
| L1 (cm) | 9.86 ± 0.21 | 9.88 ± 0.31 | 9.80 ± 0.32 |
| L2 (cm) | 10.97 ± 0.23 | 10.73 ± 0.40 | 11.11 ± 0.37 |
| W1 (g) | 8.90 ± 1.00 | 8.95 ± 0.69 | 8.89 ± 0.61 |
| W2 (g) | 11.96 ± 1.42 | 11.67 ± 0.92 | 12.39 ± 0.78 |
| TLG (cm) | 1.11 ± 0.10 b | 0.85 ± 0.15 c | 1.31 ± 0.15 a |
| BWG (g) | 3.06 ± 0.51 ab | 2.72 ± 0.37 b | 3.50 ± 0.32 a |
| FCR | 1.82 ± 0.29 a | 1.88 ± 0.27 a | 1.50 ± 0.14 b |
| FCE | 0.57 ± 0.09 b | 0.54 ± 0.07 b | 0.67 ± 0.06 a |
| SGR (% day−1) | 0.49 ± 0.05 b | 0.44 ± 0.05 b | 0.55 ± 0.04 a |
| RGR (%) | 34.34 ± 3.69 b | 30.44 ± 3.65 b | 39.48 ± 3.63 a |
| DGR (% day−1) | 30.60 ± 5.08 ab | 27.20 ± 3.66 b | 35.00 ± 3.25 a |
| Survival (%) | 100 | 72 | 100 |
| Parameter | Treatments | Analysis of Variance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | D3 | Adj SS | Adj MS | F | p | |
| WBC (×109 L−1) | 45.40 ± 1.10 b | 54.57 ± 7.25 ab | 65.53 ± 7.75 a | 609.6 | 304.82 | 8.26 | 0.019 |
| LYM (%) | 72.00 ± 0.90 a | 81.00 ± 8.16 a | 69.33 ± 6.13 a | 224.2 | 112.11 | 2.13 | 0.199 |
| MON (%) | 4.30 ± 0.16 a | 5.10 ± 0.41 a | 4.90 ± 0.16 a | 1.04 | 0.52 | 4.73 | 0.059 |
| RBC (×106 mm−3) | 0.96 ± 0.12 b | 1.94 ± 0.75 a | 2.55 ± 0.11 a | 3.85 | 1.92 | 6.48 | 0.032 |
| Hb (g dL−1) | 11.95 ± 1.41 a | 11.30 ± 1.93 a | 12.27 ± 2.21 a | 1.46 | 0.73 | 0.14 | 0.874 |
| HCT (%) | 38.27 ± 1.51 a | 38.97 ± 0.26 a | 41.67 ± 1.17 a | 19.29 | 9.64 | 5.19 | 0.049 |
| MCV (pg) | 407.21 ± 67.04 a | 237.62 ± 100.01 ab | 163.86 ± 6.70 b | 93,424 | 46,712 | 6.43 | 0.032 |
| MCH (fl) | 128.00 ± 10.61 a | 72.88 ± 5.13 b | 48.35 ± 5.43 c | 9984.1 | 4992.03 | 59.27 | 0.000 |
| MCHC (%) | 31.13 ± 2.45 a | 29.01 ± 4.99 a | 29.35 ± 4.63 a | 7.76 | 3.89 | 0.15 | 0.865 |
| PLT (×103 mm−3) | 23.01 ± 0.91 c | 29.00 ± 1.63 b | 34.07 ± 1.72 a | 183.69 | 91.84 | 28.50 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Debi, S.; Salam, M.A.; Das, S.K.; Alam, M.S.; Rahman, M.L.; Hossain, M.S.; Mazumder, S.K. Effect of Stocking Density, Multispecies Probiotics, and Biofloc on Metabolic and Physiological Responses of Puntius sophore in Laboratory Conditions. Water 2024, 16, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060820
Debi S, Salam MA, Das SK, Alam MS, Rahman ML, Hossain MS, Mazumder SK. Effect of Stocking Density, Multispecies Probiotics, and Biofloc on Metabolic and Physiological Responses of Puntius sophore in Laboratory Conditions. Water. 2024; 16(6):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060820
Chicago/Turabian StyleDebi, Sutapa, Mohammad Abdus Salam, Simon Kumar Das, Md. Shahanoor Alam, Mohammad Lutfar Rahman, Md. Shakhawate Hossain, and Sabuj Kanti Mazumder. 2024. "Effect of Stocking Density, Multispecies Probiotics, and Biofloc on Metabolic and Physiological Responses of Puntius sophore in Laboratory Conditions" Water 16, no. 6: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060820
APA StyleDebi, S., Salam, M. A., Das, S. K., Alam, M. S., Rahman, M. L., Hossain, M. S., & Mazumder, S. K. (2024). Effect of Stocking Density, Multispecies Probiotics, and Biofloc on Metabolic and Physiological Responses of Puntius sophore in Laboratory Conditions. Water, 16(6), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060820








