Alkaline Chemical Neutralization to Treat Acid Mine Drainage with High Concentrations of Iron and Manganese
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Acid Mining Drainage and Reagents
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Characterization of the Acid Mine Drainage
2.2.2. Neutralization Performance Experiments of NaOH and Shell Powder
2.2.3. The Optimal Dosage Experiments of NaOH
2.2.4. The Optimal Neutralization Time Experiments of NaOH
2.2.5. Characterization of the Neutralized Residues
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Quality of the Raw Acid Mine Drainage
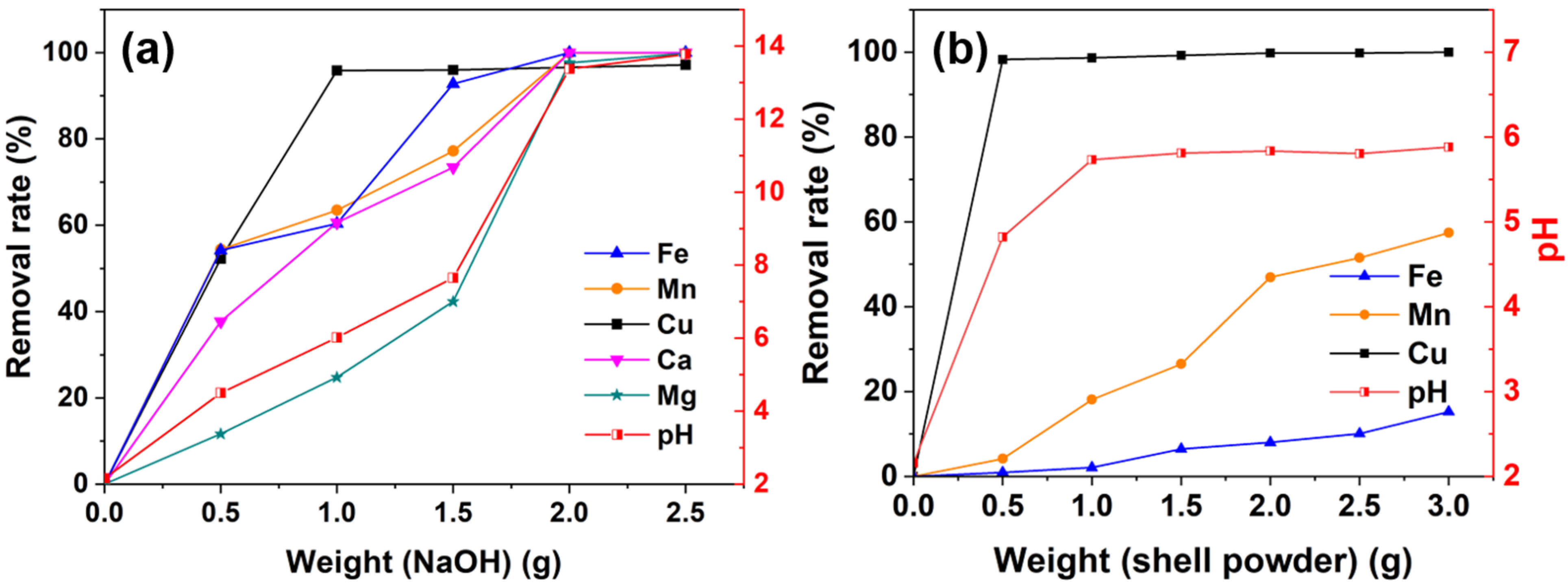
3.2. Performances of NaOH and Shell Powder during the Acid Mine Drainage Treatment
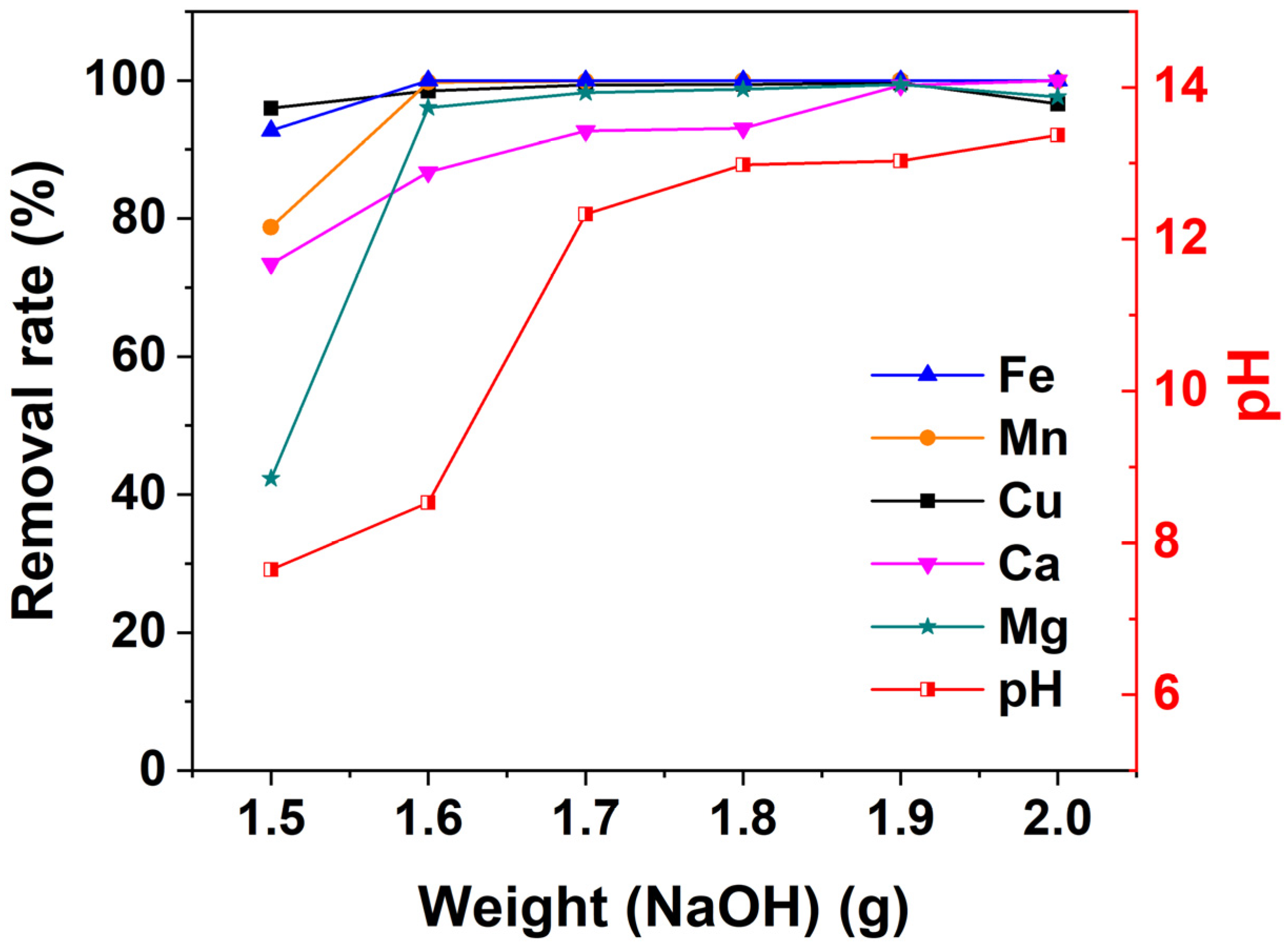
3.3. The Optimal Dosage of NaOH of the Acid Mine Drainage Treatment
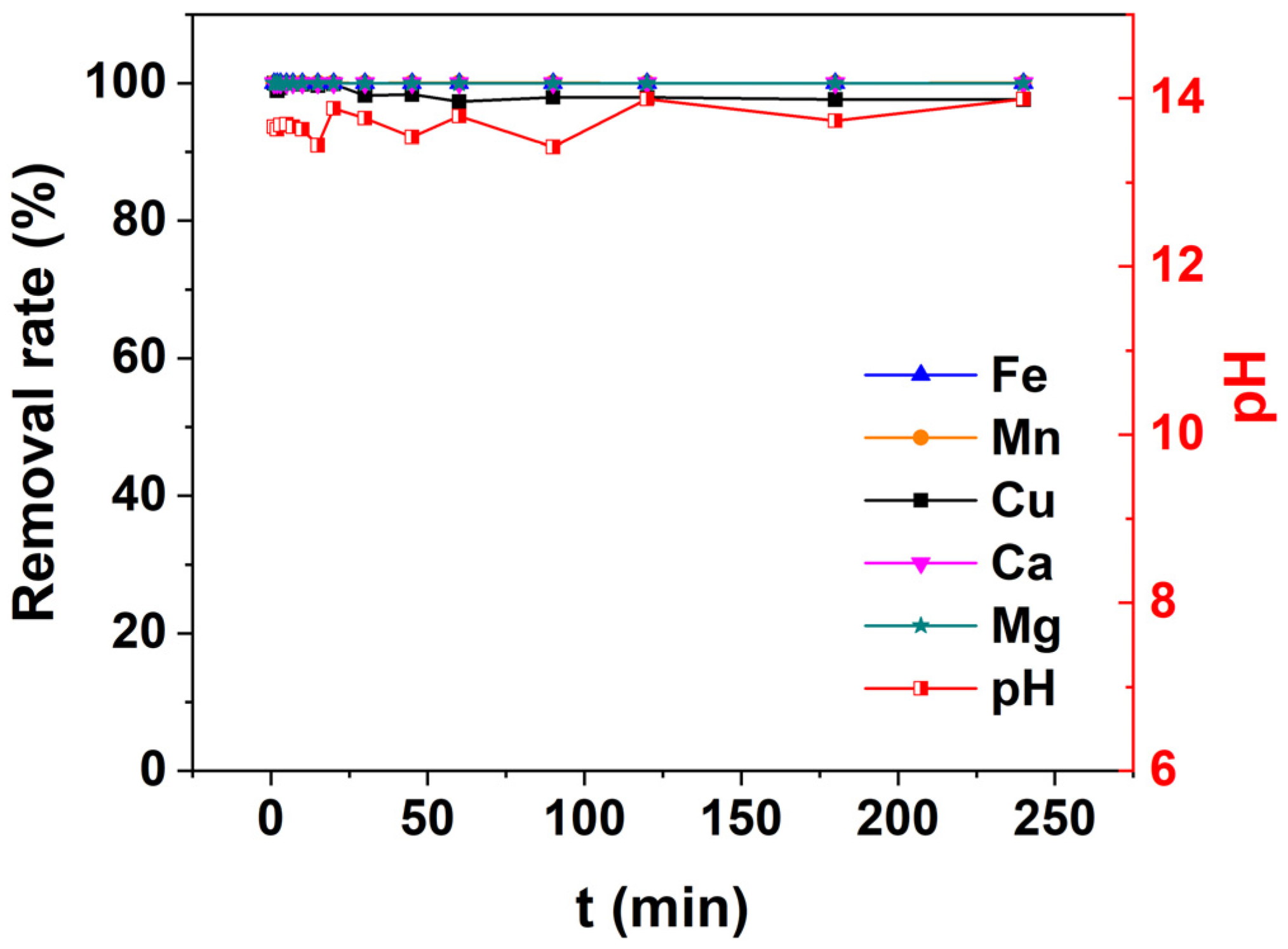
3.4. The Optimal Neutralization Time of the Acid Mine Drainage Treatment
3.5. Characterization of the Neutralized Residues
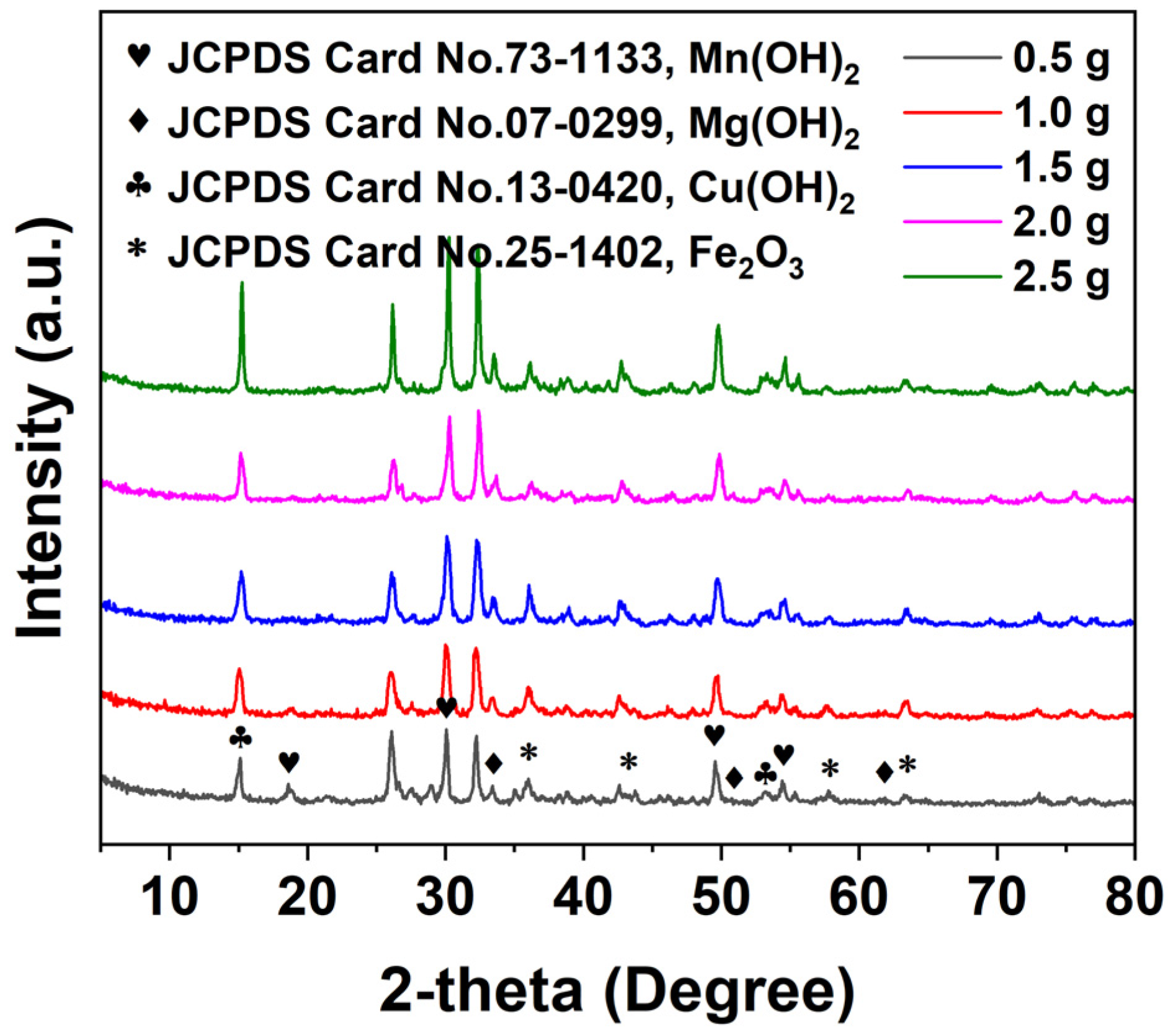
3.5.1. XRD Analysis
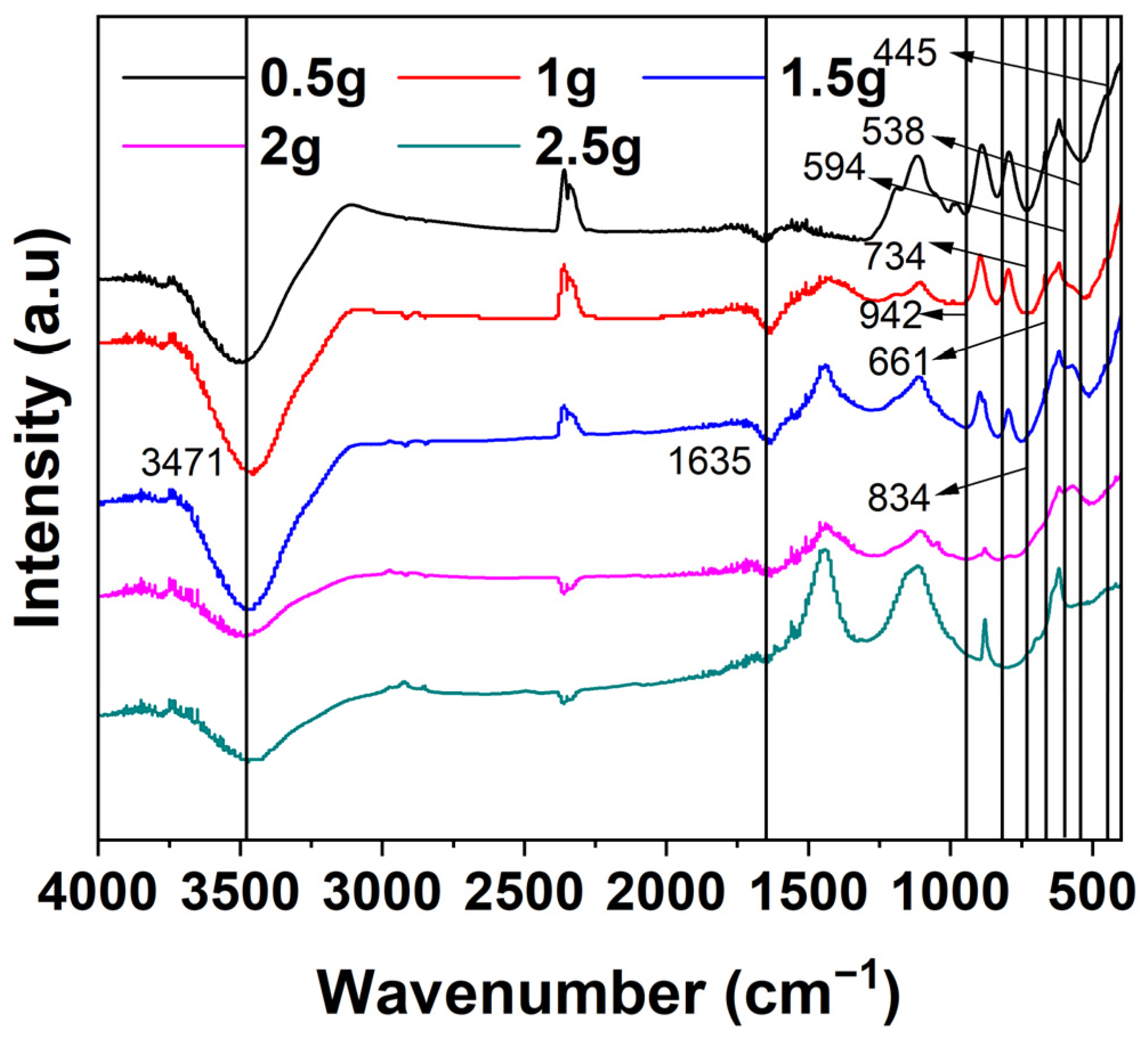
3.5.2. FTIR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daraz, U.; Li, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Iqbal, R.; Ditta, A. Remediation technologies for acid mine drainage: Recent trends and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, G.; Ryu, S.; Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S. A critical review on remediation, reuse, and resource recovery from acid mine drainage. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1110–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabelin, C.B.; Veerawattananun, S.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N.; Igarashi, T. Pyrite oxidation in the presence of hematite and alumina: I. Batch leaching experiments and kinetic modeling calculations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Aniagor, C.O.; Ajala, O.J.; Oba, S.N.; Iwuchukwu, F.U.; Ahmadi, S.; Igwegbe, C.A. A review of treatment technologies for the mitigation of the toxic environmental effects of acid mine drainage (AMD). Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Fan, R.; Yang, S.; Li, C. Development and status of the treatment technology for acid mine drainage. Min. Metall. Explor. 2021, 38, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, R.; Banda, J.F.; Hao, C.; Dong, H.; Pei, L.; Guo, D.; Wei, P.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H. Contrasting seasonal variations of geochemistry and microbial community in two adjacent acid mine drainage lakes in Anhui Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Review: Acid mine drainage (AMD) in abandoned coal mines of Shanxi, China. Water 2021, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Li, X.; Seno, K.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailings recycling. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulonen, M.L.K.; Baeza, J.A.; Gabriel, D.; Guisasola, A. Optimisation of the operational parameters for a comprehensive bioelectrochemical treatment of acid mine drainage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Guerreiro, N.; Simões, I.; Imaginário, M.J.; Palma, P. Assessment of the environmental impact of acid mine drainage on surface water, stream sediments, and macrophytes using a battery of chemical and ecotoxicological indicators. Water 2021, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Dong, Z.; Fu, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Tian, S.; Ning, P. Insight into the kinetic analysis of acid mine drainage treated by carbonate rock. Environ. Technol. 2022, 45, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ye, Y.; Yao, N.; Hu, N.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y. A critical review of prevention, treatment, reuse, and resource recovery from acid mine drainage. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 329, 129666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhou, B.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Li, N. Bibliometric overview of research trends on heavy metal health risks and impacts in 1989–2018. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 276, 123249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarathne, A.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Assessment of ecological and human health risks of metals in urban road dust based on geochemical fractionation and potential bioavailability. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbar Khan, A.; Akhter, G.; Ge, Y.; Shahid, M.; Rahman, K.U. Development of artificial geochemical filter to treat acid mine drainage for safe disposal of mine water in Salt Range Portion of Indus Basin—A lab to pilot scale study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardi, J.A.; Bonotto, D.M. Hydrogeochemical features of surface water and groundwater contaminated with acid mine drainage (AMD) in coal mining areas: A case study in southern Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18911–18927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Hu, Q.; Gao, X.; Li, C.; Luo, M.; Wang, Y. Effects of Fe-rich acid mine drainage on percolation features and pore structure in carbonate rocks. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Hatton-Jones, B.W.; Millar, G.J. Alternative neutralisation materials for acid mine drainage treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 22, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Mamba, B.B. Evaluation of charcoal ash nanoparticles pollutant removal capacity from acid mine drainage rich in iron and sulfate. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 251, 119720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.; Yusof, N.; Lau, W.J.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F. Recent trends of heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by membrane technologies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 76, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Reig, M.; Gibert, O.; Cortina, J.L. Integration of nanofiltration membranes in recovery options of rare earth elements from acidic mine waters. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 210, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, A.; Ho, H.-J.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshida, H.; Hayakawa, Y.; Yamasaki, A. Comparative study of acid mine drainage neutralization by calcium hydroxide and concrete sludge–derived material. Miner. Eng. 2022, 188, 107819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Cheng, K.Y.; Morris, C.; Douglas, G.; Ginige, M.P.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, L.; Kaksonen, A.H. Sequential hydrotalcite precipitation and biological sulfate reduction for acid mine drainage treatment. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiiskila, J.D.; Sarkar, D.; Panja, S.; Sahi, S.V.; Datta, R. Remediation of acid mine drainage-impacted water by vetiver grass (Chrysopogon zizanioides): A multiscale long-term study. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 129, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pat-Espadas, A.M.; Loredo Portales, R.; Amabilis-Sosa, L.E.; Gómez, G.; Vidal, G. Review of Constructed Wetlands for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. Water 2018, 10, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Pakshirajan, K. Continuous removal and recovery of metals from wastewater using inverse fluidized bed sulfidogenic bioreactor. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 284, 124769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchichi, A.; Hamou, M.O.; Edahbi, M.; Bobocioiu, E.; Neculita, C.M.; Benzaazoua, M. Passive treatment of acid mine drainage from the Sidi-Kamber mine wastes (Mediterranean coastline, Algeria) using neighbouring phosphate material from the Djebel Onk mine. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Y. Construction and carbon source optimization of a microbial-plant coupled reactor for treating acid mine drainage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 78862–78873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Mao, Q.; Luo, L.; Deng, Y. Removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by red mud–based geopolymer pervious concrete: Batch and long–term column studies. Polymers 2022, 14, 5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolonen, E.-T.; Sarpola, A.; Hu, T.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Acid mine drainage treatment using by-products from quicklime manufacturing as neutralization chemicals. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, P.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ma, T. A review of acid mine drainage: Formation mechanism, treatment technology, typical engineering cases and resource utilization. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 1240–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cunfang, L.; Quan, X.; Cao, D. Mechanism of acid mine drainage remediation with steel slag: A review. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30205–30213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, R.; Coyte, R.; Wang, Z.; Das, D.; Vengosh, A. Water quality implications of the neutralization of acid mine drainage with coal fly ash from India and the United States. Fuel 2022, 330, 125675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.-J.; Iizuka, A.; Vadapalli, V.R.K.; Coetzee, H.; Petrik, L.; Petersen, J.; Ojumu, T. Potential investigation of concrete fines as an alternative material: A novel neutralizer for acid mine drainage treatment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 102985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, A.; Parbhakar-Fox, A.; Meffre, S.; Cooke, D.R. Alkaline industrial wastes—Characteristics, environmental risks, and potential for mine waste management. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kwon, D.; Yang, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, Y.T. Comparison of Fe and Mn removal using treatment agents for acid mine drainage. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yang, H.; Tan, K.; Hou, S.; Cai, J.; Yuan, X.; Lan, Q.; Cao, J.; Yan, S. Treatment and recovery of iron from acid mine drainage: A pilot-scale study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, Y.-W.; Cho, D.-W.; Yim, G.-J.; Park, H.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Geochemical assessment of gypsum scale formation in the hydrated lime neutralization facility of the Daedeok Mine, South Korea. Minerals 2022, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G. Inorganic and Analytical Chemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 416–417. [Google Scholar]
- Santomartino, S.; Webb, J.A. Estimating the longevity of limestone drains in treating acid mine drainage containing high concentrations of iron. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 2344–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovleva, E.; Mäkilä, E.; Salonen, J.; Sitarz, M.; Wang, S.; Sillanpää, M. Acid mine drainage (AMD) treatment: Neutralization and toxic elements removal with unmodified and modified limestone. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-Y.; Hou, C.-C.; Chen, Q.-Q.; Wang, C.-J.; Lv, X.-J.; Zhong, J.; Fu, W.-F.; Che, C.-M.; Chen, Y. Cu(OH)2 supported on Fe(OH)3 as a synergistic and highly efficient system for the dehydrogenation of ammonia-borane. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liao, P.; Finfrock, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.; Shu, C.; Liu, P. Metal (Fe, Cu, and As) transformation and association within secondary minerals in neutralized acid mine drainage characterized using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 139, 105242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.; Chrysochoou, M. Mechanisms of chromate, selenate, and sulfate adsorption on Al-substituted ferrihydrite: Implications for ferrihydrite surface structure and reactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3589–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toupance, T.; Kermarec, M.; Lambert, J.-F.; Louis, C. Conditions of formation of copper phyllosilicates in silica-supported copper catalysts prepared by selective adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Andrews, L. Infrared spectra of M(OH)1,2,3 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) molecules in solid argon and the character of first row transition metal hydroxide bonding. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 10035–10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Foteinis, S.; Chatzisymeon, E. Co-treatment of acid mine drainage and municipal wastewater effluents: Emphasis on the fate and partitioning of chemical contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) | GB28661-2012 |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 2.16 | 6–9 |
| Zn (mg/L) | undetected | 2.0 |
| Cu (mg/L) | 6.54 | 0.5 |
| Mn (mg/L) | 621.29 | 2.0 |
| Fe (mg/L) | 77.54 (g/L) | 5.0 |
| Cd (mg/L) | undetected | 0.1 |
| Cr (mg/L) | undetected | 1.5 |
| Pb (mg/L) | 0.06 | 1.0 |
| Ni (mg/L) | undetected | 1.0 |
| Ag (mg/L) | undetected | 0.5 |
| Ca (mg/L) | 12.39 | / |
| Mg (mg/L) | 55.04 | / |
| Metals | Concentrations | GB28661-2012 | Precipitation Reaction Equations | KSP [40] | Ranges of pH for Metal Precipitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 77.54 g/L (1.39 mol/L) | 5.0 mg/L (8.95 × 10−5 mol/L) | [18] | 4.0 × 10−38 | 1.5~2.9 |
| [18] | 8.0 × 10−16 | 6.4~9.5 | |||
| Cu | 6.54 mg/L (1.03 × 10−4 mol/L) | 0.5 mg/L (7.87 × 10−6 mol/L) | 2.2 × 10−20 | 6.2~6.7 | |
| Mn | 621.29 mg/L (1.13 × 10−2 mol/L) | 2.0 mg/L (3.64 × 10−5 mol/L) | 1.9 × 10−13 | 8.6~9.9 | |
| Ca | 12.39 mg/L (3.09 × 10−5 mol/L) | / | [5] | 9.1 × 10−6 | / |
| 5.5 × 10−6 | >13.6 | ||||
| Mg | 55.04 mg/L (2.26 × 10−3 mol/L) | / | 1.8 × 10−11 | >10.0 |
| Materials | Dosages (g) | Metal Concentrations (mg/L) | pH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Mn | Cu | Ca | Mg | |||
| NaOH | 0.5 | 35.50 | 283.33 | 3.13 | 7.73 | 48.62 | 4.50 |
| 1.0 | 30.73 | 226.85 | 0.27 | 4.89 | 41.41 | 6.02 | |
| 1.5 | 5.63 | 141.67 | 0.26 | 3.30 | 31.75 | 7.65 | |
| 2.0 | 0 | 0.56 | 0.22 | 0 | 1.30 | 13.37 | |
| 2.5 | 0 | 0.54 | 0.19 | 0 | 0.10 | 13.77 | |
| Shell powder | 0.5 | 76,800.1 | 595.21 | 0.11 | / | / | 4.82 |
| 1.0 | 75,912.2 | 508.65 | 0.09 | / | / | 5.73 | |
| 1.5 | 72,508.8 | 456.48 | 0.05 | / | / | 5.81 | |
| 2.0 | 71,325.0 | 329.61 | 0.01 | / | / | 5.84 | |
| 2.5 | 69,697.2 | 301.16 | 0.01 | / | / | 5.80 | |
| 3.0 | 65,701.8 | 264.40 | 0 | / | / | 5.88 | |
| NaOH (g) | Metal Concentrations (mg/L) | Final pH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Mn | Cu | Ca | Mg | ||
| 1.5 | 5.63 | 141.67 | 0.25 | 3.30 | 31.75 | 7.65 |
| 1.6 | 1.52 | 1.77 | 0.10 | 1.65 | 2.17 | 8.53 |
| 1.7 | 1.48 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 12.33 |
| 1.8 | 1.48 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 12.98 |
| 1.9 | 1.45 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.31 | 13.03 |
| 2.0 | 0 | 0.56 | 0.22 | 0 | 1.30 | 13.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, P.; Zhang, R.; Hu, M. Alkaline Chemical Neutralization to Treat Acid Mine Drainage with High Concentrations of Iron and Manganese. Water 2024, 16, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060821
Zhao P, Zhang R, Hu M. Alkaline Chemical Neutralization to Treat Acid Mine Drainage with High Concentrations of Iron and Manganese. Water. 2024; 16(6):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060821
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Pingping, Ruiming Zhang, and Mengdi Hu. 2024. "Alkaline Chemical Neutralization to Treat Acid Mine Drainage with High Concentrations of Iron and Manganese" Water 16, no. 6: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060821
APA StyleZhao, P., Zhang, R., & Hu, M. (2024). Alkaline Chemical Neutralization to Treat Acid Mine Drainage with High Concentrations of Iron and Manganese. Water, 16(6), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060821




