Characteristics of Groundwater Microbial Community Composition and Environmental Response in the Yimuquan Aquifer, North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
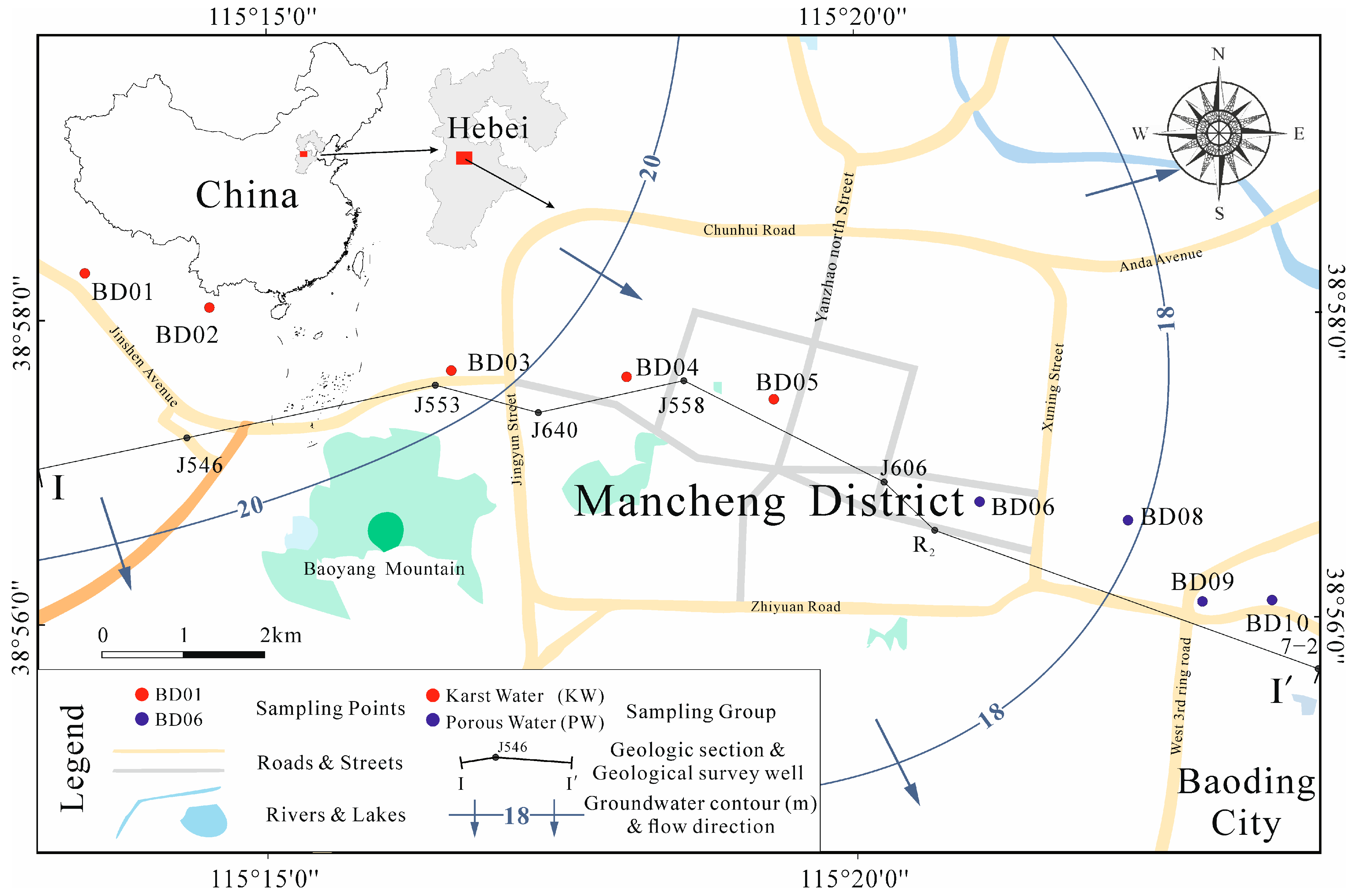
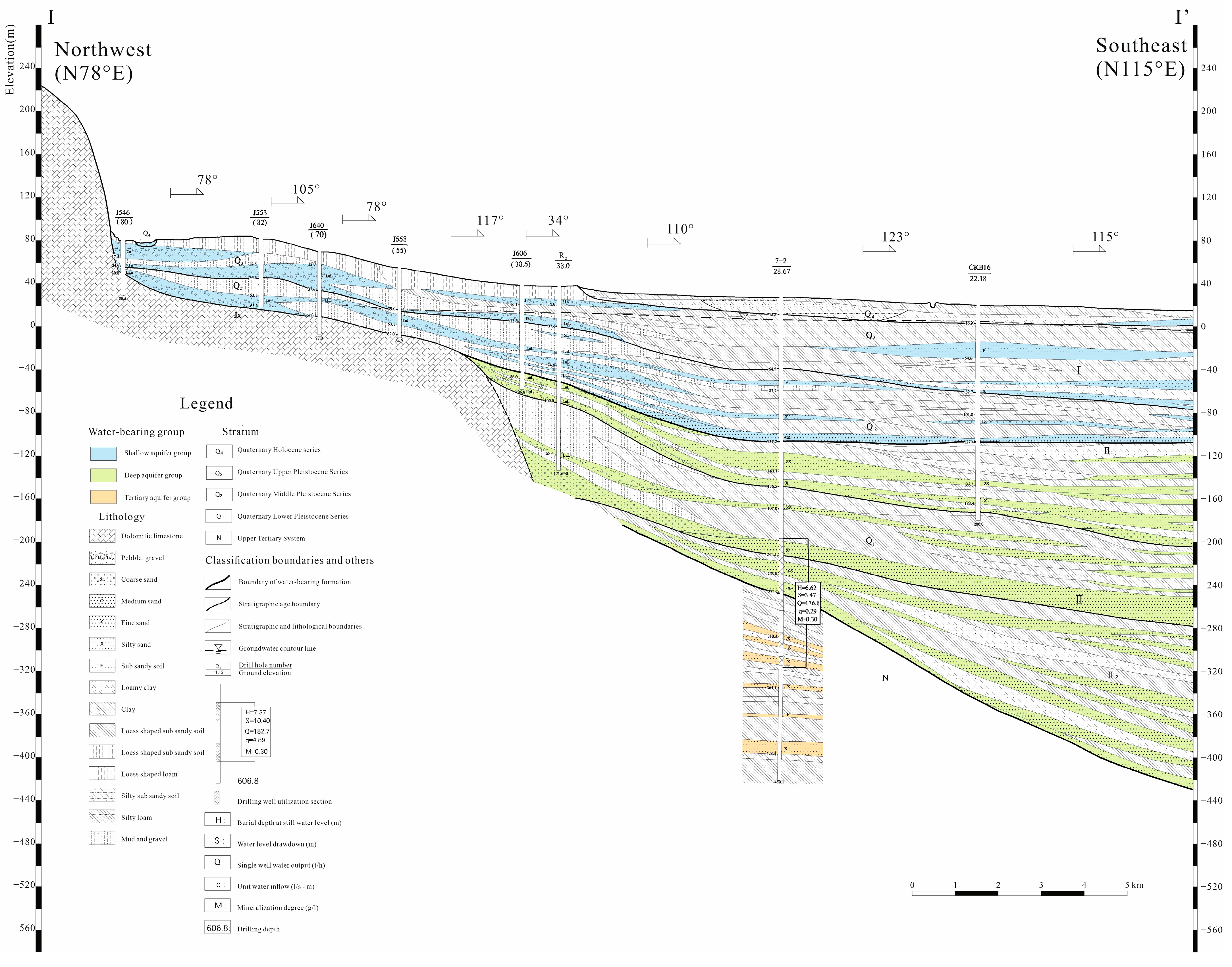
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Sample Collection and Testing
2.3. Sequence and Data Analysis
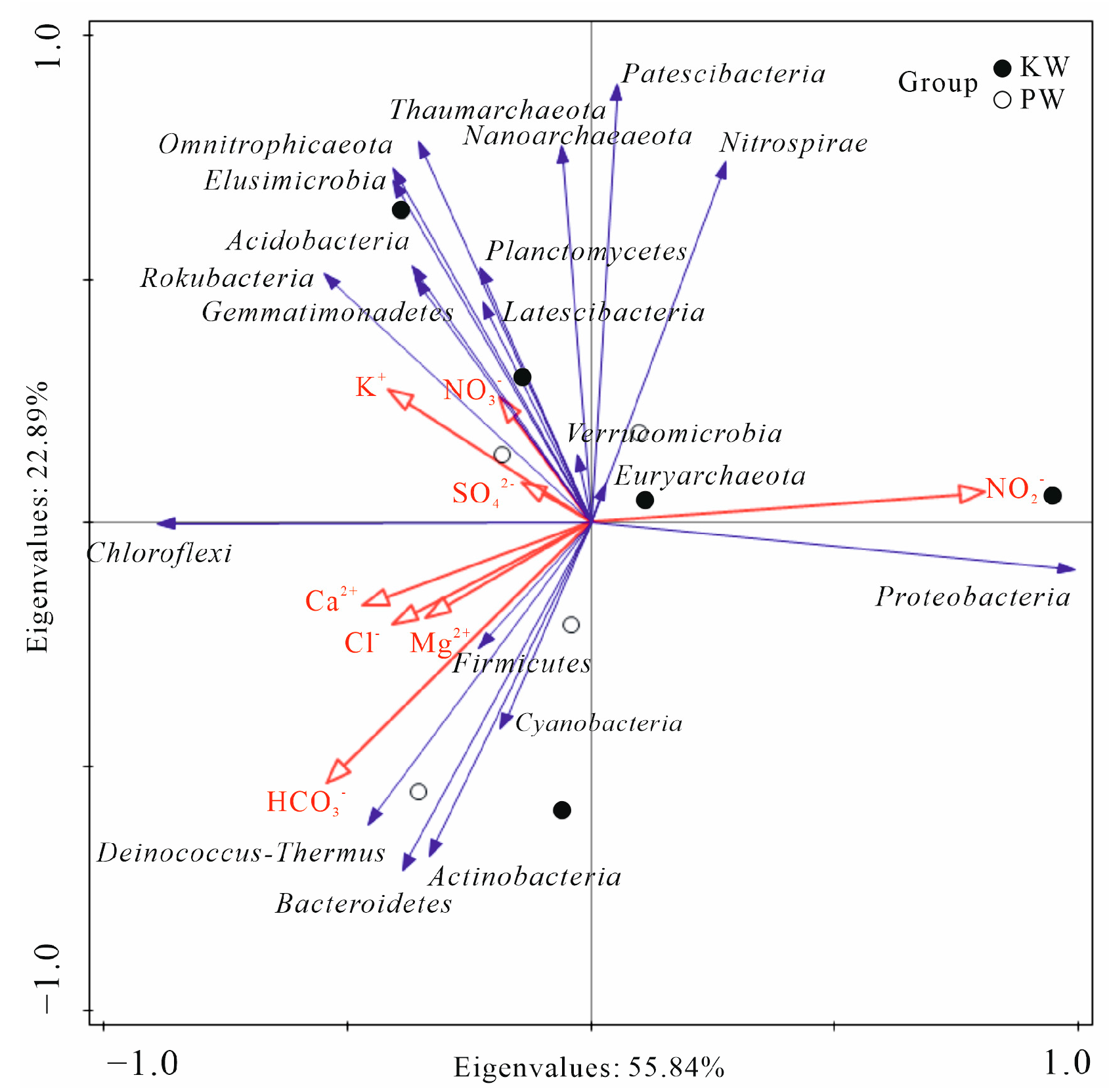
3. Results and Analysis
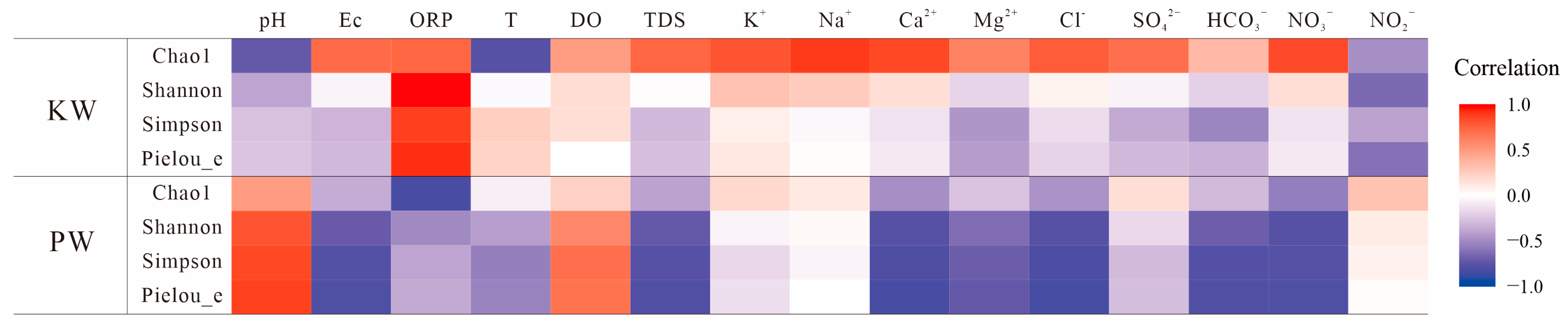
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics
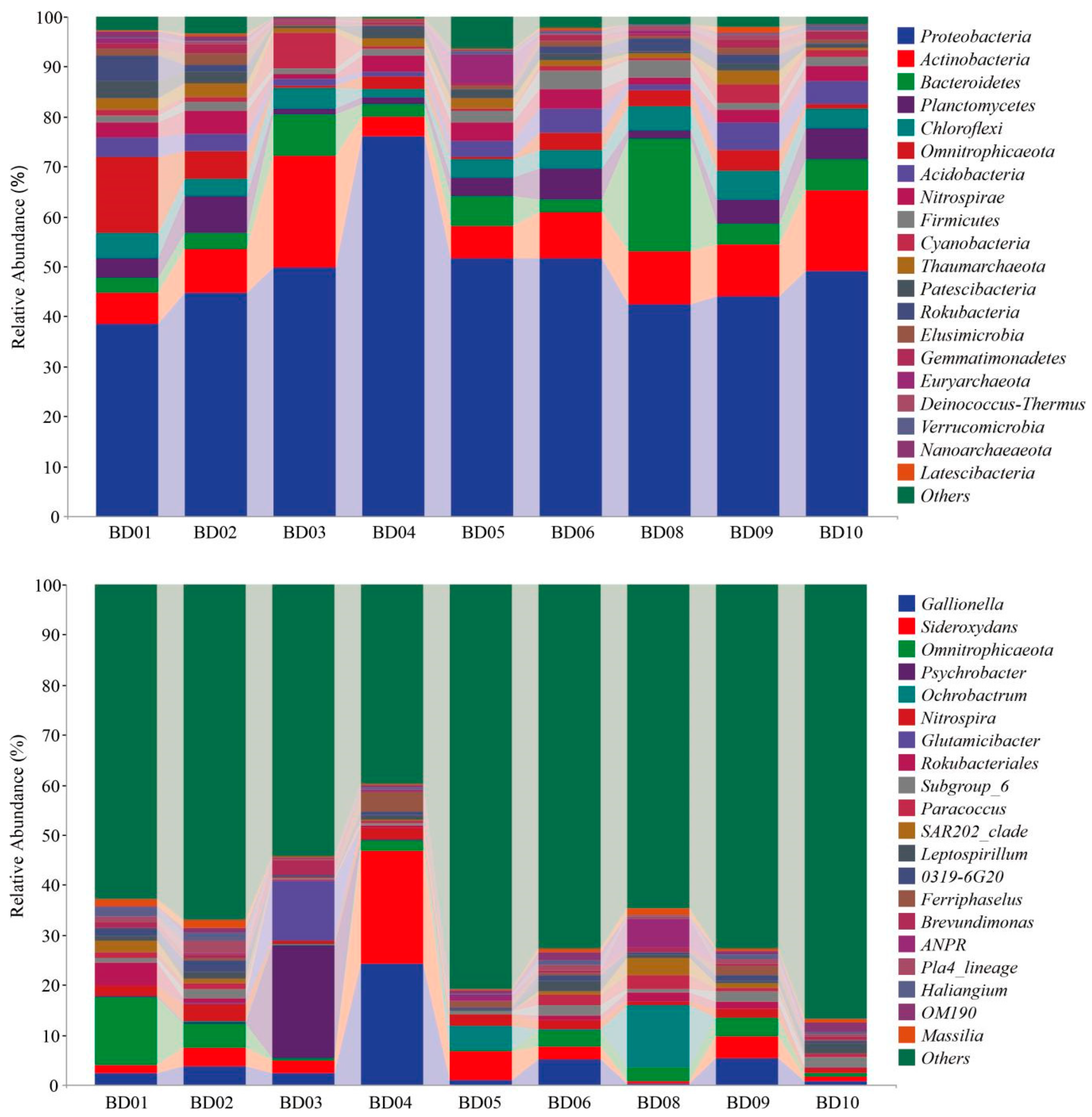
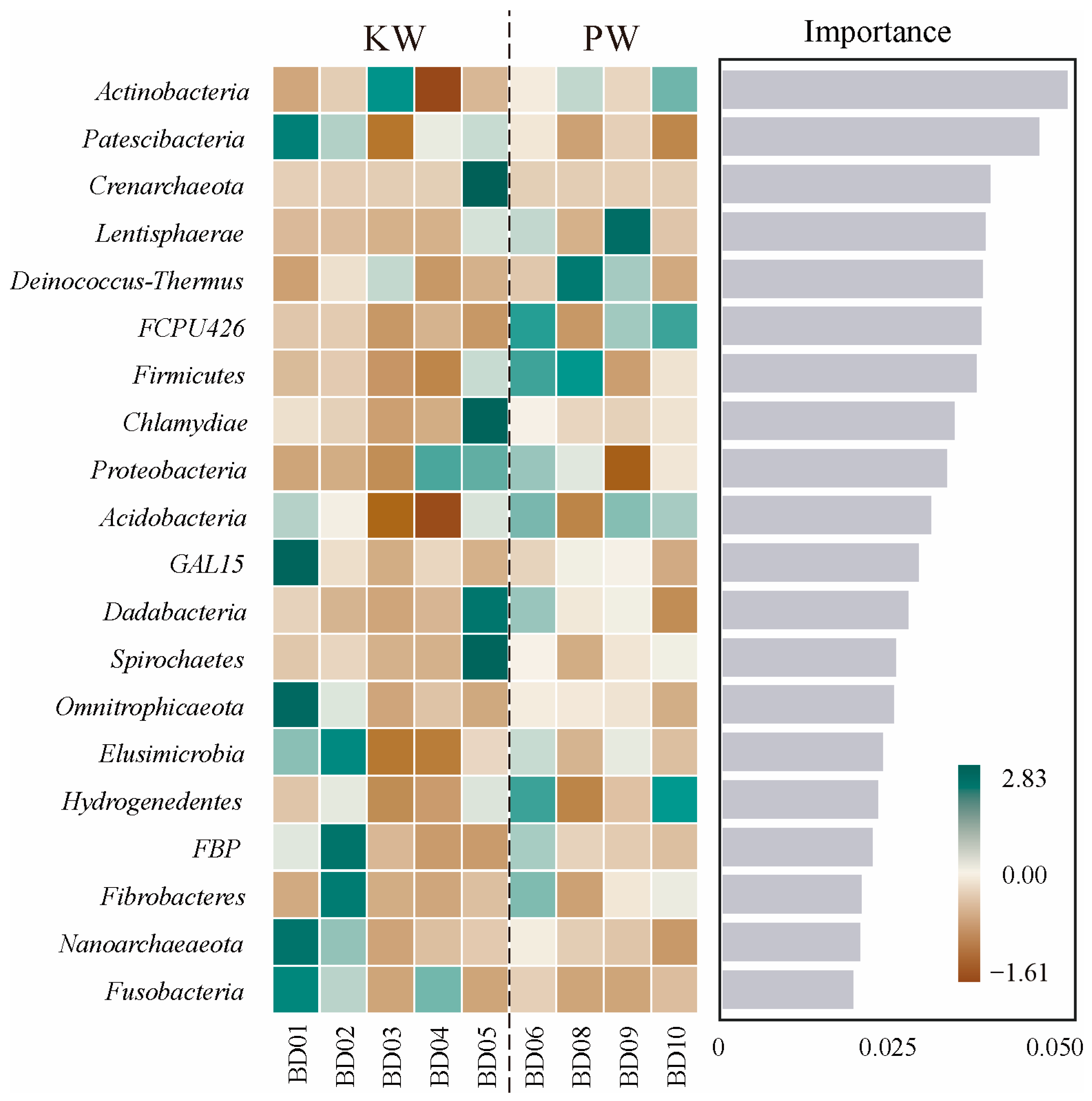
3.2. Microbial Community Structure
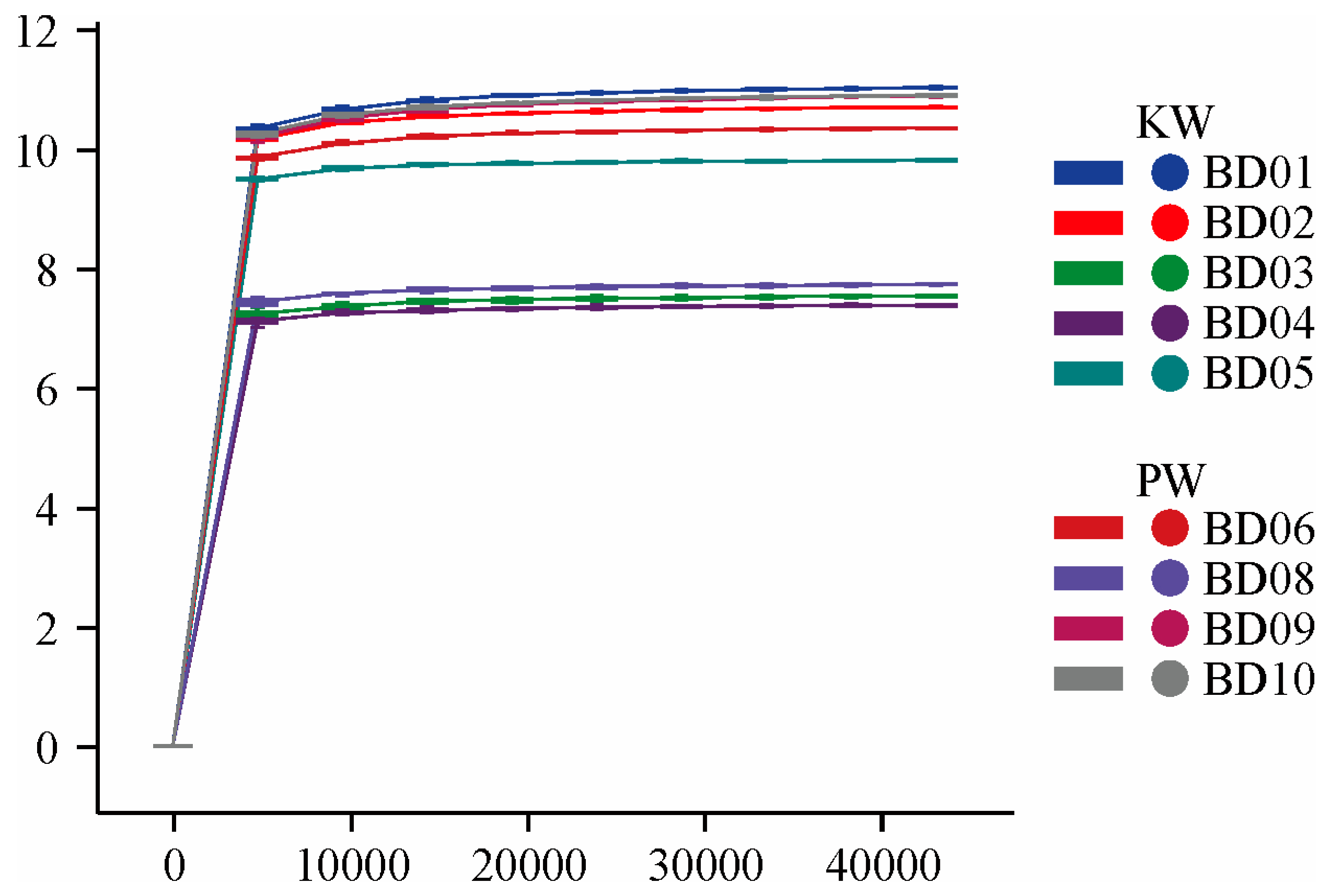
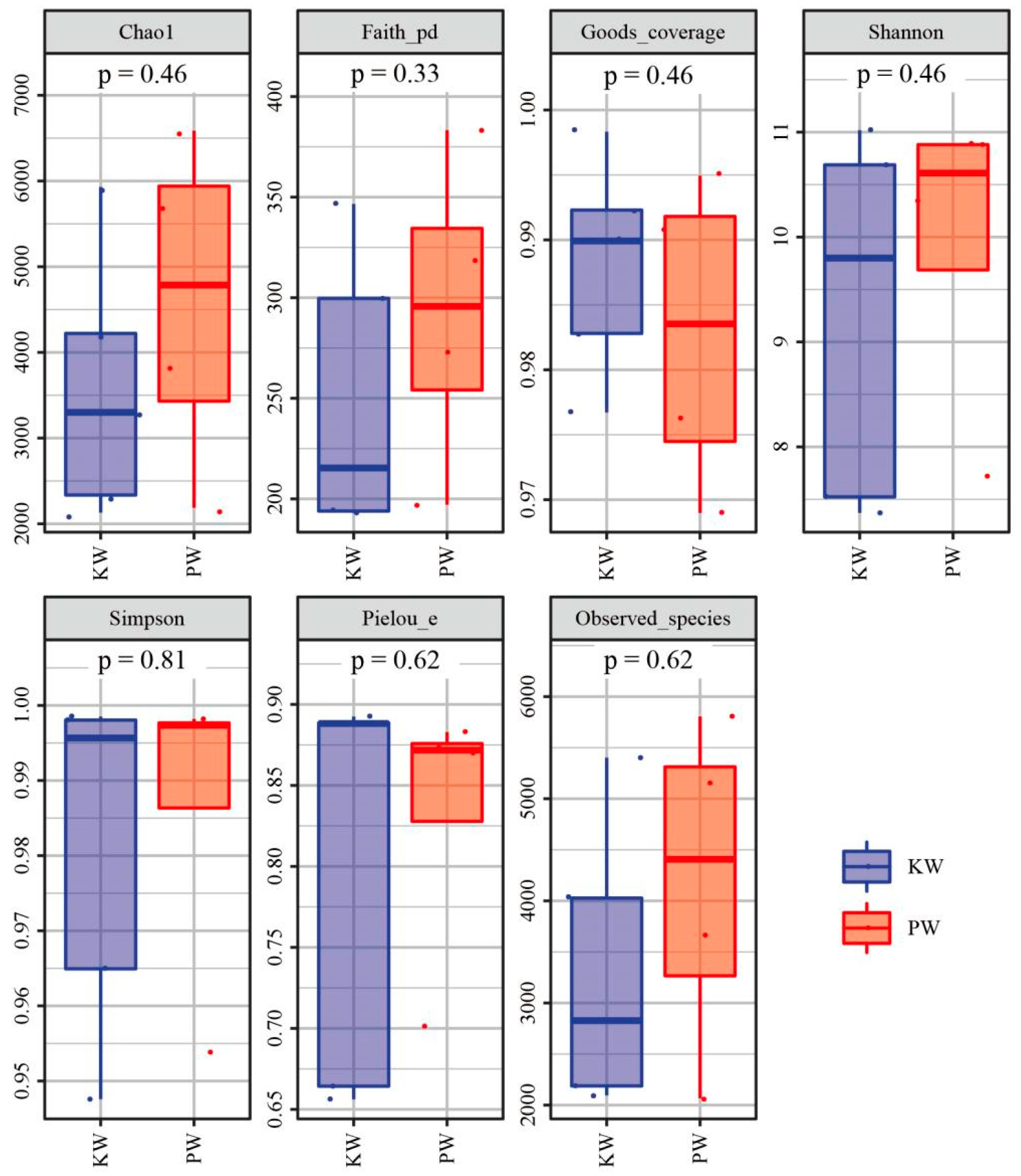
3.2.1. Diversity Analysis
3.2.2. Microbial Composition Analysis
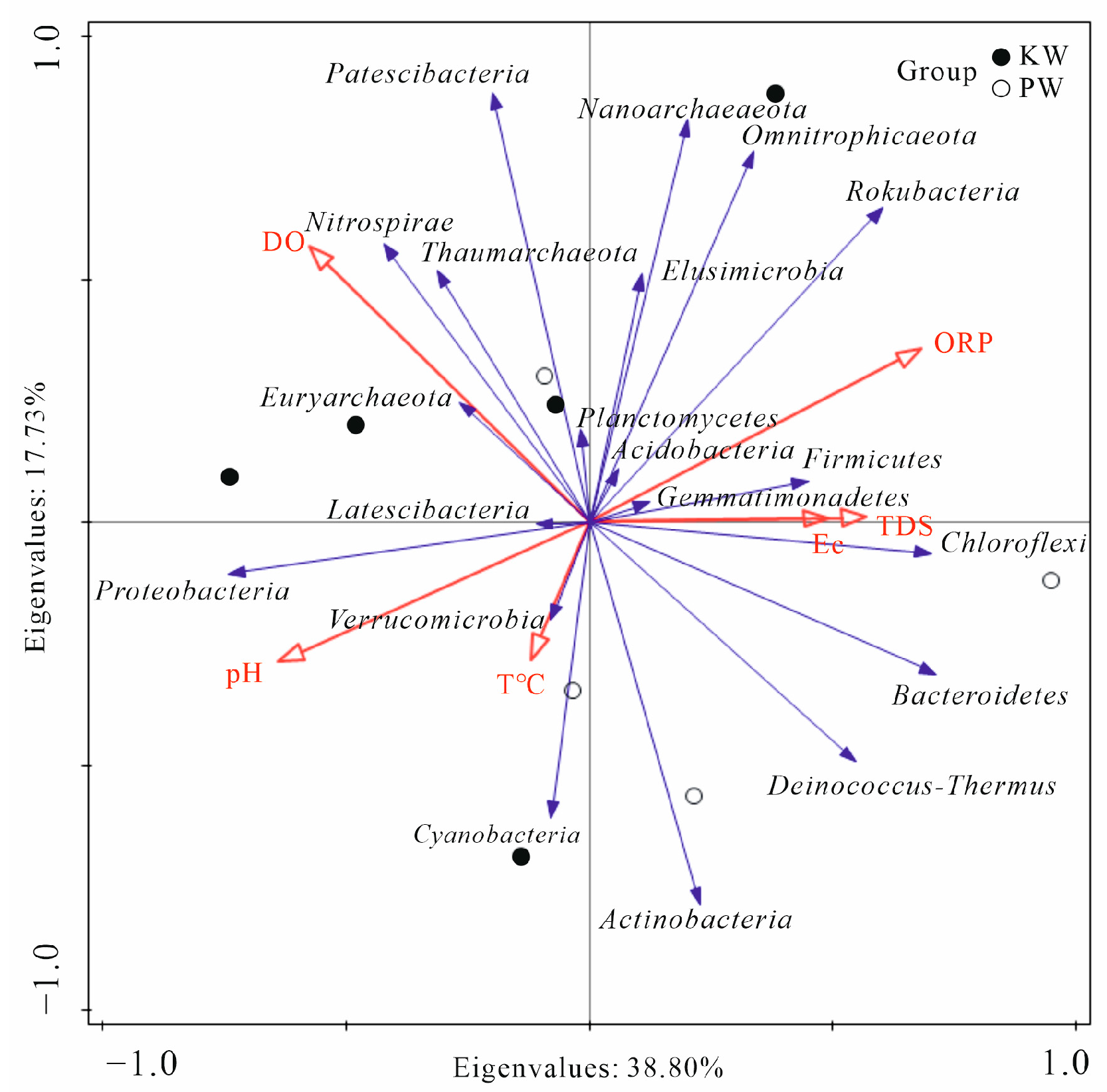
3.2.3. Analysis of Differences in Microbial Community Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medici, G.; Lorenzi, V.; Sbarbati, C.; Manetta, M.; Petitta, M. Structural Classification, Discharge Statistics, and Recession Analysis from the Springs of the Gran Sasso (Italy) Carbonate Aquifer; Comparison with Selected Analogues Worldwide. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhor, K.; Ghasemizadeh, R.; Rajic, L.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. Assessment of groundwater quality and remediation in karst aquifers: A review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerasoli, F.; Fiasca, B.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Lombardi, A.; Tomassetti, B.; Lorenzi, V.; Vaccarelli, I.; Di Cicco, M.; Petitta, M.; Galassi, D.M.P. Assessing spatial and temporal changes in diversity of copepod crustaceans: A key step for biodiversity conservation in groundwater-fed springs. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1051295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.R.; Bianchi, T.S.; Gélinas, Y.; Allison, M.A.; Twilley, R.R. Enhanced terrestrial carbon preservation promoted by reactive iron in deltaic sediments. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Syrie, M.; Totsche, K.U.; Lehmann, R.; Herrmann, M.; Küsel, K. Groundwater bacterial communities evolve over time in response to recharge. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehncke, E.V.; Mariano, N.A. Groundwater and Its Role in Maintaining the Ecological Functions of Ecosystems—A Review. In Intensified Land and Water Use: A Holistic Perspective of Local to Regional Integration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Pandey, A.K.; Kim, S.H.; Singh, S.P.; Chaturvedi, P.; Varjani, S. Critical review on microbial community during in-situ bioremediation of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, C.E.; Gaspar, M.; Geesink, P.; Herrmann, M.; Marz, M.; Küsel, K. Biogeochemical Regimes in Shallow Aquifers Reflect the Metabolic Coupling of the Elements Nitrogen, Sulfur, and Carbon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02346-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinke, C.; Rubino, F.; Messer, L.F.; Youssef, N.; Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Brown, M.; Jeffries, T.; Tyson, G.W.; Seymour, J.R.; et al. A phylogenomic and ecological analysis of the globally abundant Marine Group II archaea (Ca. Poseidoniales ord. nov.). ISME J. 2018, 13, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiao, D.; Hao, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, R.; Huang, X.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Accessible Phreatic Groundwater Resources in the Central Shijiazhuang of North China Plain: Perspective From the Hydrogeochemical Constraints. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 747097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbel, K.L.; Greenfield, P.; Hose, G.C. Agricultural practices linked to shifts in groundwater microbial structure and denitrifying bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807 Pt 2, 150870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retter, A.; Karwautz, C.; Griebler, C. Groundwater Microbial Communities in Times of Climate Change. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 41, 509–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.N.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Deng, R. Hydroclimate variations in the Northern China Plain and their possible socio-cultural influences. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys. Geogr. 2020, 102, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. A View on Geomorphologic Zonalization of North China Plain. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2008, 25, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Li, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, W. Subregional-scale groundwater depletion detected by GRACE for both shallow and deep aquifers in North China Plain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Currell, M.J.; Guo, H. Controls on distributions of sulphate, fluoride, and salinity in aquitard porewater from the North China Plain: Long-term implications for groundwater quality. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standards for Groundwater Quality. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Fu, X.G.; Dong, Z.; Gan, S.; Wang, Z.; Wei, A. Groundwater Quality Evaluation for Potable Use and Associated Human Health Risk in Gaobeidian City, North China Plain. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 3008567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 5750-2006; Standard Test Methods for Drinking Water. Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- DD2014-15; Technical Requirements for Quality Control of Sample Analysis in Groundwater Pollution Investigation and Evaluation. Geological Survey of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Dinno, A. Nonparametric Pairwise Multiple Comparisons in Independent Groups using Dunn’s Test. Stata J. 2015, 15, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.Q.; Ding, H.; Li, S.L.; Yue, F.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Zeng, J. Hydrogeochemical Dynamics and Response of Karst Catchment to Rainstorms in a Critical Zone Observatory (CZO), Southwest China. Front. Water 2020, 2, 577511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G.; Cantrell, K.; Huang, S.; McDonald, D.; Haiminen, N.; Carrieri, A.P.; Zhu, Q.; Gonzalez, A.; McGrath, I.; Beck, K.L.; et al. Efficient computation of Faith’s phylogenetic diversity with applications in characterizing microbiomes. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalfitano, S.; Del Bon, A.; Zoppini, A.; Ghergo, S.; Fazi, S.; Parrone, D.; Casella, P.; Stano, F.; Preziosi, E. Groundwater geochemistry and microbial community structure in the aquifer transition from volcanic to alluvial areas. Water Res. 2014, 65, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D.L. The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 39, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jenkins, C.; Webb, R.I.; Fuerst, J.A. Isolation of Gemmata-like and Isosphaera-like planctomycete bacteria from soil and freshwater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, L.A.; Castelle, C.J.; Wrighton, K.C.; Thomas, B.C.; Sharon, I.; Frischkorn, K.R.; Williams, K.H.; Tringe, S.G.; Banfield, J.F. Community genomic analyses constrain the distribution of metabolic traits across the Chloroflexi phylum and indicate roles in sediment carbon cycling. Microbiome 2013, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J. 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelle, C.J.; Wrighton, K.C.; Thomas, B.C.; Hug, L.A.; Brown, C.T.; Wilkins, M.J.; Frischkorn, K.R.; Tringe, S.G.; Singh, A.; Markillie, L.M.; et al. Genomic expansion of domain archaea highlights roles for organisms from new phyla in anaerobic carbon cycling. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlemann, D.P.; Labrenz, M.; Jürgens, K.; Bertilsson, S.; Waniek, J.J.; Andersson, A.F. Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.M.; Sanford, R.A.; Ryu, H.; Bethke, C.M.; Levine, A.D.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Domingo, J.W.S. Functional microbial diversity explains groundwater chemistry in a pristine aquifer. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: From networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.L.M.; Palczewska, A.; Palczewski, J.; Kidley, N. Comparison of the Predictive Performance and Interpretability of Random Forest and Linear Models on Benchmark Data Sets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1773–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Jacques, S.M.S.; Pires, A.P.F.; Leal, J.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Farjalla, V.F.; Doebeli, M. High taxonomic variability despite stable functional structure across microbial communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 1, 0015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorholt, J.A. Microbial life in the phyllosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, C.A.; Ott, C.M.; Mister, S.J.; Morrow, B.J.; Burns-Keliher, L.; Pierson, D.L. Microbial responses to microgravity and other low-shear environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, C.J.; Brown, C.T.; Thomas, B.C.; Williams, K.H.; Banfield, J.F. Unusual respiratory capacity and nitrogen metabolism in a Parcubacterium (OD1) of the Candidate Phyla Radiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneron, A.; Perrine, C.; Rémy, G.; Marisol, G.-U. Into the darkness of the microbial dark matter: In situ activities through expression profiles of Patescibacteria populations. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1073483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloy, S. Brenner’s Encyclopedia of Genetics. Brenners Encycl. Genet. 2013, 91, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Makarova, K.S.; Aravind, L.; Wolf, Y.I.; Tatusov, R.L.; Minton, K.W.; Koonin, E.V.; Daly, M.J. Genome of the Extremely Radiation-Resistant Bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans Viewed from the Perspective of Comparative Genomics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 44–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.C.; Ringelberg, D.B.; Palmer, R.J. Quantitative Comparison of the In Situ Microbial Communities in Different Biomes; Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL): Oak Ridge, TN, USA; Tennessee University: Knoxville, TN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Manoj, K.; Shrivastava, N.; Teotia, P.; Goyal, P.; Varma, A.; Sharma, S.; Tuteja, N.; Kumar, V. Omics: Tools for Assessing Environmental Microbial Diversity and Composition. In Modern Tools and Techniques to Understand Microbes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 273–283. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitsev, G.M.; Tsitko, I.V.; Rainey, F.A.; Trotsenko, Y.A.; Uotila, J.S.; Stackebrandt, E.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M.S. New aerobic ammonium-dependent obligately oxalotrophic bacteria: Description of Ammoniphilus oxalaticus gen. nov. sp. nov. and Ammoniphilus oxalivorans gen. nov. sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48 Pt 1, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapara, T.M.; Nakatsu, C.H.; Pantea, L.M. Aerobic Biological Treatment of a Pharmaceutical Wastewater: Effect of Temperature on Cod Removal And Bacterial Community Development. Water Res. A J. Int. Water Assoc. 2001, 35, 4417–4425. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, M.W. Broad diversity of viable bacteria in ‘sterile’ (0.2 μm) filtered water. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.E. Concluding remarks—Cold spring harbor symposia on quantitative biology. Reprinted in 1991: Classics in theoretical biology. Bull. Math. Biol. 1957, 53, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibold, M.A. The Niche Concept Revisited: Mechanistic Models and Community Context. Ecology 1995, 76, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, P. Mechanisms of Maintenance of Species Diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, R.K.; Seyed, M.; Majedi, M.; Shruti, P.; Shu Harn, T.; Chek Yin, B.; Karina Yew-Hoong, G.; Sanjay, S. Effects of Light and Temperature on the Metabolic Profiling of Two Habitat-Dependent Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria. Metabolites 2022, 12, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| pH | Ec (μs/cm) | ORP (mv) | DO (mg/L) | TDS (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | Na+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | HCO3− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | NO2− (mg/L) | F− (mg/L) | H2SiO3 (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karst Water (n = 5) | Avg | 7.72 | 863.8 | 132.36 | 8.976 | 405.23 | 1.62 | 21.33 | 87.86 | 45.13 | 46.99 | 46.21 | 316.30 | 68.16 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 13.63 |
| Max | 7.83 | 1032 | 163.8 | 9.9 | 487.21 | 3.44 | 35.75 | 106.92 | 54.79 | 74.87 | 71.07 | 344.68 | 109.75 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 15.56 | |
| Min | 7.49 | 550 | 96.2 | 7.46 | 277.03 | 0.84 | 8.58 | 64.10 | 28.40 | 11.73 | 8.96 | 300.23 | 8.64 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 12.35 | |
| Porous Water (n = 4) | Avg | 7.70 | 812.75 | 166.1 | 6.92 | 413.69 | 1.22 | 17.24 | 93.64 | 43.75 | 70.67 | 18.36 | 362.19 | 26.42 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 18.29 |
| Max | 7.88 | 1129 | 190.3 | 9.09 | 572.47 | 1.56 | 29.26 | 135.75 | 56.96 | 139.40 | 22.59 | 418.98 | 41.04 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 23.96 | |
| Min | 7.44 | 581 | 128.8 | 5.18 | 275.33 | 0.86 | 9.95 | 56.36 | 32.68 | 12.66 | 11.93 | 310.58 | 10.65 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 14.85 |
| Phylum | Karst Water | Porous Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levins Niche | Types of Commonly Used Resources | Levins Niche | Types of Commonly Used Resources | |
| Omnitrophicaeota | 11.1427 | S5 = 11.32%, S6 = 10.62% | 8.6607 | S4 = 11.65%, S8 = 13.92%, S9 = 17.23% |
| Thaumarchaeota | 4.1453 | S1 = 34.59%, S3 = 17.67%, S5 = 25.14% | 6.0497 | S9 = 32.35% |
| Euryarchaeota | 3.3207 | S3 = 26.77%, S4 = 34.46%, S5 = 32.99% | 9.355 | S4 = 11.69%, S6 = 12.36%,S8 = 12.34% |
| Latescibacteria | 5.1979 | S2 = 32.32%, S4 = 18.00%, S8 = 14.49% | 3.1762 | S3 = 21.15%, S10 = 50.18% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Lian, S. Characteristics of Groundwater Microbial Community Composition and Environmental Response in the Yimuquan Aquifer, North China Plain. Water 2024, 16, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030459
Zhang H, Lv Y, Zhang T, Zhang L, Ma X, Liu X, Lian S. Characteristics of Groundwater Microbial Community Composition and Environmental Response in the Yimuquan Aquifer, North China Plain. Water. 2024; 16(3):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030459
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huaisheng, Yonggao Lv, Tao Zhang, Lei Zhang, Xuemei Ma, Xuesong Liu, and Sheng Lian. 2024. "Characteristics of Groundwater Microbial Community Composition and Environmental Response in the Yimuquan Aquifer, North China Plain" Water 16, no. 3: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030459
APA StyleZhang, H., Lv, Y., Zhang, T., Zhang, L., Ma, X., Liu, X., & Lian, S. (2024). Characteristics of Groundwater Microbial Community Composition and Environmental Response in the Yimuquan Aquifer, North China Plain. Water, 16(3), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030459






