Identification and Distribution Characteristics of Odorous Compounds in Sediments of a Shallow Water Reservoir
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
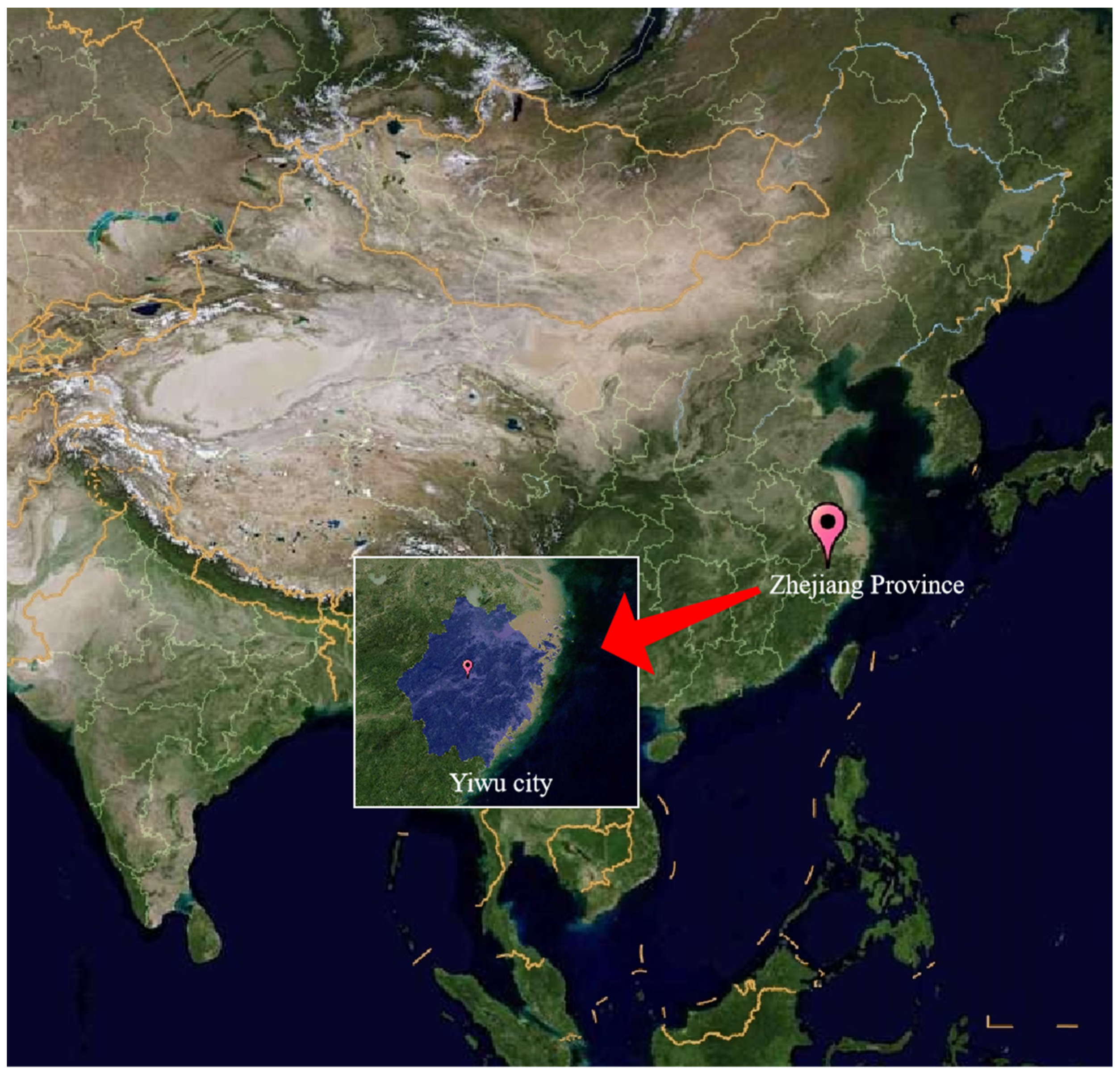
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sediment Sampling and Pre-Treatment
2.3. Chemicals and Reagents
2.4. Sensory Evaluation
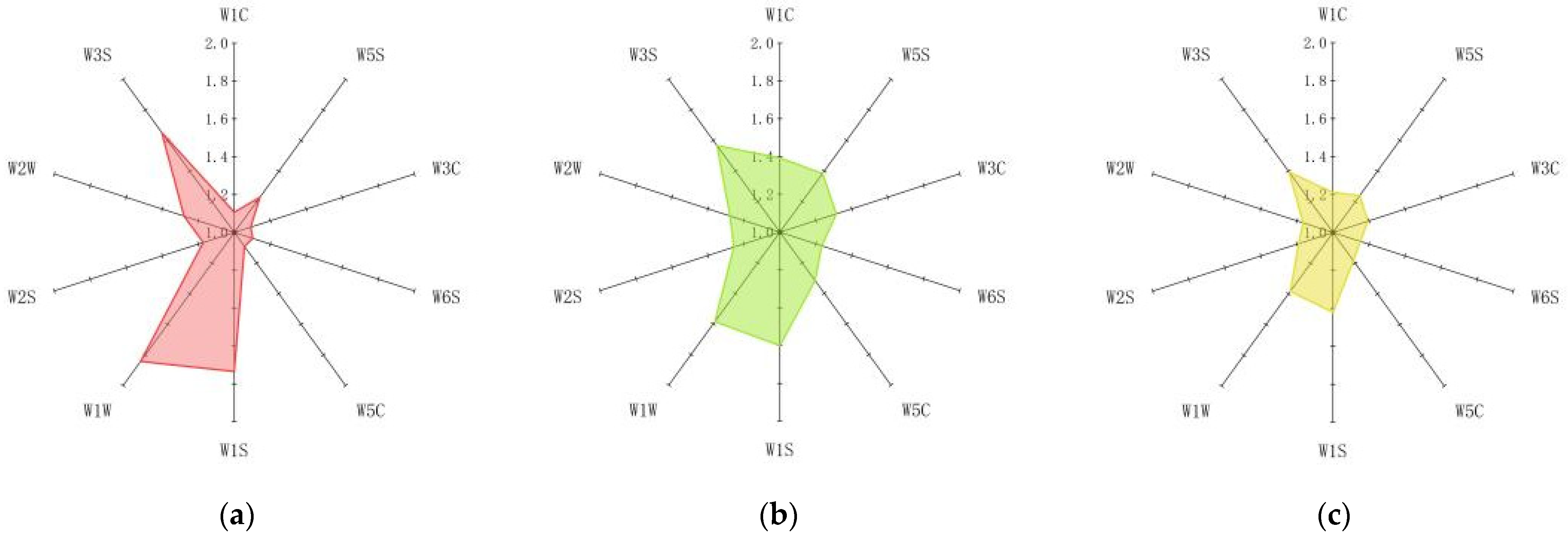
2.5. Electronic Nose
2.6. Odorant Identification
2.7. Analytical Method
3. Results and Discussion
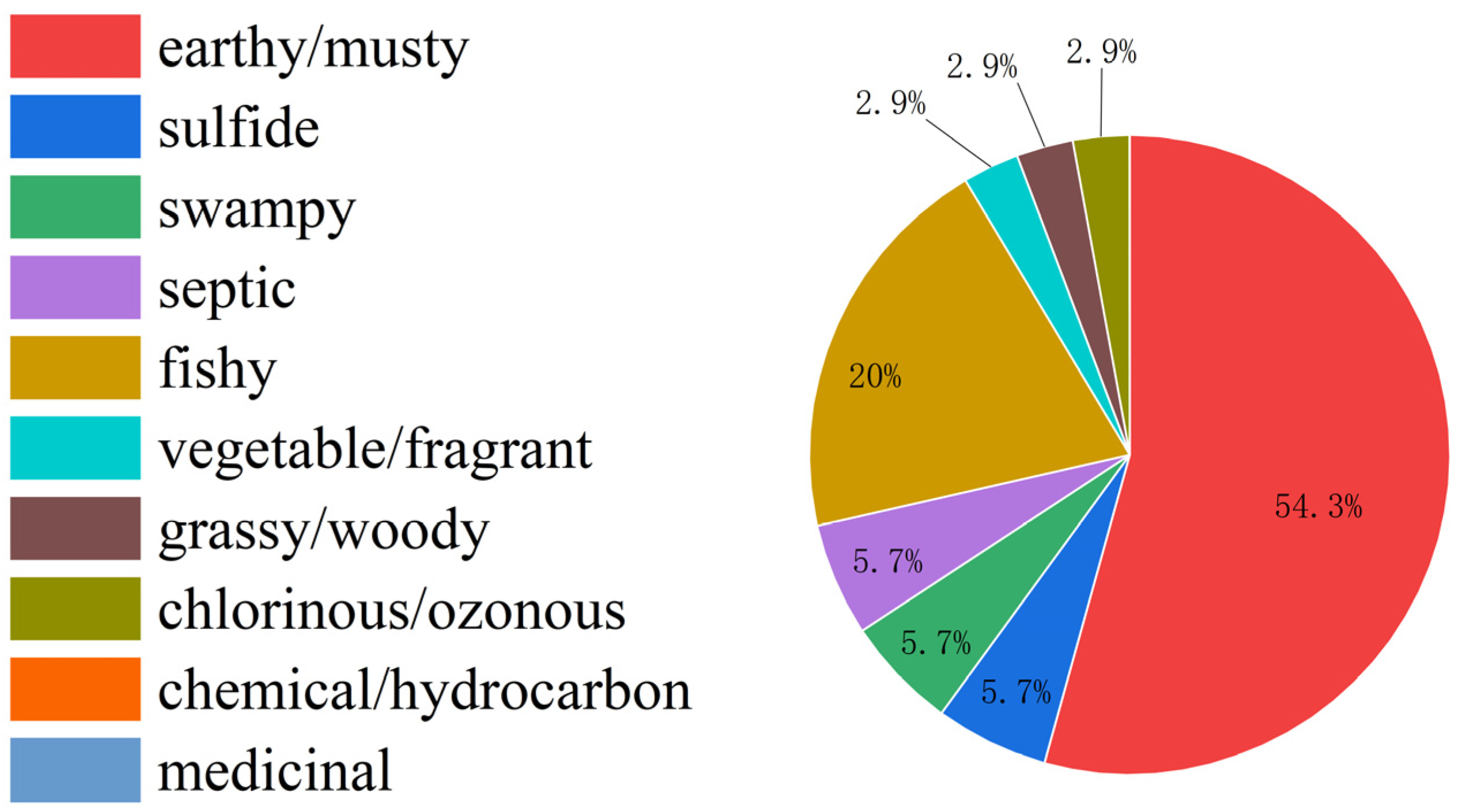
3.1. Odor Characteristics of Sediments
3.2. Odorants in Reservoir Sediments
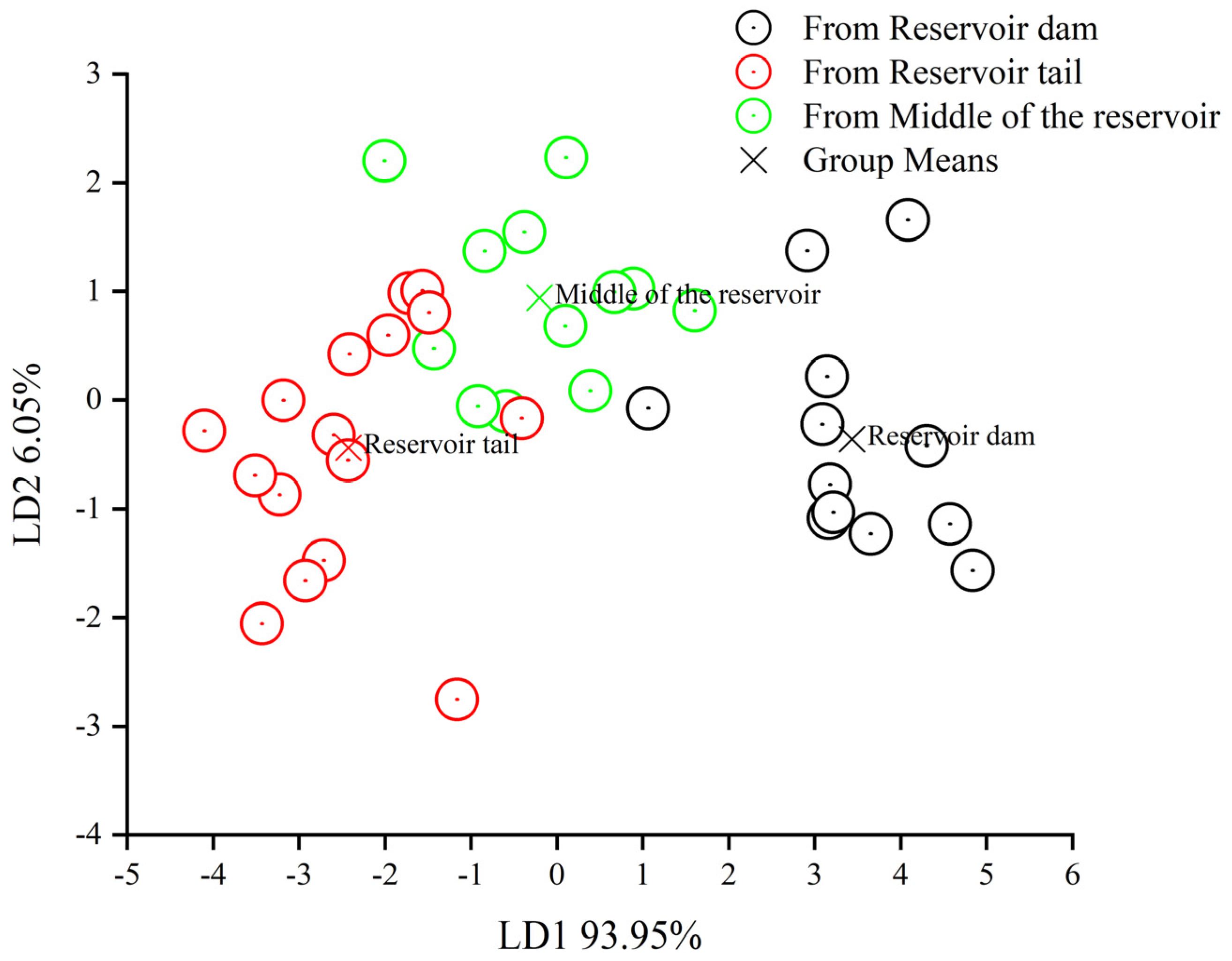
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Odorous Substances Released from Reservoir Sediments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Compound | Limit of Detection Mg·kg−1 |
|---|---|
| Methanethiol | 0.015 |
| Dimethyl sulfide | 0.026 |
| Allyl methyl sulfide | 0.028 |
| Dimethyl disulfide | 0.0041 |
| Dimethyl trisulfide | 0.0074 |
| Indole | 0.65 |
| 2-methylisoborneol | 0.0080 |
| Geosmin | 0.0038 |
| Methylphenol | 0.094 |
| Phenol | 0.023 |
| 2-chlorophenol | 0.022 |
| Name of the Sensor | Performance Characterization |
|---|---|
| W1C | Aromatic components, benzene compounds |
| W5S | Nitrogen oxides |
| W3C | Sensitive to aromatic compounds, amines |
| W6S | Exhibiting selectivity towards hydrides |
| W5C | Aromatic components of short-chain alkanes |
| W1S | High sensitivity towards methyl-based compounds |
| W1W | High sensitivity towards sulfides |
| W2S | High sensitivity towards alcohols and carbonyl compounds. |
| W2W | Exquisite sensitivity towards organic sulfides. |
| W3S | Remarkable sensitivity towards long-chain hydrocarbons. |
References
- Yu, J.W.; Zhao, Y.M.; Yang, M.; Lin, T.-F.; Guo, Z.H.; Gu, J.N.; Li, S.; Han, W. Occurrence of odour-causing compounds in different source waters of China. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2009, 58, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ding, C.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Chen, T. Diagnosing complex odor problems occurring in micro-polluted source water: Primary approach and application. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, N.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M. Simultaneous quantification of fifty-one odor-causing compounds in drinking water using gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Yu, J.; Yang, M.; An, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, N.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, D. Occurrence of odor problems in drinking water of major cities across China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yu, J.; Yang, K.; Wen, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M. Identification of complex septic odorants in Huangpu River source water by combining the data from gas chromatography-olfactometry and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography using retention indices. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 556, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Guo, Q.; Sun, D.; Su, M.; An, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. Occurrence of swampy/septic odor and possible odorants in source and finished drinking water of major cities across China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Ellakany, H.F.; Abaza, S.S.; Geneedy, A.M.; Salem, H.M.; Taha, A.E.; Swelum, A.A.; Omer, F. Undesirable odour substances (geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol) in water environment: Sources, impacts and removal strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Han, M.; An, W.; Yu, J. Anoxia remediation and internal loading modulation in eutrophic lakes using geoengineering method based on oxygen nanobubbles. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 714, 136766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomans, B.P.; Smolders, A.; Intven, L.M.; Pol, A.; Op, D.; Van Der Drift, C. Formation of dimethyl sulfide and methanethiol in anoxic freshwater sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4741–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Rai, P.K.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, E. The role of algae and cyanobacteria in the production and release of odorants in water. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Yan, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, P.; Wu, X. Release of odorants from sediments of the largest drinking water reservoir in Shanghai: Influence of pH, temperature, and hydraulic disturbance. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Liu, X. Distribution characteristics of typical volatile sulfides in sediments in west nearshore zone of Taihu. Ecol. Sci. 2018, 37, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.; Huang, G.; Hao, M.; Cui, J.; Wu, A.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; Li, T. Release characteristics of sulfur in black and odorous water in cities against the change of environmental factors. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 13072–13078. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L.; Association, A.P.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J. Restructuring of Urban Form in the Developed Area in China Based on RS and GIS: A Case Study of Yiwu. Mod. Urban Res. 2011, 26, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Viciano-Tudela, S.; Sendra, S.; Parra, L.; Jimenez, J.M.; Lloret, J. Proposal of a Gas Sensor-Based Device for Detecting Adulteration in Essential Oil of Cistus ladanifer. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, S.; Ciepiela, F.; Jakubowska, M. Computer vision analysis of sample colors versus quadruple-disk iridium-platinum voltammetric e-tongue for recognition of natural honey adulteration. Measurement 2023, 209, 112514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Hofmann, R. Adsorption and biodegradation of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin in drinking water granular activated carbon filters: A review and meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yu, J.; Su, M.; Jia, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, C.; Burch, M.; Yang, M. Production and fate of fishy odorants produced by two freshwater chrysophyte species under different temperature and light conditions. Water Res. 2019, 157, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yu, J.; Su, M.; Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Cao, N.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, P. Synergistic effect of musty odorants on septic odor: Verification in Huangpu River source water. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 653, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, O.; Pratscher, J.; Richa, K.; Rostant, W.; Ul Haque, M.; Murrell, J.; Todd, J. Methanethiol and dimethylsulfide cycling in Stiffkey saltmarsh. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomans, B.; Pol, A.; Op den Camp, H. Microbial cycling of volatile organic sulfur compounds in anoxic environments. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y. A review on sulfur transformation during anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste: Mechanisms, influencing factors and resource recovery. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 865, 161193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Jüttner, F. Malodorous volatile organic sulfur compounds: Sources, sinks and significance in inland waters. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 210–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, H.; Eyice, Ö. Microbial cycling of methanethiol. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2019, 33, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Keil, R.G.; Benner, R. What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomans, B.P.; Luderer, R.; Steenbakkers, P.; Pol, A.; van der Drift, C.; Vogels, G.D.; Op den Camp, H. Microbial populations involved in cycling of dimethyl sulfide and methanethiol in freshwater sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.A.; Mohammadi, S.S.; van Erven, T.; Berben, T.; Jetten, M.S.; Pol, A.; Op den Camp, H. Methanethiol consumption and hydrogen sulfide production by the thermoacidophilic methanotroph Methylacidiphilum fumariolicum SolV. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 857442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stets, E.G.; Hines, M.E.; Kiene, R. Thiol methylation potential in anoxic, low-pH wetland sediments and its relationship with dimethylsulfide production and organic carbon cycling. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomans, B.P.; Op den Camp, H.J.; Pol, A.; Vogels, G. Anaerobic versus aerobic degradation of dimethyl sulfide and methanethiol in anoxic freshwater sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Wu, Y. Factors affecting the production of volatile organic sulfur compounds (VOSCs) from algal-induced black water blooms in eutrophic freshwater lakes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, J.; Thomas, K. A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Ma, Y.; Cong, H.; Tan, P. Application of the technology of water lifting and aeration on improving water quality in a Deep Canyon Reservoir–a case study from northern China. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, X.; Luo, H.; Zeng, D.; Sima, M.; Huang, S. Linking microbial community and biological functions to redox potential during black-odor river sediment remediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 40392–40404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Huang, T. Analysis of Water-Lifting Aerator Performance Based on the Volume of Fluid Method. Water 2023, 15, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, T.; Gong, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S. Field research on mixing aeration in a drinking water reservoir: Performance and microbial community structure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.A.; Ferragut, C. Epipelon biomass responses to different restoration techniques in a eutrophic environment. Environ. Manag. 2023, 72, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.M.; de Almeida Castilho, M.C.; Henry, R.; Ferragut, C. Epipelon, phytoplankton and zooplankton responses to the experimental oligotrophication in a eutrophic shallow reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łopata, M.; Grochowska, J.K.; Augustyniak-Tunowska, R.; Tandyrak, R. Possibilities of Improving Water Quality of Degraded Lake Affected by Nutrient Overloading from Agricultural Sources by the Multi-Point Aeration Technique. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R.; Rosińska, J.; Podsiadłowski, S. Internal phosphorus loading as the response to complete and then limited sustainable restoration of a shallow lake. In Annales De Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2019; Volume 55, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, X.; Pan, H.; Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; He, M. Driving Factors for Black-Odor-Related Microorganisms and Potential Self-Remediation Strategies. Sustainability 2022, 15, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Dai, B.; Zou, P.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Bi, X. Effect of different microbial methods on purifying black-odor water based on three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 14, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chengyang, H.; Ying, T.; He, X. Application Research on Deodorization Effect of Domestic Waste by One Microbial Deodorizer. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 446, p. 032019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Meng, G.; Deng, Z.; Li, M.; Chang, J.; Dai, T.; Fang, X. Progress in research on VOC molecule recognition by semiconductor sensors. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2020, 38, 2008018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali-Baskaran, R.K.; Mooventhan, P.; Das, D.; Dixit, A.; Sharma, K.C.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Kaushal, P.; Ghosh, P.K. The future of plant volatile organic compounds (pVOCs) research: Advances and applications for sustainable agriculture. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 200, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talens, J.B.; Pelegri-Sebastia, J.; Sogorb, T.; Ruiz, J.L. Prostate cancer detection using e-nose and AI for high probability assessment. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.B.; Bachute, M.R.; Kotecha, K. Artificial Perception of the Beverages: An in-depth Review of the Tea sample. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82761–82785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sie, S.H.; Lee, J.L.; Chen, Y.R.; Chou, T.I.; Wu, P.C.; Chuang, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chen, I.-C.; Lu, C.-C.; et al. A miniature electronic nose for breath analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–16 December 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 35.2.1–35.2.4. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Fuentes, S.; Hernandez-Brenes, C. Smart detection of faults in beers using near-infrared spectroscopy, a low-cost electronic nose and artificial intelligence. Fermentation 2021, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Chen, I.T.; Yang, H.C.; Chen, Y.J. An AI-powered Electronic Nose System with Fingerprint Extraction for Aroma Recognition of Coffee Beans. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Odorant Type | Compound | M/Z1 a | M/Z2 a | OTC b mg·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Septic/swampy | Methanethiol | 47 | 48 | 0.0016 |
| Dimethyl sulfide | 62 | 47 | 0.0084 | |
| Allyl methyl sulfide | 88 | 73 | 0.0018 | |
| Dimethyl disulfide | 94 | 79 | 0.029 | |
| Dimethyl trisulfide | 126 | 45 | 0.014 | |
| Indole | 130 | 131 | 11 | |
| Earthy/musty | 2-methylisoborneol | 95 | 107 | 0.00070 |
| Geosmin | 112 | 41 | 0.0010 | |
| Chemical/phenolic | Methylphenol | 128 | 64 | 0.12 |
| Phenol | 94 | 66 | 21 | |
| 2-chlorophenol | 128 | 64 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Identification and Distribution Characteristics of Odorous Compounds in Sediments of a Shallow Water Reservoir. Water 2024, 16, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030455
Wang J, Zhu H, Wang C, Zhang L, Zhang R, Jiang C, Wang L, Tan Y, He Y, Xu S, et al. Identification and Distribution Characteristics of Odorous Compounds in Sediments of a Shallow Water Reservoir. Water. 2024; 16(3):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030455
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiahe, Hongbin Zhu, Cong Wang, Longji Zhang, Rong Zhang, Cancan Jiang, Lei Wang, Yingyu Tan, Yi He, Shengjun Xu, and et al. 2024. "Identification and Distribution Characteristics of Odorous Compounds in Sediments of a Shallow Water Reservoir" Water 16, no. 3: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030455
APA StyleWang, J., Zhu, H., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Zhang, R., Jiang, C., Wang, L., Tan, Y., He, Y., Xu, S., & Zhuang, X. (2024). Identification and Distribution Characteristics of Odorous Compounds in Sediments of a Shallow Water Reservoir. Water, 16(3), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030455









