Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Iron and the Response of Chlorophyll-a in Zhanjiang Bay, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area and Monitoring Station Arrangement
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Quality Control
2.4. Research Methods
2.4.1. Calculation Method for Land-Based Iron Input Flux
2.4.2. Correlation Analysis
2.4.3. Data Statistics and Analysis Methods
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations in Iron Content in the Coastal Seawater of Zhanjiang Bay
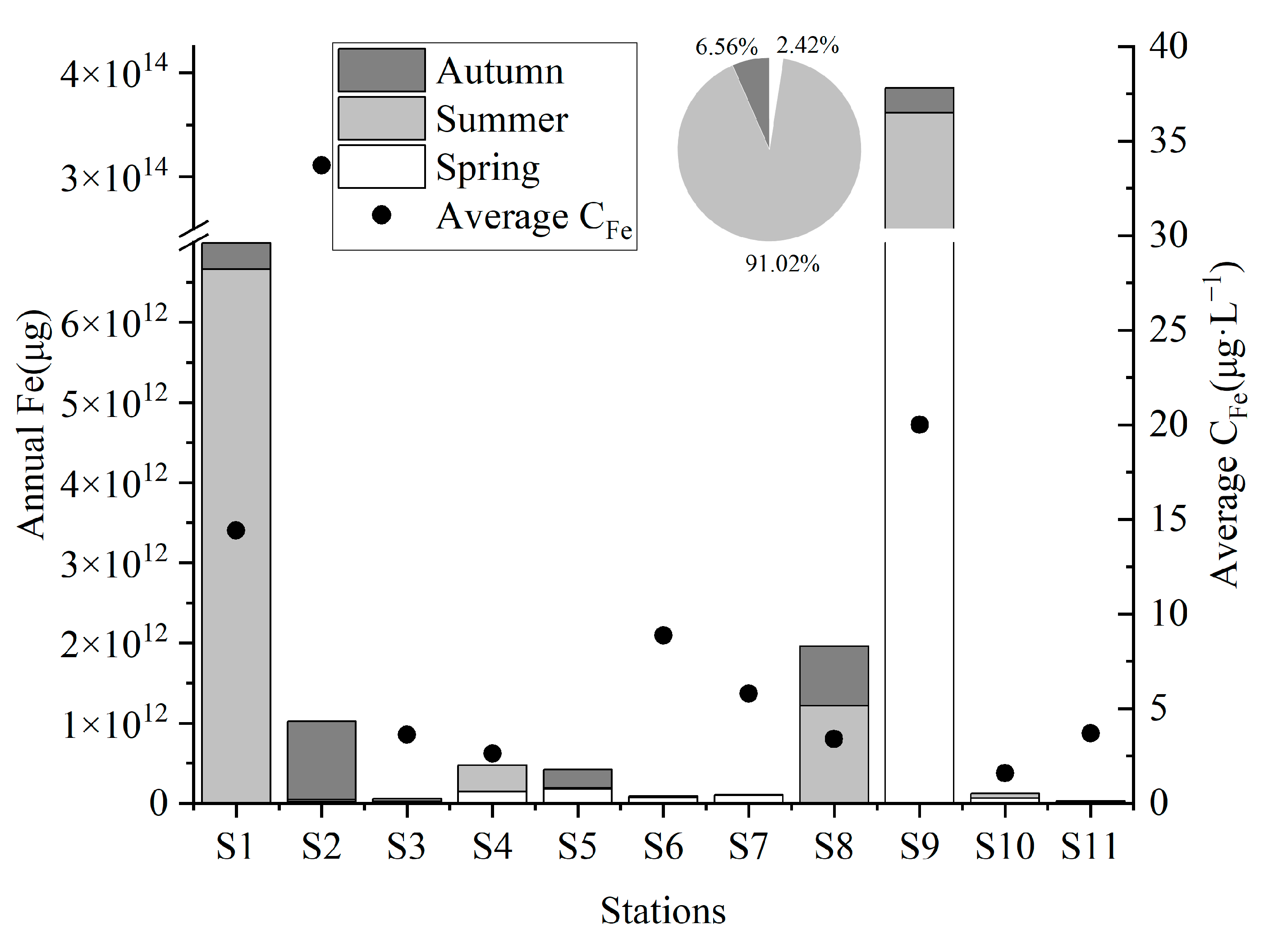
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations in Terrestrial Input Iron in Zhanjiang Bay
3.3. Variations in Environmental Factors in the Coastal Seawater of Zhanjiang Bay
3.4. The Relationship between Iron and Nutrients, Chlorophyll-a, and Other Environmental Factors in Zhanjiang Bay
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Fe Concentration in Zhanjiang Bay with Other Estuaries and Bays around the World
4.2. Correlation Analysis of Iron in Zhanjiang Bay Waters with Other Environmental Factors
4.3. Impact of Terrestrial Iron Inputs on the Coastal Seawater of Zhanjiang Bay
4.4. Impact of Iron on Primary Productivity in the Bay Waters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, S.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, J. The State of Arts: Sources, Microbial Processes and Ecological Effects of Iron in the Marine Environment. Adv. Earth Sci. 2019, 34, 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.-y.; Tao, W.-y.; Han, H.-t.; Pan, F.; Pan, D.-w. Continuous analysis of dissolved reactive iron at fixed-point of Yellow Sea coast. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruland, K.W.; Middag, R.; Lohan, M.C. Controls of Trace Metals in Seawater. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 19–51. ISBN 978-0-08-098300-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sunda, W.G. Feedback Interactions between Trace Metal Nutrients and Phytoplankton in the Ocean. Front. Microbio. 2012, 3, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, G.R.; Sahoo, S. Role of iron in plant growth and metabolism. RAS 2015, 3, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, A.; Bowie, A.R.; Boyd, P.W.; Buck, K.N.; Johnson, K.S.; Saito, M.A. The Integral Role of Iron in Ocean Biogeochemistry. Nature 2017, 543, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogle, S.L.; Barbeau, K.A.; Gledhill, M. Heme in the Marine Environment: From Cells to the Iron Cycle. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.T.; Surma, S.; Pakhomov, E.A. Southern Ocean Biological Iron Cycling in the Pre-Whaling and Present Ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueder, U.; Jørgensen, B.B.; Kappler, A.; Schmidt, C. Photochemistry of Iron in Aquatic Environments. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabajczyk, A.; Namieśnik, J. Speciation of Iron in the Aquatic Environment. Water Environ. Res. 2014, 86, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Boyd, P.W. Marine Phytoplankton and the Changing Ocean Iron Cycle. Nat. Clim Chang. 2016, 6, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijkenberg, M.J.A.; Middag, R.; Laan, P.; Gerringa, L.J.A.; Van Aken, H.M.; Schoemann, V.; De Jong, J.T.M.; De Baar, H.J.W. The Distribution of Dissolved Iron in the West Atlantic Ocean. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnejais, L.H.; Martin, W.R.; Bothner, M.H. The Release of Dissolved Nutrients and Metals from Coastal Sediments Due to Resuspension. Mar. Chem. 2010, 121, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, P.W.; Ellwood, M.J. The Biogeochemical Cycle of Iron in the Ocean. Nat. Geosci 2010, 3, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, D.K.; Desai, F.D.; LaRoche, J. Factors Influencing the Diversity of Iron Uptake Systems in Aquatic Microorganisms. Front. Microbio. 2012, 3, 22383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, J.; Bowler, C. Iron Utilization in Marine Cyanobacteria and Eukaryotic Algae. Front. Microbio. 2012, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaked, Y.; Lis, H. Disassembling Iron Availability to Phytoplankton. Front. Microbio. 2012, 3, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhu, J.-M.; Cai, Z.-H.; Zhou, J. The Research Advance of Siderophores in Marine Microbes. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 49, 1658–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, R.D.; Hutchins, D.A.; Nodder, S.; Sanudo-Wilhelmy, S.; Tovar-Sanchez, A.; Leblanc, K.; Hare, C.E.; Boyd, P.W. Particulate Iron Dynamics during FeCycle in Subantarctic Waters Southeast of New Zealand. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, 2005GB002558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenstra, W.K.; Hermans, M.; Séguret, M.J.M.; Witbaard, R.; Severmann, S.; Behrends, T.; Slomp, C.P. Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication as Key Controls on Benthic Release and Water Column Dynamics of Iron and Manganese. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 66, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, M.; Bizsel, N.; Steinnes, E. Iron Speciation in Eutrophic and Oligotrophic Mediterranean Coastal Waters; Impact of Phytoplankton and Protozoan Blooms on Iron Distribution. Mar. Chem. 2003, 81, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, E.D.; Le Mézo, P.; Solanes Hernandez, G.; Bianchi, D.; Kroodsma, D. Growth Limitation of Marine Fish by Low Iron Availability in the Open Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, B.A.; Boyle, E.A. Iron Isotopes in the Amazon River System: Weathering and Transport Signatures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 248, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.A.; Edmond, J.M.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The Mechanism of Iron Removal in Estuaries. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1977, 41, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, C.J.; Santos, I.R.; Maher, D.T.; Sadat-Noori, M.; Schnetger, B.; Brumsack, H.-J. Dissolved Iron Exports from an Estuary Surrounded by Coastal Wetlands: Can Small Estuaries Be a Significant Source of Fe to the Ocean? Mar. Chem. 2015, 176, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. Biogeochemical Processes of Dissolved Iron in Typical Waters in the Nearshore to Continental Shelf Area of China. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, J.; Fan, C.; Zhu, B.; Fu, M.; Zhang, P. Effects of Terrestrial Input on Heavy Metals in Zhanjiang Bay, a Typical Subtropical Bay in the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 116015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jian, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, D.; Kang, X. Tracing Land-Based Microplastic Sources in Coastal Waters of Zhanjiang Bay, China: Spatiotemporal Pattern, Composition, and Flux. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 934707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Han, Y.; Chang, X.; Dai, S. Quantitative Analysis of Self-Purification Capacity of Non-Point Source Pollutants in Watersheds Based on SWAT Model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, L.-r.; Lai, J.-y.; Dai, P.-d.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.-b. Concentration, Composition and Fluxes of Land-based Nitrogen and Phosphorus Source Pollutants Input into Zhanjiang Bay in Summer. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2019, 39, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cao, R.; Lao, Q.; Chen, F.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, Q. Assessing Seasonal Nitrate Contamination by Nitrate Dual Isotopes in a Monsoon-Controlled Bay with Intensive Human Activities in South China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Peng, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H. Long-Term Harmful Algal Blooms and Nutrients Patterns Affected by Climate Change and Anthropogenic Pressures in the Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 849819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ward, B.B.; Sigman, D.M. Global Nitrogen Cycle: Critical Enzymes, Organisms, and Processes for Nitrogen Budgets and Dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 5308–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Bi, Z.; Shan, Z.; Ren, L. The Deep Challenge of Nitrate Pollution in River Water of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Long, C.; Lu, C.; Wang, D.; et al. Unveiling the Eutrophication Crisis: 20 Years of Nutrient Development in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1373716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Huang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhou, F.; Wu, J.; Jin, G.; Zhu, Q. Origin of the Particulate Organic Matter in a Monsoon-Controlled Bay in Southern China. JMSE 2021, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 730-2014; Specifications on Spot Location of Monitoring Sites Related to Coastal Area Environment. Ministry of Environmental Protection Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- HY/T 147.1-2013; Code of Practice for Marine Monitoring Technology. State Oceanic Administration Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB 17378.4-2007; The Specification for Marine Monitoring. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Liu, W. Zhanjiang Port Channel Dredging Sediment Reclamation Basf Project Land Can Save 3 Billion. Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1646967637928615586&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Publication of the Full Environmental Impact Report of the 300,000-Ton Waterway Reconstruction and Expansion Project of Zhanjiang Port. Available online: https://www.zhanjiang.gov.cn/zjsfw/bmdh/jtysj/zwgk/wgk/content/post_1356032.html (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Fan, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Fang, H.; Xia, X.; Cao, W.; Ding, S.; Hou, L.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Research Progress and Prospect of Sediment Environment and Pollution Control in China in Recent 20 Years. Adv. Earth Sci. 2021, 36, 347–373. [Google Scholar]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Boyle, E.A.; Price, N.B. The removal of dissolved humic acids and iron during estuarine mixing. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1978, 40, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, F.; Chen, F.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, Y. Spatial and Seasonal Variations of Chlorophyll a in Zhanjiang Bay, China, and Controlling Factors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1329864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankwegu, A.S.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wei, J.; Norgbey, E.; Ji, D.; Pu, Y.; Nuamah, L.A.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Nitrate Repletion during Spring Bloom Intensifies Phytoplankton Iron Demand in Yangtze River Tributary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, B.; Cossa, D.; Gagnon, P.; Pham, T.T.; Surette, C. Hydrological and Biogeochemical Dynamics of the Minor and Trace Elements in the St. Lawrence River. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1391–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerringa, L.J.A.; Rijkenberg, M.J.A.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; Verburg, T.G.; Boye, M.; De Baar, H.J.W. Kinetic Study Reveals Weak Fe-Binding Ligand, Which Affects the Solubility of Fe in the Scheldt Estuary. Mar. Chem. 2007, 103, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshikawa, M.K.; Takamatsu, T.; Takada, J.; Zhu, M.; Xu, B.; Chen, Z.; Murakami, S.; Xu, K.; Watanabe, M. Distributions of Dissolved and Particulate Elements in the Yangtze Estuary in 1997–2002: Background Data before the Closure of the Three Gorges Dam. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, K.; Babu, K.N.; Padmalal, D.; Seralathan, P. Hydrochemistry and Dissolved Nutrient Flux of Two Small Catchment Rivers, South-Western India. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 23, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Study on the Concentrations of Dissolved Iron and Its Natural Organic Ligands in the Seawater of Jiaozhou Bay. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Escoube, R.; Rouxel, O.J.; Sholkovitz, E.; Donard, O.F.X. Iron Isotope Systematics in Estuaries: The Case of North River, Massachusetts (USA). Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4045–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Alfonso, J.A.; Sánchez, L.; Calzadilla, M.; Silva, S.; LaBrecque, J.J.; Azócar, J.A. Temporal Variability of Selected Dissolved Elements in the Lower Orinoco River, Venezuela. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, M.J.; Statham, P.J.; Milani, A. Dissolved Fe(II) in a River-Estuary System Rich in Dissolved Organic Matter. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, V.E.; Miller, M.T.; Jensen, L.T.; Luther, G.W. Revisiting Mn and Fe Removal in Humic Rich Estuaries. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 209, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, F.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X. Analysis of Dissolved Oxygen and Nutrients in Zhanjiang Bay and the Adjacent Sea Area in Spring. Sustainability 2020, 12, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappler, A.; Bryce, C.; Mansor, M.; Lueder, U.; Byrne, J.M.; Swanner, E.D. An Evolving View on Biogeochemical Cycling of Iron. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paytan, A.; Street, J. Iron, Phytoplankton Growth, and the Carbon Cycle. In Metal Ions in Biological Systems, Volume 43—Biogeochemical Cycles of Elements; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Sigel, R., Eds.; Metal Ions in Biological Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; Volume 20053444, pp. 153–193. ISBN 978-0-8493-3807-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sutak, R.; Camadro, J.-M.; Lesuisse, E. Iron Uptake Mechanisms in Marine Phytoplankton. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 566691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Wakuta, Y.; Takeda, S. Distribution and Chemical Speciation of Iron on the Outer Edge of the Changjiang Diluted Water Plume of the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2022, 234, 104646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Achterberg, E.P.; Bates, N.R.; Gerringa, L.J.A.; Middag, R.; Hopwood, M.J.; Gledhill, M. Influence of Changes in pH and Temperature on the Distribution of Apparent Iron Solubility in the Oceans. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2023, 37, e2022GB007617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; De Vrieze, J.; Li, J.; Li, X. Temperature Affects Microbial Abundance, Activity and Interactions in Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwade, S.; Kuma, K.; Isoda, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Kudo, I.; Nishioka, J.; Suzuki, K. Effect of High Iron Concentrations on Iron Uptake and Growth of a Coastal Diatom Chaetoceros Sociale. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 43, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Davila, M.; Santana-Casiano, J.M.; Millero, F.J. Oxidation of Iron (II) Nanomolar with H2O2 in Seawater. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samperio-Ramos, G.; Santana Casiano, J.M.; González Dávila, M. Effect of Ocean Warming and Acidification on the Fe(II) Oxidation Rate in Oligotrophic and Eutrophic Natural Waters. Biogeochemistry 2016, 128, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Hopwood, M.J.; Groenenberg, J.E.; Engel, A.; Achterberg, E.P.; Gledhill, M. Influence of pH and Dissolved Organic Matter on Iron Speciation and Apparent Iron Solubility in the Peruvian Shelf and Slope Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9372–9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, S.D.; Persson, P.; Kritzberg, E.S. Salinity Effects on Iron Speciation in Boreal River Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9747–9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Witter, A.E.; Butler, A.; Luther, G.W. Competition among Marine Phytoplankton for Different Chelated Iron Species. Nature 1999, 400, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.K.; Doney, S.C.; Lindsay, K. Upper Ocean Ecosystem Dynamics and Iron Cycling in a Global Three-dimensional Model. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, 2004GB002220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, A.; Bopp, L.; Dutay, J.-C.; Bowie, A.R.; Chever, F.; Jean-Baptiste, P.; Bucciarelli, E.; Lannuzel, D.; Remenyi, T.; Sarthou, G.; et al. Hydrothermal Contribution to the Oceanic Dissolved Iron Inventory. Nat. Geosci 2010, 3, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bailey, D.; Lindsay, K.; Moore, J.K.; Holland, M. Impact of Sea Ice on the Marine Iron Cycle and Phytoplankton Productivity. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4713–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Lu, X.; Chen, F.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, Y.; Chen, C.; Lao, Q.; Zhang, S. Spatial-Monthly Variations and Influencing Factors of Dissolved Oxygen in Surface Water of Zhanjiang Bay, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, F. Spatial Distribution and Correlation Characteristics of Heavy Metals in the Seawater, Suspended Particulate Matter and Sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xiong, M.; Wang, S.; Tian, S.; Jin, G.; Chen, F.; Chen, C.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, Y. Impacts of Human Activities and Environmental Changes on Spatial-Seasonal Variations of Metals in Surface Sediments of Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 925567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnejais, L.H.; Martin, W.R.; Signell, R.P.; Bothner, M.H. Role of Sediment Resuspension in the Remobilization of Particulate-Phase Metals from Coastal Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, I.; Mucci, A. Trace Metal Remobilization Following the Resuspension of Estuarine Sediments: Saguenay Fjord, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L Windom, H.; Stickney, R.R. Environmental Aspects of Dredging in the Coastal Zone. C R C Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1976, 6, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F. Study on The Size Fractionated Chlorophyll a And Primary Productivty in Spring And Summer in The Yellow Sea And East China Sea. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Huang, L.; Tan, Y.; Ke, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J. Seasonal Variations of Chlorophyll a and Primary Production and Their Influencing Factors in the Pearl River Estuary. J Trop. Oceanogr. 2017, 36, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y. Distribution of ChlorophyII a and Productivity in Fujian Coastal Water. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Fu, K.; Hisayuki, A. Correlation between Chlorophyll-a and Primary Productitvty in the Southern Yellow Sea Area. J. Oceanogr. Huanghai Bohai Seas 1998, 16, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, J.A. The Iron and Molybdenum Use Efficiencies of Plant Growth with Different Energy, Carbon and Nitrogen Sources. New Phytol. 1988, 109, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.D.S.; Souza, A.E.D.; Oliva, M.A.; Pereira, E.G. Oxidative Damage and Photosynthetic Impairment in Tropical Rice Cultivars upon Exposure to Excess Iron. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Yin, L.-P. Research Progress in Chloroplast Iron Transport Proteins. Plant Physiol. J. 2017, 53, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Lin, D.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X. Excess Iron Alters the Fatty Acid Composition of Chloroplast Membrane and Decreases the Photosynthesis Rate: A Study in Hydroponic Pea Seedlings. Acta Physiol. Plant 2015, 37, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommer, M.; Specht, M.; Roy, A.-S.; Kraemer, L.; Andreson, R.; Gutowska, M.A.; Wolf, J.; Bergner, S.V.; Schilhabel, M.B.; Klostermeier, U.C.; et al. Genome and Low-Iron Response of an Oceanic Diatom Adapted to Chronic Iron Limitation. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, M.; Zhang, P.; Sun, D.; Peng, D. Unravelling Nutrients and Carbon Interactions in an Urban Coastal Water during Algal Bloom Period in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Water 2023, 15, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-J.; Huang, B.-Q.; Li, S.-X.; Zheng, F.-Y.; Huang, X.-G. Effect of Nitrate Enrichment and Diatoms on the Bioavailability of Fe(III) Oxyhydroxide Colloids in Seawater. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Station | Terrestrial Estuaries and Sewage Outlets | East Longitude/(°) | North Latitude/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Donghai Island breeding sewage outlet | 110.3478 | 21.0739 |
| P2 | Donghai Island breeding sewage outlet2 | 110.4017 | 21.0864 |
| P3 | Hongxing Reservoir River Estuary | 110.4175 | 21.0603 |
| P4 | Nanliu River Estuary | 110.3825 | 21.1519 |
| P5 | Lutang River Estuary | 110.4147 | 21.2128 |
| P6 | Wenbao River Estuary | 110.3972 | 21.2531 |
| P7 | Jinsha Bay sewage outlet | 110.3919 | 21.2703 |
| P8 | Binghu Park flood control gate | 110.3914 | 21.2792 |
| P9 | Suixi River Estuary | 110.3880 | 21.3928 |
| P10 | Dengta Park floodgate estuary | 110.4331 | 21.2536 |
| P11 | Potou Primary School sewage outlet | 110.4481 | 21.2397 |
| Environmental Element | Unit | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Mean Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| temperature | °C | 17.40 | 33.60 | 24.53 ± 5.08 |
| salinity | 18.20 | 30.57 | 25.63 ± 2.82 | |
| DO | mg/L | 5.42 | 9.59 | 7.64 ± 1.15 |
| pH | 6.84 | 8.46 | 7.94 ± 0.29 | |
| Chl-a | μg/L | 1.11 | 47.24 | 9.34 ± 11.43 |
| TDN | mg/L | 1.16 | 5.46 | 2.20 ± 0.73 |
| TDP | mg/L | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.10 ± 0.03 |
| DSi | mg/L | 0.21 | 3.39 | 1.23 ± 0.78 |
| Study Area | Survey Time | Average Concentration of CFe (μg/L) | Range of CFe Concentration (μg/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| St. Lawrence River | 1995–1996 | 4.02 ± 2.01 | [44] | |
| Scheldt estuary | 2002 | 29.95 | [45] | |
| Yangtze estuary | 1997–2002 | 4.02 | 0.56–4.52 | [46] |
| Periyar rivers | 2003.7 | 4.30 | [47] | |
| Chalakudy river | 2003.7 | 3.80 | [47] | |
| Massachusetts’ North River | 2006–2007 | 77.62–389.8 | [49] | |
| Orinoco River | 2004–2006 | 138.0 | 37.00–312.0 | [50] |
| Beaulieu River | 2012–2013 | 558.0 | 55.85–1172 | [51] |
| Broadkill River | 2015–2016 | 22.34–1049 | [52] | |
| Sanggou Bay | 2014 | 0.188 ± 0.116 | 0.079–0.520 | [26] |
| Jiaozhou Bay | 2011 | 1.29 ± 0.401 | [48] | |
| Zhanjiang Bay | 2019 | 54.34 ± 75.91 | 0.830–339.2 | This study |
| Terrestrial Station | The Average Iron Content of Terrestrial Stations (μg/L) | Adjacent Bay Station | Average Iron Content of Bay Stations (μg/L) | Iron Content Difference (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donghai Island breeding sewage outlet (P2) | 33.71 | S11 | 34.94 | 1.23 |
| Hongxing Reservoir River Estuary (P3) | 3.62 | S10 | 113.61 | 109.99 |
| Nanliu River Estuary (P4) | 2.63 | S12 | 66.14 | 63.51 |
| Lutang River Estuary (P5) | 32.78 | S15 | 24.01 | 8.77 |
| Potou Primary School sewage outlet (P11) | 3.70 | S17 | 19.71 | 16.01 |
| Jinsha Bay sewage outlet (P7) | 5.80 | S20 | 21.47 | 15.67 |
| Dengta Park flood gate (P10) | 1.60 | S19 | 17.00 | 15.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.-L.; Shi, L.-L.; Peng, D.-M.; Chen, C.-L.; Zhang, J.-B.; Zhang, P. Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Iron and the Response of Chlorophyll-a in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Water 2024, 16, 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162338
Chen Z-L, Shi L-L, Peng D-M, Chen C-L, Zhang J-B, Zhang P. Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Iron and the Response of Chlorophyll-a in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Water. 2024; 16(16):2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162338
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zi-Liang, Li-Lan Shi, De-Meng Peng, Chun-Liang Chen, Ji-Biao Zhang, and Peng Zhang. 2024. "Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Iron and the Response of Chlorophyll-a in Zhanjiang Bay, China" Water 16, no. 16: 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162338
APA StyleChen, Z.-L., Shi, L.-L., Peng, D.-M., Chen, C.-L., Zhang, J.-B., & Zhang, P. (2024). Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Iron and the Response of Chlorophyll-a in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Water, 16(16), 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162338







