A Risk Assessment of the Vegetation Ecological Degradation in Hunshandake Sandy Land, China: A Case Study of Dabusennur Watershed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Research Methods
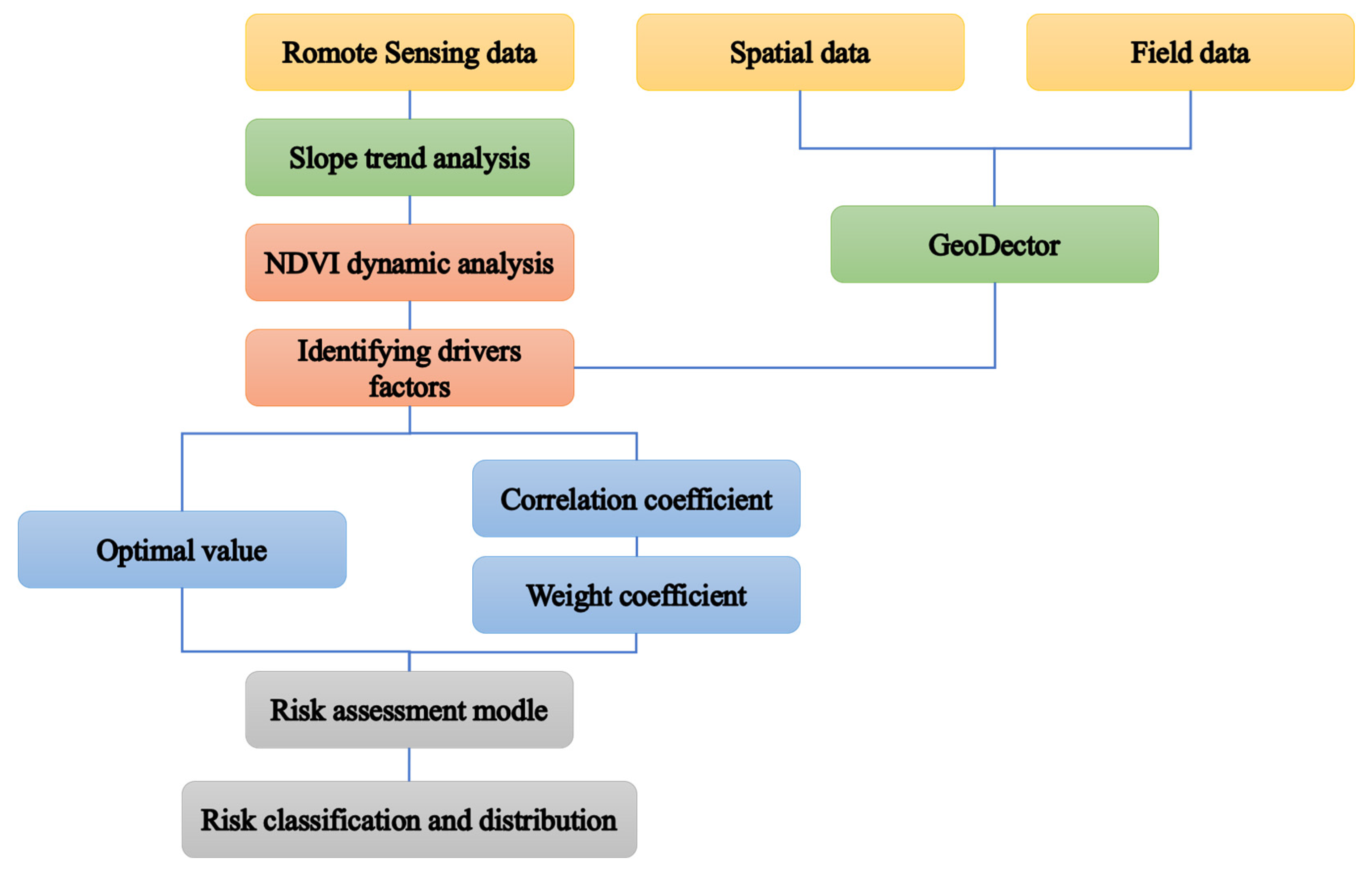
2.3.1. Workflow
2.3.2. NDVI Trend Analysis
2.3.3. GeoDetector
- (1)
- Factor detector
- (2)
- Interaction detector
2.3.4. Risk Assessment
3. Results
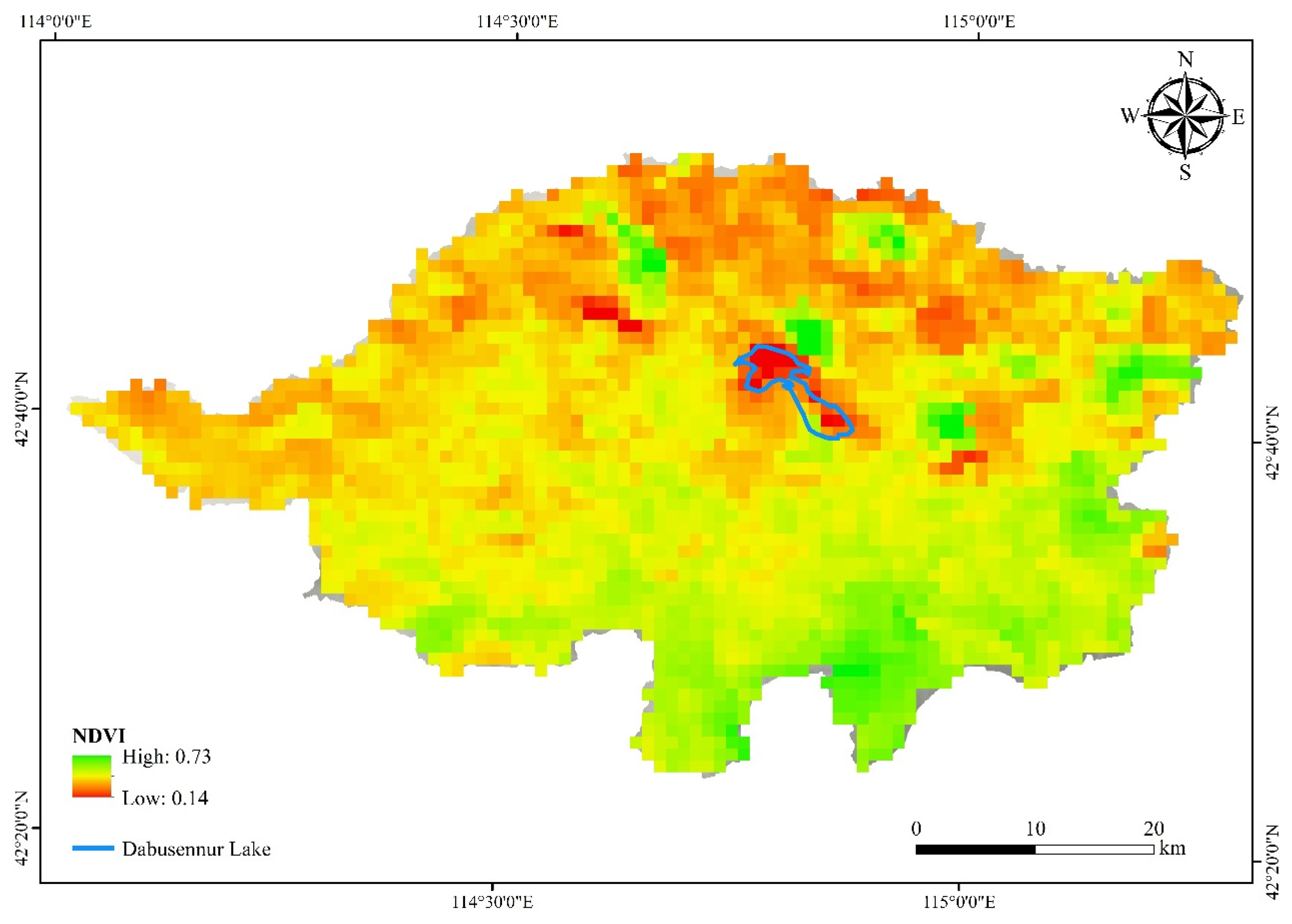
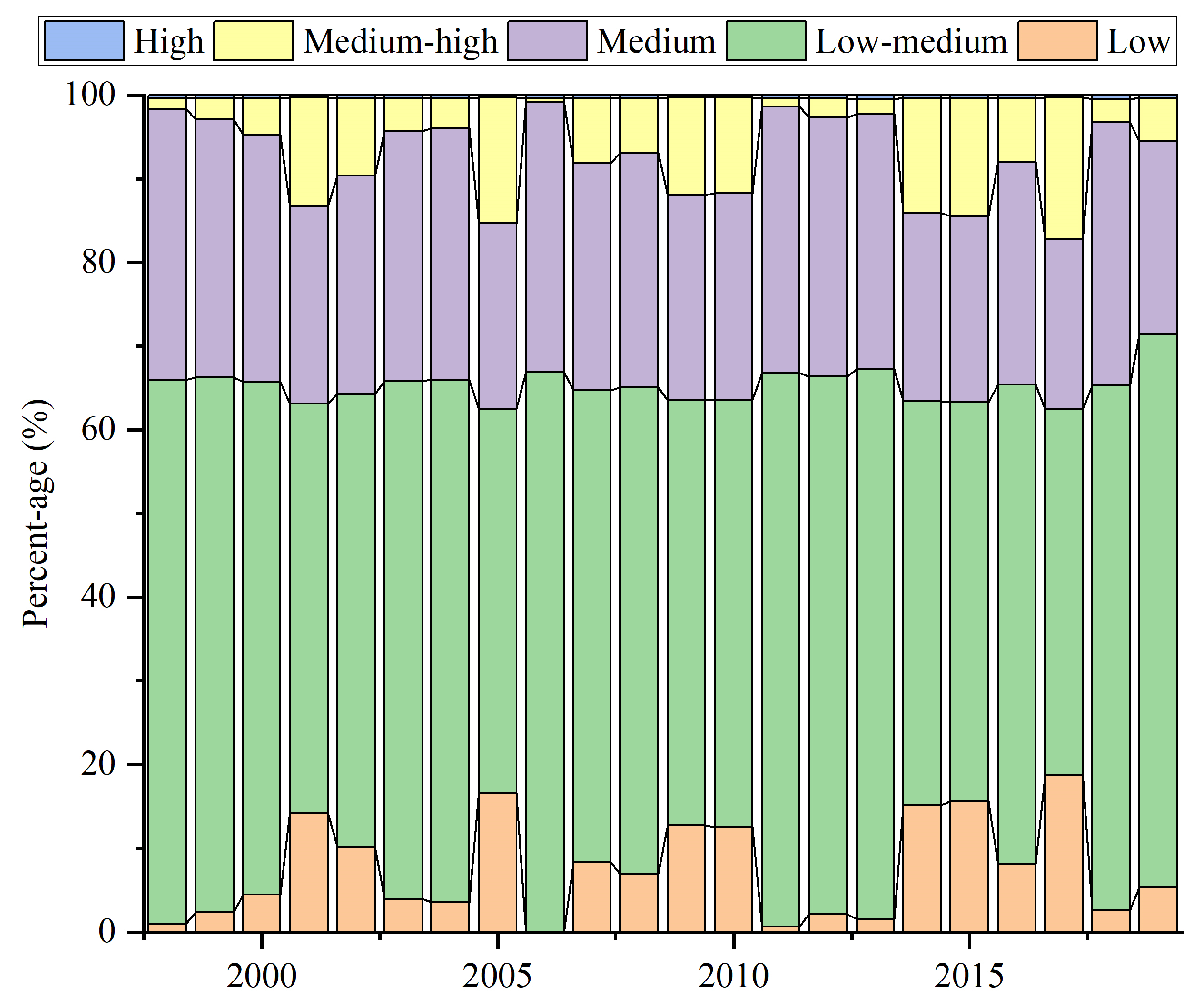
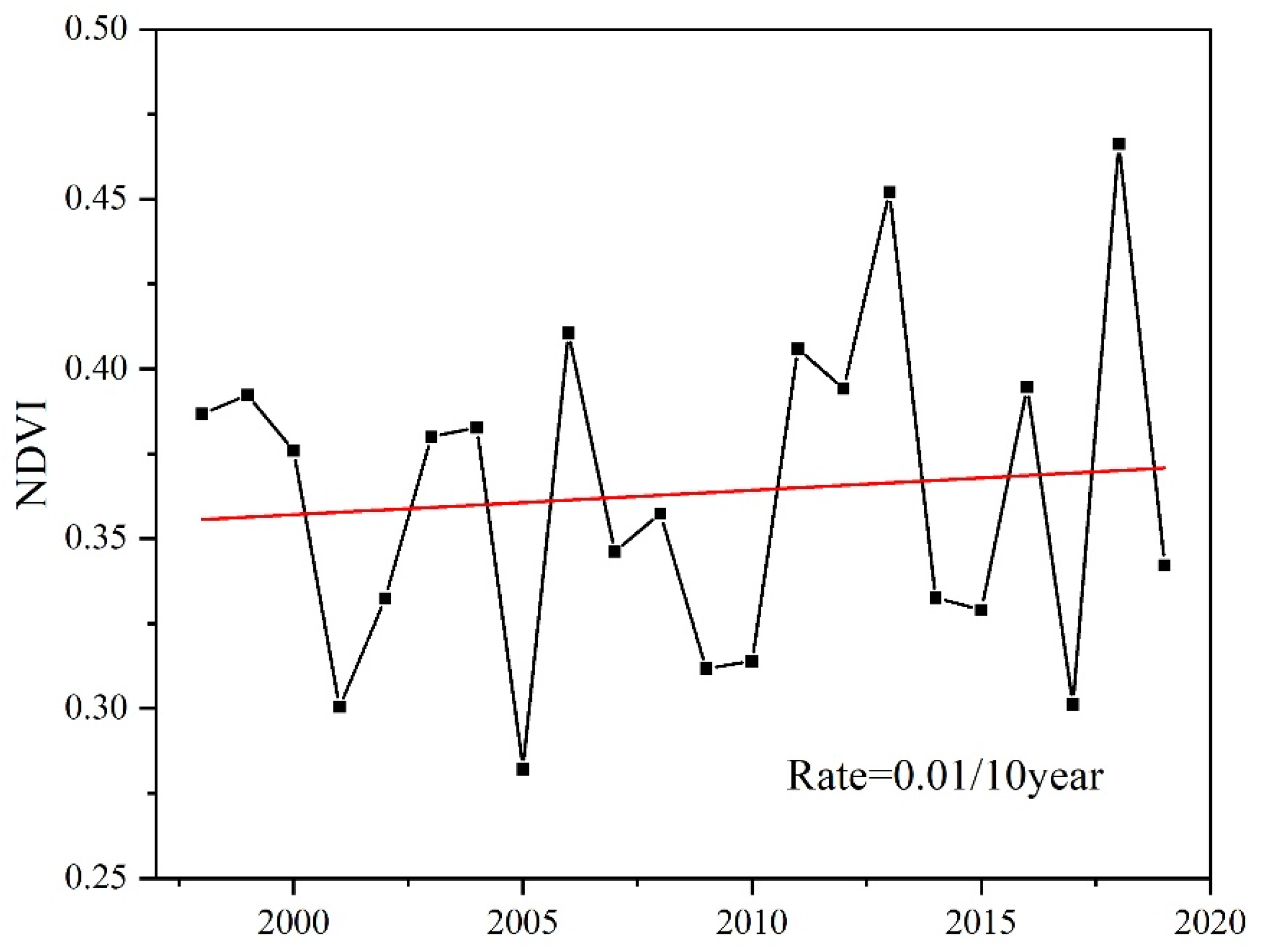
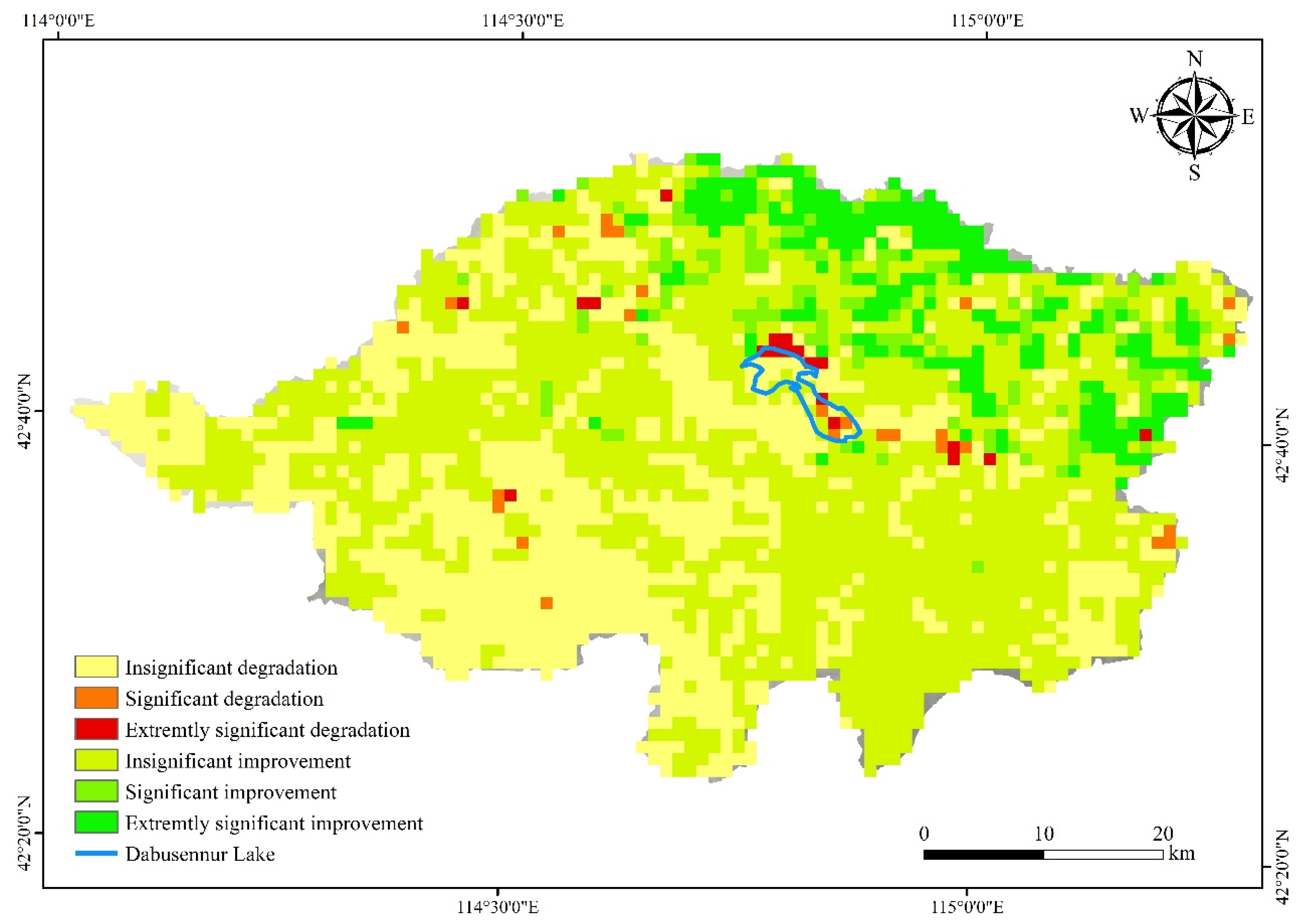
3.1. NDVI Dynamics in the DW from 1998 to 2019
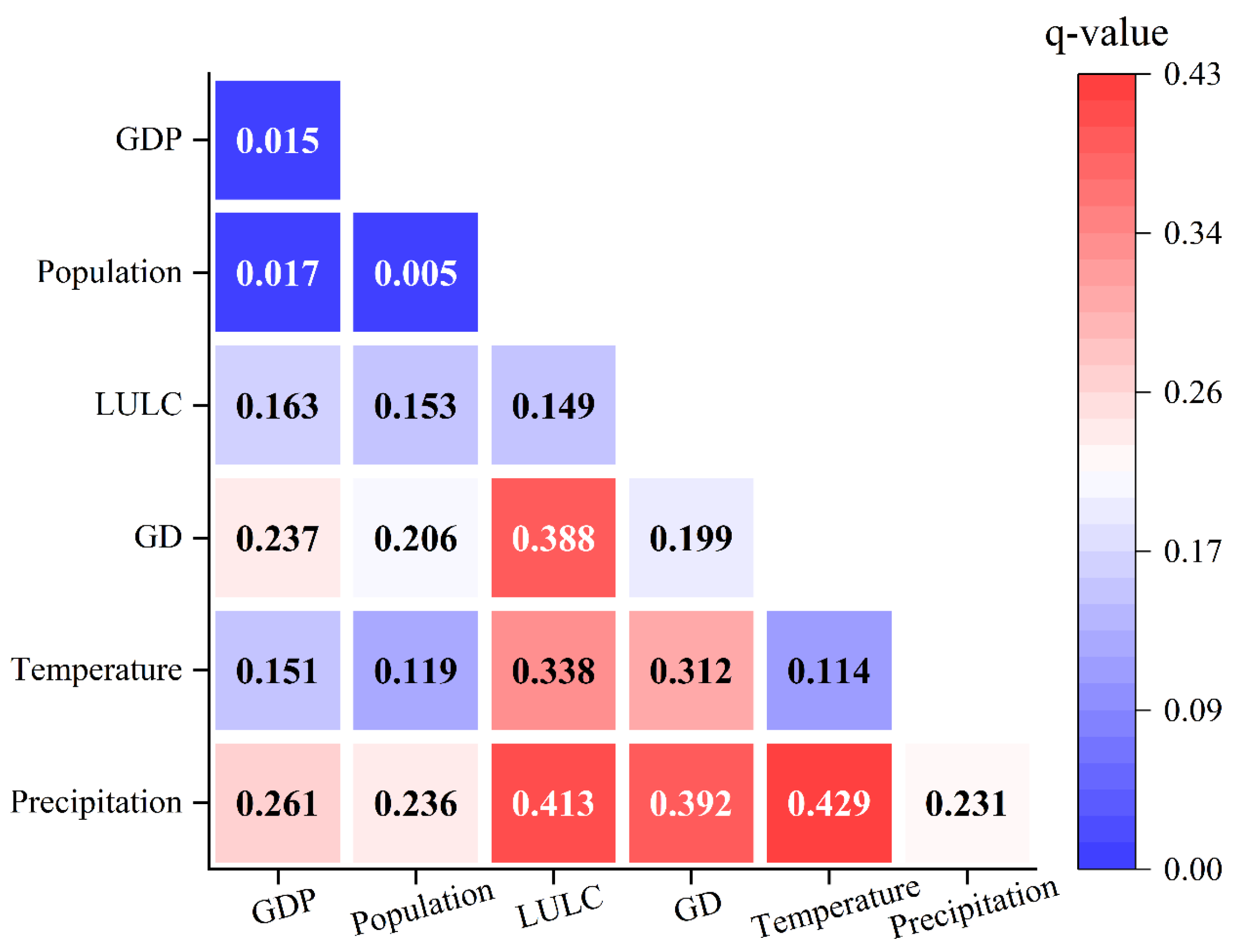
3.2. Analysis of Spatial Distribution Driving Forces of NDVI in DW
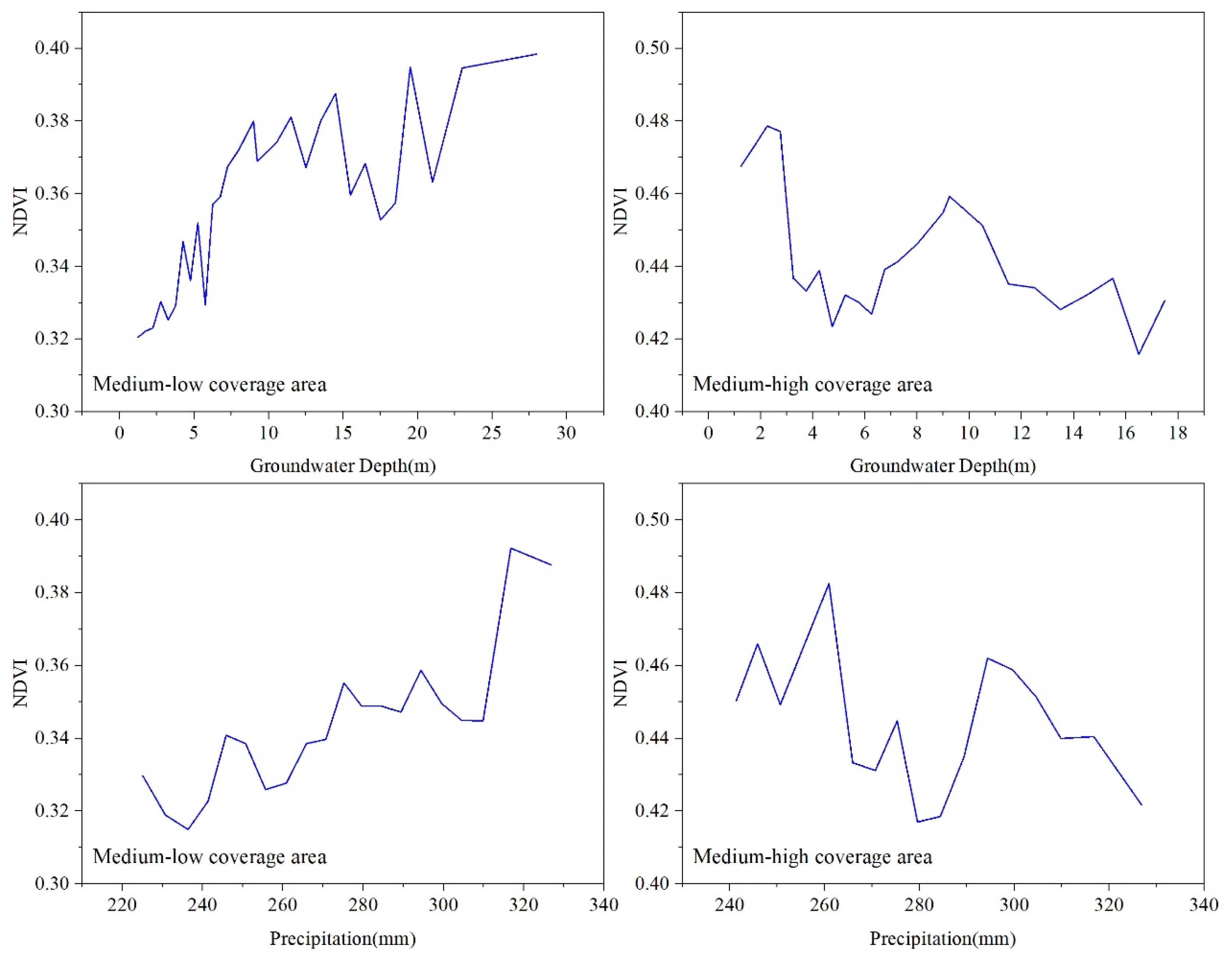
3.3. Response of NDVI to Variation of Precipitation and GD
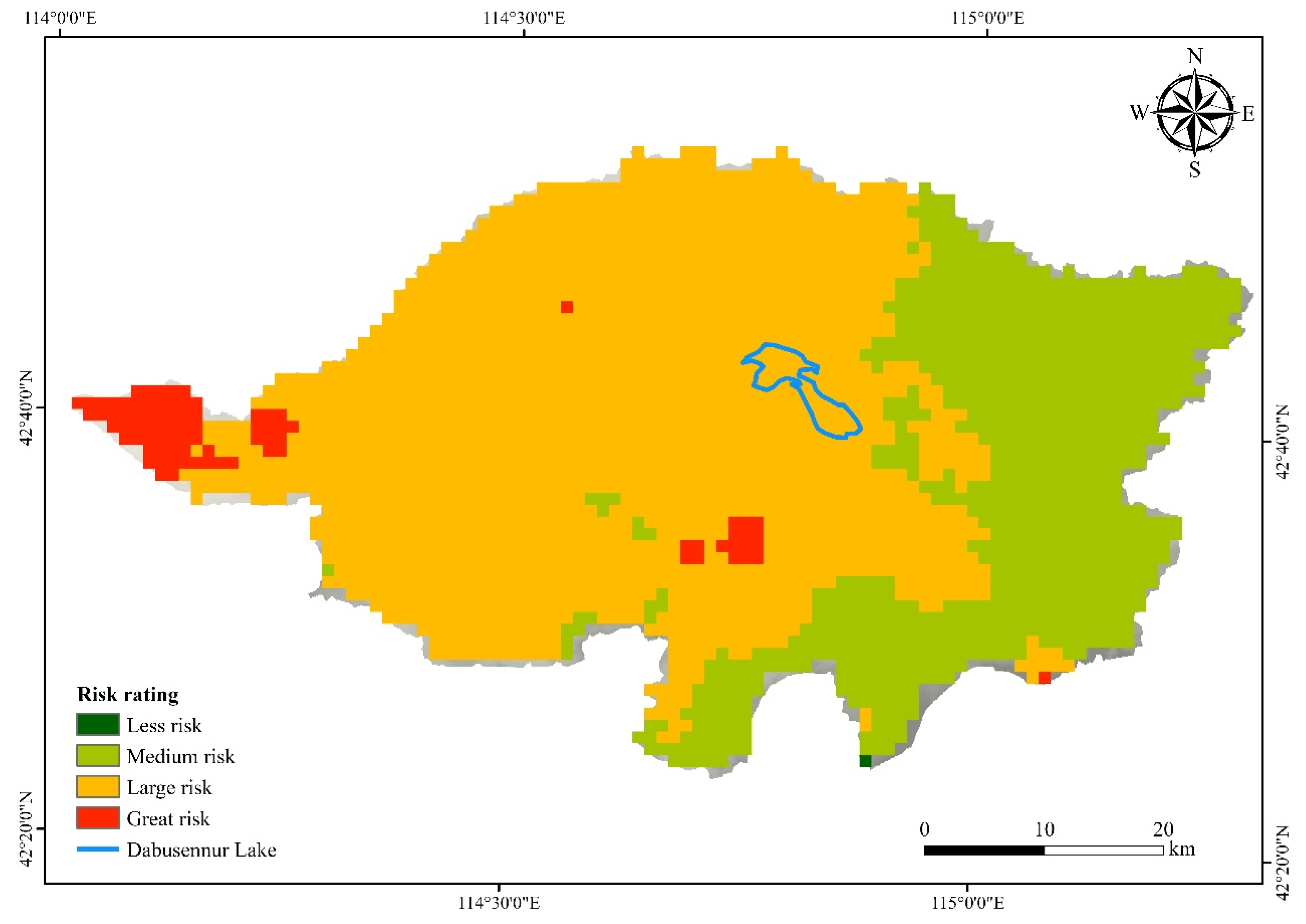
3.4. Risk Assessment of Vegetation Ecological Degradation
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Vegetation Changes
4.2. Vegetation Dynamics in Response to Climate Change and Human Activities
4.3. Vegetation Ecological Threshold
4.4. The Dependence of Vegetation on Groundwater and Precipitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, A.; Basu, T. Assessment of Peri-Urban Wetland Ecological Degradation through Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA): A Study on Chatra Wetland, India. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, T.; Crous, C.J.; Liberati, D.; Munzi, S.; Gouveia, C.; Ulm, F.; Afonso, A.C.; Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Manrique, E.; Sheppard, L.; et al. Alleviating Nitrogen Limitation in Mediterranean Maquis Vegetation Leads to Ecological Degradation: N Enrichment Degrades Ecological Partnerships and Its Functions. Land Degrad. Develop. 2017, 28, 2482–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.Y.; Takahashi, K.; Takakura, J.; Li, F.; Fujimori, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Ito, A.; Lee, D.K. How Will Deforestation and Vegetation Degradation Affect Global Fire Activity? Earth’s Future 2021, 9, e2020EF001786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, B.; Aron, M.; Loy, T.; Muhamud, N.W.; Benard, S. The Impact of Refugee Settlements on Land Use Changes and Vegetation Degradation in West Nile Sub-Region, Uganda. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huai, W.; Wang, P. Contaminant Transport in a Three-Zone Wetland: Dispersion and Ecological Degradation. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Jiang, L.; Huang, C.; An, P.; Pan, Z. Impact of Center Pivot Irrigation on Vegetation Dynamics in a Farming-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China: A Case Study in Ulanqab, Inner Mongolia. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Zhao, J.; Song, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, G.; Shen, Z.; Wu, W. Identification of Degradation Areas of Ecological Environment and Degradation Intensity Assessment in the Yellow River Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 922013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Yuan, R.; Singh, V.P.; Wu, W.; Wang, D. Dynamic Responses of Ecological Vulnerability to Land Cover Shifts over the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Meng, L.; Liu, F.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H. Distribution, Source Investigation, and Risk Assessment of Topsoil Heavy Metals in Areas with Intensive Anthropogenic Activities Using the Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Model Coupled with Self-Organizing Map (SOM). Env. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6353–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Accelerating Collaborative Innovation in Hydrological, Engineering, and Environmental Fields. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Luo, P.; Yang, H.; Luo, C. Water Yield Response to Plant Community Conversion Caused by Vegetation Degradation and Improvement in an Alpine Meadow on the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, Z. Estimating Relations of Vegetation, Climate Change, and Human Activity: A Case Study in the 400 Mm Annual Precipitation Fluctuation Zone, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Pang, B.; Qiao, X.; Xu, D.; Li, W.; Yan, Y.; Dou, H.; Ao, W.; Wang, W.; Zou, C.; et al. Vegetation Dynamics in Response to Climate Change and Human Activities in the Hulun Lake Basin from 1981 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wu, Z.; Du, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Insights on the Roles of Climate and Human Activities to Vegetation Degradation and Restoration in Beijing-Tianjin Sandstorm Source Region. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 159, 106105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhumanova, M.; Mönnig, C.; Hergarten, C.; Darr, D.; Wrage-Mönnig, N. Assessment of Vegetation Degradation in Mountainous Pastures of the Western Tien-Shan, Kyrgyzstan, Using eMODIS NDVI. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, Z.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Song, Z.; Qin, P.; Tian, X. Identification and Assessment of the Factors Driving Vegetation Degradation/Regeneration in Drylands Using Synthetic High Spatiotemporal Remote Sensing Data—A Case Study in Zhenglanqi, Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Ge, Q. Evaluating the Vegetation Destruction and Recovery of Wenchuan Earthquake Using MODIS Data. Nat. Hazards 2010, 54, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Pflugmacher, D.; Li, A.; Li, Z.; Hostert, P. Land Use and Land Cover Change in Inner Mongolia—Understanding the Effects of China’s Re-Vegetation Programs. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, L. Vegetation Degradation and Its Driving Factors in the Farming–Pastoral Ecotone over the Countries along Belt and Road Initiative. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fan, M. Identification of the Key Ecological Factors Influencing Vegetation Degradation in Semi-Arid Agro-Pastoral Ecotone Considering Spatial Scales. Acta Oecologica 2017, 85, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Cui, M.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y. Altitude and Temperature Dependence of Change in the Spring Vegetation Green-up Date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ma, R.; Shi, J.; Si, L. Effects of Groundwater Depth and Salt Content on Vegetation in Dry Lake Basins: A Case Study of Chahan Lake, Northern China. Geofluids 2022, 2022, e7393247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Zhao, Z.; Han, L.; Qian, Y.; Ou, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M. Determination of Groundwater Recharge Regime and Flowpath in the Lower Heihe River Basin in an Arid Area of Northwest China by Using Environmental Tracers: Implications for Vegetation Degradation in the Ejina Oasis. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Sun, C. Spatiotemporal Variation and Influencing Factors of Vegetation Dynamics Based on Geodetector: A Case Study of the Northwestern Yunnan Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ke, Y.; Zhu, L.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, L. Tracking Vegetation Degradation and Recovery in Multiple Mining Areas in Beijing, China, Based on Time-Series Landsat Imagery. GIScience Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 1477–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, G.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, H. Isotopes in Groundwater (2H, 18O, 14C) Revealed the Climate and Groundwater Recharge in the Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Quantifying Influences of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on Vegetation Changes Based on Geodetector: A Case Study in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L. Applying Geodetector to Disentangle the Contributions of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors to NDVI Variations in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lv, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Marsh Wetland Degradation Risk Assessment and Change Analysis: A Case Study in the Zoige Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muqi, X.; Jiang, Z.; Yuyao, H.; Yurong, G.; Shen, Z.; Yijian, T.; Chengqing, Y.; Zijian, W. The Ecological Degradation and Restoration of Baiyangdian Lake, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 1998, 13, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Jia, X.; Meng, W. How Sulfate-Rich Mine Drainage Affected Aquatic Ecosystem Degradation in Northeastern China, and Potential Ecological Risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Chen, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Ning, K. Identification of Ecological Restoration Standard for Lakes on the Inner Mongolia Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 111993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, F.; Du, J.; Hu, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Kong, X.; Fu, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. The Influence of Oil Exploitation on the Degradation of Vegetation: A Case Study in the Yellow River Delta Nature Reserve, China. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Xie, Z.; Ma, X.; Huete, A. Water Loss Due to Increasing Planted Vegetation over the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Scuderi, L.A.; Wang, X.; Scuderi, L.J.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Forman, S.; Xu, Q.; Wang, R.; Huang, W.; et al. Groundwater Sapping as the Cause of Irreversible Desertification of Hunshandake Sandy Lands, Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, C.; Nie, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zan, Y. Evaluation of the Groundwater Ecological Water Requirement in the Southeast Margin of Otindag Sandy Land Based on Allowable Groundwater Depth Drawdown. Water 2023, 15, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Li-jie, W.; Yi-long, Z.; Xiu-ya, W.; Zhan-chuan, W.; Zhou, Z. Effect of Groundwater on the Ecological Water Environment of Typical Inland Lakes in the Inner Mongolian Plateau. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 353. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Quan, Q.; Wu, B.; Mo, S. Response of Vegetation Dynamics in the Three-North Region of China to Climate and Human Activities from 1982 to 2018. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Men, B.; Yin, S. Spatiotemporal Variation of Groundwater Extraction Intensity Based on Geostatistics—Set Pair Analysis in Daxing District of Beijing, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, D.; Peng, D.; Zhang, Y. Quantifying the Influences of Natural and Human Factors on the Water Footprint of Afforestation in Desert Regions of Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and Its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Gong, J.; Dang, D.; Dou, H.; Lyu, X. Quantitative Analysis of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Influencing Vegetation NDVI Changes in Temperate Drylands from a Spatial Stratified Heterogeneity Perspective: A Case Study of Inner Mongolia Grasslands, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S. Effects of Multi-Temporal Scale Drought on Vegetation Dynamics in Inner Mongolia from 1982 to 2015, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.; Liu, B.; Zou, C.; Li, H.; McKenzie, S.; He, Y.; Gao, J.; Jia, X.; Altaf Arain, M.; Wang, S.; et al. Sensitivity of Vegetation Dynamics to Climate Variability in a Forest-Steppe Transition Ecozone, North-Eastern Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi Khusfi, Z.; Khosroshahi, M.; Roustaei, F.; Mirakbari, M. Spatial and Seasonal Variations of Sand-Dust Events and Their Relation to Atmospheric Conditions and Vegetation Cover in Semi-Arid Regions of Central Iran. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, F.; Zong, Q.; Qin, P.; Liu, C. Impact of Variations in Vegetation on Surface Air Temperature Change over the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Wenninger, J.; Zhang, E.; Hou, G.; Dong, J. Interaction between Groundwater and Trees in an Arid Site: Potential Impacts of Climate Variation and Groundwater Abstraction on Trees. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James-Pirri, M.-J.; Swanson, J.L.; Roman, C.T.; Ginsberg, H.S.; Heltshe, J.F. Ecological Thresholds for Salt Marsh Nekton and Vegetation Communities. In Application of Threshold Concepts in Natural Resource Decision Making; Guntenspergen, G.R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 291–319. ISBN 978-1-4899-8040-3. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, H.; Shan, D.; Guo, J.Y. Analysis Threshold Value of Ecological Water Require-Ment for Vegetation Restoration on Northern Grassland. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 212, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Koyama, A.; Okuro, T. Coupling Structural and Functional Thresholds for Vegetation Changes on a Mongolian Shrubland. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, C.; He, Y.; He, T. Soil Characteristics and Response Thresholds of Salt Meadow on Lake Beaches of the Ordos Platform. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1050757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzedakis, P.C.; Frogley, M.R.; Lawson, I.T.; Preece, R.C.; Cacho, I.; de Abreu, L. Ecological Thresholds and Patterns of Millennial-Scale Climate Variability: The Response of Vegetation in Greece during the Last Glacial Period. Geology 2004, 32, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas-Vilarrúbia, T.; González-Sampériz, P.; Morellón, M.; Gil-Romera, G.; Pérez-Sanz, A.; Valero-Garcés, B. Diatom and Vegetation Responses to Late Glacial and Early Holocene Climate Changes at Lake Estanya (Southern Pyrenees, NE Spain). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 392, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Xiao, C.; Wang, G.; Liang, X. Study on Ecological Threshold of Groundwater in Typical Salinization Area of Qian’an County. Water 2021, 13, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, J.; McGwire, K.; Morton, C.; Snyder, K.; Peterson, S.; Erickson, T.; Niswonger, R.; Carroll, R.; Smith, G.; Allen, R. Assessing the Role of Climate and Resource Management on Groundwater Dependent Ecosystem Changes in Arid Environments with the Landsat Archive. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpakairi, K.S.; Dube, T.; Dondofema, F.; Dalu, T. Spatio–Temporal Variation of Vegetation Heterogeneity in Groundwater Dependent Ecosystems within Arid Environments. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 69, 101667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.-S. The Impact of Groundwater Depth on the Spatial Variance of Vegetation Index in the Ordos Plateau, China: A Semivariogram Analysis. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, M.S.I.; Grau, A.V.; McDonnell, J.J.; Herbohn, J. Tropical Forest Water Source Patterns Revealed by Stable Isotopes: A Preliminary Analysis of 46 Neighboring Species. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 494, 119355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, N.; Fu, B. Inter-Comparison of Stable Isotope Mixing Models for Determining Plant Water Source Partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.T.; Sprenger, M.; Bowen, G.J.; Brooks, J.R. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Plant Source Water: O and H Isotope Ratios from Precipitation to Xylem Water. In Stable Isotopes in Tree Rings; Siegwolf, R.T.W., Brooks, J.R., Roden, J., Saurer, M., Eds.; Tree Physiology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 8, pp. 501–535. ISBN 978-3-030-92697-7. [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf, J.; Tetzlaff, D.; Dubbert, M.; Dubbert, D.; Smith, A.; Soulsby, C. Xylem Water in Riparian Willow Trees (Salix Alba) Reveals Shallow Sources of Root Water Uptake by in Situ Monitoring of Stable Water Isotopes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 2073–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, L.; Han, D. A δ2H Offset Correction Method for Quantifying Root Water Uptake of Riparian Trees. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

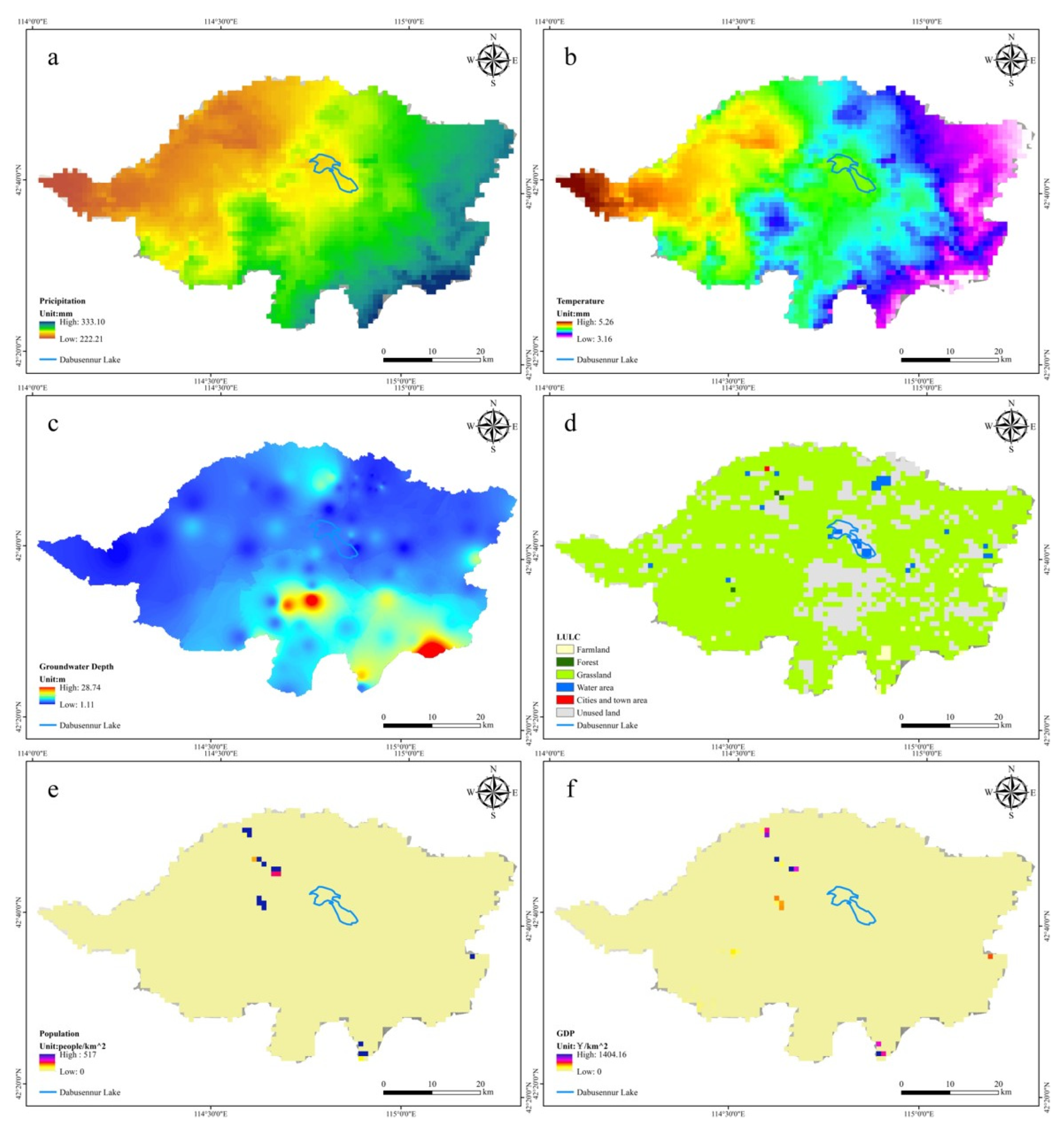
| Date Name | Date Type | Time | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | Raster (1000 m) | 1998–2019 | RESDC (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 3 August 2024) |
| Precipitation | Stations | 1998–2019 | NMIC (http://data.cma.cn, accessed on 3 August 2024) |
| Temperature | Stations | 1998–2019 | NMIC (http://data.cma.cn, accessed on 3 August 2024) |
| GD | Points (6/10 km2) | 2020 | Field survey |
| LULC | Raster (1000 m) | 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015 | RESDC (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 3 August 2024) |
| Population | Raster (1000 m) | 2010 | RESDC (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 3 August 2024) |
| GDP | Raster (1000 m) | 2010 | RESDC (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 3 August 2024) |
| Criterion of Interval | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Nonlinear weakening | |
| Single-factor nonlinear weakening | |
| Dual factor enhancement | |
| Independence | |
| Nonlinear enhancement |
| Level | NDVI | Area (km2) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low coverage area | 0–0.2 | 18.10 | 0.62% |
| Low-medium coverage area | 0.2–0.4 | 2173.91 | 74.81% |
| Medium coverage area | 0.4–0.6 | 710.89 | 24.46% |
| Medium-high coverage area | 0.6–0.8 | 3.02 | 0.10% |
| High coverage area | 0.8–1 | 0.00 | 0 |
| Level | Change Degree | Area (km2) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slope > 0, p < 0.01 | Extremely significant improvement | 241.32 | 8.30% |
| Slope > 0, 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05 | Significant improvement | 142.78 | 4.91% |
| Slope > 0, p ≥ 0.05 | Insignificant improvement | 1457.99 | 50.17% |
| Slope < 0, p ≥ 0.05 | Insignificant degradation | 1018.58 | 35.05% |
| Slope < 0, 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05 | Significant degradation | 26.14 | 0.90% |
| Slope < 0, p < 0.01 | Extremely significant degradation | 19.10 | 0.66% |
| Precipitation | Temperature | GD | LULC | Population | GDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.231 | 0.114 | 0.199 | 0.149 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| Assessment Factors | Optimal Value | Correlation Coefficient | Weight Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | 333.10 mm | 0.47 * | 0.55 |
| GD | 2.75 m | 0.38 * | 0.45 |
| Risk Level | Risk Degree | Risk Value | Area (km2) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Less risk | R < 0.1 | 0 | 0% |
| 3 | Medium risk | 0.1 ≤ R < 0.3 | 894.13 | 30.77% |
| 2 | Large risk | 0.3 ≤ R < 0.5 | 1922.99 | 66.17% |
| 1 | Great risk | R ≥ 0.5 | 88.80 | 3.06% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.; Ma, R.; Si, L.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, R.; Dong, W. A Risk Assessment of the Vegetation Ecological Degradation in Hunshandake Sandy Land, China: A Case Study of Dabusennur Watershed. Water 2024, 16, 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162258
Chen P, Ma R, Si L, Zhao L, Jiang R, Dong W. A Risk Assessment of the Vegetation Ecological Degradation in Hunshandake Sandy Land, China: A Case Study of Dabusennur Watershed. Water. 2024; 16(16):2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162258
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Peng, Rong Ma, Letian Si, Lefan Zhao, Ruirui Jiang, and Wanggang Dong. 2024. "A Risk Assessment of the Vegetation Ecological Degradation in Hunshandake Sandy Land, China: A Case Study of Dabusennur Watershed" Water 16, no. 16: 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162258
APA StyleChen, P., Ma, R., Si, L., Zhao, L., Jiang, R., & Dong, W. (2024). A Risk Assessment of the Vegetation Ecological Degradation in Hunshandake Sandy Land, China: A Case Study of Dabusennur Watershed. Water, 16(16), 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162258





