Effect of In Situ Aeration on Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling Control in Treating Seasonal High-Turbidity Surface Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Feed Water
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Flux and Filtration Resistance Analyses
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Morphological Observation
2.4.2. Composition Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Aeration Intensity on TMP Development
3.2. Removal Performance
3.3. Cake Layer Structures
3.3.1. Morphologies of Cake Layer
3.3.2. Internal Structures of Cake Layer
3.3.3. Microstructure of Cake Layer
3.4. Compositions of Cake Layer
3.4.1. EPS Concentration Analysis
3.4.2. Functional Group Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Xi, T.; Zhou, L.-A. Drinking Water Facilities and Inclusive Development: Evidence from Rural China. World Dev. 2024, 174, 106428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Gao, Z.; Hu, M.; Wu, X.; Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Liao, L. Development and Technology of Rural Drinking Water Supply in China. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liang, H.; Ding, A.; Qu, F.; Shao, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.; Li, G. Effects of Pre-Ozonation on the Ultrafiltration of Different Natural Organic Matter (NOM) Fractions: Membrane Fouling Mitigation, Prediction and Mechanism. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 505, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Zhao, X. Treatment of Surfactants with Concentrations below Critical Micelle Concentration by Ultrafiltration: A Mini-Review. Water Cycle 2022, 3, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadafi, M.; Wulan, D.R.; Notodarmojo, S.; Zevi, Y. Characteristics and Treatment Methods for Peat Water as Clean Water Sources: A Mini Review. Water Cycle 2023, 4, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, E.; Wu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X. A Tale of Two Water Supplies in China: Finding Practical Solutions to Urban and Rural Water Supply Problems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, C.M.; Aroua, M.K.; Hussain, M.A. Advanced Process Control for Ultrafiltration Membrane Water Treatment System. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 179, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Gu, H.; Xiao, K.; Qu, F.; Yu, H.; Wei, C. Fouling Mechanisms Analysis via Combined Fouling Models for Surface Water Ultrafiltration Process. Membranes 2020, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, B.; Dong, M. Impact of Various Coagulation Technologies on Membrane Fouling in Coagulation/Ultrafiltration Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, H.; Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, J. Continuation of a Cleaning Process: Application of MNBs-Coagulation Process to Mitigate Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Ding, Y.; Wang, B.; Qi, Z.; Bai, Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Influence of Sedimentation with Pre-Coagulation on Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling Performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Liang, H.; Cheng, X.; Yang, H.; Xu, D.; Gan, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, G. Combined Effects of Coagulation and Adsorption on Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling Control and Subsequent Disinfection in Drinking Water Treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33770–33780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordier, C.; Stavrakakis, C.; Sauvade, P.; Coelho, F.; Moulin, P. Air Backwash Efficiency on Organic Fouling of UF Membranes Applied to Shellfish Hatchery Effluents. Membranes 2018, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vroman, T.; Beaume, F.; Armanges, V.; Gout, E.; Remigy, J.-C. Critical Backwash Flux for High Backwash Efficiency: Case of Ultrafiltration of Bentonite Suspensions. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, H.G.; Da Silva Cavalcante, J.; De Aquino, M.D.; Mota, F.S.B.; Mierzwa, J.C. The Relevance of Critical Flux and Backwash Intervals Parameters for the Design of Ultrafiltration Process in the Treatment of Eutrophic Reservoirs: A Pilot Study for the Development of a Full-Scale Project. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 61, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, H.; Qu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Liang, H. Long-Term Operation of Ultrafiltration Membrane in Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Plants in China: Characteristics of Membrane Performance. Desalination 2022, 543, 116122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xiao, H.; Huang, X.; Zou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, S.; Xie, P.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J. Application of Heat-Activated Peroxydisulfate Process for the Chemical Cleaning of Fouled Ultrafiltration Membranes. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chen, C.; Guo, C.; Wang, S.; Chang, H.; Liu, B. Optimization of Aeration Conditions in the Hybrid Process of Coagulation-Ultrafiltration with Air Sparging. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2017, 66, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Waite, T.D.; Leslie, G. Numerical Simulations of Impact of Membrane Module Design Variables on Aeration Patterns in Membrane Bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.Z.; Wray, H.E.; Bérubé, P.R.; Andrews, R.C. Distribution of Surface Shear Stress for a Densely Packed Submerged Hollow Fiber Membrane System. Desalination 2015, 357, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.-Y.; Xu, P.-C.; Huang, G.-H.; Chai, T.; Hou, M.; Gao, P.-F. Effects of Aeration Parameters on Effluent Quality and Membrane Fouling in a Submerged Membrane Bioreactor Using Box–Behnken Response Surface Methodology. Desalination 2012, 302, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Dong, Y.Y.; Sun, H.J. Effect of Aeration Intensity on Membrane Fouling of Non-Woven Fibers-MBR. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 726–731, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Younas, M.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ly, Q.V.; Li, J. A Review on Hollow Fiber Membrane Module towards High Separation Efficiency: Process Modeling in Fouling Perspective. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, H.C.; Abdulsalam, M.; Ahmad Abdullahi, F.; Marlina Abd-Karim, M.; Faezah Yunos, K.; Aida Isma, M.I. Exploring the Effect of Aeration Intensity on a Modified PVDF-PEG Membrane Incorporated with Nano-MgO: Antifouling and AnT-POME Treatment. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 2189–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Nan, J.; Li, G. Air Bubbling for Alleviating Membrane Fouling of Immersed Hollow-Fiber Membrane for Ultrafiltration of River Water. Desalination 2010, 260, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, T.; Bai, Y.; Yu, S. Coagulation–Bubbling–Ultrafiltration: Effect of Floc Properties on the Performance of the Hybrid Process. Desalination 2014, 333, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, S.; Wang, E.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Q.; Jia, W. Occurrence, Health Risk, and Removal Efficiency Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds in Drinking Water Treatment Plants (DWTPs): An Investigation of Seven Major River Basins across China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruigómez, I.; González, E.; Guerra, S.; Rodríguez-Gómez, L.E.; Vera, L. Evaluation of a Novel Physical Cleaning Strategy Based on HF Membrane Rotation during the Backwashing/Relaxation Phases for Anaerobic Submerged MBR. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruigómez, I.; González, E.; Rodríguez-Gómez, L.; Vera, L. Fouling Control Strategies for Direct Membrane Ultrafiltration: Physical Cleanings Assisted by Membrane Rotational Movement. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; De Paula, E.C.; Santos, L.V.D.S.; Amaral, M.C.S. Recycled Reverse Osmosis Membrane Combined with Pre-Oxidation for Improved Arsenic Removal from High Turbidity Waters and Retrofit of Conventional Drinking Water Treatment Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Organic Matter Content and Crop Yield. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 27A–32A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Cui, Z.; Li, J. Investigation of Shear-Force Distribution in the Hollow Fiber Membrane Module Based on FBG Sensing Technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 116458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Ma, J.; Han, M.; Chen, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, G. Membrane Fouling Control in Ultrafiltration Technology for Drinking Water Production: A Review. Desalination 2011, 272, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Dereli, R.K.; Ozturk, I.; Roest, K.; van Lier, J.B. A Review on Dynamic Membrane Filtration: Materials, Applications and Future Perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K. Comparative Study of Membrane Fouling with Aeration Shear Stress in Filtration of Different Substances. Membranes 2023, 13, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Yang, F.; Shi, B.; Zhang, H. A Comprehensive Study on Membrane Fouling in Submerged Membrane Bioreactors Operated under Different Aeration Intensities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 59, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, A.; Prieske, H.; Meyer, E.-L.; Senger, G.; Kraume, M. Advantageous and Detrimental Effects of Air Sparging in Membrane Filtration: Bubble Movement, Exerted Shear and Particle Classification. Desalination 2010, 250, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Jefferson, W.A.; Lan, H.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Synergistic Process Using Fe Hydrolytic Flocs and Ultrafiltration Membrane for Enhanced Antimony(V) Removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Fan, H.; Lu, C.; Zhao, K.; Qi, J. A Pilot-Scale Study of the Integrated Floc-Ultrafiltration Membrane-Based Drinking Water Treatment Process. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Qu, F.-S.; Liang, H.; Li, K.; Bai, L.-M.; Li, G.-B. Control of Submerged Hollow Fiber Membrane Fouling Caused by Fine Particles in Photocatalytic Membrane Reactors Using Bubbly Flow: Shear Stress and Particle Forces Analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksana, F.; Fane, A.G.; Chen, V. Fibre Movement Induced by Bubbling Using Submerged Hollow Fibre Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 271, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lu, J.; Ma, J.; Qiang, Z. Comparative Study of Ozonation and Synthetic Goethite-Catalyzed Ozonation of Individual NOM Fractions Isolated and Fractionated from a Filtered River Water. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, W.; Chen, Y.; He, D.; Isaev, A.B.; Zhu, M. Dissolved Oxygen in Aeration-Driven Piezo-Catalytic for Antibiotics Pollutants Removal in Water. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P.; Jefferson, B.; Gregory, J.; Parsons, S.A. A Review of Floc Strength and Breakage. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3121–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence Excitation−Emission Matrix Regional Integration to Quantify Spectra for Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, H.; Tang, X. Influence of Operation Modes on Gravity-Driven Membrane Process in Treating the Secondary Effluent: Flux Improvement and Biocake Layer Property. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Wang, R.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, W.; Liang, D.; Zhang, M.; Liao, Y.; Tang, C. Reaction Heterogeneity in the Bridging Effect of Divalent Cations on Polysaccharide Fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidt, E.; Meissl, K. The Applicability of Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy in Waste Management. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

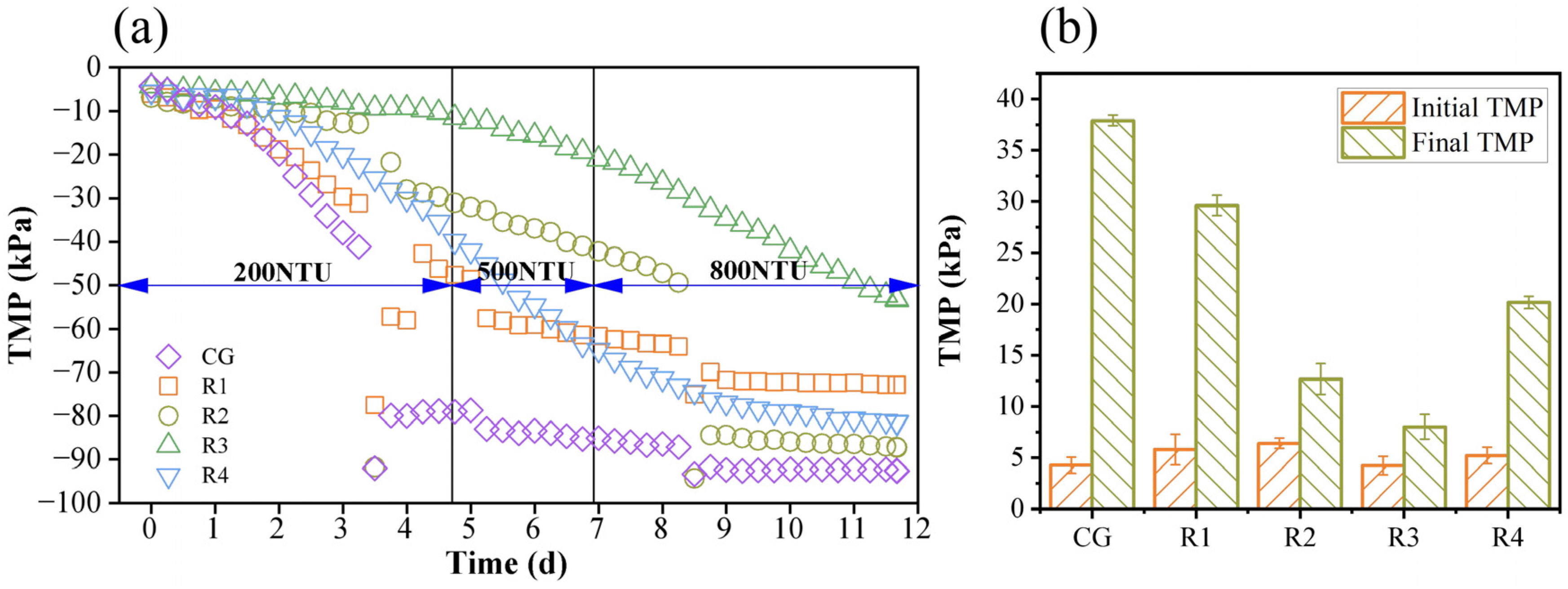

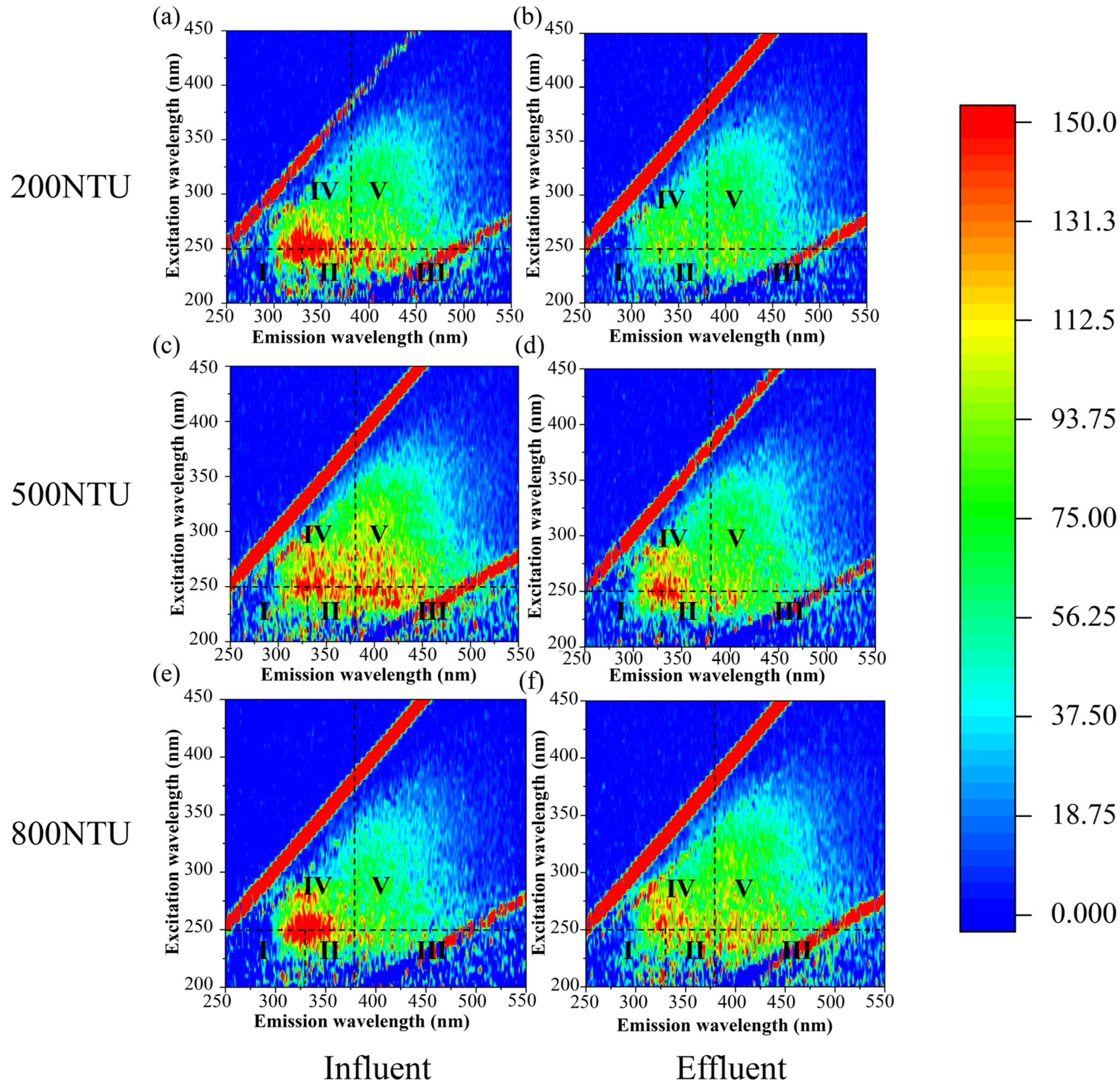
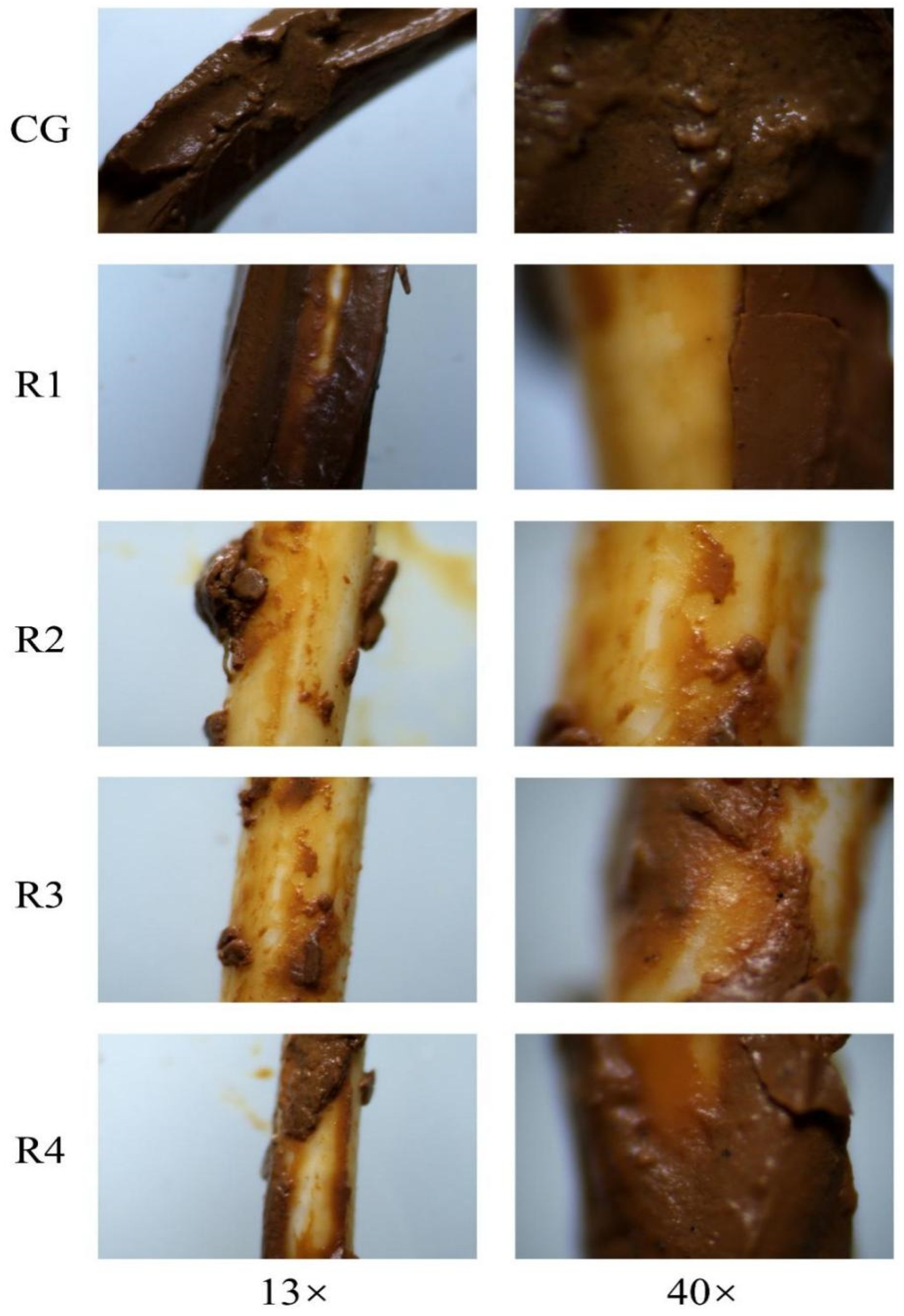
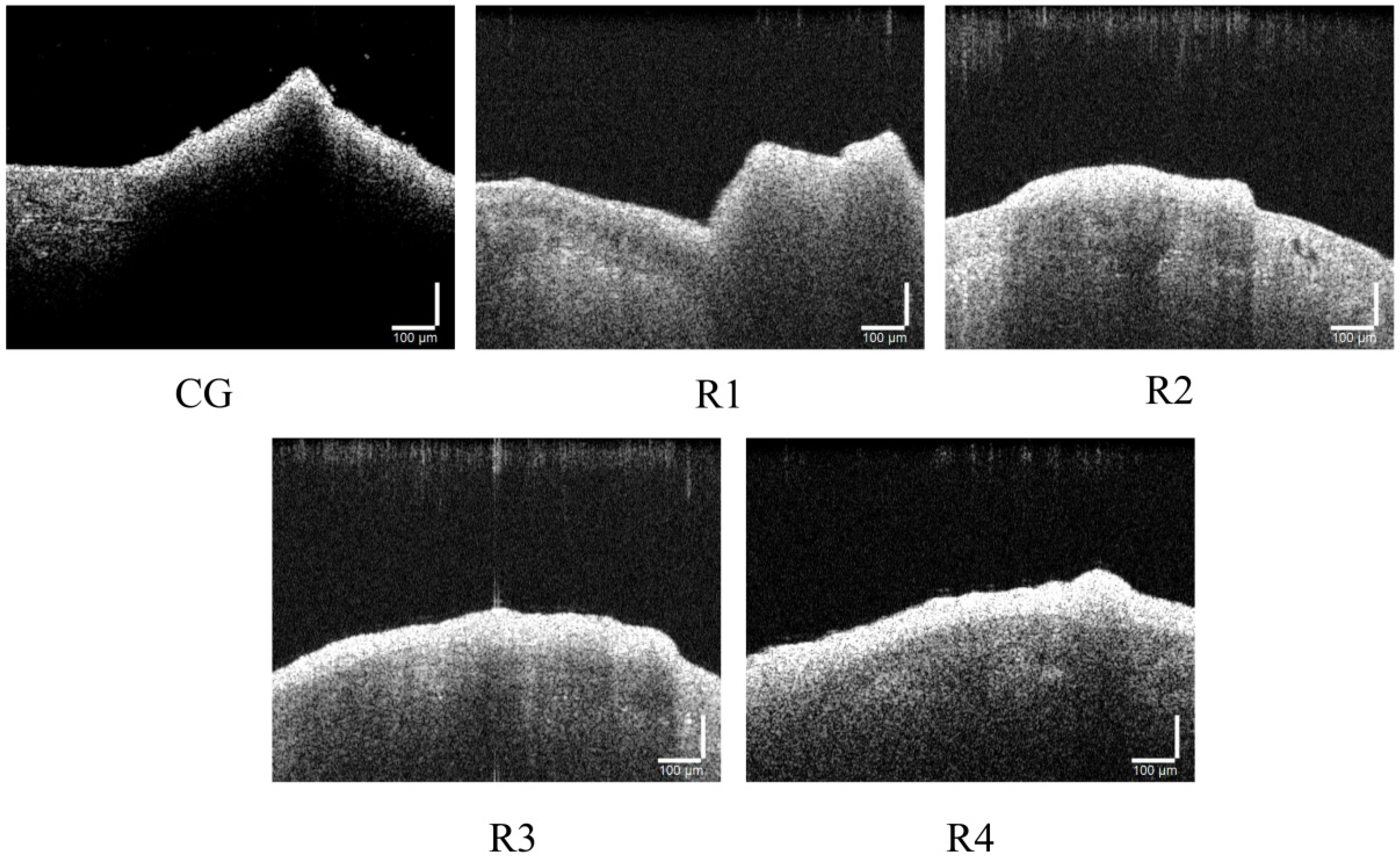



| Parameters | Control Group | Reactor1 | Reactor2 | Reactor3 | Reactor4 | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aeration intensity | 0 | 0.4 m3/(m2·min) | 0.8 m3/(m2·min) | 1.2 m3/(m2·min) | 1.6 m3/(m2·min) | - |
| Stage I | 200 NTU | 200N TU | 200 NTU | 200 NTU | 200 NTU | 115 h |
| Stage II | 500 NTU | 500 NTU | 500 NTU | 500 NTU | 500 NTU | 53 h |
| Stage III | 800 NTU | 800 NTU | 800 NTU | 800 NTU | 800 NTU | 114 h |
| Process | Raw Water | Turbidity (NTU) | UV254 (cm−1) | COD (mg/L) | Aeration Intensity | d(TMP)/dt | Control Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flocculation–UF (backwashing, aeration) | Surface water (containing Sb) | 0.3–1.0 | 0.01–0.013 | - | 0.155 m3/(m2·min) | 0.043 kPa/h | ** | [38] |
| Oxidation-integrated floc-UF (backwashing, aeration) | River water | 9.05–35.1 | - | 5–33 | 5 m3/h | 0.023 kPa/h | ** | [39] |
| Coagulation–UF (aeration) | Lake water | 1.08–2.27 | 0.030–0.052 | - | 40 mL/min | 0.30–0.80 kPa/h | ** | [26] |
| UF (aeration) | TiO2—HA suspension | - | - | - | 3.2 L/min | 0.414 kPa/h | *** | [40] |
| UF (aeration) | River water | 11.3 ± 1.06 | 0.105 ± 0.006 | - | 0.083 m3/(m2·min) | 3 kPa/h | ** | [25] |
| UF (aeration) | Yeast suspension | - | - | - | 0.083 m3/(m2·min) | 1.4 kPa/h | *** | [41] |
| UF (aeration) | Soil model water | 200–800 | 0.020–0.028 | 2.455–3.057 | 1.2 m3/(m2·min) | 0.063–0.284 kPa/h | *** | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Hu, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, A.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X. Effect of In Situ Aeration on Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling Control in Treating Seasonal High-Turbidity Surface Water. Water 2024, 16, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152195
Luo J, Hu Y, Guo X, Wang A, Lin C, Zhang Y, Wang H, Wang Y, Tang X. Effect of In Situ Aeration on Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling Control in Treating Seasonal High-Turbidity Surface Water. Water. 2024; 16(15):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152195
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jiaoying, Yating Hu, Xishou Guo, Ao Wang, Chenghai Lin, Yaru Zhang, Haochun Wang, Yanrui Wang, and Xiaobin Tang. 2024. "Effect of In Situ Aeration on Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling Control in Treating Seasonal High-Turbidity Surface Water" Water 16, no. 15: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152195
APA StyleLuo, J., Hu, Y., Guo, X., Wang, A., Lin, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Wang, Y., & Tang, X. (2024). Effect of In Situ Aeration on Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling Control in Treating Seasonal High-Turbidity Surface Water. Water, 16(15), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152195







