A Cost-Effective and Straightforward Approach for Conducting Short- and Long-Term Biomonitoring of Gold Mine Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Strategy
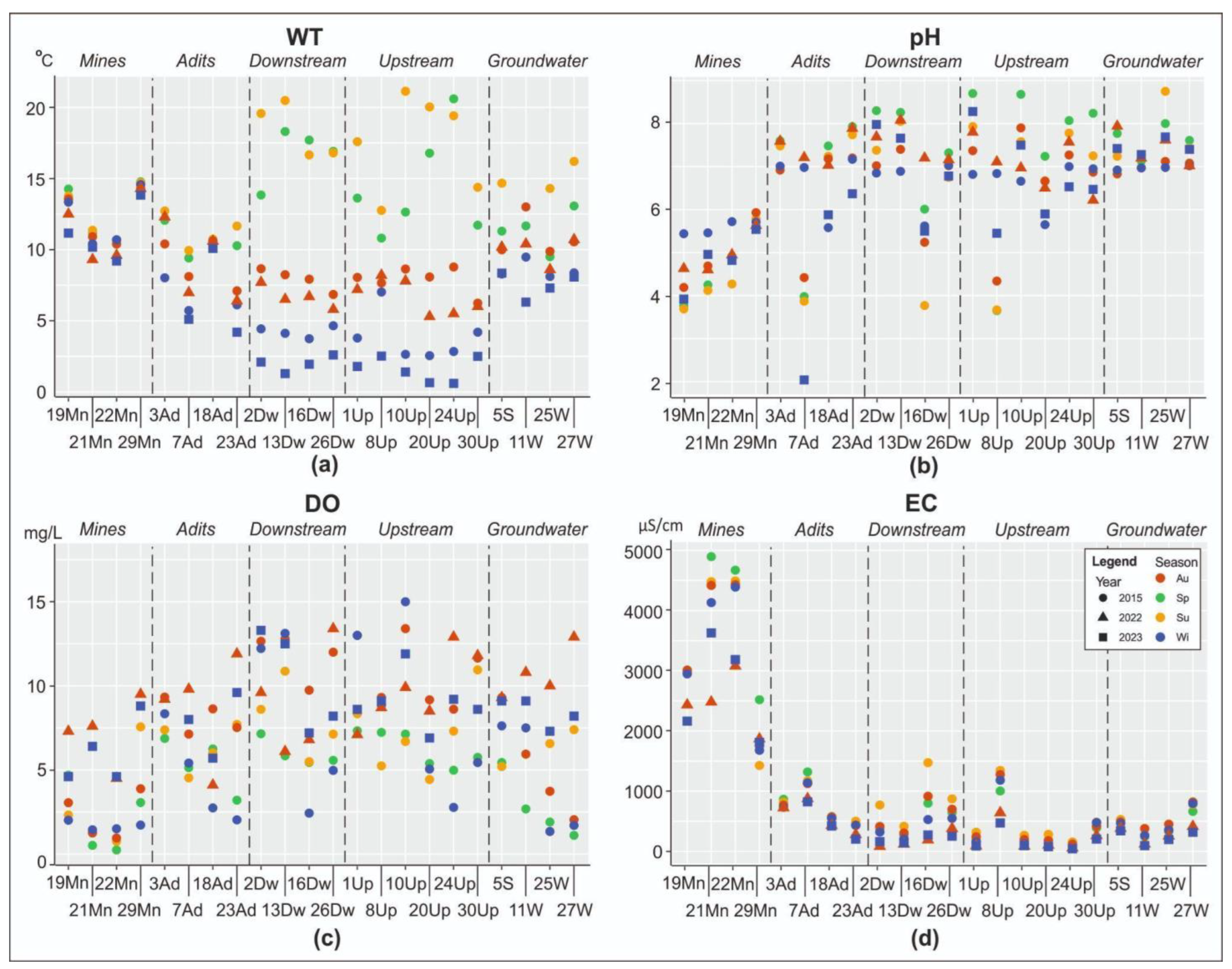
2.3. Physicochemical and Environmental Parameters
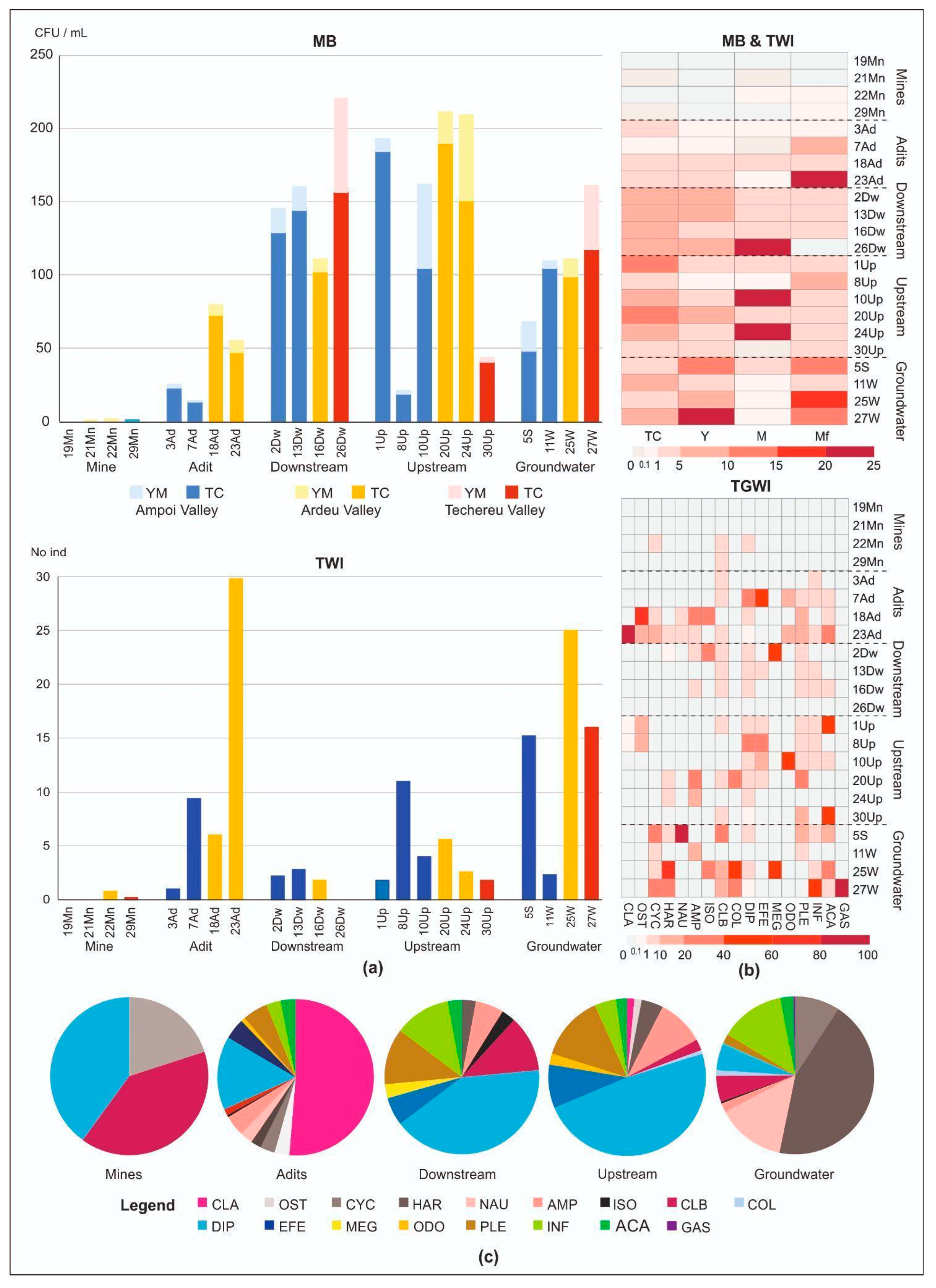
2.4. Culturable Microbiota and Water Invertebrates Assessment
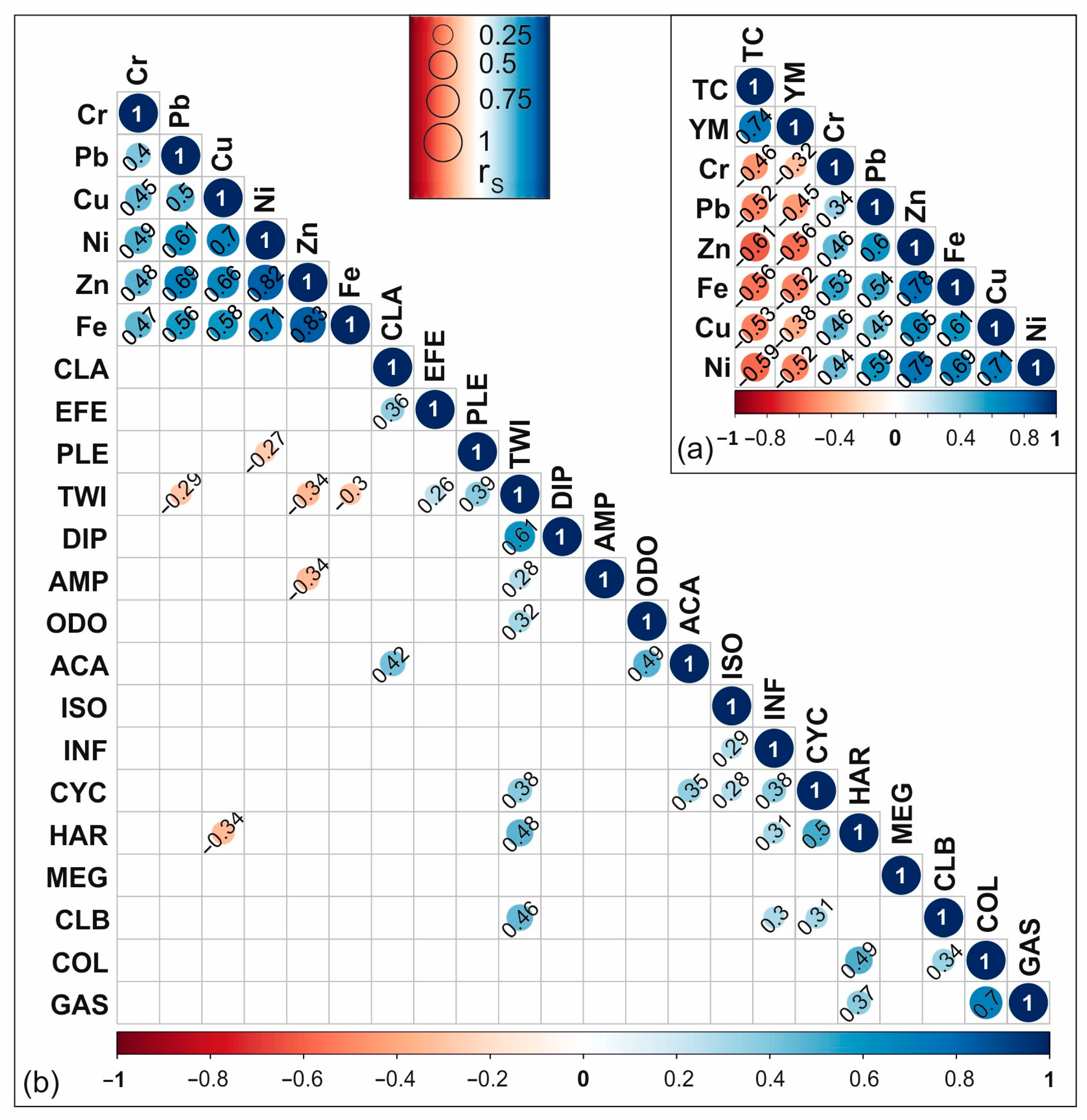
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sites’ Geology and Physicochemical Features of Waters
3.2. Culturable Microbiota and Water Invertebrates in the GMAZ
3.3. The Relationship between Biota, Environment, and Geochemical Features of Water Sites
3.4. Mining Pollution over Time
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ericsson, M.; Löf, O. Mining’s Contribution to National Economies between 1996 and 2016. Miner. Econ. 2019, 32, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munyai, R.; Ogola, H.J.O.; Modise, D.M. Microbial Community Diversity Dynamics in Acid Mine Drainage and Acid Mine Drainage-Polluted Soils: Implication on Mining Water Irrigation Agricultural Sustainability. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 701870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, A.; Arias, J.; López, J.; Santos, L.; Venegas, C.; Duarte, M.; Ortíz-Ardila, A.; de Parra, N.; Campos, C.; Zambrano, C.C. Evaluation of the Effect of Gold Mining on the Water Quality in Monterrey, Bolívar (Colombia). Water 2020, 12, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brännvall, M.-L.; Bindler, R.; Emteryd, O.; Nilsson, M.; Renberg, I. Stable Isotope and Concentration Records of Atmospheric Lead Pollution in Peat and Lake Sediments in Sweden. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 100, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renberg, I.; Brännvall, M.L.; Bindler, R.; Emteryd, O. Stable Lead Isotopes and Lake Sediments—A Useful Combination for the Study of Atmospheric Lead Pollution History. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 292, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakete, S.; Moonga, G.; Wahl, A.-M.; Mambrey, V.; Shoko, D.; Moyo, D.; Muteti-Fana, S.; Tobollik, M.; Steckling-Muschack, N.; Bose-O’Reilly, S. Biomonitoring of Arsenic, Cadmium and Lead in Two Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Areas in Zimbabwe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 4762–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogola, J.S.; Mitullah, W.V.; Omulo, M.A. Impact of gold mining on the environment and human health: A case study in the Migori gold belt, Kenya. Environ. Geochem. Health 2002, 24, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujere, N.; Isidro, M. Impacts of Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining on Water Quality in Mozambique and Zimbabwe. In Practice, Progress, and Proficiency in Sustainability; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 101–119. ISBN 9781466695597. [Google Scholar]
- Shotyk, W.; Weiss, D.; Appleby, P.G.; Cheburkin, A.K.; Gloor, R.; Kramers, J.D.; Reese, S.; Van Der Knaap, W.O. History of Atmospheric Lead Deposition since 12,370 (14)C Yr BP from a Peat Bog, Jura Mountains, Switzerland. Science 1998, 281, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-García, L.C.; Sánchez-Palencia, F.J.; Torres-Ruiz, J. Tertiary and Quaternary Alluvial Gold Deposits of Northwest Spain and Roman Mining (NW of Duero and Bierzo Basins). J. Geochem. Explor. 2000, 71, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, M.B.; Wolfe, A.P. Intensive Pre-Incan Metallurgy Recorded by Lake Sediments from the Bolivian Andes. Science 2003, 301, 1893–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Merino, L.; Martínez Cortizas, A.; Reher, G.S.; López-Sáez, J.A.; Mighall, T.M.; Bindler, R. Reconstructing the Impact of Human Activities in a NW Iberian Roman Mining Landscape for the Last 2500 Years. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 50, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillman, A.L.; Abbott, M.B.; Valero-Garcés, B.L.; Morellon, M.; Barreiro-Lostres, F.; Bain, D.J. Lead Pollution Resulting from Roman Gold Extraction in Northwestern Spain. Holocene 2017, 27, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mighall, T.M.; Timberlake, S.; Foster, I.D.L.; Krupp, E.; Singh, S. Ancient Copper and Lead Pollution Records from a Raised Bog Complex in Central Wales, UK. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, Z. The Importance of Water and Conscious Use of Water. Int. J. Hydrol. 2020, 4, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhariya, D.; Khan, R.; Thakur, G.S. Impact of Mining Activity on Water Resource: An Overview Study. In Proceedings of the National Seminar on Recent Practices & Innovations in Mining Industry, Raipur, India, 19–20 February 2016; pp. 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Gold Mining Industry Environmental Pollution Types and Effects. Available online: https://www.longdom.org/open-access/gold-mining-industry-environmental-pollution-types-and-effects.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Mambou Ngueyep, L.L.; Takougang Kingni, S.; Ayiwouo Ngounouno, M.; Ndi, A.A. The Impact of Gold Mining Exploitation on the Physicochemical Quality of Water: Case of Batouri (Cameroon). Int. J. Energy Water Res. 2021, 5, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrance, K.W.; Redwood, S.D.; Cecchi, A. The Impact of Artisanal Gold Mining, Ore Processing and Mineralization on Water Quality in Marmato, Colombia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4265–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, A.M.; Nieto, J.M.; Olías, M.; Cánovas, C.R. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Seasonal Influence on the Pollution by Acid Mine Drainage in the Odiel River Basin (SW Spain). Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, D.C.; Cociuba, I.; Baciu, C.; Cozma, A. Origin and Geochemistry of Mine Water and Its Impact on the Groundwater and Surface Running Water in Post-Mining Environments: Zlatna Gold Mining Area (Romania). Aquat. Geochem. 2017, 23, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission of the European Communities. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fu, J.; Shi, J.; Jiang, G. Biomonitoring: An Appealing Tool for Assessment of Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Ecosystem. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 606, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Seget, Z.; Cycoń, M.; Kozdrój, J. Metal-Tolerant Bacteria Occurring in Heavily Polluted Soil and Mine Spoil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 28, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashola, M.O.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Babalola, O.O. Heavy Metal Pollution from Gold Mines: Environmental Effects and Bacterial Strategies for Resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Šmejkalová, M.; Mikanová, O.; Borůvka, L. Effects of Heavy Metal Concentrations on Biological Activity of Soil Micro-Organisms. Plant Soil Environ. 2003, 49, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajapaksha, R.M.C.P.; Tobor-Kapłon, M.A.; Bååth, E. Metal Toxicity Affects Fungal and Bacterial Activities in Soil Differently. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2966–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyedu-Ababio, T.K.; Baird, D. Response of Meiofauna and Nematode Communities to Increased Levels of Contaminants in a Laboratory Microcosm Experiment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 63, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.G.; Bett, B.J. The Use of Meiofauna in Marine Pollution Impact Assessment. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1989, 96, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicol, D.M.; Stapleton, M.G. Impact of Acid Mine Drainage on Benthic Communities in Streams: The Relative Roles of Substratum vs. Aqueous Effects. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 119, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dills, G.; Rogers, D.T., Jr. Macroinvertebrate Community Structure as an Indicator of Acid Mine Pollution. Environ. Pollut. 1974, 6, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, P.A.; Hamel, C.; Ayala, A.; Bervoets, L. Macroinvertebrate Community Response to Acid Mine Drainage in Rivers of the High Andes (Bolivia). Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, P.; Reid, I.; Wood, P.J. Changes in Macroinvertebrate Community Structure Provide Evidence of Neutral Mine Drainage Impacts. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberländer-Târnoveanu, E. Aurul și Argintul Daciei—Origine, Exploatare, Analize. In Aurul și argintul antic al României; Muzeul Național de Istorie a României: București, Romania, 2013; pp. 16–35. [Google Scholar]
- Vlad, Ș.-N.; Orlandea, E. Metallogeny of the Gold Quadrilateral: Style and Characteristics of Epithermal—Subvolcanic Mineralized Structures, South Apuseni Mts., Romania. Stud. Univ. Babes-Bolyai Geol. 2004, 49, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlad, S. Perspective Targeting CuAuMo Porphyries of Romanian Carpathians: Blind Porphyry Mineralization and Its Variable Distal Expression as Vein and Skarns. Open Geosci. 2011, 3, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, M.; Zobrist, J.; Senila, M.; Levei, E.-A.; Abraham, B.; Dold, B.; Balteanu, D. Environmental Pollution by Mining Activities—A Case Study in the Criş Alb Valley, Western Carpathians, Romania. Geo-Eco-Marina 2008, 14, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milu, V.; Leroy, J.; Peiffert, C. Water Contamination Downstream from a Copper Mine in the Apuseni Mountains, Romania. Environ. Geol. 2002, 42, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERA-MIN Joint Call 2013 Results: Summary Reports. Available online: https://www.era-min.eu/sites/default/files/docs/era-min_catalogue_2013_0.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Orlandea, E.; Vlad, Ş.-N. A Novel Conceptual Model of Intrusion Related Gold Bearing Systems and Exploration Tools. Stud. Univ. Babes-Bolyai Geol. 2020, 63, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, S.; Tămaş, C.G.; Cauuet, B.; Munoz, M. Lead Isotope Analyses of Gold–silver Ores from Roşia Montană (Romania): A First Step of a Metal Provenance Study of Roman Mining Activity in Alburnus Maior (Roman Dacia). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botezan, C.; Constantin, V.; Meltzer, M.; Radovici, A.; Pop, A.; Alexandrescu, F.; Stefanescu, L. Is There Sustainable Development after Mining? A Case Study of Three Mining Areas in the Apuseni Region (Romania). Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2020, 12, 9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerwerk, N.; Bloesch, J.; Baumgartner, C.; Bittl, T.; Čerba, D.; Csányi, B.; Davideanu, G.; Dokulil, M.; Frank, G.; Grecu, I.; et al. The Danube River Basin. In Rivers of Europe; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 81–180. [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies, M. L’or Controversé de Transylvanie. Rev. Geogr. Est 2009, 49, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcoş, M.; Berbeleac, I.; Bordea, S.; Bordea, J.; Mantea, G.; Boștinescu, S. Republica Socialista România Harta Geologică 74c Zlatna Sheet; Editura Institutului Geologic al României: Bucharest, Romania, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Roșu, E. Neogene Magmatism in the Apuseni Mountains, Romania. Evolution and Geochemical Features. Rom. J. Miner. Deposit 2001, 79, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Papp, D.C. Analysis of the Radiogenic Carbon-14 Record of Groundwater at the Zlatna Post-Mining Site (Romania). Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 16, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, D.; Epure, L.; Meleg, I.N.; Cociuba, I. Preliminary Results on the Quality of Drinking Water Sources in the Runcuri Plateau. Trav. Inst. Spéol. Emil Racovitza 2019, 58, 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- The Power Project. Available online: https://power.larc.nasa.gov (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Find Geospatial Learning Resources. Available online: http://www.learngeomatics.com/ (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA). Available online: https://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/reanalysis/MERRA/data_access/ (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Land Monitoring Service. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R Package Version 1.0.12. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783319242774. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.G.; Carl, P. Performance Analytics: Econometric Tools for Performance and Risk Analysis (R Package Version 2.0.4). 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=PerformanceAnalytics (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: AnRPackage for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. R Package Version 1.0.7. Cran—Package Factoextra. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/factoextra/index.html (accessed on 5 March 2023).
- Badino, G. Cave Temperatures and Global Climatic Change. Int. J. Speleol. 2004, 33, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Gong, X.; Yuan, D.; Jiang, G.; Cao, J.; Lin, Y.; Lo, K.F.A.; Chen, C. Response of Drip Water Temperature to Climate Variability: A Case Study in Xiaoyan Cave, Southwest China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatan, E.-L. Gold Mining Industry Influence on the Environment and Possible Phytoremediation Applications. In Phytorestoration of Abandoned Mining and Oil Drilling Sites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 373–408. ISBN 9780128212004. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, D.; Younger, P.L.; Arnesen, R.-T.; Iversen, E.R.; Banks, S.B. Mine-Water Chemistry: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Environ. Geol. 1997, 32, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkovića, J.; Muhić-Šaracb, T.; Kolarc, M. Chemical Characterization of Acid Mine Drainage from an Abandoned Gold Mine Site. Chem. Listy 2014, 108, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lintnerova, O.; Sucha, V.; Stresko, V. Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Acid Mine Fe-Precipitates from the Mine Slovak Mining Regions. Geol. Carpathica 1999, 50, 394–404. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Ganesh, A. Water Quality Indicators: Bacteria, Coliphages, Enteric Viruses. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2013, 23, 484–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, G.; Bharagava, R.N.; Kaithwas, G.; Raj, A. Microbial Indicators, Pathogens and Methods for Their Monitoring in Water Environment. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, C.; Drăghici, C.; Borda, D. The Polluting Effect of Slaughterhouse Waste Waters Discharged into Surface Waters. In Proceedings of the Animals and Environment, Volume 2: Proceedings of the XIIth ISAH Congress on Animal Hygiene, Warsaw, Poland, 4–8 September 2005; Krynski, A., Wrzesien, R., Eds.; BEL Studio sp. z.o.o: Warsaw, Poland, 2005; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Oarga, A.; Griessler Bulc, T.; Jenssen, P.; Mulec, J. Monitoring of Microbial Indicator Groups in Organically Heavily Loaded Wastewater Treatment Systems by Using RIDA@COUNT Kits. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 3886–3893. [Google Scholar]
- Some, S.; Mondal, R.; Mitra, D.; Jain, D.; Verma, D.; Das, S. Microbial Pollution of Water with Special Reference to Coliform Bacteria and Their Nexus with Environment. Energy Nexus 2021, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, D.R.; Cociuba, I.; Epure, L.; Cruceru, N.; Meleg, I.N. The Interplay of Environment and Biota in Assessing the Freshwater Quality in Karst. Diversity 2022, 14, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epure, L.; Borda, D.R. Groundwater Contamination and the Relationship between Water Chemistry and Biotic Components in a Karst System (Bihor Mountains, Romania). Trav. Inst. Speol. 2014, 53, 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Borda, D.; Năstase-Bucur, R.; Spînu, M.; Uricariu, R.; Mulec, J. Aerosolized Microbes from Organic Rich Materials: Case Study of Bat Guano from Caves in Romania. J. Caves. Karst Stud. 2014, 76, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulec, J.; Oarga, Á. Ecological Evaluation of Air and Water Habitats in the Great Cavern of Santo Tomás, Cuba. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2014, 85, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerič, B.; Pipan, T.; Mulec, J. Diversity of Culturable Bacteria and Meiofauna in the Epikarst of Škocjanske Jame Caves (Slovenia). Acta Carsol. 2016, 33, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiz, L.; Groth, I.; Gonzalez, I.; Saiz-Jimenez, C. Microbiological Study of the Dripping Waters in Altamira Cave (Santillana Del Mar, Spain). J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 36, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.B.; Hallberg, K.B. The Microbiology of Acidic Mine Waters. Res. Microbiol. 2003, 154, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, N.P. Microorganisms and Their Application in Mining and Allied Industries. Mater. Today 2023, 72, 2886–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterritt, R.M.; Lester, J.N. The Microbiological Control of Mine Waste Pollution. Miner. Environ. 1979, 1, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, L.; Falagán, C. The Microbiology of Metal Mine Waste: Bioremediation Applications and Implications for Planetary Health. Geohealth 2021, 5, e2020GH000380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulec, J.; Krištůfek, V.; Chroňáková, A. Monitoring of Microbial Indicator Groups in Caves through the Use of RIDA®COUNT Kits. Acta Carsol. 2012, 41, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulec, J.; Krištůfek, V.; Chroňáková, A. Comparative Microbial Sampling from Eutrophic Caves in Slovenia and Slovakia Using RIDA®COUNT Test Kits. Int. J. Speleol. 2012, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman Wieder, R.; Lang, G. Influence of Wetlands and Coal Mining on Stream Water Chemistry. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1984, 23, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobberteen, R.A.; Nickerson, N.H. Use of Created Cattail (Typha) Wetlands in Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Manag. 1991, 15, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, O.; Cameselle, C.; Reddy, K.R. Mine Tailing Disposal Sites: Contamination Problems, Remedial Options and Phytocaps for Sustainable Remediation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.-E.; Sloane, D.R.; Strezov, V. Assessment of Impacts of Coal Mining in the Region of Sydney, Australia on the Aquatic Environment Using Macroinvertebrates and Chlorophyll as Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerhardt, A.; de Bisthoven, L.J.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Effects of Acid Mine Drainage and Acidity on the Activity of Choroterpes Picteti (Ephemeroptera: Leptophlebiidae). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 48, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.A.; Ryan, M.M. Impact of Mining and Industrial Pollution on Stream Macroinvertebrates: Importance of Taxonomic Resolution, Water Geochemistry and EPT Indices for Impact Detection. Hydrobiologia 2016, 772, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wu, N.; Tang, T.; Cai, Q.; Park, Y.-S. Effects of Heavy Metals on Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities in High Mountain Streams. Ann. Limnol. 2010, 46, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Sánchez, A.E.; Rodríguez-Romero, A.J.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; López-López, E.; Sundermann, A. Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages in Rivers Influenced by Mining Activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iepure, S.; Selescu, L. Relationship between Heavy Metals and Hyporheic Invertebrate Community Structure in the Middle Basin of the Aries River (Transylvania, North-Western Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2009, 7, 125–148. [Google Scholar]
- Bonacina, L.; Fasano, F.; Mezzanotte, V.; Fornaroli, R. Effects of Water Temperature on Freshwater Macroinvertebrates: A Systematic Review. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2023, 98, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, C.J.; McGarvey, D.J.; Larson, J.H.; Cross, W.F.; Allen, D.C.; Benke, A.C.; Brey, T.; Huryn, A.D.; Jones, J.; Murphy, C.A.; et al. Precipitation and Temperature Drive Continental-Scale Patterns in Stream Invertebrate Production. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamid, A.; Bhat, S.U.; Jehangir, A. Assessment of Ecological Characteristics of Macroinvertebrate Communities and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors in a Stream Ecosystem. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 37, 746–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angilletta, M.J. Evolutionary Thermal Biology. In Thermal Adaptation: A Theoretical and Empirical Synthesis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castella, E.; Adalsteinsson, H.; Brittain, J.E.; Gislason, G.M.; Lehmann, A.; Lencioni, V.; Lods-Crozet, B.; Maiolini, B.; Milner, A.M.; Olafsson, J.S.; et al. Macrobenthic Invertebrate Richness and Composition along a Latitudinal Gradient of European Glacier-Fed Streams. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1811–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, H.F.; Rivers-Moore, N. Ecological Consequences of Global Climate Change for Freshwater Ecosystems in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2014, 110, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimm, N.B.; Fisher, S.G. Stability of Periphyton and Macroinvertebrates to Disturbance by Flash Floods in a Desert Stream. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1989, 8, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Death, R.G. The Effect of Habitat Stability on Benthic Invertebrate Communities: The Utility of Species Abundance Distributions. Hydrobiologia 1996, 317, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiles, M.R.; Wallace, J.B. Macroinvertebrate Production in a Headwater Stream during Recovery from Anthropogenic Disturbance and Hydrologic Extremes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 2402–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jowett, I.G. Hydraulic Constraints on Habitat Suitability for Benthic Invertebrates in Gravel-Bed Rivers. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, C.; Caldwell, P.; Sun, G.; McNulty, S.; Zhang, Y. A Model to Predict Stream Water Temperature across the Conterminous USA. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2178–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, R.; Nukazawa, K.; Kazama, S.; Takemon, Y. Variation in Benthic Invertebrate Abundance along Thermal Gradients within Headwater Streams of a Temperate Basin in Japan. Hydrobiologia 2015, 762, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, C.K.; Hering, D. Community Structure or Function: Effects of Environmental Stress on Benthic Macroinvertebrates at Different Spatial Scales. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1380–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Pyne, M.I.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Cuhaciyan, C.C.; Carlisle, D.M. Developing Linkages between Species Traits and Multiscaled Environmental Variation to Explore Vulnerability of Stream Benthic Communities to Climate Change. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 1441–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdonschot, R.C.M.; Kail, J.; McKie, B.G.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. The Role of Benthic Microhabitats in Determining the Effects of Hydromorphological River Restoration on Macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 2016, 769, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonard, P.; Estrada Rendon, C.M.; Amara, G.; Roussy, J.; Tobin, J.; Degorce-Dumas, J.R. Natural Attenuation Study of the Impact of Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) in the Site of Carnoulès. In Biohydrometallurgy and the Environment Toward the Mining of the 21st Century—Proceedings of the International Biohydrometallurgy Symposium; Process Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 587–594. ISBN 9780444501936. [Google Scholar]
- Sakala, E.; Fourie, F.; Gomo, M.; Madzivire, G. Natural Attenuation of Acid Mine Drainage by Various Rocks in the Witbank, Ermelo and Highveld Coalfields, South Africa. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Zipper, C.E.; Rose, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; Nairn, R.; McDonald, L.M.; Kleinmann, R.L. Review of Passive Systems for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Mulligan, C.N. Natural Attenuation Processes for Remediation of Arsenic Contaminated Soils and Groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurjovec, J.; Ptacek, C.J.; Blowes, D.W. Acid Neutralization Mechanisms and Metal Release in Mine Tailings: A Laboratory Column Experiment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tum, S.; Toda, K.; Matsui, T.; Kikuchi, R.; Kong, S.; Meas, P.; Ear, U.; Ohtomo, Y.; Otake, T.; Sato, T. Seasonal Effects of Natural Attenuation on Drainage Contamination from Artisanal Gold Mining, Cambodia: Implication for Passive Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
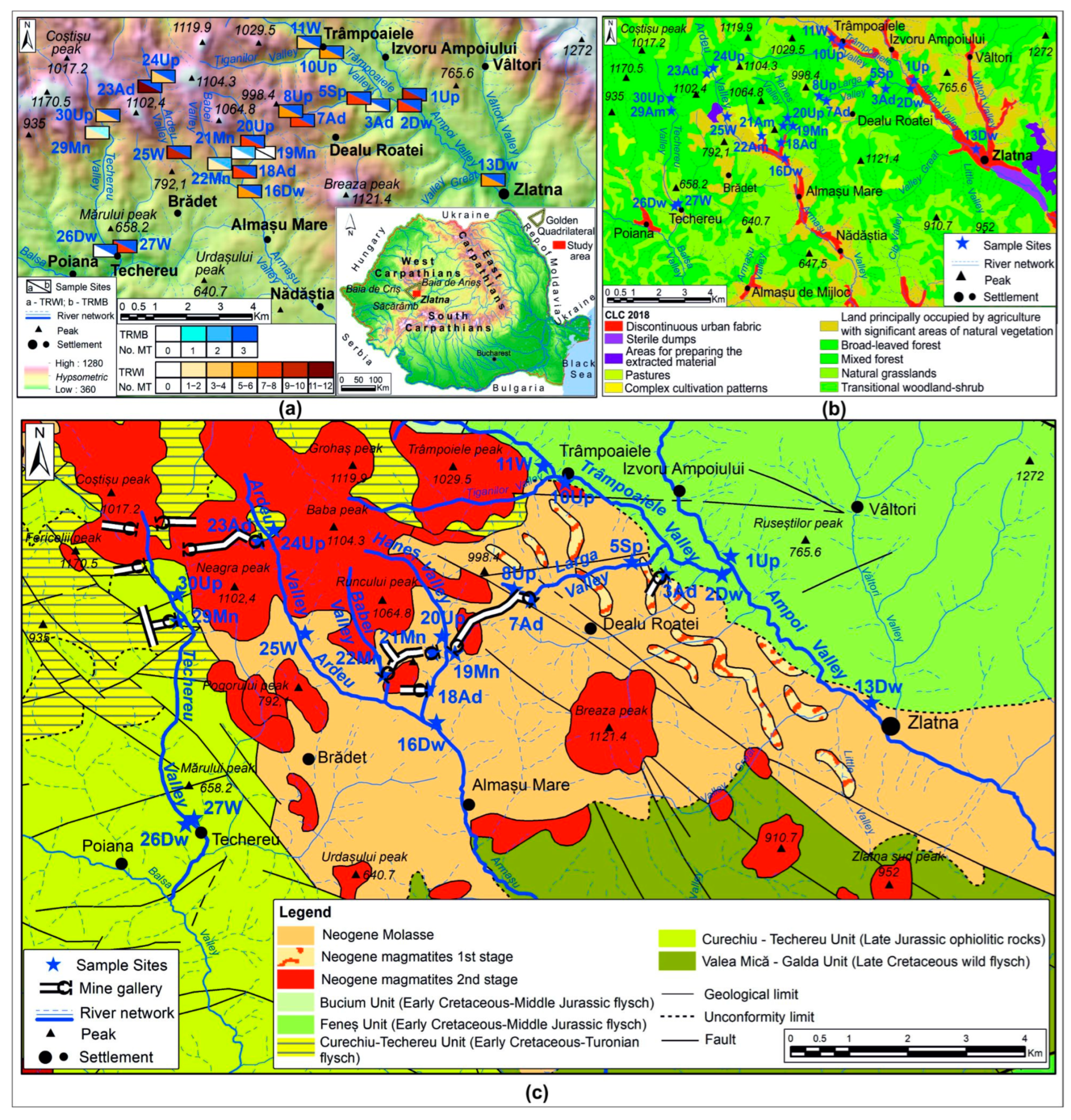
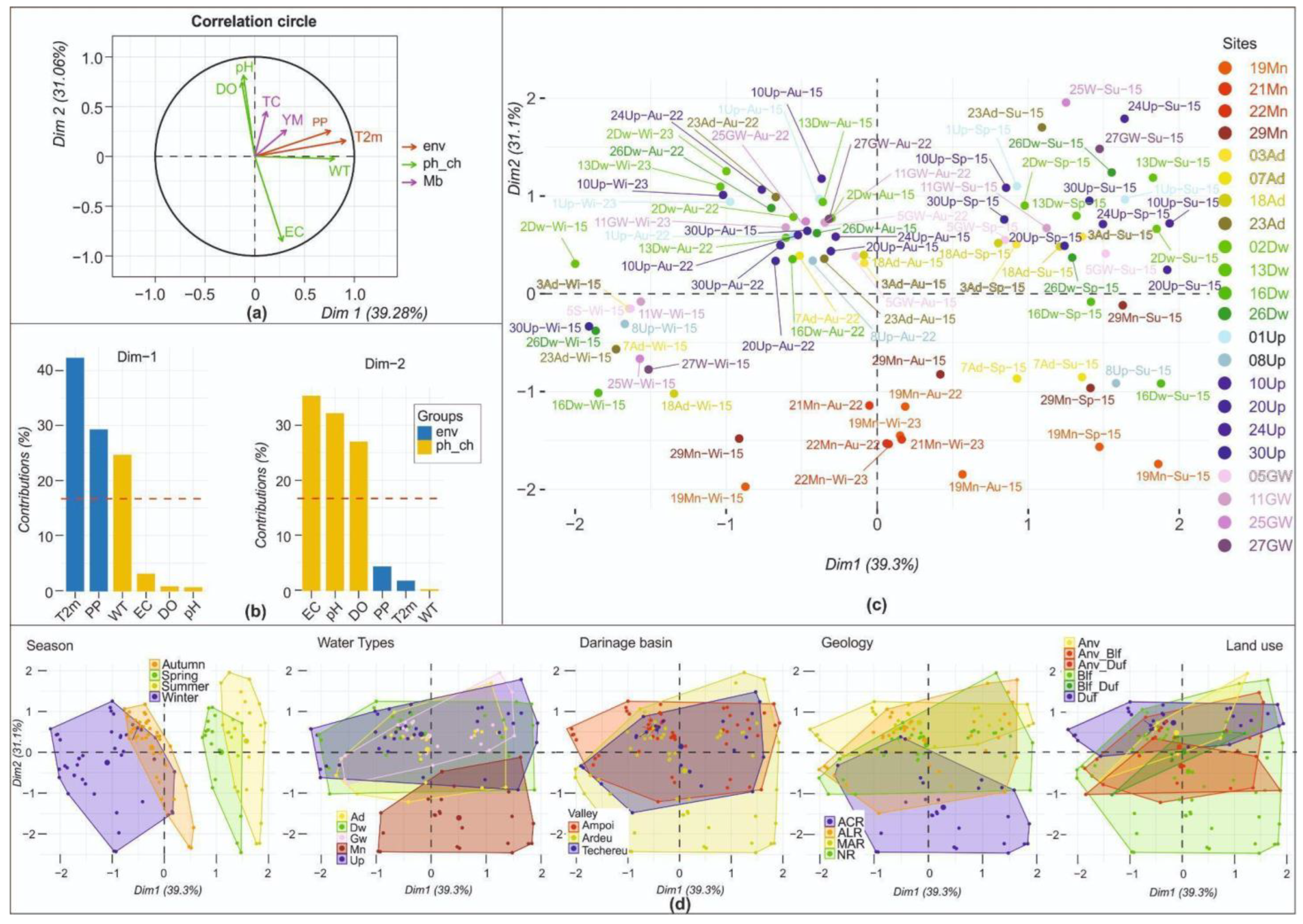
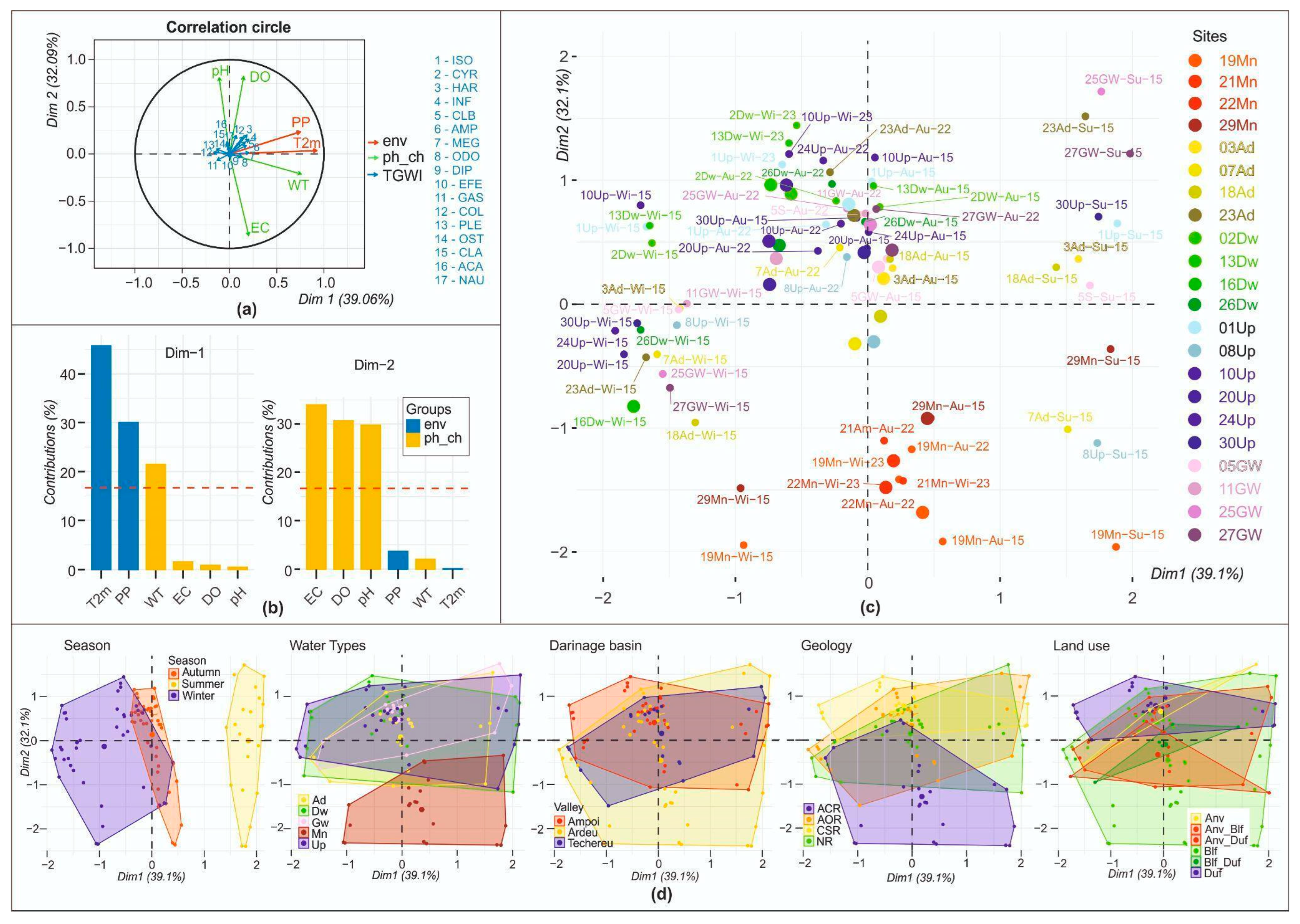
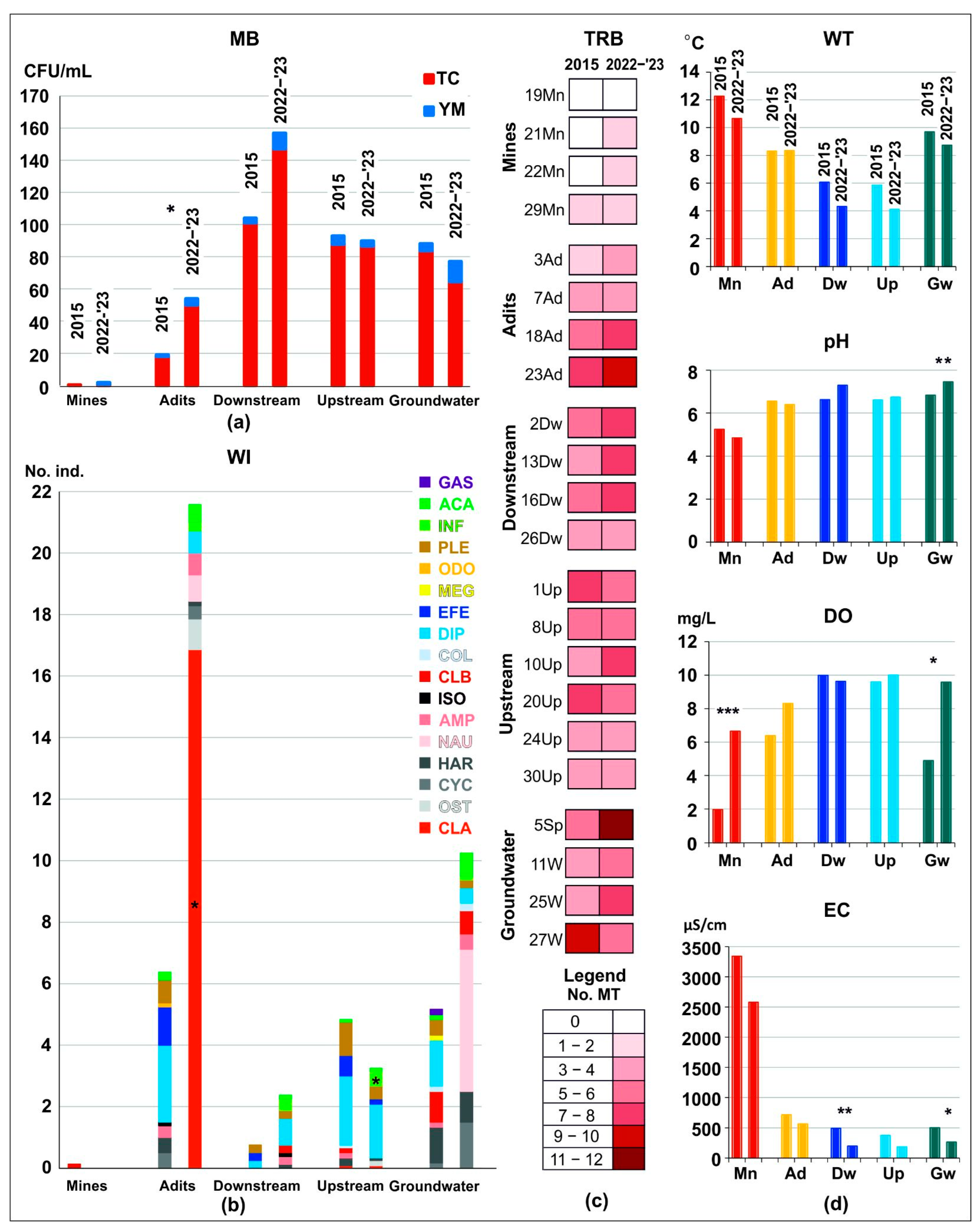
| Drainage Basin | Site Name and Water Type | Site Coding | Water Sampling Source | Geology | Land Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampoi | Ampoi upstream | 1 Up | surface running | CSR | Duf |
| Trâmpoaiele downstream | 2 Dw | surface running | CSR | Duf | |
| IPEG adit | 3 Ad | natural pool with vegetation/bog | NR | Blf | |
| Larga spring | 5 S | concrete basin | NR | Anv_Blf | |
| Larga adit | 7 Ad | free flow, abundant vegetation/bog | ACR | Anv_Blf | |
| Larga creek | 8 Up | surface running | ACR | Blf | |
| Trâmpoaiele upstream | 10 Up | surface running | CSR | Duf | |
| Trâmpoaiele well | 11 W | groundwater | CSR | Duf | |
| Ampoi downstream | 13 Dw | surface running | CSR | Duf | |
| Ardeu | Ardeu downstream | 16 Dw | surface running | NR | Anv_Duf |
| Toți Sfinții adit | 18 Ad | free flow, abundant vegetation/bog | NR | Blf_Duf | |
| Haneș I mine | 19 Mn | concrete drain with free flow | ACR | Blf | |
| Haneș upstream | 20 Up | running | NR | Blf | |
| Haneș II mine | 21 Mn | small concrete pool with free flow/bog | ACR | Blf | |
| Valea Babei mine | 22 Mn | small concrete pool with free flow/bog | ACR | Blf | |
| 23 August adit | 23 Ad | large natural pool with abundant vegetation/bog | AOR | Blf | |
| Ardeu upstream | 24 Up | surface running | AOR | Blf | |
| Ardeu well | 25 W | groundwater | NR | Anv | |
| Techereu | Techereu downstream | 26 Dw | surface running | AOR | Anv_Blf |
| Techereu well | 27 W | groundwater | AOR | Anv_Blf | |
| Podul Ionului mine | 29 Mn | free flow/bog | AOR | Blf | |
| Techereu upstream | 30 Up | running | AOR | Blf |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borda, D.R.; Cociuba, I.; Cruceru, N.; Papp, D.C.; Meleg, I.N. A Cost-Effective and Straightforward Approach for Conducting Short- and Long-Term Biomonitoring of Gold Mine Waters. Water 2023, 15, 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162883
Borda DR, Cociuba I, Cruceru N, Papp DC, Meleg IN. A Cost-Effective and Straightforward Approach for Conducting Short- and Long-Term Biomonitoring of Gold Mine Waters. Water. 2023; 15(16):2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162883
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorda, Daniela R., Ioan Cociuba, Nicolae Cruceru, Delia C. Papp, and Ioana N. Meleg. 2023. "A Cost-Effective and Straightforward Approach for Conducting Short- and Long-Term Biomonitoring of Gold Mine Waters" Water 15, no. 16: 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15162883





