Presence of Microplastics in the Food Web of the Largest High-Elevation Lake in North America
Abstract
1. Introduction
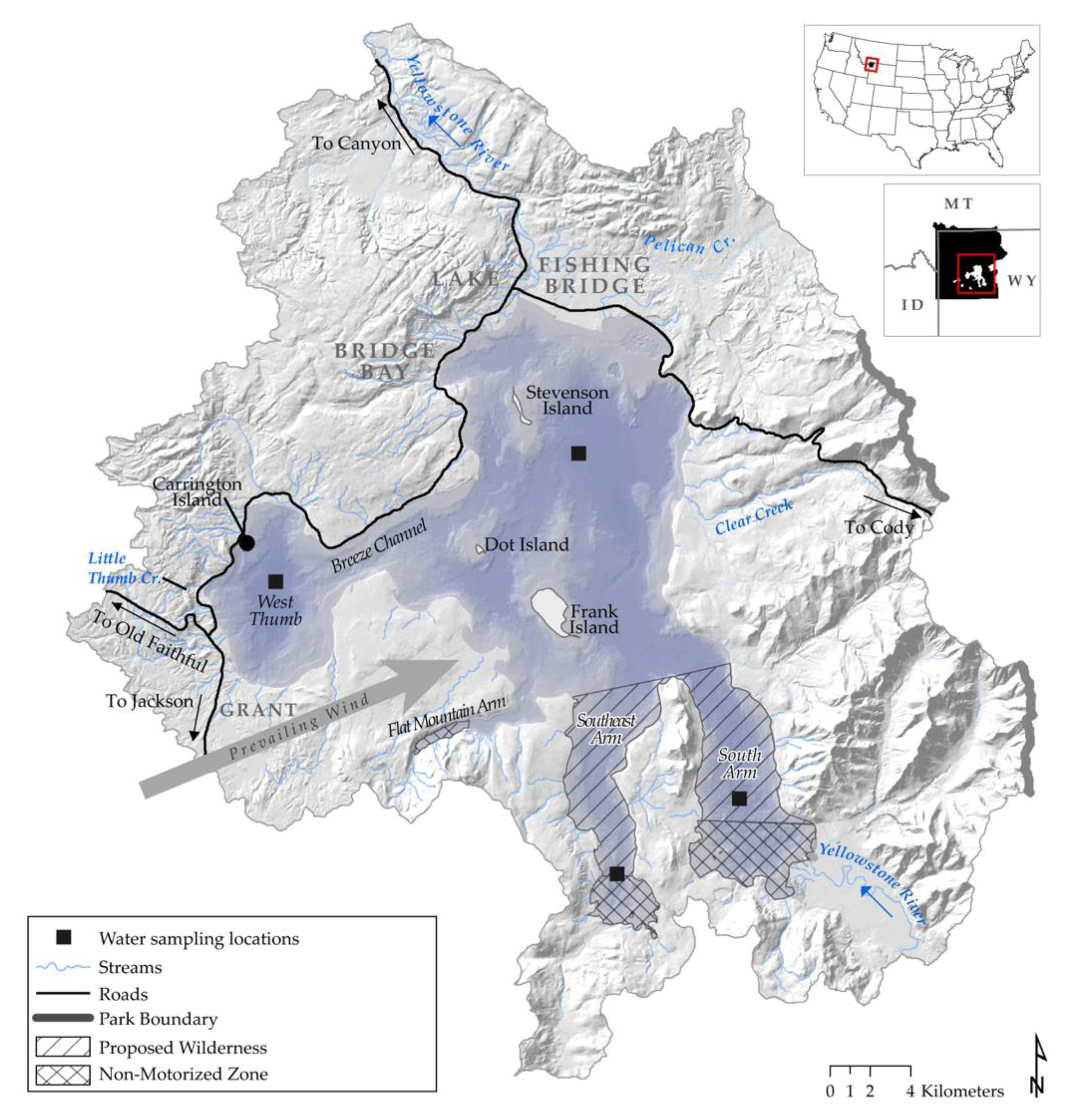
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrade, M.C.; Winemiller, K.O.; Barbosa, P.S.; Fortunati, A.; Chelazzi, D.; Cincinelli, A.; Giarrizzo, T. First account of plastic pollution impacting freshwater fishes in the Amazon: Ingestion of plastic debris by piranhas and other serrasalmids with diverse feeding habits. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekman, M.B.; Wekerle, C.; Lorenz, C.; Primpke, S.; Hasemann, C.; Gerdts, G.; Bergmann, M. Tying up loose ends of microplastic pollution in the Arctic: Distribution from the sea surface through the water column to deep-sea sediments at the Hausgarten Observatory. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4079–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the environment and human health: Current consensus and future trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assas, M.; Qiu, X.; Chen, K.; Ogawa, H.; Xu, H.; Shimasaki, Y.; Oshima, Y. Bioaccumulation and reproductive effects of fluorescent microplastics in medaka fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.F.M.; Moreira, F.T.; Turra, A. Trophic transference of microplastics under a low exposure scenario: Insights on the likelihood of particle cascading along marine food-webs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kurobe, T.; Flores, I.; Teh, S.J. Early warning signs of endocrine disruption in adult fish from the ingestion of polyethylene with and without sorbed chemical pollutants from the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, S.; Huang, G.Y.; Lee, I.; Schlenk, D. Fish and seabird gut conditions enhance desorption of estrogenic chemicals from commonly-ingested plastic items. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4588–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. The impact of polystyrene microplastics on feeding, function and fecundity in the marine copepod Calanus helgolandicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Lopes, C.; Oliveira, P.; Bessa, F.; Otero, V.; Henriques, B.; Raimundo, J.; Caetano, M.; Vale, C.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics in wild fish from North East Atlantic Ocean and its potential for causing neurotoxic effects, lipid oxidative damage, and human health risks associated with ingestion exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 134625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Gasperi, J.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Tassin, B. Plastic particle ingestion by wild freshwater fish: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12974–12988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Poirier, D.G.; Helm, P.A.; Bayoumi, M.; Rochman, C.M. No evidence of spherical microplastics (10–300 μm) translocation in adult rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after a two-week dietary exposure. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, K.J.; Yeatman, E. Microplastic hotspots in the Snake and Lower Columbia rivers: A journey from the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem to the Pacific Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, P.; Pizzul, E.; Bertoli, M.; Anselmi, S.; Kušće, M.; Menconi, V.; Prearo, M.; Renzi, M. First insights into plastic and microplastic occurrence in biotic and abiotic compartments, and snow from a high-mountain lake (Carnic Alps). Chemosphere 2020, 265, 129121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.R.; Le Roux, G.; Durántez Jiménez, P.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, S.M. The effects of microplastic pollution on aquatic organisms. In Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Environments: An Emerging Matter of Environmental Urgency; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 249–270. ISBN 9780128137475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdogan, Z.; Guven, B. Microplastics in the environment: A critical review of current understanding and identification of future research needs. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Places in Yellowstone—Yellowstone National Park (U.S. National Park Service). Available online: https://www.nps.gov/yell/learn/kidsyouth/places.htm (accessed on 28 March 2020).
- Koel, T.M.; Tronstad, L.M.; Arnold, J.L.; Gunther, K.A.; Smith, D.W.; Syslo, J.M.; White, P.J. Predatory fish invasion induces within and across ecosystem effects in Yellowstone National Park. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Park Service Visitation Statistics—Yellowstone National Park (U.S. National Park Service). Available online: https://www.nps.gov/yell/planyourvisit/visitationstats.htm (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Kaplinski, M.A. Geomorphology and Geology of Yellowstone Lake, Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. Master’s Thesis, Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gresswell, R.E.; Liss, W.J.; Larson, G.L.; Bartlein, P.J. Influence of basin-scale physical variables on life history characteristics of cutthroat trout in Yellowstone Lake. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1997, 17, 1046–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, N.G. Limnology of Yellowstone Lake in Relation to the Cutthroat Trout; US Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Koel, T.M.; Arnold, J.L.; Bigelow, P.E.; Brenden, T.O.; Davis, J.D.; Detjens, C.R.; Doepke, P.D.; Ertel, B.D.; Glassic, H.C.; Gresswell, R.E.; et al. Yellowstone Lake Ecosystem restoration: A case study for invasive fish management. Fishes 2020, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzycki, J.R.; Beauchamp, D.A.; Yule, D.L. Effects of introduced lake trout on native cutthroat trout in Yellowstone Lake. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syslo, J.M.; Guy, C.S.; Koel, T.M. Feeding ecology of native and nonnative salmonids during the expansion of a nonnative apex predator in Yellowstone Lake, Yellowstone National Park. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2016, 145, 476–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronstad, L.M.; Hall, R.O.; Koel, T.M.; Gerow, K.G.; Hall, R.O., Jr.; Koel, T.M.; Gerow, K.G. Introduced lake trout produced a four-level trophic cascade in Yellowstone Lake. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2010, 139, 1536–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käppler, A.; Fischer, D.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Schernewski, G.; Labrenz, M.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Voit, B. Analysis of environmental microplastics by vibrational microspectroscopy: FTIR, Raman or both? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8377–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, S.; Chen, M.; Wagner, J.; Wang, Z.M.; Wall, S. Molecular identification of polymers and anthropogenic particles extracted from oceanic water and fish stomach—A Raman micro-spectroscopy study. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellasi, A.; Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Galafassi, S.; Volta, P.; Bettinetti, R. Microplastic contamination in freshwater environments: A review, focusing on interactions with sediments and benthic organisms. Environments 2020, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, M.-S.; Lee, J.-K.; Park, J.-H.; Zoh, K.-D. Distributions of microplastics in surface water, fish, and sediment in the vicinity of a sewage treatment plant. Water 2020, 12, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Jürgens, M.D.; Lahive, E.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Vijver, M.G. The influence of exposure and physiology on microplastic ingestion by the freshwater fish Rutilus rutilus (roach) in the River Thames, UK. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahney, J.; Hallerud, M.; Heim, E.; Hahnenberger, M.; Sukumaran, S. Plastic rain in protected areas of the United States. Science 2020, 368, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Cárdenas, A.; O’Halloran, J.; van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; Jansen, M.A.K. Rapid fragmentation of microplastics by the freshwater amphipod Gammarus duebeni (Lillj.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.Y.; Bruce, T.F.; Bridges, W.C.; Klaine, S.J. Responses of Hyalella azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, C.J.; Feiner, Z.S.; Malinich, T.D.; Höök, T.O. A meta-analysis of the effects of exposure to microplastics on fish and aquatic invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, D.; Duarte, B.; Paiva, F.; Caçador, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 178, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Prat, J.; Mudrock, E.; Hettinger, R.; et al. A ubiquitous tire rubber–derived chemical induces acute mortality in coho salmon. Science 2020, 371, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqash, N.; Prakash, S.; Kapoor, D.; Singh, R. Interaction of freshwater microplastics with biota and heavy metals: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample Type | Locations | Number of Samples | Number of Samples with Extracted Particles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water surface | Stevenson Island, West Thumb, South Arm, Southeast Arm | 4 | 4 |
| Water vertical | Stevenson Island, West Thumb, South Arm, Southeast Arm | 4 | 3 |
| Amphipod | Carrington Island | 32 | 1 |
| Lake trout | Adjacent to Stevenson Island | 5 | 2 |
| Yellowstone cutthroat trout | Adjacent to Stevenson Island | 5 | 1 |
| Sample Type | Location | Number of Particles in Sample | Color of Particles (Count) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water surface | Stevenson Island | 11 | Black (2), blue (2), red (3), light blue (1), green/blue * (1), brown (2) |
| Water surface | West Thumb | 7 | White (2), black (1), green (2), blue * (2) |
| Water surface | South Arm | 11 | Red * (2), blue * (2), black (2), dark blue (1), black/grey (1), white/grey (1), red (1), green (1) |
| Water surface | Southeast Arm | 3 | Black/grey (1), tan (1), light blue (1) |
| Water vertical | West Thumb | 5 | Black (2), blue (3), green (1) |
| Water vertical | South Arm | 3 | Light blue (1), red (1), green (1) |
| Water vertical | Southeast Arm | 2 | Blue * (1), grey (1) |
| Amphipod | Carrington Island | 1 | Green/blue * (1) |
| Lake trout | Adjacent to Stevenson Island | 2 | Black * (1), blue (1) |
| Lake trout | Adjacent to Stevenson Island | 1 | Blue (1) |
| Yellowstone cutthroat trout | Adjacent to Stevenson Island | 3 | Blue (3) |
| Sample Type | Location | Material Identification | Particle Measurements (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water surface | Stevenson Island | Glass fiber | 0.62 (length), 0.03 (width) |
| Water surface | Stevenson Island | Polyvinyl alcohol material (PVA) * | NA |
| Water surface | West Thumb | Isotactic polypropylene * | 0.51 (diameter) |
| Water surface | West Thumb | Glass fiber | 0.48 (length), 0.03 (width) |
| Water surface | South Arm | Glass fiber | 2.46 (length) |
| Water surface | South Arm | Cellulosic material | 0.974 (length) |
| Water vertical | Southeast Arm | Cellulosic material | 1.52 (length), 0.03 (width) |
| Amphipod | Carrington Island | Tyrin 4211 (chlorinated polyethylene) * | 0.68 (length), 0.03 (width) |
| Lake trout | Adjacent to Stevenson Island | Polysulfide rubber * | 1.95 (length), 0.03 (width) |
| Lake trout | Adjacent to Stevenson Island | Cellulose fiber | 1.33 (length), 0.02 (width) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Driscoll, S.C.; Glassic, H.C.; Guy, C.S.; Koel, T.M. Presence of Microplastics in the Food Web of the Largest High-Elevation Lake in North America. Water 2021, 13, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030264
Driscoll SC, Glassic HC, Guy CS, Koel TM. Presence of Microplastics in the Food Web of the Largest High-Elevation Lake in North America. Water. 2021; 13(3):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030264
Chicago/Turabian StyleDriscoll, Stephanie C., Hayley C. Glassic, Christopher S. Guy, and Todd M. Koel. 2021. "Presence of Microplastics in the Food Web of the Largest High-Elevation Lake in North America" Water 13, no. 3: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030264
APA StyleDriscoll, S. C., Glassic, H. C., Guy, C. S., & Koel, T. M. (2021). Presence of Microplastics in the Food Web of the Largest High-Elevation Lake in North America. Water, 13(3), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030264






