Abstract
Nutrient enrichment and eutrophication are among the main problems that lead to the deterioration of water quality in lakes and reservoirs. In this study, spatial and temporal variations in the concentrations of organic and inorganic species of nitrogen and phosphorus in the water column of Lake Paranoá-DF (Brazil) were evaluated between 2016 and 2017. Seasonality was the main factor in the variations in concentrations of the investigated parameters. Additionally, we found differences in behavior for different nutrients and other variables that indicate different main sources of each nutrient as well as different biogeochemical processes predominating in each season. For example, the electrical conductivity (EC), dissolved silicon, PO43−, and NO3− showed mean concentrations significantly higher in the rainy season, indicating greater inputs in these periods (which is in part related to increasing soil leaching and runoff). Agricultural activities were the main source of NO3− and wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) proved to be the main source of nutrients, mainly NH4+ and all forms of phosphorus. These two allochthonous sources are also the determining factors of the trophic state and the degradation of the water quality of Lake Paranoá. The lake is in the transition process from a mesotrophic to a eutrophic condition.
1. Introduction
Water quality and productivity of lakes and reservoirs are largely controlled by the quantity and quality of external nutrient loads [1]. An excess of nutrients, in turn, can greatly intensify the natural eutrophication process, currently considered as one of the main problems affecting water quality [2,3]. Furthermore, climate warming will tilt the CH4 balance towards higher lake emission with this impact exacerbated by the eutrophication of the lakes [4]. As has been widely reported in the literature, lakes and reservoirs are important sources of atmospheric methane. A recent estimate of global CH4 emission suggests that freshwater systems emit 103 Tg year−1 of CH4, with lakes contributing 62% to these total emissions [5].
In the last few decades, the water cycle and biogeochemical processes, especially those involving nitrogen and phosphorus, have undergone significant changes in many lakes and reservoirs, especially those located in large urban centers. This is due to increasing pressure from anthropogenic activities such as intensive agriculture, livestock cultivation, disposal of industrial and domestic effluents, among others [6,7]. These types of pollution are divided in two main categories: point and non-point sources. A sewage water flow is an example of point source. It enters the water at a single and readily identified site [8]. In this case, it becomes easier to define pollution control measures. Nonpoint sources, on the other hand, are those from broad areas, such as the fertilizers and pesticides leached from agricultural land. These are harder to identify and monitor [8].
The changes mentioned above, caused by point and/or nonpoint sources, have caused a series of environmental, social, and economic problems resulting from the degradation of water quality, leading to a loss of environmental goods and services provided by these aquatic systems [9]. These are due to the changes generated in the dynamics and availability of inorganic and organic species of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) [9,10,11].
Urban reservoirs are particularly vulnerable to anthropogenic impacts, as they receive all types of material and pollutants from the drainage basin, which includes nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) [12,13], either by soil leaching and/or by discharge of raw or treated domestic effluents, leading to a deterioration in water quality and its consequent socio-environmental impacts.
Hydrological regimes are key drivers of productivity in freshwater ecosystems but are also increasingly impacted by human activity [13]. From a study involving 13 African lakes, Gownaris et al. [14] found lower production and biomass at higher trophic level in systems with greater water level fluctuation compared to more stable ones.
Another factor that can have a significant contribution to the eutrophication is the water residence time (WRT). Noori et al. [15] found that the WRT in the Sabalan Lake (Iran) varied from hundreds to thousands of days, which was longer than other lakes and reservoirs with the same or much greater storage capacity. The authors concluded that this factor, combined with hyper-nutrient enrichment, mainly controlled eutrophication in the Sabalan reservoir.
Most studies have focused on lakes and reservoirs in temperate and shallow environments. There is little information on tropical environments, such as Lake Paranoá [16,17], a deep reservoir, located in the urban area of Brasília, Federal District, Brazil.
Tropical lakes differ from lakes of temperate regions in many ways. One of the most important of these is their radiation level, which is higher in tropical regions. Furthermore, there is not much seasonal variation in the radiation which, combined with a small Coriolis effect at low latitudes, creates weakly or non-stratified lakes with relatively warm and uniform temperatures [18]. Two features distinguish nutrient dynamics in tropical lakes from the temperate ones: the absence of temperature-induced convective mixing in the tropical lakes due to lack of thermal stratification; and the significantly higher fluxes of allochthonous Fe and Mn oxides (hydrate) from the intensively weathered tropical soils of the catchment [18].
The lack of knowledge about the behavior and response of deep tropical lakes and reservoirs to excessive nutrient loads and their effects on trophic states indicates a pressing need to understand the biogeochemical processes of these ecosystems [19].
In the case of Lake Paranoá, there is further concern as this reservoir has recently begun to be used for public supply. The proposed use of water from the Lake Paranoá for public supply dates to 2014, with the actual proposal implemented only in 2017, when a serious water crisis was registered. According to the Federal District Water, Energy and Basic Sanitation Regulatory Agency (ADASA), the Santa Maria and Descoberto reservoirs, used until then for public supply of the Brasília region, had the lowest levels registered up to that time (21.6% and 14.3%, respectively) [20].
Population growth has added to the lower volume of reservoir capacity in recent decades, causing negative impacts on the supply of drinking water in the hydrographic basin of Lake Paranoá [21]. As this is an urban source, its use for public supply raises concerns about the presence of potentially toxic components if there is no control of the trophic level of the reservoir [22]. To maintain the water level and allow the water collection for public supply, it was necessary to reduce the flow through the dam located downstream from the lake. This resulted in an increase in water residence time, leading to a deterioration of its quality. This reinforces the urgent need to generate information that allows decision makers to better manage this water resource.
The goal of this study was to assess the water quality and dynamics of organic and inorganic species of nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Paranoá, identifying possible seasonal and spatial differences in concentrations, and identifying the main sources of the nitrogen and phosphorus, as well as the predominant biogeochemical processes operating in the system and the current trophic state and trend. The results of this study should contribute to a better knowledge and understanding of the functioning of this type of system, as well as to better management of this water resource for the purpose of its multiple uses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Lake Paranoá is an urban reservoir located in the city of Brasilia, the Brazilian capital (Figure 1). Constructed in 1959, it is a deep artificial lake, with an average water depth of 12.42 m (max. 38 m, near the dam) and a surface area of 37.5 km2.
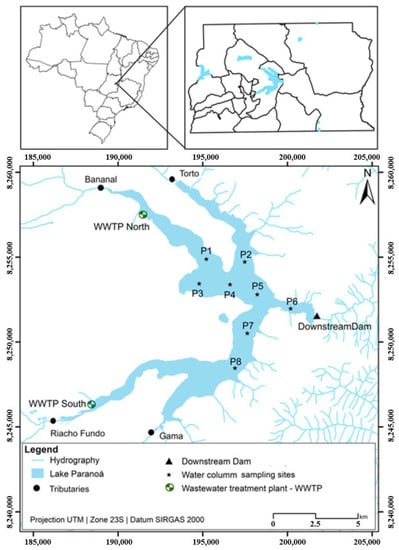
Figure 1.
Study area and sampling sites in the Lake Paranoá.
The catchment area is 1034 km2 and there are four main tributaries that discharge into Lake Paranoá: the Riacho Fundo and Gama streams at the south and the Bananal and Torto streams at the north.
The reservoir has a maximum storage capacity of 498 × 106 m3 and there is no significant water level variation throughout the year (less than 10%). The retention time of the water in the lake used to be 0.82 years until the period of the present study, when it increased to more than two years, due to a reduction of the discharge through the dam [23].
Lake Paranoá also receives effluents from two wastewater treatment plants (WWTP North and WWTP South). According to Mar da Costa et al. [24], the treatment plants operate using similar processes, biological removal of nutrients and tertiary activated sludge, followed by an additional flotation treatment to upgrade phosphorus removal.
The regional climate, according to the Köppen-Geiger classification [25], is the Savannah Climate (named: Aw) type, with two distinct seasons: a dry season during winter (historically, May–September) and a wet season during summer (historically, October–April), with annual average precipitation of 1600 to 1700 mm.
Effective wet and dry seasons were defined for this study based on the of monthly rainfall registered over the period of the study. The seasonality in the Midwest region of Brazil is defined by a well-marked rainy season and a well-marked drought period. There are no significant variations in the average temperature throughout the year, as occurs in temperate climate countries (Figure 2). Thus, the data for the months of October 2016, December 2016, and February 2017 were grouped as rainy season; while the months of April, June, and August 2017 represent the months of drought.
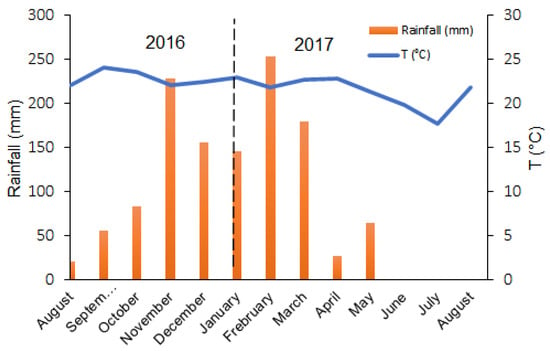
Figure 2.
Precipitation and air temperature records for the study time. Data source: Brazilian National Institute of Meteorology (INMET).
The annual cumulative rainfall was 1214 mm, alternating between dry season with precipitation below 251 mm and wet season with precipitation above 963 mm [23].
2.2. Sample Collection
The water samples were collected during five field trips (December 2016, February 2017, April 2017, June 2017, 17 August 2017) from eight points distributed along Lake Paranoá (P1–P8, Figure 1), in both wet and dry periods. Water samples were collected at two depths: subsurface (1 m below the surface) and bottom (1 m above the bottom), using a horizontal Van Dorn sampler. The water samples were then transferred to previously cleaned polypropylene bottles and to BOD bottles which were accommodated in thermal boxes, under refrigeration, and transported to the laboratory.
2.3. Sample Preparation and Chemical Analysis
All reagents used were analytic grade and were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA). Ultrapure water by Millipore™ system (18 mΩ cm) were used for the reagent solutions preparation.
Twenty-two water quality parameters were analyzed on-site, in the laboratory or calculated based on primary data, as explained below. Physical-chemical parameters of water: pH, turbidity, electrical conductivity (EC), temperature (T °C), and dissolved oxygen (DO) were measured on-site using a previously calibrated YSI 6600 V2 probe (Yellow Springs Instruments™).
Water samples were filtered through two types of filters: a 0.45 µm cellulose acetate membranes from Sartorius Stedim Biotech (Gotingen, Germany) for analysis of dissolved inorganic and organic nutrients and dissolved silica (Si) in the filtered water and a glass fiber (GFF) from Sartorius Stedim Biotech (Gotingen, Germany) for chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) determination. The samples destined for ammonium analysis were preserved with the addition of a phenol solution. Ammonium (NH4+), nitrite (NO2−), nitrate (NO3−) and orthophosphate (PO43−) were determined according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater [26], by phenate, colorimetric (Griess reaction), cadmium reduction and ascorbic acid methods, respectively, with all measurements made using a UV-VIS spectrophotometer Agilent Cary 8454 (Agilent Technologies, Petaling Jaya, Malaysa). All determinations were conducted on the same day or the day after the collection. In the latter case, the samples were kept under refrigeration.
The cellulose acetate filters were used for the determination the total suspended solids (TSS), based in the particulate mass retained and water volume filtered.
Unfiltered water samples were used to determine total organic nitrogen (TON) and total organic phosphorus (TOP). All samples destined for the determination of the organic forms of nutrients, total and dissolved ones, had been previously digested (using a specific persulfate solution for each of the nutrients) in an autoclave at 120 °C for 50 min, to liberate the inorganic forms of N or P [26]. The digestion was performed on the sampling day and the digested and acidified samples were kept under refrigeration until the time of analysis. These resulting inorganic forms were then determined as described above for the original inorganic forms, as nitrate for the N and as orthophosphate for P.
Particulate organic nitrogen (PON) and particulate organic phosphorus (POP) were calculated by the difference between TON and DON, TOP and DOP, respectively. The concentrations of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) were calculated by the sum of their respective organic and inorganic species.
The five days biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) was determined for the subsurface water samples by difference between initial and final dissolved oxygen concentrations (after five days of water sample incubation) measured by Winkler’s method [26].
Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) samples were filtered (GFF filters), extracted in 100% acetone, and analyzed by molecular absorption spectrometry method [27], using a UV-VIS spectrophotometer Agilent Cary 8454 (Agilent Technologies, Malaysa).
The detection limits (LD) were calculated according to the method described by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), based on the blank measurements [28]. All spectrophotometric measurements, except for Chl-a, were made using the external calibration method (analytical curve).
2.4. Geospatial Analysis of Variables Dataset of Surface Water
Spatial distribution maps of the average concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus and environmental variables were generated from georeferenced data in ArcMap 10.3 (ArcGis™, Redlands, CA, USA), using the Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) interpolation spatial analysis tool [29,30].
2.5. Trophic Status Assessment
There are many simplified models in the literature for calculating the trophic status of reservoirs located in temperate climate regions. The trophic state indexes (TSI) comprise relative values, based on regression equations derived from specific data or from the direct application of the average concentration of one or more main variables: Chl-a, TP, and phosphorus load (LP) and transparency (S), therefore, subject to local differences depending on the model adopted [31].
Modabberi et al. [32], for example, successfully applied the Carlson’s trophic state index, a model often cited in the literature, in the assessing the trophic state of Caspian Sea, using remotely sensed Chl-a data.
According to Cunha et al. [33], however, comparisons with criteria available in the literature suggested that trophic state limits for temperate systems are not suitable for tropical/subtropical reservoirs and may overestimate their enrichment condition. These authors then proposed a model adapted from Carlson’s original model [34], known as the Lamparelli model [33,35].
Many other models originally developed for temperate aquatic systems were then recently adapted for application to tropical lakes and reservoirs.
The use of different models for the same environment contributes to a better diagnosis of the current trophic state of the aquatic ecosystem and its tendency [20,36].
The evaluation of the trophic state of Lake Paranoá was carried out using three different models, adapted to tropical regions that make up the Trophic State Index (TSI), briefly described below:
The model proposed by Thomann and Mueller [37], was applied to the reservoir data and calculates the individual direct use of the average concentrations of total phosphorus (PT), chlorophyll (Chl-a) and oxygen saturation degree (Sat. OD %).
The model developed by the Pan American Center for Sanitary Engineering and Environmental Sciences (CEPIS) by Salas and Martino [38] is an extension of the work of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) [36] and is described in Equation (1):
where: [TP] is the total P concentration of the lake water in mg L−1, LP is the P loading rate, TR is the calculated retention, and Z is the average reservoir depth [31,33].
The model proposed by Lamparelli [33,35] for tropical reservoirs was developed from the classic model of Carlson (1977) and established new relationships to determine the TSI, generating the model that uses concentrations (µg L−1) of: total phosphorus (TP) (Equation (2)) and chlorophyll a (Chl-a) (Equation (3)), and calculating the value of the TSI (Equation (4)) from the average of the indexes obtained through Equations (2) and (3).
The trophic classes established the by the application of each model are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Trophic classes according to the different models used to assess trophic state in tropical lakes and reservoirs.
2.6. Statistical Data Analysis
Spearman rank-order correlations (Spearman R coefficient) were used to assess the correlation structure between variables, since the datasets had a non-normal distribution. The Mann-Whitney U test (significance level of p < 0.05) was used to examine concentration differences between wet and dry seasons, as well as surface and bottom waters, for each investigated variable. Box plot analysis was used to show the seasonal variability of parameter values based on the median, standard error, and confidence interval (95%).
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on the data matrix to investigate the spatiotemporal discriminations between samples according to the variables. Hierarchical Analysis (HCA) was used to identify possible data groups and the main grouping condition (time × space), considering the main variables found in the PCA analysis. All statistical analyses were performed using the statistical package Statistica 6.0 (Statsoft™, Tulsa, OK, USA). These two multivariate statistical analysis techniques have been successfully applied to monitoring the water quality of aquatic systems [39,40].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seasonal Variation
The data showed that there is no thermal stratification in Lake Paranoá (Figure 3), unlike those registered in other reservoirs located in the Northern region of Brazil such as Balbina, Tucuruí, Samuel, and Curuá-Una. In these reservoirs, thermal stratification promotes the formation of a thermocline between a depth of 2 and 3 m, which generally causes important differences in the vertical distribution of various chemical parameters [41]. In the absence of thermocline formation in Lake Paranoá, there are no vertical variations in the distribution of physicochemical and biological variables resulting from the restriction of homogenization of the water column due to the density barrier caused by a pronounced vertical difference in temperature.
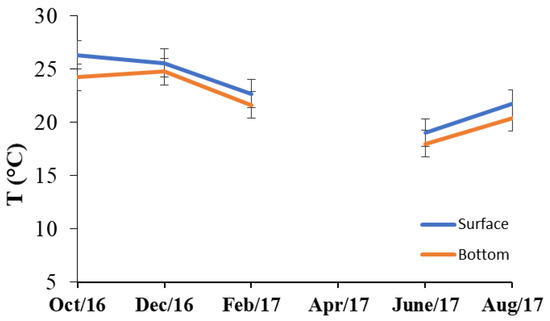
Figure 3.
Water temperature variation according to the sampling depth in Lake Paranoá along the study time.
In shallow lakes and reservoirs, such as the 40 studied by Brazil et al. [42] in the northeaster of Brazil, some stratification occurs due to the resuspension process. In deep reservoirs this process is common only when the drawdown of water level occurs [43] or in high -turbidity event during storm generated currents [44]. However, this is not the case of Lake Paranoá, which is a deep lake with stable water level and not usually subject to several windy storms that can cause significant resuspension process.
Therefore, the temporal distribution of the investigated variables is discussed here considering the datasets from the two sampling depths and the eight sampling points in an integrated manner. Mean and standard deviation values of water quality parameters among sampling months at Lake Paranoá Reservoir are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Mean and standard deviation values of water quality parameters among sampling months at Lake Paranoá Reservoir, including wet and dry seasons. Except for T (°C), turbidity (NTU), Chl-a (µg L−1), DO saturation (%). and EC (µS cm−1), the rest are in mg L−1. UM, unmeasured; LD, detection limit.
We compared the rainy and dry periods, which define the seasonality of the region. The median values of physical—chemical parameter (T, EC, DO, Turbidity), the nitrogen inorganic forms (NO3−, NO2−, NH4+), inorganic phosphorus (PO43−), Si and Chl-a showed significantly differences between seasons (Mann-Whitney U test, p < 0.05)); while the organic forms of nitrogen (DON, PON), organic forms of phosphorus (POD, POP), DO Saturation degree (%), BOD5, TSS, and pH showed no significant differences between rainy and dry seasons. (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7).
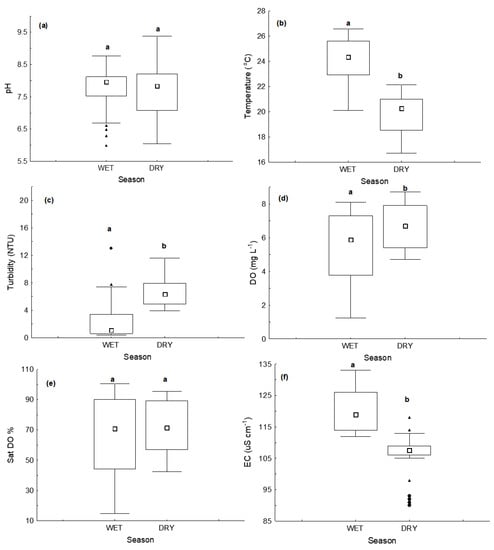
Figure 4.
Box and whisker plots of seasonal variation in water quality variables: (a) pH, (b) T °C, (c) Turbidity, (d) DO, (e) Sat. DO %, (f) EC. Small white squares represent median values, boxes represent the interquartile range, range bars show the maximum and minimum values, black triangles represent the extremes and black diamonds show the outliers. Different letters (a and b) over box plots indicate a significant difference (Mann-Whitney U test, p < 0.05).
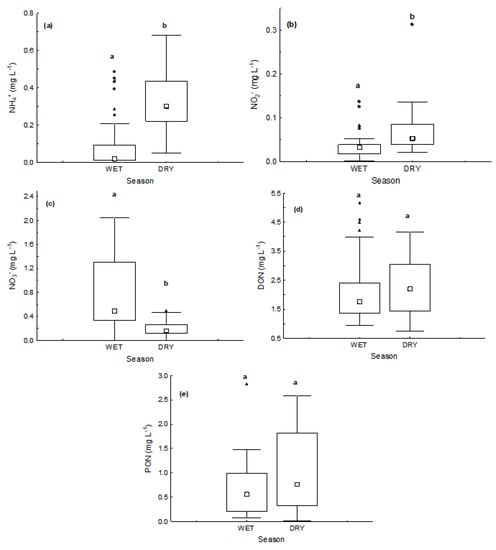
Figure 5.
Box and whisker plots of seasonal variation of water quality variables: (a) NH4+, (b) NO2−, (c) NO3− (d) DON, and (e) PON. Small white squares represent median values, boxes represent the interquartile range, range bars show the maximum and minimum values, black triangles represent the extremes and black diamonds the outliers. Different letters (a and b) over box plots indicate a significant difference (Mann-Whitney U test, p < 0.05).
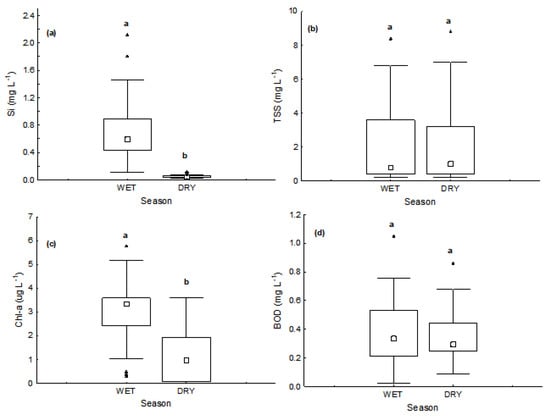
Figure 6.
Box and whisker plots of seasonal variation of water quality variables: (a) Si, (b) TSS, (c) Chl-a, and (d) BOD5. Small white square represents median values, boxes represent the interquartile range, range bars show the maximum and minimum values, black triangles represent the extremes and black diamonds show the outliers. Different letters (a and b) over box plots indicate a significant difference (Mann-Whitney U test, p < 0.05).
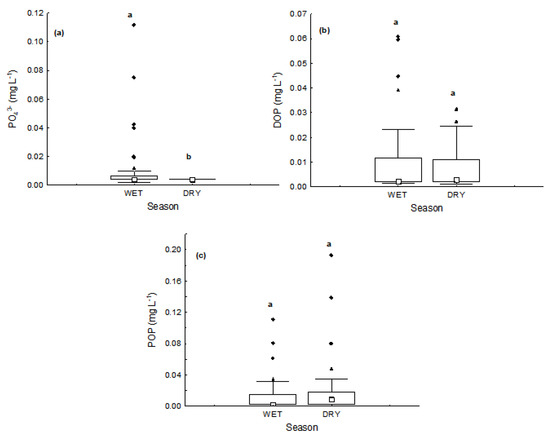
Figure 7.
Box and whisker plots of seasonal variation of water quality variables: (a) PO43−, (b) DOP, (c) POP. Small white squares represent median values, boxes represent the interquartile range, range bars show the maximum and minimum values, black triangles represent the extremes and black diamonds show the outliers. Different letters (a and b) over box plots indicate a significant difference (Mann-Whitney U test, p < 0.05).
The opposite behavior between nitrate and other forms of inorganic nitrogen between wet and dry seasons (Figure 5a–c) suggests that nitrate comes from a different source and/or there are different predominant biogeochemical processes in the two seasons.
According to Barbosa et al. [23] the annual load of NO3− for Lake Paranoá in the period of this study was of 48.55 tons in the rainy period and 26.85 tons in the dry period, the main contribution coming from the tributaries of the southern region (mainly the Riacho Fundo stream). Two wastewater treatment plants, the WWTP North and WWTP South, provide the major annual contribution of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) (275 Mg, 66.8%) in the form of NH4+ with the load being higher in the dry season. These data confirm the hypothesis of different sources for NO3− and NH4+ for the lake water. These data also indicate that the NO3− come mainly from the runoff of agricultural soils, since the tributaries of the southern region cross agricultural areas. This can be co-supported by significantly higher values of water electrical conductivity (p < 0.05, Figure 4f) and dissolved silica (p < 0.05, Figure 6a) in the wet season. Significant positive correlation between NO3− concentrations and EC (Spearman R = 0.442664; p = 0.00009) and NO3− and Si concentrations (Spearman R = 0.355016; p = 0.0012) also corroborate this hypothesis.
The increase in the supply of NO3− of allochthonous origin and its strong direct correlation with Chl-a (Spearman R = 0.75; p = 0.006895), on the other hand, indicate an increase in autotrophic activity in the rainy season. This shows that nitrogen can be also a limiting factor for phytoplankton growth in the dry period, since the temperature, which is not very variable, has a lesser influence on primary production in tropical lakes. This source-limited nitrogen is a frequent feature of tropical lakes, which normally have a low external supply of nitrogen [45].
The influence of the rainfall on nutrient concentration, autotrophic activity, and water quality in lakes depends on several factors in a complex manner such as rainfall regime, lake depth, level variation and retention time, and human activities in the drainage basin.
Brasil et al. [42] evaluated the processes that govern the cycling of nutrients in 40 reservoirs in northeastern Brazil. They found the highest average concentrations NO3− in the rainy season, but with a predominance of autotrophic activity in the dry season. The increase in the concentrations of Chl-a in this environment happens in the dry period due to the fact that, unlike Lago Paranoá, the reservoirs in question are shallow, thereby being subject to resuspension processes. On the other hand, Tibebe et al. [46] evaluated the nutrient cycling and trophic status of the tropical lake Tana, located in Ethiopia, and found average concentrations of Chl-a (38 µg L−1) and NO3− (0.763 mg L−1) higher in the rainy season, as in lake Paranoá. Lake Tana is also a shallow lake and is threatened by anthropogenic (agricultural and industrial) and climatic factors.
Magesh et al. [47] also verified the influence of rainfall on the availability of nitrogenous nutrients in a tropical reservoir (Karayar reservoir) and found lower concentrations in the rainy season and higher concentrations in the dry period, both NO3− and NH4+. The authors found NO3− values ranging from 0.29 to 0.56 mg L−1 in the dry season and between 0.012 and 0.014 mg L−1 in the rainy season. In the same period, the variation of NH4+ was 0.57 to 0.64 mg L−1 in the dry period and from 0.184 to 0.198 mg L−1 in the rainy period. This reservoir, however, is in a pristine area of Southern India and is surrounded by forests.
In the period covered by this study (2016–2017), Barbosa et al. [23] found that inorganic nitrogen species were retained by the Lake Paranoá reservoir. By combining this information with the fact that there is a decrease in NO3− concentrations (Figure 5c), accompanied by an increase in NO2− and NH4+ concentrations (Figure 5a,b, respectively), in the dry season, we can conclude that this is due, at least in part, to the predominance of heterotrophic processes in the water column.
According to Mengis et al. [48], a fraction of NO3− dissolved in lake waters can be consumed by ammonification, while denitrification can occur in the deeper parts of these aquatic systems. These processes may contribute to the NH4+ concentrations found in the lake waters in the dry season, compared to the contribution of the discharge from the WWTPs, which continue in the dry period, while the NO3− inputs are greatly reduced.
Dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) was the predominant form both in the wet season and in the dry season (Table 2), with no significant difference (p > 0.05) in the average concentrations between seasons. Likewise, the organic compounds (DOP and POP) were the predominant forms of phosphorus in both seasons (Table 2, Figure 7b,c) with no significant difference (p > 0.05) in concentrations between seasons.
The inorganic form of phosphorus (PO43−) was found in quantities above de detection limit of the method (LD = 0.002 mg L−1) only in the beginning of the rainy season, in October and December (Table 2) and was the predominant form at this time. At the end of rainy season and at the dry season only the organic forms (DOP and POP) were found, with POP being the predominant form (Figure 7b,c).
The very low concentration of inorganic soluble phosphorus in the water column can be attributed to scavenging by Fe(hydr)oxides, which are abundant in the tropical soils [18].
The low availability of phosphorus in the lake water is also evidenced by the high N:P ratio which ranges from 74 and 193, with an average value of 137. Batista and Fonseca [49] reported an average value for N:P of 228 for the period between October 2009 and September 2010 for the lake Paranoá waters.
Early empirical studies demonstrated that P limited the primary productivity in most lakes [50]. However, the influence of N or N:P ratios on phytoplankton biomass are now well established and nitrogen and phosphorus commonly co-limit primary production in lakes [51].
TN:TP are often selected as an important factor in classified lakes. Eutrophic lakes can have low N:P ratio compared to lakes surrounded by natural land cover, but this depends also on the type of the agriculture [52]. Lakes in regions dominated by row-crop commonly have high N:P ratio.
3.2. Spatial Distribution
The non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test showed that there are no significant spatial differences (p > 0.05) in Lake Paranoá among sampling points for the investigated quality water variables. However, the spatial variation can be better analyzed through concentration distribution maps The maps presented here (Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11) correspond to the mean concentrations of variables on the surface water.
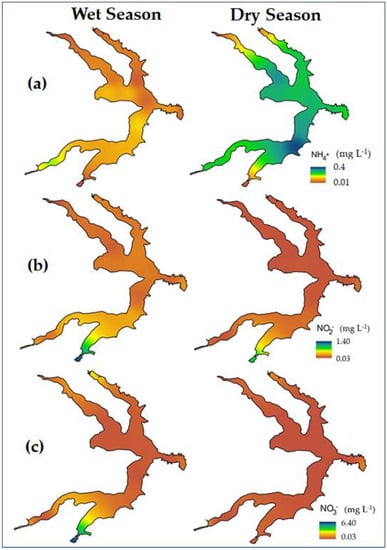
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of water quality variables: (a) NH4+, (b) NO3−, and (c) NO2− for wet and dry season.
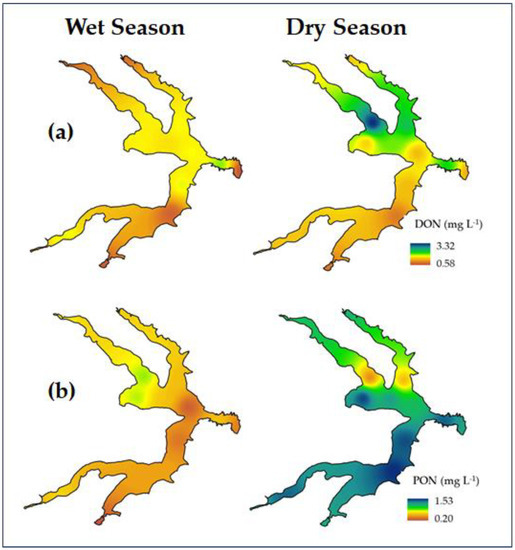
Figure 9.
Spatial distribution of water quality variables: (a) DON and (b) PON for wet and dry season.
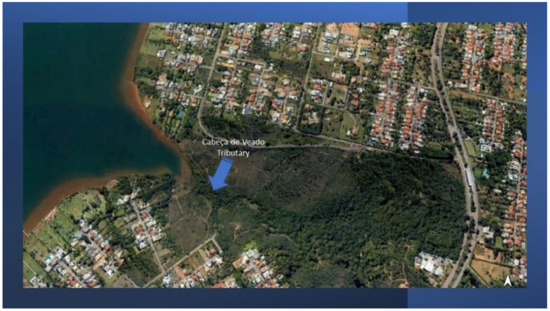
Figure 10.
Satellite image (Goggle Earth®) showing Cabeça de Veado tributary and its surrounding area.
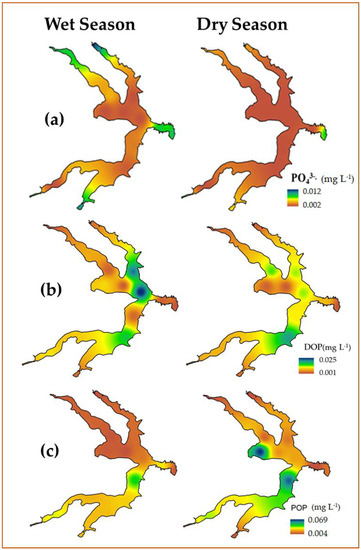
Figure 11.
Spatial distribution of water quality variables: (a) PO43−, (b) DOP, and (c) POP for wet and dry season.
The different forms of inorganic nitrogen (Figure 8a–c) showed different behavior in terms of distribution along the Lake Paranoá.
In the NH4+ distribution, for the rainy season, the southern part of the lake has higher concentrations than the northern one (Figure 8a). In the dry period, as we already mentioned, the concentrations are higher than in the wet season, but there is relatively homogeneous distribution along the lake. In this period, the lowest concentrations are located near the mouths of the tributaries (Figure 8a), except for the Riacho Fundo, indicating that the tributaries are not the main source of this nutrient.
NO2− and NO3− were similarly distributed in the wet season (Figure 8b,c), with higher concentrations found in the southern portion of the lake, particularly close to the mouth of the tributaries, suggesting that these are its main source. In the dry season, the NO2− continues to show a difference between the northern and southern portions of the lake. Meanwhile, NO3− has a uniform distribution with low concentrations throughout the lake (Figure 8c).
Both organic forms of nitrogen (DON and PON) showed the same patterns of distribution in the wet season and an opposite pattern in the dry season (Figure 9a,b). In the rainy season, both had a higher concentration in the northern part of the lake. In the dry season, the DON was more concentrated in the northern portion of the lake and the PON showed higher concentrations in the southern and central parts. These results suggest that each chemical species had a different origin.
This mapping of nutrient distribution is an important tool in identifying nutrient sources. In the spatial distribution of DON, PON (Figure 9a,b) and NH4+ (Figure 8a) in the dry period, an area of greater concentration near point 8 was evident, wherein there is a small tributary that flows into the right bank of the lake. This suggests that this tributary could be another source of nutrients for the lake, in addition to those already known.
The so-called Cabeça de Veado tributary is small and surrounded by vegetation in an environmental protection zone (Figure 10). However, the satellite image (Google Earth®) demonstrates urban sprawl around the tributary, suggesting that the nutrients may be coming from clandestine sewage release at this point.
The different forms of phosphorus also showed distinct patters of distribution among different chemical species of phosphorus: dissolved inorganic, dissolved organic (DOP) and particulate organic (POP). (Figure 11a–c). The inorganic chemical specie (PO43−) showed higher concentrations in the extreme areas, near the main tributaries and near the dam in the wet season (Figure 11a). While, in the dry season this nutrient was found only in the area near the dam. The unexpected highest concentration near the dam in the dry season could be an indication that there are allochthonous and unknow sources of PO43− there.
The DOP showed a very irregular distribution with no defined pattern (Figure 11b). The only relevant aspect in this case is the occurrence of the same higher concentration zone near point 8, as seen for some nitrogen species, which supports the hypothesis that the tributary Cabeça de Veado is another allochthonous source of nutrient for the Lake Paranoá.
The POP showed the same pattern of distribution in both seasons with higher concentrations found in the southern area of the lake (Figure 11c).
Data available from the official website of the Basic Sanitation Company of the Federal District (CAESB) [53] indicates that the WWTP south is operating close to maximum capacity, which may be compromising the process of phosphorus removal.
These results indicate that tributaries, especially the Riacho Fundo, and the WWTP south are the main allochthonous sources of phosphorus. The average concentration of total phosphorus (TP) in the Lake Paranoá is close to (dry season: 0.03 mg L−1) or above (wet season: 0.05 mg L−1) to the quality condition limit foreseen by the resolution of the National Environmental Council (CONAMA nº 357/05, Class 2) [54], which established the maximum concentration of 0.03 mg L−1 for lakes and reservoirs.
Other water quality parameters, such as Chl-a, BDO5, TSS, and dissolved Si, can help to understand the predominant biogeochemical processes in Lake Paranoá, on a spatial and temporal scale, as well as identified the influence of anthropogenic activities on these processes.
Chl-a and BDO5 showed an inverse patter of spatial distribution in the rainy season (Figure 11a,b). Chl-a had higher mean concentrations in the northern portion of the lake, while BDO5 showed higher mean concentrations in the southern portion for the same period. These results indicated that the northern regions of the lake have a better water quality that stimulates primary production in spring and summer, as expected; in the southern portion, heterotrophic activity predominates. Several factors can explain this anomalous behavior. On the one hand, a high nitrate load coming from the tributaries of the south in the form the leaching agricultural soil in the wet season [23] can inhibit primary production as described by Filstrup et al. [51]. On the other hand, the greater load of organic matter and other substances from the WWTP south, can also exert an inhibitory on photosynthetic activity. Finally, the mean higher concentrations of TSS in the southern portion of the lake in this period (Figure 12d) may reduce light penetration and contribute to the reduction of photosynthetic activities.
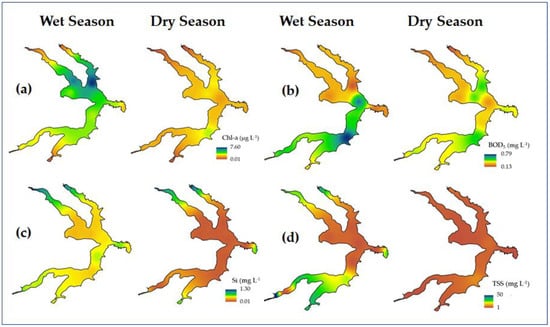
Figure 12.
Spatial distribution of water quality variables: (a) Chl-a, (b) BOD5, (c) Si and, (d) TSS for wet and dry season.
The spatial distribution map of TSS in the rainy season (Figure 12d) clearly shows the allochthonous input of suspended material from the tributaries, especially from the Riacho Fundo, which has the most urbanized, densely populated sub-basin, in addition to containing the largest agricultural area of the region. All of this results in soils which are more susceptible to erosion. A very homogeneous spatial distribution with low levels of TSS was observed for TSS in the dry season, as expected.
Dissolved Si also serves as a soil leach tracer for dissolved chemical substances. As show in the maps in Figure 12c, Si presented a relatively homogeneous distribution throughout the lake in both the wet and dry season, with the only difference being that in the wet season, the concentrations were higher.
These results also show the negative impact of extensive and unsustainable land use and occupation, leaving the soil uncovered and subject to erosion and leaching [10]. Sediments carried into the lake cause siltation, leading to a reduction in the water storage capacity. In addition to the water quality deterioration discussed above, another relevant aspect of the expansion of the agricultural and urban areas around the Lake Paranoá is the possible reduction of the volume and flow of its tributaries over the years, harming the maintenance of water level in the reservoir as well as its quality. Climate change could further amplify these effects [4].
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on the data matrix to investigate the spatiotemporal discriminations between samples according to the variables, as mentioned before (Figure 13). This analysis showed that 10 variables and 3 factors extracted 73.9% of the data variance (eigenvalues: Factor 1-4.48907; Factor 2-1.657037; Factor 3-1.243233). Of this, the first factor (PC1) extracted 44.89% of the variance, while PC2 explained 16.57% of the variance (Figure 13a) and PC3, 12.43% (Figure 13b). PC1 was correlated positively with turbidity (NTU), NH4+ and NO2− and negatively with temperature, Chl-a, NO3−, EC, and Si. Turbidity (NTU), NH4+, and temperature are inversely correlated, and these three variables have the major contribution to the factor 1. DO was the variable that characterized the PC2, this being negatively related to it. TON characterized the PC3, being negatively related to it.
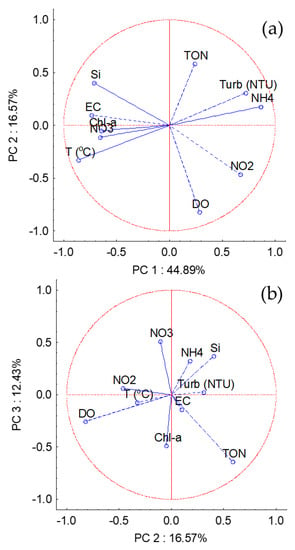
Figure 13.
PCA analysis of Lake Paranoá reservoir water quality parameter. (a) PC1 × PC2 and (b) PC2 × PC3.
The combination of NO3−, Si, and EC in the composition of PC1 confirms that the origin of the NO3− is mainly the leaching of agricultural soils and their runoff. It is also evident that the primary production was stimulated in the spring and summer seasons, with higher temperatures and greater availability of nutrients.
These results confirm that the rainfall regime, which defines the seasonality of the region, is responsible for the greater variability of the data and for the greater input of some nutrients to the lake water.
The inverse correlation between DO and Chl-a indicate that primary production has little influence on the degree of the lake water oxygenation level. So, the variance extracted by PC2 show that it is due mainly to the temperature seasonal variation.
PCA analysis also served to highlight the main variables to be used in a Hierarchical Analysis (HCA) to identify possible data groups and the main grouping condition (time × space) (Figure 14).
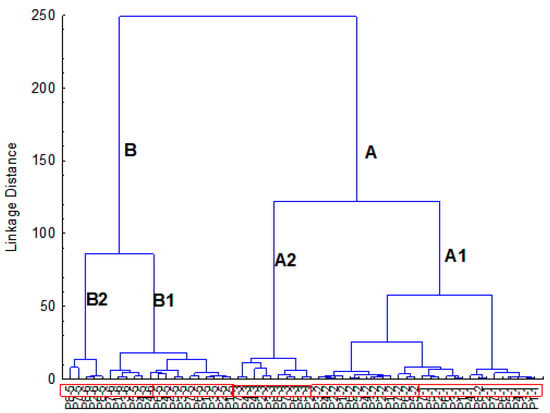

Figure 14.
Hierarchical analysis (HCA) with the 10 main variables and 3 factors for Lake Paranoá reservoir data. The code in the x- axis represents: the sampling point (ex: P1) and the collection number (ex: 3- collection date: February 2017). Group A -samples from wet season; Group B-samples from dry season. Subgroup A1-early wet season samples; Subgroup A2-samples from the end of the wet season. Subgroup B1-grouped samples from June/2017 and Subgroup B2- samples from June and august/2017.
The HCA grouped similar samples into two main groups, A and B. Group A collected all samples from the wet season (collections from the numbers 1 to 3), while group B gathered the samples from the dry season. Collection number 4 does not appear in the graph due to the lack of some parameters considered in the HCA (see Table 2). These results clearly show the dominance of the temporal factor (seasonality) over the spatial in the water quality of the lake. Furthermore, particularly in the rainy season, it is possible to verify that there is an evolution of the water quality from the beginning of the season to its end, as shown by sub-groups A1 and A2. Similarly, but not so marked, the same behavior is observed in the dry season (sub-groups B1 and B2).
3.3. Trophic State Evaluation
Since its filling in 1959, there have already been warnings about the lake’s aging due to the vegetation cover present on its bottom. The anthropogenic actions developed in the drainage basin caused an acceleration of the eutrophication process, which reach its maximum in 1970 [55]. This eutrophication scenario prevailed in Lake Paranoá until the mid-1990s, when finally, a process of recovering the lake and treating wastewater at the tertiary level began [56]. However, the rapid urban expansion of Brasília in recent years [57]), as well as the expansion of the agricultural areas, has led to an increase of nutrient load [58].
Eutrophic waters provide greater treatment difficulty and increase treatment costs. The excessive presence of phytoplankton caused by the enrichment of water in nutrients, substantially affects the treatment of water captured in the reservoir, since it must be removed. The color, odor and taste these nutrients produce must be removed, generating, for example, increased use of chemical products and more frequent cleaning of the filters in the treatment plant. For this reason, it is essential to study reservoirs subject to the eutrophication process, aiming at a management plan to prevent the deterioration of water quality [59].
The evaluation of the trophic state of Lake Paranoá was carried out using three different models, adapted to tropical regions that give rise to the Trophic State Index (TSI) as mentioned in the methodology section.
According to the model of the Thomann and Miller [37] the Lake Paranoá reservoir evaluation varies between oligotrophic to eutrophic, according to parameter used. From a mean concentration of Chl-a, a TSI of 1.97 was obtained, which would classify the reservoir as oligotrophic. The mean values of total phosphorus (TP) resulted in an TSI of 27.33, which correspond to a mesotrophic state. Finally, considering the oxygen saturation index the TSI was 49.29, classifying the lake as being eutrophic.
In the model proposed by Salas and Martino [38] which considers the loads of the TP, the TSI found was 64.27, which classifies the reservoir as eutrophic.
The Lamparelli model evaluates the trophic state by the mean concentrations of TP (TSI = 54.5) and Chl-a (TSI = 50.05), which results in a global TSI equal to 52.12, which corresponds to a mesotrophic classification.
Based on these results, we can conclude that the Lake Paranoá reservoir is in an intermediate stage, evolving from mesotrophic to eutrophic condition. This agrees with the study carried out in 2012 by Mar da Costa et al. [24] which classified the lake as meso-eutrophic, according to Lamparelli model.
In another study, conducted in 2003, which applied the Salas and Martino model, the calculated phosphorus load was 171 kg day−1, compatible with mesotrophic state [60].
The comparison of the results obtained in the present study with the one from 2003, mentioned above, corroborates the conclusion that Lake Paranoá reservoir has once again evolved from a mesotrophic to eutrophic conditions, after having been recovered from the eutrophic condition in the 1990s.
4. Conclusions
The results showed that seasonality, defined by a period of rain and another of drought, is the main factor that governs the variation in water quality in Lake Paranoá, while the spatial variation is not very significant. The variables of electrical conductivity (EC), temperature, dissolved silica, chlorophyll-a, PO43− and NO3− had significantly higher mean concentrations in the rainy season. While NH4+, NO2−, dissolved oxygen and turbidity had higher average values in the dry season.
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) proved to be the main source of nutrients, mainly NH4+ and all forms of phosphorus, while agricultural activities were the main source of NO3−. These two allochthonous sources are also the determining factors of the trophic state and the degradation of the water quality of Lake Paranoá reservoir.
The lake is in the transition process from a mesotrophic to an eutrophic condition. This indicates the urgent need to expand and improve the treatment capacity of the existing WWTPs, to increase the protection of soils and reduce erosion and leaching of nutrients to the reservoir. Therefore, the approach in this study proves to be an appropriate and important tool for the understanding the dynamics of nutrients in deep tropical reservoirs, enabling the implementation of water resource management mechanisms that focus on reducing the input of nitrogen and phosphorus and consequent development of the eutrophication process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.R.B., D.B.d.S. and J.d.S.B.B.; methodology, D.B.d.S., J.d.S.B.B. and V.R.B.; software, D.B.d.S., J.d.S.B.B., V.R.B. and T.B.L.; validation, D.B.d.S., J.d.S.B.B. and V.R.B.; formal analysis, D.B.d.S., J.d.S.B.B. and V.R.B., investigation, D.B.d.S., J.d.S.B.B., V.R.B. and T.B.L.; resources, V.R.B.; data curation, D.B.d.S., J.d.S.B.B. and V.R.B., writing—original draft preparation, D.B.d.S. and V.R.B., writing—review and editing, V.R.B. and J.d.S.B.B.; visualization, D.B.d.S. and J.d.S.B.B.; supervision, V.R.B.; project administration, V.R.B.; funding acquisition, V.R.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Distrito Federal (FAPDF), grant number 0193.000996/15.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Companhia de Saneamento Ambiental de do Distrito Federal (CAESB) for the provision of the data from the wastewater treatment plants, Companhia Energética de Brasília (CEB) for authorizing access to the downstream dam spot and the Instituto Brasília Ambiental (Ibram) for lending the multiparametric probe used in this study. The English text of this paper has been revised by Sidney Pratt, Canadian, MAT (he Johns Hopkins University), RSAdip (Cambridge University).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Polis, G.A.; Anderson, W.B.; Holt, R.D. Toward an integration of landscape and food web ecology: The dynamics of spatially subsidized food webs. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1997, 28, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.A.; Padedda, B.M.; Kaštovský, J.; Buscarinu, P.; Sechi, N.; Virdis, T.; Lugliè, A. Effects of trophic status on microcystin production and the dominance of cyanobacteria in the phytoplankton assemblage of Mediterranean reservoirs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, F.K.L.; Fonseca, B.M.; Felisberto, S.A. Community structure of periphytic Zygnematophyceae (Streptophyta) in urban ponds from central Brazil (Goiânia, GO). Acta Limnol. Bras. 2018, 30, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda-Jauregui, A.; Hoyos-Santillan, J.; Martinez-Cruz, K.; Antony, K.M.W.; Casper, P.; Belomonte-Izquierdo, Y.; Thalasso, F. Eutrophication exacerbates the impact of climate warming on lake methane emission. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Brown, E.T.; Crowe, S.; Kalsev, S. Sediment geochemistry and contribution to carbon and nutrient cycling in a deep meromictic tropical Lake: Lake Malawi (East Africa). J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Rai, S.C.; Pal, J.; Sharma, E. Hydrology and nutrient dynamics of a sacred lake in Sikkim Himalaya. Hydrobiologia 1999, 416, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cai, Z.; Yang, R.; Ti, C.; Xia, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Ma, A. Nitrogen budget and riverine nitrogen output in a rice paddy dominated agricultural watershed in eastern China. Biogeochemistry 2011, 106, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan, S.E. Environmental Chemistry, 7th ed.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 500–501. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.K.; Bouska, W.W.; Eitzmann, J.L.; Pilger, T.J.; Pitts, K.L.; Riley, A.J.; Schloesser, J.T.; Thornbrugh, D.J. Policy Analysis Eutrophication of U.S. Freshwaters: Damages. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupas, R.; Delmas, M.; Dorioz, J.M.; Garnier, J.; Moatar, F.; Gascuel-Odoux, C. Assessing the impact of agricultural pressures on N and P loads and eutrophication risk. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Lu, X.; David, F.B.; Joshi, U.M.; Zhang, L. Nitrogen dynamics at the sediment-water interface in a tropical reservoir. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, L.; Albuquerque, A.L.S.; Brenner, M.; Bonotto, D.M.; Sabaris, T.P.P.; Pires, M.A.F.; Cotrim, M.E.B.; Bicudo, D.C. The eutrophication history of a tropical water supply reservoir in Brazil. J. Paleolimnol. 2014, 51, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzal-Almeida, S.; Salim, A.; Andrade, M.R.M.; Nascimento, M.N.; Bini, L.M.; Bicudo, D.C. Effects of land use and spatial processes in water and surface sediment of tropical reservoir at local and regional scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gownaris, N.J.; Routons, K.J.; Kaufman, L.; Kolding, J.; Lwiza, K.M.M.; Pikitch, E.K. Water level fluctuation and ecosystem functioning of lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Ansari, E.; Jeong, Y.-W.; Aradpour, S.; Maghrebi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Bateni, S.M. Hyper-nutrient enrichment status in the Sabalan Lake, Iran. Water 2021, 13, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.W. Particles dynamics in a deep reservoir trigged by tryphoons. J. Hydrol. 2011, 406, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, G.; Jiang, H.; Wamg, J.; Liu, C. Impact of revised thermal stability on polluant transport time in a deep reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, S.A.; O’Neill, A.H.; Katsev, S.; Hehamussa, P.; Haffner, G.D.; Sundby, B.; Mucci, A.; Fowle, D.A. The biogeochemistry of tropical lakes: A case study from Lake Matano, Indonesia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.J.; Los, F.J.; Burger, D.F.; Lu, X.X. A modelling approach to determine systematic nitrogen transformations in a tropical reservoir. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADASA. Sistema de Informações sobre Recursos Hídricos DF. Available online: http://gis.adasa.df.gov.br/portal/home/ (accessed on 9 March 2019).
- Governo do Distrito Federal e Territórios (GDF). Zoneamento Ecológico-Econômico do DF Subproduto 3.1—Relatório do Meio Físico e Biótico. Available online: https://www.zee.dfgov.br (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- De Carvalho Pires, V.A. Metodologia para apoio à gestão estratégica de reservatórios de usos múltiplos: O caso do Lago Paranoá, no Distrito Federal. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, J.S.B.; Silva, D.B.; Bellotto, V.R.; Lima, T.B. Nitrogen ans Phosphorous Budget for a Deep Tropical Reservoir of the Brazilian Savannah. Water 2019, 11, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar Da Costa, N.Y.; Boaventura, G.R.; Mulholland, D.S.; Araújo, D.F.; Moreira, R.C.A.; Faial, K.F.C.; Bonfim, E.O. Biochemical mechanisms controlling trophic state and micropolluant concentrations in a tropical artificial lake. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carmouze, J.-P.; Bellotto, V.R.; Maddock, J.; Romanazzi, A. A versatile in situ sediment pore water sampler. Mangroves Salt Marshes 1997, 1, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUPAC Technical Report; Thompson, M.; Ellison, S.L.R.; Wood, R. Harmonized guideliness for single laboratory validation of methods of analysis. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 835–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in environmental sciences: Performance and impact factors. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouni, I.; Louhichi, G.; Ghrabi, A. Use of GIS based Inverse Distance Weighted interpolationto assesss surface water quality: Case of Wadi El Bey, Tunisia. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.E.; Löffler, H.; Rast, W.; Straskraba, M. Lake and Reservoir Management, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 107–130. [Google Scholar]
- Modabberi, A.; Noori, R.; Madani, K.; Ehsani, A.H.; Mehr, A.D.; Hooshyaripor, F.; Kløve, B. Caspian Sea is eutrophying: The alarming message of satellite data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 124047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.G.F.; do Calijuri, M.C.; Lamparelli, M.C. A trophic state index for tropical/subtropical reservoirs (TSItsr). Ecol. Eng. 2013, 60, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamparelli, M.C. Graus de Trofia em Corpos D’água do Estado de São Paulo: Avaliação dos Métodos de Monitoramento. Ph.D. Thesis, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (OECD) The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Eutrophication of Waters Monitoring Assessment and Control; OECD: Paris, France, 1982; p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Thomann, R.; Mueller, J.A. A Principles of Water Quality Modeling and Control, 1st ed.; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1987; p. 644. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, H.; Martino, P. A simplified phosphorous trophic state model for warm-water tropical lakes. Water Res. 1991, 25, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkler, N.R.; Bortolin, T.A.; Cocconi, J.; Mendes, L.A.; Schnider, V.E. Spatial and temporal assessment of water quality data using multivariate statistical techniques. Ciênc. Nat. 2016, 38, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woldeab, B.; Beyene, A.; Ambelu, A.; Buffam, I.; Mereta, S.T. Seasonal and spatial variation of reservoirwater quality in the southwest of Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearnside, P.M. Hidrelétricas como “fábricas de metano”: O papel do reservatório em áreas de floresta tropical na emissão de gases de efeito estufa. Oecologia Bras. 2008, 12, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brasil, J.; Attayde, J.L.; Vasconcelos, F.R.; Dantas, D.D.; Huzcar, V.L. Drought-indiced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in a tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2016, 770, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernieu, W.S. Effects of reservoir drawdown in resuspension of deltaic sediments in Lake Powell. J. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1997, 13, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, R.; Boegman, L.; Bouffard, D.; Rao, Y.R. Sediment resuspension mechanisms and their contributions to high-turbidity events in a large lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1045–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.M. Causes for the high frequency of nitrogen limitation in tropical lakes. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. Verh. 2002, 28, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibebe, D.; Kassa, Y.; Melaku, A.; Lakew, S. Investigation of spatial temporal variation of selected water quality parameters and trophic status of Lake Tana for susteinablemanagements, Ethiopia. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, N.S.; Chandraseak, N.; Krishnakuman, S. Geospatial analysis of dissolved nutrient dataset in the surface water of Karayar reservoir, Southern India. Data Brief 2017, 13, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengis, M.; Gächter, R.; Wehrli, B. Nitrogen in two deep eutrophic lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, B.D.; Fonseca, B.M. Phytoplankton in the central region of Paranoá Lake, Federal District of Brazil: Na ecological and sanitary approach. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2018, 23, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.A. Advances in defining critical loading levels for phosphorus in lake eutrophication. Mem. 1st Ital. Idrobiol. 1976, 33, 53–83. [Google Scholar]
- Filstrup, C.T.; Wagner, T.; Oliver, S.K.; Stow, C.A.; Webster, K.E.; Stanley, E.H.; Downing, J.A. Evidence for regional nitrogen stress on chlorophyll a in lakes across large landscape and climate gradients. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.A.; McCauley, E. The Nitrogen:phosphorus relationship in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAESB. Wastewater Treatment Plants. Available online: https://atlascaesb.maps.arcgis.com/apps/MapJournal/index.html?appid=9babae05a8a1444180cdf3df83f67fb72019 (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- National Council for the Environment -CONAMA n° 357/05 Resolution. Available online: http://pnqa.ana.gov.br/Publicacao/RESOLUCAO_CONAMA_n_357.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2019).
- Ferrante, J.E.T.; Rancan, L.; Braga Netto, P.; Meio, F. Olhares Sobre o Lago Paranoá, 1st ed.; Fonseca, F.O., Braga Netto, P., Cavalvante, C.V., Eds.; Secretaria de Meio Ambiente e Recursos Hídricos: Brasília, Brasil, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 45–79. [Google Scholar]
- Programa de despoluição do Lagoa Paranoá, Governo do Distrito Federal e Territórios. World Water Forum. Available online: https://www.agenciabrasilia.df.gov.br/2018/02/28/programa-de-despoluicao-do-lago-paranoa-sera-apresentado-no-forum-mundial-da-agua/ (accessed on 4 February 2019).
- Projeções e Estimativas da População do Brasil e das Unidades da Federação. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/apps/populacao/projecao/index.html (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Liporoni, L.M. Estudo Preliminar da Qualidade da Água do Lago Paranoá, Brasília-DF, Utilizando um Modelo de Qualidade de Água Bidimensional. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, T.F.; Campelo Neto, J. Dinâmica de Nitrogênio e fósforo em reservatório na região semiárida utilizando balanço de massa. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agrícola Ambient. 2014, 18, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.G.F.; Ogura, A.P.; Calijuri, M.D.C. Nutrient reference concentration and trophic state boundaries in subtropical reservoir. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).