First Record of Colonial Ascidian, Botrylloides diegensis Ritter and Forsyth, 1917 (Ascidiacea, Stolidobranchia, Styelidae), in South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
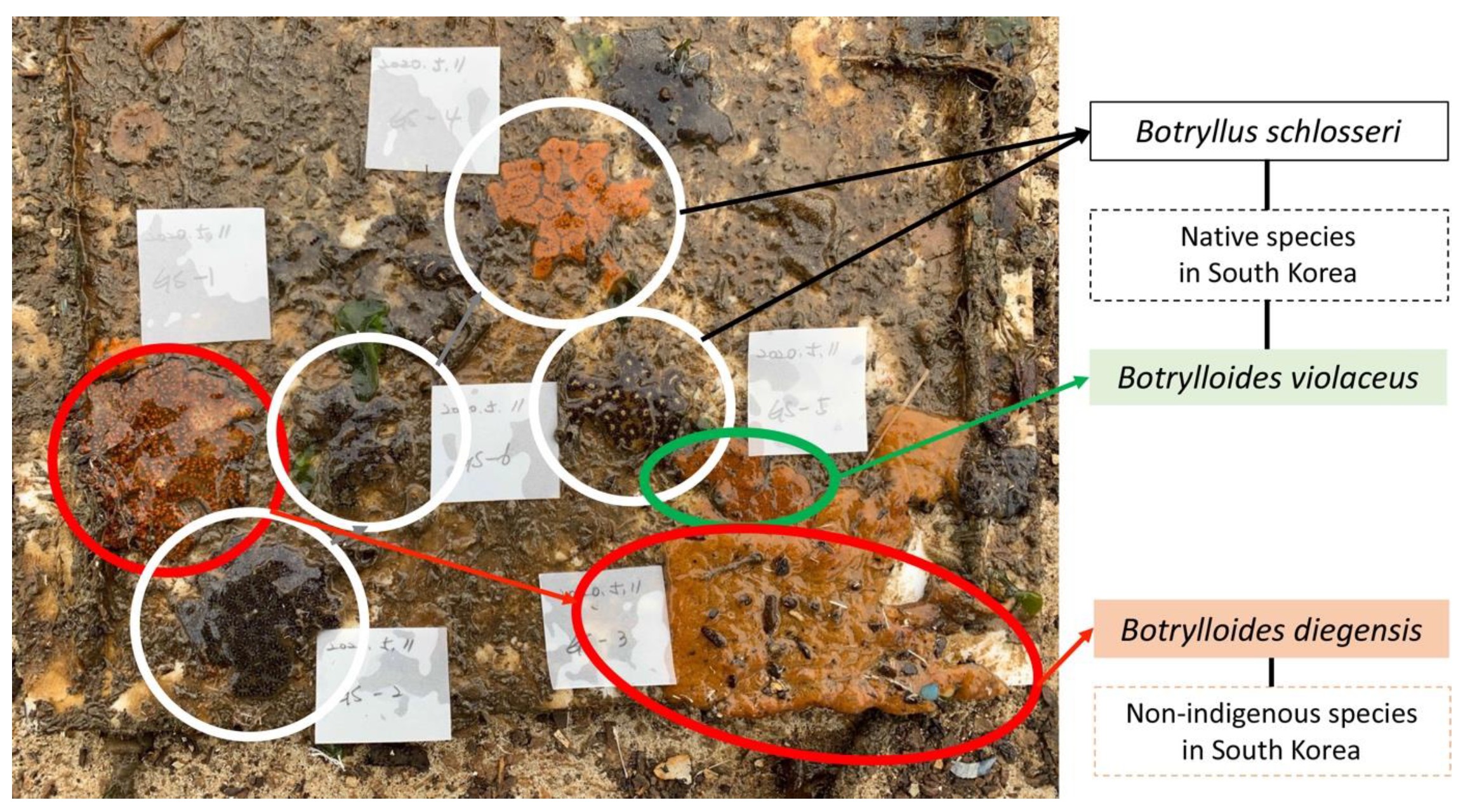
2.1. Sample Collection and Identification
2.2. DNA Extraction and Amplification of DNA Barcoding Region
2.3. DNA Barcoding Data Analysis
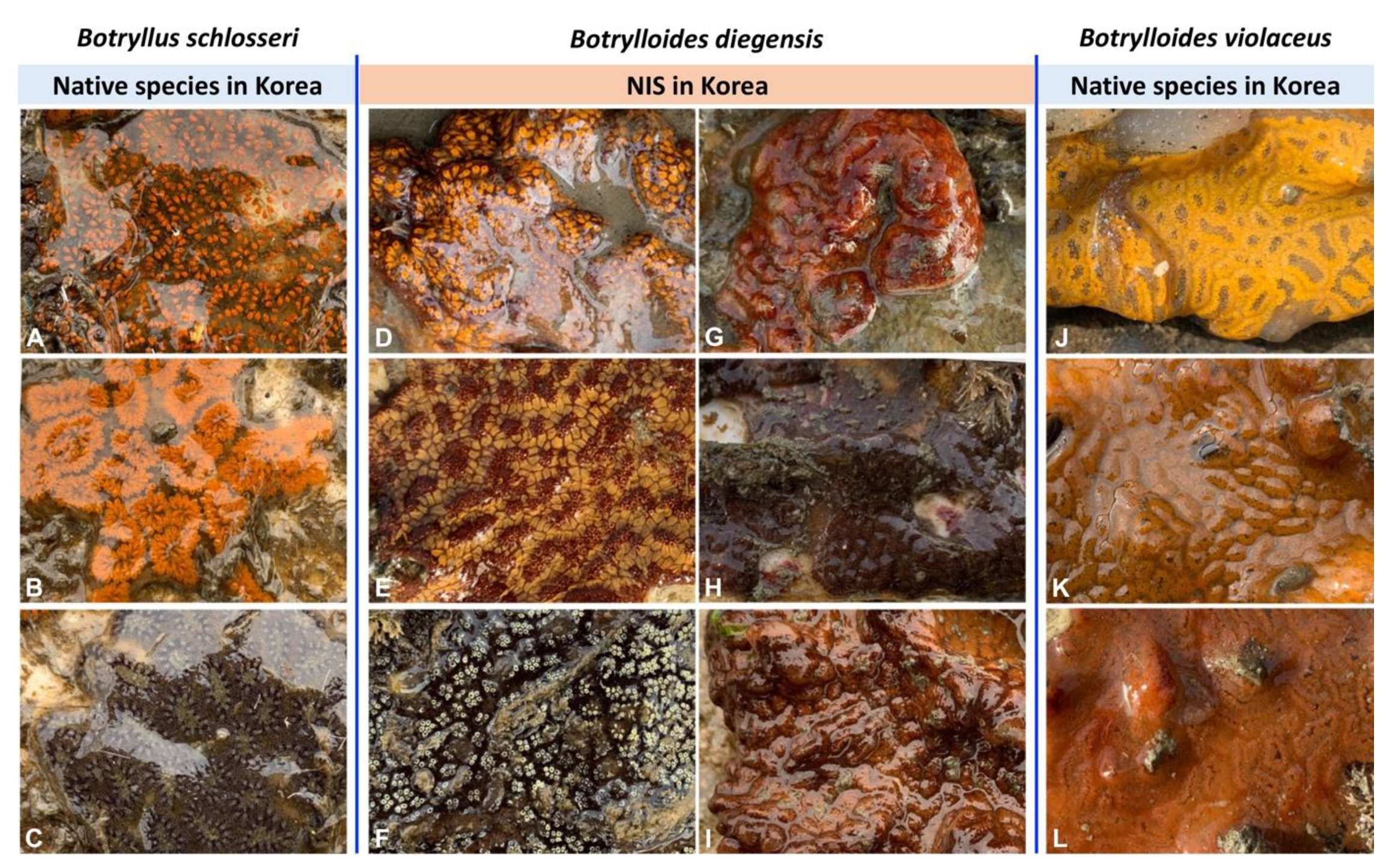
3. Results
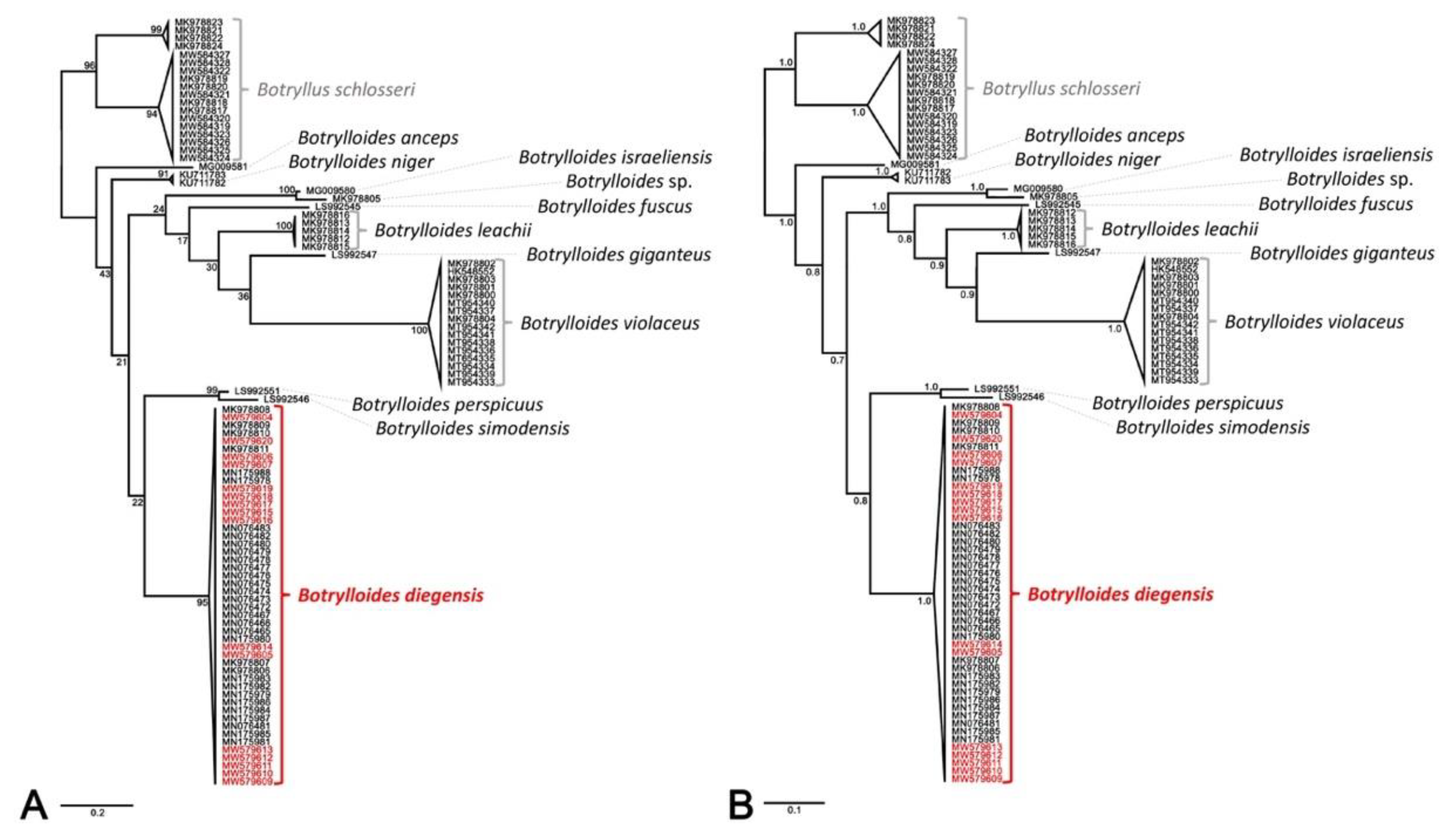
3.1. DNA Barcoding Analysis for B. diegensis from South Korea and Other Colonial Ascidians
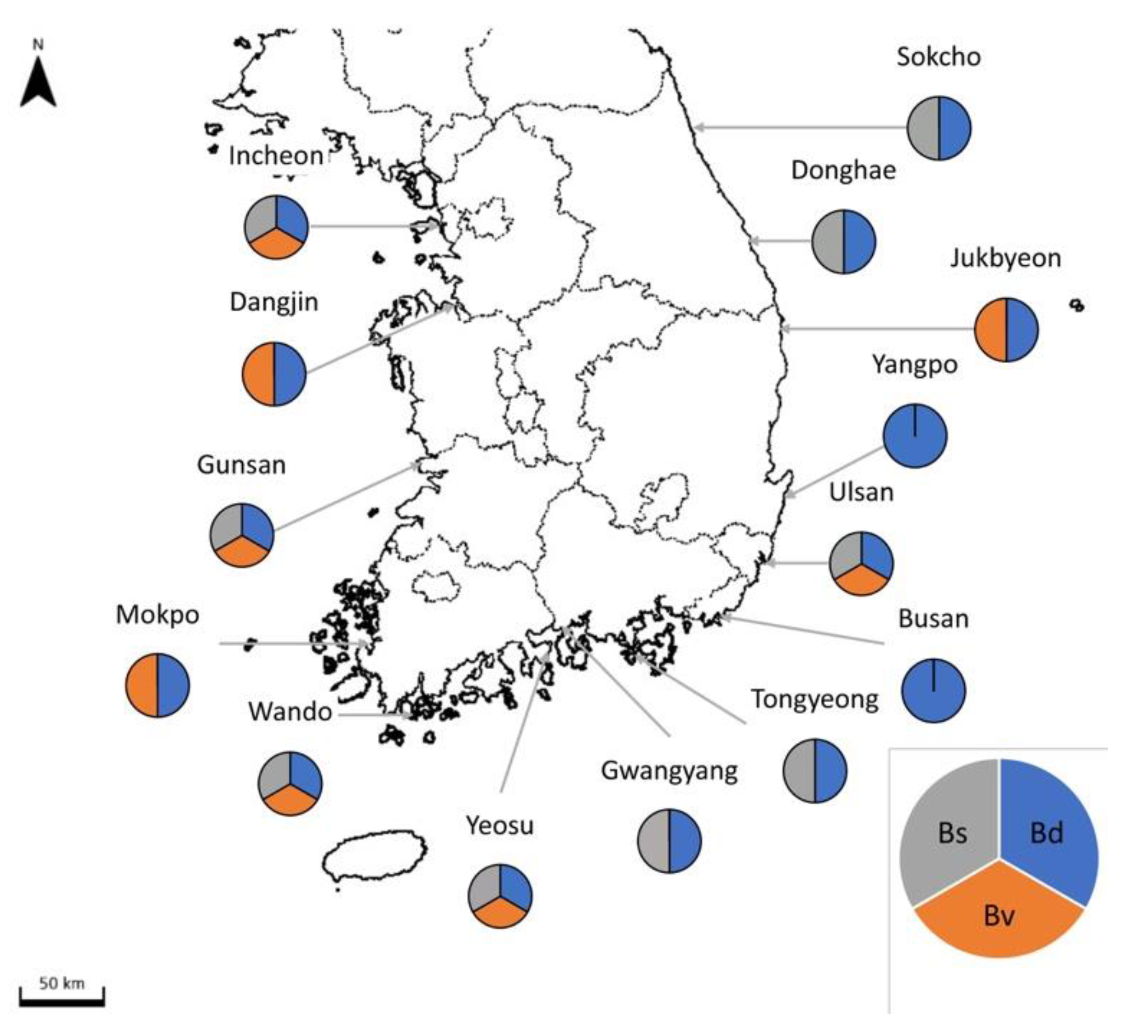
3.2. Distributions of B. diegensis and Other Similar Native Colonial Ascidians in South Korea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nunes, A.L.; Katsanevakis, S.; Zenetos, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Gateways to alien invasions in the European seas. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 9, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, J.A.; Galil, B.S.; Carvalho, G.R.; Rius, M.; Viard, F.; Piraino, S. Recommendations for developing and applying genetic tools to assess and manage biological invasions in marine ecosystems. Mar. Policy 2017, 85, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viard, F.; Roby, C.; Turon, X.; Bouchemousse, S.; Bishop, J. Cryptic diversity and database errors challenge non-indigenous species surveys: An illustration with Botrylloides spp. in the English channel and Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.D.D.; Roby, C.; Yunnie, A.L.E.; Wood, C.A.; Leveque, L.; Turon, X.; Viard, F. The southern hemisphere ascidian Asterocarpa humilis is unrecognised but widely established in NW France and Great Britain. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McGlashan, D.; Ponniah, M.; Cassey, P.; Viard, F. Clarifying marine invasions with molecular markers: An illustration based on mtDNA from mistaken calyptraeid gastropod identifications. Biol. Invasions 2008, 10, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, V.; Pascual, M.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Turon, X. When invasion biology meets taxonomy: Clavelina oblonga (Ascidiacea) is an old invader in the Mediterranean Sea. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comtet, T.; Sandionigi, A.; Viard, F.; Casiraghi, M. DNA (meta)barcoding of biological invasions: A powerful tool to elucidate invasion processes and help managing aliens. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 905–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, P.J.; Fotedar, S.; Munoz, J.; Hewitt, M.J.; Lukehurst, S.; Hourston, M.; Wellington, C.; Duggan, R.; Bridgwood, S.; Massam, M.; et al. Establishment of a taxonomic and molecular reference collection to support the identification of species regulated by the Western Australian Prevention List for Introduced Marine Pests. Manag. Biol. Invasion 2017, 8, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.F.; Stefaniak, L.; Saito, Y.; Gemmill, C.E.C.; Cary, S.C.; Fidler, A.E. Increased inter-colony fusion rates are associated with reduced COI haplotype diversity in an invasive colonial ascidian Didemnum vexillum. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.F.; Abbott, C.L.; Saito, Y.; Fidler, A.E. Comparison of whole mitochondrial genome sequences from two clades of the invasive ascidian, Didemnum vexillum. Mar. Genom. 2015, 19, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniak, L.; Zhang, H.; Gittenberger, A.; Smith, K.F.; Holsinger, K.; Lin, S.; Whitlatch, R.B. Determining the native region of the putatively invasive ascidian Didemnum vexillum Kott, 2002. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 422–423, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nydam, M.L.; Giesbrecht, K.B.; Stephenson, E.E. Origin and dispersal history of two colonial ascidian clades in the Botryllus schlosseri species complex. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkar, N.; Gittenberger, A.; Lambert, G.; Rius, M.; Moreira da Rocha, R.; Swalla, B.J.; Turon, X. Ascidiacea World Database. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species. 2021. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=103529 (accessed on 26 April 2021).
- Cohen, A.N.; Harris, L.H.; Bingham, B.L.; Carlton, J.T.; Chapman, J.W.; Lambert, C.C.; Lambert, G.; Ljubenkov, C.; Murray, S.N.; Rao, L.C.; et al. Rapid assessment survey for exotic organisms in southern California bays and harbors, and abundance in port and non-port areas. Biol. Invasions 2005, 7, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkanin, C.; Fofonoff, P.W.; Larson, K.; Lambert, G.; Dijkstra, J.A.; Ruiz, G.M. Spatial and temporal dynamics of ascidian invasions in the continental United States and Alaska. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pyo, J.; Shin, S. A new record of invasive alien colonial tunicate Clavelina lepadiformis (Ascidiacea: Aplousobranchia: Clavelinidae) in Korea. ASED 2011, 27, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, J.; Lee, T.; Shin, S. Two newly recorded invasive alien ascidians (Chordata, Tunicata, Ascidiacea) based on morphological and molecular phylogenetic analysis in Korea. Zootaxa 2012, 3368, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokioka, T. Pacific Tunicata of the United States National Museum; United States National Museum Bulletin 251; Smithsonian Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; Volume 251, pp. 1–247. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, B.J. The ascidians (Tunicata) from Chindo island, Korea. Korean J. Syst. Zool. 1995, 11, 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, R.; Manni, L.; Mastrototaro, F.; Gissi, C.; Gasparini, F. Fixation, description and DNA barcode of a neotype for Botryllus schlosseri (Pallas, 1766) (Tunicata, Ascidiacea). Zootaxa 2017, 4353, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nydam, M.L.; Lemmon, A.R.; Cherry, J.R.; Kortyna, M.L.; Clancy, D.L.; Hernandez, C.; Sarah Cohen, C. Phylogenomic and morphological relationships among the botryllid ascidians (Subphylum Tunicata, Class Ascidiacea, Family Styelidae). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; Jeremy, R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, P.J.; Lukehurst, S.S.; Simpson, T.; Rocha, R.M.; Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; Wellington, C.; McDonald, J.; Snow, M.; Kennington, J. Multiple introductions and regional spread shape the distribution of the cryptic ascidian Didemnum perlucidum in Australia: An important baseline for management under climate change. Aquat. Invasions 2021, 16, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonna, M.; Gasparini, F.; Huchon, D.; Montesanto, F.; Haddas-Sasson, M.; Ekins, M.; McNamara, M.; Mastrototaro, F.; Gissi, C. An elongated COI fragment to discriminate botryllid species and as an improved ascidian DNA barcode. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokioka, T. Contributions to Japanese ascidian fauna XX. The outline of Japanese ascidian fauna as compared with that of the Pacific coasts of North America. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1963, 11, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T. The ascidians of the Japan Sea II. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1991, 35, 25–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, B.J. Taxonomic study on the prochordates from Korea 1 (Ascidians). Korean Cult. Res. Inst. Trans. 1966, 8, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, B.J. A study on the classification and the distribution of the Korean ascidians. J. Korean Res. Inst. Better Living 1971, 6, 103–166. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, B.J. On the classification and the distribution of the marine benthic animals in Korea (3. Ascidians). J. Korean Res. Inst. Better Living 1975, 15, 121–169. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, B.J.; Huh, M.K. A systematic study on the ascidians in Korea. J. Korean Res. Inst. Better Living 1984, 33, 99–136. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, B.J.; Lee, J.E. A systematic study on the ascidians from Cheju island, Korea. Korean J. Syst. Zool. 1989, 5, 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, B.J.; Lee, J.E. A systematic study on the ascidians in Korea. Korean J. Syst. Zool. 1991, 7, 195–220. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, B.J.; Choe, B.L.; Song, J.I. Biosystematic studies on the marine fouling invertebrates in Korea—A systematic study on the ascidians from Chundo island (Onsan Bay), Korea. Korean J. Syst. Zool. 1996, 7, 195–220. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, B.J.; Park, K.S. Taxonomy of ascidians from Geojedo island in Korea. Korean J. Syst. Zool. 1998, 14, 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Carlton, J.T. Setting Ascidian Invasions on the Global Stage. In Proceedings of the International Invasive Sea Squirt Conference, 21–22 April 2005; Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 2005. Available online: http://www.whoi.edu/page.do?pid=11421&tid=282&cid=16303 (accessed on 20 April 2007).
- Carlton, J.T. Deep invasion ecology and the assembly of communities in historical time. In Biological Invasions in Marine Ecosystems: Ecological, Management, and Geographic Perspectives; Rilov, G., Crooks, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 13–56. [Google Scholar]
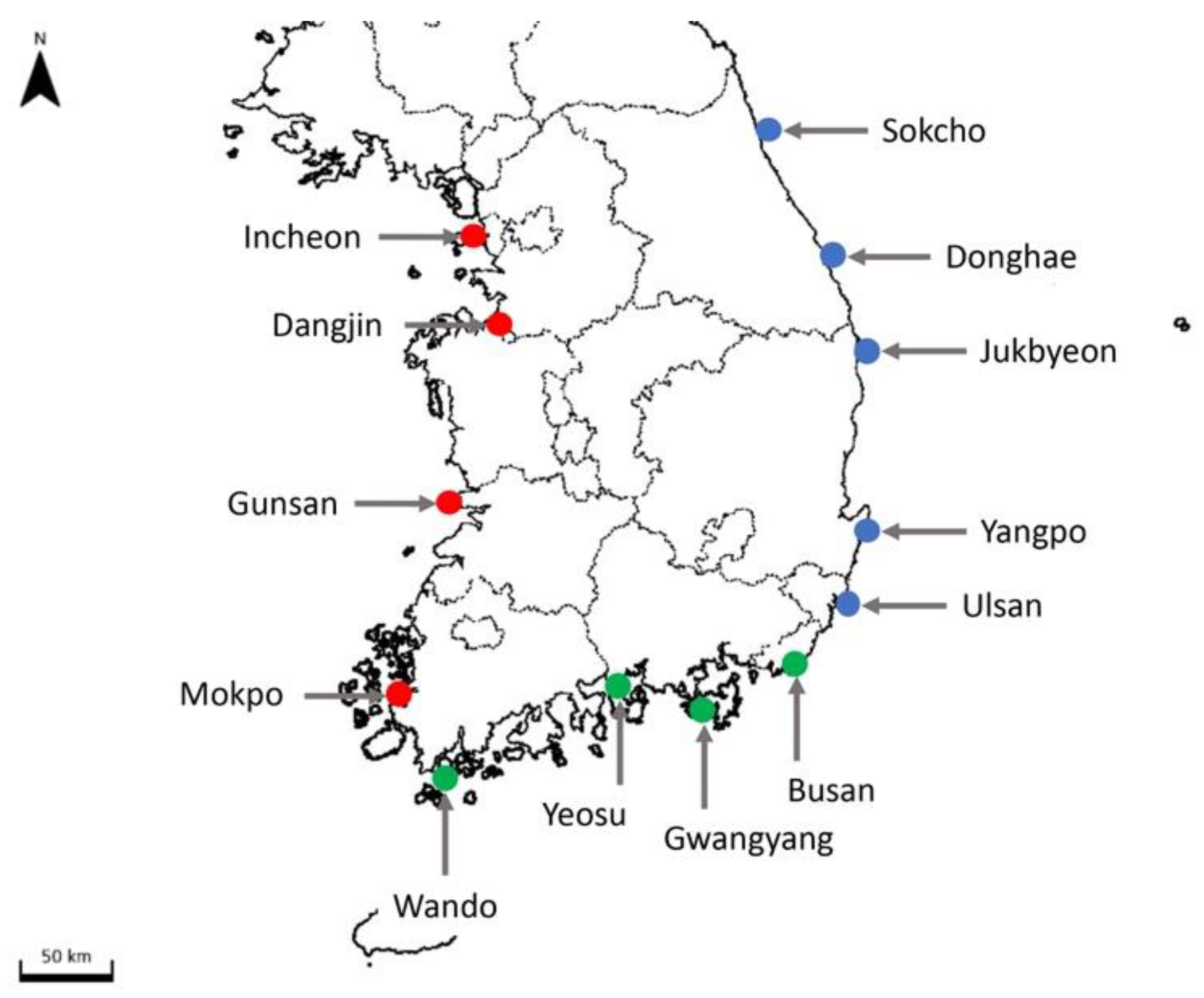

| Locality | Region | GIS Coordinates | Survey Date (2020) | Water Temp. (°C) | Salinity (psu) | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Incheon | Yellow Sea | 37.460556 N, 126.625278 E | 11 May | 14.9 | 30.1 | 8.02 |
| 2 | Dangjin | 36.986944 N, 126.746111 E | 11 May | 15.0 | 30.6 | 8.19 | |
| 3 | Gunsan | 35.935833 N, 126.516667 E | 11 May | 15.5 | 31.3 | 8.25 | |
| 4 | Mokpo | 34.783861 N, 126.389222 E | 12 May | 15.7 | 29.7 | 8.08 | |
| 5 | Wando | Korea Strait | 34.317354 N, 126.753546 E | 12 May | 15.1 | 33.5 | 8.09 |
| 6 | Yeosu | 34.717166 N, 127.749114 E | 12 May | 17.2 | 32.9 | 8.18 | |
| 7 | Gwangyang | 34.908611 N, 127.726111 E | 12 May | 18.2 | 31.5 | 8.09 | |
| 8 | Tongyeong | 34.827222 N, 128.389222 E | 13 May | 16.3 | 34.0 | 8.03 | |
| 9 | Busan | 35.099722 N, 129.755635 E | 13 May | 17.1 | 34.5 | 8.07 | |
| 10 | Ulsan | East Sea | 35.511111 N, 129.385833 E | 13 May | 18.0 | 33.8 | 8.07 |
| 11 | Yangpo | 35.877818 N, 129.519892 E | 14 May | 13.7 | 34.4 | 8.09 | |
| 12 | Jukbyeon | 37.055556 N, 129.419444 E | 14 May | 14.9 | 34.1 | 8.10 | |
| 13 | Donghae | 37.498889 N, 129.134356 E | 14 May | 14.5 | 34.3 | 8.16 | |
| 14 | Sokcho | 38.210444 N, 128.596249 E | 15 May | 15.7 | 34.1 | 8.12 | |
| Species | Collecting Sites | GenBank Accession No. | Sequence Length (bp) | Primers * | Color of Colony ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Botrylloides diegensis | Incheon | MW579604 | 672 | 1 | Light brown, dark brown |
| Gunsan | MW579609 | 672 | 1 | Brown | |
| MW579615 | 672 | 1 | Light brown, dark brown | ||
| Yeosu | MW579611 | 672 | 1 | White, dark purple | |
| MW579612 | 672 | 1 | Dark purple | ||
| MW579613 | 672 | 1 | Light brown, dark brown | ||
| Tongyeong | MW579620 | 867 | 2 | Light brown, dark brown | |
| Ulsan | MW579610 | 867 | 2 | Light brown | |
| MW579617 | 672 | 1 | Dark purple | ||
| MW579618 | 672 | 1 | Light brown | ||
| Yangpo | MW579605 | 672 | 1 | Yellow, dark purple | |
| MW579606 | 672 | 1 | Lemon, purple | ||
| MW579607 | 672 | 1 | Lemon, dark purple | ||
| MW579619 | 672 | 1 | Brown, dark brown | ||
| Donghae | MW579615 | 672 | 1 | Light brown, brown | |
| Sokcho | MW579616 | 867 | 2 | Dark brown | |
| Botryllus schlosseri | Incheon | MW584324 | 856 | 2 | Purple |
| Gunsan | MW584320 | 856 | 2 | Dark purple | |
| MW584321 | 856 | 2 | Light brown | ||
| MW584322 | 856 | 2 | Brown | ||
| MW584323 | 856 | 2 | Brown | ||
| MW584327 | 856 | 2 | Purple | ||
| Yeosu | MW584326 | 856 | 2 | Dark purple | |
| Ulsan | MW584325 | 856 | 2 | Dark purple with yellow line | |
| Donghae | MW584319 | 856 | 2 | Dark purple | |
| Sokcho | MW584328 | 856 | 2 | Dark purple |
| Title | Species | n * | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | B. diegensis (Korea) | 16 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | B. diegensis (other regions) ** | 22 | 0.3 | 0.2 | |||||||||||
| 3 | B. anceps | 1 | 15.9 | 16.0 | NA | ||||||||||
| 4 | B. fuscus | 1 | 21.0 | 21.2 | 21.2 | NA | |||||||||
| 5 | B. giganteus | 1 | 18.8 | 18.9 | 22.2 | 21.9 | NA | ||||||||
| 6 | B. israeliense | 1 | 18.2 | 18.2 | 21.8 | 22.4 | 18.8 | NA | |||||||
| 7 | B. leachii | 5 | 17.2 | 17.1 | 20.0 | 19.6 | 16.2 | 19.9 | 0.4 | ||||||
| 8 | B. nigrum | 2 | 16.4 | 16.5 | 15.1 | 17.8 | 20.6 | 20.9 | 19.1 | 0.8 | |||||
| 9 | B. perspicuus | 1 | 15.8 | 16.0 | 18.4 | 18.9 | 23.1 | 20.3 | 20.3 | 16.5 | NA | ||||
| 10 | B. simodensis | 1 | 17.3 | 17.3 | 18.0 | 19.2 | 21.2 | 22.8 | 22.2 | 17.1 | 9.1 | NA | |||
| 11 | B. violaceus | 16 | 24.2 | 24.4 | 22.1 | 24.8 | 22.7 | 25.8 | 22.5 | 21.6 | 23.4 | 23.4 | 1.3 | ||
| 12 | Botrylloides sp. | 1 | 20.0 | 20.2 | 21.3 | 23.1 | 19.8 | 6.7 | 20.9 | 20.9 | 22.1 | 23.2 | 23.5 | NA | |
| 13 | Botryllus schlosseri | 18 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 18.2 | 20.9 | 21.2 | 23.2 | 22.3 | 18.3 | 19.2 | 19.5 | 24.4 | 22.9 | 6.5 |
| Locality | GIS | 2017 | 2018 | 2020 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | Jul. | Aug. | Sep. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | Jun. | Jul. | Aug. | Feb. | May | Jul. | Oct. | |
| 1. Incheon | 37.460556 | 126.625278 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| 2. Dangjin | 36.986944 | 126.516667 | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||
| 3. Gunsan | 35.935833 | 126.516667 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||
| 4. Mokpo | 34.783861 | 126.389222 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 5. Wando | 34.317354 | 126.753546 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||
| 6. Yeosu | 34.717166 | 127.749114 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 7. Gwangyang | 34.908611 | 127.726111 | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||
| 8. Tongyeong | 34.827222 | 128.389222 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 9. Busan | 35.099722 | 129.755635 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||
| 10. Ulsan | 35.099722 | 129.755635 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||
| 11. Yangpo | 35.511111 | 129.385833 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 12. Jukbyeon | 35.877818 | 129.519892 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 13. Donghae | 37.498889 | 129.134356 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 14. Sokcho | 38.210444 | 128.596249 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, T.; Shin, S. First Record of Colonial Ascidian, Botrylloides diegensis Ritter and Forsyth, 1917 (Ascidiacea, Stolidobranchia, Styelidae), in South Korea. Water 2021, 13, 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162164
Lee T, Shin S. First Record of Colonial Ascidian, Botrylloides diegensis Ritter and Forsyth, 1917 (Ascidiacea, Stolidobranchia, Styelidae), in South Korea. Water. 2021; 13(16):2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162164
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Taekjun, and Sook Shin. 2021. "First Record of Colonial Ascidian, Botrylloides diegensis Ritter and Forsyth, 1917 (Ascidiacea, Stolidobranchia, Styelidae), in South Korea" Water 13, no. 16: 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162164
APA StyleLee, T., & Shin, S. (2021). First Record of Colonial Ascidian, Botrylloides diegensis Ritter and Forsyth, 1917 (Ascidiacea, Stolidobranchia, Styelidae), in South Korea. Water, 13(16), 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162164






