Baseline Study on Microplastics in Indian Rivers under Different Anthropogenic Influences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selected Rivers
2.2. Sampling Sites
2.3. Meteorological Conditions
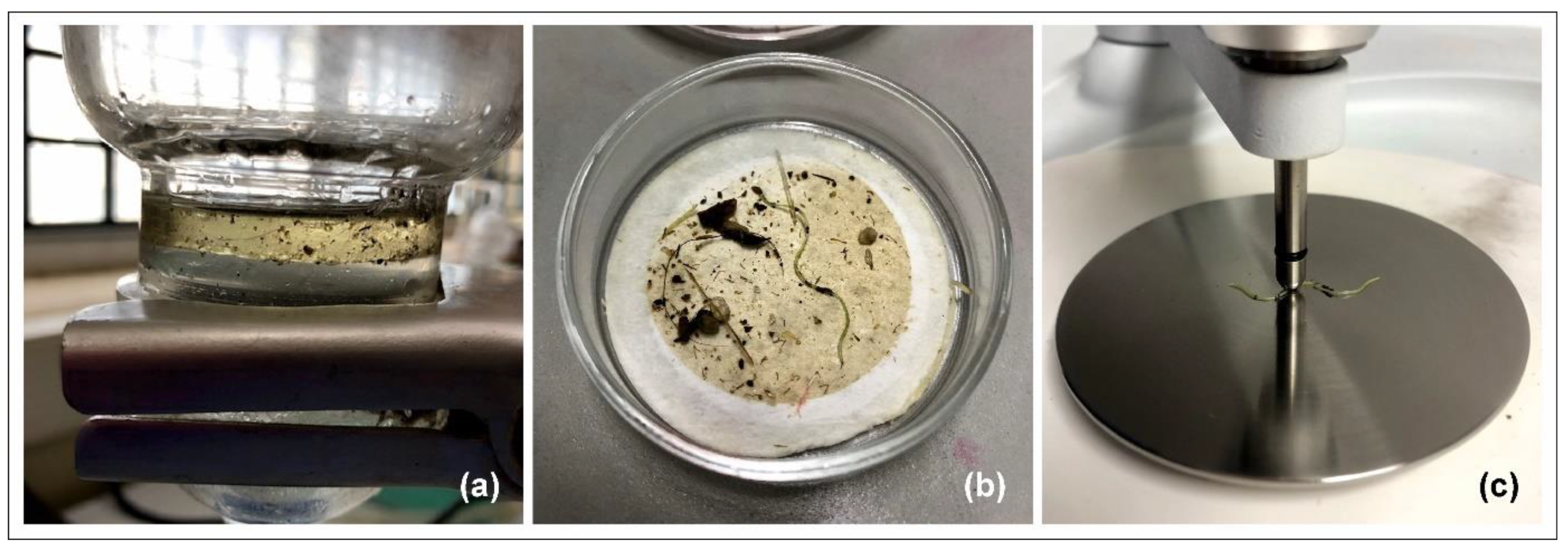
2.4. Sampling Methodology
2.5. Sample Preparation and Analysis
- MPvis [n/sample]:
- Number of microscopically identified MP particles
- perror [%]:
- Theoretical error ratio of polymer identification
- MPblank [n]:
- Average number of MP particles occurring by cross contamination
- V [L]:
- Sampling volume determined by the mechanical flow meter
2.6. Statistical Analysis
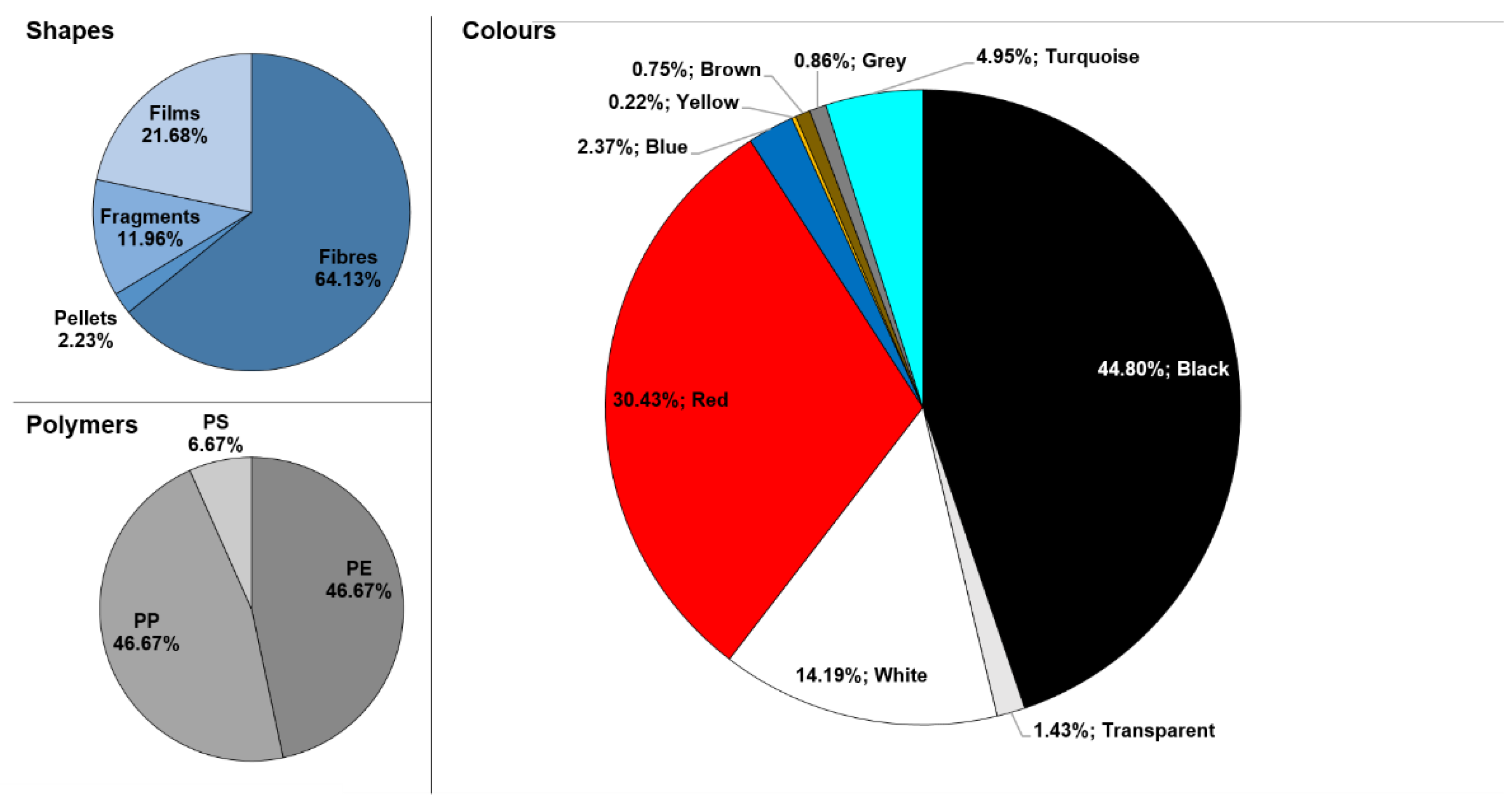
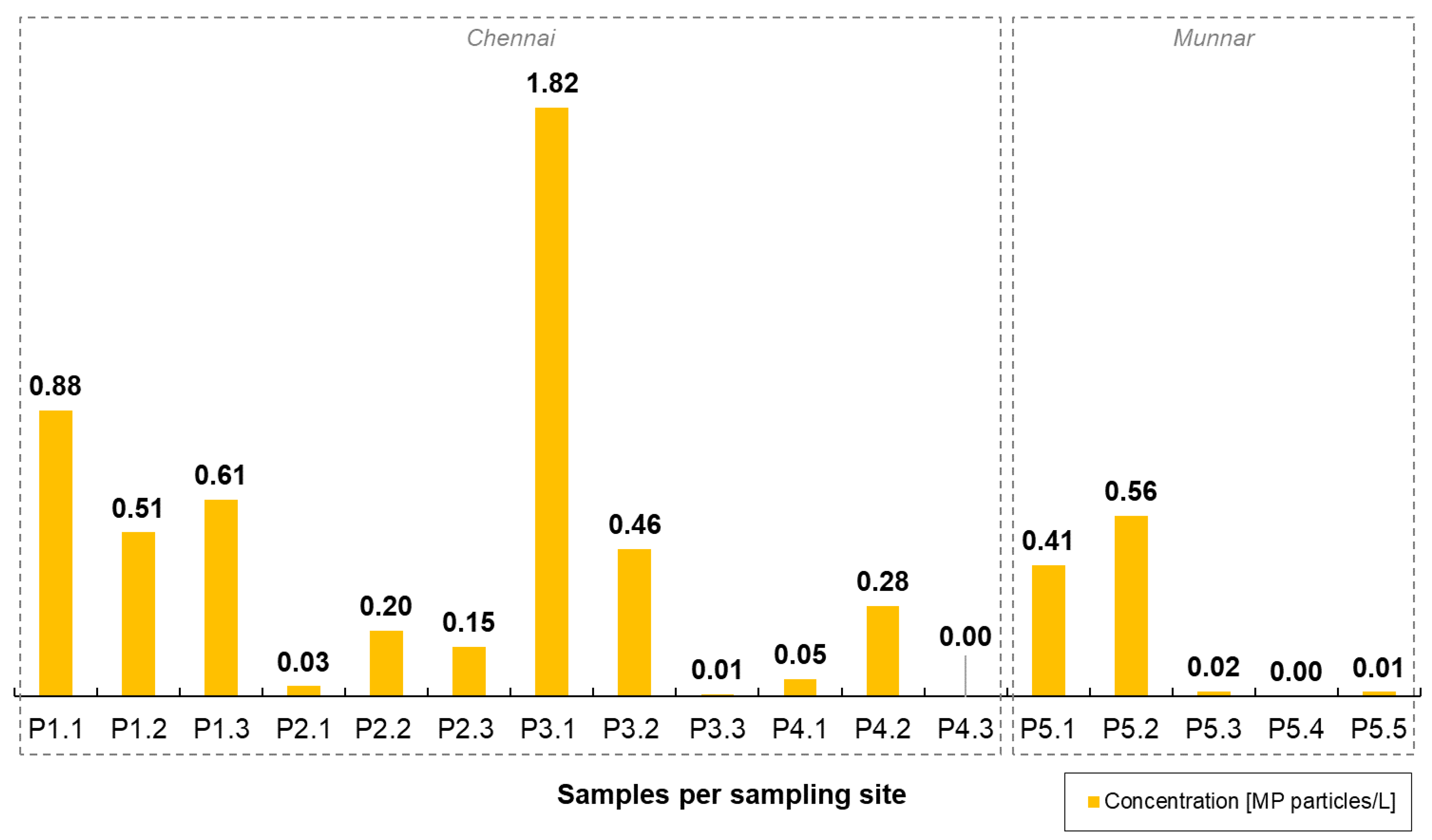
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistical Analyses
3.2. Comparison to Other Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arthur, C.; Baker, J.; Bamford, H. Proceedings of the International Research Workshop on the Occurrence, Effects and Fate of Microplastic Marine Debris, Tacoma, WA, USA, 9–11 September 2008.
- Horton, A.A.; Svendsen, C.; Williams, R.J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E. Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames, UK–Abundance, sources and methods for effective quantification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, M.; De Meester, S.; Van Landuyt, L.; De Clerck, K.; Janssen, C.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeken, I.; Primpke, S.; Beyer, B.; Gütermann, J.; Katlein, C.; Krumpen, T.; Bergmann, M.; Hehemann, L.; Gerdts, G. Arctic sea ice is an important temporal sink and means of transport for microplastic. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dris, R.; Imhof, H.; Sanchez, W.; Gasperi, J.; Galgani, F.; Tassin, B.; Laforsch, C. Beyond the ocean: Contamination of freshwater ecosystems with (micro-)plastic particles. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, J.; Wright, S.L.; Dris, R.; Collard, F.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Kelly, F.J.; Tassin, B. Microplastics in air: Are we breathing it in? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldschläger, K.; Lechthaler, S.; Stauch, G.; Schüttrumpf, H. The way of microplastic through the environment–Application of the source-pathway-receptor model (review). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, L.J.J.; van Emmerik, T.; van der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L. More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rech, S.; Macaya-Caquilpán, V.; Pantoja, J.; Rivadeneira, M.; Madariaga, D.J.; Thiel, M. Rivers as a source of marine litter–A study from the SE Pacific. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 82, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; Van Der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.-W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napper, I.E.; Baroth, A.; Barrett, A.C.; Bhola, S.; Chowdhury, G.W.; Davies, B.F.; Duncan, E.M.; Kumar, S.; Nelms, S.E.; Niloy, N.H.; et al. The abundance and characteristics of microplastics in surface water in the transboundary Ganges River. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.; Biswas, A.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water bodies of india: A review. Res. Environ. Life Sci. 2014, 7, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopal, T.; Giridharan, L.; Jayaprakash, M. Characterization and Risk Assessment Studies of Bed Sediment of River Adyar: An Application of Speciation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2009, 3, 581–598. [Google Scholar]
- Amrutha, K.; Warrier, A.K. The first report on the source-to-sink characterization of microplastic pollution from a riverine environment in tropical India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, R.; Robin, R.; Purvaja, R.; Ganguly, D.; Anandavelu, I.; Raghuraman, R.; Hariharan, G.; Ramakrishna, A.; Ramesh, R. Microplastics along the beaches of southeast coast of India. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, J.P.; Mathews, G.; Raj, K.D.; Laju, R.; Bharath, M.S.; Kumar, P.D.; Arasamuthu, A.; Grimsditch, G. Marine debris—An emerging threat to the reef areas of Gulf of Mannar, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, R.; Karthik, R.; Purvaja, R.; Ganguly, D.; Anandavelu, I.; Mugilarasan, M.; Ramesh, R. Holistic assessment of microplastics in various coastal environmental matrices, southwest coast of India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyasakar, A.; Neelavannan, K.; Krishnakumar, S.; Prabaharan, G.; Priyanka, T.S.A.; Magesh, N.; Godson, P.; Srinivasalu, S. Macrodebris and microplastic distribution in the beaches of Rameswaram Coral Island, Gulf of Mannar, Southeast coast of India: A first report. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruthy, S.; Ramasamy, E. Microplastic pollution in Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India: The first report of microplastics in lake and estuarine sediments in India. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerasingam, S.; Ranjani, M.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Bagaev, A.; Mukhanov, V.; Litvinyuk, D.; Verzhevskaia, L.; Guganathan, L.; Vethamony, P. Microplastics in different environmental compartments in India: Analytical methods, distribution, associated contaminants and research needs. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvana, N.; Savitha, S.; Durga Devi, G.; Prakash, P. A Correlation Study of the Major and Trace metals present in the riverine sediments of the river Kortalaiyar in Tamilnadu, India. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2015, 7, 3121–3125. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeshan, G.; Anandasabari, K.; Poornavel, S. Groundwater quality of kosasthalaiyar river basin, thiruvallur district, Tamil Nadu, India. Int. J. Innov. Res. Eng. Technol. 2015, 4, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, R.; Ramachandran Purvaja, G.; Chand Parashar, D.; Kumar Gupta, P.; Prasad Mitra, A. Anthropogenic Forcing on methane efflux from Polluted Wetlands (Adyar River) of Madras City, India. Ambio 1997, 26, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Nammalwar, P.; Pakshirajan, P. Ecotoxicological effects of industrial pollution in the estuarine Grey mullets with reference to aquaculture along the Madras coast. In Proceedings of the IV National Symposium on Environment, Madras, India, 7–10 February 1995. [Google Scholar]
- World Population Review. Chennai Population. 2019. Available online: http://worldpopulationreview.com/world-cities/chennai/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K.P.; Manjusree, T.M.; Arunkumar, K.S. Seasonal variation in major ion chemistry of a tropical mountain river, the southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 2333–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, V.; Vijith, H.; Geetha, N.; Shiny, R. Regional Scale Erosion Assessment of a Sub-tropical Highland Segment in the Western Ghats of Kerala, South India. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 3715–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K.P.; Abe, G.; Kannan, N. Morphometrical analysis of two tropical mountain river basins of contrasting environmental settings, the southern Western Ghats, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 66, 2353–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- India Meteorological Department. Seasonal Rainfall Distribution for Tamil Nadu & Puducherry of Date 26.11.2019. 2019. Available online: http://www.imdchennai.gov.in/dailyweekly.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Meteorological Centre Thiruvananthapuram. Performance of North East Monsoon 2019 over Idukki: From 01-Oct-2019 to 26-Nov-2019. 2019. Available online: https://www.imdtvm.gov.in/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=63&Itemid=89 (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.G.; Suaria, G.; Perold, V.; Pierucci, A.; Bornman, T.G.; Aliani, S. Sampling microfibres at the sea surface: The effects of mesh size, sample volume and water depth. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Pojar, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sampling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, F.; Demars, C.; Wieser, O.; Kunz, M.; De Alencastro, L.F. Plastic pollution in Swiss surface waters: Nature and concentrations, interaction with pollutants. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Hauk, A.; Walter, U.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics profile along the Rhine River. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Methods for sampling and detection of microplastics in water and sediment: A critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechthaler, S.E.; Hildebrandt, L.; Stauch, G.; Schüttrumpf, H. Canola oil extraction in conjunction with a plastic free separation unit optimises microplastics monitoring in water and sediment. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 5128–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechthaler, S.; Schwarzbauer, J.; Reicherter, K.; Stauch, G.; Schüttrumpf, H. Regional study of microplastics in surface waters and deep sea sediments south of the Algarve Coast. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechthaler, S.E.; Esser, V.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Stauch, G. Why analysing microplastics in floodplains matters: Application in a sedimentary context. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesch, C.; Elert, A.M.; Wörner, M.; Braun, U.; Klein, R.; Paulus, M. Assuring quality in microplastic monitoring: About the value of clean-air devices as essentials for verified data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scopetani, C.; Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Chelazzi, D.; Cincinelli, A.; Setälä, H.; Pflugmacher, S. Self-contamination from clothing in microplastics research. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noren, F. Small Plastic Particles in Coastal Swedish Waters. 2008. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284312290 (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Kanhai, L.D.K.; Officer, R.; Lyashevska, O.; Thompson, R.C.; O’Connor, I. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition along a latitudinal gradient in the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.L.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Munno, K.; Hurley, R.R.; Welden, N.A. Is It or Isn’t It: The Importance of Visual Classification in Microplastic Characterization. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldschläger, K.; Schüttrumpf, H. Erosion Behavior of Different Microplastic Particles in Comparison to Natural Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13219–13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.; Woodward, J.; Rothwell, J.J. Microplastic contamination of river beds significantly reduced by catchment-wide flooding. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzetto, L.; Bussi, G.; Futter, M.N.; Butterfield, D.; Whitehead, P.G. A theoretical assessment of microplastic transport in river catchments and their retention by soils and river sediments. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2016, 18, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, V.; Hariprasad, V.; Mohan, R.; Ramasubramanian, R. Diurnal variations in the water quality of sewage polluted Adyar mangrove water, east coast of India. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 1994, 23, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Konechnaya, O.; Schwanen, C.; Schwarzbauer, J. Application of multi-step approach for comprehensive identification of microplastic particles in diverse sediment samples. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, M.; Sampath, S.; Muñoz-Arnanz, J.; Jiménez, B.; Chakraborty, P. Plasticizers and bisphenol A in Adyar and Cooum riverine sediments, India: Occurrences, sources and risk assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2789–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowri, V.S.; Ramachandran, S.; Ramesh, R.; Pramiladevi, I.R.R.; Krishnaveni, K. Application of GIS in the study of mass transport of pollutants by Adyar and Cooum Rivers in Chennai, Tamilnadu. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 138, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, K.; Seshachalam, S.; Neelavannan, K.; Anburaj, V.; Rachel, M.; Ravi, S.; Bharath, M.; Achyuthan, H. Quantification of microplastic in Red Hills Lake of Chennai city, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 33297–33306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasalu, S.; Natesan, U.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Kalam, N.; Anbalagan, S.; Sujatha, K.; Alagarasan, C. Microplastics as an emerging threat to the freshwater ecosystems of Veeranam lake in south India: A multidimensional approach. Chemosphere 2021, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, M.; Nallathambi, G.; Srinivasalu, S. Fate and Transport of Microplastics from Water Sources. Curr. Sci. 2019, 117, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.; Jeyasanta, K.I.; Sathish, N.; Booth, A.M.; Edward, J.P. Profiling microplastics in the Indian edible oyster, Magallana bilineata collected from the Tuticorin coast, Gulf of Mannar, Southeastern India. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Liboiron, M.; Kiessling, T.; Charron, L.; Alling, A.; Lebreton, L.; Richards, H.; Roth, B.; Ory, N.C.; Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; et al. Microplastic sampling with the AVANI trawl compared to two neuston trawls in the Bay of Bengal and South Pacific. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comnea-Stancu, I.R.; Wieland, K.; Ramer, G.; Schwaighofer, A.; Lendl, B. On the Identification of Rayon/Viscose as a Major Fraction of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Discrimination between Natural and Manmade Cellulosic Fibers Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Lambert, S. Microplastics Are Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Freshwater Environments: An Overview. In Freshwater Microplastics: Emerging Environmental Contaminants? Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
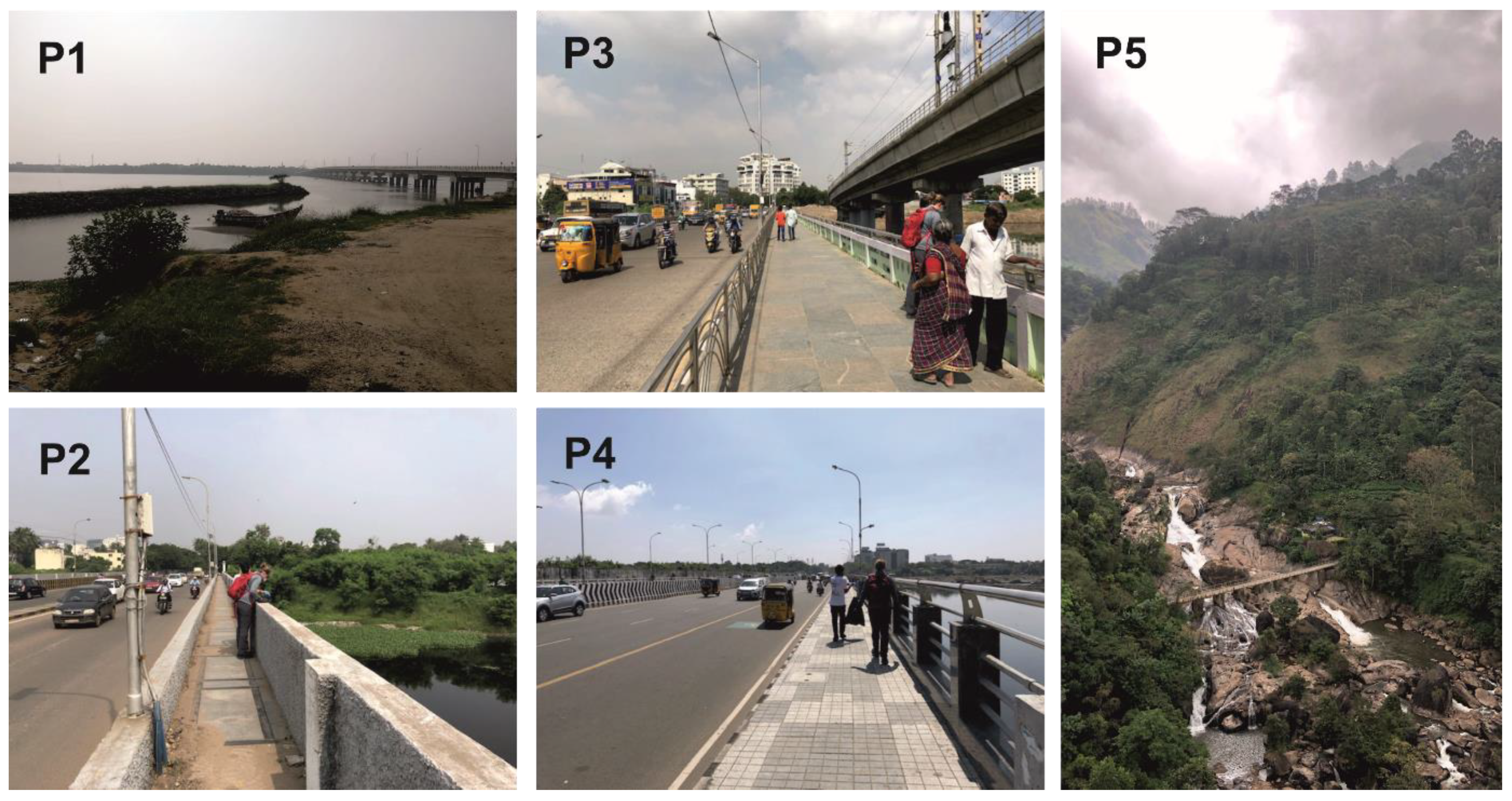



| River | Sampling Point | Number | Coordinates | Sampling Dates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kosasthalaiyar (Chennai) | Ennore Creek Flyover Bridge (P1) | 3 | “13°13′45.88″ N″ “80°19′8.08″ E″ | 06, 08, 11 November 2019 |
| Adyar (Chennai) | Anna Salai Bridge (P2) | 3 | “13°1′33.80″ N″ “80°14′37.27″ E″ | 06, 08, 11 November 2019 |
| Adyar (Chennai) | Kotturpurnam Bridge (P3) | 3 | “13°1′2.44″ N″ “80°13′30.15″ E″ | 06, 08, 11 November 2019 |
| Adyar (Chennai) | Thiru-Vi-Ka Bridge (P4) | 3 | “13°0′46.98″ N″ “80°15′33.18″ E″ | 06, 08, 11 November 2019 |
| Muthirappuzhayar (Munnar) | Attukad Waterfalls Bridge (P5) | 5 | “10°3′12.39″ N″ “77°3′31.47″ E″ | 22, 23, 24, 25, 26 November 2019 |
| Parameter | MPtotal/V | Fibres/V | Pellets/V | Fragments/V | Films/V | CMP/D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r [-] | −0.06 | −0.09 | 0.15 | −0.05 | 0.11 | −0.20 |
| p [-] | 0.829 | 0.727 | 0.557 | 0.849 | 0.661 | 0.559 |
| Compartment | Location | Average MP Concentration | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| River | Adyar River, Tamil Nadu | 0.33 particle/L | This study |
| Kosasthalaiyar River, Tamil Nadu | 0.67 particle/L | This study | |
| Multhirappuzhayar River, Kerala | 0.20 particle/L | This study | |
| Ganges, India/Bangladesh | 0.038 particle/L | Napper et al. (2021) [12] | |
| Netravathi River, Karnataka | 288 pieces/m³ | Amrutha and Warrier (2020) [15] | |
| Lake | Red Hills Lake, Tamil Nadu | 5.9 particles/L | Gopinath et al. (2020) [53] |
| Veeranam Lake, Tamil Nadu | 28 items/km2 | Bharath K et al. (2021) [54] | |
| Coast | In front of Kerala, southwest coast of India | 1.25 ± 0.88 particles/m3 | Robin et al. (2020) [18] |
| Chennai marina | 11 items/L | Ganesan et al. (2019) [55] | |
| Tuticorin, Gulf of Mannar | 12.14–31.05 items/L | Patterson et al. (2019) [56] | |
| Offshore of Bay of Bengal | 16,107 ± 47,077 items/km2 | Eriksen et al. (2018) [57] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lechthaler, S.; Waldschläger, K.; Sandhani, C.G.; Sannasiraj, S.A.; Sundar, V.; Schwarzbauer, J.; Schüttrumpf, H. Baseline Study on Microplastics in Indian Rivers under Different Anthropogenic Influences. Water 2021, 13, 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121648
Lechthaler S, Waldschläger K, Sandhani CG, Sannasiraj SA, Sundar V, Schwarzbauer J, Schüttrumpf H. Baseline Study on Microplastics in Indian Rivers under Different Anthropogenic Influences. Water. 2021; 13(12):1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121648
Chicago/Turabian StyleLechthaler, Simone, Kryss Waldschläger, Chavapati Gouse Sandhani, S. A. Sannasiraj, V. Sundar, Jan Schwarzbauer, and Holger Schüttrumpf. 2021. "Baseline Study on Microplastics in Indian Rivers under Different Anthropogenic Influences" Water 13, no. 12: 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121648
APA StyleLechthaler, S., Waldschläger, K., Sandhani, C. G., Sannasiraj, S. A., Sundar, V., Schwarzbauer, J., & Schüttrumpf, H. (2021). Baseline Study on Microplastics in Indian Rivers under Different Anthropogenic Influences. Water, 13(12), 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121648








