Submarine Groundwater Discharge in a Coastal Bay: Evidence from Radon Investigations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
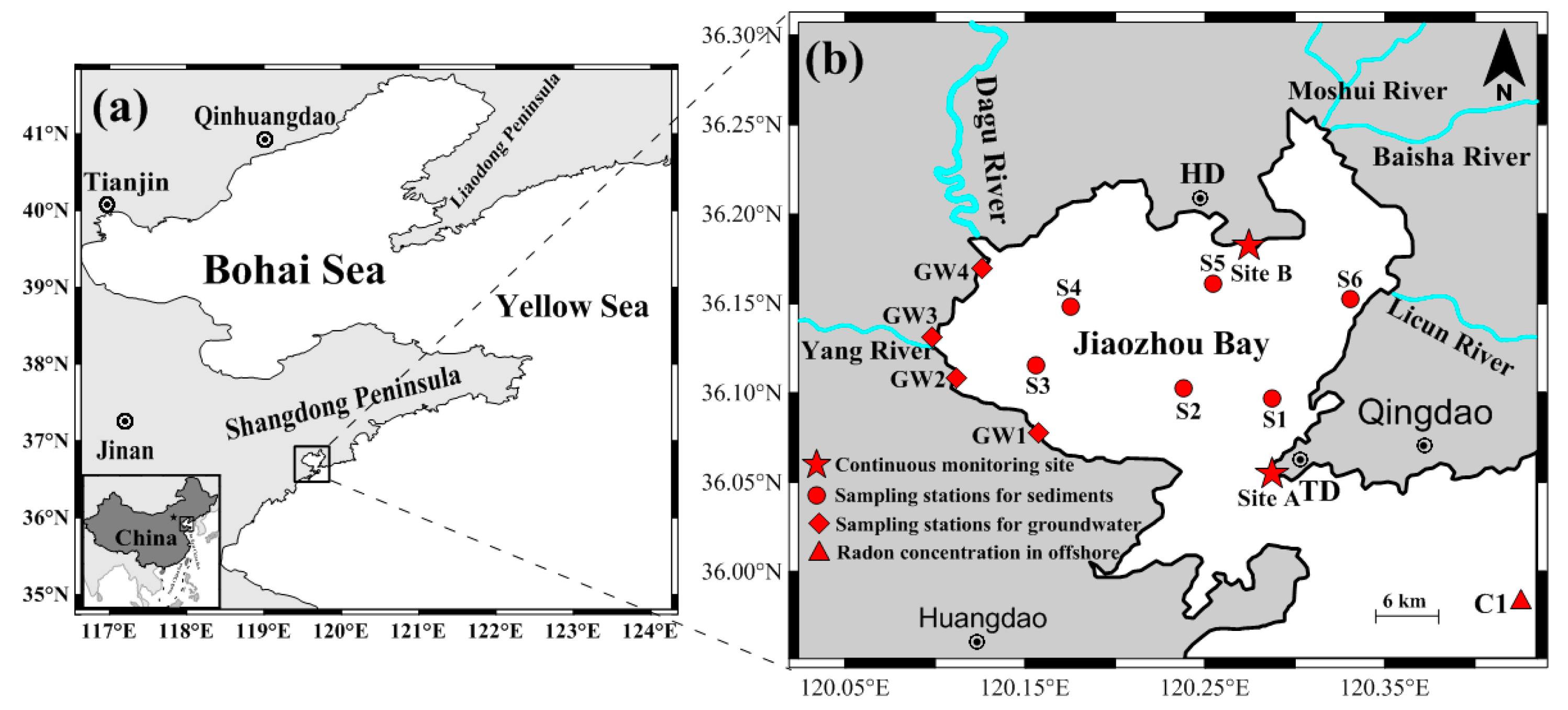
2.1. Study Site
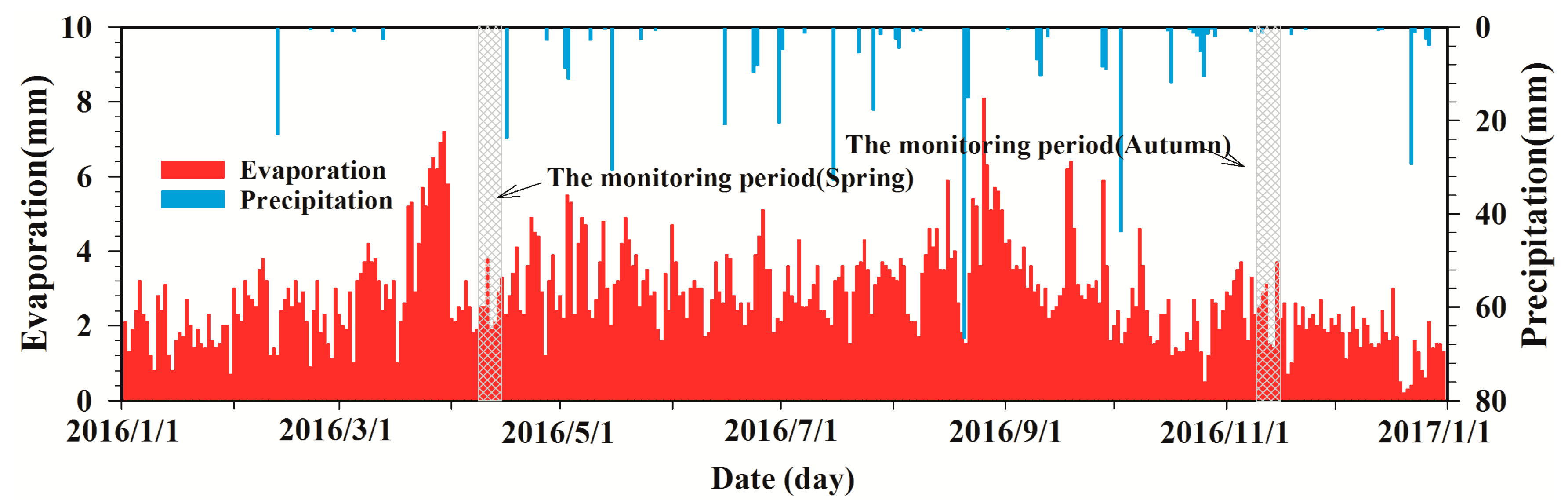
2.2. Time-Series Deployments
2.3. 226Ra Enrichment and Analysis
2.4. Determination of 222Rn in Pore Water
2.5. Radon Mass Balance Model
3. Results
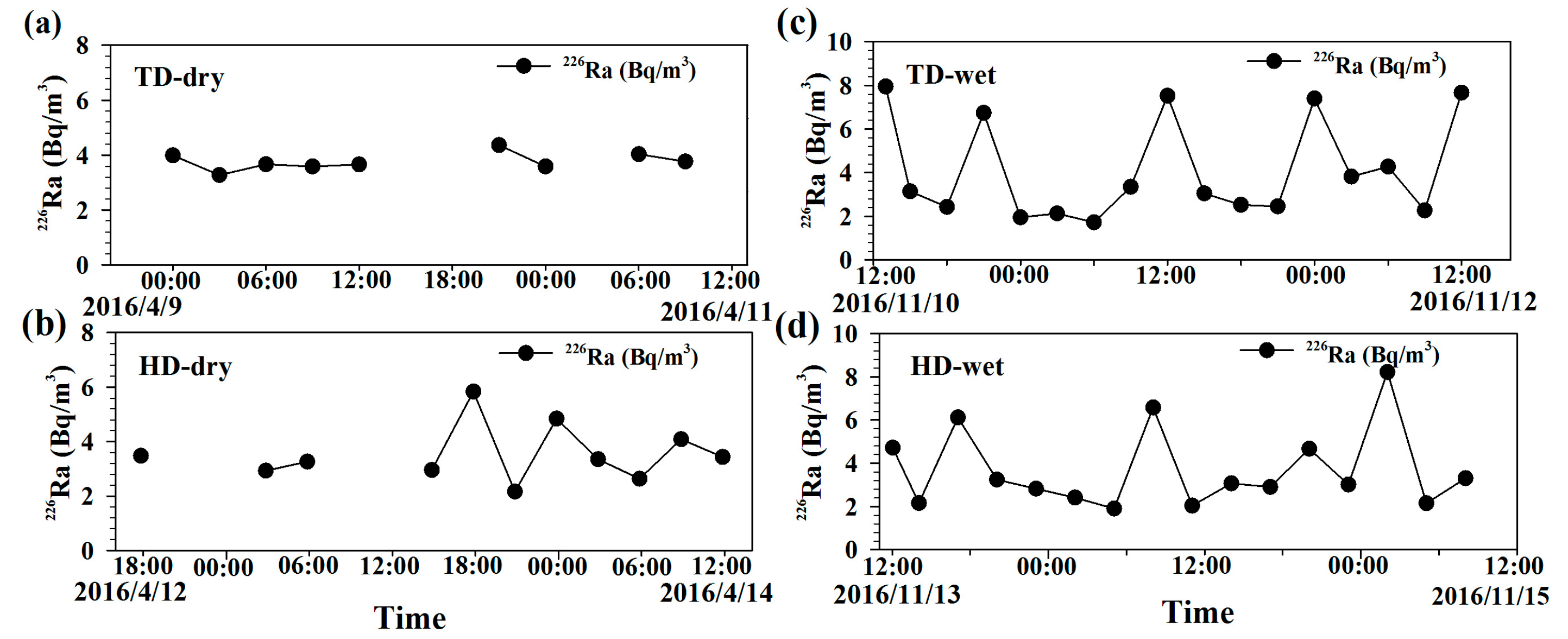
3.1. 222Rn Inventory and 226Ra Supply
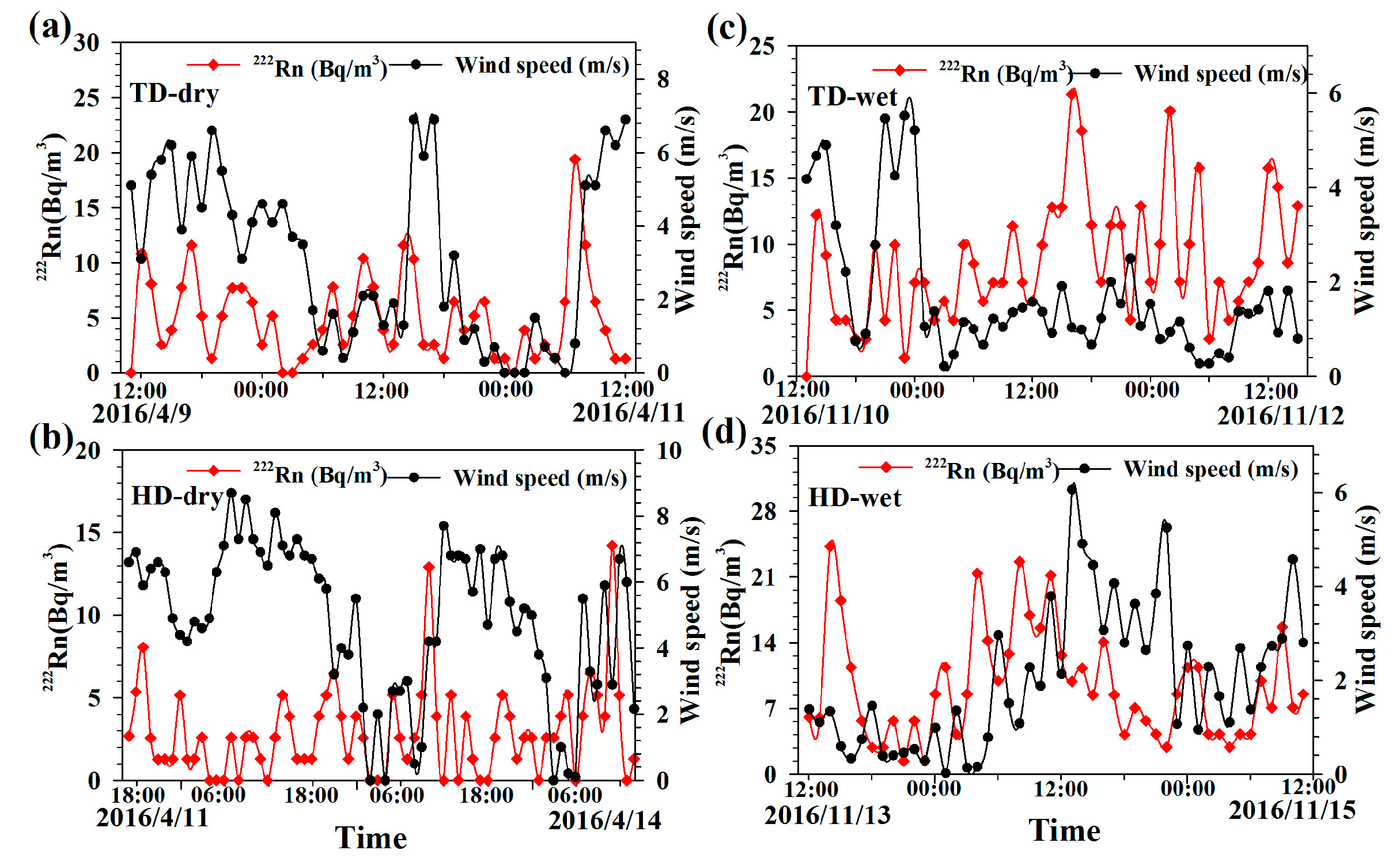
3.2. Tidal Effects
3.3. Atmospheric Loss
3.4. Diffusive Flux From Bottom Sediments
3.5. Mixing Loss and SGD Flux
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainty Analysis
4.2. SGD Fluxes for Different Sites and Seasons
4.3. Comparisons with Local River Inputs
4.4. Comparisons with Previous Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burnett, W.C.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Huettel, M.; Moore, W.S.; Taniguchi, M. Groundwater and pore water inputs to the coastal zone. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. The Effect of Submarine Groundwater Discharge on the Ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Ryu, J.-W.; Yang, H.-S.; Yun, S.-T. Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) into the Yellow Sea revealed by 228Ra and 226Ra isotopes: Implications for global silicate fluxes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 237, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Key, R.M. Submarine groundwater discharge revealed by 228Ra distribution in the upper Atlantic Ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Jiao, J.J.; Barry, D.A.; Li, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, C.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.-W.; et al. Submarine fresh groundwater discharge into Laizhou Bay comparable to the Yellow River flux. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.Y.; Kim, G.; Primeau, F.W.; Moore, W.S.; Cho, H.-M.; Devries, T.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Charette, M.A.; Cho, Y.-K. Global estimate of submarine groundwater discharge based on an observationally constrained radium isotope model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8438–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makings, U.; Santos, I.R.; Maher, D.T.; Golsby-Smith, L.; Eyre, B.D. Importance of budgets for estimating the input of groundwater-derived nutrients to an eutrophic tidal river and estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 143, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J. Submarine groundwater discharge and nutrient loadings in Tolo Harbor, Hong Kong using multiple geotracer-based models, and their implications of red tide outbreaks. Water Res. 2016, 102, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, C.; Wang, C.; Xiao, K.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Guo, H. Estimation of submarine groundwater discharge and associated nutrient fluxes in eastern Laizhou Bay, China using 222Rn. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Eyre, B.D.; Huettel, M. The driving forces of porewater and groundwater flow in permeable coastal sediments: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 98, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.L.; Santos, I.R.; Maher, D.T. Seasonal exports and drivers of dissolved inorganic and organic carbon, carbon dioxide, methane and δ13C signatures in a subtropical river network. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 575, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.J.; Rapaglia, J.P.; Cochran, J.K.; Bokuniewicz, H.J. Radium mass-balance in Jamaica Bay, NY: Evidence for a substantial flux of submarine groundwater. Mar. Chem. 2007, 106, 419–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandersi, C.J.; Santos, I.R.; Barcellos, R.; Filho, E.S. Elevated concentrations of dissolved Ba, Fe and Mn in a mangrove subterranean estuary: Consequence of sea level rise? Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 43, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; An, A.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, K. Nutrient inputs through submarine groundwater discharge in an embayment: A radon investigation in Daya Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Dan, S.F. Submarine groundwater discharge and its implication for nutrient budgets in the western Bohai Bay, China. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 212, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.-W.; Kim, G.; Lee, W.-C.; Oh, H.-T. The role of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) in nutrient budgets of Gamak Bay, a shellfish farming bay, in Korea. J. Sea Res. 2010, 64, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Lixin, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, X. Factors influencing the distribution of 223Ra and 224Ra in the coastal waters off Tanggu and Qikou in Bohai bay. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 109, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborski, J.; Rogers, A.D.; Bokuniewicz, H.J.; Cochran, J.K.; Young, C. Identification and quantification of diffuse fresh submarine groundwater discharge via airborne thermal infrared remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. The subterranean estuary: A reaction zone of ground water and sea water. Mar. Chem. 1999, 65, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Aggarwal, P.; Aureli, A.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Cable, J.; Charette, M.; Kontar, E.; Krupa, S.; Kulkarni, K.; Loveless, A.; et al. Quantifying submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone via multiple methods. Sci. Total. Environ. 2006, 367, 498–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.R. A device for measuring seepage flux in lakes and estuaries1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.-W. Estimation of seawater–groundwater exchange rate: Case study in a tidal flat with a large-scale seepage face (Laizhou Bay, China). Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 23, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Smith, C.F.; Paulsen, R.J.; O’Rourke, D.; Krupa, S.L.; Christoff, J.L. Spatial and temporal distributions of submarine groundwater discharge rates obtained from various types of seepage meters at a site in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Boufadel, M.C. Long-term persistence of oil from the Exxon Valdez spill in two-layer beaches. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.A.; Mulligan, A.E.; Harvey, C.F. Seasonal oscillations in water exchange between aquifers and the coastal ocean. Nature 2005, 436, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Yang, J.; Wilson, A.M.; Michael, H.A.; Geng, X.; Smith, E.; Boufadel, M.; Yuan, P.; et al. Effects of Tidally Varying Salinity on Groundwater Flow and Solute Transport: Insights From Modelling an Idealized Creek Marsh Aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 9656–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichments. Nature 1996, 380, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, W.; Schubert, M. Submarine groundwater discharge revealed by 222Rn: Comparison of two continuous on-site 222Rn-in-water measurement methods. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Zheng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, K. Improvement of evaluation of water age and submarine groundwater discharge: A case study in Daya Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Scholten, J.; Schmidt, A.; Comanducci, J.F.; Pham, M.; Mallast, U.; Knöller, K. Submarine Groundwater Discharge at a Single Spot Location: Evaluation of Different Detection Approaches. Water 2014, 6, 584–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Dulai, H. Estimating the dynamics of groundwater input into the coastal zone via continuous radon-222 measurements. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 69, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, D.R.; Santos, I.R.; Erler, D.V.; Befus, K.M.; Cardenas, M.B.; Eyre, B.D. Estimating submarine groundwater discharge in a South Pacific coral reef lagoon using different radioisotope and geophysical approaches. Mar. Chem. 2013, 156, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Knoeller, K.; Rocha, C.; Einsiedl, F. Evaluation and source attribution of freshwater contributions to Kinvarra Bay, Ireland, using 222Rn, EC and stable isotopes as natural indicators. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.; Brueggemann, L.; Knoeller, K.; Schirmer, M. Using radon as an environmental tracer for estimating groundwater flow velocities in single-well tests. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Su, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, K.; Li, Y.-B.; Wang, X.-L. Assessment of long-term water quality variation affected by high-intensity land-based inputs and land reclamation in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.-L. Historical Changes in Nutrient Structure and its Influences on Phytoplantkon Composition in Jiaozhou Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 52, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; De Zhu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.S.; Deng, B.; Zhao, M.-X.; Liu, G.Q.; Du, J.Z.; Ren, J.L.; et al. Environmental change in Jiaozhou Bay recorded by nutrient components in sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Lu, C.; Liu, S. Dynamics of biogenic silica dissolution in Jiaozhou Bay, western Yellow Sea. Mar. Chem. 2015, 174, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-G.; Feng, G.; Bai, J.; Chen, M.; Maqbool, F. Effect of copper exposure on bacterial community structure and function in the sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, China. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, M.; An, A.; Qu, W.; Wan, L.; Zheng, C.; et al. Improving Estimation of Submarine Groundwater Discharge Using Radium and Radon Tracers: Application in Jiaozhou Bay, China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 8263–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Zheng, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Seawater-groundwater exchange and nutrients carried by submarine groundwater discharge in different types of wetlands at Jiaozhou Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, X. The spatial distribution of dissolved and particulate heavy metals and their response to land-based inputs and tides in a semi-enclosed industrial embayment: Jiaozhou Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10480–10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, J. Enhanced anthropogenic heavy metal dispersal from tidal disturbance in the Jiaozhou Bay, North China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 161, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Li, G.; Wang, P. Anthropogenic Influences on the Tidal Prism and Water Exchanges in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Y.P. Characteristics of sedimentary environment and tidal inlet evolution of Jiaozhou Bay. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 20, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.D.; Wang, X.H.; Bao, X.W. Land reclamation and its impact on tidal dynamics in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Z.; Gao, H.; Gao, Z.; Feng, S. Simulation of the Lagrangian tide-induced residual velocity in a tide-dominated coastal system: A case study of Jiaozhou Bay, China. Ocean Dyn. 2012, 62, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Guo, Z.R.; Ma, Z.Y.; Yuan, X.J. Distribution characteristics and influence factors of 222Rn in riverine water and groundwater around Jiaozhou Bay. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2015, 37, 490–496. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, N.; Zheng, G. Environmental changes reflected by sedimentary geochemistry in recent hundred years of Jiaozhou Bay, North China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-P.; Yang, G.-P.; Lu, X.-L.; Ding, H.-B.; Zhang, H. Distributions of dissolved monosaccharides and polysaccharides in the surface microlayer and surface water of the Jiaozhou Bay and its adjacent area. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 63, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Song, D. Large inputs of groundwater and associated fluxes of alkalinity and nutrients into Jiaozhou Bay, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durridge Company Inc. RAD AQUA: Continuous Radon-in-Water Accessory for the RAD7 User Manual; Durridge Company Inc.: Billerica, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, M.; Paschke, A.; Lieberman, E.; Burnett, W.C. Air–Water Partitioning of 222Rn and its Dependence on Water Temperature and Salinity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3905–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Burnett, W.C.; Dulai, H.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Moore, W.S. Measurement of224Ra and226Ra Activities in Natural Waters Using a Radon-in-Air Monitor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4680–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, D.R.; Burnett, W.C.; Cable, P.H.; Clark, S.B. A multiple approach to the determination of radon fluxes from sediments. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1998, 236, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Petermann, E.; Stollberg, R.; Gebel, M.; Scholten, J.; Knöller, K.; Lorz, C.; Glück, F.; Riemann, K.; Weiß, H.; et al. Improved Approach for the Investigation of Submarine Groundwater Discharge by Means of Radon Mapping and Radon Mass Balancing. Water 2019, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, J.E.; Martin, J.B. In situ evaluation of nearshore marine and fresh pore water transport into Flamengo Bay, Brazil. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J.; Moore, W.S.; Lee, C.M. Submarine groundwater discharge estimation in an urbanized embayment in Hong Kong via short-lived radium isotopes and its implication of nutrient loadings and primary production. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 82, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Using 222Rn to estimate submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) and the associated nutrient fluxes into Xiangshan Bay, East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.E. Numerical study to hydrodynamic Conditions of the Jiaozhou Bay. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre, S.; Wanninkhof, R.; Chanton, J.P. Trace gas exchange across the air–water interface in freshwater and coastal marine environments. In Biogenic Trace Gases: Measuring Emission From Soil and Water; Matson, P.A., Harriss, R.C., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 52–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, M.J.; Burnett, W.C. Submarine groundwater discharge estimates at a Florida coastal site based on continuous radon measurements. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilson, M.E.Q. An Introduction to the Chemistry of the Sea; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; p. 431. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, C.S.; Kipphut, G.W.; Klump, J.V. Sediment-Water Chemical Exchange in the Coastal Zone Traced by in situ Radon-222 Flux Measurements. Science 1980, 208, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.J.; Guo, Z.R.; Li, W.Q.; Ma, Z.Y.; Wang, B. Estimating submarine groundwater discharge in the Jiaozhou Bay using radium isotopes. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2014, 43, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Du, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S. Nutrient input through submarine groundwater discharge in two major Chinese estuaries: The Pearl River Estuary and the Changjiang River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 203, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Eyre, B.D. Radon tracing of groundwater discharge into an Australian estuary surrounded by coastal acid sulphate soils. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Lao, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, J.; Santos, I.R. Submarine Groundwater Discharge-Derived Carbon Fluxes in Mangroves: An Important Component of Blue Carbon Budgets? J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 6962–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalt, N.; Murgulet, D.; Hu, X. Relating estuarine geology to groundwater discharge at an oyster reef in Copano Bay, TX. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adyasari, D.; Oehler, T.; Afiati, N.; Moosdorf, N. Environmental impact of nutrient fluxes associated with submarine groundwater discharge at an urbanized tropical coast. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 221, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

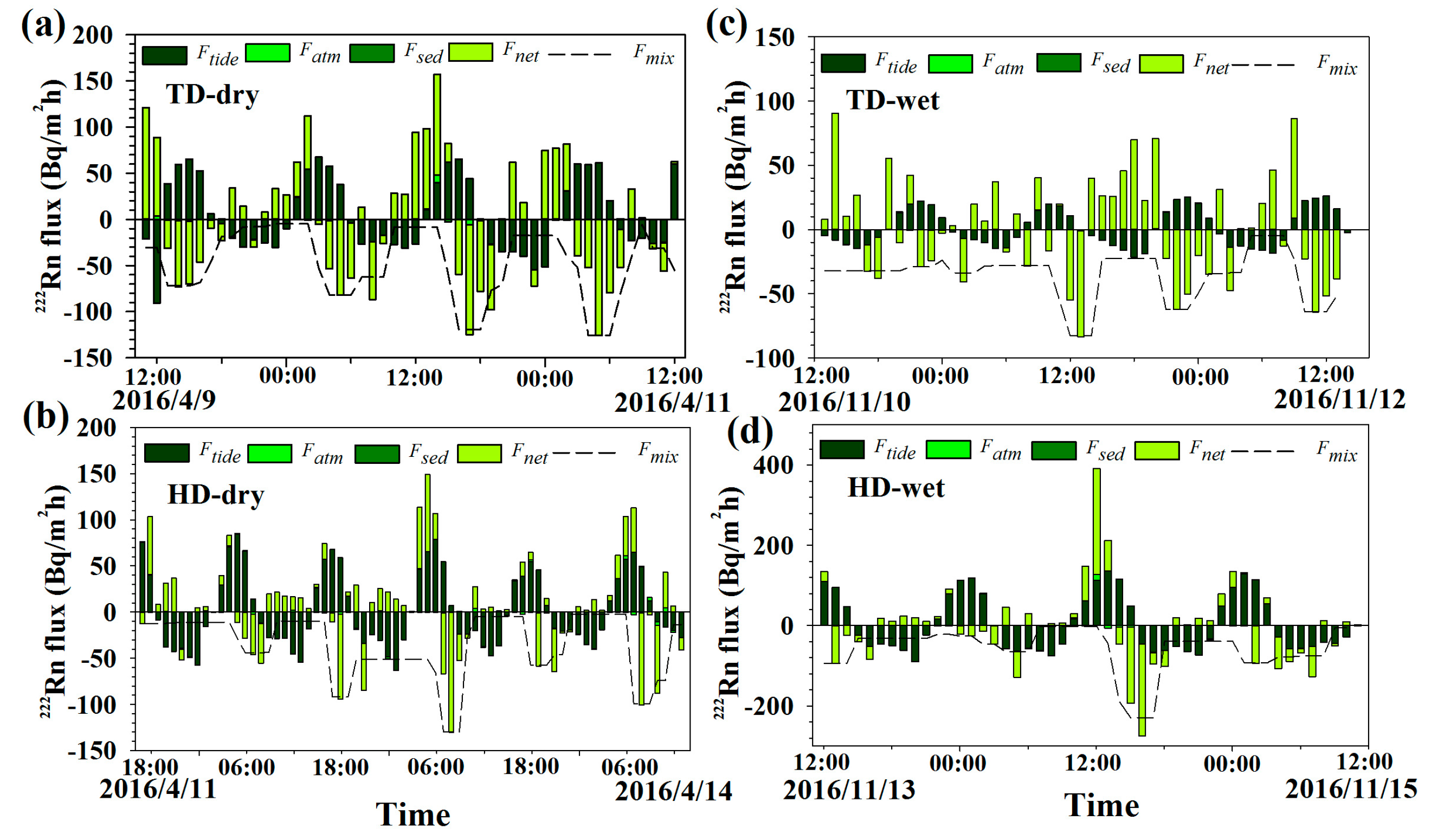
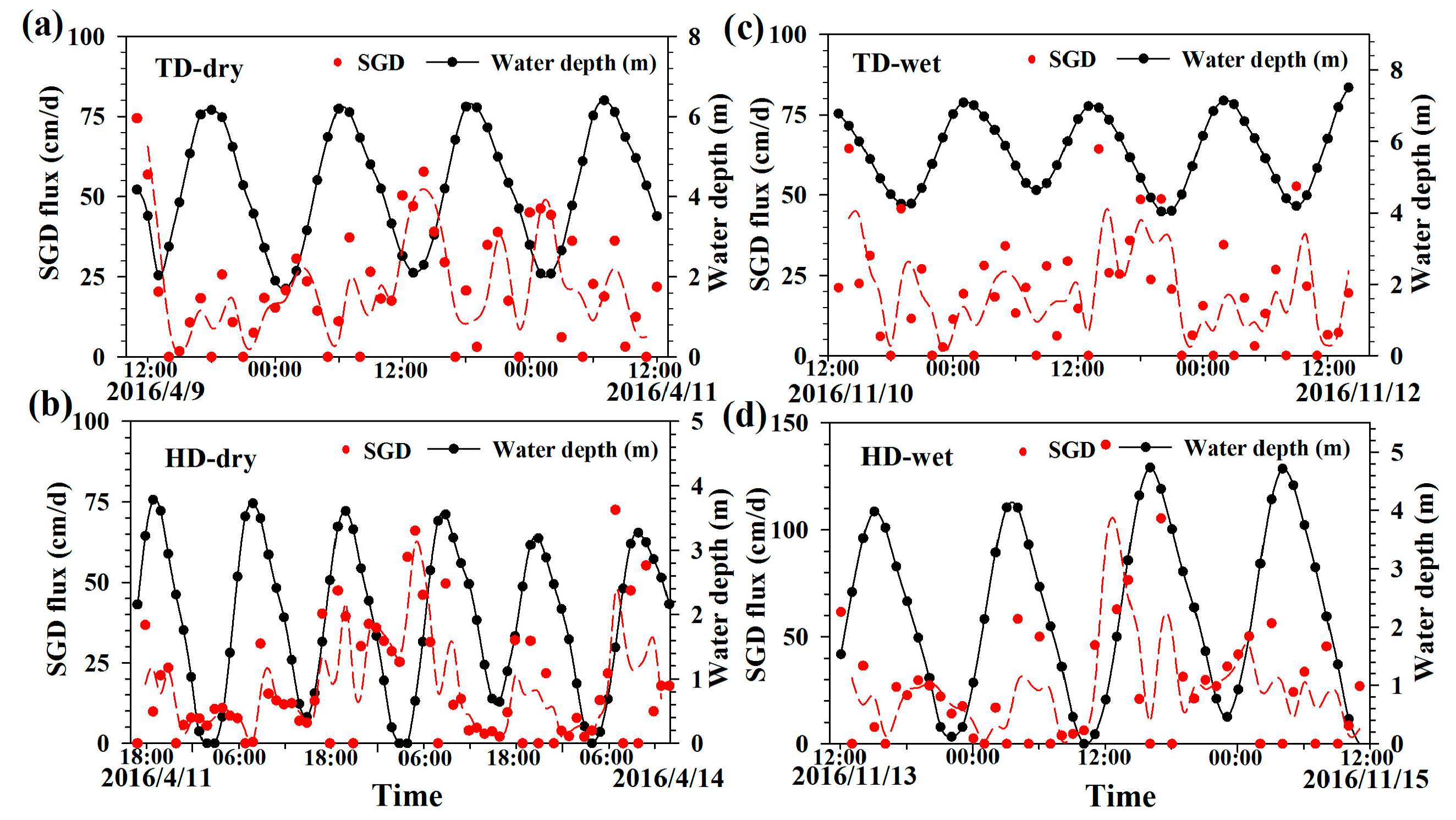
| 222Rn Fluxes (Bq/(m2 h)) | TD (Dry Season) | HD (Dry Season) | TD (Wet Season) | HD (Wet Season) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinks | ||||
| Fatm | 0.02 ± 1.65 | 0.05 ± 1.49 | (−0.31 ± 22.5) × 10−2 | −0.02 ± 6.69 |
| dI/dt | 0.65 ± 54.4 | 1.71 ± 52.2 | 2.13 ± 33.2 | −3.53 ± 103.6 |
| Fmix | −47.0 ± 38.2 | −35.7 ± 35.1 | −35.9 ± 19.0 | −58.8 ± 56.7 |
| Ftide-Outflux | −26.2 ± 17.6 | −28.1 ± 15.1 | −10.4 ± 11.8 | −50.4 ± 18.3 |
| Sources | ||||
| Ftide-Influx | 45.9 ± 18.5 | 45.5 ± 22.6 | 15.6 ± 7.5 | 80.0 ± 39.4 |
| Fsed | (0.01 ± 1.26) × 10−2 | (−0.06 ± 2.02) × 10−2 | (−0.10 ± 8.41) × 10−3 | (0.02 ± 1.99) × 10−2 |
| FSGD | 44.5 ± 36.9 | 36.3 ± 36.7 | 37.0 ± 32.2 | 51.2 ± 54.8 |
| Study Site | Methodology | SGD (cm/d) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jiaozhou Bay, China | 224Ra and 226Ra | 9 (autumn), 4 (spring) | [65] |
| 223Ra, 224Ra, 226Ra, 228Ra | 4.9~7.5, 4.3~6.5, 4.0~7.2, 3.0~5.7 | [40] | |
| Darcy’s law | 3.6 × 10−3~7.6 | [41] | |
| 222Rn | 12.3 (winter) 17.8 (summer) | [51] | |
| 222Rn | TD: 21.9 (dry season) 19.5 (wet season) HD: 17.8 (dry season) 26.9 (wet season) | This study | |
| Pearl River Estuary, China | 224Ra | 23~50 (dry season) 6~14 (wet season) | [66] |
| Richmond River Estuary, Australia | 222Rn | 6~10 (dry season) 37~59 (wet season) | [67] |
| Maowei Sea, China | 222Rn | 3~69 (wet season) 2~38 (dry season) | [68] |
| Copano Bay, South Texas, USA | 222Rn | Reef and margin: 51.3~73.9 (spring) 17.9~39.5 (summer) Paleovalleys: 23~40.8 (spring) 12.3~26.7 (summer) | [69] |
| Jepara, Indonesia | 222Rn | 37 (Awur) 52 (Bandengan) | [70] |
| Daya Bay, China | 222Rn | 28.2 (northwest site) 30.9 (middle-east site) | [14] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, K. Submarine Groundwater Discharge in a Coastal Bay: Evidence from Radon Investigations. Water 2020, 12, 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092552
Luo M, Zhang Y, Li H, Wang X, Xiao K. Submarine Groundwater Discharge in a Coastal Bay: Evidence from Radon Investigations. Water. 2020; 12(9):2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092552
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Manhua, Yan Zhang, Hailong Li, Xuejing Wang, and Kai Xiao. 2020. "Submarine Groundwater Discharge in a Coastal Bay: Evidence from Radon Investigations" Water 12, no. 9: 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092552
APA StyleLuo, M., Zhang, Y., Li, H., Wang, X., & Xiao, K. (2020). Submarine Groundwater Discharge in a Coastal Bay: Evidence from Radon Investigations. Water, 12(9), 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092552







