The Use of Straw Mulches to Mitigate Soil Erosion under Different Antecedent Soil Moistures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Preparation and Erosion Plots
2.2. Straw Mulch and Soil Moisture
2.3. Rainfall Simulator and Rainfall Intensity
2.4. Measurement of Runoff and Soil Loss
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Loss, Sediment Concentration and Runoff
3.2. Soil Erosion Rates, Considering Different Soil Moisture Conditions and Straw Mulches
4. Discussion
4.1. Straw Mulches Effect on Changes in Soil Loss and Sediment Concentration
4.2. Antecedent Soil Moisture Effect on Changes in Soil Loss and Sediment Concentration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panagos, P.; Katsoyiannis, A. Soil erosion modelling: The new challenges as the result of policy developments in Europe. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Beguería, S.; Nadal-Romero, E.; González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Lana-Renault, N.; Sanjuan, Y. A meta-analysis of soil erosion rates across the world. Geomorphology 2015, 239, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Tu, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y. The effect of plant hedgerows on the spatial distribution of soil erosion and soil fertility on sloping farmland in the purple-soil area of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwango, S.B.; Msanya, B.M.; Mtakwa, P.W.; Kimaro, D.N.; Deckers, J.; Poesen, J. Effectiveness of Mulching under Miraba in Controlling Soil Erosion, Fertility Restoration and Crop Yield in the Usambara Mountains, Tanzania. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 27, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, V.M.; Gómez-Plaza, A.; Martínez-Mena, M. The role of antecedent soil water content in the runoff response of semiarid catchments: A simulation approach. J. Hydrol. 2003, 284, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasik, K.; Gorski, D.; Popek, Z.; Hejduk, L. Estimating the annual sediment yield of a small agricultural catchment in central Poland. In Erosion and Sediments Yields in the Changing Environment, Proceedings of a Symposium Held at the Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, CAS Chengdu, China, 11–15 October 2012; IAHS Publ: Wallingford, UK, 2012; Volume 356, pp. 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski, A.; Lee, H.; Hejduk, L.; Banasik, K. Predicted small catchment responses to heavy rainfalls with SEGMO and two sets of model parameters. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci. SGGW Land Reclam. 2014, 46, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavian, A.; Sabet, S.H.; Solaimani, K.; Jafari, B. Simulating the effects of land use changes on soil erosion using RUSLE model. Geocarto Int. 2016, 32, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, J.; Santos, L.; Mujtaba, B.; De Lima, M.I.P. Laboratory assessment of the influence of rice straw mulch size on soil loss. Adv. Geosci. 2019, 48, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Yakupoğlu, T.; Dindaroğlu, T.; Terol, E.; Mora-Navarro, G.; Arabameri, A.; Radziemska, M.; Novara, A.; Kavian, A.; et al. Tillage Versus No-Tillage. Soil Properties and Hydrology in an Organic Persimmon Farm in Eastern Iberian Peninsula. Water 2020, 12, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, G.T.; Tebeje, A.K.; Demisse, S.S.; Belete, M.A.; Jemberrie, M.A.; Teshome, W.M.; Mengistu, D.T.; Teshale, E.Z. Time Series Land Cover Mapping and Change Detection Analysis Using Geographic Information System and Remote Sensing, Northern Ethiopia. Airsoil Water Res. 2018, 11, 1178622117751603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pimentel, D.; Burgess, M. Soil Erosion Threatens Food Production. Agriculture 2013, 3, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerdà, A. Soil moisture regime under simulated rainfall in a three years abandoned filed in southeast Spain. Phys. Chem. Earth 1995, 20, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iserloh, T.; Fister, W.; Seeger, M.; Willger, H.; Ries, J. A small portable rainfall simulator for reproducible experiments on soil erosion. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Is the hillslope position relevant for runoff and soil loss activation under high rainfall conditions in vineyards? Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2020, 20, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Keesstra, S.D.; Cerdà, A. Soil Erosion as an Environmental Concern in Vineyards. The Case Study of Celler del Roure, Eastern Spain, by Means of Rainfall Simulation Experiments. Beverages 2018, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arabkhedri, M. Report Research Project Estimate Special Deposition in the Country; Research Center Soil and Watershed Management: Tehran, Iran, 2001; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Arabameri, A.; Cerdà, A.; Pradhan, B.; Tiefenbacher, J.P.; Lombardo, L.; Bui, D.T. A methodological comparison of head-cut based gully erosion susceptibility models: Combined use of statistical and artificial intelligence. Geomorphology 2020, 359, 107136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Yousefi, S.; Kornejady, A.; Cerdà, A. Performance assessment of individual and ensemble data-mining techniques for gully erosion modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayoubi, S.; Mokhtari, J.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Zeraatpisheh, M. Erodibility of calcareous soils as influenced by land use and intrinsic soil properties in a semiarid region of central Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Telfer, M.W.; Blake, W.H.; Fathabadi, A. Aeolian sediment fingerprinting using a Bayesian mixing model. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosaffaie, J.; Talebi, A.A. Statistical View to the Water Erosion in Iran. Ext. Dev. Watershed Manag. 2014, 2, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Besalatpour, A.A.; Hajabbasi, M.A.; Ayoubi, S.; Afyuni, M.; Jalalian, A.; Schulin, R. Soil shear strength prediction using intelligent systems: Artificial neural networks and an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2012, 58, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, S.; Jabbari, M.; Khademi, H. Multiple linear modeling between soil properties, magnetic susceptibility and heavy metals in various land uses. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MohammadKhan, S.; Ahmadi, H.; Jafari, M. Relationship between soil erosion, slope, parent material, and distance to road (Case study: Latian Watershed, Iran). Arab. J. Geosci. 2010, 4, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Azari, M.; GhaderiVangah, B. Field evaluation of the Hillslope Erosion Model (HEM) in Iran. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 99, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavian, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Gholami, L.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Assessment of the Spatiotemporal Effects of Land Use Changes on Runoff and Nitrate Loads in the Talar River. Water 2018, 10, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jourgholami, M.; Abari, M.E. Effectiveness of sawdust and straw mulching on postharvest runoff and soil erosion of a skid trail in a mixed forest. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 109, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavian, A.; Gholami, L.; Mohammadi, M.; Spalevic, V.; Soraki, M.F. Impact of Wheat Residue on Soil Erosion Processes. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2018, 46, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khadem, A.; Raiesi, F. Response of soil alkaline phosphatase to biochar amendments: Changes in kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics. Geoderma 2019, 337, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Agbede, T.M.; Ejue, W.S.; Aboyeji, C.M.; Dunsin, O.; Aremu, C.O.; Owolabi, A.O.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Okunlola, O.F.; Adesola, O.O. Biochar, poultry manure and NPK fertilizer: Sole and combine application effects on soil properties and ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) performance in a tropical Alfisol. Open Agric. 2020, 5, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Novara, A.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Fernández, M.P.; Di Prima, S.; Cerdà, A. Straw mulch as a sustainable solution to decrease runoff and erosion in glyphosate-treated clementine plantations in Eastern Spain. An assessment using rainfall simulation experiments. Catena 2019, 174, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Tarolli, P.; Cerdà, A. Mulching practices for reducing soil water erosion: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 161, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernett, A.P.; Disketer, E.G.; Richardson, E.C. Evaluation of mulching methods for erosion control on newly prepared and seeded highway back slope. Agron. J. 1967, 59, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.E. Influence of Mulches on Runoff, Erosion, and Soil Moisture Depletion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1966, 30, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekalu, K.O.; Olorunfemi, I.; Osunbitan, J. Grass mulching effect on infiltration, surface runoff and soil loss of three agricultural soils in Nigeria. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robichaud, P.; Jordan, P.; Lewis, S.; Ashmun, L.; Covert, S.; Brown, R. Evaluating the effectiveness of wood shred and agricultural straw mulches as a treatment to reduce post-wildfire hillslope erosion in southern British Columbia, Canada. Geomorphology 2013, 197, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Keesstra, S.D. An economic, perception and biophysical approach to the use of oat straw as mulch in Mediterranean rainfed agriculture land. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, G.; Wei, J.; Jiang, F.; Wang, M.-K.; Huang, Y.-H. Mulching effects on erosion from steep slopes and sediment particle size distributions of gully colluvial deposits. Catena 2018, 160, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvar, E.; Hajizadeh, Z.; Ghasemieh, H. Sediment yield, runoff and hydraulic characteristics in straw and rock fragment covers. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wei, W.; Pan, D. Effects of rainfall and terracing-vegetation combinations on water erosion in a loess hilly area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Liu, Y.-F.; Jia, C.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Liu, B.-R.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zheng, J.; Wu, G.-L. Effects of mosaic-pattern shrub patches on runoff and sediment yield in a wind-water erosion crisscross region. Catena 2019, 174, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Unger, P.W. Soil Water Accumulation under Different Precipitation, Potential Evaporation, and Straw Mulch Conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Orenes, F.; Guerrero, C.; Roldan, A.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Cerdà, A.; Campoy, M.; Zornoza, R.; Bárcenas, G.; Caravaca, F.; Bárcenas-Moreno, G. Soil microbial biomass and activity under different agricultural management systems in a semiarid Mediterranean agroecosystem. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 109, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Lavee, H. Effects of size and incorporation of synthetic mulch on runoff and sediment yield from interrils in a laboratory study with simulated rainfall. Soil Tillage Res. 1991, 21, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Soil Erosion and Conservation; Longman Scientific and Technical: Harlow, UK, 1986; p. 298. [Google Scholar]
- Cammeraat, E.L.H. Scale dependent thresholds in hydrological and erosion response of a semi-arid catchment in southeast Spain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, S.H. Effect of antecedent soil moisture content on rainwash erosion. Catena 1985, 12, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govers, G.; Loch, R. Effects of initial water content and soil mechanical strength on the runoff erosion resistance of clay soils. Soil Res. 1993, 31, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadat, F.; Taimeh, A.Y. Effect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedent soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledi Darvishan, A.; Sadeghi, S.H.R.; Homaee, M.; Arabkhadri, M. Affectability of runoff threshold and coefficient from rainfall intensity and antecedent soil moisture content in laboratorial erosion plots. Iran Water Res. J. 2014, 8, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Yang, M. Combined influences of wheat-seedling cover and antecedent soil moisture on sheet erosion in small-flumes. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, E.; Sarah, P. Combined effect of rain temperature and antecedent soil moisture on runoff and erosion on Loess. Catena 2017, 158, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, C.; Potter, T.; Nuti, R.; Franklin, D.; Bosch, D. Antecedent water content effects on runoff and sediment yields from two Coastal Plain Ultisols. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, L.; Karimi, N.; Kavian, A. Soil and water conservation using biochar and various soil moisture in laboratory conditions. Catena 2019, 182, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannering, J.V.; Meyer, L.D. The Effects of Various Rates of Surface Mulch on Infiltration and Erosion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1963, 27, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHaan, R. Mulching for erosion control. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1970, 34, 928–931. [Google Scholar]
- Poulenard, J.; Podwojewski, P.; Janeau, J.-L.; Collinet, J. Runoff and soil erosion under rainfall simulation of Andisols from the Ecuadorian Páramo: Effect of tillage and burning. Catena 2001, 45, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruy, S.; Findeling, A.; Chadoeuf, J. Effect of mulching techniques on plot scale runoff: FDTF modeling and sensitivity analysis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 326, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, A.H.; Woods, S.W. Effectiveness of aerial seeding and straw mulch for reducing post-wildfire erosion, north-western Montana, USA. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Dami, I.; Mathers, H.M.; Dick, W.A.; Doohan, D. The Effect of Straw Mulch on Simulated Simazine Leaching and Runoff. Weed Sci. 2011, 59, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, L.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Homaee, M. Straw Mulching Effect on Splash Erosion, Runoff, and Sediment Yield from Eroded Plots. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 77, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, B.; Wu, F. Effects of wheat stubble on runoff, infiltration, and erosion of farmland on the Loess Plateau, China, subjected to simulated rainfall. Solid Earth 2017, 8, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niziolomski, J.C.; Simmons, R.W.; Rickson, R.J.; Hann, M.J. Efficacy of mulch and tillage options to reduce runoff and soil loss from asparagus interrows. Catena 2020, 191, 104557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakupoğlu, T.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Cerdà, A. Potential Benefits of Polymers in Soil Erosion Control for Agronomical Plans: A Laboratory Experiment. Agronomy 2019, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giménez-Morera, A.; Sinoga, J.D.R.; Cerdà, A. The impact of cotton geotextiles on soil and water losses from Mediterranean rainfed agricultural land. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadfar, M.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Khanjani, M.J.; Hazbavi, Z. Effects of rates and time of zeolite application on controlling runoff generation and soil loss from a soil subjected to a freeze-thaw cycle. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, D.L.; McLaughlin, R. Erosion control effectiveness of straw, hydromulch, and polyacrylamide in a rainfall simulator. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Effects of plastic film combined with straw mulch on grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in Loess Plateau. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 172, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xie, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.; Huang, Z.; He, S.; Rong, X. Effects of rice straw mulching and soybean planting around the maize block on maize yield, nutrient utilization and runoff loss. J. South. Agric. 2019, 50, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, D.M.; Bryan, R.B. The relationship of soil loss by interrill erosion to slope gradient. Catena 2000, 38, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Lei, T.; Yu, J.; Shainberg, I.; Mamedov, A.I.; Ben-Hur, M.; Levy, G.J. Runoff and Interrill Erosion in Sodic Soils Treated with Dry PAM and Phosphogypsum. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukal, S.S.; Sarkar, M. Laboratory simulation studies on splash erosion and crusting in relation to surface roughness and raindrop size. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 2011, 59, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Black, C.A.; Evans, D.D.; White, J.L.; Newsmonger, L.E.; Clarkem, F.E. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2: Wisconsin; American Society of Agronomy Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.S.; Tripathi, N.; Singh, S.K. Impact of degradation on nitrogen transformation in a forest ecosystem of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 125, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defersha, M.B.; Quraishi, S.; Melesse, A.M. The effect of slope steepness and antecedent moisture content on interrill erosion, runoff and sediment size distribution in the highlands of Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavian, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Cerdà, A.; Fallah, M.; Gholami, L. Design, manufacture and calibration of the SARI portable rainfall simulator for field and laboratory experiments. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquies, J.; Scharff, M.; Hallock, B. The design and construction of a rainfall simulator. In Proceedings of the International Erosion Control Association (IECA), 34th Annual Conference and Expo, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24–28 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chouksey, A.; Lambey, V.; Nikam, B.R.; Aggarwal, S.P.; Dutta, S. Hydrological Modelling Using a Rainfall Simulator over an Experimental Hillslope Plot. Hydrology 2017, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavian, A.; Alipour, A.; Soleimani, K.; Gholami, L.; Smith, P.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. The increase of rainfall erosivity and initial soil erosion processes due to rainfall acidification. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 33, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerdà, A. Effects of rock fragment cover on soil infiltration, interrill runoff and erosion. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 52, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalevic, V. Impact of Land Use on Runoff and Soil Erosion in Polimlje. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture of the University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.-P.; Li, F.-H.; Yang, S.-M. Effect of polyacrylamide application on runoff, erosion and soil nutrient loss under simulated rainfall. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissen, V.; Sánchez-Hernández, R.; Kampichler, C.; Reyes, R.R.; Sepulveda-Lozada, A.; Ochoa-Goana, S.; De Jong, B.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Hernández-Daumas, S.; De Jong, B.H. Effects of land-use change on some properties of tropical soils—An example from Southeast Mexico. Geoderma 2009, 151, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, N.M.; Wah, Y.B. Power comparisons of shapiro wilk, kolmogorov smirnov, lilliefors and anderson darling tests. J. Stat. Model. Anal. 2011, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; Xia, J.; Zeng, R.; Cai, C.; Wang, T. Dynamic study of infiltration rate for soils with varying degrees of degradation by water erosion. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenbrenner, J.W.; Macdonald, L.H.; Rough, D. Effectiveness of three post-fire rehabilitation treatments in the Colorado Front Range. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2989–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tejada, M.; Gonzalez, J.L. Effects of Application of a By-Product of the Two-Step Olive Oil Mill Process on Maize Yield. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Smets, T.; Fullen, M.A.; Poesen, J.; Booth, C. Effectiveness of geotextiles in reducing runoff and soil loss: A synthesis. Catena 2010, 81, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukal, S.S.; Sarkar, M. Splash erosion and infiltration in relation to mulching and polyviny alcohol application in semiarid tropics. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2010, 56, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, S.A.; Martins, M.A.; Malvar, M.C.; Ben-Hur, M.; Keizer, J.J. Polyacrylamide application versus forest residue mulching for reducing post-fire runoff and soil erosion. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.M.; Moradi, E.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Cerdà, A. Spatial variability of soil roughness in persimmon plantations: A new combined ISUM (improved stock unearthing method) approach. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, M.; Errea, M.P.; Beguería, S.; Arnáez, J.; Martí, C.; García-Ruiz, J. Catchment soil moisture and rainfall characteristics as determinant factors for discharge/suspended sediment hysteretic loops in a small headwater catchment in the Spanish pyrenees. J. Hydrol. 2004, 288, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyata, S.; Kosugi, K.; Gomi, T.; Mizuyama, T. Effects of forest floor coverage on overland flow and soil erosion on hillslopes in Japanese cypress plantation forests. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 06402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.; Gil, J. Effects of mulching on soil physical properties and runoff under semi-arid conditions in southern Spain. Catena 2010, 81, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Hazbavi, Z.; Kiani-Harchegani, M. Controllability of runoff and soil loss from small plots treated by vinasse-produced biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, B.; Barbero-Sierra, C.; Bienes, R.; Marques, M.; García-Díaz, A. Soil loss in an olive grove in Central Spain under cover crops and tillage treatments, and farmer perceptions. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 17, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Novara, A.; Fernández, M.P.; Kapović-Solomun, M.; Keesstra, S.D. Policies can help to apply successful strategies to control soil and water losses. The case of chipped pruned branches (CPB) in Mediterranean citrus plantations. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Panagos, P.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Fernández, M.P.; Cerdà, A. The potential of straw mulch as a nature-based solution for soil erosion in olive plantation treated with glyphosate: A biophysical and socioeconomic assessment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, A.; Helming, K.; Diestel, H. Effect of antecedent soil water content and rainfall regime on microrelief changes. Soil Technol. 1997, 10, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, H.; Samson, B.K.; Stephan, H.M.; Songyikhangsuthor, K.; Homma, K.; Kiyono, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Shiraiwa, T.; Horie, T. Biochar amendment techniques for upland rice production in Northern Laos. Field Crop. Res. 2009, 111, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.A.; Fleming, P.; Davis, D.D.; Horton, R.; Wang, B.; Karlen, D.L. Impact of biochar amendments on the quality of a typical Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 2010, 158, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orsham, A.; Akhond Ali, A.M.; Behnia, A. Effect study of soil moistures on amounts of runoff and sediment using simulated rainfall. Iran. Iran. J. Range Desert Res. 2010, 16, 445–455. [Google Scholar]





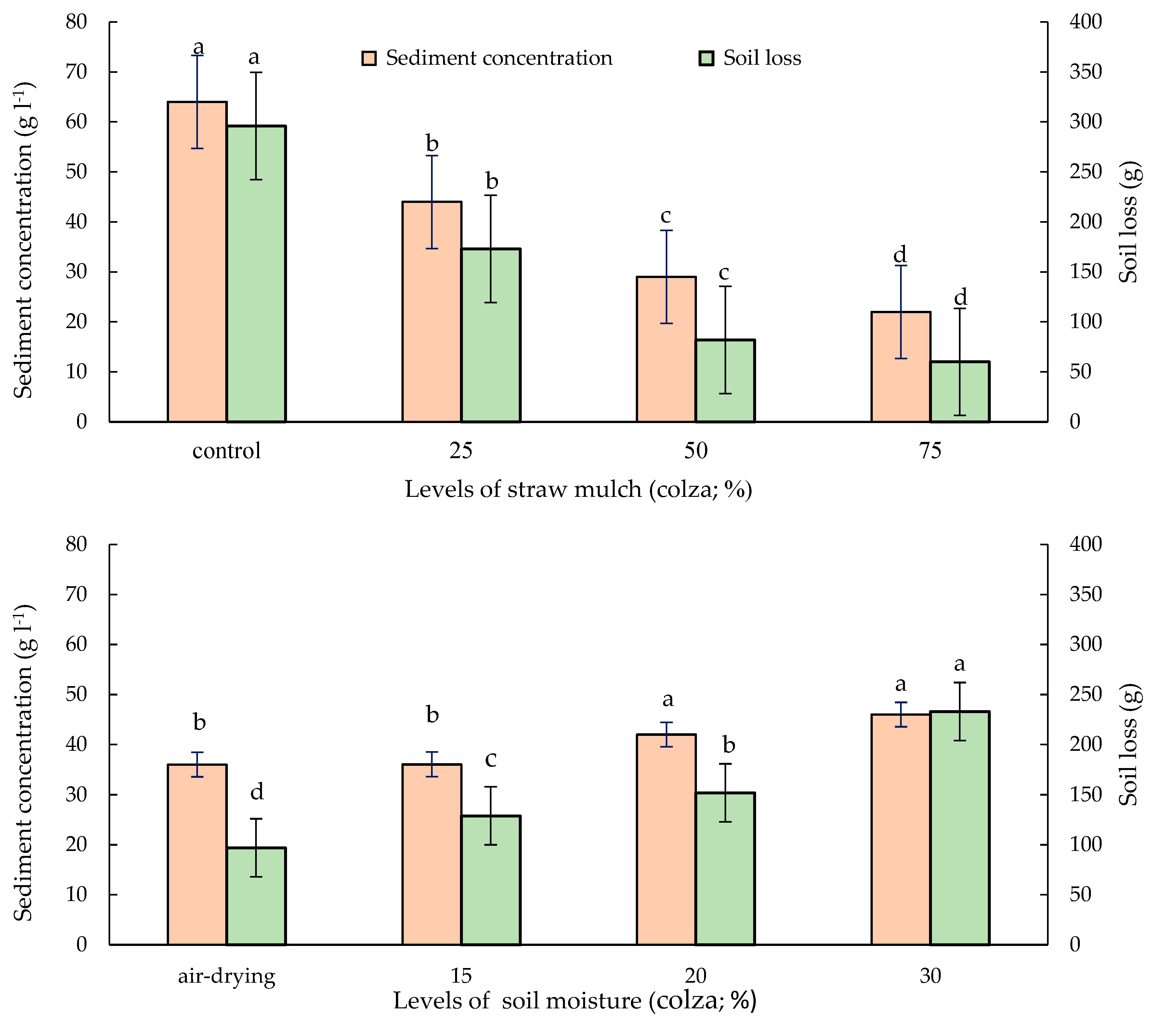
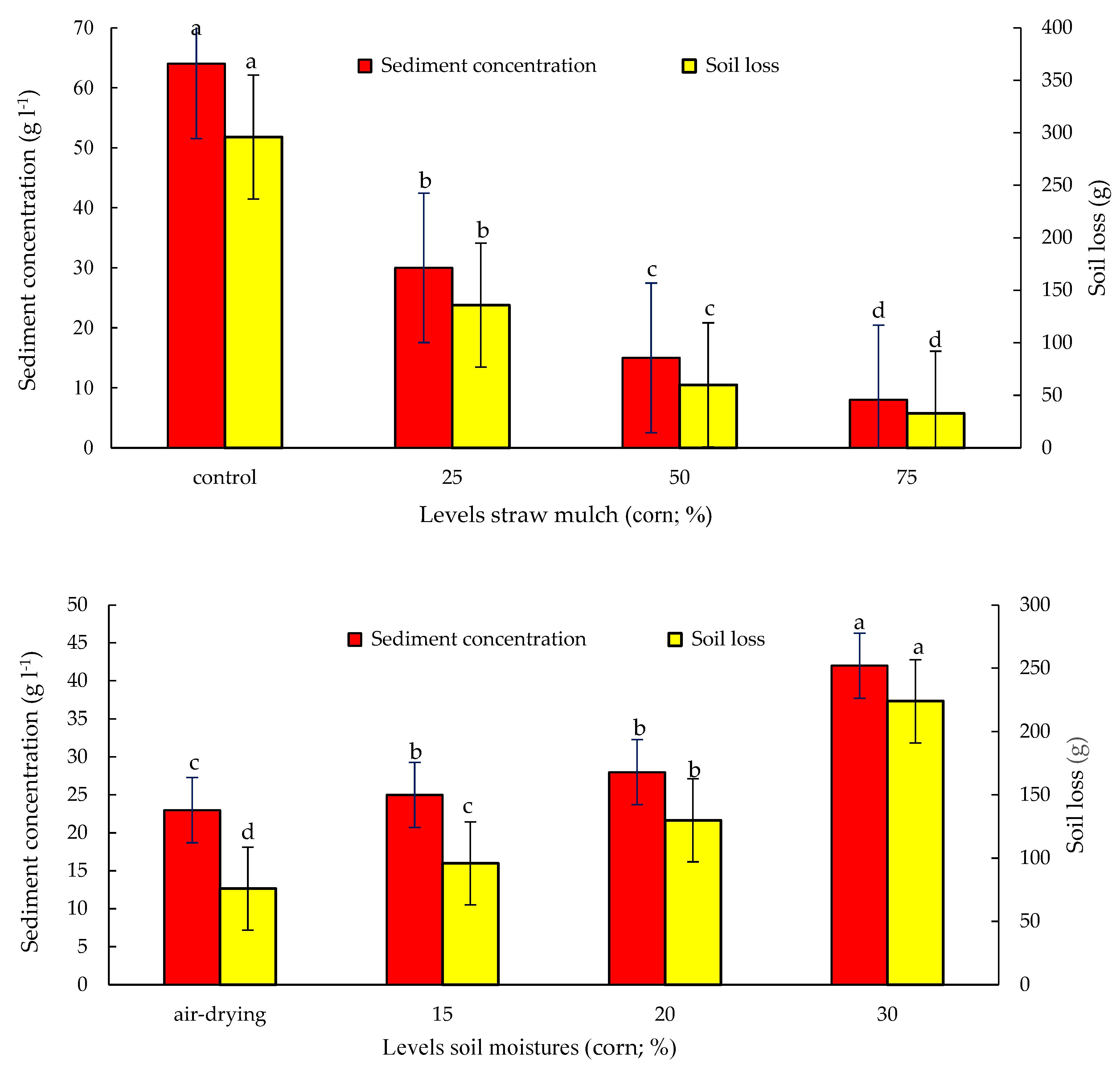
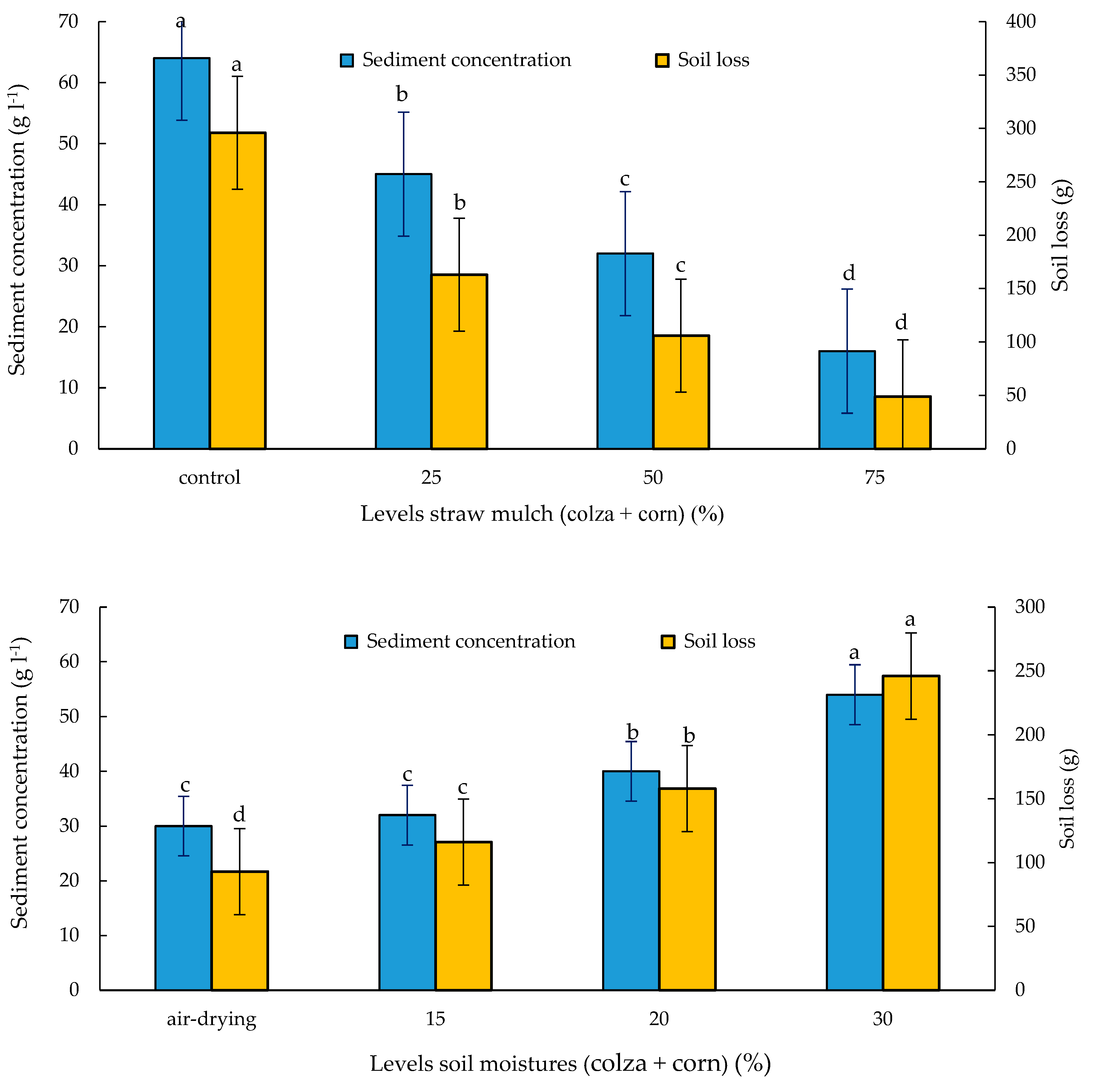
| Treatment | Cover% | ASM% | R (L) | SC (g L−1) | SL (g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | M | C | M | C | M | |||
| colza | 25 | 0 | 3.450 | 3.131 | 56 | 35 | 193 | 111 |
| 15 | 4.028 | 3.520 | 51 | 48 | 202 | 171 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 3.990 | 56 | 47 | 266 | 188 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 4.858 | 94 | 46 | 522 | 224 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 3.874 | 64.25 | 44 | 295.75 | 173.5 | ||
| 50 | 0 | 3.450 | 1.863 | 56 | 29 | 193 | 55 | |
| 15 | 4.028 | 2.038 | 51 | 41 | 202 | 83 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 3.913 | 56 | 21 | 266 | 85 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 4.543 | 94 | 23.05 | 522 | 104 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 3.089 | 64.25 | 28.51 | 295.75 | 81.75 | ||
| 75 | 0 | 3.450 | 1.293 | 56 | 22 | 193 | 29.06 | |
| 15 | 4.028 | 1.821 | 51 | 30 | 202 | 58 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 3.725 | 56 | 18 | 266 | 68 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 4.203 | 94 | 19 | 522 | 83 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 2.760 | 64.25 | 22.25 | 295.75 | 59.51 | ||
| Corn | 25 | >0 | >3.450 | 3.213 | 56 | 18 | >193 | >60 |
| 15 | 4.028 | 3.963 | 51 | 22 | 202 | 89 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 4.640 | 56 | 33 | 266 | 155 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 5.346 | 94 | 45 | 522 | 241 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 4.290 | 64.25 | 29.5 | 295.75 | 136.25 | ||
| 50 | 0 | 3.450 | 2.901 | 56 | 13 | 193 | 40 | |
| 15 | 4.028 | 3.656 | 51 | 17 | 202 | 64 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 4.451 | 56 | 14 | 266 | 64 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 4.726 | 94 | 17 | 522 | 79 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 3.933 | 64.25 | 15.25 | 295.75 | 61.75 | ||
| 75 | 0 | 3.450 | 2.251 | 56 | 5 | 193 | 12 | |
| 15 | 4.028 | 3.330 | 51 | 9 | 202 | 30 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 4.313 | 56 | 8 | 266 | 36 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 4.583 | 94 | 11 | 522 | 52 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 3.619 | 64.25 | 8.25 | 295.75 | 32.5 | ||
| colza+ corn | 25 | 0 | 3.450 | 3.143 | 56 | 33 | 193 | 103 |
| 15 | 4.028 | 3.501 | 51 | 38 | 202 | 134 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 3.650 | 56 | 52 | 266 | 185 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 3.905 | 94 | 57 | 522 | 225 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 3.561 | 64.25 | 45.25 | 295.75 | 478.25 | ||
| 50 | 0 | 3.450 | 2.430 | 56 | 24 | 193 | 59 | |
| 15 | 4.028 | 3.283 | 51 | 27 | 202 | 90 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 3.456 | 56 | 35 | 266 | 121 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 3.656 | 94 | 42 | 522 | 155 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 3.206 | 64.25 | 32 | 295.75 | 106.25 | ||
| 75 | 0 | 3.450 | 1.776 | 56 | 8 | 193 | 15 | |
| 15 | 4.028 | 2.883 | 51 | 13 | 202 | 40 | ||
| 20 | 4.710 | 3.203 | 56 | 16 | 266 | 58 | ||
| 30 | 5.501 | 3.466 | 94 | 23 | 522 | 82 | ||
| Mean | 4.422 | 2.832 | 64.25 | 15 | 295.75 | 51.22 | ||
| Source | Dependent Variable | df | Mean Square | Value F | Significant Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil moisture | colza | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 3 | 301.035 | 8 | 0.000 ** |
| Soil loss (g) | 3 | 40,821 | 97 | 0.000 ** | ||
| corn | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 3 | 860 | 30 | 0.000 ** | |
| Soil loss (g) | 3 | 51,212 | 119.09 | 0.000 ** | ||
| colza + corn | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 3 | 1429.09 | 48 | 0.000 ** | |
| Soil loss (g) | 3 | 54,772 | 124 | 0.000 ** | ||
| Straw mulches | colza | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 3 | 4215 | 121 | 0.000 ** |
| Soil loss (g) | 3 | 138,305.08 | 329 | 0.000 ** | ||
| Corn | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 3 | 7476 | 262 | 0.000 ** | |
| Soil loss (g) | 3 | 166,603 | 387 | 0.000 ** | ||
| colza + corn | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 3 | 5069 | 171 | 0.000 ** | |
| Soil loss (g) | 3 | 134,075 | 305 | 0.000 ** | ||
| Moisture × Straw mulch | colza | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 9 | 453 | 31 | 0.000 ** |
| Soil loss (g) | 9 | 13,362 | 13.04 | 0.000 ** | ||
| corn | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 9 | 270 | 9 | 0.000 ** | |
| Soil loss (g) | 9 | 13,733 | 31 | 0.000 ** | ||
| colza + corn | Sediment concentration (g L−1) | 9 | 172 | 5 | 0.000 ** | |
| Soil loss (g) | 9 | 11,013 | 25 | 0.000 ** |
| Treatment | ASM (%) | R | SC | SL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25% | 50% | 75% | 25% | 50% | 75% | 25% | 50% | 75% | ||
| 0 | 9.24 | 46 | 62.52 | 37.5 | 48.21 | 60.71 | 42.48 | 71.50 | 84.94 | |
| 15 | 12.61 | 49.40 | 54.79 | 5.88 | 19.60 | 41.17 | 15.34 | 58.91 | 71.28 | |
| colza | 20 | 15.28 | 16.92 | 20.91 | 16.07 | 62.5 | 67.85 | 29.32 | 68.04 | 74.43 |
| 30 | 11.68 | 17.41 | 23.59 | 51.06 | 75.47 | 79.78 | 57.08 | 80.07 | 84.09 | |
| Mean | 12.20 | 32.43 | 40.45 | 27.62 | 51.45 | 62.38 | 36.06 | 69.63 | 78.69 | |
| 0 | 6.86 | 15.91 | 34.75 | 67.85 | 76.78 | 91.07 | 68.91 | 79.27 | 93.78 | |
| 15 | 1.61 | 9.23 | 17.32 | 56.86 | 66.66 | 82.35 | 55.94 | 68.31 | 85.14 | |
| corn | 20 | 1.48 | 5.49 | 8.42 | 41.07 | 75 | 85.71 | 41.72 | 75.93 | 86.46 |
| 30 | 2.81 | 14.08 | 16.68 | 52.12 | 81.91 | 88.29 | 53.83 | 84.86 | 90.03 | |
| Mean | 3.19 | 11.17 | 19.29 | 54.47 | 75.09 | 86.85 | 55.10 | 77.09 | 88.85 | |
| 0 | 8.89 | 29.56 | 48.52 | 41.07 | 57.14 | 85.71 | 46.63 | 69.43 | 92.22 | |
| 15 | 13.08 | 18.49 | 28.42 | 25.49 | 47.05 | 74.50 | 33.66 | 55.44 | 80.19 | |
| colza + corn | 20 | 22.50 | 26.62 | 31.99 | 7.14 | 37.5 | 71.42 | 30.45 | 54.51 | 78.19 |
| 30 | 29.01 | 33.53 | 36.99 | 39.36 | 55.31 | 75.53 | 56.89 | 70.30 | 84.29 | |
| Mean | 18.37 | 27.05 | 36.48 | 28.26 | 49.25 | 76.79 | 41.91 | 62.42 | 83.72 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kavian, A.; Kalehhouei, M.; Gholami, L.; Jafarian, Z.; Mohammadi, M.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. The Use of Straw Mulches to Mitigate Soil Erosion under Different Antecedent Soil Moistures. Water 2020, 12, 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092518
Kavian A, Kalehhouei M, Gholami L, Jafarian Z, Mohammadi M, Rodrigo-Comino J. The Use of Straw Mulches to Mitigate Soil Erosion under Different Antecedent Soil Moistures. Water. 2020; 12(9):2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092518
Chicago/Turabian StyleKavian, Ataollah, Mahin Kalehhouei, Leila Gholami, Zeinab Jafarian, Maziar Mohammadi, and Jesús Rodrigo-Comino. 2020. "The Use of Straw Mulches to Mitigate Soil Erosion under Different Antecedent Soil Moistures" Water 12, no. 9: 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092518
APA StyleKavian, A., Kalehhouei, M., Gholami, L., Jafarian, Z., Mohammadi, M., & Rodrigo-Comino, J. (2020). The Use of Straw Mulches to Mitigate Soil Erosion under Different Antecedent Soil Moistures. Water, 12(9), 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092518







