Electricity Generation, Salt and Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Community in Aircathode Microbial Desalination Cell for Saline-Alkaline Soil-Washing Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
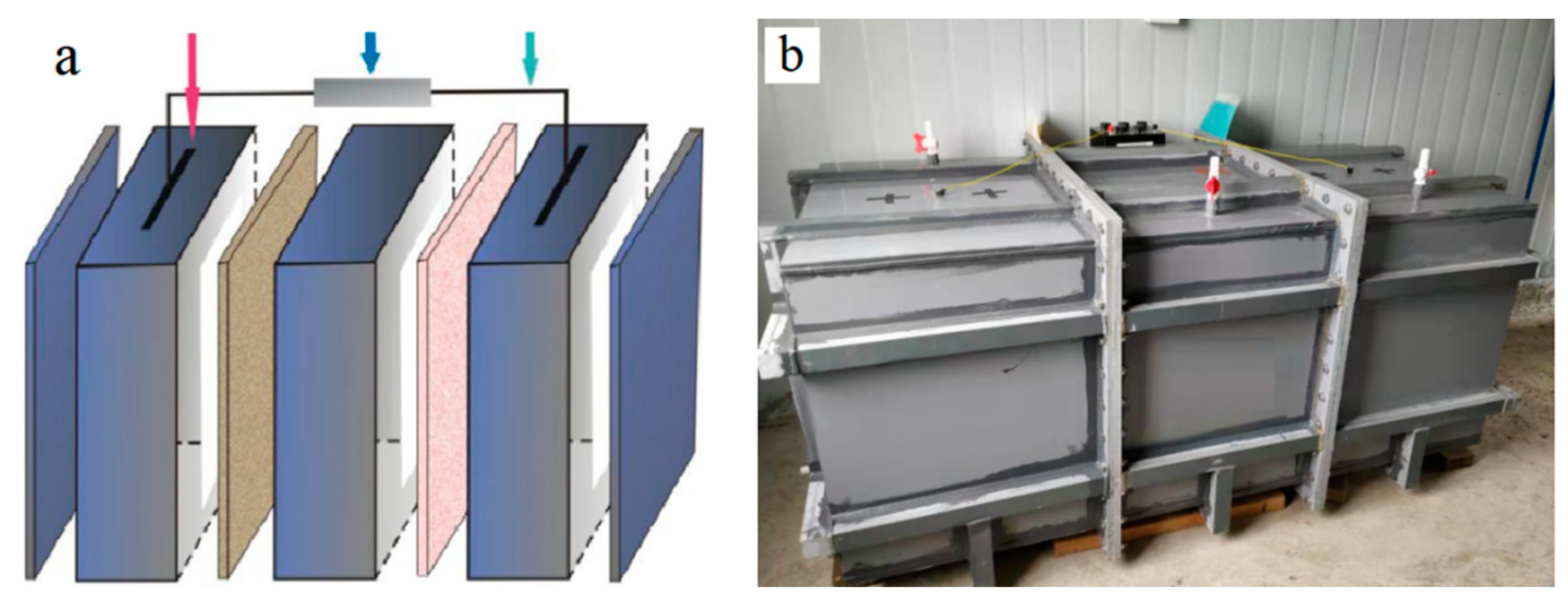
2.1. AMDC Construction
2.2. System Inoculation
2.3. Experimental Operation
2.4. Experimental Test and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
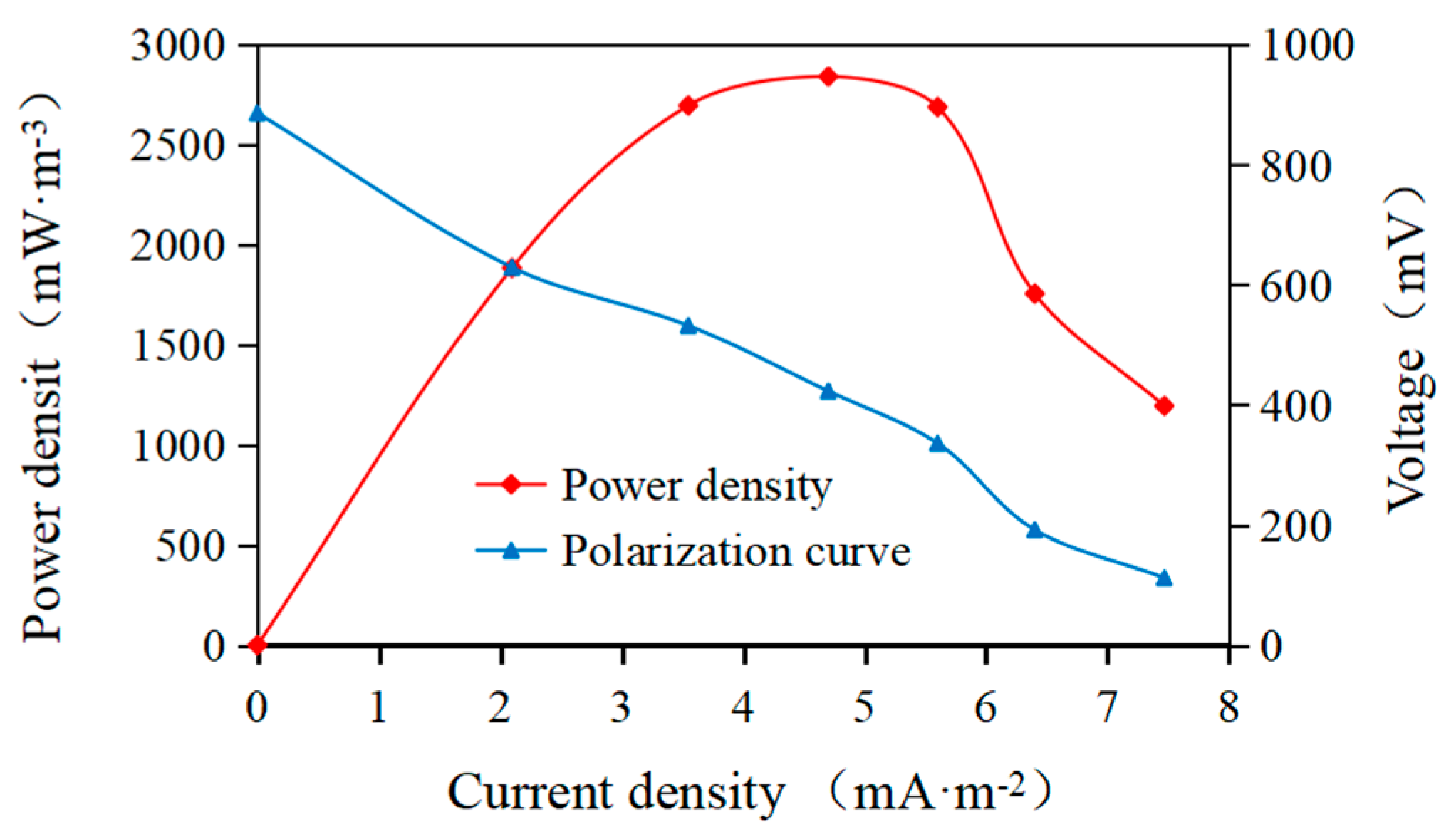
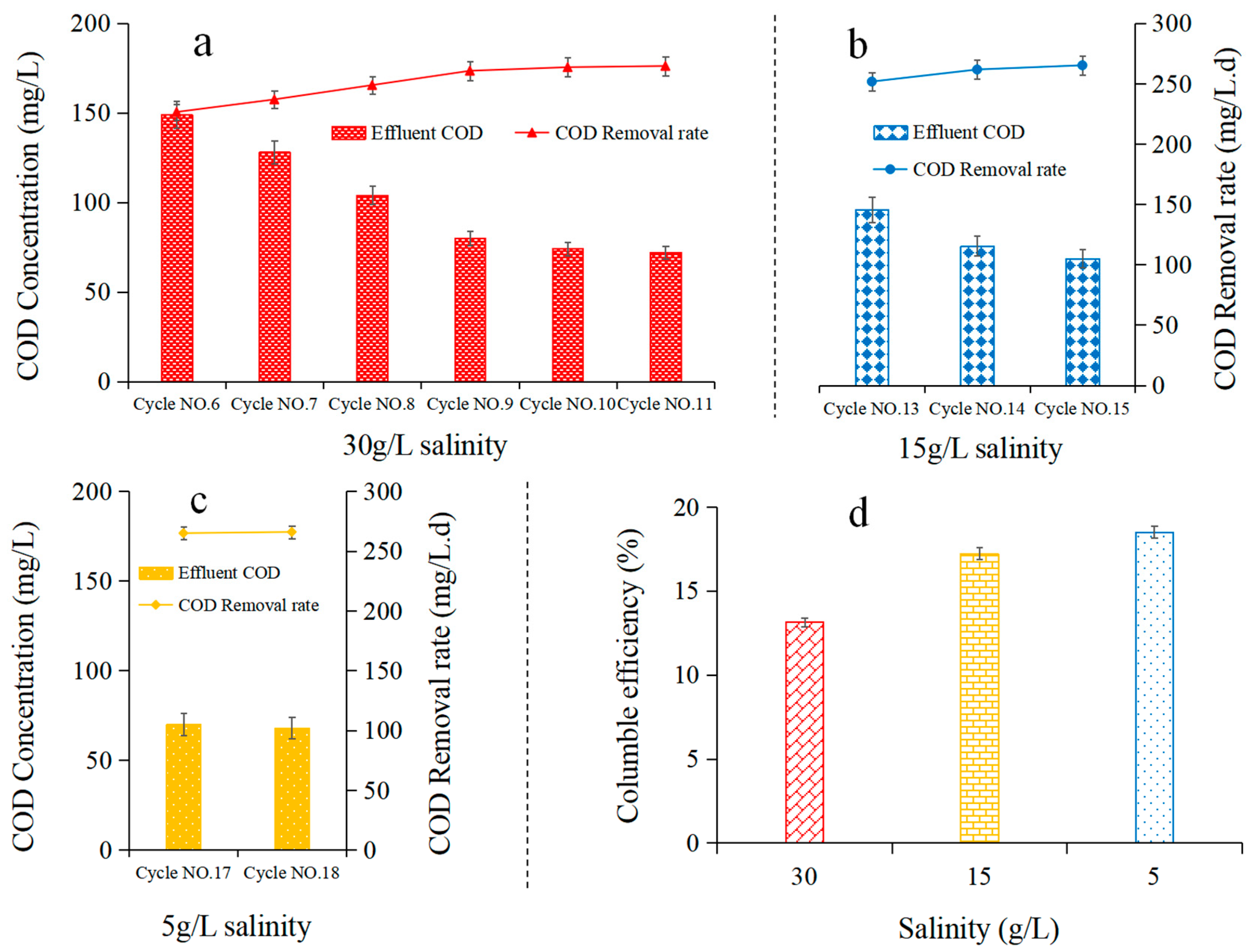
3.1. Impact of Salinity on Performance and Start Up of AMDC
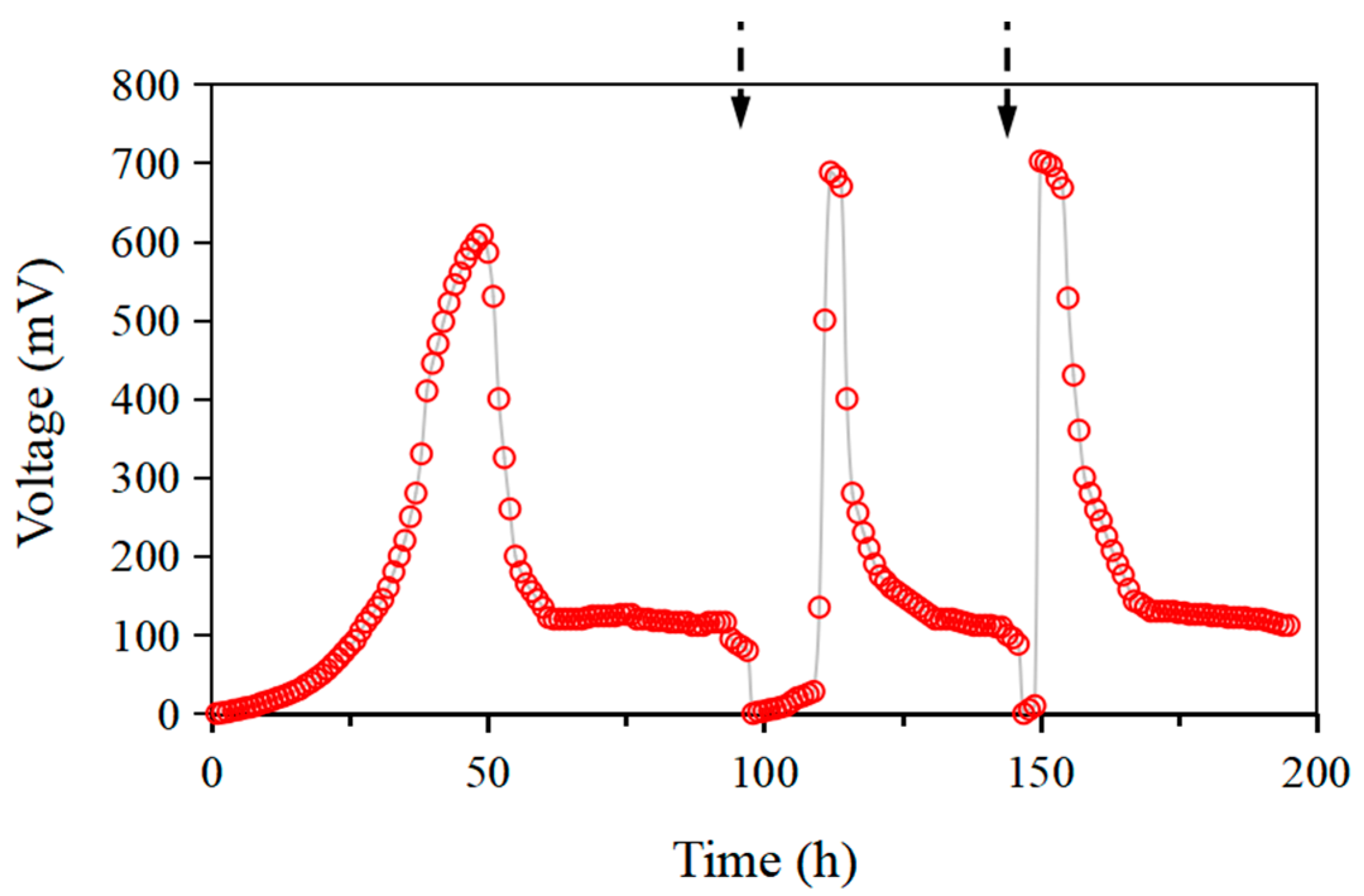
3.1.1. Start-Up of AMDC
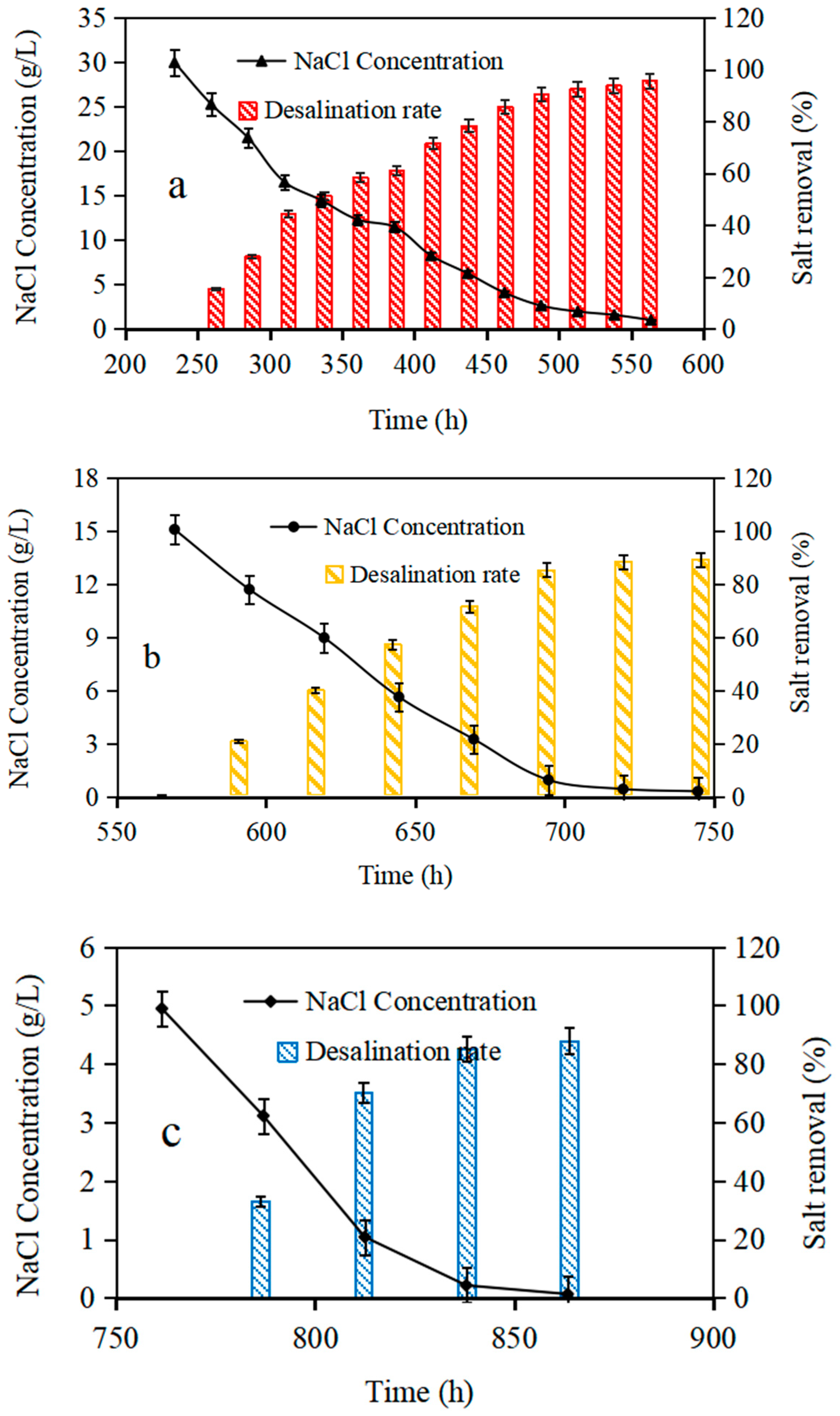
3.1.2. Desalination Performance under Diverse Salinity Concentrations
3.1.3. Organic Removal and Coulomb Efficiency under Diverse Salinity Concentration
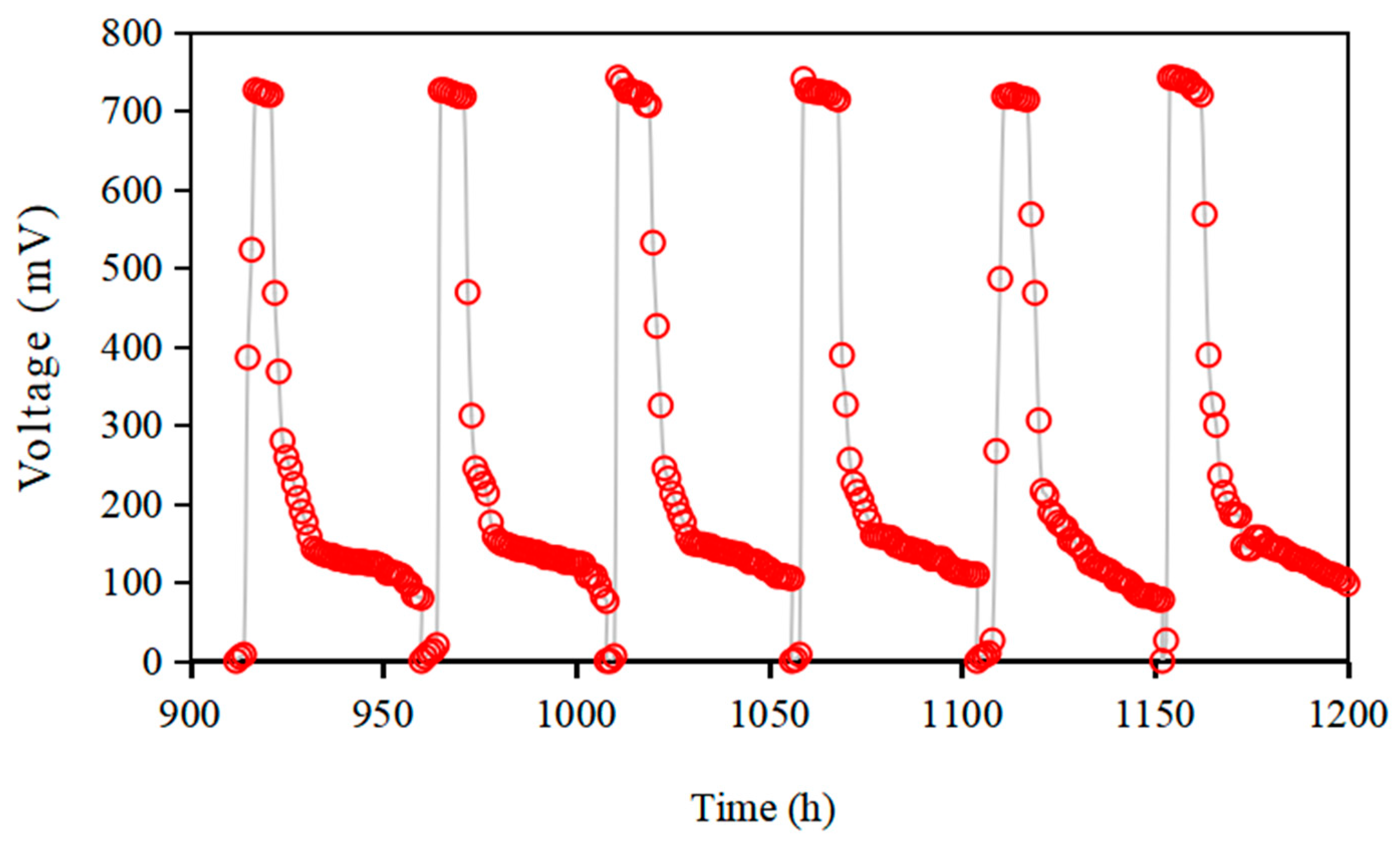
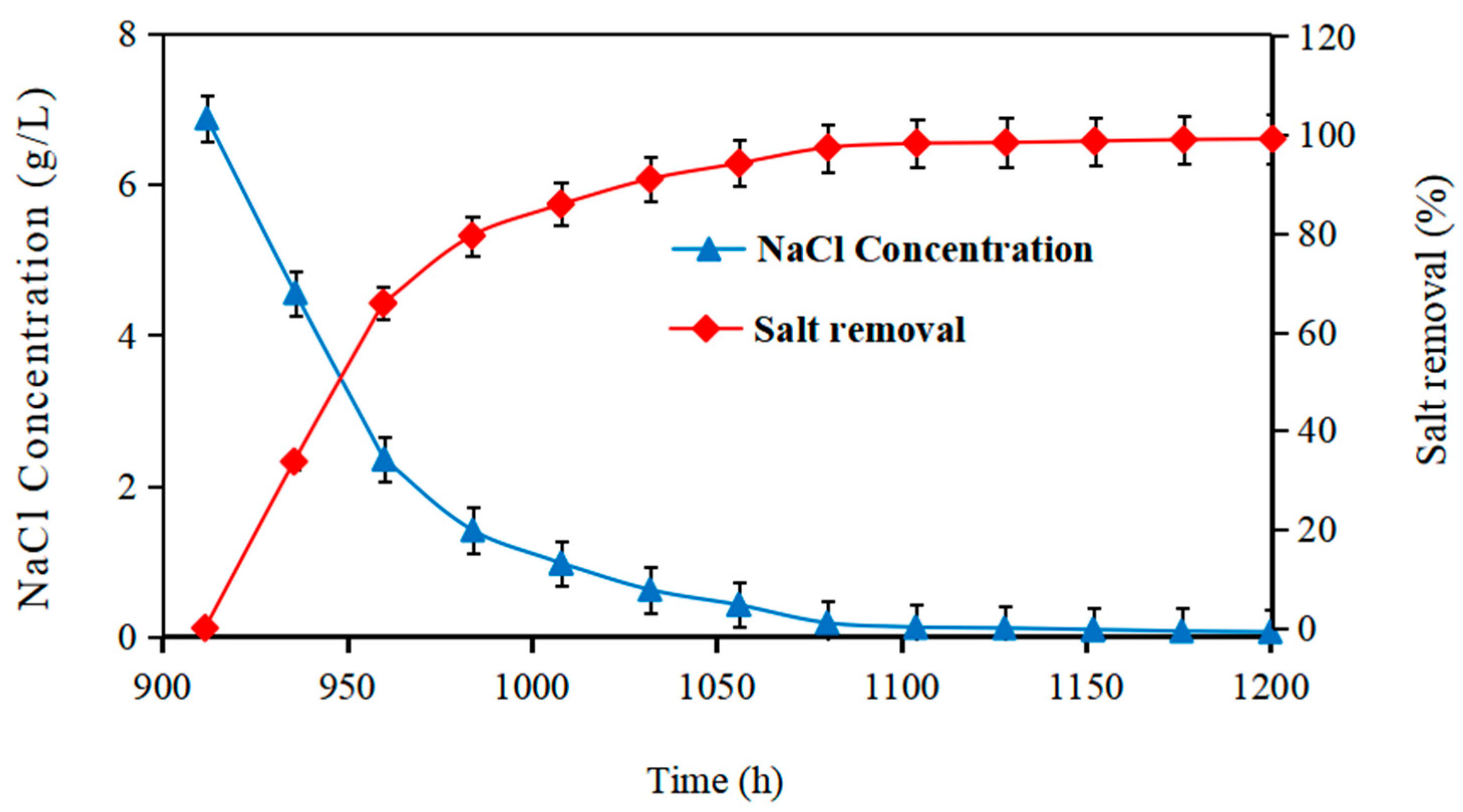
3.2. AMDC Treatment Results and Analysis of Saline-Alkaline Soil-Washing Water
3.2.1. AMDC Power Generation and Desalination Efficiency
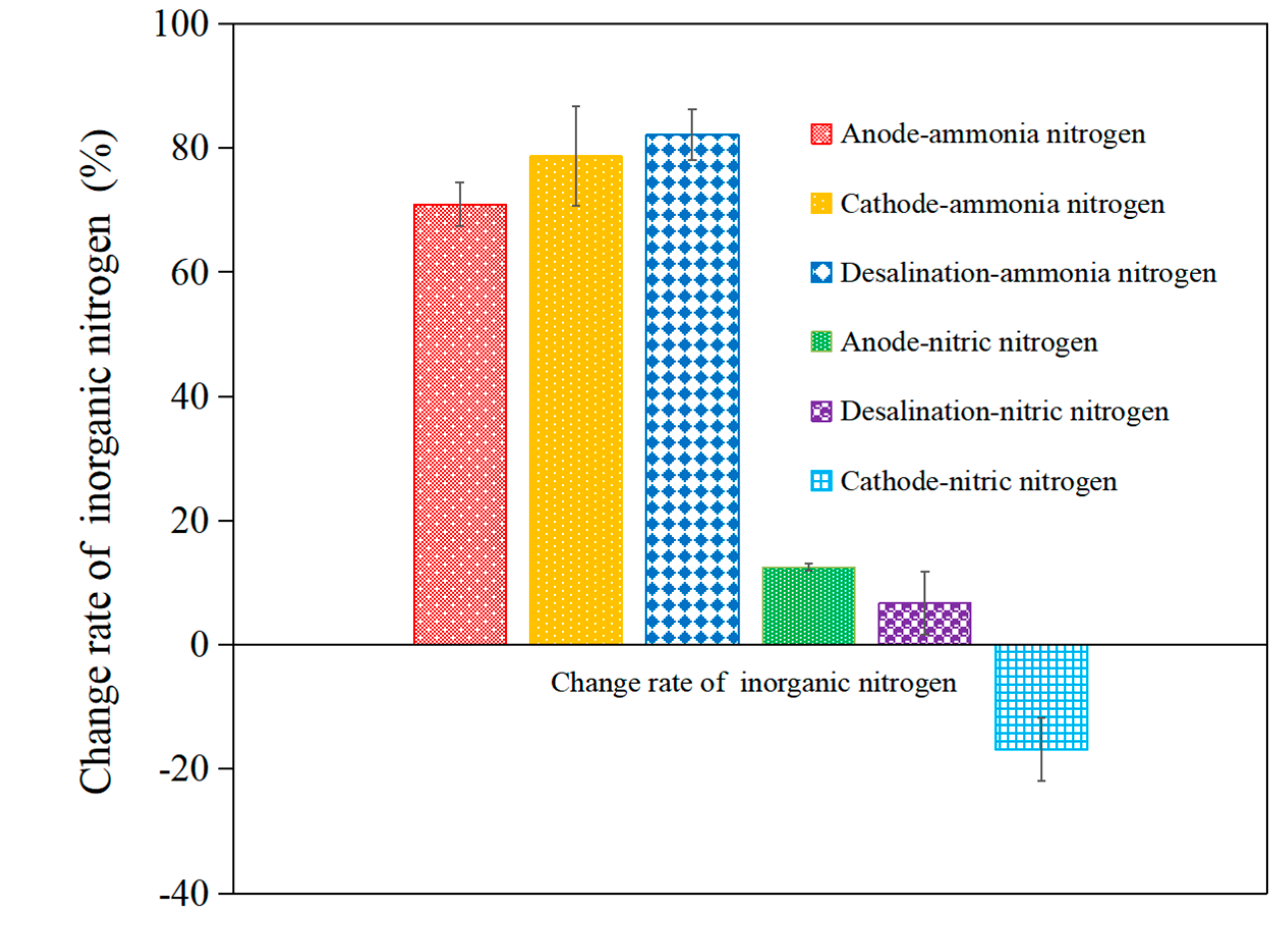
3.2.2. Change Efficiency in Inorganic Nitrogen Concentration of the AMDC
3.3. Analysis of Microbial Community Diversity
3.3.1. Microbial Diversity Index
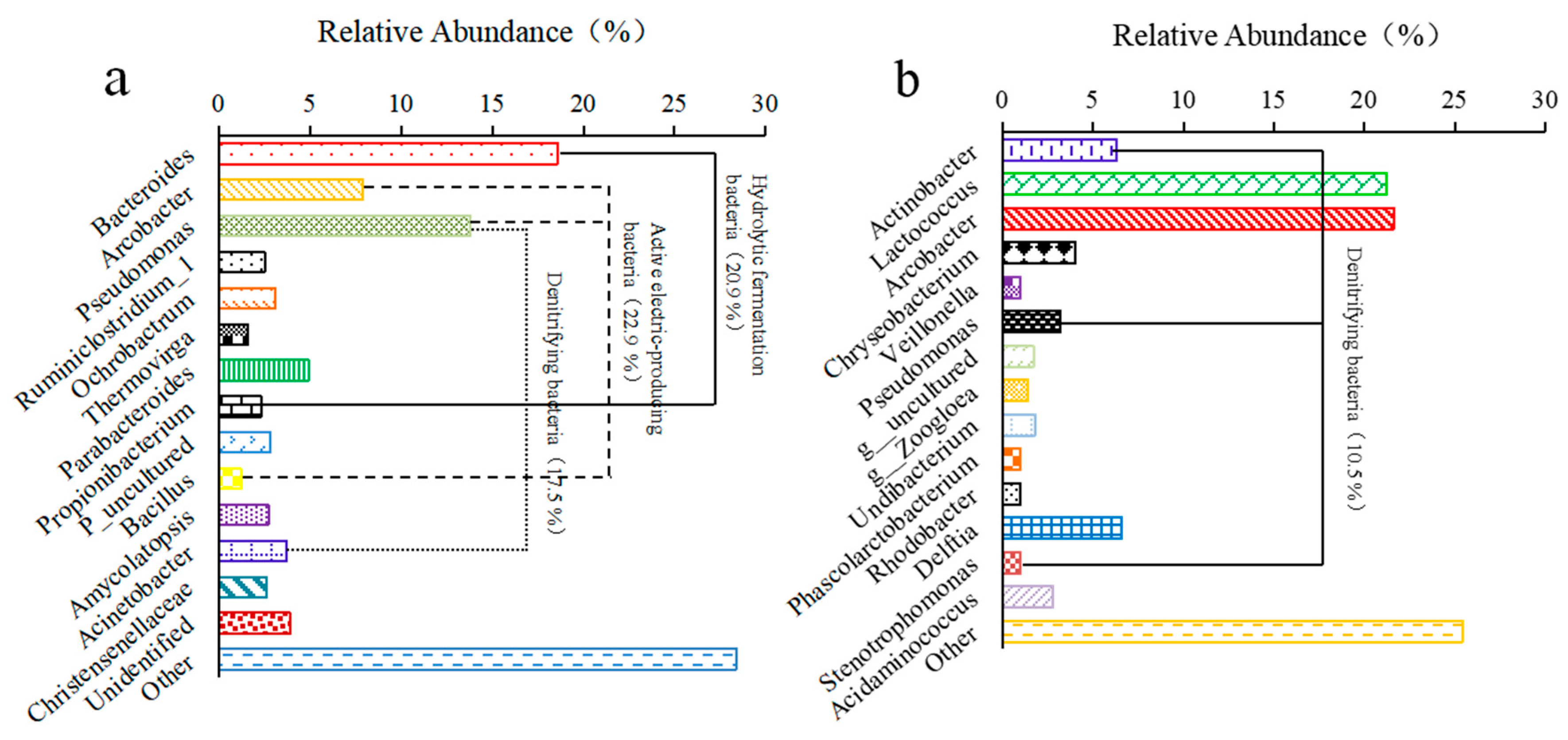
3.3.2. Microbial Communities in the Genus Levels
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Salinity conditions affect the performance of microbial desalination cell. With the decrease of salinity, the desalination cycle and rate become shorter and the salt removal increases. At higher salinity, salt ion transfer in the desalination chamber leads to charge accumulation and longer desalination time. Low-salinity wastewater can solve the negative effects of charge accumulation and ohmic loss in wastewater, and overcome the low conductivity problem of high-salinity wastewater as the system substrate.
- (2)
- The experimental results show that the pollutants removal rate and desalination effect of AMDC can meet the conditions when it is used to treat the actual coastal saline-alkaline soil-washing water, but the output power cannot meet the actual demand, and there is a limit of water treatment. AMDC can assist in the primary desalination of brine such as coastal saline-alkaline soil-washing water, or the secondary desalination of water after the initial desalination of water treatment equipment. However, as an independent application of desalination equipment in engineering projects, the effect has not yet been achieved, which needs further research and improvement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, X.J.; Geng, C.Y.; Han, J.Q.; Zhou, Y.M. Effects of warming onmineral element contents in leaves of dominant species and in soils in Changbai Mountain tundra. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2016, 7, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, E.; Rains, D.W. Advances in Salt Tolerance. Plant Soil 1987, 99, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, I.S.; Lobo, M.C.; Hernández, R.I.B.; Varaldo, H.M.P. Remediation of saline soils by a two-step process: Washing and amendment with sludge. Geoderma 2015, 247, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Kong, Q.C.; Liang, Y.X. Research on Recycling of Washing Water in Saline land. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2010, 16, 263–265. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.F.; Fu, G.K.; Zhang, Z. High-efficiency salt, sulfate and nitrogen removal and microbial community in biocathode microbial desalination cell for mustard tuber wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.A.; Yadav, J.S.P. Removal during leaching and availability of iron and manganese in pyrite and farmyard-manure-treated alkali soil. Soil Sci. 1989, 147, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, X.M. Infiltration of melting saline ice water in soil columns: Consequences on soil moisture and salt content. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, G.; Qin, P. The prediction of ecological potential for developing salt-tolerant oil plants on coastal saline land in Sheyang Saltern, China. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.X.; Huang, X.; Liang, P.; Xiao, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Logan, B.E. A new method for water desalination using microbial desalination cells. Environ. Sci Technol. 2009, 43, 7148–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamun, A.; Ahmad, W.; Baawain, M.S.; Khadem, M.; Dhar, B.R. A review of microbial desalination cell technology: Configurations, optimization and applications. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 183, 458–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Logan, B.E. Series assembly of microbial desalination cells containing stacked electrodialysis cells for partial or complete seawater desalination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5840–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokabian, B.; Gude, V.G.; Smith, R.; Brooks, J.P. Evaluation of anammox biocathode in microbial desalination and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimia, A.; Kebria, D.Y.; Najafpour, G.D. Co-treatment of septage and municipal wastewater in a quadripartite microbial desalination cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, K.C.; Cai, J.X.; Liang, S.; Wu, S.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liang, P.; Huang, X. A ten liter stacked microbial desalination cell packed with mixed ion-exchange resins for secondary effluent desalination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9917–9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, S.H.; Lu, F.; Yang, J.P.; Yang, F. Treatment of chromium wastewater by new microbial desalination cells. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 5, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.P.; Feng, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Lv, J.W.; He, W.H.; Logan, B.E. Simultaneous water desalination and electricity generation in a microbial desalination cell with electrolyte recirculation for pH control. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 106, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.D.; Li, R.Y.; Casey, F.; Ren, Z.M.; Ji, M. Investigation on the performance of microbial capacity desalination cell. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 6, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Mehanna, M.; Saito, T.; Yan, J.L.; Hickner, M.; Cao, X.; Huang, X.; Logan, B.E. Using microbial desalination cells to reduce water salinity prior to reverse osmosis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.P.; Li, X.F.; Wang, X.H. Endogenous inorganic carbon buffers accumulation and self-buffering capacity enhancement of air-cathode microbial fuel cells through anolyte recycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.S.; Drew, D.M.; He, Z. Efficient salt removal in a continuously operated upflow microbial desalination cell with an air cathode. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Q.; Huang, Z.; Dosoretz, C.; He, Z. Integrated experimental investigation and mathematical modeling of brackish water desalination and wastewater treatment in microbial desalination cells. Water Res. 2015, 77, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehanna, M.; Kiely, P.D.; Call, D.F.; Logan, B.E. Microbial electrodialysis cell for simultaneous water desalination and hydrogen gas production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9578–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehab, N.A.; Amy, G.L.; Logan, B.E.; Saikaly, P.E. Enhanced water desalination efficiency in an air-cathode stacked microbial electrodeionization cell (SMEDIC). J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Davidson, M.; Zuo, Y.; Ren, Z.Y. Recycled tire crumb rubber anodes for sustainable power production in microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 5863–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.L.; Lu, J.L.; Zhao, Z.M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Cheng, M.Q.; Zhang, J.W. Simultaneous bioelectricity generation, desalination, organics degradation, and nitrogen removal in air-cathode microbial desalination cells. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 794–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.L.; Cheng, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Cheng, M.Y.; Lu, J.L. Influence of COD concentration on performance of a three-chambers microbial desalination cells. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2019, 10, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zuo, K.C.; Liang, P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, X. Influence of Salt and Substrate Concentration on Performance of Microbial Desalination Cell. China Water Wastewater 2016, 11, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, R.; Abdelsalam, E.; Hisham, A.H. Evaluating the performance of Microbial Desalination Cells subjected to different operating temperatures. Desalination 2019, 462, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Nan, J.; Fengm, Y. Using bacterial catalyst in the cathode of microbial desalination cell to improve wastewater treatment and desalination. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 125, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Water Works Association; American Public Health Association; Water Pollution Control Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.F.; Fu, G.K.; Zhang, Z. Simultaneous nutrient and carbon removal and electricity generation in self-buffered biocathode microbial fuel cell for high-salinity mustard tuber wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.P. The Configuration and Performance of Microbial Desalination Cell under Continuous Flow; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, B.E.; Hamelers, B.; Rozendal, R.; Schröder, U.; Keller, J.; Freguia, S.; Peter, A.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K. Microbial fuel cells: Methodology and technology. Environ. Sci Technol. 2006, 40, 5181–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.F.; Zheng, X.Y.; Lu, Y.B.; Liu, G.L.; Luo, H.P.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.D.; Jin, S. Development of microbial community within the cathodic biofilm of single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.D.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jiao, Y.; Lee, D.J. Effect of cathode types on long-term performance and anode bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, M.D.; Scott, K.; Curtis, T.P.; Head, I.M. Effect of increasing anode surface area on the performance of a single chamber microbial fuel cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M. Effects of Electrode Materials and Catalyst on Microbial Fuel Cells’ Performance with Aged Landfill Leachate; Chongqing University: Chongqing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.F.; Song, Z.Z.; Lv, S.; Zha, Z.T.; Chen, S.H. Effect of anode COD on electricity generation and desalination of mustard production wastewater MDC and microbial community analysis under ammonia nitrogen removal. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 14, 943–954. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorovich, V.; Knighton, M.C.; Pagaling, E.; Ward, F.B.; Free, A.; Goryanin, I. A Novel Electrochemically Active Bacterium Phylogenetically Related to Arcobacter butzleri Isolated from a Microbial Fuel Cell. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7326–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimje, V.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Jean, J.S.; Reddy, A.S.; Fan, C.W.; Pan, K.Y.; Liu, H.T.; Chen, J.L. Stable and high energy generation by a strain of Bacillus subtilis in a microbial fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2009, 190, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, X.Y.; Yan, Z.Y.; Shen, H.B.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Zheng, T.; Jiang, M.; Wei, P.; Jia, H.H.; et al. An integrated aerobic-anaerobic strategy for performance enhancement of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-inoculated microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liu, L.H.; Sun, D.; Ren, N.Q.; Lee, D.J. Isolation of Fe(III)-reducing fermentative bacterium Bacteroides sp. W7 in the anode suspension of a microbial electrolysis cell(MEC). Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 3178–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.H.; Kong, C.H. Enhanced removal of p-nitrophenol in a microbial fuel cell after long-term operation and the catabolic versatility of its microbial community. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 3391, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.L.; Lin, M.; Wang, Z.Q.; Fu, H.X.; Yang, H.P.; Jiang, W.Y.; Yang, S.T. Metabolic engineering of Propionibacterium freudenreichii subsp. shermanii for xylose fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khater, D.Z.; El-Khatib, K.M.; Hassan, H.M. Microbial diversity structure in acetate single chamber microbial fuel cell for electricity generation. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.J.; Zhang, Z.M.; Yu, Z.D.; Dai, X.; Xu, X.Y.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Zhu, L. Evolution and functional analysis of extracellular polymeric substances during the granulation of aerobic sludge used to treat p-chloroaniline wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.C.; Tian, Y.; He, Z.W.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, J. Performance and mechanism of a novel algal-bacterial symbiosis system based on sequencing batch suspended biofilm reactor treating domestic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Location | Mode | pH | Ammonium (mg/L) | Nitrate Nitrogen (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anode chamber | Influent | 6.67 ± 0.01 | 42.72 ± 2.15 | 2.39 ± 0.18 |
| Effluent | 5.77 ± 0.03 | 12.44 ± 0.15 | 2.09 ± 0.04 | |
| Desalination chamber | Influent | 6.13 ± 0.08 | 1.51 ± 0.21 | 2.34 ± 0.16 |
| Effluent | 6.04 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.18 | 2.18 ± 0.02 | |
| Cathode chamber | Influent | 6.92 ± 0.04 | 18.67 ± 0.84 | 0.97 ± 0.05 |
| Effluent | 7.82 ± 0.04 | 3.98 ± 0.20 | 1.13 ± 0.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Lu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Electricity Generation, Salt and Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Community in Aircathode Microbial Desalination Cell for Saline-Alkaline Soil-Washing Water Treatment. Water 2020, 12, 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082257
Xu C, Lu J, Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Zhang J. Electricity Generation, Salt and Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Community in Aircathode Microbial Desalination Cell for Saline-Alkaline Soil-Washing Water Treatment. Water. 2020; 12(8):2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082257
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chenglong, Jialei Lu, Zhimiao Zhao, Yinjiang Zhang, and Jiawei Zhang. 2020. "Electricity Generation, Salt and Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Community in Aircathode Microbial Desalination Cell for Saline-Alkaline Soil-Washing Water Treatment" Water 12, no. 8: 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082257
APA StyleXu, C., Lu, J., Zhao, Z., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2020). Electricity Generation, Salt and Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Community in Aircathode Microbial Desalination Cell for Saline-Alkaline Soil-Washing Water Treatment. Water, 12(8), 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082257




