Enhanced Treatment of Pharmaceutical Wastewater by an Improved A2/O Process with Ozone Mixed Municipal Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. PW (Pharmaceutical Wastewater) and DW (Domestic Wastewater) Characteristics
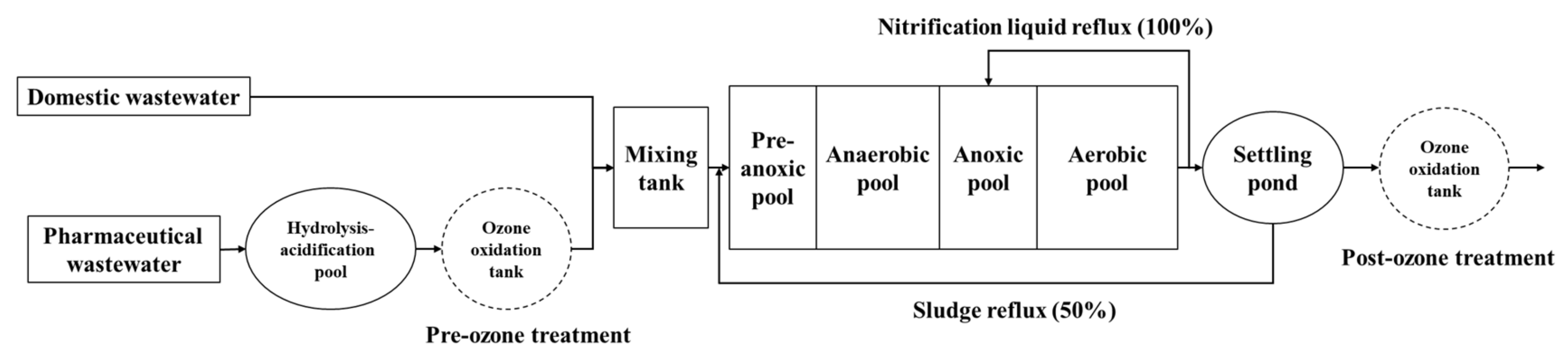
2.2. Improved A2/O Process with Pre-Ozone and Post-Ozone Treatment
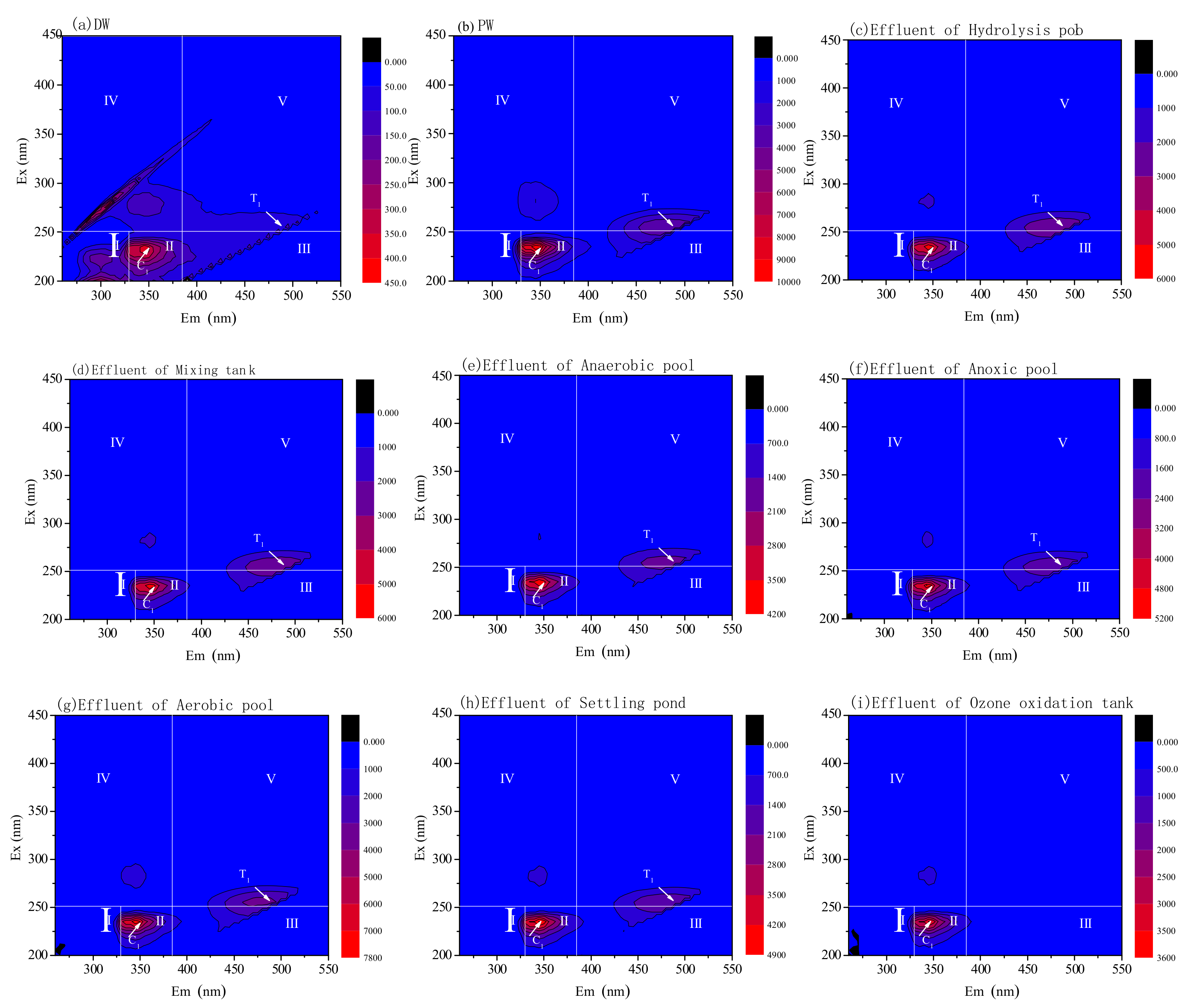
2.3. Three-Dimensional Fluorescence, Water Quality and Microbial Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
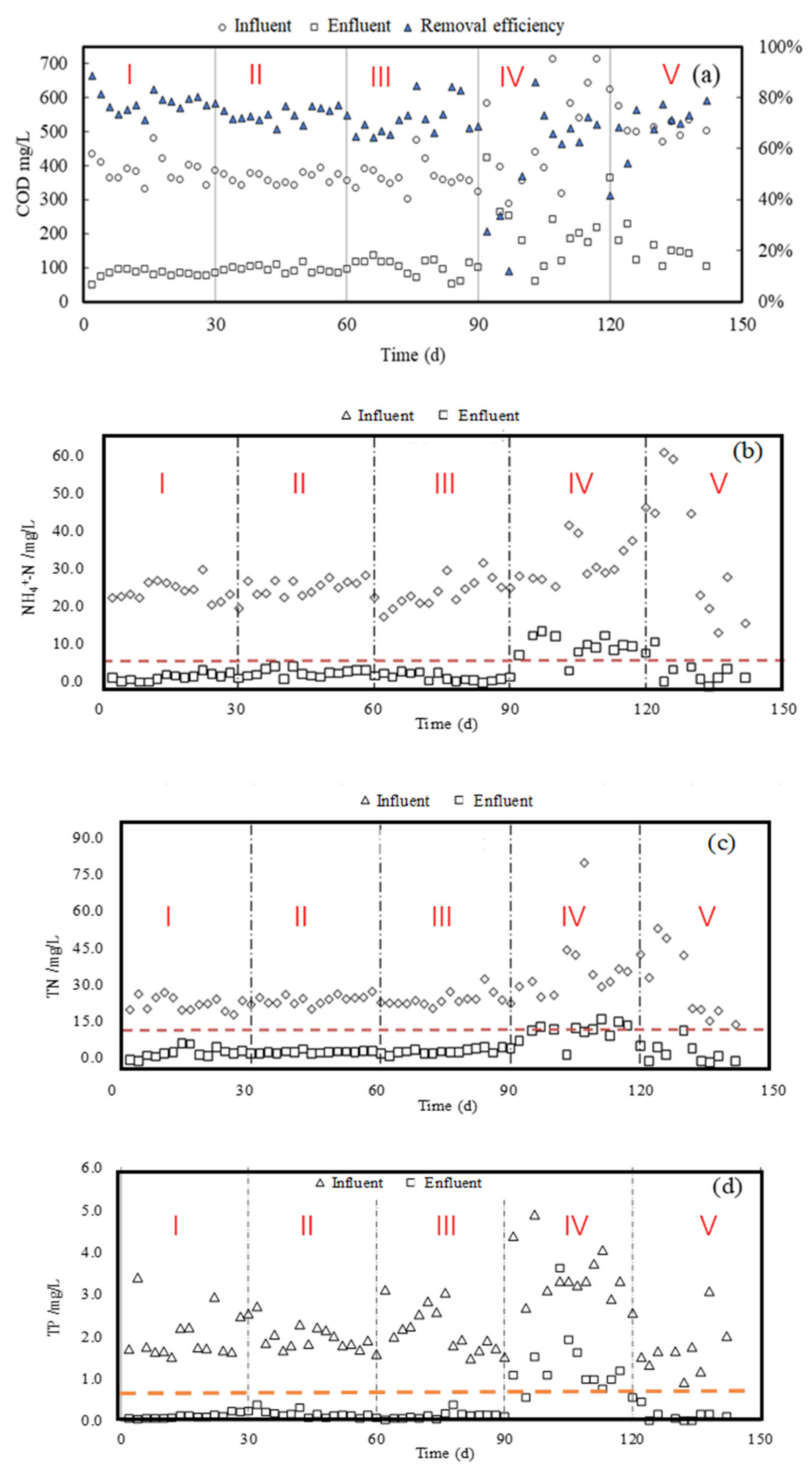
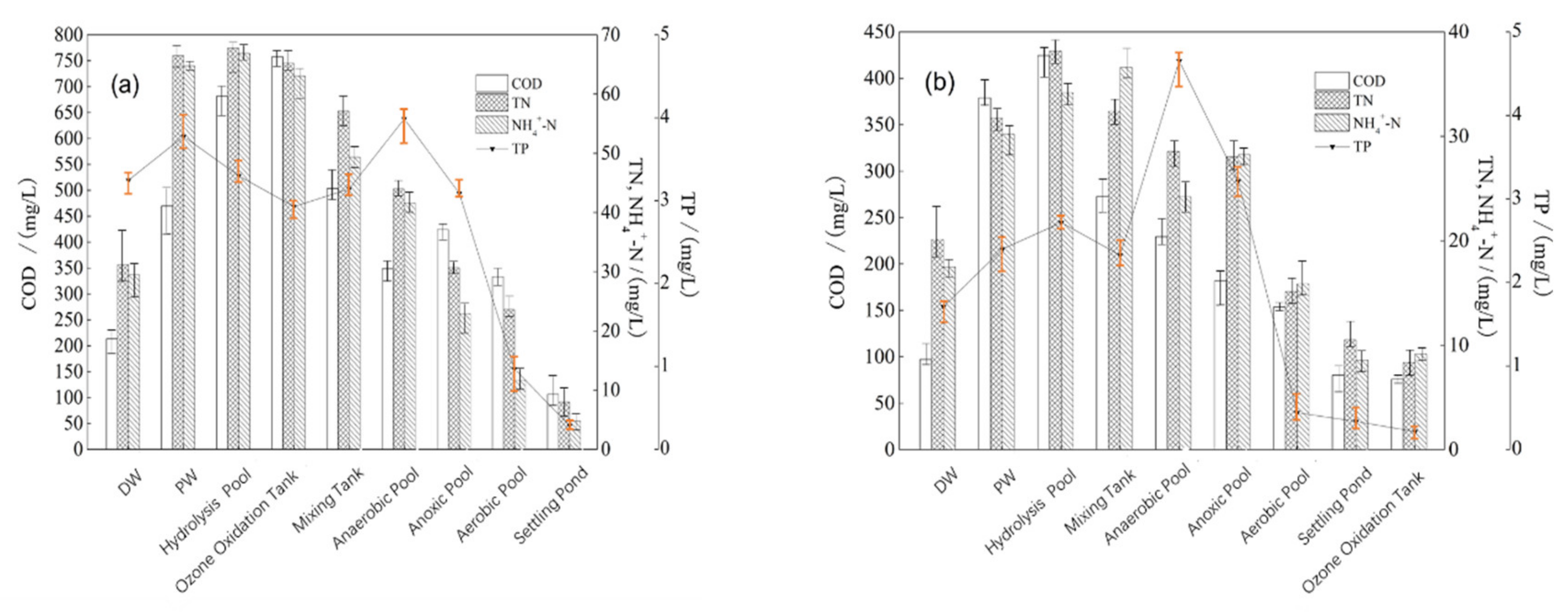
3.1. COD and N/P Removal by Pre-Ozone Treatment with Different Mixing Ratios of PW and DW
3.2. COD and N/P Removal by Post-Ozone Treatment after Biological Treatment
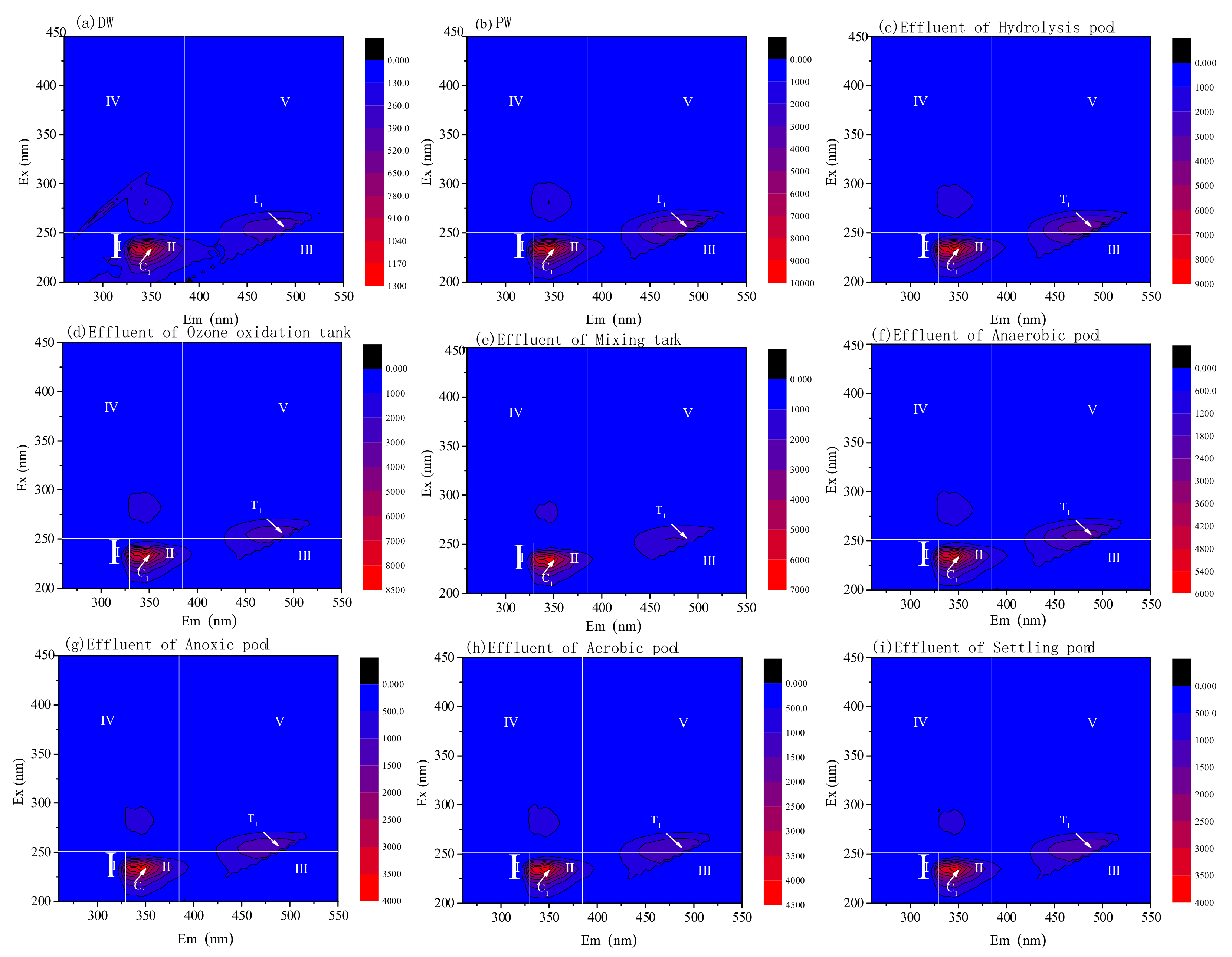
3.3. DOM Removal Characters for Pre-Ozone and Post-Ozone Treatment
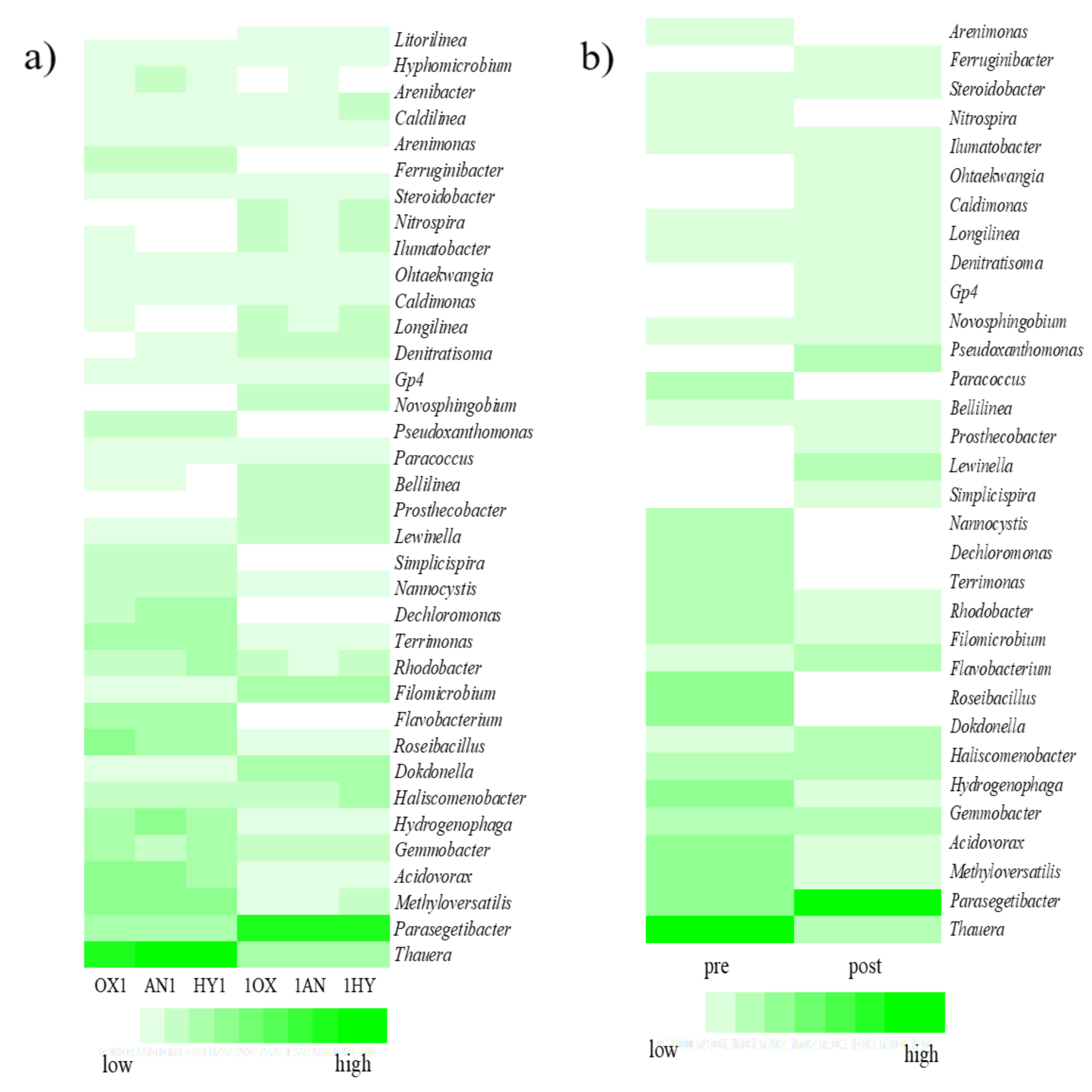
3.4. Microbial Community Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A2/O | anaerobic–anoxic–aerobic-ozone |
| COD | chemical oxygen demand |
| BOD | biochemical oxygen demand |
| PW | pharmaceutical wastewater |
| DW | domestic wastewater |
| DOM | dissolved organic matter |
| TP | total phosphorus |
| TN | total nitrogen |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
| HRT | hydraulic retention time |
| SRT | sudge residence time |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| MLSS | mixed liquor suspended solid |
References
- Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. A review on removing pharmaceutical contaminants from wastewater by constructed wetlands: Design, performance and mechanism. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 468–469, 908–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ji, F.; Xu, X. Treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater using interior micro-electrolysis/Fenton oxidation-coagulation and biological degradation. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Iwase, T.; Kita, S.; Watanabe, Y. Influence of residual organic macromolecules produced in biological wastewater treatment processes on removal of pharmaceuticals by NF/RO membranes. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3751–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svojitka, J.; Dvořák, L.; Studer, M.; Straub, J.; Frömelt, H.; Wintgens, T. Performance of an anaerobic membrane bioreactor for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtiaga, A.; Perez, G.; Ibañez, R.; Ortiz, I. Removal of pharmaceuticals from a WWTP secondary effluent by ultrafiltration/reverse osmosis followed by electrochemical oxidation of the RO concentrate. Desalination 2013, 331, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margot, J.; Kienle, C.; Magnet, A.; Weil, M.; Rossi, L.; De Alencastro, L.F.; Abegglen, C.; Thonney, D.; Chèvre, N.; Schärer, M.; et al. Treatment of micropollutants in municipal wastewater: Ozone or powdered activated carbon? Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 461, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcıoğlu, I.A.; Ötker, M. Treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing antibiotics by O3 and O3/H2O2 processes. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.M.; Göbel, A.; Joss, A.; Hermann, N.; Löffler, D.; McArdell, C.S.; Ried, A.; Siegrist, H.; Ternes, T.A.; Von Gunten, U. Oxidation of Pharmaceuticals during Ozonation of Municipal Wastewater Effluents: A Pilot Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4290–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Canonica, S.; Von Gunten, U. Efficiency and energy requirements for the transformation of organic micropollutants by ozone, O3/H2O2 and UV/H2O2. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3811–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, J.; Wang, D.; Meng, P.; Zeng, M. Optimization and interpretation of O3 and O3/H2O2 oxidation processes to pretreat hydrocortisone pharmaceutical wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. AC/O3-BAC processes for removing refractory and hazardous pollutants in raw water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.M.; Spiliotopoulou, A.; Chhetri, R.K.; Casas, M.E.; Bester, K.; Andersen, H.R.; Kaarsholm, K.M.S. Ozonation for source treatment of pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater—Ozone lifetime and required ozone dose. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, Y.; Mamane, H.; Zucker, I.; Avisar, D. Treating wastewater from a pharmaceutical formulation facility by biological process and ozone. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcioğlu, I.A.; Ötker, M. Pre-Treatment of Antibiotic Formulation Wastewater by O3, O3/H2O2, and O3/UV Processes. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2004, 28, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Battimelli, A.; Loisel, D.; Garcia-Bernet, D.; Carrere, H.; Delgenes, J.-P. Combined ozone pretreatment and biological processes for removal of colored and biorefractory compounds in wastewater from molasses fermentation industries. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.; Brar, S.K.; Tyagi, R.; Surampalli, R. Physico-chemical pre-treatment and biotransformation of wastewater and wastewater Sludge—Fate of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, J.; Gabriel, D.; Lafuente, J. Improving the nitrogen removal efficiency of an A2/O based WWTP by using an on-line Knowledge Based Expert System. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2109–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, J.; Gabriel, D.; Lafuente, J. Effect of internal recycle on the nitrogen removal efficiency of an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2/O) wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Tao, T.; Zhang, J.; You, G.-L. Performance evaluation of a modified anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2/O) process treating low strength wastewater. Desalination 2009, 249, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Q.; Zhang, F.; Bi, X.J.; Zhang, B. Contrast between Inverted A2/O process and Improved A2/O process in full-scale test. Technol. Water Treat. 2008, 34, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Song, Y. Advanced treatment of antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater by catalytic ozonation combined with BAF process. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2019, 13, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Song, Y.; Zeng, P. Start-up of membrane bioreactor used in the treatment of fosphnomycin pharmaceutical wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 34, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeling, S.; Narmandakh, A.; Schmitt, O.; Gad’on, N.; Schühle, K.; Fuchs, G. Phenylphosphate Synthase: A New Phosphotransferase Catalyzing the First Step in Anaerobic Phenol Metabolism in Thauera aromatica. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 8044–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breinig, S.; Schiltz, E.; Fuchs, G. Genes Involved in Anaerobic Metabolism of Phenol in the Bacterium Thauera aromatica. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5849–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zheng, M.; Han, Y.; Han, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, W. Synergistic degradation on phenolic compounds of coal pyrolysis wastewater (CPW) by lignite activated coke-active sludge (LAC-AS) process: Insights into succession of microbial community under selective pressure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Holliger, C. Dynamics of Microbial Community Structure of and Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal by Aerobic Granules Cultivated on Propionate or Acetate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8041–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, T.; Wei, H.; Dou, W.; Jiang, L.-M.; Lv, Y. Co-treatment of reject water from sludge dewatering and supernatant from sludge lime stabilization process for nutrient removal: A cost-effective approach. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Geng, J.; Ren, Z.; Guo, G.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Effect of COD/N and COD/P ratios on the PHA transformation and dynamics of microbial community structure in a denitrifying phosphorus removal process. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 88, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, J. Effect of temperature downshifts on a bench-scale hybrid A/O system: Process performance and microbial community dynamics. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xiong, J.; Wong, P.K.; Ao, Z. Enhancing tetrabromobisphenol A biodegradation in river sediment microcosms and understanding the corresponding microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Index | PW | DW |
|---|---|---|
| COD | 650 ± 150 mg/L | 300 ± 100 mg/L |
| BOD/COD | <0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| TN | 45 ± 15 mg/L | 41 ± 9 mg/L |
| NH4+-N | 30 ± 2 mg/L | 31 ± 2 mg/L |
| TP | 3.0 ± 0.5 mg/L | 2.3 ± 0.3 mg/L |
| pH | 8.0 ± 0.5 | 7.5 ± 0.4 |
| Category | Hydrocarbon | Phenols | Esters | Aldehydes and Ketones | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 44 | 20 | 39 | 30 | 89 |
| Content | 22.5 ± 13.5% | 16 ± 5% | 29 ± 21% | 22.5 ± 14% | 29.5 ± 11.5% |
| Inlet Flow /(L/h) | Mixed Liquor Suspended Solid/(g/L) | Dissolved Oxygen/(mg/L) | Nitrification Liquid Reflux Ratio | Sludge Reflux Ratio | Hydraulic Retention Time/h | Sludge Residence Time/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 3.26 ± 0.74 | 3.2 ± 0.7 | 100% | 50% | 14.3 ± 0.8 | 18 ± 3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Du, C.; Qian, F.; Song, Y.; Xiang, L. Enhanced Treatment of Pharmaceutical Wastewater by an Improved A2/O Process with Ozone Mixed Municipal Wastewater. Water 2020, 12, 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102771
Wang J, Du C, Qian F, Song Y, Xiang L. Enhanced Treatment of Pharmaceutical Wastewater by an Improved A2/O Process with Ozone Mixed Municipal Wastewater. Water. 2020; 12(10):2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102771
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian, Cong Du, Feng Qian, Yonghui Song, and Liancheng Xiang. 2020. "Enhanced Treatment of Pharmaceutical Wastewater by an Improved A2/O Process with Ozone Mixed Municipal Wastewater" Water 12, no. 10: 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102771
APA StyleWang, J., Du, C., Qian, F., Song, Y., & Xiang, L. (2020). Enhanced Treatment of Pharmaceutical Wastewater by an Improved A2/O Process with Ozone Mixed Municipal Wastewater. Water, 12(10), 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102771




