Effects of Additional Carbon Sources in the Biodegradation of 1,4-Dioxane by a Mixed Culture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enrichment of Mixed Consortium of 1,4-Dioxane-Degrading Bacteria
2.2. Determination of Kinetic Coefficients for 1,4-Dioxane Biodegradation
2.3. Effects of the Presence of Other Carbon Sources on 1,4-Dioxane Biodegradation
2.4. Analytical Method
3. Results and Discussion
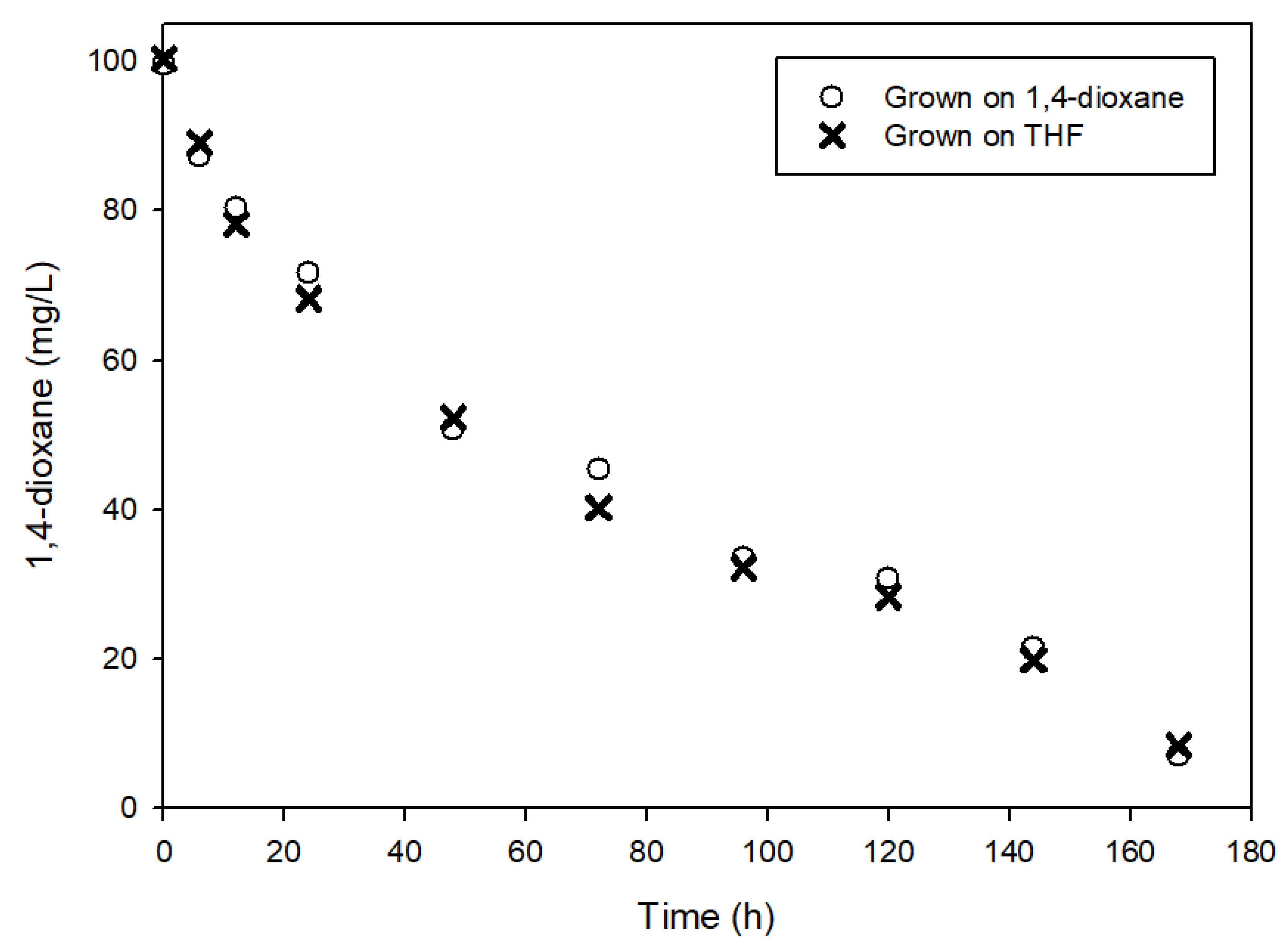
3.1. Determination of Kinetic Parameters
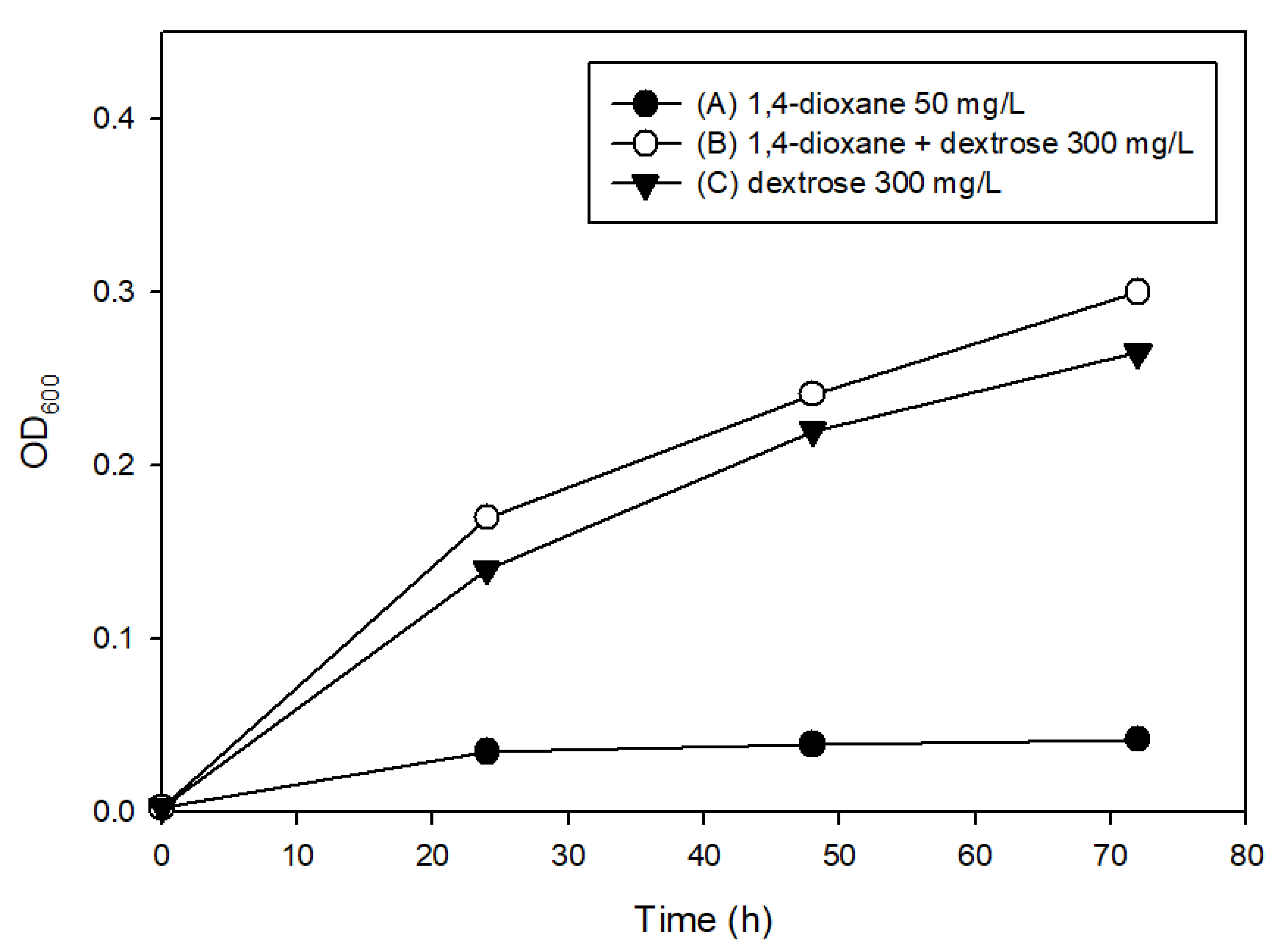
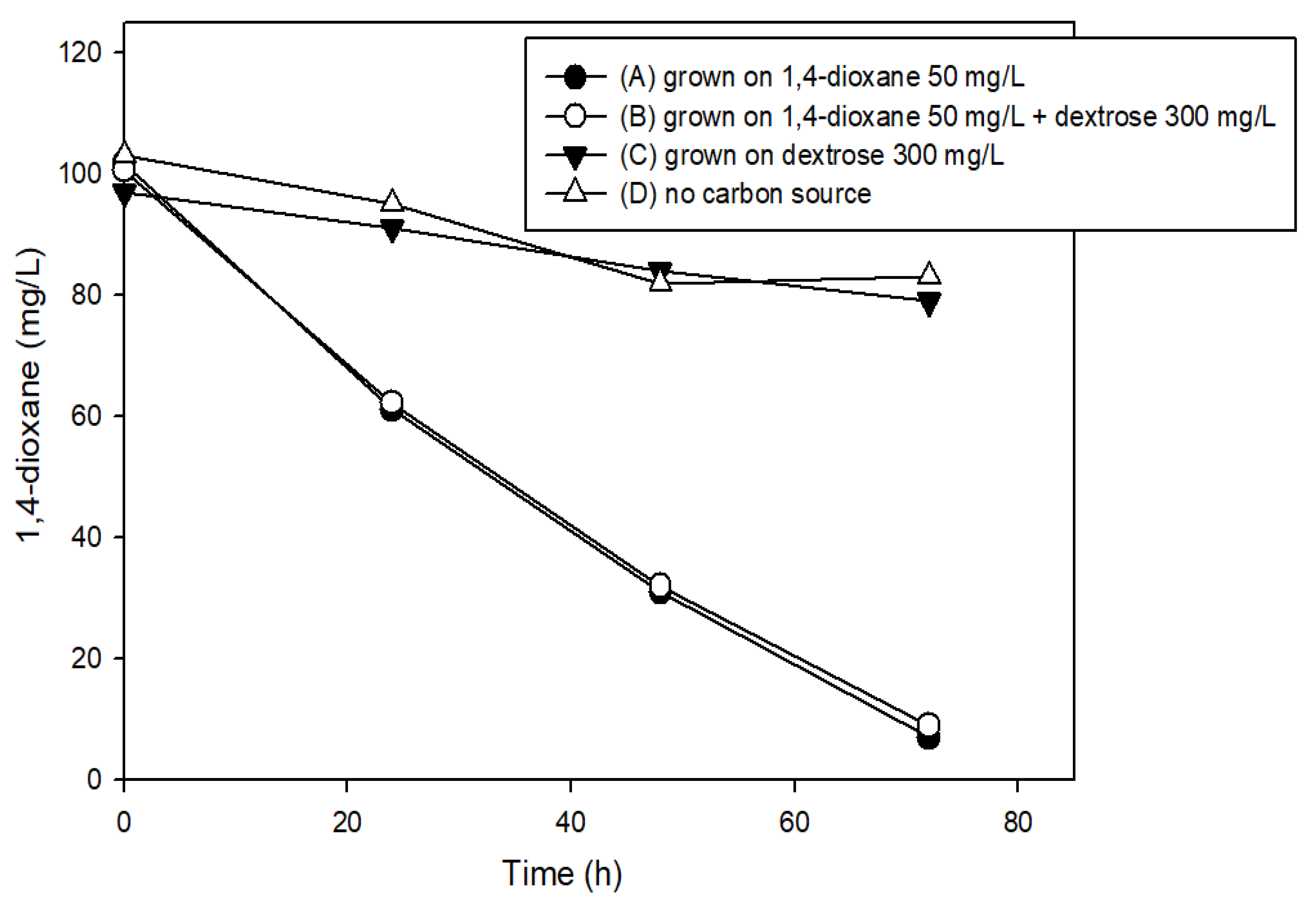
3.2. The Effects of Easily Degradable Carbon Sources
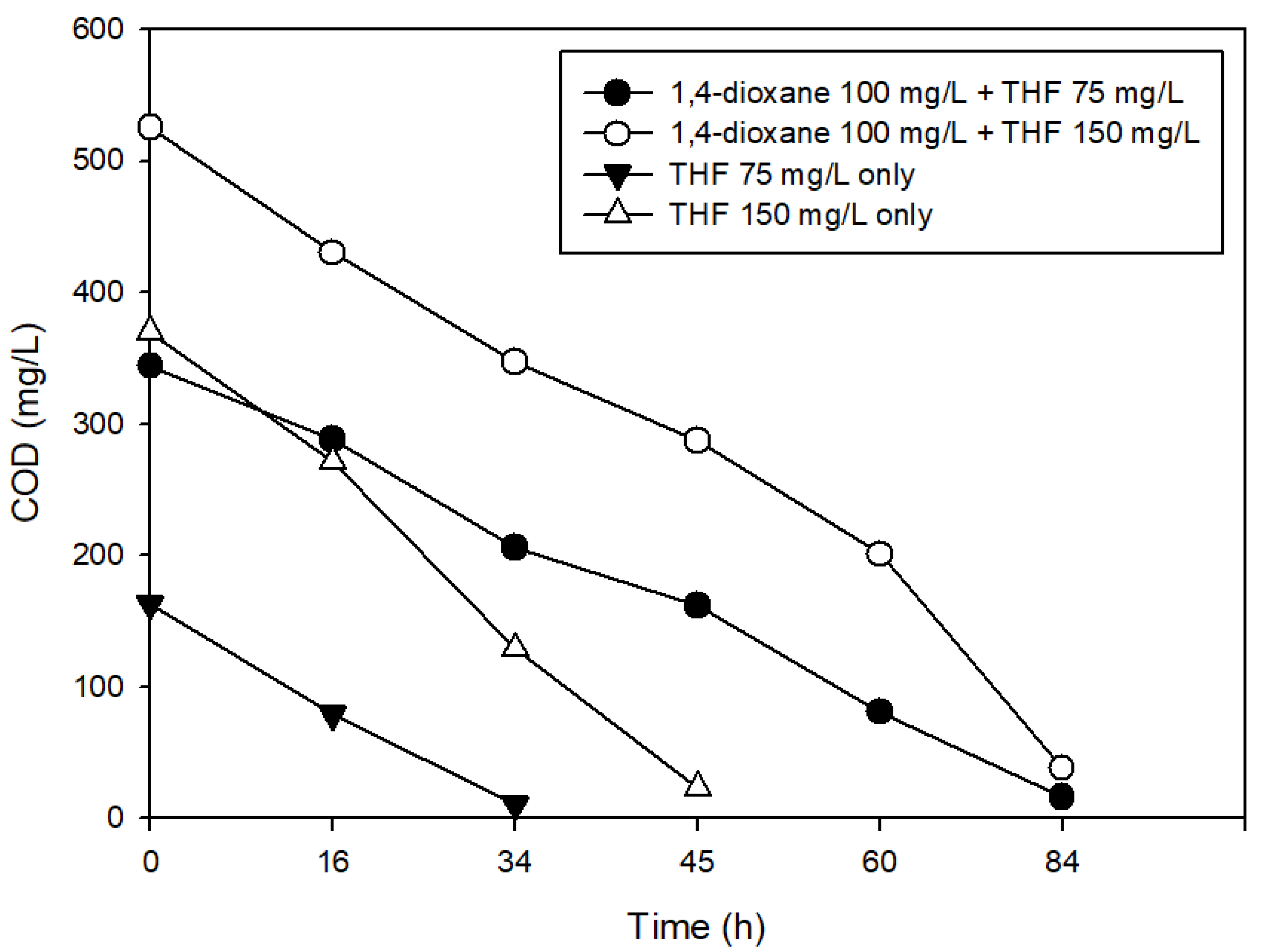
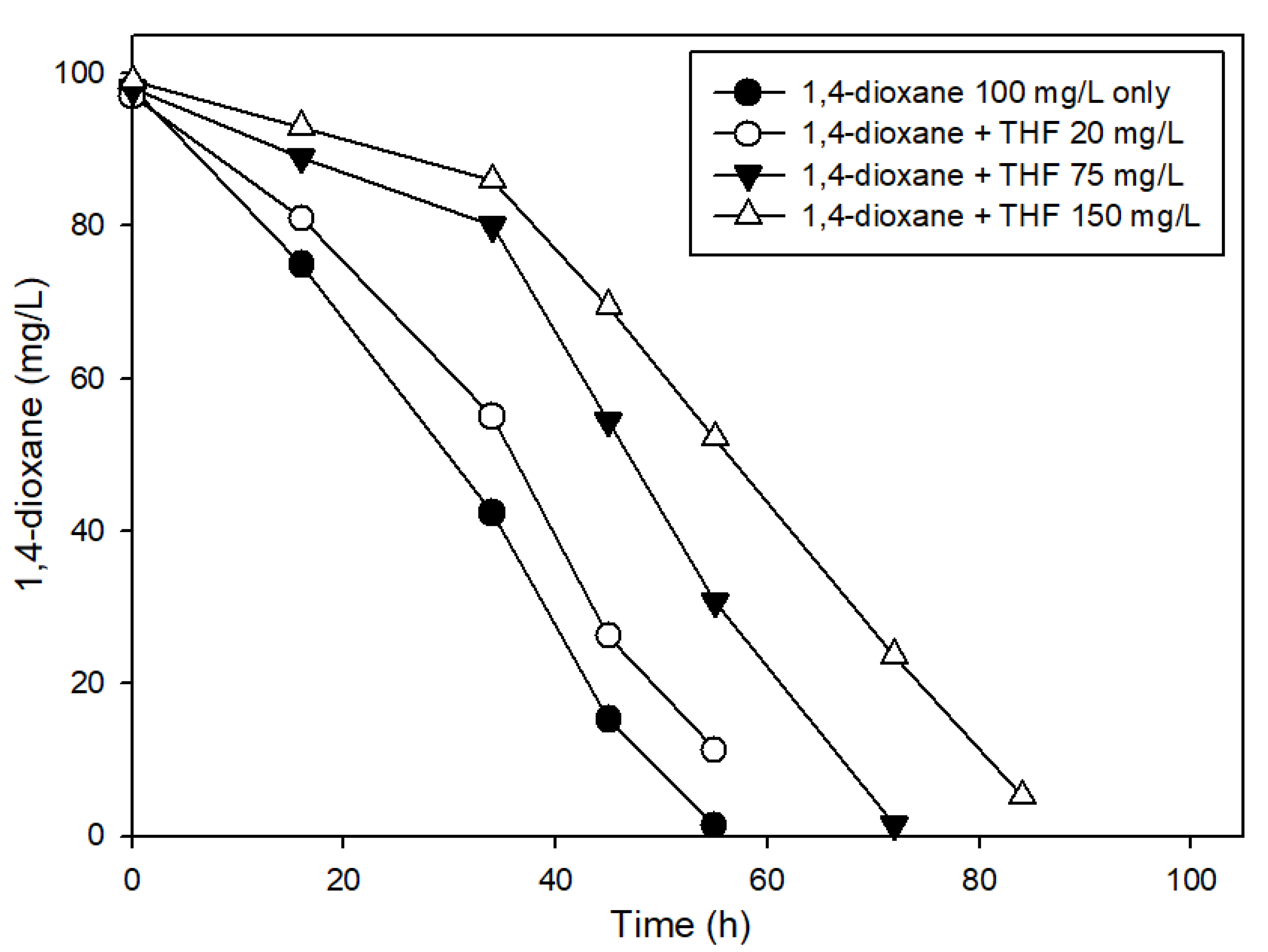
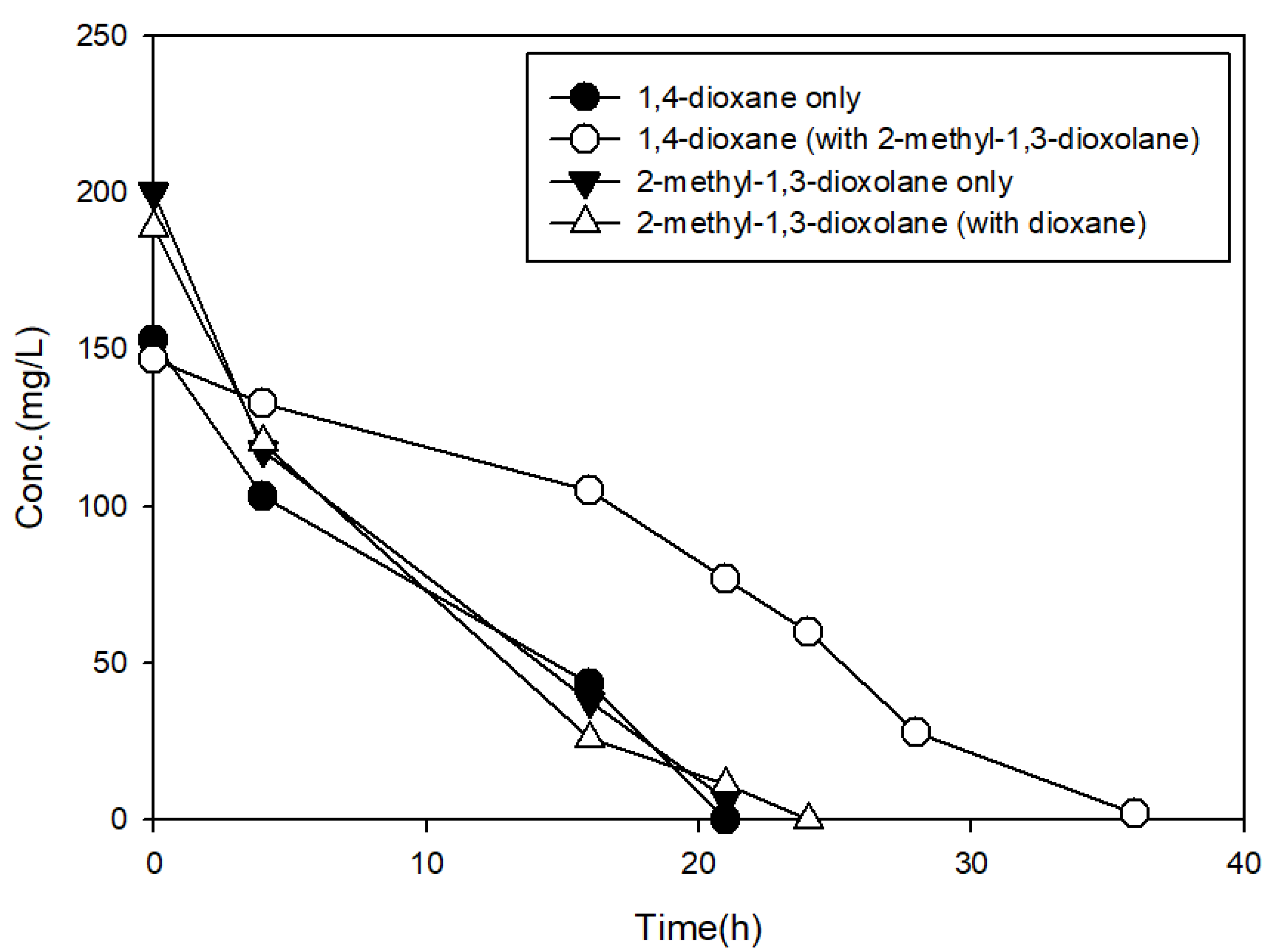
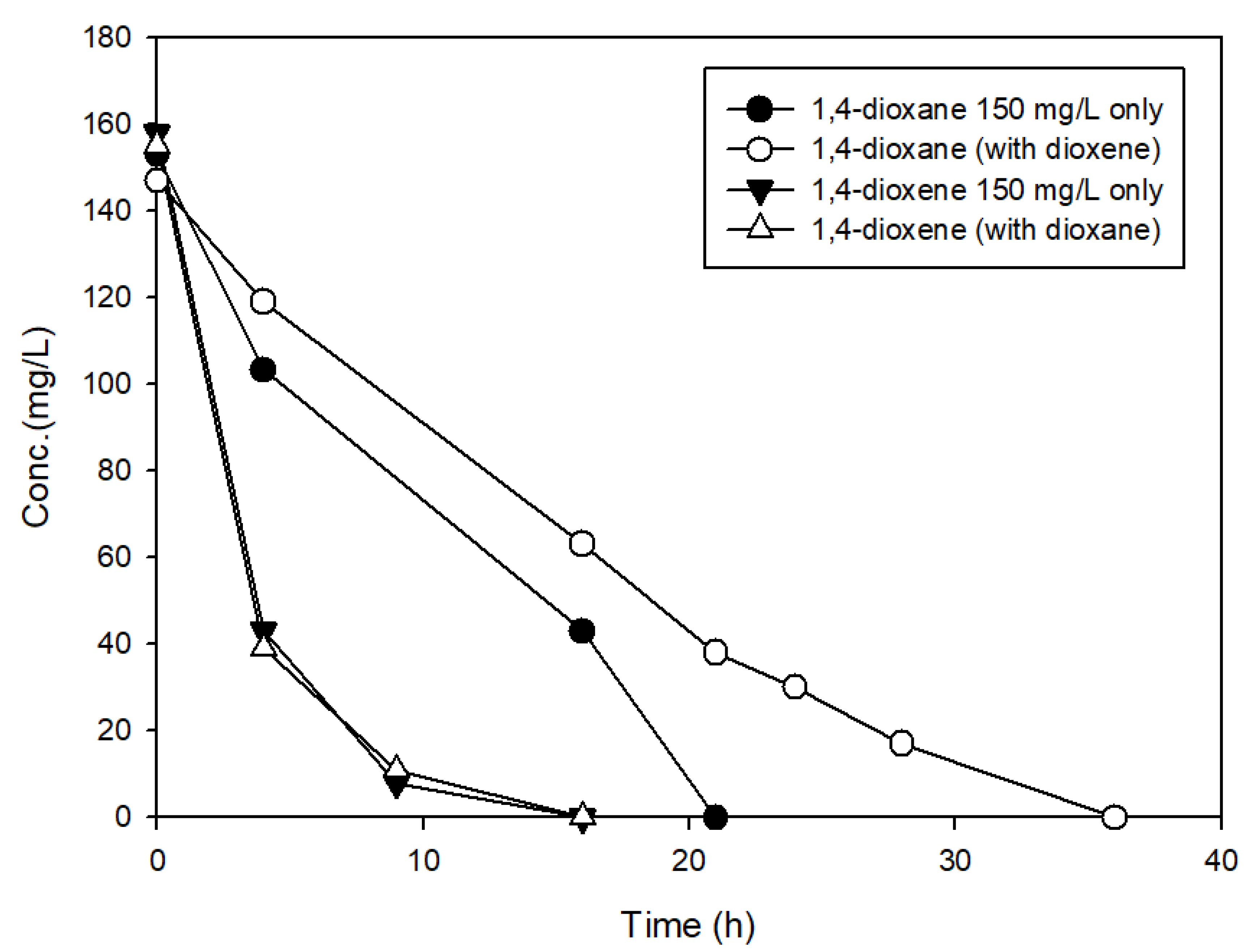
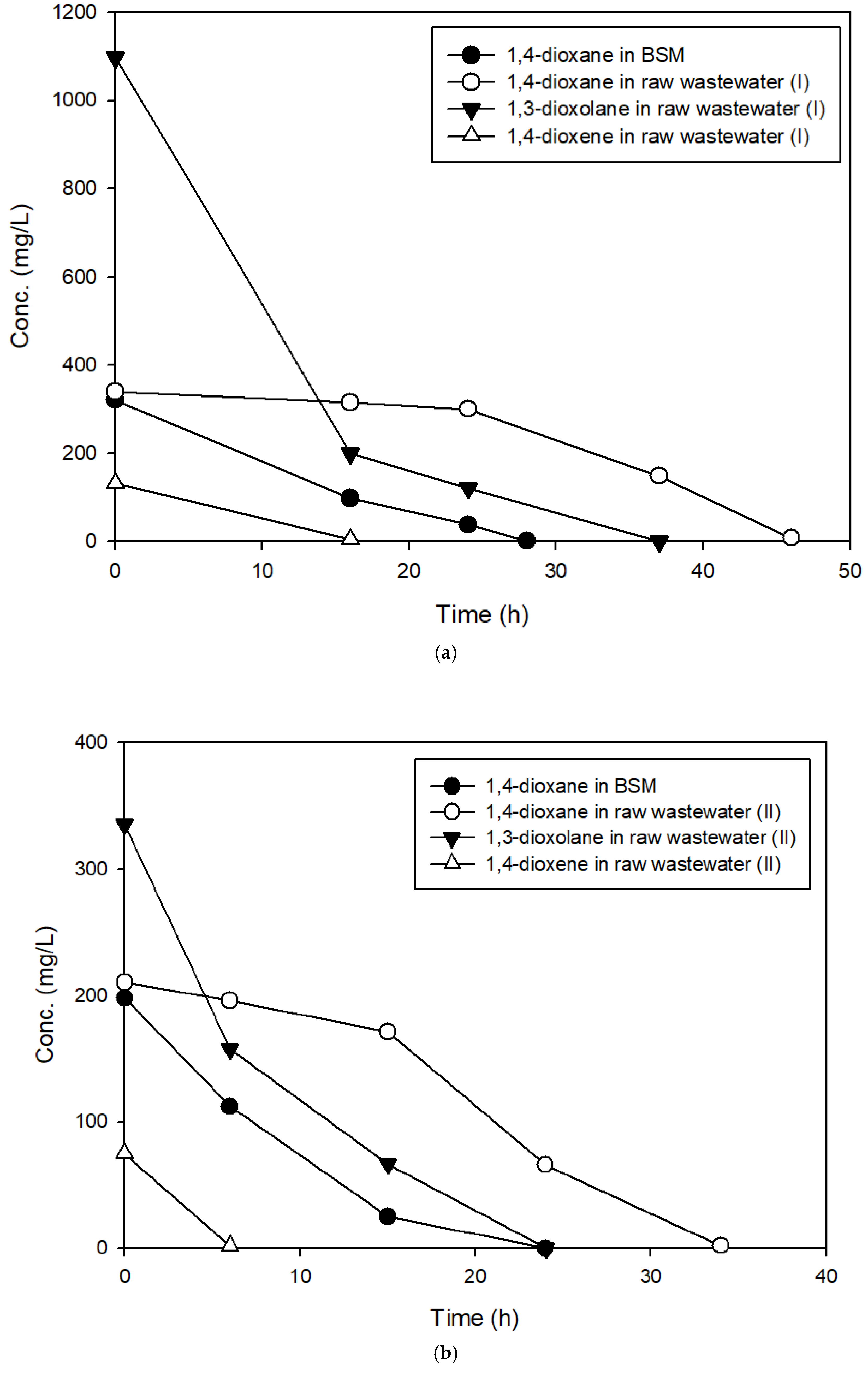
3.3. The Effects of Structural Analogs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popoola, A.V. Mechanism of the reaction involving the formation of dioxane byproduct during the production of poly (ethylene terephthalate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 43, 1875–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGuiseppi, W.; Walecka-Hutchison, C.; Hatton, J. 1,4-Dioxane Treatment Technologies. Remediat. J. 2016, 27, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzinger, P.; Banerjee, R.; Rezes, R.; Streger, S.H.; McClay, K.; Schaefer, C.E. Potential for cometabolic biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane in aquifers with methane or ethane as primary substrates. Biodegradation 2017, 28, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sock, S.M. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Biodegradation as a Treatment Alternative for the Removal of 1, 4-Dioxane. Master’s Thesis, Clemson University, Clemson, SC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, A. Distribution of 1,4-dioxane in relation to possible sources in the water environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 227, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, K.; Udagawa, M.; Sei, K.; Ike, M. Pilot test of biological removal of 1,4-dioxane from a chemical factory wastewater by gel carrier entrapping Afipia sp. strain D1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Johnson, N.W.; Gedalanga, P.B.; Adamson, D.; Newell, C.; Mahendra, S. Response and recovery of microbial communities subjected to oxidative and biological treatments of 1,4-dioxane and co-contaminants. Water Res. 2019, 149, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Ko, K.; A Ramsay, J. Biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane by a Flavobacterium. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, A.; Sepulveda, A.; Foster, K.; Kruk, T.; Nickelsen, M.G.; Gillan, M.; Mohr, T.K. 1,4-Dioxane: Emerging technologies for an emerging contaminant. Remediat. J. 2019, 29, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M. Nonbiodegradable and other racalcitrant molecules. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1973, 15, 611–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, D.; Tsunoda, T.; Sawada, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Sei, K.; Ike, M. Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of metals on 1,4-dioxane degradation by four different 1,4-dioxane-degrading bacteria. Chemosphere 2019, 238, 124606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Cao, J.; Feng, Q.; Fang, F.; Chen, Y. Inhibition of 1, 4-dioxane on the denitrification process by altering the viability and metabolic activity of Paracoccus denitrificans. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27274–27282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lu, X.; Polasko, A.; Johnson, N.W.; Miao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Mahendra, S.; Gu, B. Co-contaminant effects on 1,4-dioxane biodegradation in packed soil column flow-through systems. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaka, K.; Udagawa, M.; Kimura, Y.; Sei, K.; Ike, M. Biological 1,4-Dioxane Wastewater Treatment by Immobilized Pseudonocardia sp. D17 on Lower 1,4-Dioxane Concentration. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2016, 14, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bernhardt, D.; Diekmann, H. Degradation of dioxane, tetrahydrofuran and other cyclic ethers by an environmental Rhodococcus strain. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1991, 36, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Parales, R.; E Adamus, J.; White, N.; May, H.D. Degradation of 1,4-dioxane by an actinomycete in pure culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 4527–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, P.; Kroppenstedt, R.M. Pseudonocardia benzenivorans sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendra, S.; Cohen, L.A. Pseudonocardia dioxanivorans sp. nov., a novel actinomycete that grows on 1,4-dioxane. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendra, S.; Petzold, C.J.; Baidoo, E.E.; Keasling, J.D.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. Identification of the Intermediates of in Vivo Oxidation of 1,4-Dioxane by Monooxygenase-Containing Bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7330–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Jeon, J.-R.; Murugesan, K.; Kim, E.-J.; Chang, Y.-S. Biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane and transformation of related cyclic compounds by a newly isolated Mycobacterium sp. PH-06. Biodegradation 2008, 20, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, D.; Tsunoda, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Ike, M.; Sei, K. 1,4-Dioxane degradation characteristics of Rhodococcus aetherivorans JCM 14343. Biodegradation 2018, 29, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlweyer, U.; Thiemer, B.; Schräder, T.; Andreesen, J.R. Tetrahydrofuran degradation by a newly isolated culture of Pseudonocardia sp. strain K1. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 186, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, D.; Tsunoda, T.; Sawada, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Saito, Y.; Sei, K.; Ike, M. 1,4-Dioxane degradation potential of members of the genera Pseudonocardia and Rhodococcus. Biodegradation 2016, 27, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenker, M.J.; Borden, R.; A Barlaz, M. Modeling Cometabolism of Cyclic Ethers. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2002, 19, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasko, A.L.; Zulli, A.; Gedalanga, P.B.; Pornwongthong, P.; Mahendra, S. A Mixed Microbial Community for the Biodegradation of Chlorinated Ethenes and 1,4-Dioxane. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 6, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusher, T.R.; Shimizu, T.; Inoue, C.; Chien, M.-F. Enrichment and Analysis of Stable 1,4-dioxane-Degrading Microbial Consortia Consisting of Novel Dioxane-Degraders. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burback, B.L.; Perry, J.J. Biodegradation and biotransformation of groundwater pollutant mixtures by Mycobacterium vaccae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Anagnostu, G.; Chaphalkar, P. Biodegradation of dioxane and diglyme in industrial waste. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Environ. Sci. Eng. Toxicol. 1994, 29, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, M.J.; Borden, R.; A Barlaz, M. Biodegradation of 1,4-Dioxane Using Trickling Filter. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; So, M.H.; Kim, C.-G. Optimization of biological wastewater treatment conditions for 1,4-dioxane decomposition in polyester manufacturing processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Johnson, N.W.; Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Zhong, M.; Dong, Y.; Mahendra, S. Mechanisms of 1,4-Dioxane Biodegradation and Adsorption by Bio-Zeolite in the Presence of Chlorinated Solvents: Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14538–14547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Johnson, N.W.; Phan, T.; Heck, K.; Gedalanga, P.B.; Zheng, X.; Adamson, D.; Newell, C.; Wong, M.S.; Mahendra, S. Monitoring, assessment, and prediction of microbial shifts in coupled catalysis and biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane and co-contaminants. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenker, M.J.; Borden, R.; Barlaz, M.A. Mineralization of 1,4-dioxane in the presence of a structural analog. Biodegradation 2000, 11, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, P.; Hyman, M.R.; Smith, C.; El Mugammar, H.; Chu, M.-Y.; Nickelsen, M.; Aravena, R. Enrichment with Carbon-13 and Deuterium during Monooxygenase-Mediated Biodegradation of 1,4-Dioxane. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas-Rodriguez, F.J.; Freedman, D.L. Aerobic biodegradation kinetics for 1, 4-dioxane under metabolic and cometabolic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 350, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sei, K.; Kakinoki, T.; Inoue, D.; Soda, S.; Fujita, M.; Ike, M. Evaluation of the biodegradation potential of 1,4-dioxane in river, soil and activated sludge samples. Biodegradation 2010, 21, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barajas-Rodriguez, F.J.; Murdoch, L.C.; Falta, R.W.; Freedman, D.L. Simulation of in situ biodegradation of 1, 4-dioxane under metabolic and cometabolic conditions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 223, 103464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedalanga, P.B.; Madison, A.; Miao, Y.; Richards, T.; Hatton, J.; DiGuiseppi, W.H.; Wilson, J.; Mahendra, S. A Multiple Lines of Evidence Framework to Evaluate Intrinsic Biodegradation of 1,4-Dioxane. Remediat. J. 2016, 27, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Mathieu, J.; Hatton, J.; DiGuiseppi, W.; Alvarez, P.J. Hindrance of 1, 4-dioxane biodegradation in microcosms biostimulated with inducing or non-inducing auxiliary substrates. Water Res. 2017, 112, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, T.; Morishita, F.; Sugiyama, Y.; Ichikawa, D.; Mayumi, D.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ogata, A.; Muraoka, K.; Habe, H.; Hori, T. Identification of active and taxonomically diverse 1,4-dioxane degraders in a full-scale activated sludge system by high-sensitivity stable isotope probing. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2376–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rittmann, B.E.; McCarthy, P.L. Environmental Biotechnology: Principles and Applications. In McGraw-Hill Series in Water Resources and Environmental Engineering; Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Limited: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, K.; Cuiffetti, L.; Hyman, M.R. Metabolism and Cometabolism of Cyclic Ethers by a Filamentous Fungus, a Graphium sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5514–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-Z.; Jin, X.-J.; Chen, J.; Ye, J.; Jiang, N.-X.; Chen, J. Intermediates and substrate interaction of 1,4-dioxane degradation by the effective metabolizer Xanthobacter flavus DT8. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 106, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
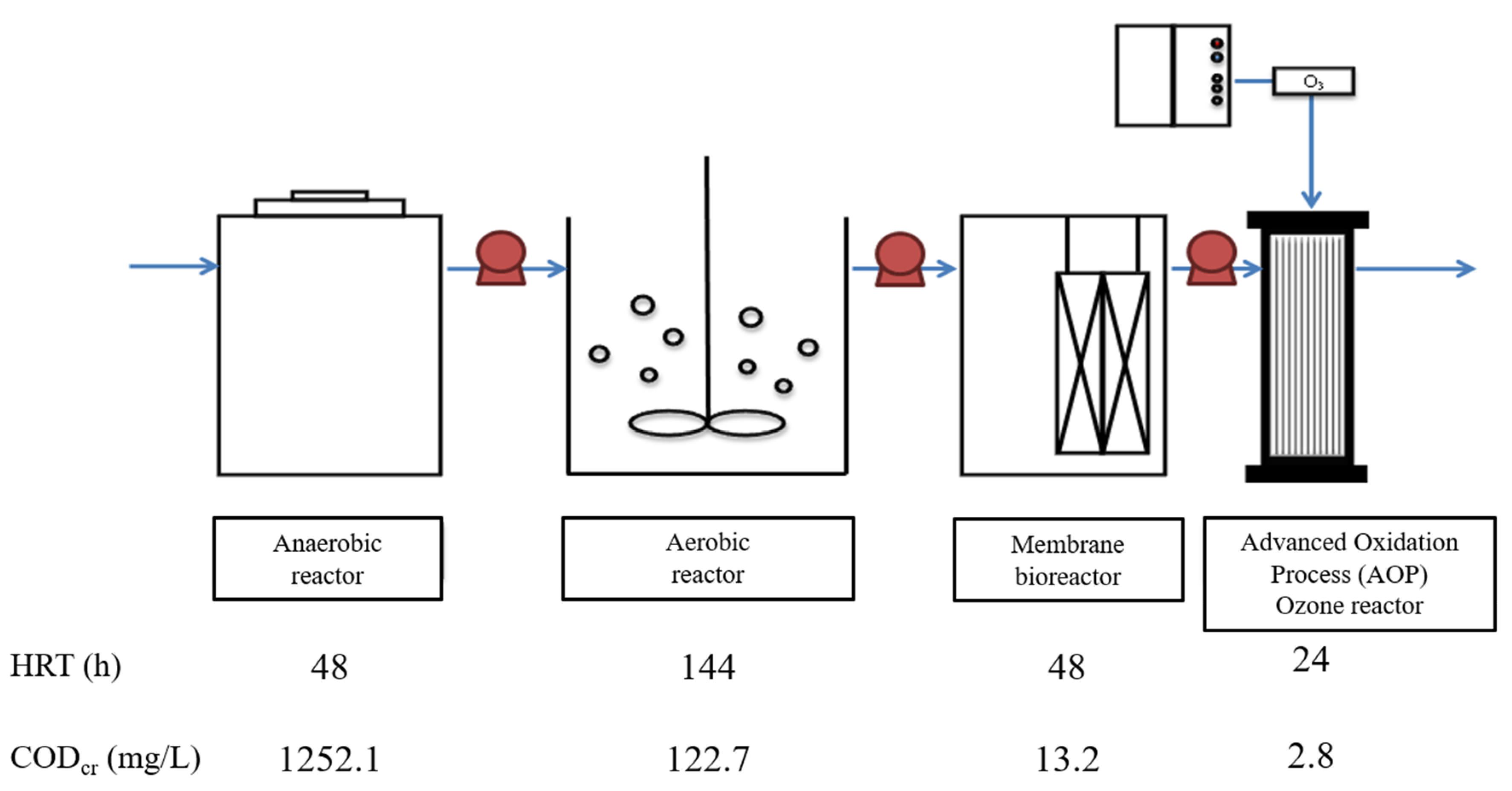
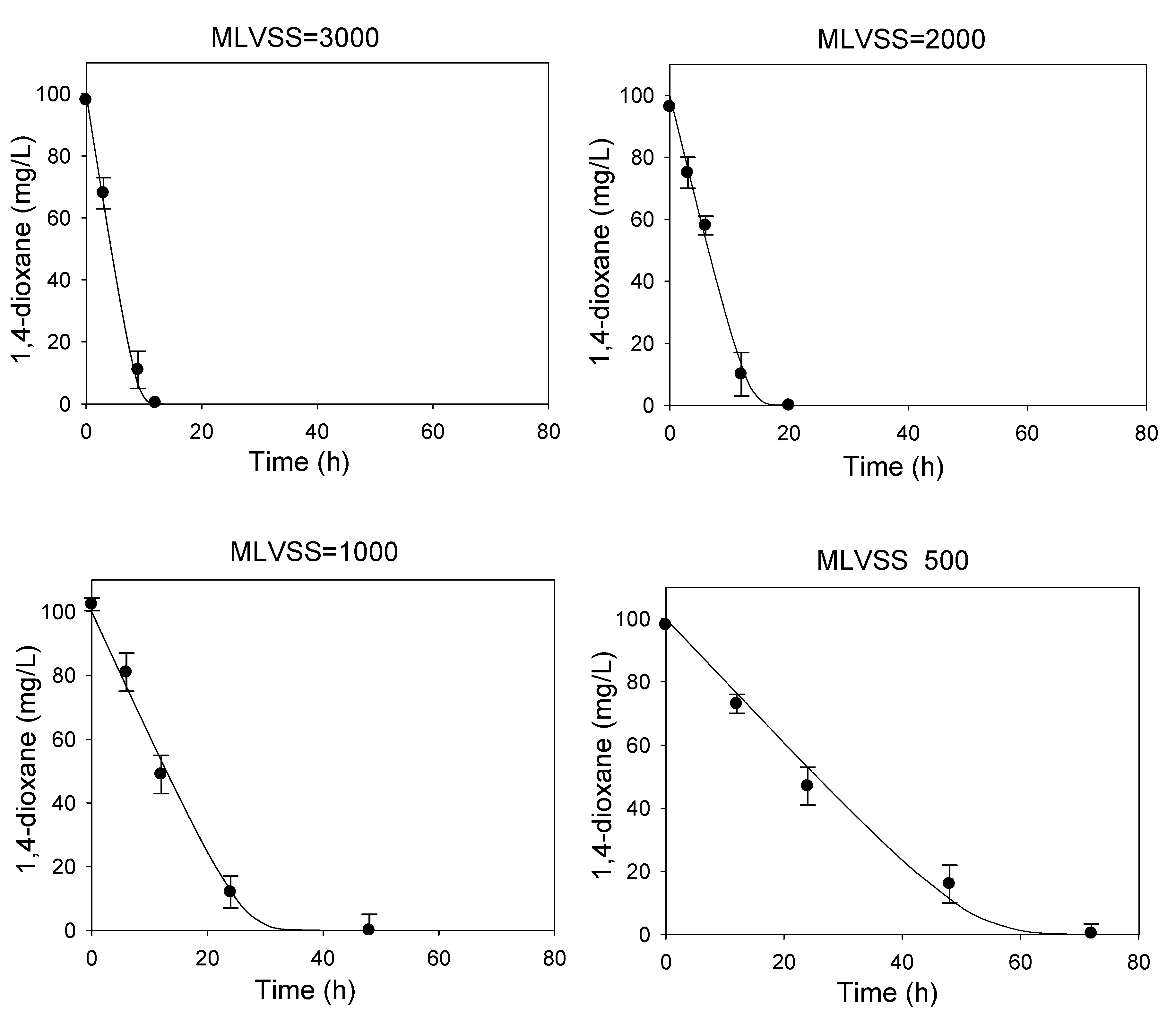
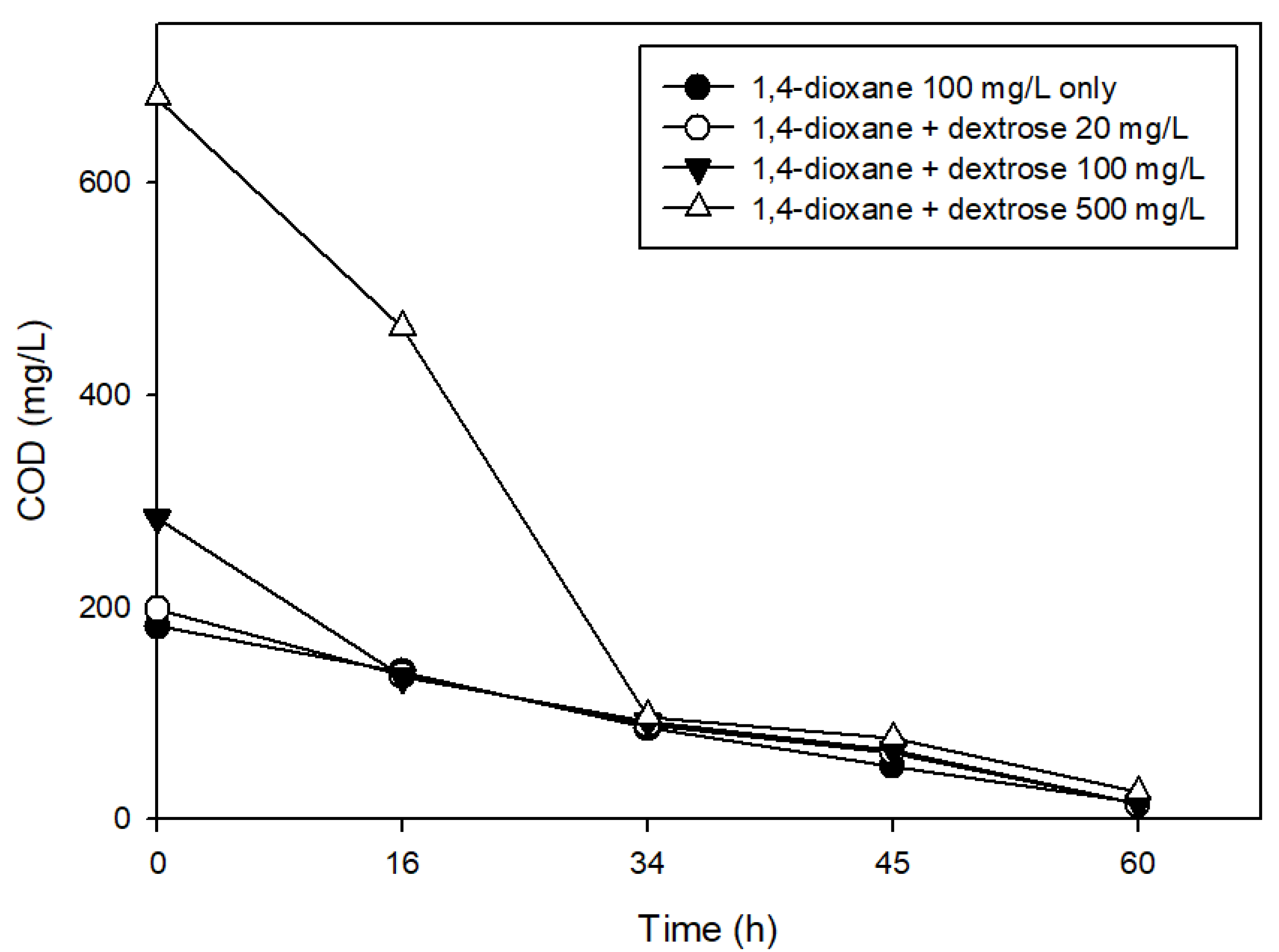
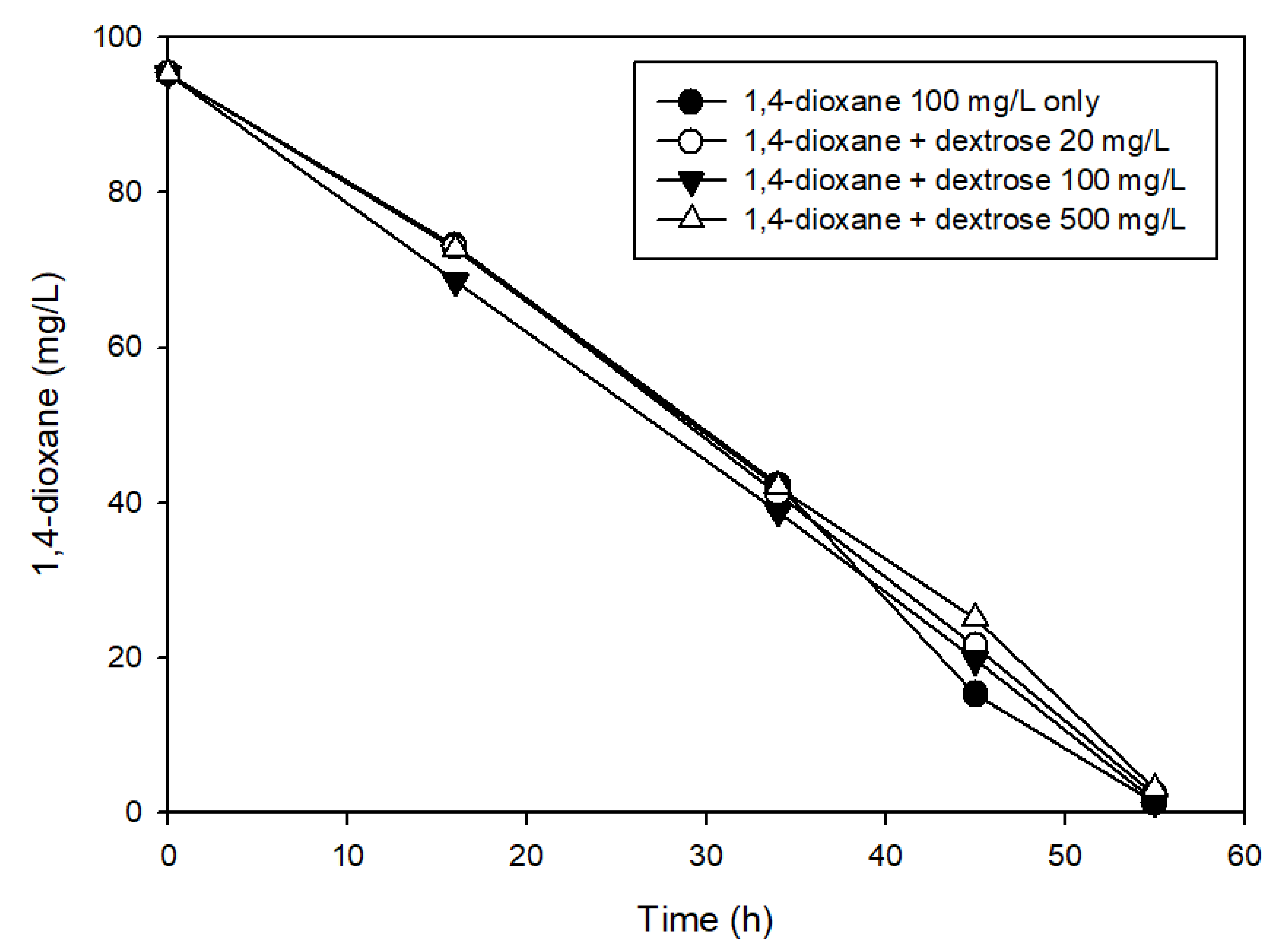
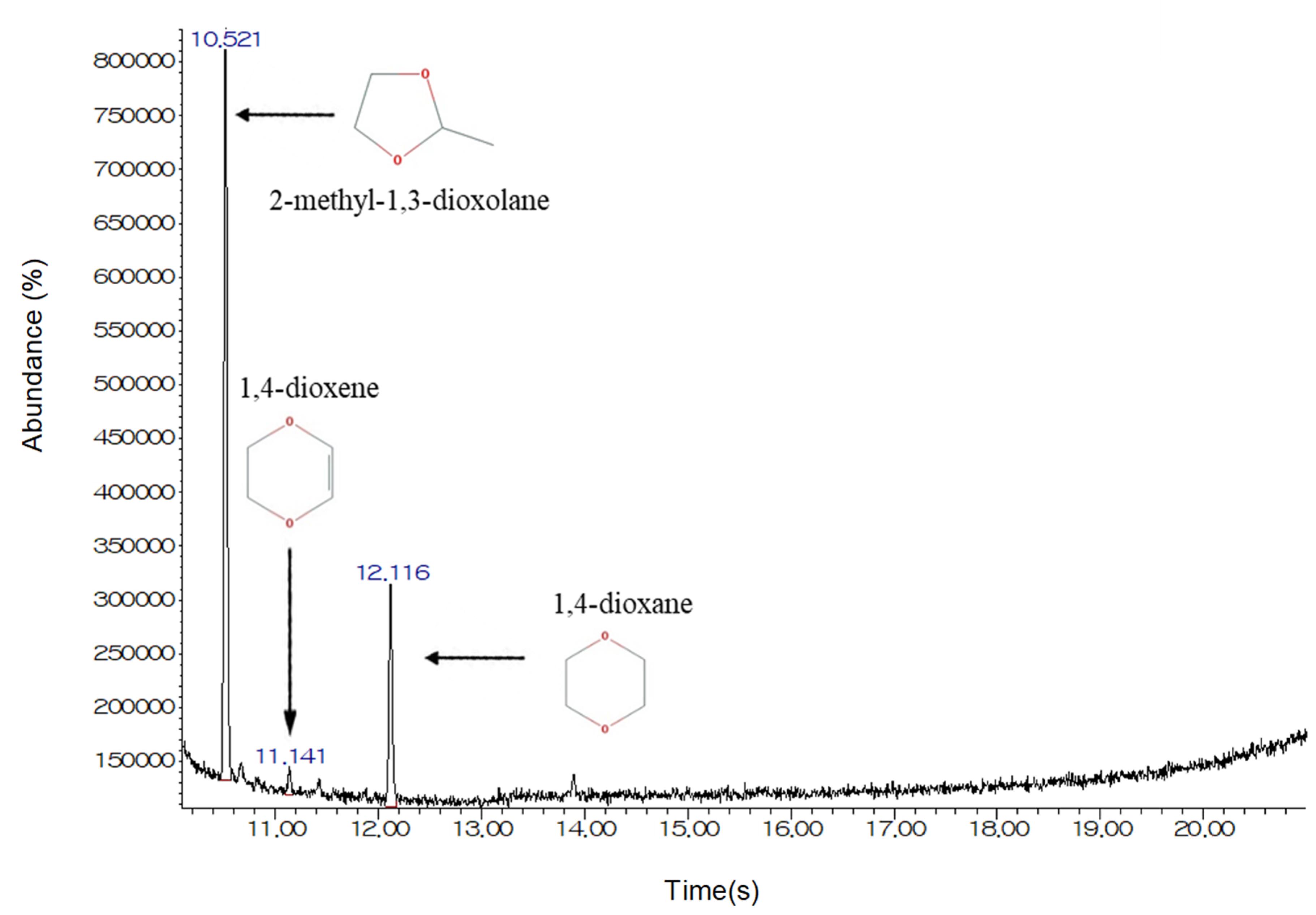
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| 2-Methyl-1,3-dioxolane (mg/L) | 335.49–1082.8 |
| 1,4-Dioxene (mg/L) | 76.27–132.12 |
| 1,4-Dioxane (mg/L) | 188.7–320.6 |
| CODcr (mg/L) | 1250–2882 |
| Suspended solids (mg/L) | 106–178 |
| pH | 8.4–8.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.H.; Wie, Y.M.; Jahng, D.; Yeom, I.T. Effects of Additional Carbon Sources in the Biodegradation of 1,4-Dioxane by a Mixed Culture. Water 2020, 12, 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061718
Lee KH, Wie YM, Jahng D, Yeom IT. Effects of Additional Carbon Sources in the Biodegradation of 1,4-Dioxane by a Mixed Culture. Water. 2020; 12(6):1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061718
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kang Hoon, Young Min Wie, Deokjin Jahng, and Ick Tae Yeom. 2020. "Effects of Additional Carbon Sources in the Biodegradation of 1,4-Dioxane by a Mixed Culture" Water 12, no. 6: 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061718
APA StyleLee, K. H., Wie, Y. M., Jahng, D., & Yeom, I. T. (2020). Effects of Additional Carbon Sources in the Biodegradation of 1,4-Dioxane by a Mixed Culture. Water, 12(6), 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061718




