Consistent Boundary Conditions for Age Calculations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Age Distribution Function and Its First Two Moments
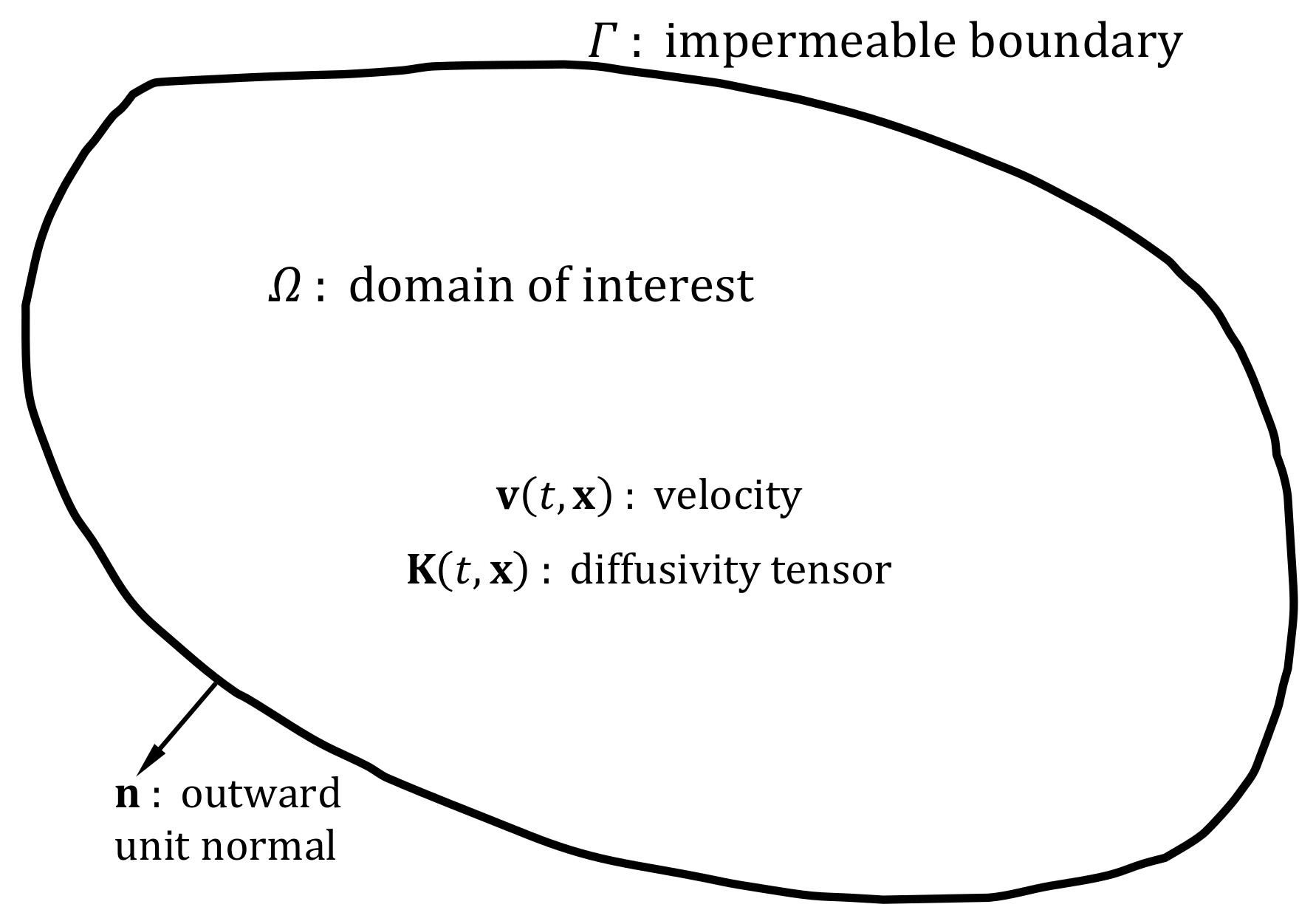
3. Consistent Insulating, Departure, and Arrival Boundary Conditions
3.1. Insulating Boundary
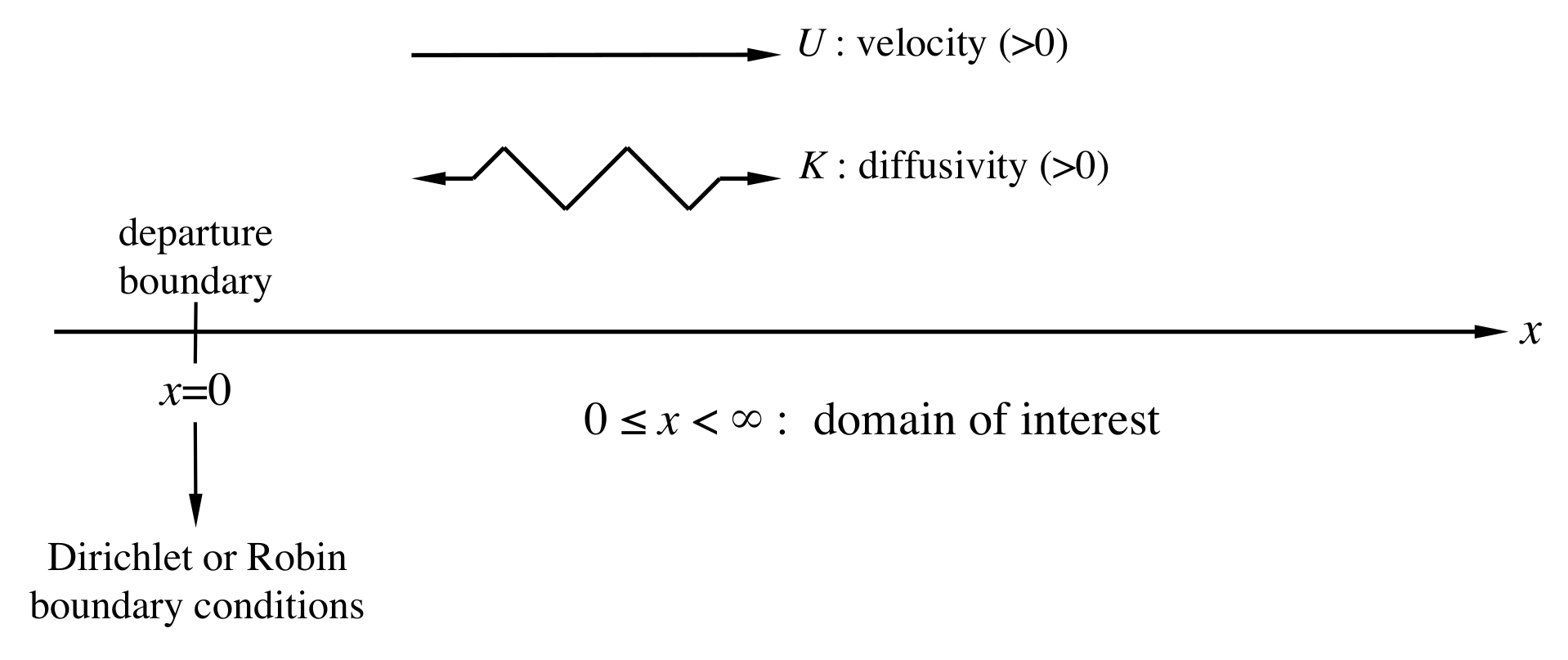
3.2. Departure Boundary
3.3. Departure Boundary: An Alternative Approach
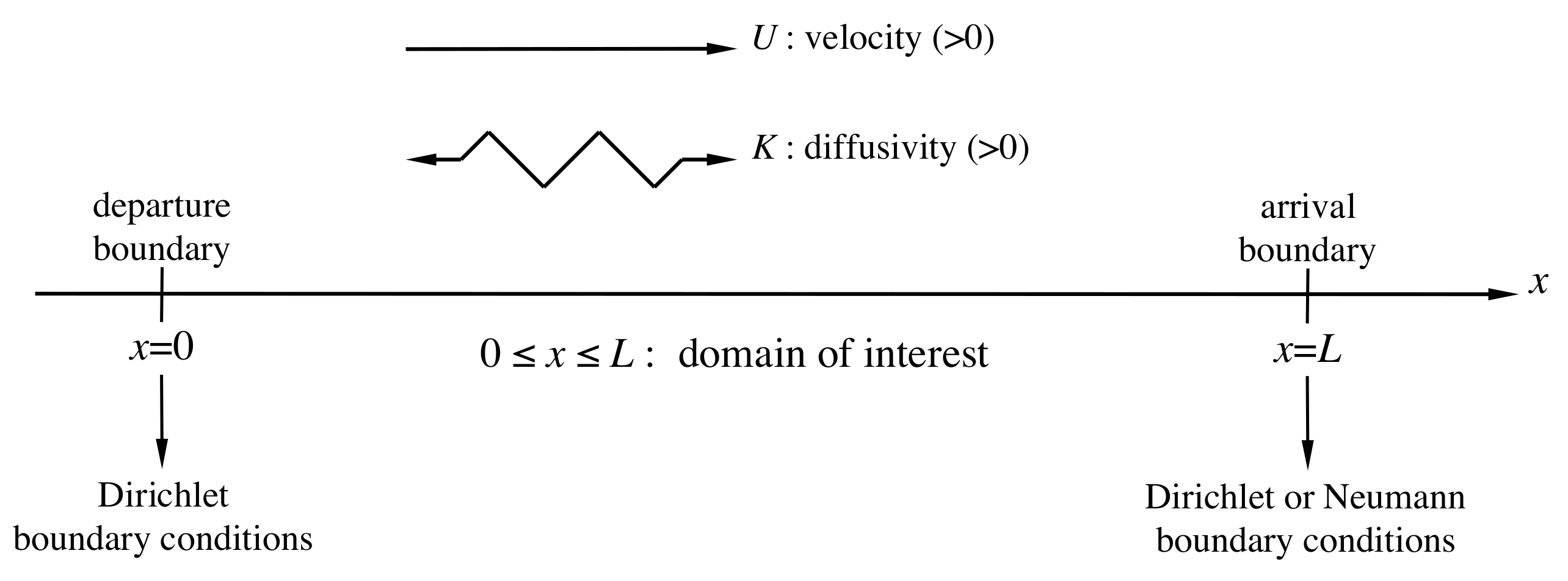
3.4. Arrival Boundary
3.5. Arrival Boundary: An Alternative Approach
3.6. Gas Exchanges through the Water–air Interface
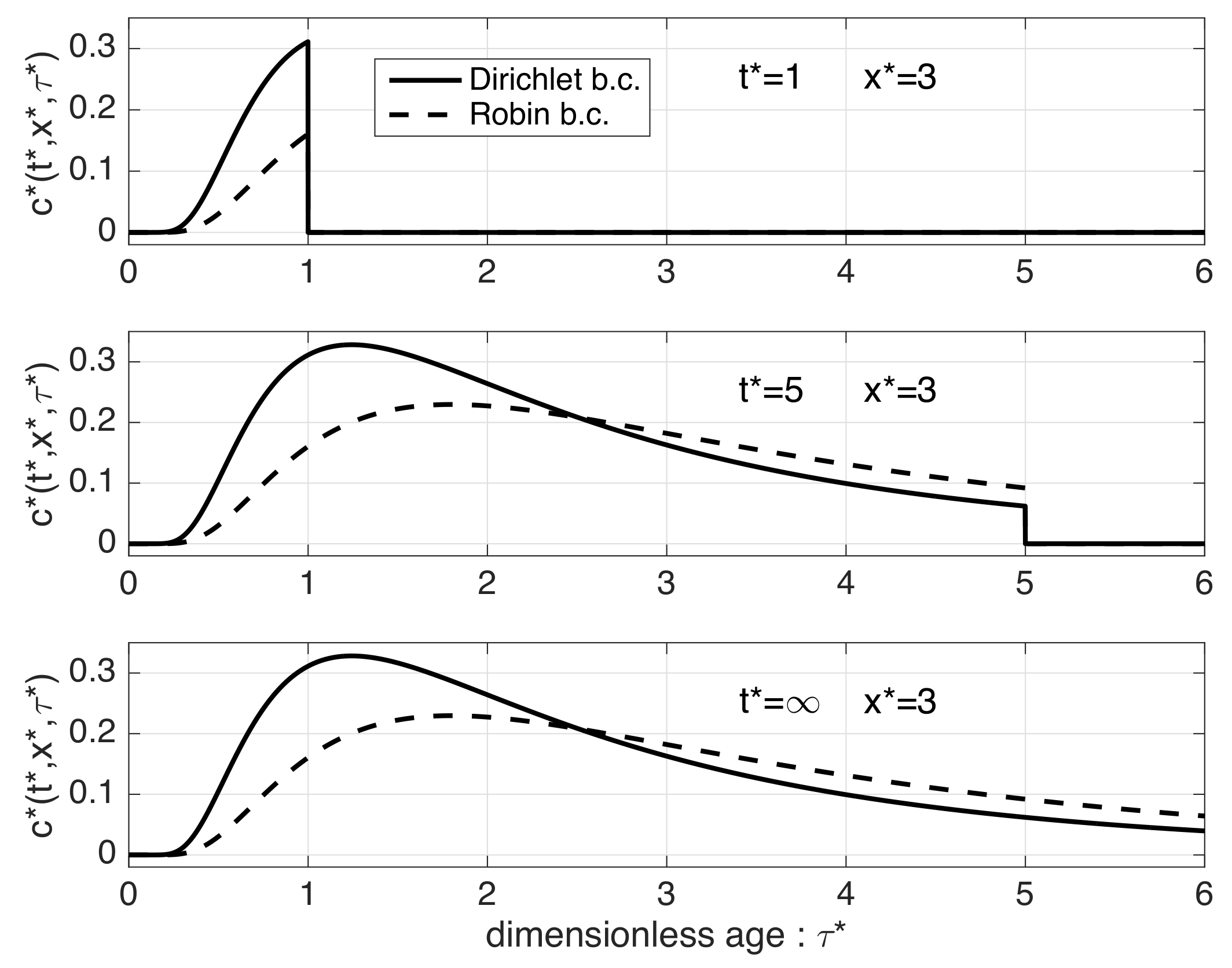
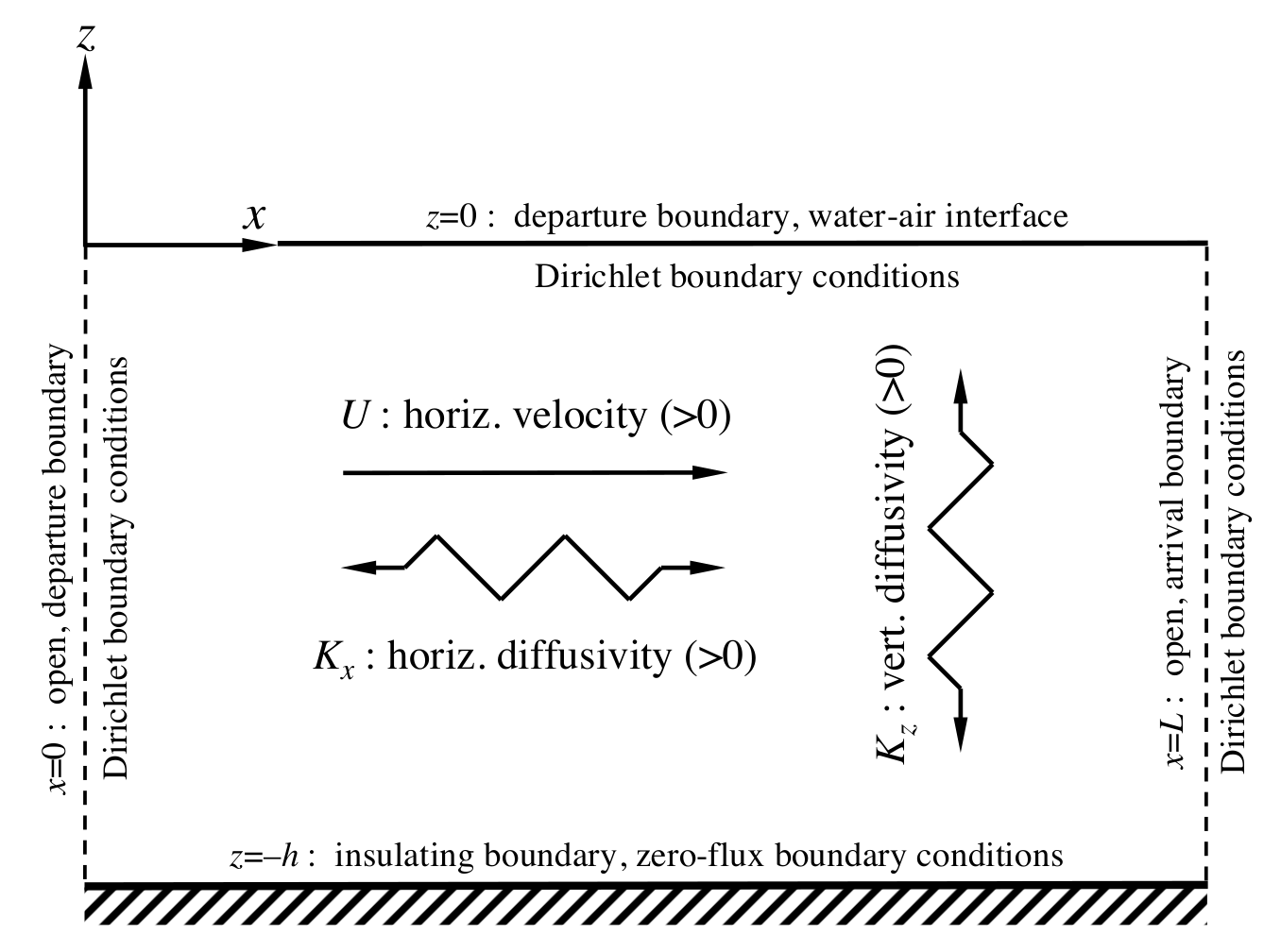
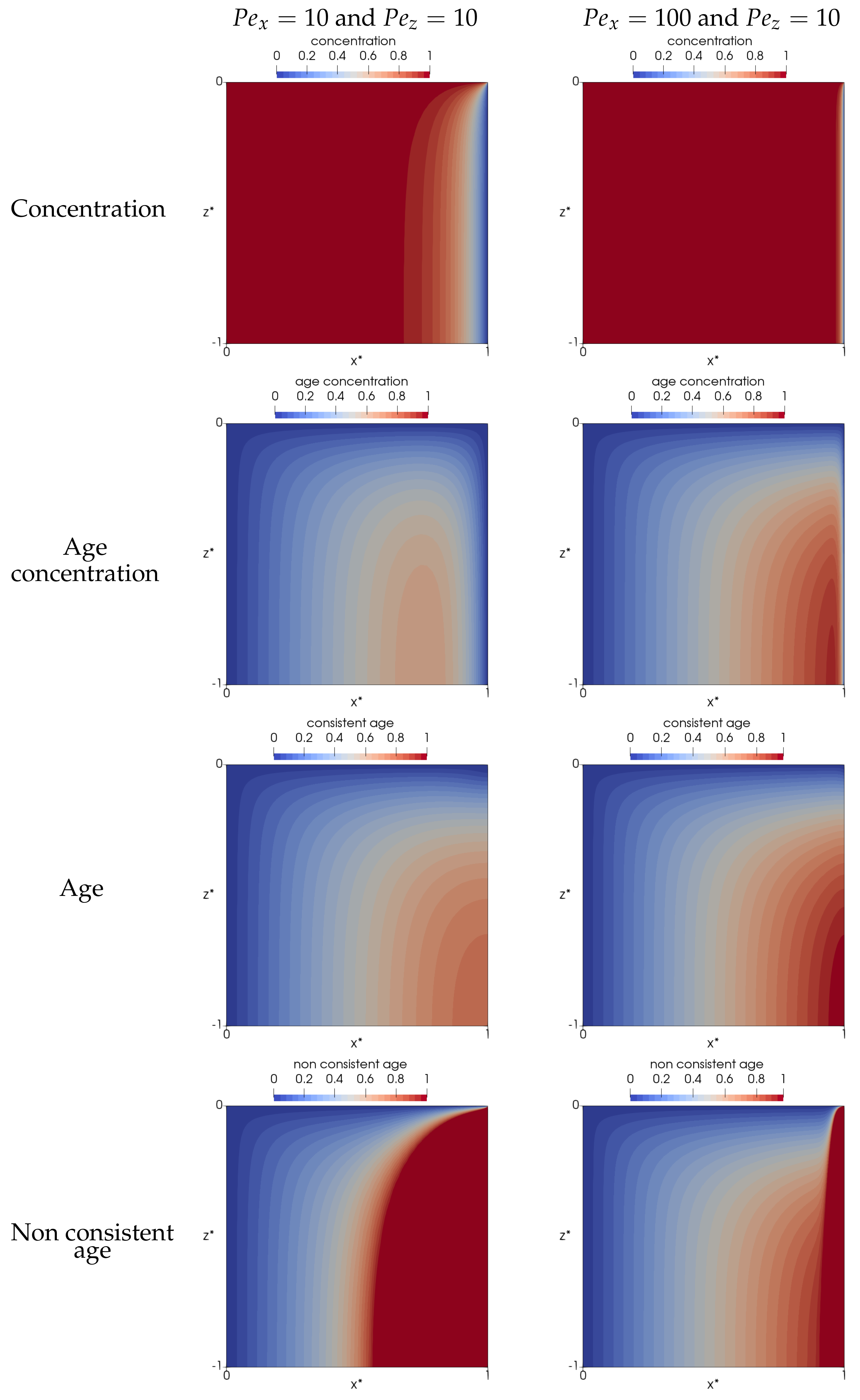
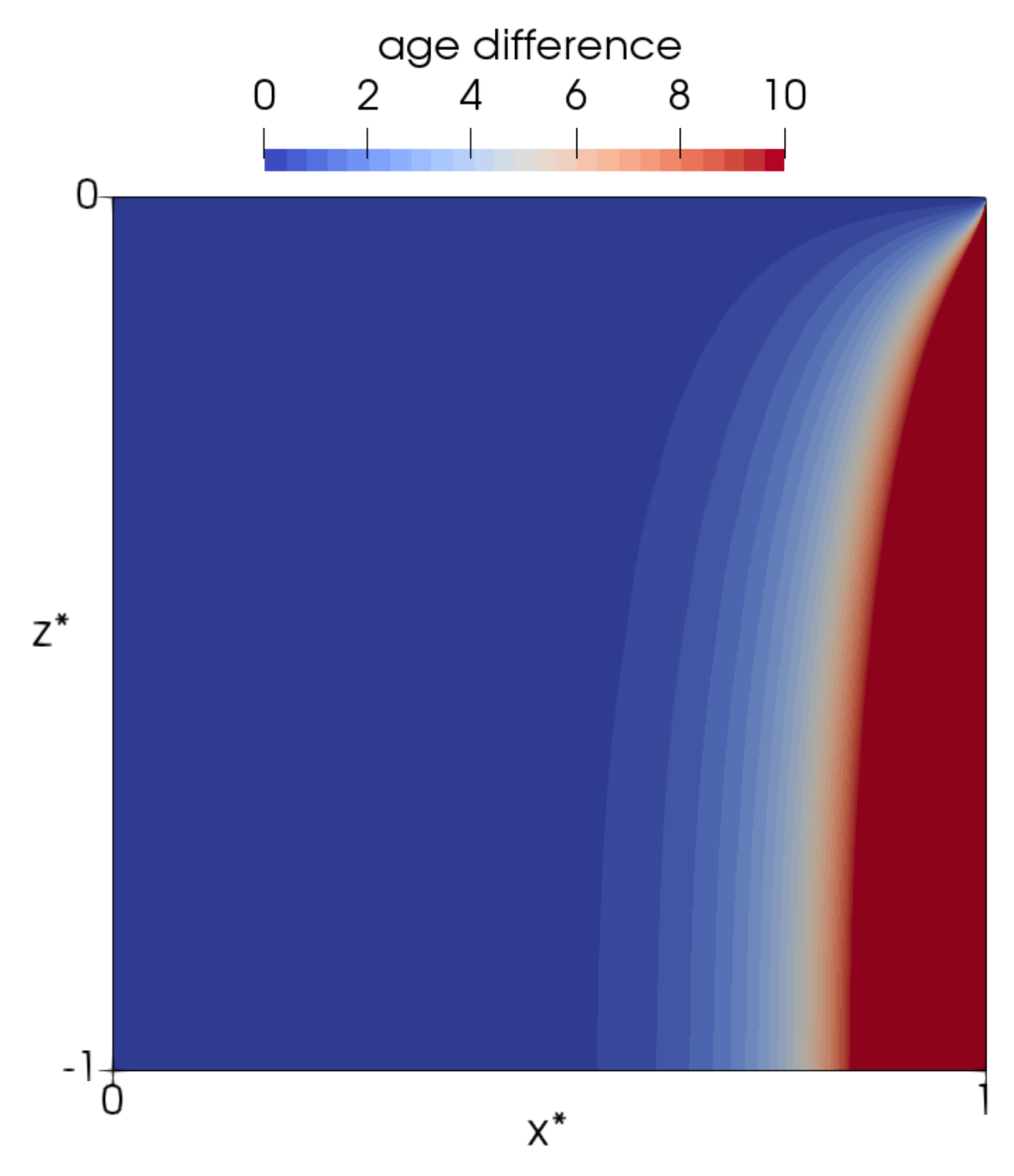
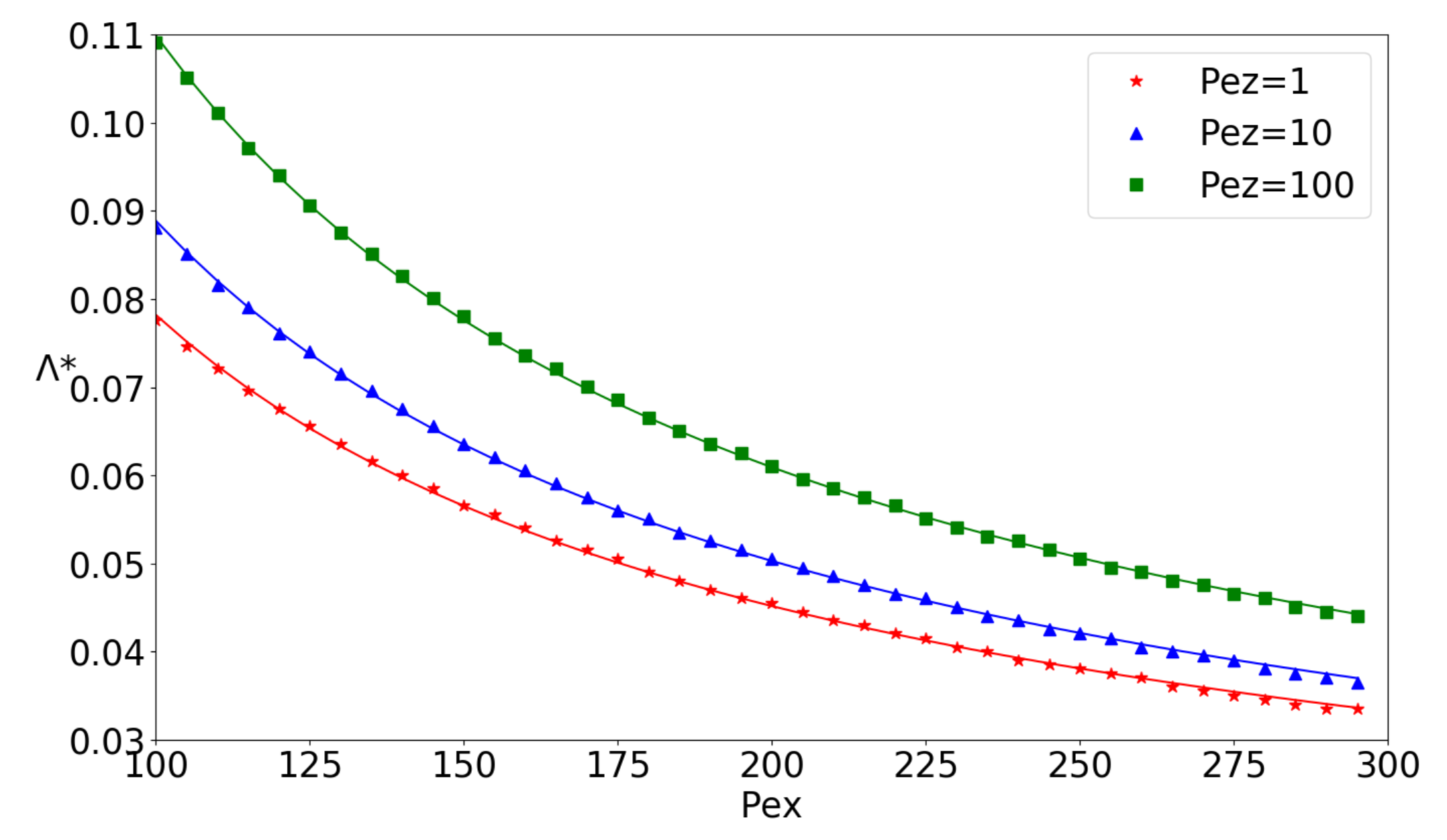
4. A Simple Ventilation Assessment Problem
5. Discussion and Conclusions
- Set out the reasons why the age, rather than other timescales (or diagnoses of another nature), is likely to be of use to help interpret the aquatic processes under consideration;
- Select the constituent whose (mean) age is to be evaluated and explain the rationale of this choice;
- Define the age, especially where and when the age of a particle of the constituent under study is to set or reset to zero, as well as where, when, and how this particle will cease to be taken into consideration;
- Build the boundary conditions for the age distribution function in accordance with the outcome of the previous three steps;
- Derive consistent boundary conditions for the concentration and age concentration using the methodology developed in this article (see also Appendix D).
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
Appendix D
References
- Hall, T.M.; Plumb, R.A. Age as a diagnostic of stratospheric transport. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Hall, T.M. Transit-time and tracer-age distributions in geophysical flows. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 3539–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waugh, D.W.; Hall, T.M. Age of stratospheric air: Theory, observations, and models. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orbe, C.; Waugh, D.W.; Newman, P.A.; Steenrod, S. The transit-time distribution from the Northern Hemisphere midlatitude surface. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 3785–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronkers, J.; Zimmerman, J.T.F. Some principles of mixing in tidal lagoons. In Proceedings of the Oceanologica Acta, N° SP, Actes Symposium International sur les lagunes côtières, SCOR/IABO/UNESCO, Bordeaux, France, 8–14 September 1982; pp. 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Helder, W.; Ruardij, P. A one-dimensional mixing and flushing model of the Ems-Dollard estuary: calculation of time scales at different river discharges. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1982, 15, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.T.F. Estuarine Residence Times. Hydrodynamics of Estuaries; Kjerfve, B., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; Volume I, pp. 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Delesalle, B.; Sournia, A. Residence time of water and phytoplankton biomass in coral reef lagoons. Cont. Shelf Res. 1992, 12, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, J.C.; Breton, M.; Guegueniat, P. A 2D long term advection—dispersion model for the Channel and southern North Sea Part B: Transit time and transfer function from Cap de La Hague. J. Mar. Syst. 1995, 6, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Baptista, A.M. Diagnostic modeling of residence times in estuaries. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, W.J. Studying subtropical thermocline ventilation and circulation using tritium and 3He. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 15817–15831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, E.; Wang, J.; Mooers, C.N.K. A two-compartment model for understanding the simulated three-dimensional circulation in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Cont. Shelf Res. 1998, 18, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campin, J.M.; Fichefet, T.; Duplessy, J.C. Problems with using radiocarbon to infer ocean ventilation rates for past and present climates. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 165, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréfouët, S.; Pagès, J.; Tartinville, B. Water renewal time for classification of atoll lagoons in the Tuamotu Archipelago (French Polynesia). Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haine, T.W.N.; Hall, T.M. A generalized transport theory: Water-mass composition and age. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 1932–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsen, N.E.; Cloern, J.E.; Lucas, L.V.; Monismith, S.G. A comment on the use of flushing time, residence time, and age as transport time scales. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waugh, D.W.; Vollmer, M.K.; Weiss, R.F.; Haine, T.W.N.; Hall, T.M. Transit time distributions in Lake Issyk-Kul. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braunschweig, F.; Martins, F.; Chambel, P.; Neves, R. A methodology to estimate renewal time scales in estuaries: the Tagus Estuary case. Ocean. Dyn. 2003, 53, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, D.W.; Hall, T.M.; Haine, T.W.N. Relationships among tracer ages. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrejev, O.; Myrberg, K.; Lundberg, P.A. Age and renewal time of water masses in a semi-enclosed basin—Application to the Gulf of Finland. Tellus Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2004, 56, 548–558. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrhman, M.A. Simplified modeling of flushing and residence times in 42 embayments in New England, USA, with special attention to Greenwich Bay, Rhode Island. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Drange, H.; Bentsen, M.; Johannessen, O.M. Tracer-derived transit time of the waters in the eastern Nordic Seas. Tellus Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2005, 57, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornaton, F.; Perrochet, P. Groundwater age, life expectancy and transit time distributions in advective–dispersive systems: 1. Generalized reservoir theory. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 1267–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornaton, F.; Perrochet, P. Groundwater age, life expectancy and transit time distributions in advective–dispersive systems; 2. Reservoir theory for sub-drainage basins. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 1292–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucco, A.; Perilli, A.; De Falco, G.; Ghezzo, M.; Umgiesser, G. Water circulation and transport timescales in the Gulf of Oristano. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 22, S307–S331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Primeau, F. The diffusive ocean conveyor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouon, A.; Douillet, P.; Ouillon, S.; Fraunié, P. Calculations of hydrodynamic time parameters in a semi-opened coastal zone using a 3D hydrodynamic model. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 1395–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, G.H.; Lehr, J.H.; Perrochet, P. Groundwater Age; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 325. [Google Scholar]
- Orre, S.; Gao, Y.; Drange, H.; Nilsen, J.E.Ø. A reassessment of the dispersion properties of 99Tc in the North Sea and the Norwegian Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 68, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torréton, J.P.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Jouon, A.; Faure, V.; Jacquet, S.; Douillet, P. Correspondence between the distribution of hydrodynamic time parameters and the distribution of biological and chemical variables in a semi-enclosed coral reef lagoon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucco, A.; Umgiesser, G.; Ferrarin, C.; Perilli, A.; Canu, D.M.; Solidoro, C. Eulerian and lagrangian transport time scales of a tidal active coastal basin. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plus, M.; Dumas, F.; Stanisière, J.Y.; Maurer, D. Hydrodynamic characterization of the Arcachon Bay, using model-derived descriptors. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucas, L.V. Implications of estuarine transport for water quality. Contemp. Issues Estuar. Phys. 2010, 273–303. [Google Scholar]
- Maltrud, M.; Bryan, F.; Peacock, S. Boundary impulse response functions in a century-long eddying global ocean simulation. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2010, 10, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcante, G.H.; Kjerfve, B.; Feary, D.A. Examination of residence time and its relevance to water quality within a coastal mega-structure: The Palm Jumeirah Lagoon. J. Hydrol. 2012, 468, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, A.; Deleersnijder, E.; Primeau, F. The leaky funnel model revisited. Tellus Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2012, 64, 19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grifoll, M.; Del Campo, A.; Espino, M.; Mader, J.; González, M.; Borja, Á. Water renewal and risk assessment of water pollution in semi-enclosed domains: Application to Bilbao Harbour (Bay of Biscay). J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 109, S241–S251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andutta, F.P.; Ridd, P.V.; Deleersnijder, E.; Prandle, D. Contaminant exchange rates in estuaries–New formulae accounting for advection and dispersion. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 120, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delhez, E.J.M.; Wolk, F. Diagnosis of the transport of adsorbed material in the Scheldt estuary: A proof of concept. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 128, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldo, A.; Benettin, P.; Harman, C.J.; Hrachowitz, M.; McGuire, K.J.; Van Der Velde, Y.; Bertuzzo, E.; Botter, G. Storage selection functions: A coherent framework for quantifying how catchments store and release water and solutes. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4840–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viero, D.P.; Defina, A. Renewal Time Scales in Tidal Basins: Climbing the Tower of Babel. Sustainable Hydraulics in the Era of Global Change; Erpicum, S., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2016; pp. 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Viero, D.P.; Defina, A. Water age, exposure time, and local flushing time in semi-enclosed, tidal basins with negligible freshwater inflow. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 156, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiatt, M.; Castañeda-Moya, E.; Twilley, R.; Hodges, B.R.; Passalacqua, P. Channel-island connectivity affects water exposure time distributions in a coastal river delta. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 2212–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Mu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, F.; Li, Y.; Lin, L. Water Residence Time in a Typical Tributary Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water 2019, 11, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dippner, J.W.; Bartl, I.; Chrysagi, E.; Holtermann, P.L.; Kremp, A.; Thoms, F.; Voss, M. Lagrangian Residence Time in the Bay of Gdansk, Baltic Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drouzy, M.; Douillet, P.; Fernandez, J.M.; Pinazo, C. Hydrodynamic time parameters response to meteorological and physical forcings: toward a stagnation risk assessment device in coastal areas. Ocean. Dyn. 2019, 69, 967–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gross, E.; Andrews, S.; Bergamaschi, B.; Downing, B.; Holleman, R.; Burdick, S.; Durand, J. The Use of Stable Isotope-Based Water Age to Evaluate a Hydrodynamic Model. Water 2019, 11, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huguet, J.R.; Brenon, I.; Coulombier, T. Characterisation of the Water Renewal in a Macro-Tidal Marina Using Several Transport Timescales. Water 2019, 11, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Soetaert, K.; Gerkema, T. Decomposing the intra-annual variability of flushing characteristics in a tidal bay along the North Sea. J. Sea Res. 2019, 155, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, C.; Delhez, E.J.M. Diagnosis of the sediment transport in the Belgian Coastal Zone. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Shen, J. A model diagnostic study of age of river-borne sediment transport in the tidal York River Estuary. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2010, 10, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Geyer, W.R. Sediment transport time scales and trapping efficiency in a tidal river. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 2042–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, E.J.M. On the concept of exposure time. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 71, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.T.F. Mixing and flushing of tidal embayments in the western Dutch Wadden Sea part I: Distribution of salinity and calculation of mixing time scales. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1976, 10, 149–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, B.; Rodhe, H. A note on the concepts of age distribution and transit time in natural reservoirs. Tellus 1973, 25, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, H. Fundamental concepts of exchange and transport time scales in a coastal sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1984, 3, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, G.; Sarmiento, J.L. Tracer dating and ocean ventilation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1990, 95, 9377–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- England, M.H. The age of water and ventilation timescales in a Global Ocean model. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1995, 25, 2756–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delhez, E.J.M.; Campin, J.M.; Hirst, A.C.; Deleersnijder, E. Toward a general theory of the age in ocean modelling. Ocean. Model. 1999, 1, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirst, A.C. Determination of water component age in ocean models: Application to the fate of North Atlantic Deep Water. Ocean. Model. 1999, 1, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, E. On the Timescales Relevant to a Linear Transport-Decay Reservoir Model; Technical Report; Université Catholique de Louvain: Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2019; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2078.1/219115 (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- de Brye, B.; de Brauwere, A.; Gourgue, O.; Delhez, E.J.M.; Deleersnijder, E. Water renewal timescales in the Scheldt Estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 94, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, E.J.M.; Lacroix, G.; Deleersnijder, E. The age as a diagnostic of the dynamics of marine ecosystem models. Ocean. Dyn. 2004, 54, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.; Deleersnijder, E. Diagnoses of vertical transport in a three-dimensional finite element model of the tidal circulation around an island. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, J.; Gustafsson, K.E.; Söderkvist, J.; Hansen, J.L. Ventilation of bottom water in the North Sea–Baltic Sea transition zone. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 75, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.A.M.; Primeau, F.; Deleersnijder, E.; Heemink, A. Tracing the ventilation pathways of the deep North Pacific Ocean using Lagrangian particles and Eulerian tracers. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 1261–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, L.; Lin, J.; Lin, B.; Zhao, H. Vertical water renewal in a large estuary and implications for water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 135593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sebille, E.; Griffies, S.M.; Abernathey, R.; Adams, T.P.; Berloff, P.; Biastoch, A.; Blanke, B.; Chassignet, E.P.; Cheng, Y.; Cotter, C.J.; et al. Lagrangian ocean analysis: Fundamentals and practices. Ocean. Model. 2018, 121, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, E.; Campin, J.M.; Delhez, E.J. The concept of age in marine modelling: I. Theory and preliminary model results. J. Mar. Syst. 2001, 28, 229–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deleersnijder, E.; Mouchet, A.; Delhez, E.J.M.; Beckers, J.M. Transient behaviour of water ages in the World Ocean. Math. Comput. Model. 2002, 36, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, E.J.M.; Deleersnijder, E. The concept of age in marine modelling: II. Concentration distribution function in the English Channel and the North Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 31, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garabedian, P. Partial Differential Equations; Chelsea Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1964; 672p. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Haas, L. Calculating age and residence time in the tidal York River using three-dimensional model experiments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Lin, J. Modeling study of the influences of tide and stratification on age of water in the tidal James River. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.E.M. Modeling the pathways and ages of inflowing salt-and freshwater in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 610–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, H. The age of Yellow River water in the Bohai Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radtke, H.; Neumann, T.; Voss, M.; Fennel, W. Modeling pathways of riverine nitrogen and phosphorus in the Baltic Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, J.; Mortensen, J.; Rysgaard, S. Seasonal surface layer dynamics and sensitivity to runoff in a high Arctic fjord (Young Sound/Tyrolerfjord, 74 N). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 6461–6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärnä, T.; Baptista, A.M. Water age in the Columbia River estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 183, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rayson, M.D.; Gross, E.S.; Hetland, R.D.; Fringer, O.B. Time scales in Galveston Bay: An unsteady estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 2268–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Liang, B.; Xin, L.; Zhao, Y. Numerical Study on the Influences of Hydrodynamic Factors on Water Age in the Liao River Estuary, China. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 80, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Park, K.; Shen, J.; Dzwonkowski, B.; Yu, X.; Yoon, B.I. Role of baroclinic processes on flushing characteristics in a highly stratified estuarine system, Mobile Bay, Alabama. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 4518–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; He, G.; Fang, H.; Bai, S.; Huang, L. Numerical simulation of water age and its potential effects on the water quality in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z.; Gong, W. Evaluation of the total maximum allocated load of dissolved inorganic nitrogen using a watershed—Coastal ocean coupled model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, F.; Fennel, K.; Laurent, A. Quantifying the relative importance of riverine and open-ocean nitrogen sources for hypoxia formation in the northern Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 5451–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Yuan, D.; Guo, L.; Nie, J.; Du, J. Hydrodynamics and water circulation in the New York/New Jersey Harbor: A study from the perspective of water age. J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 199, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Sun, J.; Tao, L.; Li, Y.; Nie, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, R.; Yuan, D. Combined Effect of Tides and Wind on Water Exchange in a Semi-Enclosed Shallow Sea. Water 2019, 11, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Kong, J.; Tao, J. Modeling the Water-Flushing Properties of the Yangtze Estuary and Adjacent Waters. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2019, 18, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, J.M.; Delhez, E.; Deleersnijder, E. Some properties of generalized age-distribution equations in fluid dynamics. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2001, 61, 1526–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Deleersnijders, E.; Delhez, E.J.M.; Crucifix, M.; Beckers, J.M. On the symmetry of the age field of a passive tracer released into a one-dimensional fluid flow by a point-source. Bull. de la Soc. R. des Sci. de Liège 2001, 70, 5–21. Available online: https://popups.uliege.be/0037-9565/index.php?id=1392 (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Deleersnijder, E. Water Renewal of a Region of Freshwater Influence (ROFI): Mathematical Properties of Some of the Relevant Diagnostic Variables; Technical Report; Université Catholique de Louvain: Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2019; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2078.1/220841 (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Deleersnijder, E.; Delhez, E.J.M. Symmetry and asymmetry of water ages in a one-dimensional flow. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 48, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.M.; Haine, T.W.N. Tracer age symmetry in advective–diffusive flows. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 48, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.D. An idealized model of the world ocean. Part I: The global-scale water masses. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1989, 19, 1730–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goosse, H.; Campin, J.M.; Tartinville, B. The sources of Antarctic bottom water in a global ice–ocean model. Ocean. Model. 2001, 3, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornaton, F.J. Transient water age distributions in environmental flow systems: The time-marching Laplace transform solution technique. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delhez, E.J.M.; Deleersnijder, E.; Mouchet, A.; Beckers, J.M. A note on the age of radioactive tracers. J. Mar. Syst. 2003, 38, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, É.J.; Deleersnijder, É. The boundary layer of the residence time field. Ocean. Dyn. 2006, 56, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, E. A Conjecture about Age Inequalities; Technical Report; Université Catholique de Louvain: Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2019; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2078.1/227647 (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Beckers, J.M. YAAI: Yet Another Age Inequality; Technical Report; Université de Liège: Liège, Belgium, 2020; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2268/245381 (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Liss, P.S. Gas Transfer: Experiments and Geochemical Implications. In Air-Sea Exchange of Gases and Particles; NATO ASI Series (Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences); Liss, P.S., Slinn, W.G.N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 241–298. [Google Scholar]
- Wanninkhof, R. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1992, 97, 7373–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähne, B.; Haußecker, H. Air-water gas exchange. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1998, 30, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haine, T.W.N. On tracer boundary conditions for geophysical reservoirs: How to find the boundary concentration from a mixed condition. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanninkhof, R. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean revisited. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2014, 12, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, E. On the Impact of the Atmosphere on the Time-Varying Age of a Passive Tracer in the Ocean; Technical Report; Université Catholique de Louvain: Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2017; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2078.1/184324 (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Hong, B.; Gong, W.; Peng, S.; Xie, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Xu, H. Characteristics of vertical exchange process in the Pearl River estuary. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2016, 19, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärnä, T.; Legat, V.; Deleersnijder, E. A baroclinic discontinuous Galerkin finite element model for coastal flows. Ocean. Model. 2013, 61, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallaeys, V.; Kärnä, T.; Delandmeter, P.; Lambrechts, J.; Baptista, A.M.; Deleersnijder, E.; Hanert, E. Discontinuous Galerkin modeling of the Columbia River’s coupled estuary-plume dynamics. Ocean. Model. 2018, 124, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delandmeter, P.; Lambrechts, J.; Legat, V.; Vallaeys, V.; Naithani, J.; Thiery, W.; Remacle, J.F.; Deleersnijder, E. A fully consistent and conservative vertically adaptive coordinate system for SLIM 3D v0. 4 with an application to the thermocline oscillations of Lake Tanganyika. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delhez, É.J.; de Brye, B.; de Brauwere, A.; Deleersnijder, E. Residence time vs influence time. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 132, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, A.; Cornaton, F.; Deleersnijder, E.; Delhez, E.J. Partial ages: diagnosing transport processes by means of multiple clocks. Ocean. Dyn. 2016, 66, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orlanski, I. A simple boundary condition for unbounded hyperbolic flows. J. Comput. Phys. 1976, 21, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israeli, M.; Orszag, S.A. Approximation of radiation boundary conditions. J. Comput. Phys. 1981, 41, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, A.F.; Kantha, L.H. Open boundary condition for circulation models. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1985, 111, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, P.; Pinardi, N. Lateral open boundary conditions for nested limited area models: A scale selective approach. Ocean. Model. 2008, 20, 134–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsen, E.A.; Engedahl, H. Implementation and testing of a lateral boundary scheme as an open boundary condition in a barotropic ocean model. Coast. Eng. 1987, 11, 603–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, J.; Thacker, W. A pretty good sponge: Dealing with open boundaries in limited-area ocean models. Ocean. Model. 2008, 20, 270–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blayo, E.; Debreu, L. Revisiting open boundary conditions from the point of view of characteristic variables. Ocean. Model. 2005, 9, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham Van, C.; De Brye, B.; De Brauwere, A.; Hoitink, A.; Soares-Frazao, S.; Deleersnijder, E. Numerical Simulation of Water Renewal Timescales in the Mahakam Delta, Indonesia. Water 2020, 12, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gräwe, U.; Wolff, J.O. Suspended particulate matter dynamics in a particle framework. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2010, 10, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräwe, U.; Deleersnijder, E.; Shah, S.H.A.M.; Heemink, A.W. Why the Euler scheme in particle tracking is not enough: the shallow-sea pycnocline test case. Ocean. Dyn. 2012, 62, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, C. Oceanic age and transient tracers: Analytical and numerical solutions. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2002, 107, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1959; 510p. [Google Scholar]
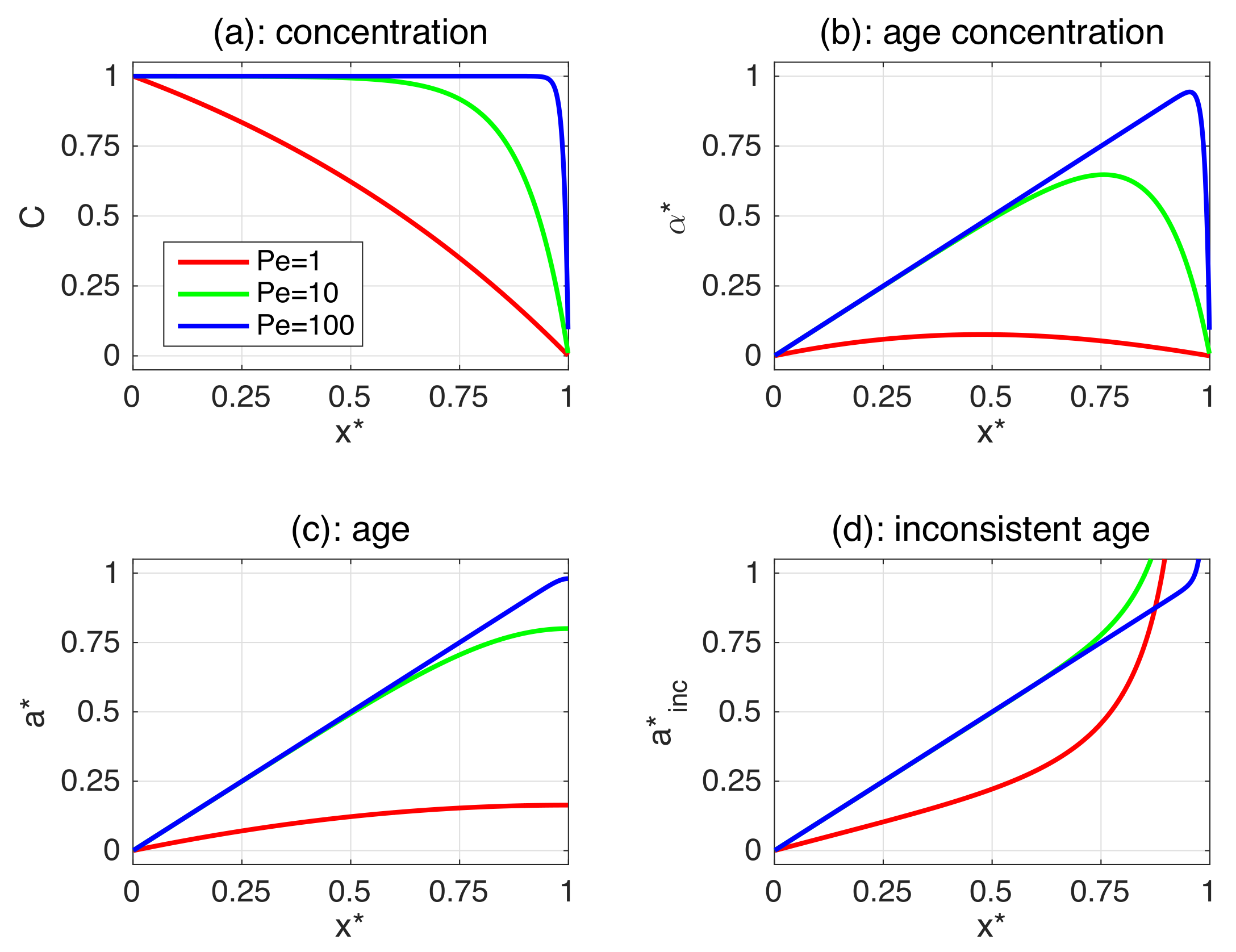
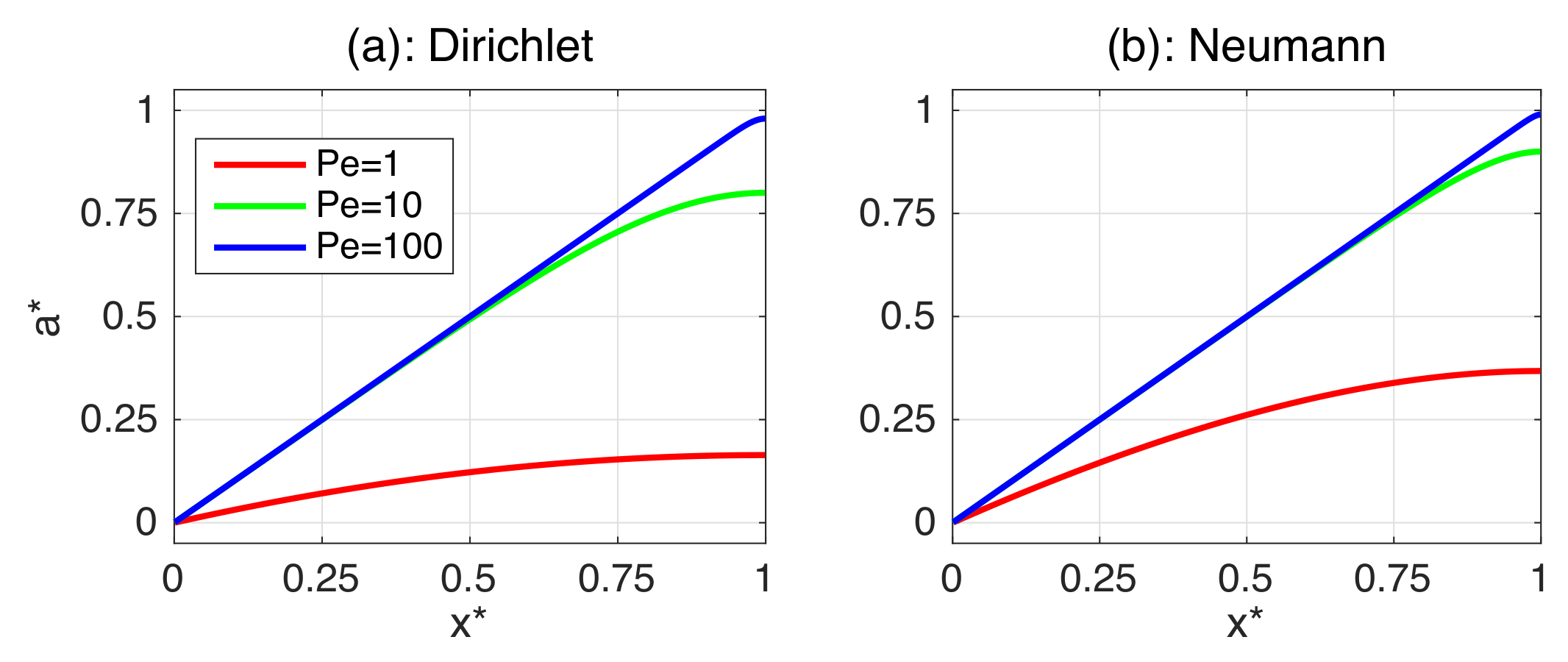
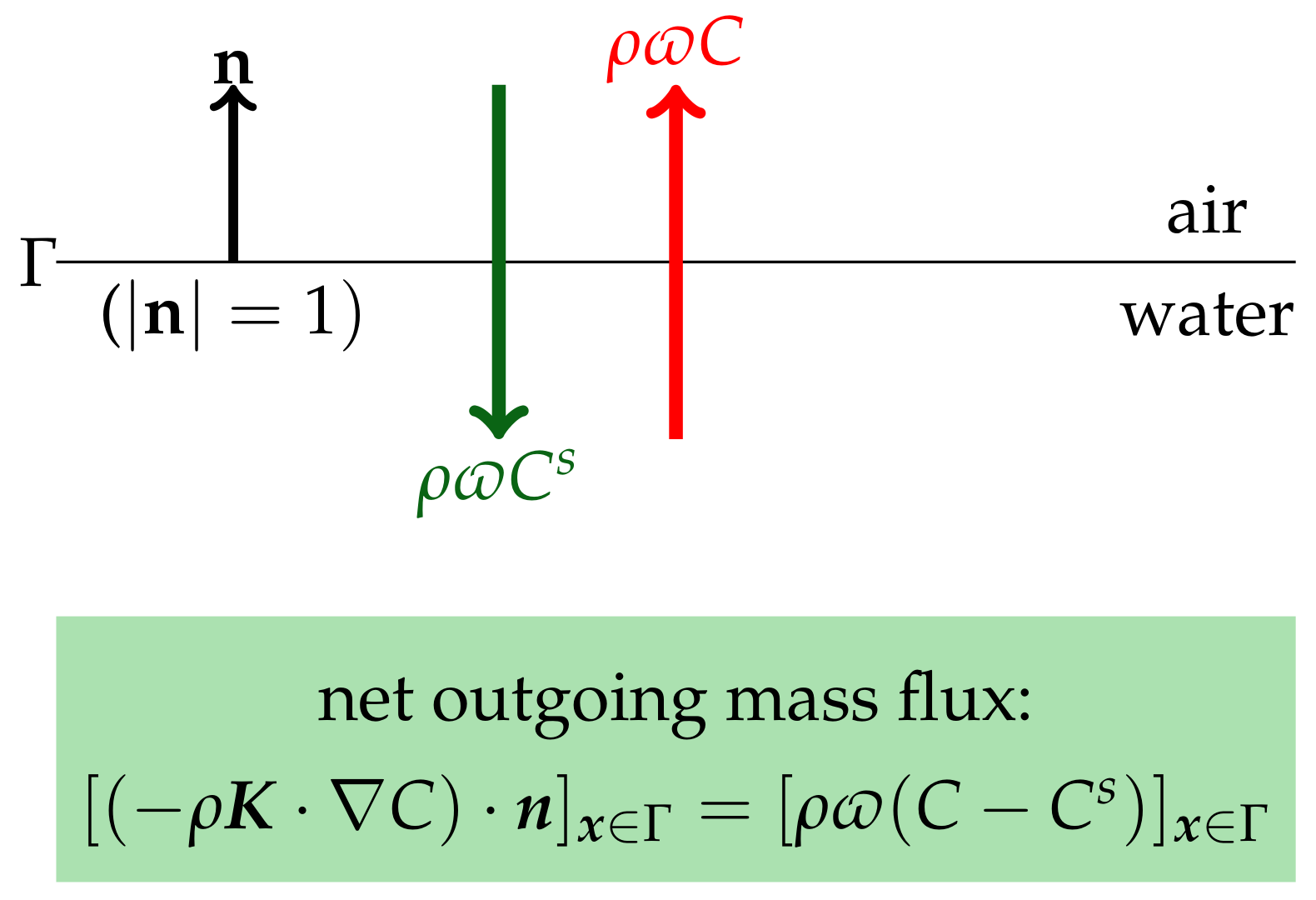
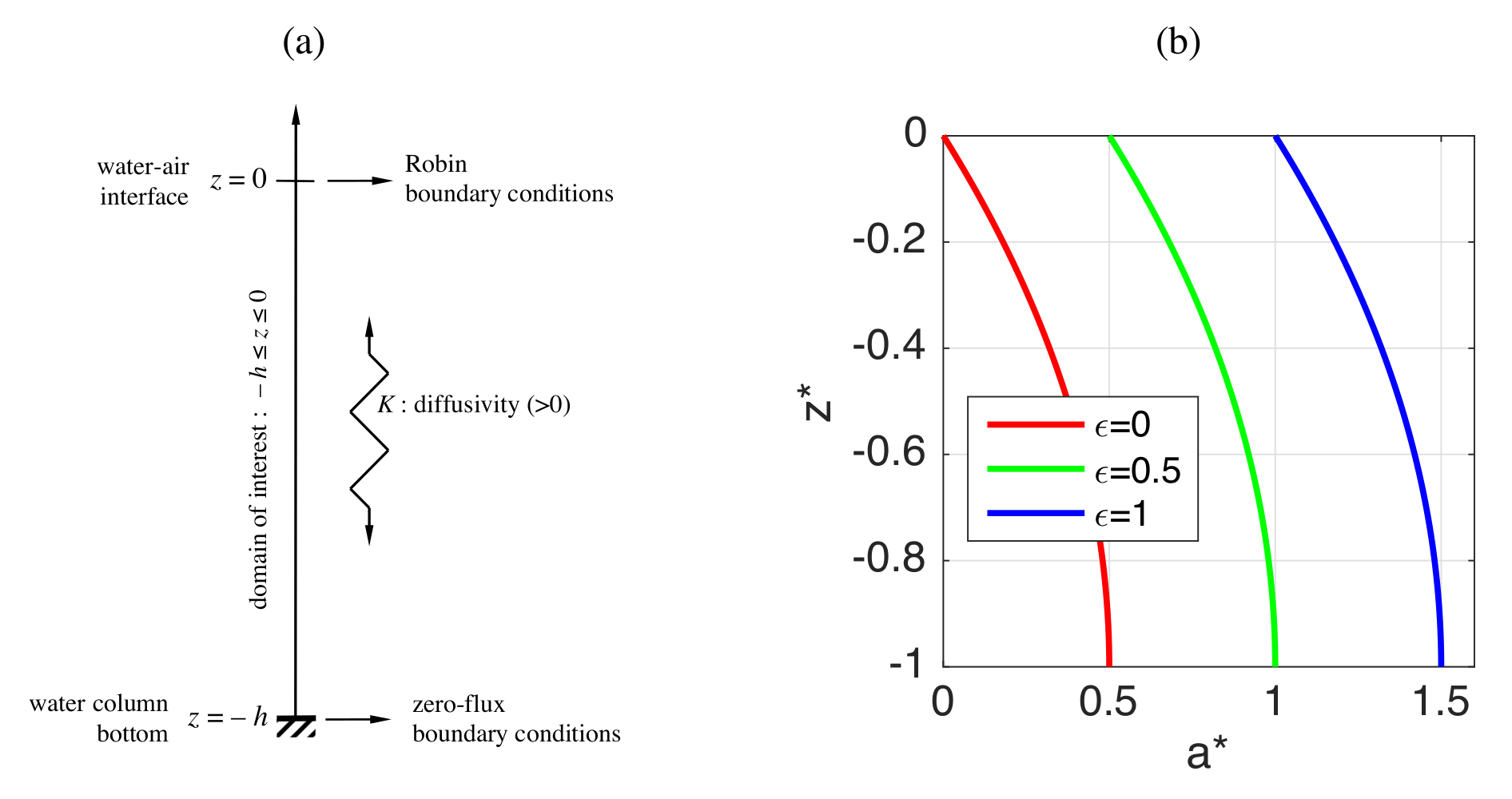
| Variable | Outgoing (Upward) | Incoming (Downward) Specific Flux | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Flux | General Expression | |||
| age distribution function | ||||
| concentration | ||||
| age concentration | 0 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deleersnijder, E.; Draoui, I.; Lambrechts, J.; Legat, V.; Mouchet, A. Consistent Boundary Conditions for Age Calculations. Water 2020, 12, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051274
Deleersnijder E, Draoui I, Lambrechts J, Legat V, Mouchet A. Consistent Boundary Conditions for Age Calculations. Water. 2020; 12(5):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051274
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeleersnijder, Eric, Insaf Draoui, Jonathan Lambrechts, Vincent Legat, and Anne Mouchet. 2020. "Consistent Boundary Conditions for Age Calculations" Water 12, no. 5: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051274
APA StyleDeleersnijder, E., Draoui, I., Lambrechts, J., Legat, V., & Mouchet, A. (2020). Consistent Boundary Conditions for Age Calculations. Water, 12(5), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051274







