Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen Transport in the Qiandao Lake Basin, a Large Hilly Monsoon Basin of Southeastern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
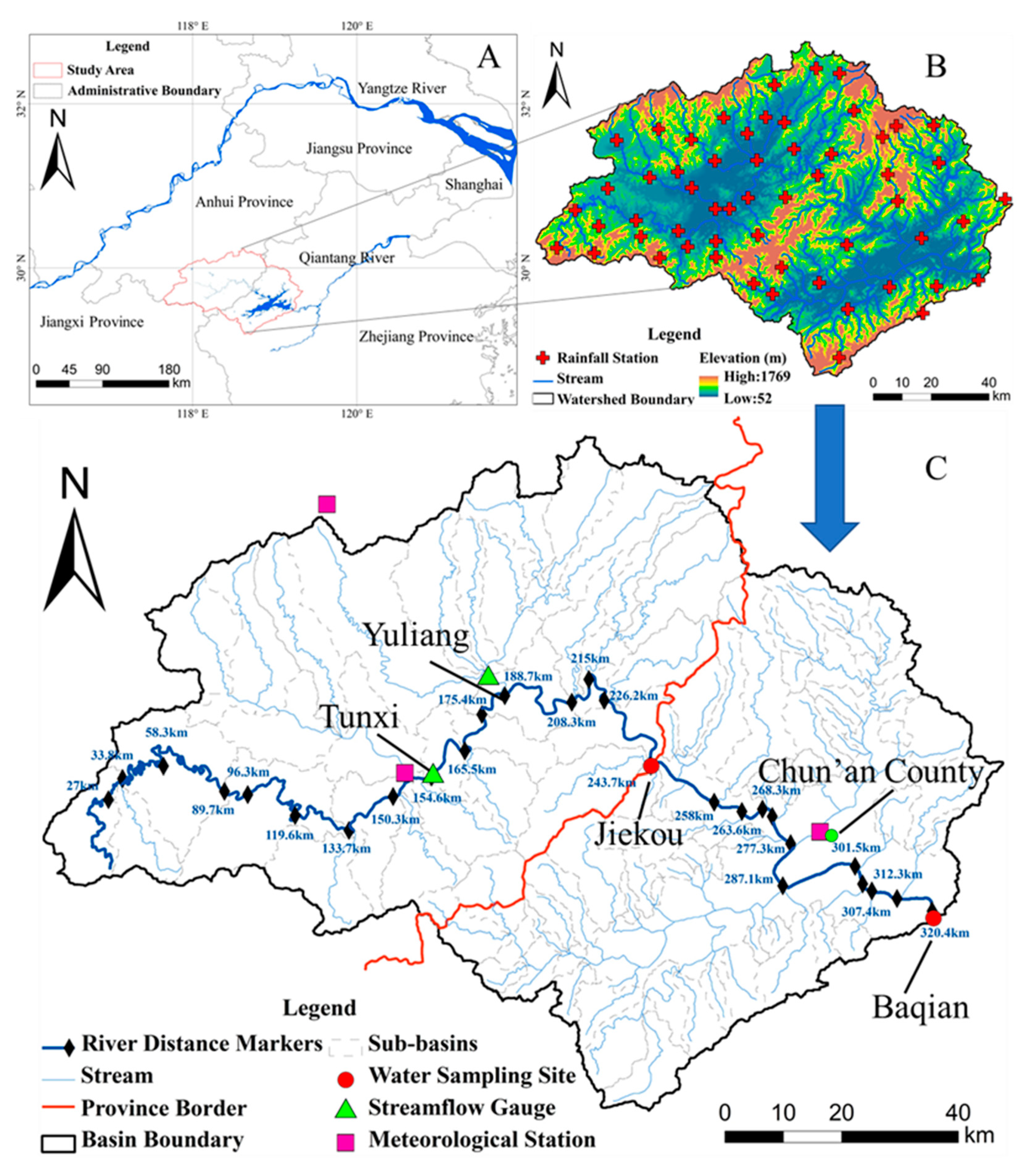
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. SWAT Model Configuration
3. Results
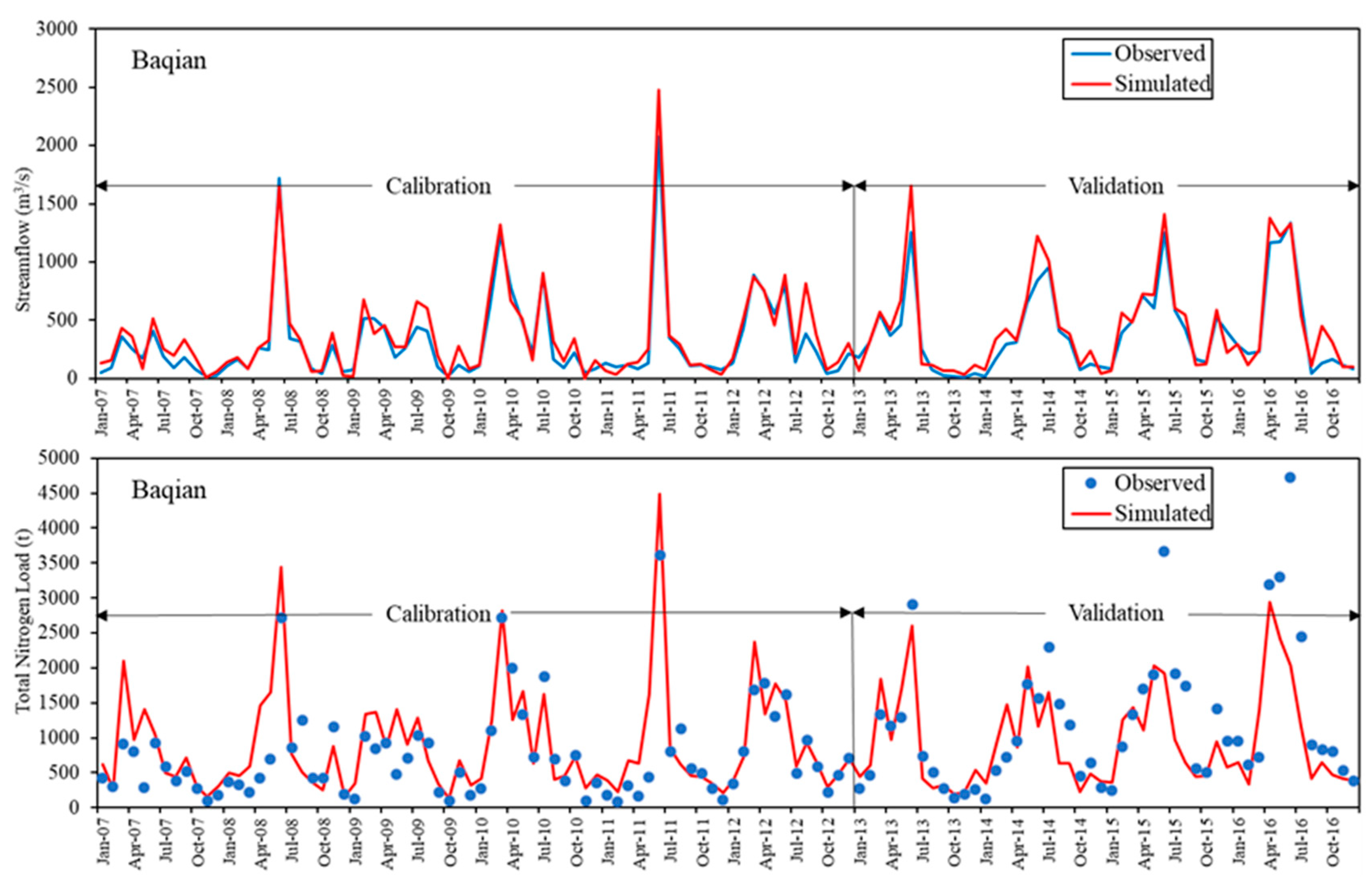
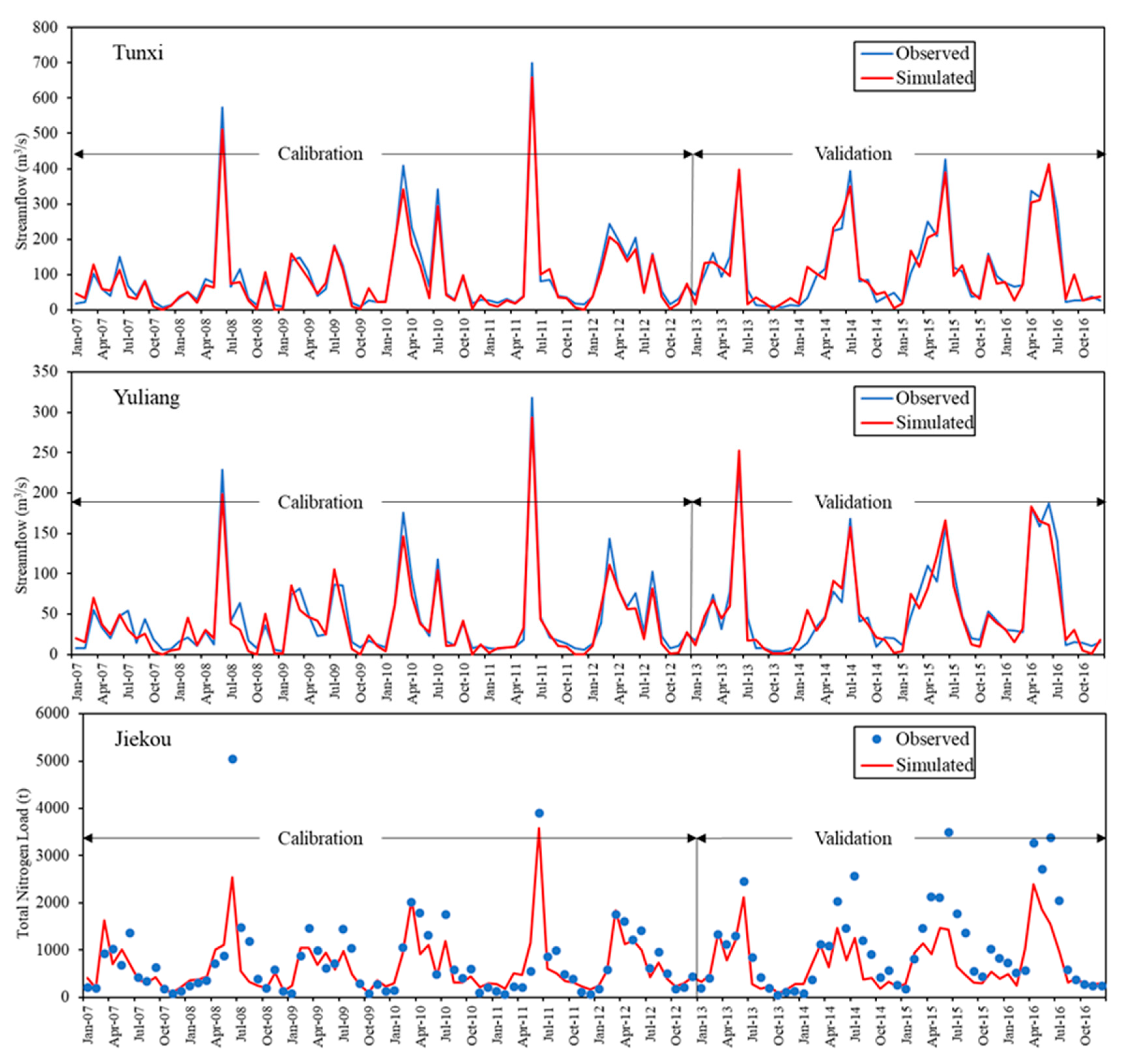
3.1. Calibration and Sensitivity Analysis of the SWAT Model
3.2. Validation of Streamflow and TN Loads
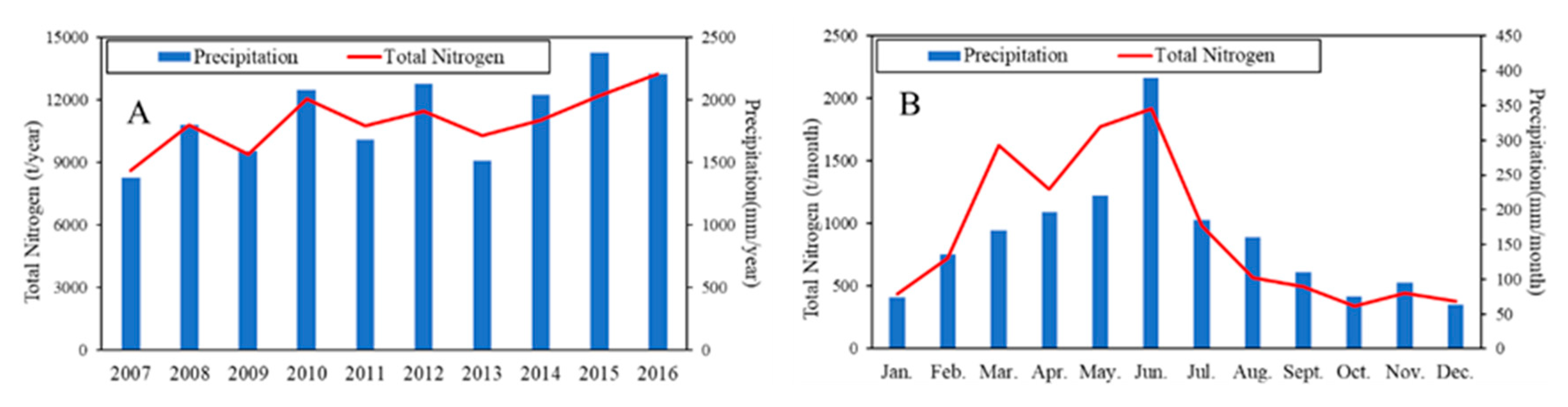
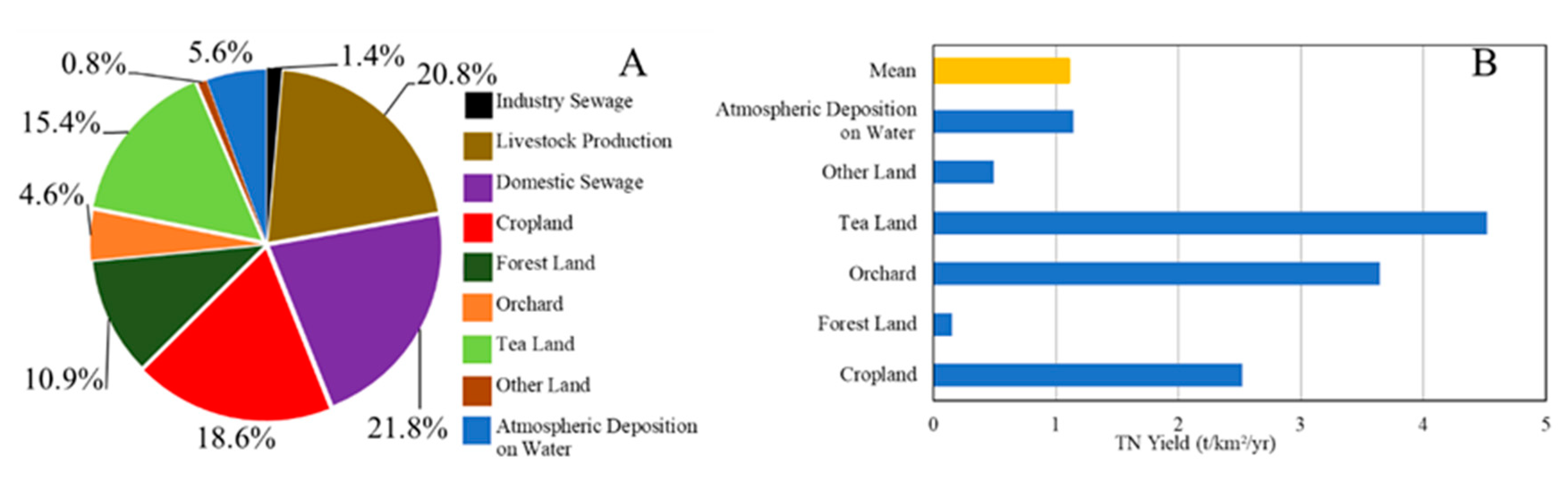
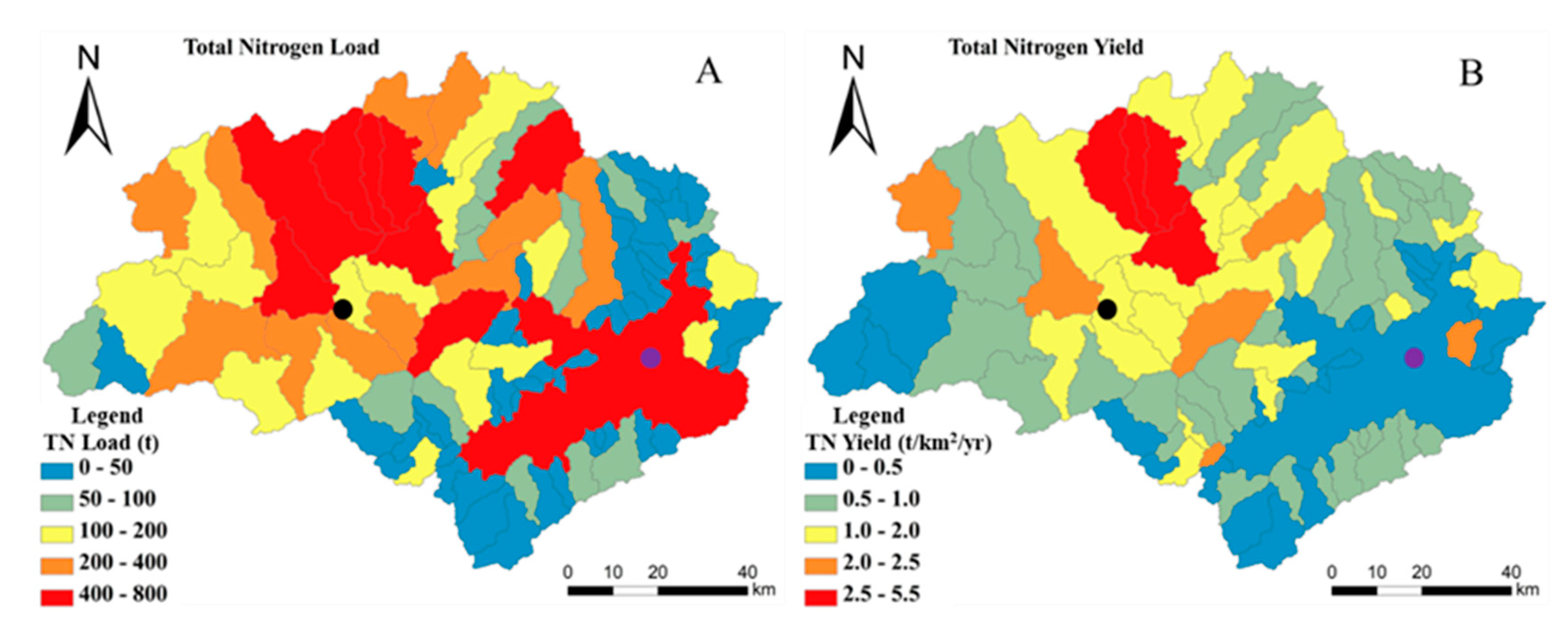
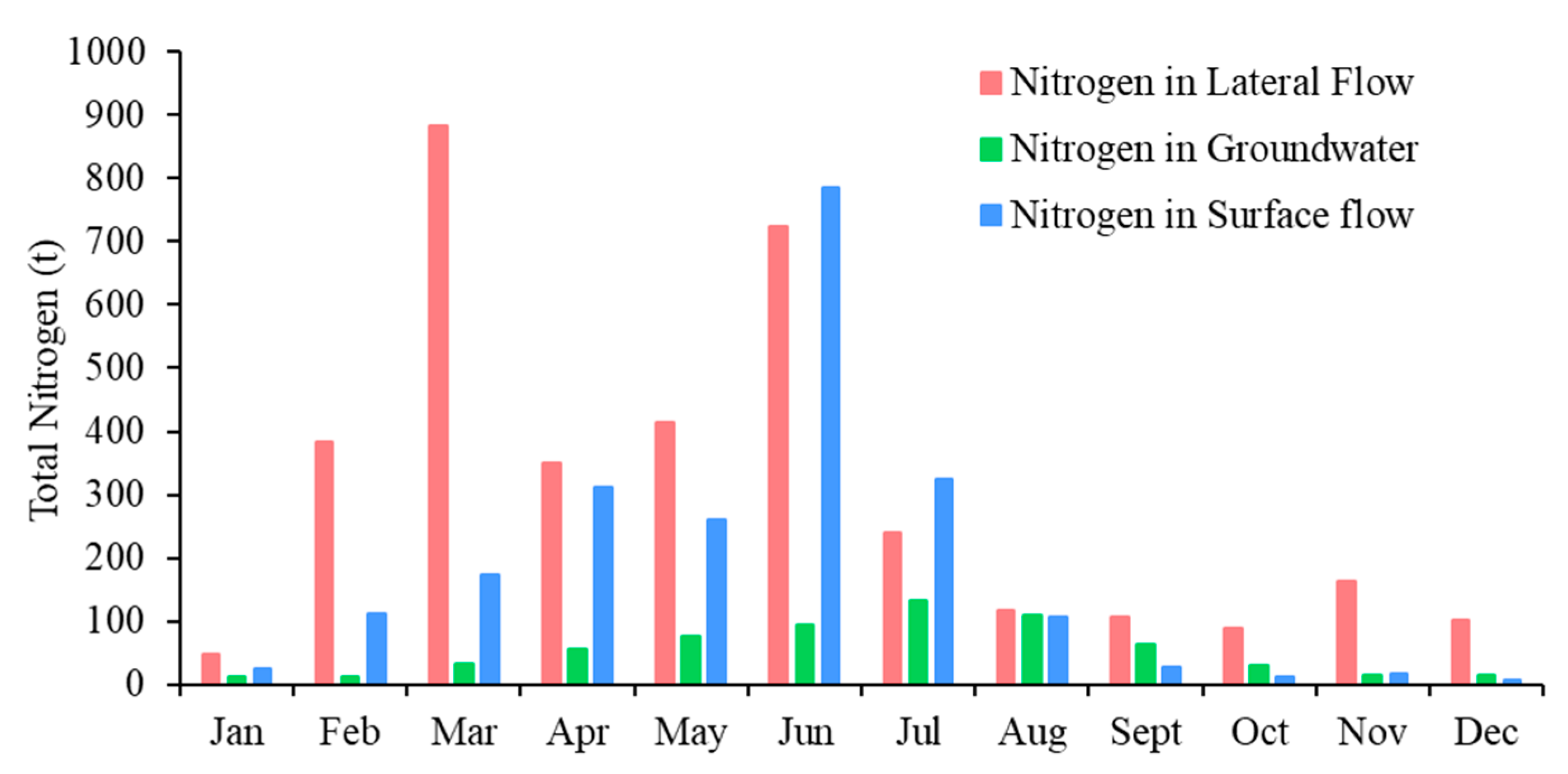
3.3. Spatiotemporal Patterns of TN Loads and Yields
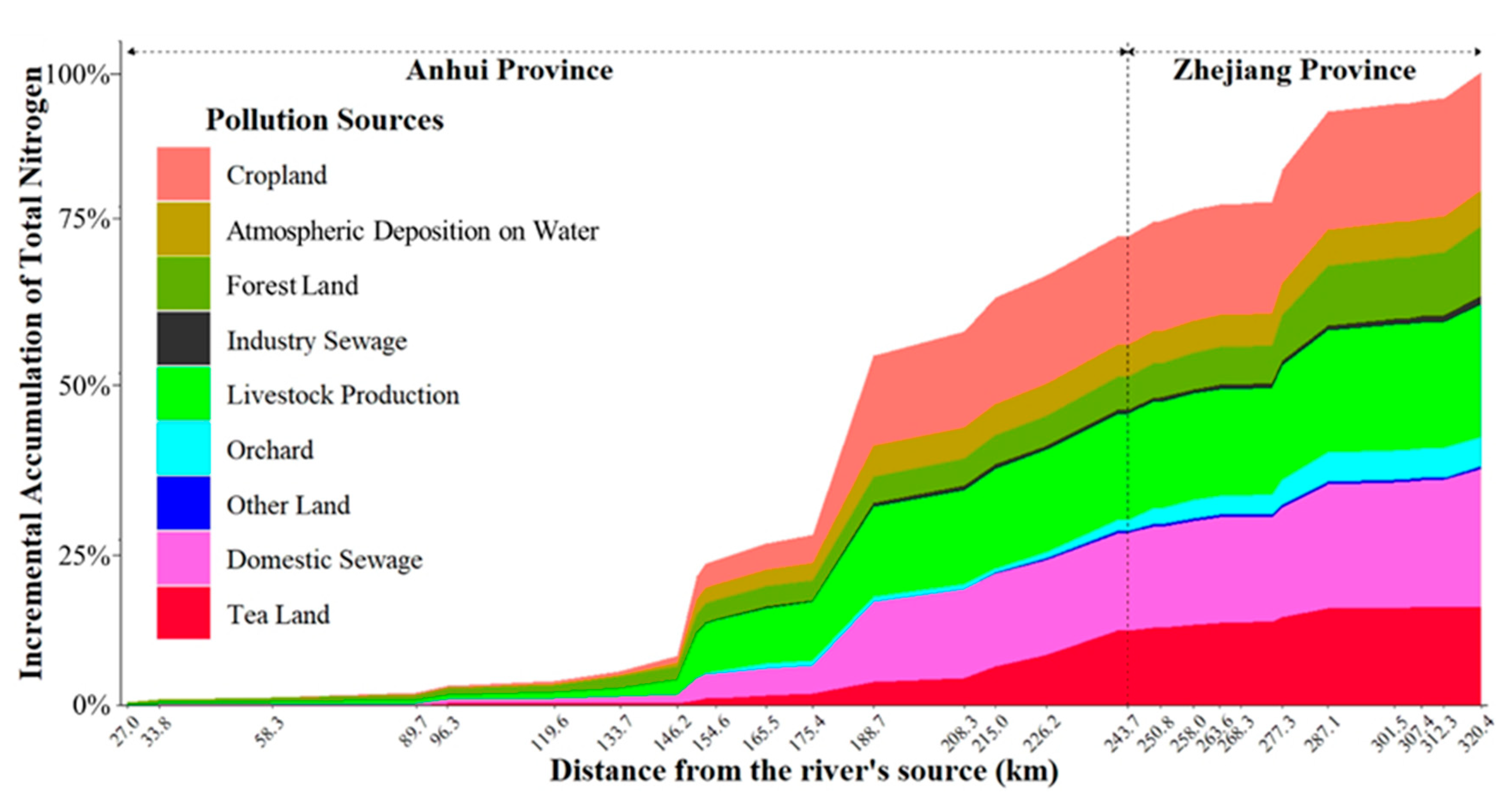
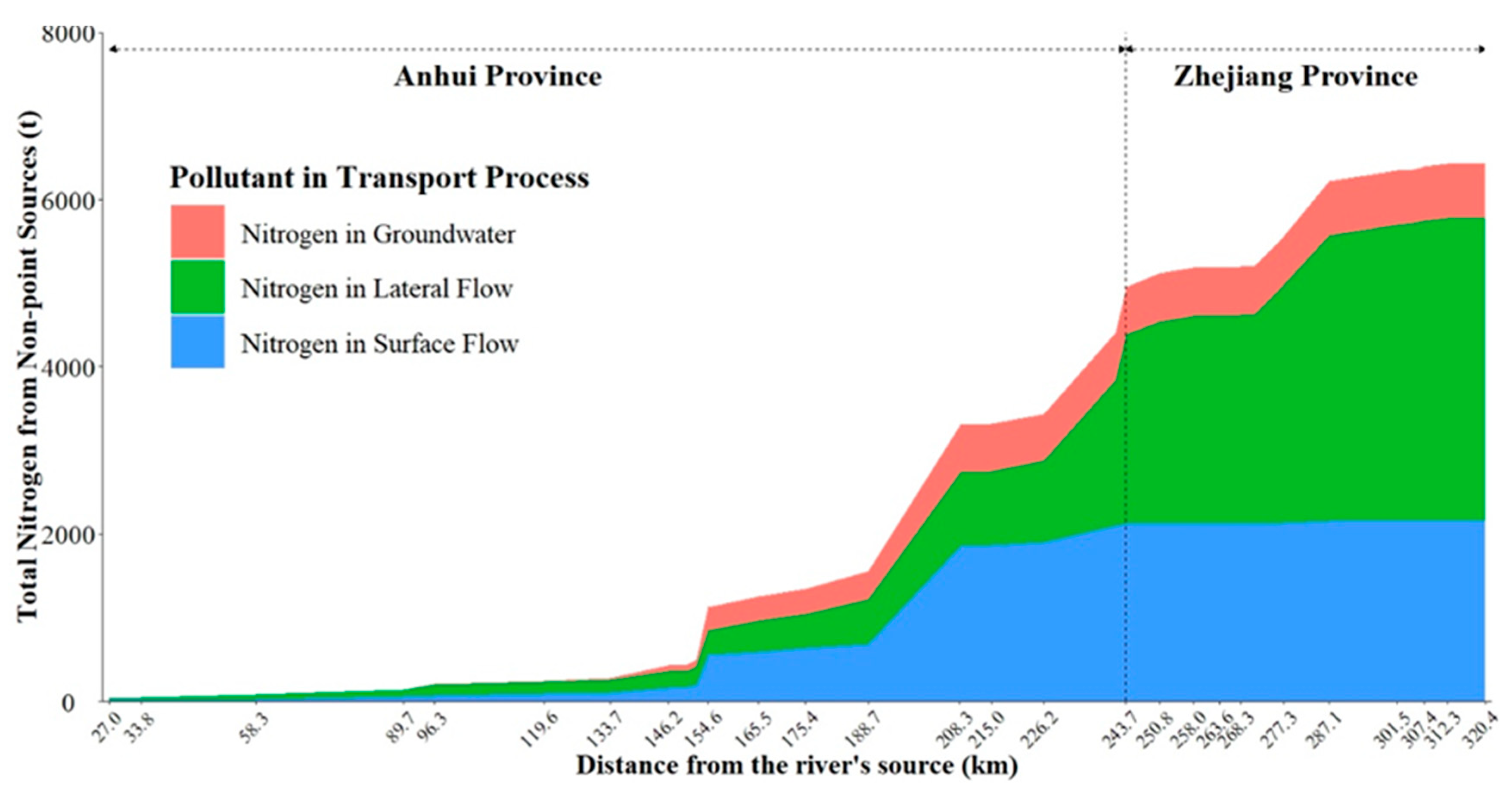
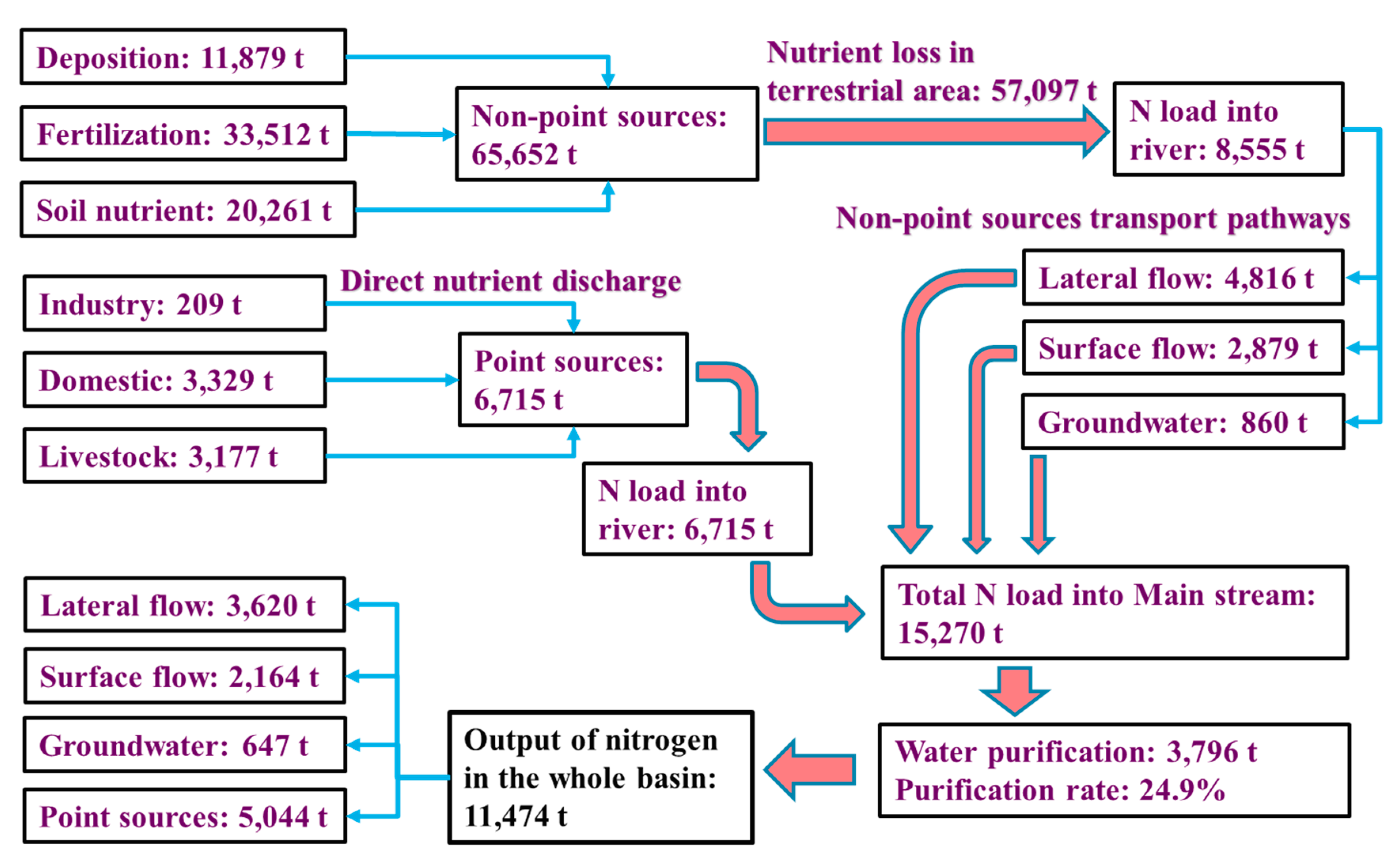
3.4. Sources and Spatial Dynamics of TN Entering the Main Reach of the Xin’anjiang River
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of TN Transport
4.2. The Basin’s N Cycle and Implications for Pollution Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markogianni, V.; Mentzafou, A.; Dimitriou, E. Assessing the impacts of human activities and soil erosion on the water quality of Plastira mountainous Mediterranean Lake, Greece. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Liang, T.; Zheng, D.; Wei, X. A method coupled with remote sensing data to evaluate non-point source pollution in the Xin’anjiang catchment of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 430, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayyeri, H.; Zandi, S. Evaluation of the effect of river style framework on water quality: Application of geomorphological factors. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Hu, C. A Comprehensive Study of the Effect of Input Data on Hydrology and non-point Source Pollution Modeling. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1505–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, J.; Hong, H. Modeling nutrient sources, transport and management strategies in a coastal watershed, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Chen, D. A modification of the Regional Nutrient Management model (ReNuMa) to identify long-term changes in riverine nitrogen sources. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Que, Z.; Seidou, O.; Droste, R.L.; Wilkes, G.; Sunohara, M.; Topp, E.; Lapen, D.R. Using AnnAGNPS to Predict the Effects of Tile Drainage Control on Nutrient and Sediment Loads for a River Basin. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.K.; Regmi, R.K.; Masago, Y.; Fukushi, K.; Kumar, P.; Saraswat, C. Assessment of Bagmati river pollution in Kathmandu Valley: Scenario-based modeling and analysis for sustainable urban development. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2017, 9–10, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Han, L. Spatial hydrological responses to land use and land cover changes in a typical catchment of the Yangtze River Delta region. Catena 2018, 170, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lan, J.; Li, H.; Liu, F.; Luo, L.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liu, M. Estimation of external nutrient loadings from the main tributary (Xin’anjiang) into Lake Qiandao, 2006–2016. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1534–1546. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Fohrer, N. SWAT2000: Current capabilities and research opportunities in applied watershed modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzio, M.D.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.G. A GIS-Coupled Hydrological Model System for the Watershed Assessment of Agricultural Nonpoint and Point Sources of Pollution. Trans. GIS 2010, 8, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerro, I.; Antiguedad, I.; Srinavasan, R.; Sauvage, S.; Volk, M.; Sanchez-Perez, J.M. Simulating land management options to reduce nitrate pollution in an agricultural watershed dominated by an alluvial aquifer. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Withers, P.J.A.; May, L.; Jarvie, H.P.; Jordan, P.; Doody, D.; Foy, R.H.; Bechmann, M.; Cooksley, S.; Dils, R.; Deal, N. Nutrient emissions to water from septic tank systems in rural catchments: Uncertainties and implications for policy. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 24, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malago, A.; Bouraoui, F.; Vigiak, O.; Grizzetti, B.; Pastori, M. Modelling water and nutrient fluxes in the Danube River Basin with SWAT. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 196–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Recknagel, F.; Meyer, W.; Frizenschaf, J.; Shrestha, M.K. Modelling the impacts of altered management practices, land use and climate changes on the water quality of the Millbrook catchment-reservoir system in South Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, G.R.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, N.; Shin, D.S.; Choi, J.; Hyun, G.; Jeon, J.-H.; Ok, Y.S.; Lim, K.J. Evaluation of SWAT sub-daily runoff estimation at small agricultural watershed in Korea. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavan, M.; White, S.; Holman, I.P. Evaluation of River Water Quality Simulations at a Daily Time Step—Experience with SWAT in the Axe Catchment, UK. Clean-Soil AirWater 2011, 39, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuppad, P.; Douglas-Mankin, K.R.; Koelliker, J.K.; Hutchinson, J.M.S. SWAT Discharge Response to Spatial Rainfall Variability in a Kansas Watershed. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Warren, R.; He, Y.; Ye, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, G. Impacts of climate change on TN load and its control in a River Basin with complex pollution sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, G.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, B.; Zhu, J. The Impacts of Climate Variability and Land Use Change on Streamflow in the Hailiutu River Basin. Water 2018, 10, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Peng, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, H.; Chen, J. Analysis of current pollutant loads and investigation of total pollutant discharge limits in Qiandao Lake. Water Resour. Prot. 2014, 30, 53–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- MEP. Chinese Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002); Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Da, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Xu, H.; Liu, M.; Lan, J.; Wang, Y.; WU, Z.; Zheng, W. Influence of Hydrometeorogical Process on Nutrient Dynamics in Qiandao Lake. J. Hydroecol. 2019, 40, 9–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhu, M. Spatial-temporal variations of water quality parameters in Xin’anjiang Reservoir (Lake Qiandao) and the water protection strategy. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 836–845. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; Lan, J.; He, J.; Yu, Z. Vertical distribution of phytoplankton and physico-chemical characteristics in the lacustrine zone of Xin’anjiang Reservoir( Lake Qiandao) in subtropic China during summer stratification. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 460–465. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, T.; Sha, J.; Wang, Y. Application of Regional Nutrient Management Model in Tunxi Catchment: In Support of the Trans-boundary Eco-compensation in Eastern China. Clean-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The World Fertilizer Outlook; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; Xie, L.; Liu, B. Association of extreme precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin with global air-sea heat fluxes and moisture transport. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 3020–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Variability of precipitation extremes and dryness/wetness over the southeast coastal region of China, 1960–2014. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4656–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueppke, S.G.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Chen, D.; Ou, W. An Integrative Framework to Control Nutrient Loss: Insights from Two Hilly Basins in China’s Yangtze River Delta. Water 2019, 11, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MWR. Hydrological Data of River Basins in China; Ministry of Water Resources of China: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- CBS. Chun’an Statistical Yearbook; Chun’an Bureau of Statistic, China: Hangzhou, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- HBS. Huangshan Statistical Yearbook; Huangshan Bureau of Statistic, China: Huangshan, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Uniyal, B.; Jha, M.K.; Verma, A.K. Assessing Climate Change Impact on Water Balance Components of a River Basin Using SWAT Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4767–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Rouholahnejad, E.; Vaghefi, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H.; Kløve, B. A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: Calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, P.; Zhou, M.; Deng, H.; Lyu, J.; Cao, W.; Takara, K.; Nover, D.; Geoffrey Schladow, S. Impact of forest maintenance on water shortages: Hydrologic modeling and effects of climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models, part I. A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Liew, M.W.V.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shrestha, N.K.; Wang, J. Assessing climate change impacts on stream temperature in the Athabasca River Basin using SWAT equilibrium temperature model and its potential impacts on stream ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Gong, Y.W.; Li, Y.H.; Hong, Q.; Xu, L.; Liu, R.M. A comparison of WEPP and SWAT for modeling soil erosion of the Zhangjiachong Watershed in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Huang, M.; Ma, M.; Wei, J.; Hu, W.; Chouhan, S. Evaluating sources and processing of nonpoint source nitrate in a small suburban watershed in China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.K.; Xu, J.M. Restoration of surface soil fertility of an eroded red soil in southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 80, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Liang, T. Non-point source pollution modelling using Soil and Water Assessment Tool and its parameter sensitivity analysis in Xin’anjiang catchment, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Duan, Z.; Disse, M.; Chiogna, G. Evaluation of precipitation input for SWAT modeling in Alpine catchment: A case study in the Adige river basin (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campling, P.; Gobin, A.; Feyen, J. Temporal and spatial rainfall analysis across a humid tropical catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Time Variation Characteristics of the Main Inflow Nutrient at Xin’anjiang Reservoir and Its Impact factors in 2007–2016. Environ. Monit. China 2019, 35, 95–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenborg, T.O.; Hinsby, K.; van Roosmalen, L.; Stisen, S. Assessment of climate change impacts on the quantity and quality of a coastal catchment using a coupled groundwater–surface water model. Clim. Chang. 2011, 113, 1025–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Luo, D.; Luo, X.; Tang, D.; Chen, S. Agriculture non-point source pollution control measures of Qiandao lake area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 18, 126–129. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Case Studies on Remuneration of Positive Externalities (RPE); Payments for Environmental Services (PES): Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Y. The first eco-compensation for crossing provinces of downstream and upstream in China: A model of Xinanjiang River. Environ. Prot. 2016, 14, 38–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Pan, D. Detecting subsurface phytoplankton layer in Qiandao Lake using shipborne lidar. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Wollheim, W.M.; Mulholland, P.J.; Webster, J.R.; Meyer, J.L.; Tank, J.L.; Marti, E.; Bowden, W.B.; Valett, H.M.; Hershey, A.E.; et al. Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 2001, 292, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhan, C.; Ye, A.Z. Water Quality Management in China: The Case of the Huai River Basin. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2011, 27, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zuo, D. Effect of land use types on stream water quality under seasonal variation and topographic characteristics in the Wei River basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Nie, X. Inferring land use and land cover impact on stream water quality using a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach in the Xitiaoxi River Watershed, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Luo, W.; Wu, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, B.; Phyoe, W.; Wang, F. Historical record of nutrients inputs into the Xin’an Reservoir and its potential environmental implication. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 20330–20341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G. Land use and land cover change and regional economic development: The revelation of the change in cropland area in the Yangtze River delta during the past 50 years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2004, 59, 41–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, W.; Yang, G.; Nie, X. Reduction of nitrogen and phosphorus emission and zoning management targeting at water quality of lake or reservoir systems: A case study of Shahe Reservoir within Tianmuhu Reservoir area. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 785–798. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Pueppke, S.; Diao, Y.; Nie, X.; Geng, J.; Chen, D.; Pang, J. Nutrient loss is sensitive to land cover changes and slope gradients of agricultural hillsides: Evidence from four contrasting pond systems in a hilly catchment. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q. The Study of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Control Policy System. Master’s Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; He, B.; Chen, Y.; Tang, X. Impacts of human activities and climate change on the water environment of Lake Poyang Basin, China. Geoenviron. Disasters 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Li, H.; Nie, X.; Xu, X. Nitrogen and phosphorus budget of different land use types in hilly area of Lake Taihu upper river basin. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 829–837. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Beven, K.; Heathwaite, L.; Haygarth, P.; Walling, D.; Brazier, R.; Withers, P. On the concept of delivery of sediment and nutrients to stream channels. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Howarth, R.W.; Hong, B.; Swaney, D.P.; Guo, H.C. Estimating net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs (NANI) in the Lake Dianchi basin of China. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4577–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomer, M.D.; Moorman, T.B.; Kovar, J.L.; Cole, K.J.; Nichols, D.J. Eleven years of runoff and phosphorus losses from two fields with and without manure application, Iowa, USA. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 168, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadas, P.A.; Powell, J.M. Monitoring nutrient loss in runoff from dairy cattle lots. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 181, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, T.L.; Bosch, D.D.; Strickland, T.C. Tillage impact on herbicide loss by surface runoff and lateral subsurface flow. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530–531, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, R.B.; Boyer, E.W.; Smith, R.A.; Schwarz, G.E.; Moore, R.B. The Role of Headwater Streams in Downstream Water Quality. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suescún, D.; Villegas, J.C.; León, J.D.; Flórez, C.P.; García-Leoz, V.; Correa-Londoño, G.A. Vegetation cover and rainfall seasonality impact nutrient loss via runoff and erosion in the Colombian Andes. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 17, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Liao, K.; Lv, L. Optimizing the spatial pattern of land use types in a mountainous area to minimize non-point nitrogen losses. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Swaney, D.P.; Hong, B.; Howarth, R.W.; Han, H.; Li, X. Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs and riverine phosphorus fluxes in highly populated headwater watersheds in China. Biogeochemistry 2015, 126, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZPMF. Horizontal Ecological Compensation Agreement for Upstream and Downstream of Xinanjiang River Basin; Zhejiang Provincial Ministry of Finance: Hangzhou, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, Z.; Zuo, J.; Wang, L.; Nie, X. Characteristics of Nitrogen Loss through Surface-Subsurface Flow on Red Soil Slopes of Southeast China. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2018, 50, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Ni, H.; Wang, H. Research on characteristics of nitrogen loss in sloping land under different rainfall intensities. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 27, 4576–4582. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, J. Sediment, runoff, nitrogen and phosphorus losses of sloping cropland of quaternary red soil in Northern Jiangxi. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 162–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.N.; Reaney, S.M.; Heathwaite, A.L. Representation of landscape hydrological connectivity using a topographically driven surface flow index. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Sadeghi, A.; Linker, L.; Arnold, J.; Shenk, G.; Wu, J. Simulated soil water content effect on plant nitrogen uptake and export in watershed management. In Quantifying and Understanding Plant Nitrogen Uptake for Systems Modeling; Ma, L., Ahuja, L.R., Bruulsema, T., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 277–304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal dynamics of nitrogen and phosphorus input budgets in a global hotspot of anthropogenic inputs. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, R.A. Role of subsurface flow in generating surface runoff. 2. Upstream source areas. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Kendall, A.D.; Hyndman, D.W.; Diao, Y.; Geng, J.; Pang, J. Nitrogen transport and retention in a headwater catchment with dense distributions of lowland ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigelhofer, G.; Hein, T.; Bondar-Kunze, E. Phosphorus and nitrogen dynamics in riverine systems: Human impacts and management options. In Riverine Ecosystem Management; Scmutz, S., Sendzimir, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Fang, S. Practices, perceptions, and implications of fertilizer use in East-Central China. Ambio 2015, 44, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, P. Estimation of Nonpoint Source Pollutant Loads and Optimization of the Best Management Practices (BMPs) in the Zhangweinan River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 882–891. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Park, S.W.; Lee, J.J.; Yoo, K.H. Applying SWAT for TMDL programs to a small watershed containing rice paddy fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 79, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fu, B.; Gao, G. Redlines for the greening of China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 33, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, G.; Barnett, J. China’s ambitious ecological red lines. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyabalanage, S.; Samarakoon, K.K.; Adikari, S.B.; Hewawasam, T. Impact of soil and water conservation measures on soil erosion rate and sediment yields in a tropical watershed in the Central Highlands of Sri Lanka. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenger, A.S.; Atkinson, S.; Santini, T.; Falinski, K.; Hutley, N.; Albert, S.; Horning, N.; Watson, J.E.M.; Mumby, P.J.; Jupiter, S.D. Predicting the impact of logging activities on soil erosion and water quality in steep, forested tropical islands. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 044035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, S.O.; Almeida, C.A.; Calderon, M.; Mallea, M.A.; Gonzalez, P. Assessment of the water self-purification capacity on a river affected by organic pollution: Application of chemometrics in spatial and temporal variations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 10583–10593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Definition | Cropland | Orchard | Forest Land | Tea Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVSTI | Harvest index for land cover/plant [(kg/ha)/kg/ha)] | 0.45 | 0.10 | 0.76 | 0.07 |
| RDMX | Maximum root depth for land cover/plant (m) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 0.5 |
| CNYLD | Normal fraction of nitrogen in seed for land cover/plant (kg N/kg seed) | 0.0199 | 0.0019 | 0.0015 | 0.0246 |
| Parameter | Definition | Range | Calibrated Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrology | |||
| CN2.mgt (Forest land) | Default SCS curve number for moisture conditions | 35–98 | 97.9261 |
| OV_N.hru | Default Manning’s ‘n’ value for overland flow | 0.01–30 | 0.9790 |
| TRNSRCH.bsn | Fraction of transmission losses partitioned to the deep aquifer | 0–1 | 0.0039 |
| Nitrogen | |||
| RCN.bsn | Concentration of nitrogen in rainfall | 0–15 | 0.0412 |
| NPERCO.bsn | Nitrogen percolation coefficient | 0–1 | 0.0020 |
| SOL_NO3.chm | Initial nitrate conc. in soil layer | 0–100 | 27.5619 |
| Station | Streamflow | Station | Total Nitrogen | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | |||
| R2 | Baqian | 0.97 | 0.97 | Baqian | 0.77 | 0.78 |
| ENS | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.65 | 0.68 | ||
| PBIAS | −14.4% | −12% | −18.1% | 1.3% | ||
| R2 | Yuliang | 0.95 | 0.95 | Jiekou | 0.75 | 0.71 |
| Tunxi | 0.98 | 0.97 | ||||
| ENS | Yuliang | 0.94 | 0.92 | Jiekou | 0.74 | 0.62 |
| Tunxi | 0.97 | 0.93 | ||||
| PBIAS | Yuliang | 9.9% | 2.1% | Jiekou | 14.6% | 22.6% |
| Tunxi | 8.9% | 1.5% | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Pueppke, S.G.; Pang, J.; Diao, Y. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen Transport in the Qiandao Lake Basin, a Large Hilly Monsoon Basin of Southeastern China. Water 2020, 12, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041075
Chen D, Li H, Zhang W, Pueppke SG, Pang J, Diao Y. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen Transport in the Qiandao Lake Basin, a Large Hilly Monsoon Basin of Southeastern China. Water. 2020; 12(4):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041075
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Dongqiang, Hengpeng Li, Wangshou Zhang, Steven G. Pueppke, Jiaping Pang, and Yaqin Diao. 2020. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Nitrogen Transport in the Qiandao Lake Basin, a Large Hilly Monsoon Basin of Southeastern China" Water 12, no. 4: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041075





