Influencing Factors of the Spatial–Temporal Variation of Layered Soils and Sediments Moistures and Infiltration Characteristics under Irrigation in a Desert Oasis by Deterministic Spatial Interpolation Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
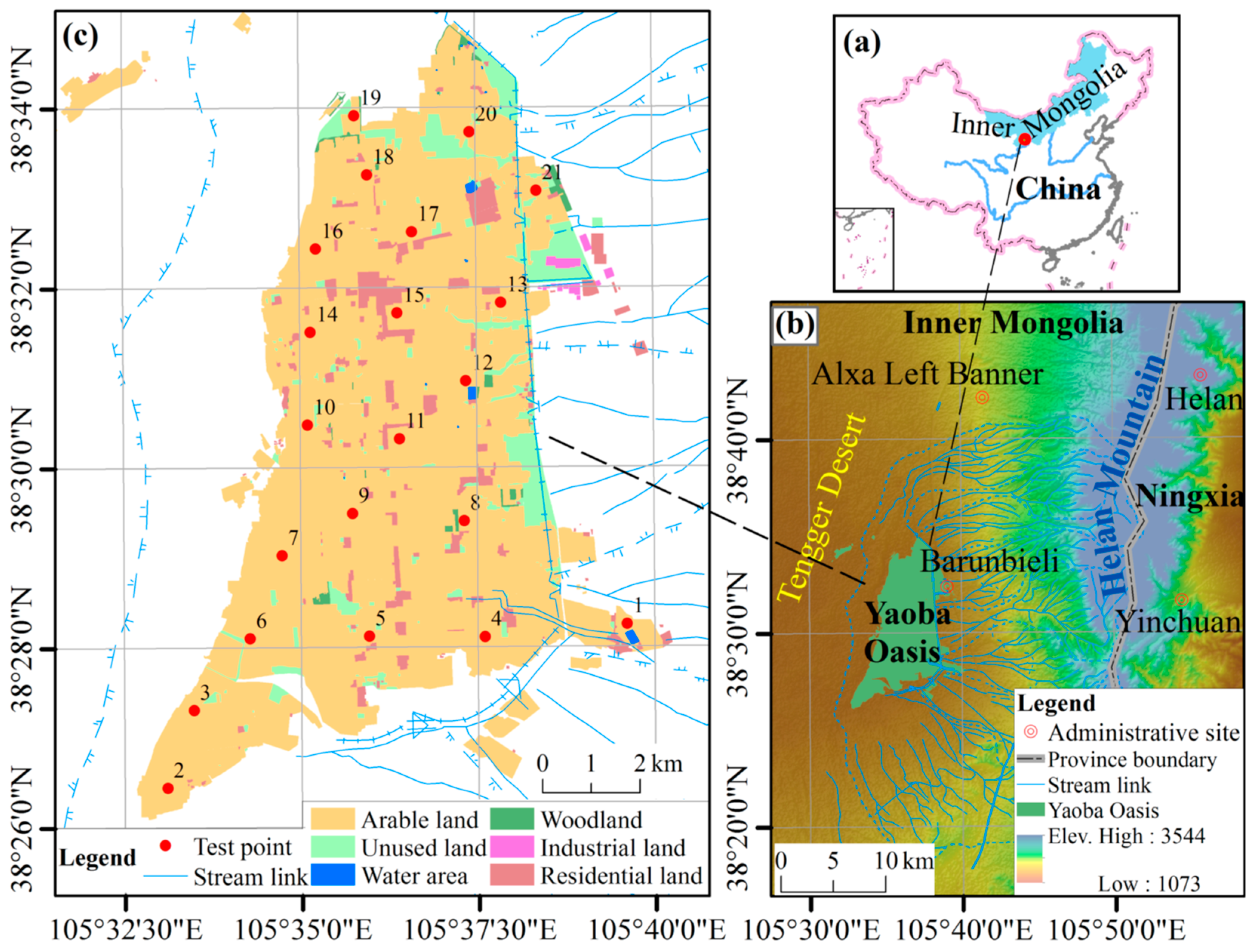
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Test Design and Datasets
2.2.1. Point Layout and In Situ Tests
2.2.2. Sampling and Measurement of Soil Physical Properties
2.2.3. Calibration of Neutron Moisture Meter and Observation Schedule of the Soils and Sediments Moistures
2.3. Deterministic Spatial Interpolation Methods
2.3.1. MRBF
2.3.2. IDW
2.3.3. LPRI and Determination of Regression Equations
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
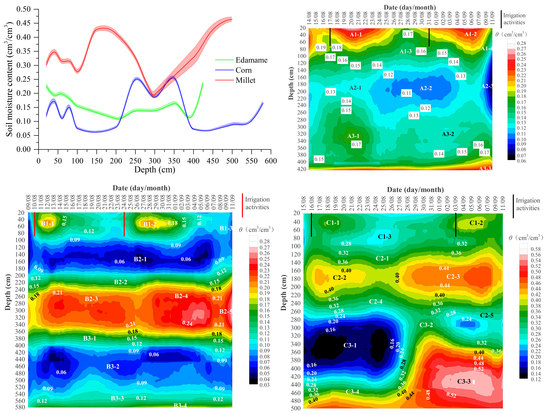
3.1. Spatial Ditribution of the Soils and Sediments Moistures
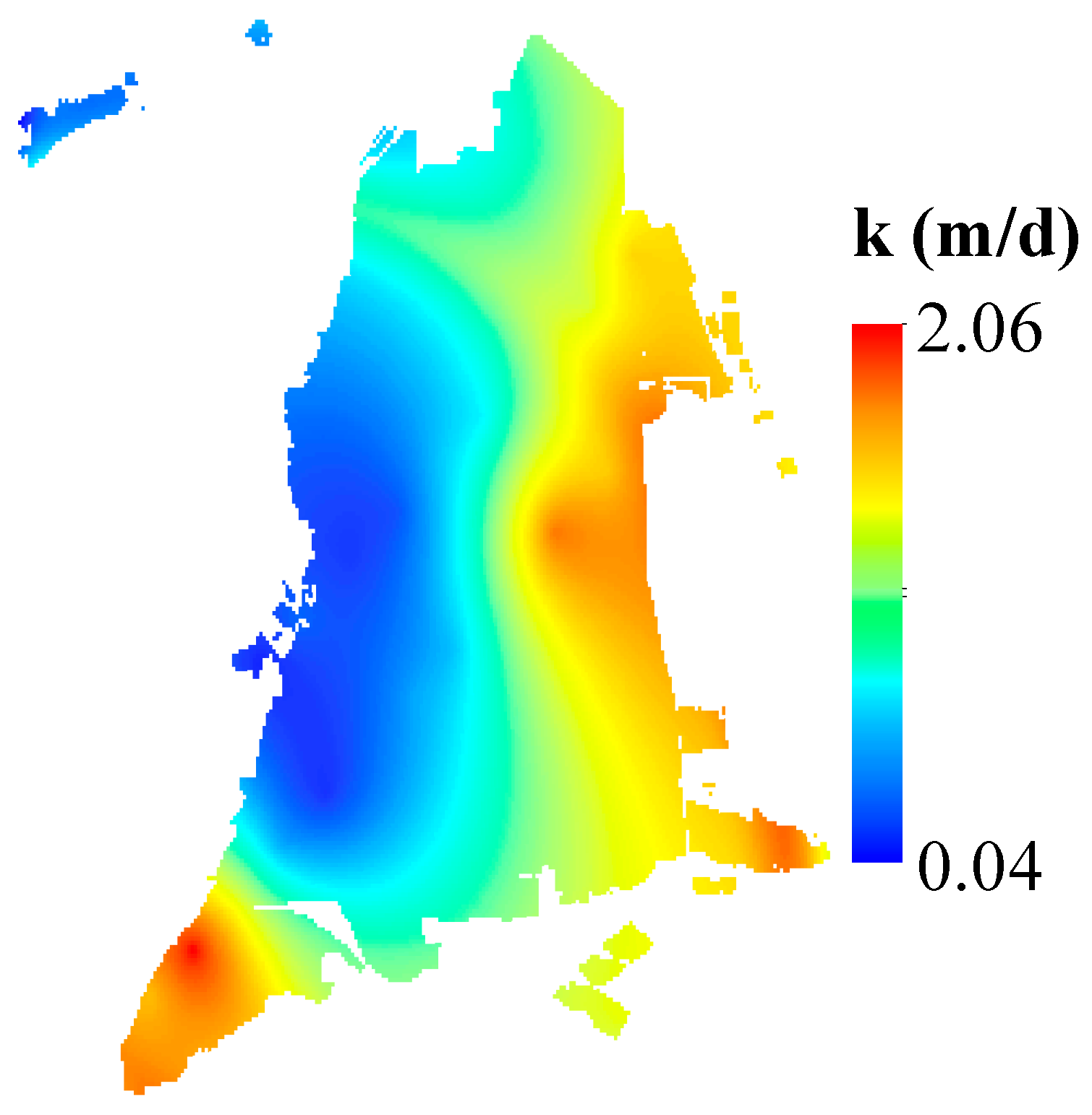
3.1.1. Regional Distribution of Soil Moisture and the Influence Factors
3.1.2. Layered Soil Moisture Characteristics
3.2. Vertical Distribution of Soil Moisture at Individual Points
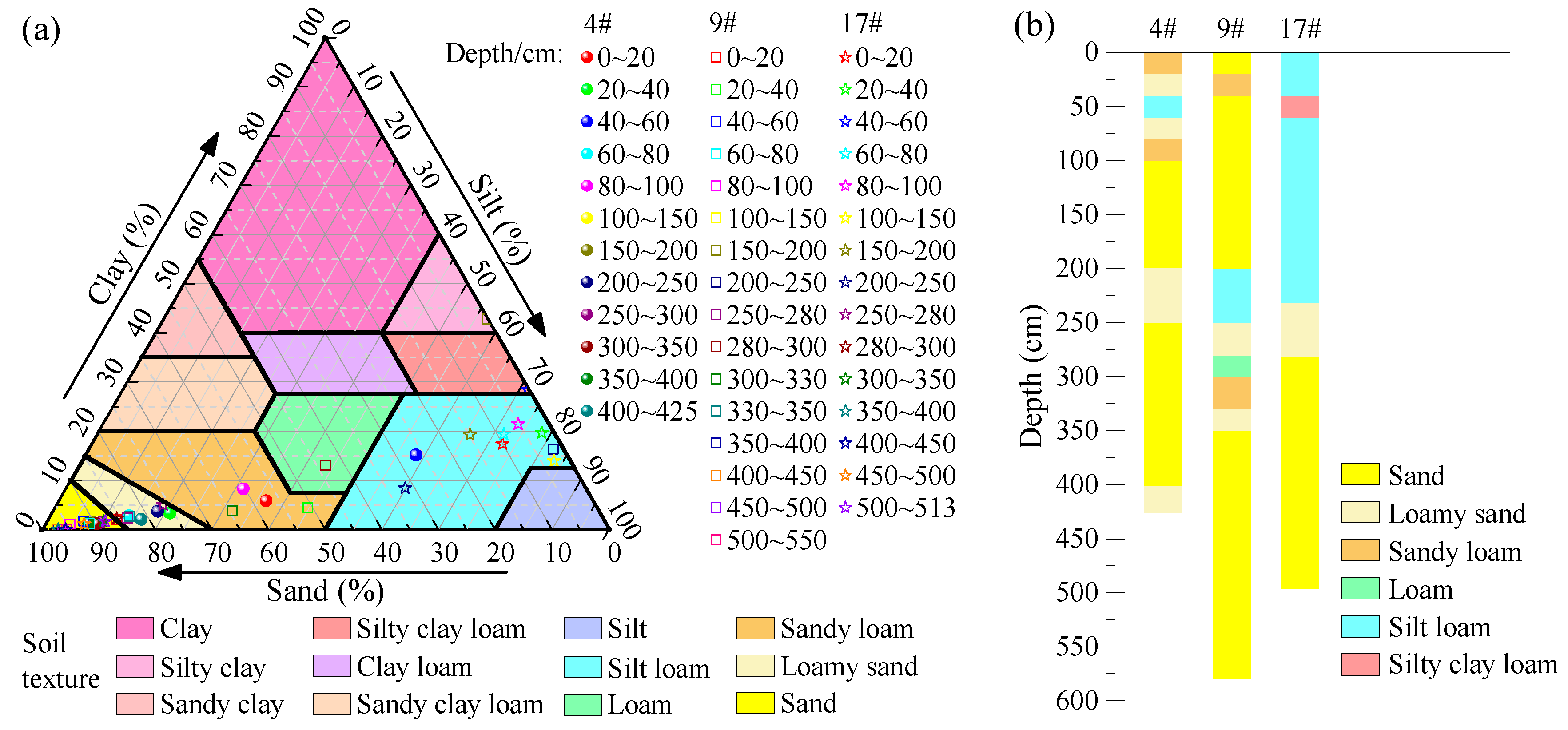
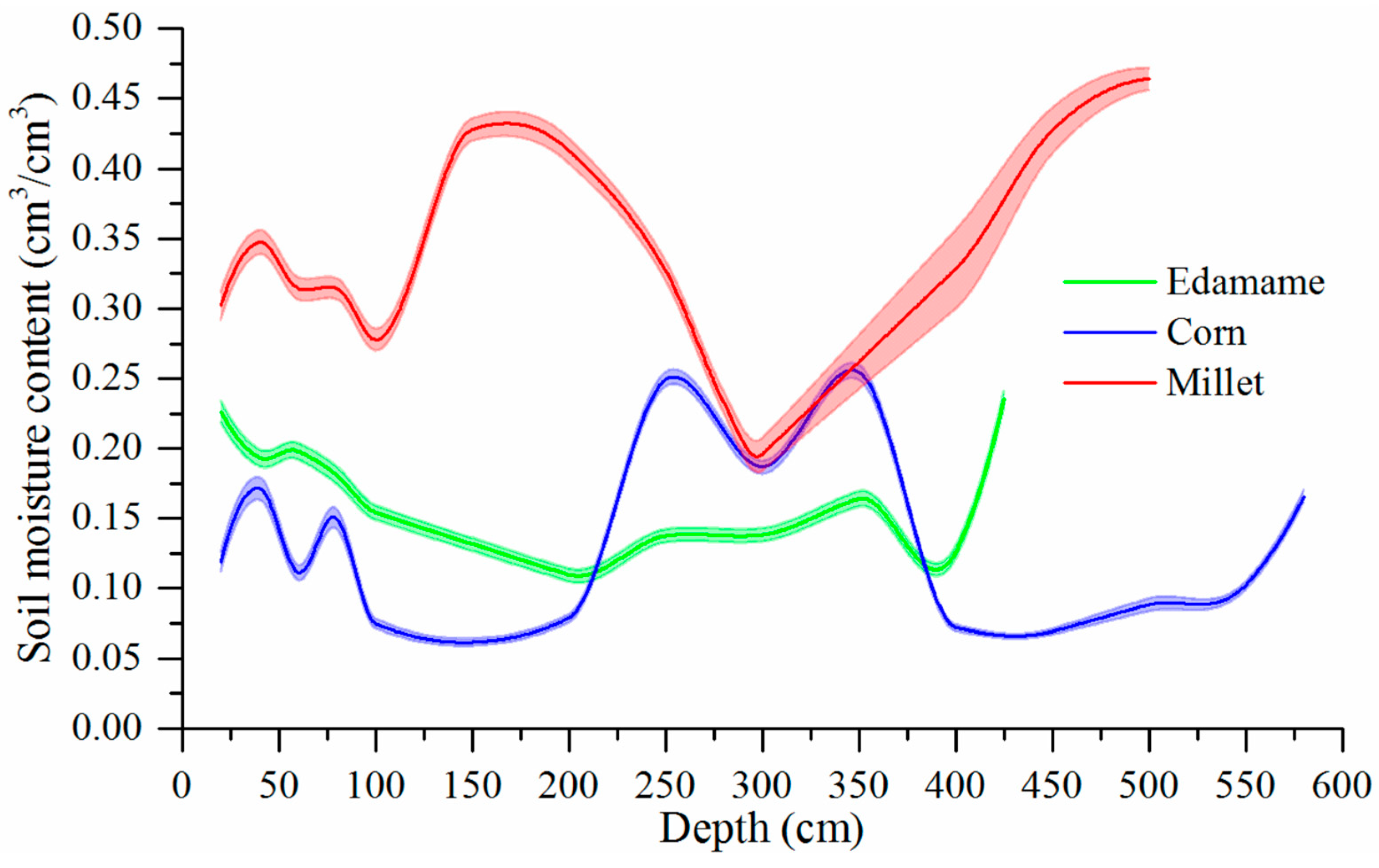
3.2.1. Influence of Soil Texture on the Soil Moisture
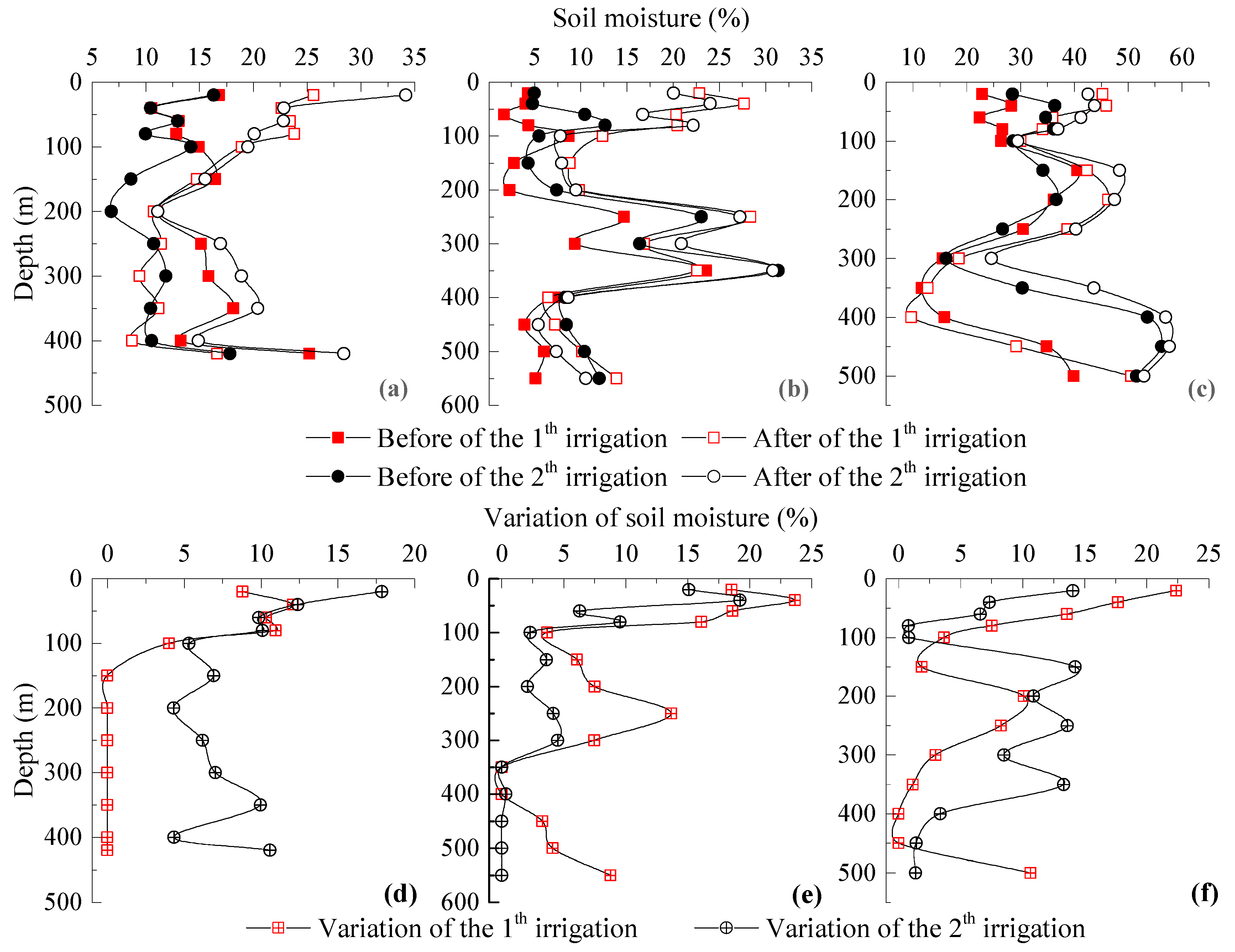
3.2.2. Variation Characteristics of Soil Moisture Affected by Irrigation Activities
3.3. Influence Factors of Vertical Soil Moisture along Profiles
3.3.1. Influence of Soil Moisture Requirement
3.3.2. Influence of the Layered Soil Textures
3.3.3. Influence of Preferential Flow
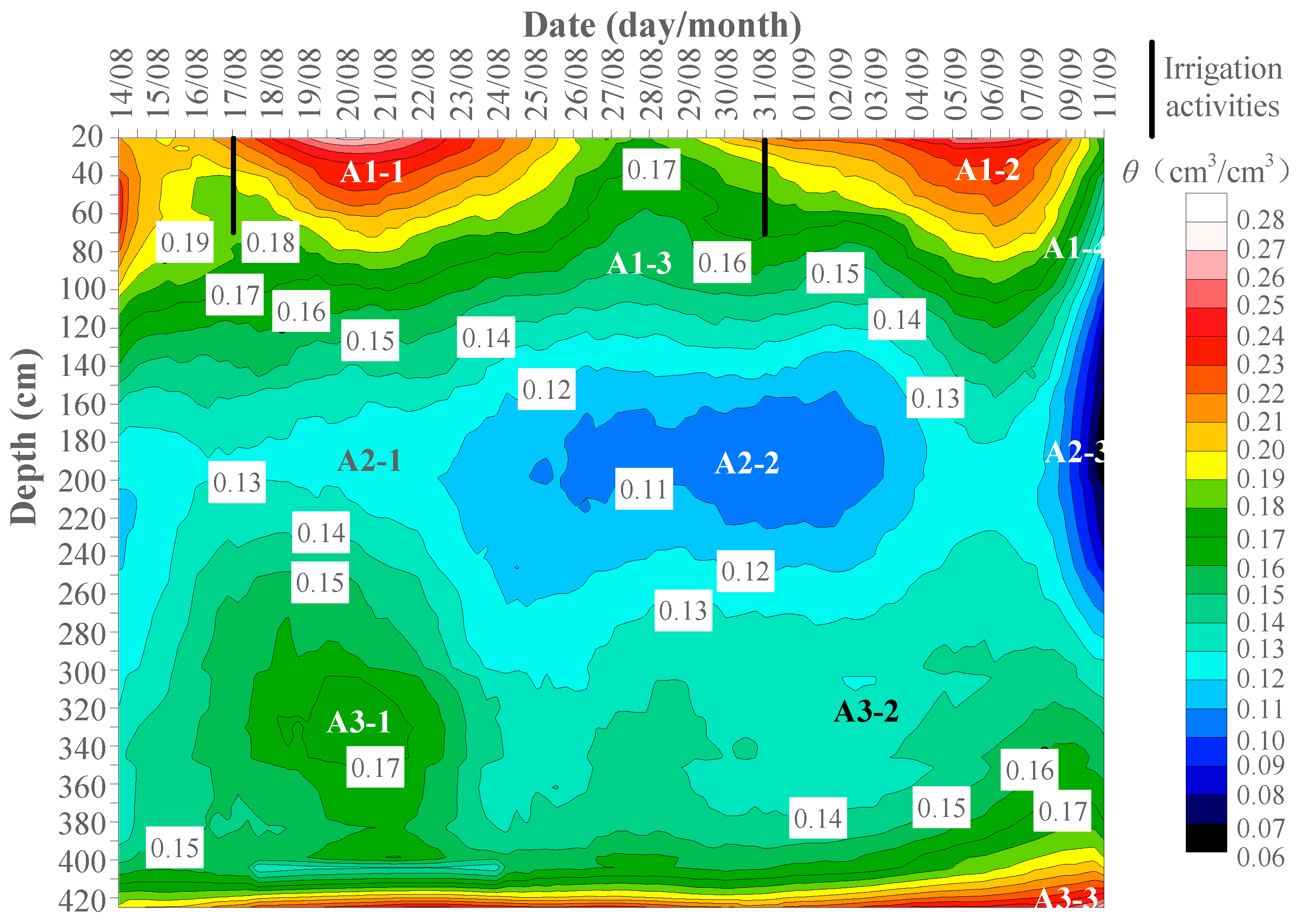
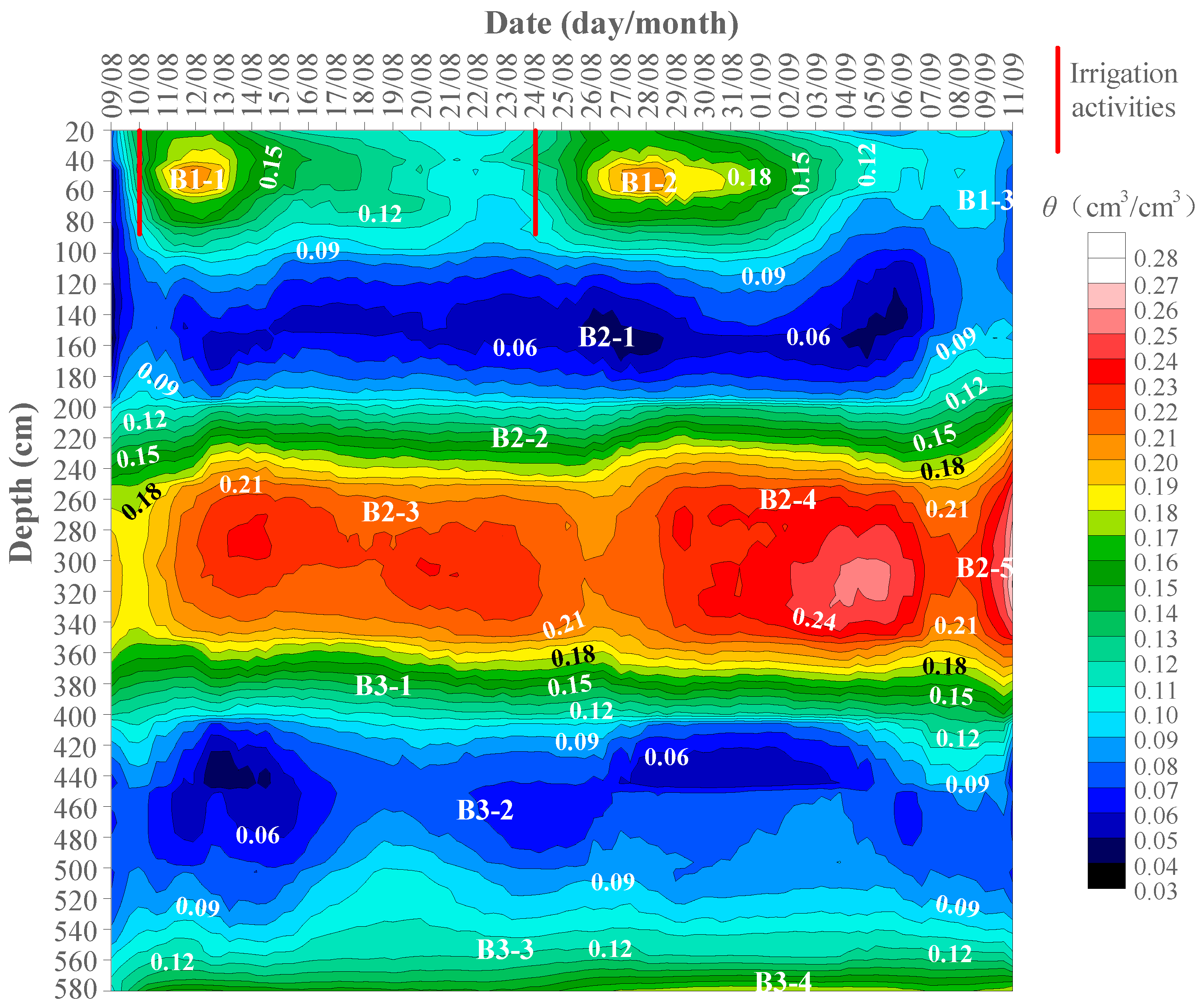
3.4. Spatial–Temporal Variation of the Layered Soils and Sediments Moistures
3.4.1. Variation of Soil Moisture Content with Time within 1 m
3.4.2. Variation of Soil Water Content with Time within 1–3 m
3.4.3. Variation of Soil Moisture Content with Time below 3 m
3.5. Infiltration Pattern and Stage Characteristics
3.6. Limitations and Future Research
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Depth | Soil Particle Composition (%) | Soil Texture | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Initial Water Content (cm3/cm3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Clay | Silt | ||||
| 4# | ||||||
| 0–20 | 57.4 | 5.9 | 36.7 | Sandy loam | 1.61 | 0.23 |
| 20–40 | 75.7 | 3.3 | 21.0 | Loamy sand | 1.58 | 0.18 |
| 40–60 | 26.4 | 15.1 | 58.5 | Silt loam | 1.51 | 0.21 |
| 60–80 | 83.2 | 2.8 | 14.0 | Loamy sand | 1.58 | 0.20 |
| 80–100 | 60.3 | 8.2 | 31.5 | Sandy loam | 1.61 | 0.16 |
| 100–200 | 89.5 | 1.6 | 8.9 | Sand | 1.52 | 0.12 |
| 200–250 | 77.7 | 3.7 | 18.6 | Loamy sand | 1.58 | 0.13 |
| 250–400 | 89.9 | 1.3 | 8.8 | Sand | 1.52 | 0.16 |
| 400–425 | 81.4 | 2.1 | 16.5 | Loamy sand | 1.58 | 0.22 |
| 9# | ||||||
| 0–20 | 85.7 | 2.0 | 12.3 | Sand | 1.49 | 0.12 |
| 20–40 | 50.9 | 4.3 | 44.8 | Sandy loam | 1.61 | 0.18 |
| 40–200 | 93.7 | 1.0 | 5.3 | Sand | 1.52 | 0.10 |
| 200–250 | 1.6 | 16.3 | 82.1 | Silt loam | 1.51 | 0.19 |
| 250–280 | 83.6 | 2.4 | 14.0 | Loamy sand | 1.58 | 0.26 |
| 280–300 | 43.3 | 13.1 | 43.6 | Loam | 1.50 | 0.13 |
| 300–350 | 64.5 | 3.8 | 31.7 | Sandy loam | 1.61 | 0.25 |
| 350–580 | 96.5 | 0.0 | 3.5 | Sand | 1.52 | 0.08 |
| 17# | ||||||
| 0–40 | 6.0 | 18.5 | 75.5 | Silt loam | 1.51 | 0.34 |
| 40–60 | 0.0 | 28.4 | 71.6 | Silt clay loam | 1.56 | 0.33 |
| 60–250 | 12.6 | 16.5 | 70.9 | Silt loam | 1.51 | 0.37 |
| 250–300 | 80.8 | 3.6 | 15.6 | Loamy sand | 1.58 | 0.22 |
| 300–500 | 92.2 | 0.9 | 6.9 | Sand | 1.52 | 0.38 |
References
- Han, D. Knowledge of a few issues on oasis. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 1995, 9, 13–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postel, S. The Last Oasis: Facing Water Scarcity; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Shen, Y. Water and ecological security: Dealing with hydroclimatic challenges at the heart of China’s Silk Road. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Luo, G.; Hamdi, R.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Maeyer, P.D.; Kurban, A. Numerical simulations of the impacts of mountain on oasis effects in arid Central Asia. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, K.; Zhou, Y. Progress in the study of oasis-desert interactions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230–231, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yu, P.; Ling, H. Oasis evolution and water resource utilization of a typical area in the inland river basin of an arid area: A case study of the Manas River valley. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Yang, M.; Li, S. Groundwater level prediction for the arid oasis of Northwest China based on the artificial bee colony algorithm and a back-propagation neural network with double hidden layers. Water 2019, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, F.; Decheng, L.; Yuguo, Z.; Jinling, Y. Modeling spatio–temporal distribution of soil moisture by deep learning-based cellular automata model. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 734–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, Q. Geostatistical analysis of temporal and spatial variations in groundwater levels and quality in the Minqin oasis, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Huo, Z.; Feng, S.; Mao, X.; Kang, S.; Jin, C.; Xu, J.; Steenhuis, T.S. Evaluation of spatial interpolation methods for groundwater level in an arid inland oasis, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; He, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, L. Quantifying the impacts of land use/land cover change on groundwater depletion in Northwestern China—A case study of the Dunhuang oasis. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, W. The spatio–temporal variability of groundwater depth in a typical desert-oasis ecotone. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 124, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S. Land use/cover change impacts on water table change over 25 years in a desert-oasis transition zone of the Heihe River Basin, China. Water 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Zhang, Y.D.; Chu, Y.; Shi, Q.D.; Pan, X. Primary analysis on groundwater, soil moisture and salinity in Fukang oasis of Southern Junggar Basin. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Z.; Sai, J. Relationship between soil salinization and groundwater hydration in Yaoba Oasis, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, F.; Li, J.; Gu, Q.; Yang, S.; Wu, D.; Feng, J.; Ding, J. Characterizing and modeling regional-scale variations in soil salinity in the arid oasis of Tarim Basin, China. Geoderma 2017, 305, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Gao, G.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y. Soil water content variations and hydrological relations of the cropland-treebelt-desert land use pattern in an oasis-desert ecotone of the Heihe River Basin, China. Catena 2014, 123, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucco, G.; Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Influence of land use on soil moisture spatial–temporal variability and monitoring. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, M. Temporal stability analysis identifies soil water relations under different land use types in an oasis agroforestry ecosystem. Geoderma 2016, 271, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shao, M. Temporal stability of soil moisture in an oasis of northwestern China. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 2725–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shao, M.A. Temporal stability of surface soil moisture in a desert area of northwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.X.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Hu, R. Spatio-temporal variability of root zone soil moisture in artificially revegetated and natural ecosystems at an arid desert area, NW China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 79, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, F. Statistical analysis of the temporal stability of soil moisture in three desert regions of northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, D.; Fan, J.; Wang, Q. Spatiotemporal variability of surface-soil moisture of land uses in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, A.; Maeyer, P.D. The Spatiotemporal Response of Soil Moisture to Precipitation and Temperature Changes in an Arid Region, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Lu, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Sai, J.; Liu, X. Application of HYDRUS-1D model for research on irrigation infiltration characteristics in arid oasis of Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starks, P.J.; Heathman, G.C.; Jackson, T.J.; Cosh, M.H. Temporal stability of soil moisture profile. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Shao, M.; Jia, X. Spatial pattern of soil moisture and its temporal stability within profiles on a loessial slope in northwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 495, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evett, S.R.; Schwartz, R.C.; Tolk, J.A.; Howell, T.A. Soil profile water content determination: Spatiotemporal variability of electromagnetic and neutron probe sensors in access tubes. Vadose Zone J. 2009, 8, 926–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Duan, Z.; Wang, N. Spatio-temporal variability in remotely sensed surface soil moisture and its relationship with precipitation and evapotranspiration during the growing season in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Hao, X.; Kang, S. Spatiotemporal variability of soil moisture as affected by soil properties during irrigation cycles. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Wang, Z.; Hao, J. Application of regression isogram to dynamic analysis of soil moisture variations with time and space. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 1997, 31, 112–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J. Temporal and spatial variability of red soil water under different ground covers by regression isogram. J. Irrig. Drain. 2009, 28, 90–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics of the preferential flow and its response to irrigation amount in oasis cropland. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 1454–1460. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhao, W.; Yan, J. A review of researches of preferential flow in desert-oasis region. J. Desert Res. 2017, 37, 1189–1195. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, J.M.; Flury, M. Uniform and preferential flow mechanisms in the vadose zone. In Conceptual Models of Flow and Transport in the Fractured Vadose Zone; National Research Council, Ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 149–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, A.L.; Shein, E.V.; Skvortsova, E.B. Tomography of soil pores: From morphological characteristics to structural–functional assessment of pore space. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lin, W.; Wang, G. Appling dyeing tracer to investigate patterns of soil water flow and quantify preferential flow in soil columns. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 82–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shein, E.V.; Devin, B.A. Current problems in the study of colloidal transport in soil. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2007, 40, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Wang, B.; Lu, X.; Wang, X. Relationship between soil macropore and preferential flow in citrus garden. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 32, 75–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shein, E.V.; Shcheglov, D.I.; Moskvin, V.V. Simulation of water permeability processes in chernozems of the Kamennaya Steppe. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2012, 45, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shein, E.V.; Skvortsova, E.B.; Dembovetskii, A.V.; Abrosimov, K.N.; Il’In, L.I.; Shnyrev, N.A. Pore-size distribution in loamy soils: A comparison between microtomographic and capillarimetric determination methods. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2016, 49, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Fu, L. Soil macropore characteristics following conversion of native desert soils to irrigated croplands in a desert-oasis ecotone, Northwest China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 168, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; He, J.; Fu, L. Soil susceptibility to macropore flow across a desert-oasis ecotone of the Hexi Corridor, Northwest China. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodhinayake, W.; Si, B.C.; Noborio, K. Determination of hydraulic properties in sloping landscapes from tension and double-ring infiltrometers. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Study on the Infiltration Law of the Irrigation Water in the Yaoba Oasis; Chang’an University: Xi’an, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhijie, L. Analysis on the Utilization Efficiency of Agricultural Water Resources in Yaoba Irrigation Area, Alxa; Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: Hohhot, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Yang, X. ArcGIS: Spatial Analysis Experiment Tutorial of Geographical Information System, 2nd ed.; Geographic Information Systems Theory and Applications Series; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nam, M.-D.; Thanh, T.-C. Numerical solution of Navier–Stokes equations using multiquadric radial basis function networks. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2001, 37, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.; Darboux, F.; Bourennane, H.; Leguédois, S.; Silvera, N.; Phachomphon, K. Accuracy of interpolation techniques for the derivation of digital elevation models in relation to landform types and data density. Geomorphology 2006, 77, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiq, M.W.; Zhao, C.; Ni, J.; Akhtar, M. GIS-based high-resolution spatial interpolation of precipitation in mountain–plain areas of Upper Pakistan for regional climate change impact studies. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.J. Tobler’s first law and spatial analysis. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2004, 94, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, N. Tobler’s first law of geography. In The International Encyclopedia of Geography; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fang, Z.; Wei, Y. Suppressing end effect of EMD based on local polynomial regression. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China 2014, 44, 786–792. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, H.; Pan, F.; Wu, L.; Tang, Y. Spatial variability of precipitation for mountain-oasis-desert system in the Sangong River Basin. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Ren, J.; Fan, W.; Lu, N.; Dong, X. Evaluation on dynamic change and interrelations of ecosystem services in a typical mountain-oasis-desert region. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Huang, W.; Teng, F.; Wang, B.; Ni, K.; Zheng, C. Spatial variations of river–groundwater interactions from upstream mountain to midstream oasis and downstream desert in Heihe River basin, China. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Gui, D.; Lei, J.; Sun, H.; Zeng, F.; Mao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Q.; Liu, Y. Oasis microclimate effects under different weather events in arid or hyper arid regions: A case analysis in southern Taklimakan desert and implication for maintaining oasis sustainability. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 8, 2567–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszkiewicz, M.; Najm, M.A.; Beysens, D.; Alameddine, I.; El-Fadel, M. Dew as a sustainable non-conventional water resource: A critical review. Environ. Rev. 2015, 23, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, W. Dew formation and its variation in Haloxylon ammodendron plantations at the edge of a desert oasis, northwestern China. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2017, 247, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W. Dew yield and its influencing factors at the western edge of Gurbantunggut Desert, China. Water 2019, 11, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jia, Z.; Lu, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhi, W. Dew condensation time and frequency in the loess hilly region of Ansai County, northern Shaanxi Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jia, Z.; Wang, Z. Dew amount and its inducing factors in the loess hilly region of northern Shaanxi Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 3703–3710. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Characteristics of dew formation in the semi-arid Loess Plateau of Central Shaanxi Province, China. Water 2019, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, M.A.; Liu, Z.; Warrington, D.N. Regional spatial pattern of deep soil water content and its influencing factors. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, M.A.; Liu, Z. Vertical distribution and influencing factors of soil water content within 21-m profile on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geoderma 2013, 193–194, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, G.; Wang, G.; Kang, S.; Luo, H.; Zhang, D. China’s Main Crop Water Demand and Irrigation; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 1995. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, C.; Lin, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, G.; Zhang, F. Quantifying the preferential flow by dye tracer in the North China Plain. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 26, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ID | Calibration Equation | R² | Application Scope (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4# | = 0.000064Cn − 0.147965 | 0.85 | 0–80 |
| = 0.000864Cn − 2.927056 | 0.96 | 80–400 | |
| 9# | = 0.000049Cn − 0.102161 | 0.81 | 0–150 |
| = 0.000038Cn − 0.047073 | 0.82 | 150–200 | |
| = 0.000027Cn − 0.016861 | 0.84 | 200–350 | |
| = 0.000016Cn − 0.014855 | 0.81 | 350–550 | |
| 17# | = 0.000036Cn + 0.008491 | 0.95 | 0–250 |
| = 0.000070Cn − 0.189922 | 0.90 | 250–513 |
| ID | Crop Types | Observation Period | Irrigation Activities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Date | End Date | First Time | Second Time | ||
| 4# | edamame | 14 August 2015 | 11 September 2015 | 17 August 2015 | 31 August 2015 |
| 9# | corn | 09 August 2015 | 11 September 2015 | 10 August 2015 | 24 August 2015 |
| 17# | millet | 15 August 2015 | 11 September 2015 | 16 August 2015 | 3 September 2015 |
| ID | Regression Equation | R2 | F | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4# | 0.63 | 64.76 | 0.00000 | |
| 9# | 0.29 | 5.58 | 0.00005 | |
| 17# | 0.53 | 51.42 | 0.00000 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Fan, W.; Pan, W. Influencing Factors of the Spatial–Temporal Variation of Layered Soils and Sediments Moistures and Infiltration Characteristics under Irrigation in a Desert Oasis by Deterministic Spatial Interpolation Methods. Water 2019, 11, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071483
Li X, Lu Y, Zhang X, Zhang R, Fan W, Pan W. Influencing Factors of the Spatial–Temporal Variation of Layered Soils and Sediments Moistures and Infiltration Characteristics under Irrigation in a Desert Oasis by Deterministic Spatial Interpolation Methods. Water. 2019; 11(7):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071483
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Yudong Lu, Xiaozhou Zhang, Rong Zhang, Wen Fan, and Wangsheng Pan. 2019. "Influencing Factors of the Spatial–Temporal Variation of Layered Soils and Sediments Moistures and Infiltration Characteristics under Irrigation in a Desert Oasis by Deterministic Spatial Interpolation Methods" Water 11, no. 7: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071483
APA StyleLi, X., Lu, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, R., Fan, W., & Pan, W. (2019). Influencing Factors of the Spatial–Temporal Variation of Layered Soils and Sediments Moistures and Infiltration Characteristics under Irrigation in a Desert Oasis by Deterministic Spatial Interpolation Methods. Water, 11(7), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071483