Efficacy of Inactivation of Human Enteroviruses by Dual-Wavelength Germicidal Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
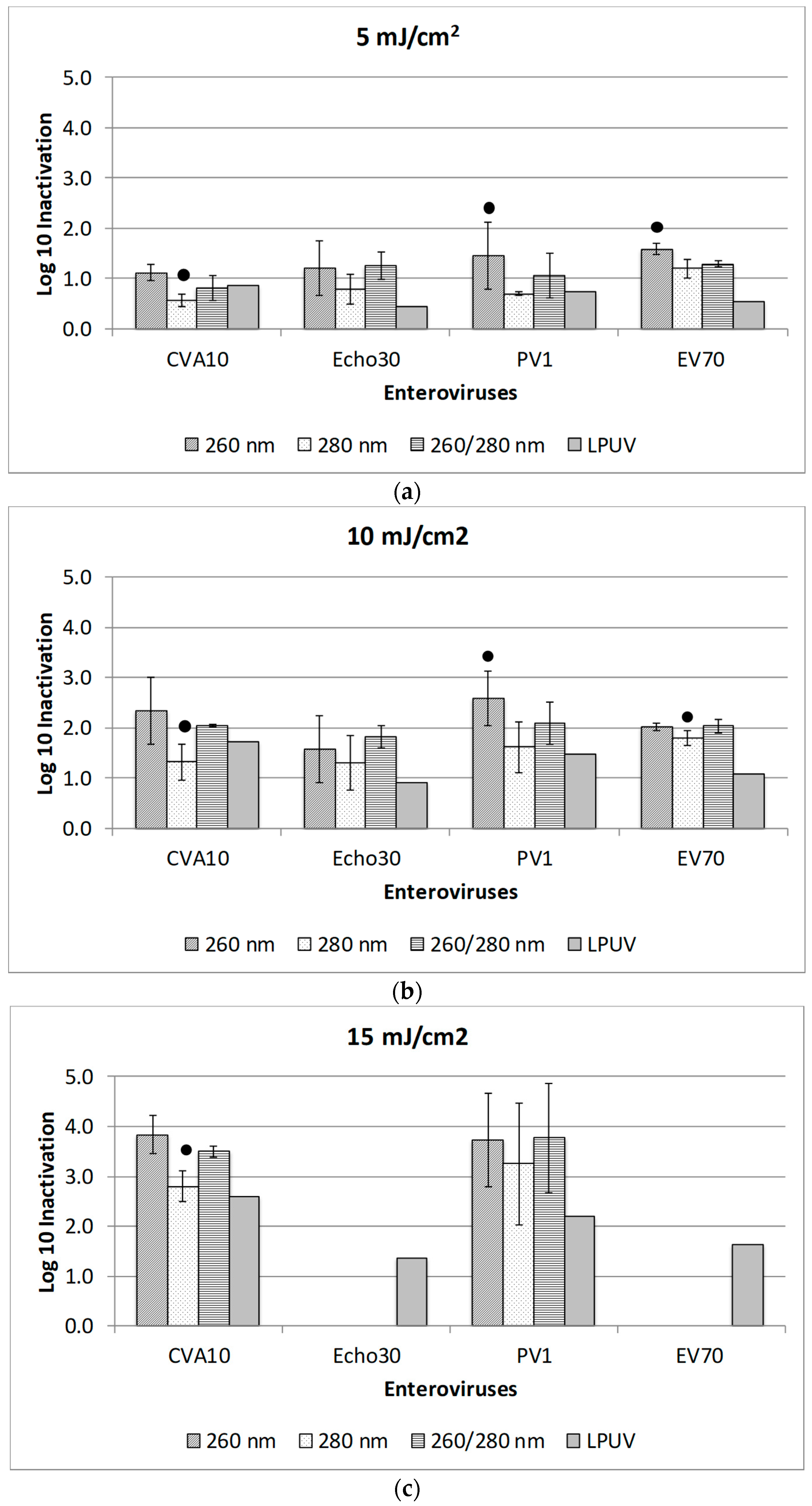
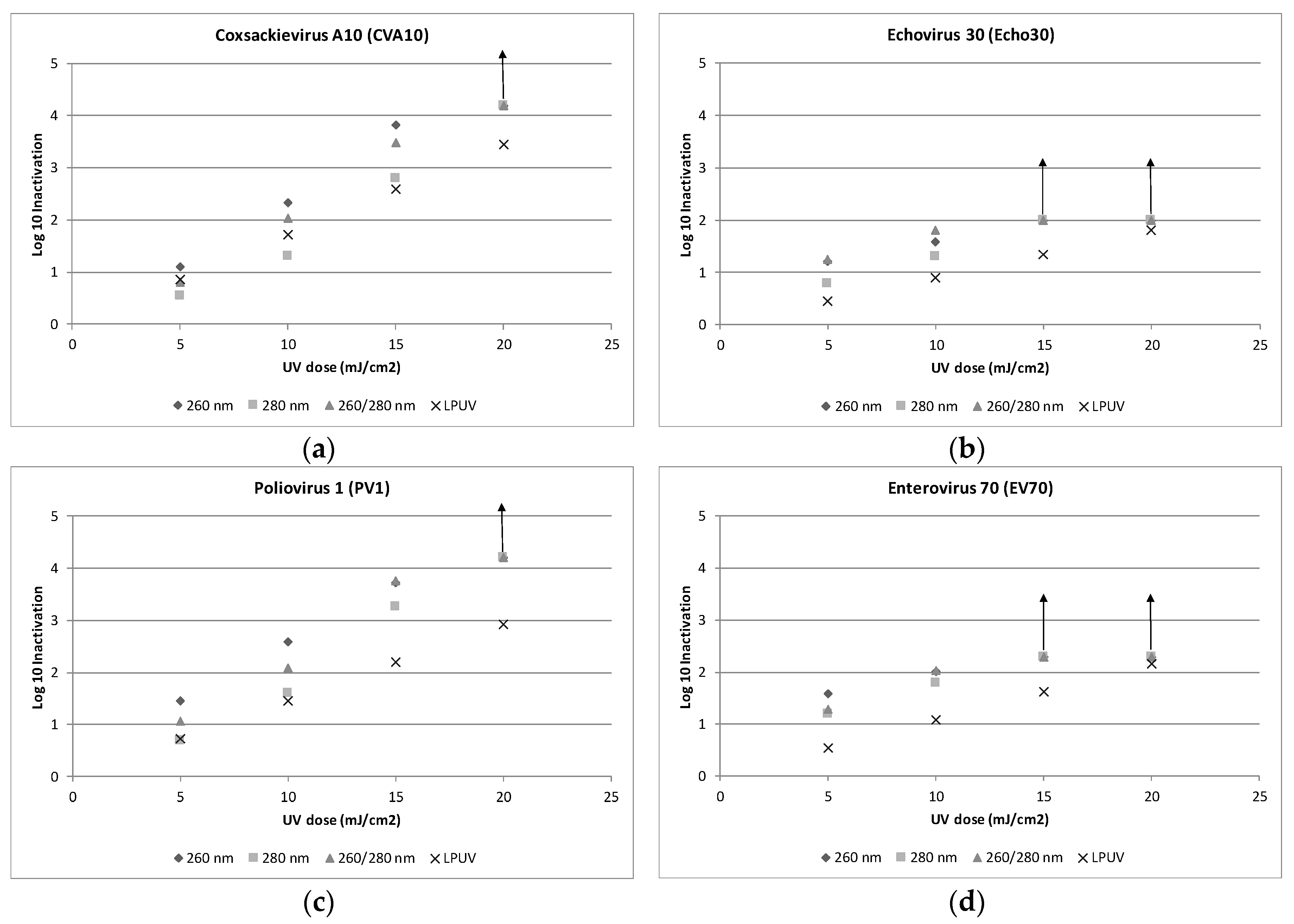
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Greninger, A.L.; Naccache, S.N.; Messacar, K.; Clayton, A.; Yu, G.; Somasekar, S.; Federman, S.; Stryke, D.; Anderson, C.; Yagi, S.; et al. A novel outbreak enterovirus D68 strain associated with acute flaccid myelitis cases in the USA (2012–14): A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F. Enterovirus D68: Acute respiratory illness and the 2014 outbreak. Emerg. Med. Clinucs N. Am. 2015, 33, e19–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-Polio Enterovirus. 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/non-polio-enterovirus/index.html (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Global Health—Global Disease Detection and Emergency Response. 2012. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/healthprotection/gdd/resources/factsheets.html (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Okoh, A.I.; Sibanda, T.; Gusha, S.S. Inadequately treated wastewater as a source of human enteric viruses in the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2620–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, J.; Leonard, M.; Greening, G.; Lewis, G. Influence of wastewater treatment process and the population size on human virus profiles in wastewater. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6267–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, N.E.; Fout, G.S.; Keely, S.P. Retrospective surveillance of wastewater to examine seasonal dynamics of enterovirus infections. mSphere 2017, 2, e00099-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List 4-Final. 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ccl/chemical-contaminants-ccl-4 (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Bolton, J.R.; Cotton, C.A. The Ultraviolet Disinfection Handbook; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2008; ISBN 9781583215845. [Google Scholar]
- Hijnen, W.A.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Medema, G.J. Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (oo)cysts in water: A review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckhow, D.A.; Linden, K.G.; Kim, J.; Shemer, H.; Makdissy, G. Effect of UV treatment on DBP formation. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2010, 102, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, G.Y.; Roser, D.; Corkish, R.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Stuetz, R. Point-of-use water disinfection using ultraviolet and visible light-emitting diodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilhunen, S.; Särkkä, H.; Sillanpää, M. Ultraviolet light-emitting diodes in water disinfection. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterley, C.; Linden, K. Demonstration and evaluation of germicidal UV-LEDs for point-of-use water disinfection. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eischeid, A.C.; Linden, K.G. Molecular Indications of Protein Damage in Adenoviruses after UV Disinfection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Würtele, M.A.; Kolbe, T.; Lipsz, M.; Külberg, A.; Weyers, M.; Kneissl, M.; Jekel, M. Application of GaN-based ultraviolet-C light emitting diodes—UV LEDs—For water disinfection. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguma, K.; Kita, R.; Sakai, H.; Murakami, M.; Takizawa, S. Application of UV light emitting diodes to batch and flow-through water disinfection systems. Desalination 2013, 328, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.E.; Rodriguez, R.A.; Linden, K.G.; Hargy, T.M.; Larason, T.C.; Wright, H.B. Wavelength dependent UV inactivation and DNA damage of adenovirus as measured by cell culture infectivity and long range quantitative PCR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Loeb, S.; Kim, J.-H. LED revolution: Fundamentals and prospects for UV disinfection applications. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Z.; Craik, S.A.; Bolton, J.R. Comparison of the action spectra and relative DNA absorbance spectra of microorganisms: Information important for the determination of germicidal fluence (UV dose) in an ultraviolet disinfection of water. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5087–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowker, C.; Sain, A.; Shatalov, M.; Ducoste, J. Microbial UV fluence-response assessment using a novel UV-LED collimated beam system. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevremont, A.C.; Farnet, A.M.; Coulomb, B.; Boudenne, J.L. Effect of coupled UV-A and UV-C LEDs on both microbiological and chemical pollution of urban wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguma, K.; Rattanakul, S.; Bolton, J.R. Application of UV light-emitting diodes to adenovirus in water. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Mohseni, M.; Taghipour, F. Application of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) for water disinfection: A review. Water Res. 2016, 94, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanakul, S.; Oguma, K. Inactivation kinetics and efficiencies of UV-LEDs against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Legionella pneumophila, and surrogate microorganisms. Water Res. 2018, 130, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.E.; Ryu, H.; Boczek, L.A.; Cashdollar, J.L.; Jeanis, K.M.; Rosenblum, J.S.; Lawal, O.R.; Linden, K.G. Evaluating UV-C LED disinfection performance and investigating potential dual-wavelength synergy. Water Res. 2017, 109, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICTV (International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses). Virus Taxonomy: The Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses, the Online (10th) Report of the ICTV-Master Species Lists. 2017. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports/ictv_online_report (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Dahling, D.R.; Wright, B.A. Optimization of the BGM cell line culture and viral assay procedures for monitoring viruses in the environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1986, 51, 790–812. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolton, J.R.; Linden, K.G.L. Standardization of methods for fluence (UV dose) determination in bench-scale uv experiments. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, K.G.; Darby, J.L. Estimating effective germicidal dose from medium-pressure UV lamps. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.K.; Ryu, H.; Gerrity, D.; Abbaszadegan, M. Development and validation of an integrated cell culture-qRTPCR assay for simultaneous quantification of coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and polioviruses in disinfection studies. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryu, H.; Schrantz, K.A.; Brinkman, N.E.; Boczek, L.A. Applicability of integrated cell culture reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR (ICC-RTqPCR) for the simultaneous detection of the four human enteric enterovirus species in disinfection studies. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 258, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerba, C.P.; Gramos, D.M.; Nwachuku, N. Comparative inactivation of enteroviruses and adenovirus 2 by UV light. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5167–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamane-Gravetz, H.; Linden, K.G.; Cabaj, A.; Sommer, R. Spectral sensitivity of Bacillus subtilis spores and MS2 coliphage for validation testing of ultraviolet reactors for water disinfection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7845–7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.E.; Rodriguez, R.A.; Hawkins, M.A.; Hargy, T.M.; Larason, T.C.; Linden, K.G. Comparison of UV-induced inactivation and RNA damage in MS2 phage across the germicidal UV spectrum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, F.L. A study of the bactericidal action of ultra violet light: III. the absorption of ultra violet light by bacteria. J. Gen. Physiol. 1930, 14, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eischeid, A.C.; Meyer, J.N.; Linden, K.G. UV disinfection of adenoviruses: Molecular indications of DNA damage efficiency. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harm, W. Biological Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, S.E.; Hull, N.M.; Poepping, C.; Linden, K.G. Wavelength-Dependent Damage to Adenoviral Proteins Across the Germicidal UV Spectrum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, H.; Beck, S.E.; Boczek, L.A.; Carlson, K.M.; Brinkman, N.E.; Linden, K.G.; Lawal, O.R.; Hayes, S.L.; Ryu, H. Efficacy of Inactivation of Human Enteroviruses by Dual-Wavelength Germicidal Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Water 2019, 11, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061131
Woo H, Beck SE, Boczek LA, Carlson KM, Brinkman NE, Linden KG, Lawal OR, Hayes SL, Ryu H. Efficacy of Inactivation of Human Enteroviruses by Dual-Wavelength Germicidal Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Water. 2019; 11(6):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061131
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Hyoungmin, Sara E. Beck, Laura A. Boczek, Kelsie M. Carlson, Nichole E. Brinkman, Karl G. Linden, Oliver R. Lawal, Samuel L. Hayes, and Hodon Ryu. 2019. "Efficacy of Inactivation of Human Enteroviruses by Dual-Wavelength Germicidal Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)" Water 11, no. 6: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061131
APA StyleWoo, H., Beck, S. E., Boczek, L. A., Carlson, K. M., Brinkman, N. E., Linden, K. G., Lawal, O. R., Hayes, S. L., & Ryu, H. (2019). Efficacy of Inactivation of Human Enteroviruses by Dual-Wavelength Germicidal Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Water, 11(6), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061131





