Is Flood Irrigation a Potential Driver of River-Groundwater Interactions and Diffuse Nitrate Pollution in Agricultural Watersheds?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
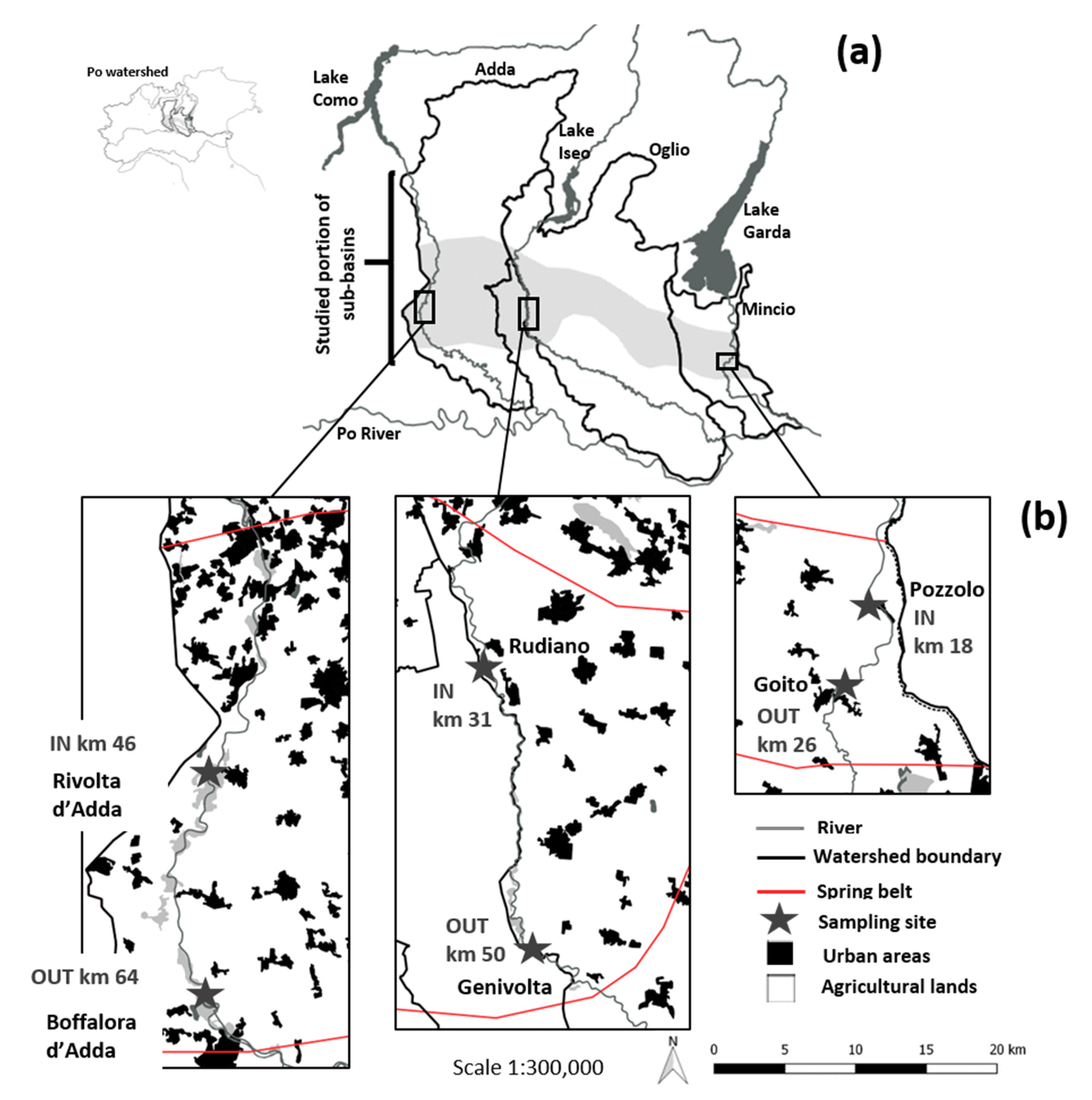
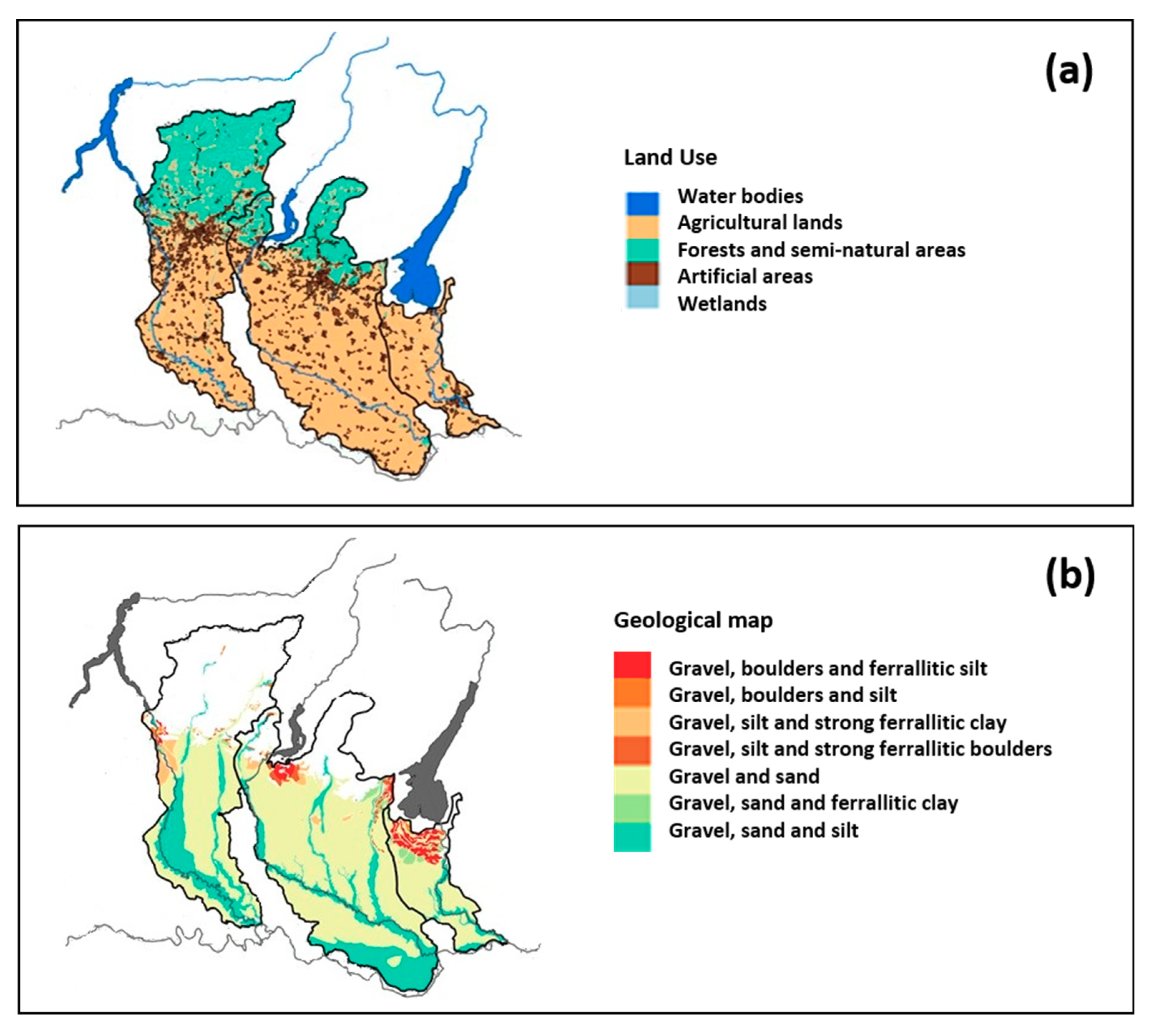
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Flow, Use, Precipitation, and Associated N Loads Calculation
2.3. Nitrogen Mass Balance Calculations at the Watershed Level
2.4. Water and N Mass Budgets along River Reaches Interacting with Groundwater: Sampling Strategies, Analytical Techniques, and Calculations
3. Results
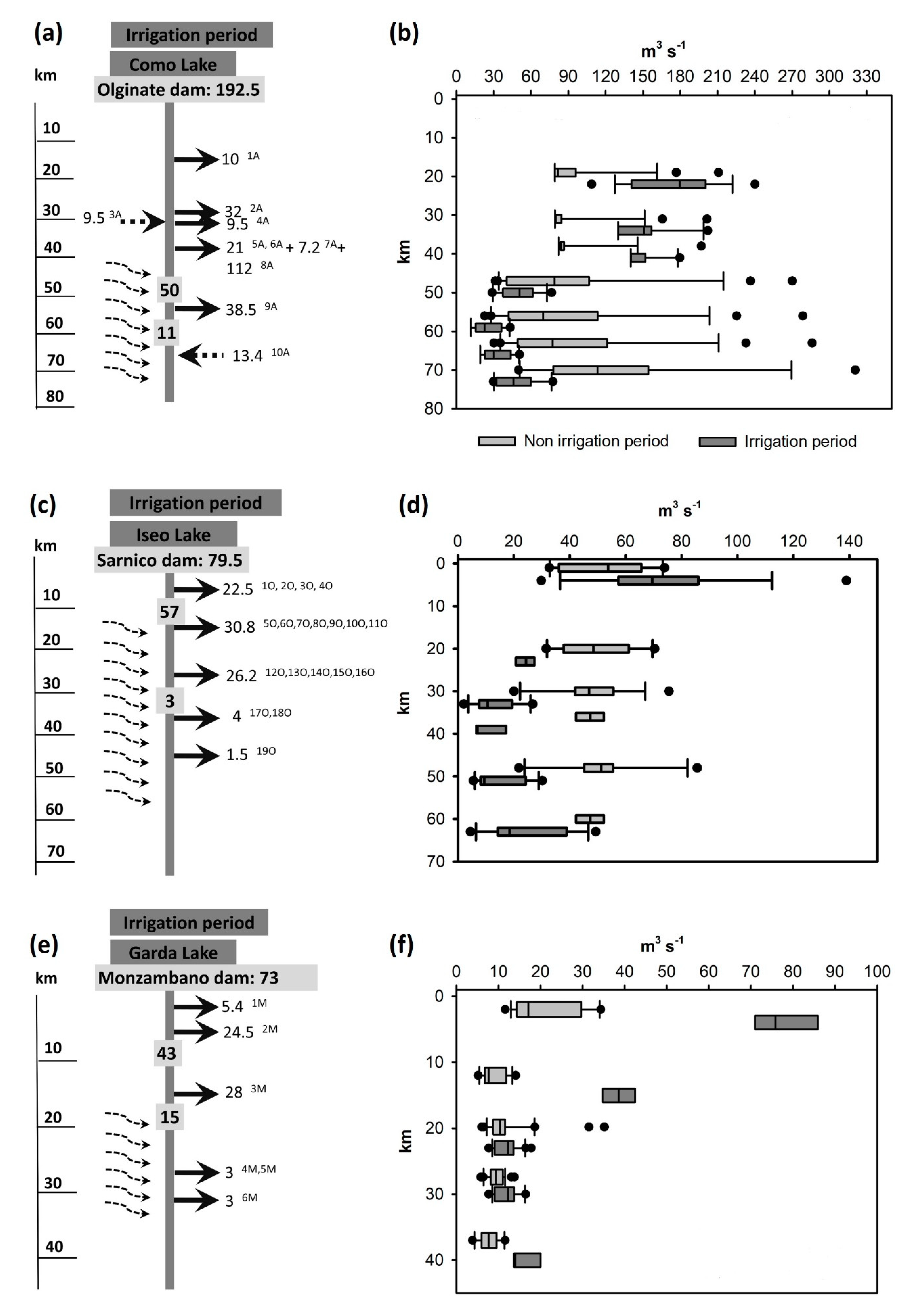
3.1. Precipitation, Water Flow, and Water Abstraction
3.2. NO3− Concentration and Electrical Conductivity
3.3. Nitrogen Mass Balances at the Watershed Scale
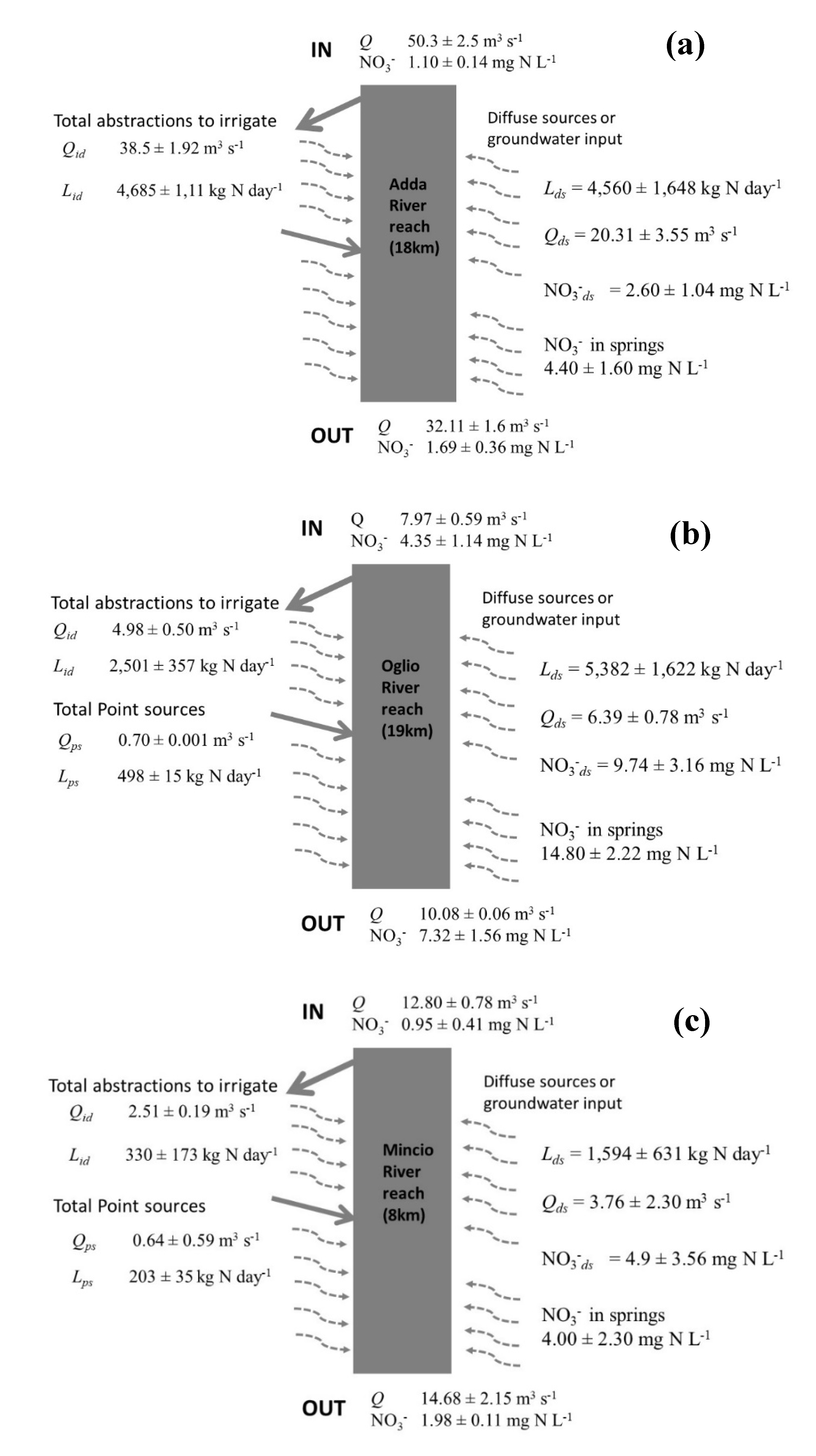
3.4. River-Groundwater Interactions: Water and N Mass Budgets and Estimated N Inputs from Groundwater
4. Discussion
4.1. Irrigation as an Important Component of the Hydrological Cycle in the Adda, Oglio, and Mincio Rivers
4.2. Excess Manure Availability and Use of Synthetic Fertilizers Result in Diffuse N Pollution in the Three Basins
4.3. Linking Irrigation and N Excess to Interpret N Mass Transfer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seizinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the Nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overeem, I.; Kettner, A.J.; Syvitski, J.P.M. 9.40 Impacts of Humans on River Fluxes and Morphology. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Shroder, J.F., Wohl, E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 828–842. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, M.; Howard, C. The European Nitrogen Assessment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barakata, M.; Cheviron, B.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R. Influence of the irrigation technique and strategies on the nitrogen cycle and budget: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Ward, M.H.; Benjamin, N.; De Kok, T.M. Does the evidence about health risks associated with nitrate ingestion warrant an increase of the nitrate standard for drinking water? Environ. Health 2006, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivett, M.O.; Buss, S.R.; Morgan, P.; Smith, J.W.N.; Bemment, C.D. Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: A review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4215–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, R.; Chan, F.; Conley, D.J.; Garnier, J.; Doney, S.C.; Marino, R.; Billen, G. Coupled biogeochemical cycles: Eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, C.M.; Pérez-Blanco, C.D. Simple Myths and Basic Maths About Greening Irrigation. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4035–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Sahagian, D. Anthropogenic disturbance of the terrestrial water cycle. Bioscience 2000, 50, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2000, 327, 22. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Directive 2006/118/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 December 2006 on the protection of groundwater against pollution and deterioration. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2006, 372, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Lassaletta, L.; García-Gómez, H.; Gimeno, B.S.; Rovira, J.V. Agriculture-induced increase in nitrate concentrations in stream waters of a large Mediterranean catchment over 25 years (1981–2005). Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6034–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Racchetti, E.; Delconte, C.A.; Sacchi, E.; Soana, E.; Laini, A.; Longhi, D.; Viaroli, P. Nitrogen balance and fate in a heavily impacted watershed (Oglio River, Northern Italy): In quest of the missing sources and sinks. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailhol, J.; Ruelle, P.; Nemeth, I. Impact of fertilisation practices on nitrogenleaching under irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2001, 20, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, M.E.; Clemente, R.S.; Gupta, A.D.; Loof, R.; Hansen, G.K. Impacts of fertigation via sprinkler irrigation on nitrate leaching and corn yield in an acid—Sulphate soil in Thailand. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 52, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, T.; Atallah, T.; Hajhasan, S.; Chranek, A. Management of nitrogen by fertigation of potato in Lebanon. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2003, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotarelli, L.; Scholberg, J.M.; Dukes, M.D.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Monitoring of nitrate leaching in Sandy soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burguete, J.; Zapata, N.; García-Navarro, P.; Maïkaka, M.; Playán, E.; Murillo, J. Fertigation in furrows and level furrow systems. II: Field experiments, modelcalibration, and practical applications. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 135, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, I.; Mailhol, J.C.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R.; Bouarfa, S.; Ruelle, P. Effect oftemporal variability in soil hydraulic properties on simulated water transferunder high-frequency drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotarelli, L.; Dukes, M.D.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Soil water distribution and nitrate leaching of drip irrigation controlled by soil moisture sensors. In Estudios en la Zona no Saturada del Suelo vol. IX; Silva, O., Carrera Ramírez, J., Eds.; Barcelona, 2009; Available online: https://abe.ufl.edu/faculty/carpena/zns/index_volumenes.shtml (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Perego, A.; Basile, A.; Bonfante, A.; De Mascellis, R.; Terribile, F.; Brenna, S.; Acutis, M. Nitrate leaching undermaize cropping systems in Po Valley (Italy). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 147, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunke, M.; Gonser, T. The ecological significance of exchange processes between rivers and groundwater. Freshwater Biol. 1997, 37, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M. Interactions between groundwater and surface water: The state of the science. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrela, P.; Petelet-Girauda, E.; Barbiera, J.; Gautier, E. Surface water–groundwater interactions in an alluvial plain: Chemical and isotopic systematics. J. Hydrol. 2003, 277, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.H.; Krause, S.; Hannah, D.M.; Boano, F. Groundwater-surface water interactions: New methods and models to improve understanding of processes and dynamics. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delconte, C.A.; Sacchi, E.; Racchetti, E.; Bartoli, M.; Mas-Pla, J.; Re, V. Nitrogen inputs to a river course in a heavily impacted watershed: A combined hydrochemical and isotopic evaluation (Oglio River Basin, N Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menció, A.; Galan, M.; Boix, D.; Mas-Pla, J. Analysis of stream-aquifer relationships: A comparison between mass balance and Darcy’s law approaches. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravazzani, G.; Curti, D.; Gattinoni, P.; Della Valentina, S.; Fiorucci, A.; Rosso, R. Assessing Groundwater Contribution to Streamflow of a Large Alpine River with Heat Tracer Methods and Hydrological Modelling. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivkovic, K.M. A top–down approach to characterise aquifer–river interaction processes. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, L.W. Groundwater Resources Sustainability: Past, Present, and Future. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4409–4424. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín, M.A.; Estrela, T.; Andreu, J.; Ferrer, J. Modeling Water Resources and River-Aquifer Interaction in the Júcar River Basin, Spain. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4337–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitta, M.; Fracchiolla, D.; Aravena, R.; Barbieri, M. Application of isotopic and geochemical tools for the evaluation of nitrogen cycling in an agricultural basin, the Fucino Plain, Central Italy. J. Hydrol. 2009, 372, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, J.S.; Brown, C.M. Detecting groundwater contamination of a river in Georgia, USA using baseflow sampling. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y. Estimation of shallow groundwater discharge and nutrient load into a river. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 38, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caschetto, M.; Barbieri, M.; Galassi, D.M.P.; Mastrorillo, L.; Rusi, S.; Stoch, F.; Di Cioccio, A.; Petitta, M. Human alteration of groundwater-surface water interactions (Sagittario River, Central Italy): Implication for flow regime, contaminant fate and invertebrate response. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1791–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellato, L.; Newman, B.D. Groundwater inputs to rivers: Hydrological, biogeochemical and ecological effects inferred by environmental isotopes. In Application of Isotope Techniques for Assessing Nutrient Dynamics in River Basins; IAEA-TECDOC-1695; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 187–217. [Google Scholar]
- Nestler, A.; Berglund, M.; Accoe, F.; Duta, S.; Xue, D.; Boeckx, P.; Taylor, P. Isotopes for improved management of nitrate pollution in aqueous resources: Review of surface water field studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccon, P.; Leis, A.; Marca, A.; Kaiser, J.; Campisi, L.; Böttcher, M.E.; Savarino, J.; Escherd, P.; Eisenhauere, A.; Erblandc, J. Multi-isotope approach for the identification and characterisation of nitrate pollution sources in the Marano lagoon (Italy) and parts of its catchment area. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 34, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotiroti, M.; Bonomi, T.; Sacchi, E.; McArthur, J.M.; Stefania, G.A.; Zanotti, C.; Taviani, S.; Patelli, M.; Nava, V.; Soler, V.; et al. The effects of irrigation on groundwater quality and quantity in a human-modified hydro-system: The Oglio River basin, Po Plain, northern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchi, E.; Acutis, M.; Bartoli, M.; Brenna, S.; Delconte, C.A.; Laini, A.; Pennisi, M. Origin and fate of nitrates in groundwater from the central Po plain: Insights from isotopic investigations. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 34, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardy Region. Piano di Tutela Delle Acque 2016 (Water Protection Plan). Available online: https://www.regione.lombardia.it/wps/portal/istituzionale/HP/DettaglioRedazionale/servizi-e-informazioni/Enti-e-Operatori/territorio/governo-delle-acque/piano-tutela-acque-pta-2016/piano-tutela-acque-pta-2016 (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Decision 2011/721/EU of 3 November 2011 on Granting a Derogation Requested by Italy with Regard to the Regions of Emilia Romagna, Lombardia, Piemonte and Veneto pursuant to Council Directive 91/676/EEC concerning the Protection of Waters Against Pollution Caused by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources. 2011, p. 36. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32011D0721 (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/1040 of 24 June 2016 on Granting a Derogation Requested by Italian Republic with Regard to the Regions of Lombardia and Piemonte Pursuant to Council Directive 91/676/EEC concerning the Protection of Waters Against Pollution Caused by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources. 2016, p. 6. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2016.169.01.0006.01.ENG&toc=OJ:L:2016:169:TOC (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Facchi, A.; Ortuani, B.; Maggi, D.; Gandolfi, C. Coupled SVAT–groundwater model for water resources simulation in irrigated alluvial plains. Environ. Model. Softw. 2004, 19, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, C.; Facchi, A.; Maggi, D. Comparison of 1D models of water flow in unsaturated soils. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassena, C.; Rienzner, M.; Ponzini, G.; Giudici, M.; Gandolfi, C.; Durante, C.; Agostani, D. Modeling water resources of a highly irrigated alluvial plain (Italy): Calibrating soil and groundwater models. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C. Nitrate leaching in temperate agroecosystems: Sources, factors and mitigating strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 64, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, C. ACQUA E IRRIGAZIONE PER NUTRIRE IL PIANETA. LA REALTÀ DELLA PIANURA PADANA LOMBARDA. Ist. Lomb. Accad. Sci. E Lett. Incontr. Stud. 2017, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRSA-CNR. Indagine Sulle Falde Acquifere Profonde Della Pianura Padana; Quaderni IRSA-CNR 51/2; CNR: Roma, Italy, 1982; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Carcano, C.; Piccin, A. Geologia Degli Acquiferi Padani della Regione Lombardia; Regione Lombardia and ENI Divisione AGIP: Firenze, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardi, C.; Panagos, P.; Hiederer, R.; Montanarella, L.; Micale, F. Report on the Activities Realized Within the Service Level Agreement between JRC and EFSA, as a Support of the FATE and ECOREGION Working Groups of EFSA PPR (SLA/EFSA-JRC/2008/01): Final Report of 15th December 2010; JRC-IES scientific and technical report: EUR 24744 EN; European Union: Luxembourg, 2011; ISBN 978-92-79-19521-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERSAL. Basi Ambientali Della Pianura—Servizio di Mappa (ArcIMS)—Rilevanze Naturalistiche e Paesaggistiche. Banca Dati Superficiale (Fontanili), ERSAL. 1998. Available online: http://www.cartografia.regione.lombardia.it/geoportale (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Università degli Studi di Milano and U.R.B.I.M. Lombardia. Tutela e Valorizzazione Dei Fontanili Del Territorio Lombardo FonTe. Quaderno Della Ricerca n. 144; Università degli Studi di Milano and U.R.B.I.M: Milano, Italy, 2012; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Burrato, P.; Ciucci, F.; Valensise, G. An inventory of river anomalies in the Po Plain, Northern Italy: Evidence for active blind thrust faulting. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 46, 865–882. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini, L.; Vercesi, P.L. I geositi della Provincia di Pavia; Luigi Ponzio e Figli Editore: Pavia, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, D.A.; Destefanis, E.; Forno, M.G.; Lasagna, M.; Masciocco, L. The genesis and the hydrogeological features of the Turin Po Plain fontanili, typical lowland springs in Northern Italy. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2014, 73, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eupolislombardia. Progetto di Accompagnamento a Supporto Del Processo di Revisione Del Piano di Tutela Delle Acque. Attività di Approfondimento Specialistico Relativo ai Corpi Idrici Sotterranei (Cod. Éupolis Lombardia Ter13016/001). Relazione di sintesi; Éupolis Lombardia: Milano, Italy, 2015; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus Europe’s Eyes on the Earth. Corine Land Cover. 2006. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Geoportale Regione Lombardia. Carta Geologica 250,000 del 1990, Mappa Digitale (Arcgis9.x). Available online: www.geoportale.regione.lombardia.it/metadati?p_p_id=PublishedMetadata_WAR_geoportalemetadataportlet&p_p_lifecycle=0&p_p_state=maximized&p_p_state=view&_PublishedMetadata_WAR_geoportalemetadataportlet_view=editPublishedMetadata&_PublishedMetadata_WAR_geoportalemetadataportlet_uuid=%7B018208BD-AD82-4D2A-B195-548D6F3432B4%7D&_PublishedMetadata_WAR_geoportalemetadataportlet_editType=view&_PublishedMetadata_WAR_geoportalemetadataportlet_fromAsset=true&rid=local (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- National Statistics Institution, 6th Agricultural Census. 2010. Available online: http://dati-censimentoagricoltura.istat.it (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Enti Regolatori dei Grandi Laghi. Available online: http://www.laghi.net (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Regione Lombardia. Sperimentazione del Deflusso Minimo Vitale (DMV). Available online: https://www.regione.lombardia.it/wps/portal/istituzionale/HP/DettaglioRedazionale/servizi-e-informazioni/Enti-e-Operatori/territorio/governo-delle-acque/deflusso-minimo-vitale/sperimentazione-deflusso-minimo-vitale (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- D.G.R. Emilia Romagna n. 1415/2016. Definizione Dei Fabbisogni Irrigui per Coltura, ai Sensi Del D.M. 31 Luglio 2015 “Approvazione Delle Linee Guida per la Regolamentazione da Parte Delle Regioni Delle Modalità di Quantificazione Dei Volumi Idrici ad Uso Irriguo. 2015. Available online: https://bur.regione.emilia-romagna.it/dettaglio-inserzione?i=05e6e223fb954aa4a44ca7fd30d4ec4e (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. FAO Rome 1998, 300, D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Joint Research Centre. European Soil Data Centre (ESDAC). Available online: http://eusoils.jrc.ec.europa.eu/library/Data/EFSA/ (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- EMEP-Co-operative Programme for Monitoring and Evaluation of the Long-range Transmission of Air pollutants in Europe. Available online: http://www.emep.int (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Oenema, O.; Kros, H.; De Vries, W. Approaches and Uncertainties in Nutrient Budgets: Implications for Nutrient Management and Environmental Policies. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 20, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, W.; Leip, A.; Reinds, G.J.; Kros, J.; Lesschen, J.P.; Bouwman, A.F. Comparison of land nitrogen budgets for European agriculture by various modeling approaches. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3254–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, L.; Romero, E.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; García-Gómez, H.; Rovira, J.V. Spatialized N budgets in a large agricultural Mediterranean watershed: High loading and low transfer. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soana, E.; Racchetti, E.; Laini, A.; Bartoli, M.; Viaroli, P. Soil Budget, Net Export, and Potential Sinks of Nitrogen in the Lower Oglio River Watershed (Northern Italy). Clean Soil Air Water 2011, 39, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, M.; Soana, E.; Laini, A.; Bresciani, M.; Bartoli, M. Soil system budgets of N, Si and P in an agricultural irrigated watershed: Surplus, differential export and underlying mechanisms. Biogeochemistry 2018, 140, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izagirre, O.; Agirre, U.; Bermejo, M.; Pozo, J.; Elosegi, A. Environmental controls of whole-stream metabolism identified from continuous monitoring of Basque streams. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, J. L’analyse de L’eau; Dunod: Paris, France, 1978; p. 1136. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewaters, 20th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- D.d.s. Regione Lombardia n. 4346 del 27/03/2018. Approvazione Della «Metodologia di Stima Dei Volumi Idrici ad Uso Irriguo, in Attuazione Della d.g.r. n. 6035/2016. Available online: https://www.regione.lombardia.it/wps/wcm/connect/8f7c5df8-e897-47b7-b5fd-62c541b9bc67/decreto-4346-2018-metodologia-stima-volumi-idrici-uso-irriguo.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CACHEID=8f7c5df8-e897-47b7-b5fd-62c541b9bc67 (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Lasagna, M.; De Luca, D.A.; Franchino, E. Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the western Po Plain (Italy): The effects of groundwater and surface water interactions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderacchi, M.; Perego, A.; Lazzari, G.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Acutis, M.; Laini, A.; Giussani, A.; Sanna, M.; Kane, D.; Trevisan, M. Avoiding social traps in the ecosystem stewardship: The Italian Fontanile lowland spring. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, N.; Senes, G.; Ferrario, P.S.; Toccolini, A. A minimum indicator set for assessing fontanili (lowland springs) of the Lombardy Region in Italy. Eur. Ctry. 2017, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISLC. Certificato di Analisi DELL’ACQUA Delle Sorgenti Bressanello e S. Antonio Dell’istituto Superiore Lattiero Caseario (Protocollo n°1766, Mantova 18/10/1996); Regione Lombardia: Mantova, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Laini, A.; Bartoli, M.; Castaldi, S.; Viaroli, P.; Capri, E.; Trevisan, M. Greenhouse gases (CO2, CH4 and N2O) in lowland springs within an agricultural impacted watershed (Po River Plain, northern Italy). Chem. Ecol. 2011, 27, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpa Lombardia. Dati e Indicatori. Available online: https://www.arpalombardia.it/Pages/Ricerca-Dati-ed-Indicatori.aspx (accessed on 7 October 2017).
- Taherisoudejani, H.; Racchetti, E.; Celico, F.; Bartoli, M. Application of QUAL2Kw to the Oglio River (Northern Italy) to assess diffuse N pollution via river-groundwater interaction. J. Limnol. 2018, 77, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaroli, P.; Soana, E.; Pecora, S.; Laini, A.; Naldi, M.; Fano, E.A.; Nizzoli, D. Space and time variations of watershed N and P budgets and their relationships with reactive N and P loadings in a heavily impacted river basin (Po river, Northern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Ma, L.; Sárdi, K.; Sisák, I.; Ma, W. Nitrogen flows in the food production chain of Hungary over the period 1961–2010. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 102, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobota, D.J.; Harrison, J.A.; Dahlgren, R.A. Influences of climate, hydrology, and land use on input and export of nitrogen in California watersheds. Biogeochemistry 2009, 94, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisvert, C.; Curie, F.; Moatar, F. Annual agricultural N surplus in France over a 70-year period. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2017, 107, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagstad, N.; Stålnacke, P.; Andersen, H.-E.; Deelstra, J.; Jansons, V.; Kyllmar, K.; Loigu, E.; Rekolainen, S.; Tumas, R. Regional variations in diffuse nitrogen losses from agriculture in the Nordic and Baltic regions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carmo, M.; García-Ruiz, R.; Ferreira, M.I.; Domingos, T. The NPK soil nutrient balance of Portuguese cropland in the 1950s: The transition from organic to chemical fertilization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaletta, L.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; Bouwman, L.; Velazquez, E.; Mueller, N.D.; Gerber, J.S. Nitrogen use in the global food system: Past trends and future trajectories of agronomic performance, pollution, trade, and dietary demand. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 095007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J.J.; Scholefield, D.; Cabral, F.; Hofman, G. The effects of nutrient losses from agriculture on ground and surface water quality: The position of science in developing indicators for regulation. Environ. Sci. Policy 2004, 7, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Watanabe, M.; Wang, Q. Changes in nitrogen budgets and nitrogen use efficiency in the agroecosystems of the Changjiang River basin between 1980 and 2000. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2008, 80, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D.M. 19/04/1999. Codex of Good Agricultural Practice (GAP). 1999. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/1999/05/04/099A3435/sg (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Diez, J.A.; Roman, R.; Caballero, R.; Caballero, A. Nitrate leaching from soils under a maize-wheat-maize sequence, two irrigation schedules and three types of fertilisers. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1997, 65, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheysari, M.; Mirlatifi, S.M.; Homaee, M.; Asadi, M.E.; Hoogenboom, G. Nitrate leaching in a silage maize field under different irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer rates. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurunc, A.; Ersahinb, S.; Yetgin Uz, B.; Sonmez, N.K.; Uz, I.; Kamana, H.; Bacalana, G.E.; Emekli, Y. Identification of nitrate leaching hot spots in a large area with contrasting soil texture and management. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Dadomo, A.; De Luca, D.A.; Mazzola, M.; Lasagna, M.; Pennisi, M.; Pilla, G.; Sacchi, E.; Saccon, P. Nitrate sources, accumulation and reduction in groundwater from Northern Italy: Insights provided by a nitrate and boron isotopic database. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 91, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascott, M.J.; Gooddy, D.C.; Wang, L.; Stuart, M.E.; Lewis, M.A.; Ward, R.S.; Binley, A.M. Global patterns of nitrate storage in the vadose zone. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meter, J.K.; Basu, N.B.; Veenstra, J.J.; Burras, C.L. The nitrogen legacy: Emerging evidence of nitrogen accunulation in anthropogenic landscapes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 035014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrocicco, M.; Colombani, N.; Castaldelli, G.; Jovanovic, N. Monitoring and modeling nitrate persistence in a shallow aquifer. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 217, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, K.K.; Gosain, A.K. Modeling hydrology, groundwater recharge and non-point nitrate loadings in the Himalayan Upper Yamuna basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 468, S102–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kløve, B.; Ala-Aho, P.; Bertrand, G.; Gurdak, J.J.; Kupfersberger, H.; Kværner, J.; Muotka, T.; Mykrä, H.; Preda, E.; Rossi, P.; et al. Climate change impacts on groundwater and dependent ecosystems. J. Hydrol. 2014, 518, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Features | Study Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| River | Adda | Oglio | Mincio |
| Alpine lake (river water origin) | Como | Iseo | Garda |
| Dam regulating lake outflow (river origin km 0) | Olginate | Sarnico | Monzambano |
| Watershed area (km2) | 3400 | 3840 | 850 |
| River length (km) | 130 | 156 | 75 |
| Portion of watersheds studied: from lake dams, i.e., km 0, to the southernmost extreme of the spring belt area (km2) | 2553 | 2200 | 650 |
| Length of studied river stretch: from dam to southernmost extreme of spring belt area (from km up to km) | 0–70 | 0–60 | 0–40 |
| Studied river stretch crossing the spring belt area (from km up to km) | 35–70 | 25–60 | 18–40 |
| Studied river segment falling within the studied river stretch crossing the spring belt area (from km up to km) | 46–64 | 31–50 | 18–26 |
| Portion of Watersheds | Adda | Oglio | Mincio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhabitants | 1,140,000 | 1,000,000 | 144,000 |
| Utilized agricultural area (UAA, % of total basin area) | 32 | 45 | 70 |
| Number of cows | 179,000 | 360,000 | 110,000 |
| Number of pigs | 360,000 | 1,100,000 | 440,000 |
| Main crops (% of UAA) | |||
| maize | 22 | 40 | 30 |
| wheat | 6 | 6 | 10 |
| feed crops | 21 | 28 | 27 |
| meadows | 42 | 14 | 10 |
| Irrigation Data | Adda | Oglio | Mincio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water volume used for irrigation (×106 m3 year−1) | 161 | 277 | 149 |
| Water volume provided by surface water (aqueduct, irrigation consortium) (%) | 87 | 84 | 96 |
| Water volume provided by groundwater (%) | 13 | 16 | 4 |
| Irrigated surface (km2) | 466 | 785 | 405 |
| Area irrigated by flooding (%) | 87 | 88 | 42 |
| Area irrigated by sprinkler (%) | 12 | 11 | 52 |
| Area irrigated by other methods (%) | 2 | 1 | 6 |
| Water Supply (m3 ha−1) | Maize | Feed Crops | Meadows |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adda | 2419 ± 1311 | 2303 ± 1340 | 2453 ± 1308 |
| Oglio | 3390 ± 677 | 3188 ± 567 | 3290 ± 703 |
| Mincio | 3649 ± 852 | 3376 ± 710 | 3706 ± 973 |
| N Budget | Adda | Oglio | Mincio |
|---|---|---|---|
| t N year−1 | t N year−1 | t N year−1 | |
| INPUT | |||
| Livestock manure | 14,428 | 26,826 | 9831 |
| Synthetic fertilizers | 7194 | 11,334 | 3211 |
| Biological fixation | 5809 | 5438 | 3592 |
| Atmospheric deposition | 668 | 793 | 388 |
| Σ input | 28,099 | 44,391 | 17,022 |
| OUTPUT | |||
| Crop uptake | 11,123 | 15,731 | 7551 |
| NH3 volatilization | 3379 | 5913 | 1976 |
| Denitrification in agricultural soils | 2162 | 3816 | 1304 |
| Σ output | 16,663 | 25,460 | 10,832 |
| Σinput − Σoutput | 11,435 | 18,931 | 6190 |
| kg N ha−1 year−1 | kg N ha−1 year −1 | kg N ha−1 year −1 | |
| INPUT | 341 | 454 | 374 |
| OUTPUT | 202 | 260 | 238 |
| SURPLUS | 139 | 193 | 136 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Racchetti, E.; Salmaso, F.; Pinardi, M.; Quadroni, S.; Soana, E.; Sacchi, E.; Severini, E.; Celico, F.; Viaroli, P.; Bartoli, M. Is Flood Irrigation a Potential Driver of River-Groundwater Interactions and Diffuse Nitrate Pollution in Agricultural Watersheds? Water 2019, 11, 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112304
Racchetti E, Salmaso F, Pinardi M, Quadroni S, Soana E, Sacchi E, Severini E, Celico F, Viaroli P, Bartoli M. Is Flood Irrigation a Potential Driver of River-Groundwater Interactions and Diffuse Nitrate Pollution in Agricultural Watersheds? Water. 2019; 11(11):2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112304
Chicago/Turabian StyleRacchetti, Erica, Francesca Salmaso, Monica Pinardi, Silvia Quadroni, Elisa Soana, Elisa Sacchi, Edoardo Severini, Fulvio Celico, Pierluigi Viaroli, and Marco Bartoli. 2019. "Is Flood Irrigation a Potential Driver of River-Groundwater Interactions and Diffuse Nitrate Pollution in Agricultural Watersheds?" Water 11, no. 11: 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112304
APA StyleRacchetti, E., Salmaso, F., Pinardi, M., Quadroni, S., Soana, E., Sacchi, E., Severini, E., Celico, F., Viaroli, P., & Bartoli, M. (2019). Is Flood Irrigation a Potential Driver of River-Groundwater Interactions and Diffuse Nitrate Pollution in Agricultural Watersheds? Water, 11(11), 2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112304











