Water Quality Assessment of a Meromictic Lake Based on Physicochemical Parameters and Strontium Isotopes (87Sr/86Sr) Analysis: A Case Study of Lubińskie Lake (Western Poland)
Abstract
1. Introduction
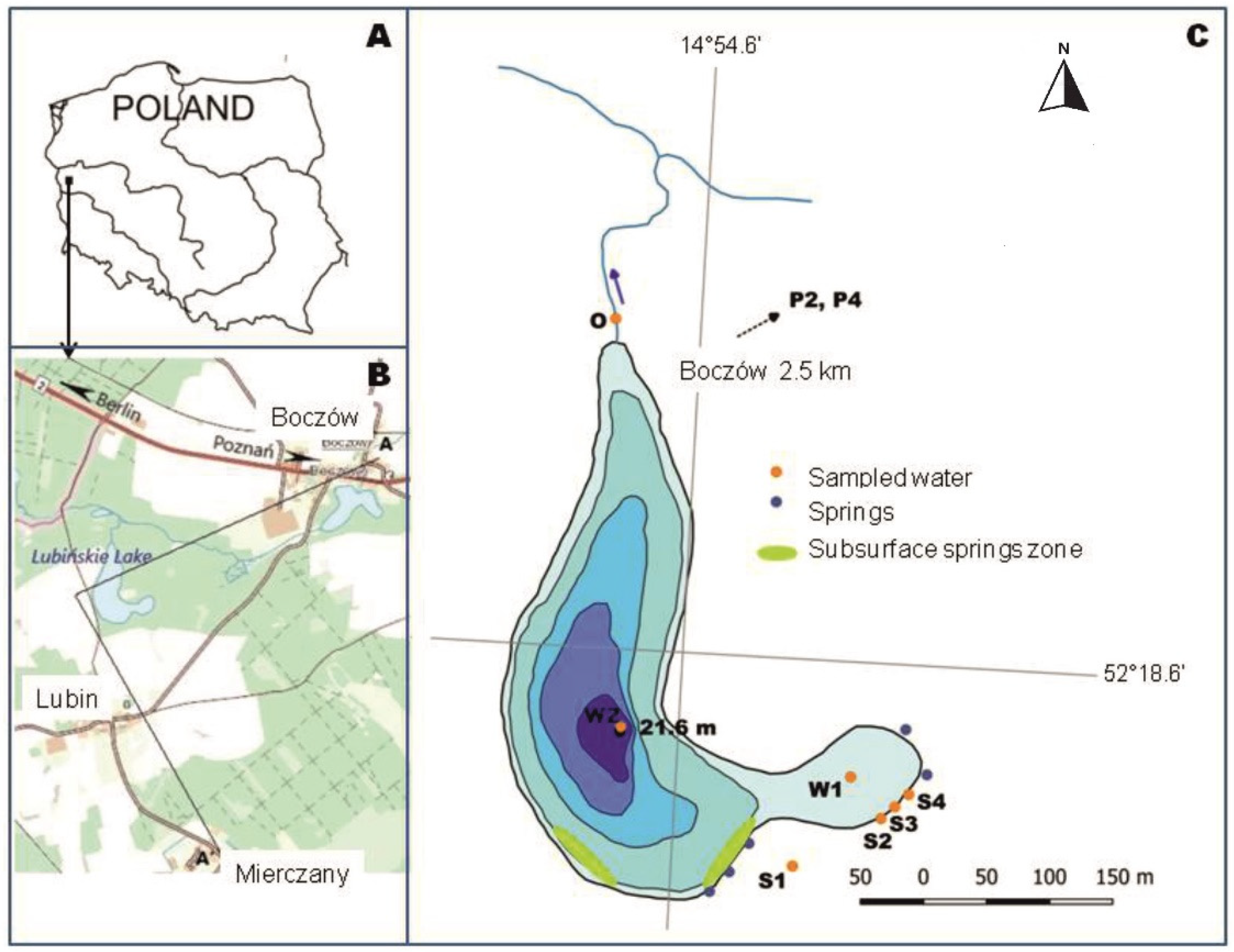
2. Study Object
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Lake Physio-Chemical Characteristics
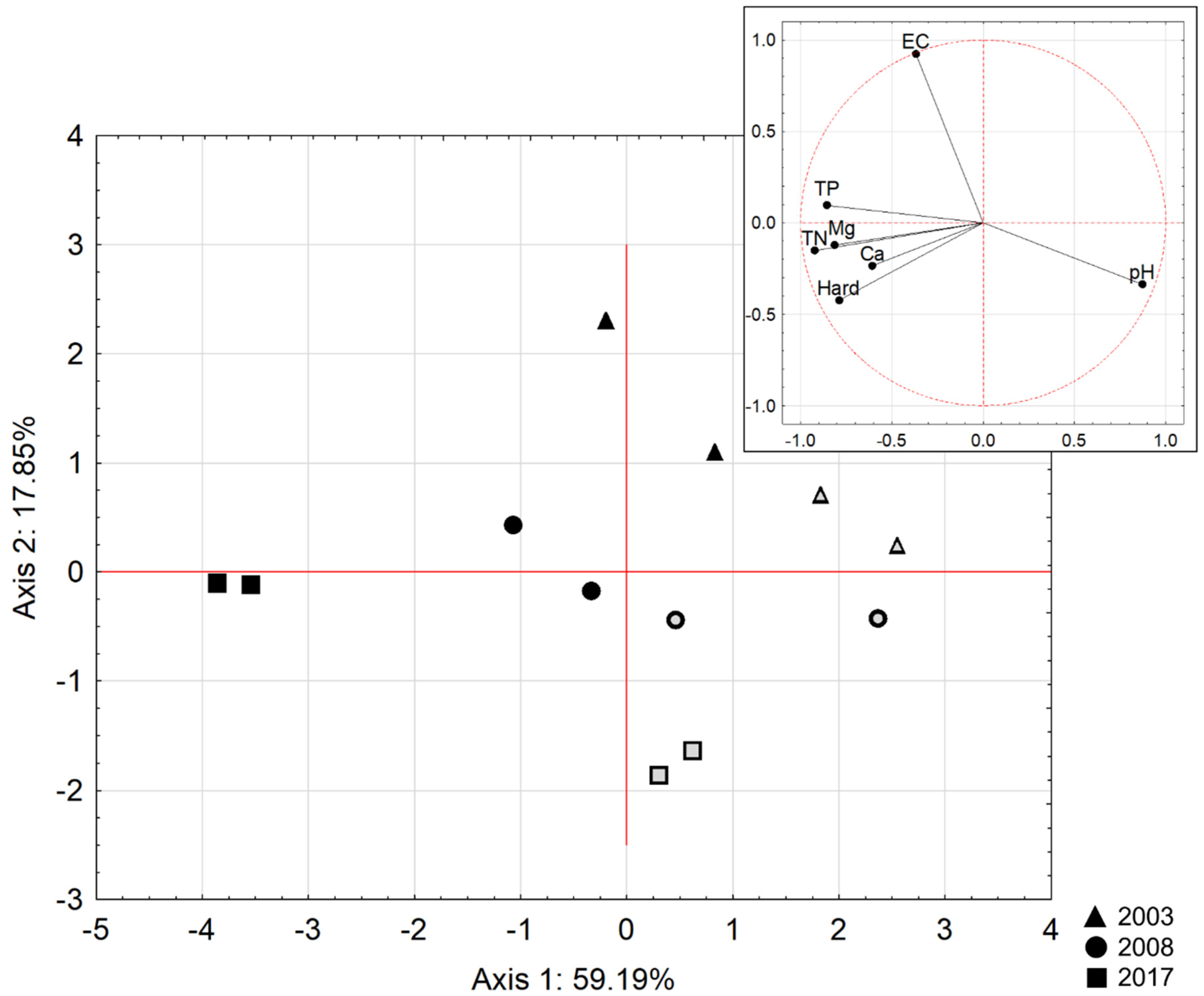
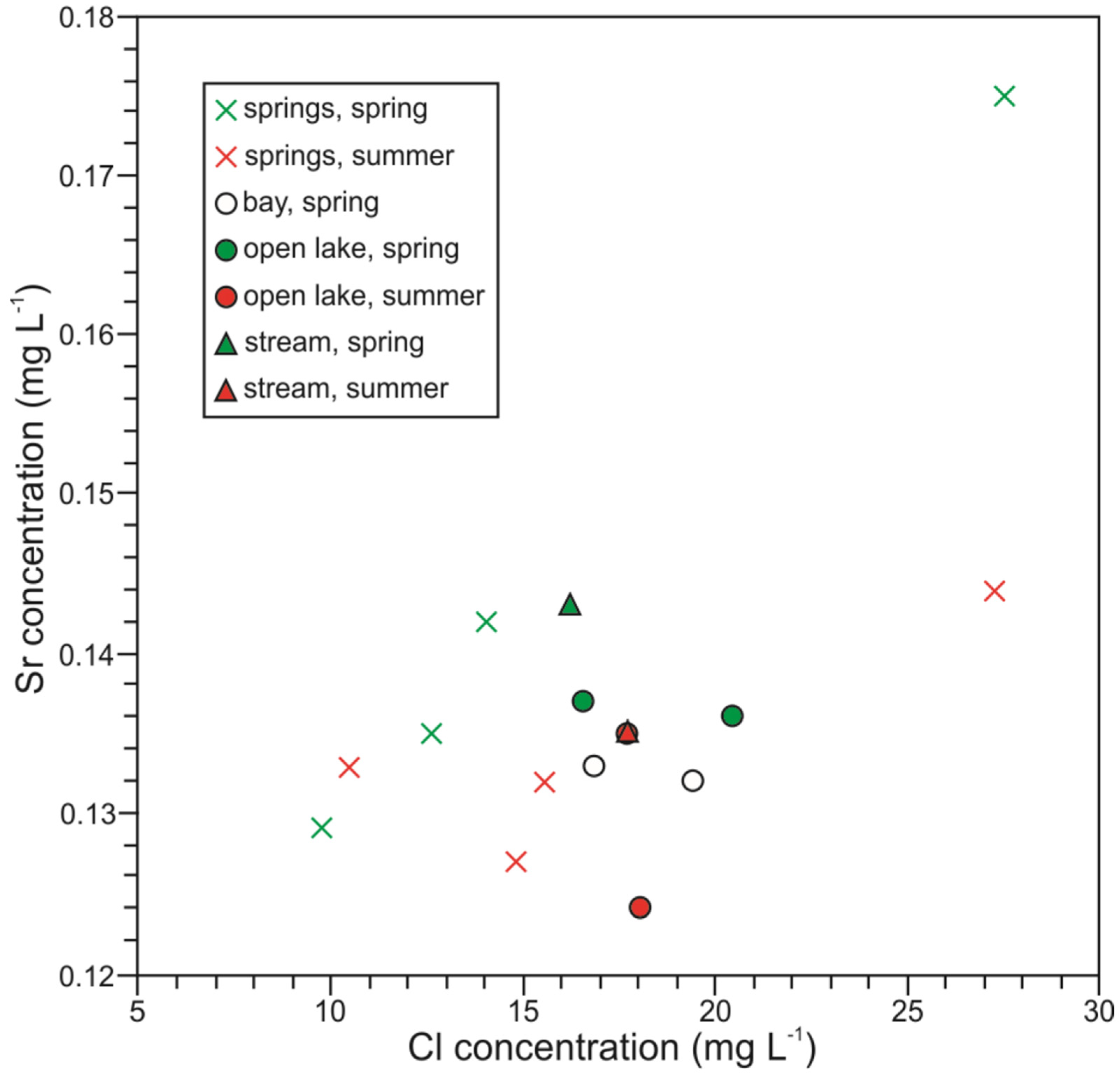
4.2. Site-to-Site Differentiation of Water Chemistry
4.3. Water Inflow to the Lake
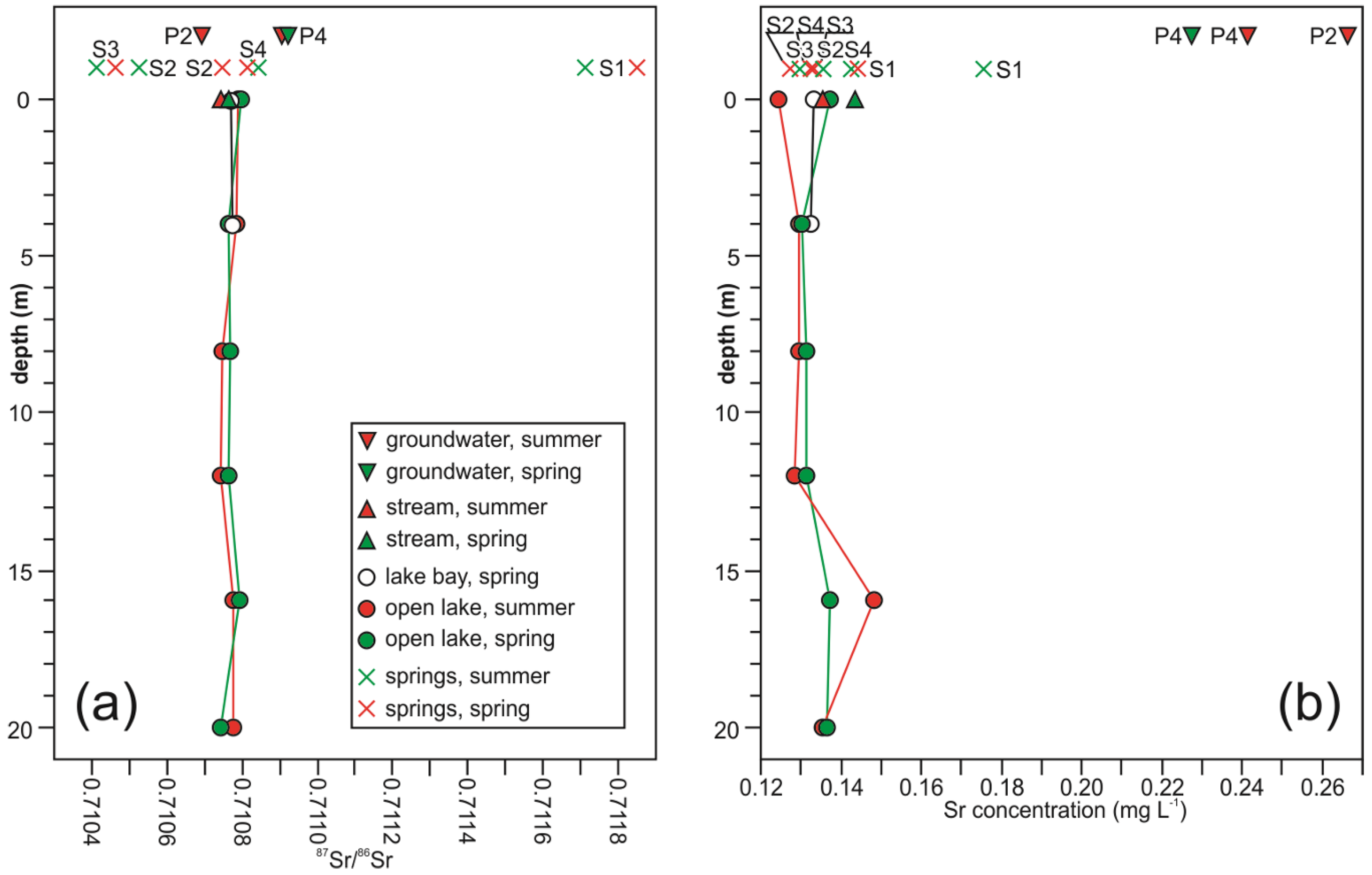
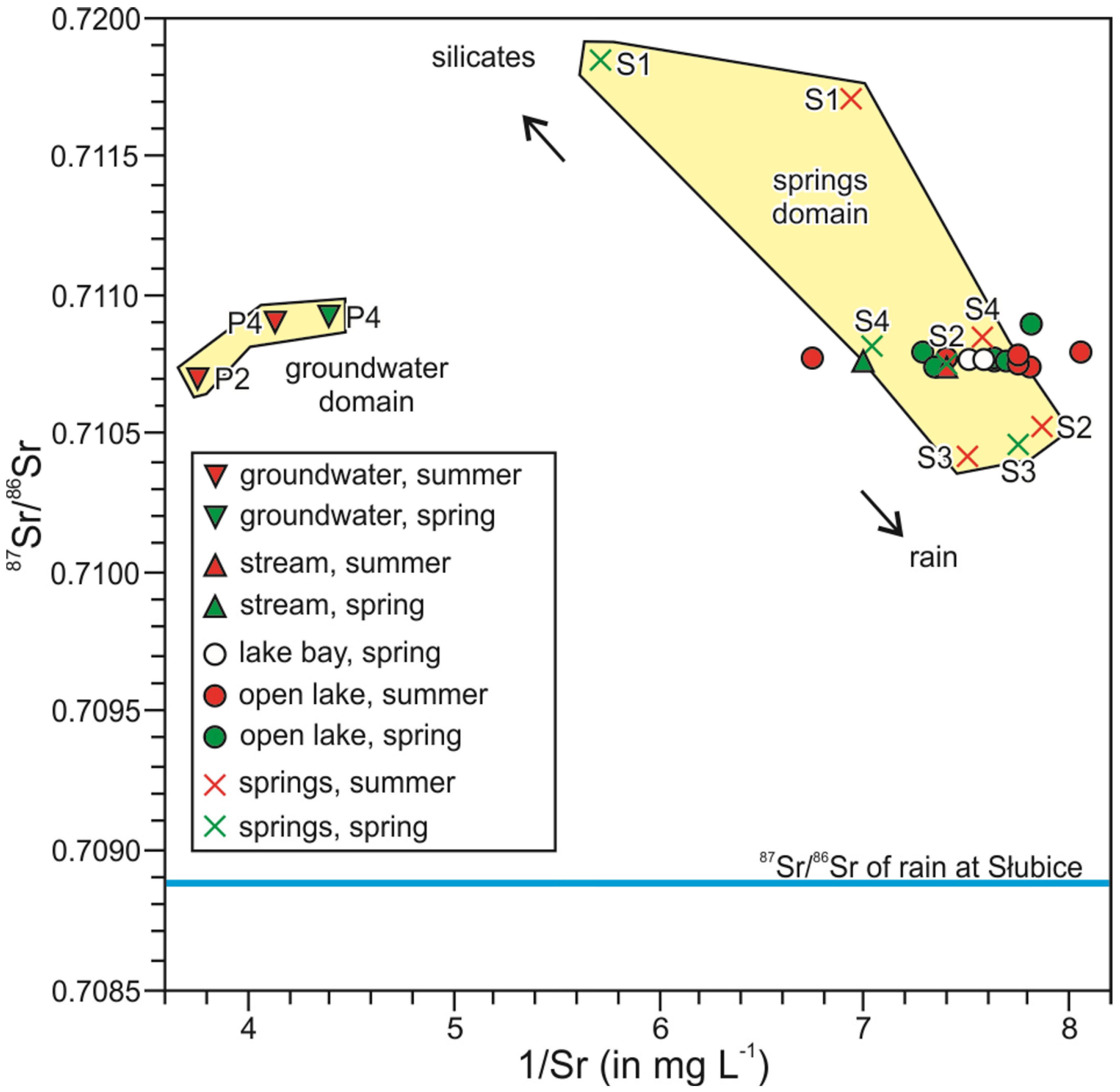
4.4. Strontium Isotope Composition in Water
5. Discussion
5.1. Water Chemistry Analysis
5.2. Strontium Isotopes Perspective
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, D.O.; Nicholls, K.H.; Allen, Y.C.; McMutry, M.J. Historical land use, phosphorus loading, and loss of fish habitat in Lake Simcoe, Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat Sci. 1996, 53 (Suppl. 1), 194–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callisto, M.; Molozzi, J.; Barbosa, J.L.E. Eutrophication of lakes. In Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences and Control, 1st ed.; Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hijosa-Valsero, M.; Bécares, E.; Fernández-Aláez, C.; Fernández-Aláez, M.; Mayo, R.; Jiménez, J.J. Chemical pollution in inland shallow lakes in the Mediterranean region (NW Spain): PAHs, insecticides and herbicides in water and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Bohn, T.J.; Podest, E.; McDonald, K.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. On the causes of the shrinking of Lake Chad. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 034021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronewold, A.D.; Stow, C.A. Water loss from the Great Lakes. Science 2014, 343, 1084–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, R.; Hu, K.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Blais, J.M.; et al. Assessing the impact of long-term changes in climate and atmospheric deposition on a shallow alpine lake from southeast Tibet. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Mao, X.; Jin, Z.; Song, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, H. Sedimentary biogeochemical record in Lake Gonghai: Implications for recent lake changes in relatively remote areas of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, E.B.; Jacoby, J.M. Pollutant Effects in Freshwater: Applied Limnology, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2004; pp. 1–520. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology, Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 1–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Choiński, A.; Ilyin, L.; Marszelewski, W.; Ptak, M. Lakes supplied by springs: Selected examples. Limnol. Rev. 2008, 8, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Cieśliński, R.; Piekarz, J.; Zieliński, M. Groundwater supply of lakes: The case of Lake Raduńskie Górne (northern Poland, Kashubian Lake District). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.T.; Marcarelli, A.M. Cyanobacteria in freshwater benthic environments. In The Ecology of Cyanobacteria; Whitton, B.A., Ed.; Springer: Durham, UK, 2012; pp. 271–289. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.K. Freshwater ecology. In Concepts and Environmental Applications, 1st ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–591. [Google Scholar]
- Last, W.M.; Smol, J.P. An Introduction to Physical and Geochemical methods Used in Paleolimnology. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments; Last, W.M., Smol, J.P., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 1–504. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, W.; Sommer, U. Ecology of Inland Waters; PWN Scientific Press: Warsaw, Poland, 2001; pp. 1–415. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, G.E. A contribution to the limnology of arid regions: Primarily founded on observations made in the Lahontan basin. Trans. Conn. Acad. Arts Sci. 1937, 33, 47–132. [Google Scholar]
- Göltenboth, F.; Timotius, K.H.; Milan, P.P.; Margraf, J. Ecology of Insular Southeast Asia; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–568. [Google Scholar]
- Bis, B. Assessing the Ecological Status Assessment of Freshwaters. In Freshwater Ecosystems in Europe–An Educational Approach; Voreadou, C., Ed.; Natural History Museum of Crete, Selena Press: Heraklion, Greece, 2008; pp. 56–69. [Google Scholar]
- Imteaz, M.A.; Asaeda, T.; Lockington, D.A. Modelling the effects of inflow parameters on lake water quality. Environ. Model. Assess. 2003, 8, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlke, J.K.; Horan, M. Strontium isotope geochemistry of groundwaters and streams affected by agriculture, Locust Grove, MD. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, T.; Nakano, T.; Igeta, A.; Tayasu, I.; Tanaka, T.; Yachi, S. Impact of fertilizer on a small watershed of Lake Biwa: Use of sulfur and strontium in environmental diagnosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, E.C.; Capo, R.C.; Stewart, B.W.; Hedin, R.S.; Weaver, T.J.; Edenborn, H.M. Strontium isotope quantification of siderite, brine and acid mine drainage contributions to abandoned gas well discharges in the Appalachian Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Jackson, R.B.; Warner, N.; Darrah, T.H.; Kondash, A. A critical review of the risk to water resources from unconventional shale gas development and hydraulic fracturing in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8334–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, L.S.; Blum, J.D.; Dvonch, J.T.; Gratz, L.E.; Landis, M.S. The use of Pb, Sr, and Hg isotopes in Great Lakes precipitation as a tool for pollution source attribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Dopieralska, J.; Belka, Z.; Walczak, A.; Siepak, M.; Jakubowicz, M. Sr isotope tracing of multiple water sources in a complex river system, Noteć River, central Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Dopieralska, J.; Belka, Z.; Walczak, A.; Siepak, M.; Jakubowicz, M. Strontium isotope identification of water mixing and recharge sources in a river system (Oder River, central Europe): A quantitative approach. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2597–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, P.; Fouillac, C.; Brach, M. A strontium isotopic study of mineral and surface waters from the Cézallier (Massif Central, France): Implications for mixing processes in areas of disseminated emergences of mineral waters. Chem. Geol. 1997, 135, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, P.; Casanova, J.; Aranyossy, J.P. Strontium isotope systematics used to decipher the origin of groundwaters sampled from granitoids: The Vienne Case (France). Chem. Geol. 2001, 177, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, P.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Barbier, J.; Gautier, E. Surface water-groundwater interactions in an alluvial plain: Chemical and isotopic systematics. J. Hydrol. 2003, 277, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojiambo, S.B.; Lyons, W.B.; Welch, K.A.; Poreda, R.J.; Johannesson, K.H. Strontium isotopes and rare earth elements as tracers of groundwater-lake water interactions, Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1789–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flusche, M.A.; Seltzer, G.; Rodbell, D.; Siegel, D.; Samson, S. Constraining water sources and hydrologic processes from the isotopic analysis of water and dissolved strontium, Lake Junin, Peru. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.D.; Gazis, C.A.; Jacobson, A.D.; Chamberlain, C.P. Carbonate versus silicate weathering in the Raikhot watershed within the High Himalayan Crystalline Series. Geology 1998, 26, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.D.; Blum, J.D.; Walter, L.M. Reconciling the elemental and Sr isotope composition of Himalayan weathering fluxes: Insight from the carbonate geochemistry of stream water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 3417–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y. Weathering, Sr fluxes, and controls on water chemistry in the Lake Qinghai catchment, NE Tibetan Plateau. Earth Surf. Process. 2010, 35, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, W.B.; Welch, K.A.; Priscu, J.C.; Tranter, M.; Royston-Bishop, G. Source of Lake Vostok cations constrained with strontium isotopes. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Dopieralska, J.; Belka, Z.; Walczak, A.; Siepak, M.; Jakubowicz, M. The strontium isotope budget of the Warta River (Poland): Between silicate and carbonate weathering, and anthropogenic pressure. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, P.; Pauwels, H.; Chabaux, F. Characterizing multiple water-rock interactions in the critical zone through Sr-isotope tracing of surface and groundwater. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 93, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capo, R.C.; Stewart, B.W.; Chadwick, O.A. Strontium isotopes as tracers of ecosystem processes: Theory and methods. Geoderma 1998, 82, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graustein, W.C.; Armstrong, R.L. The use of strontium-87/strontium-86 ratios to measure atmospheric transport into forested watersheds. Science 1983, 219, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, G. The use of natural strontium isotopes as tracers in environmental studies. Water Air Soil Poll. 1995, 79, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, D.C.; Midwood, A.J.; Miller, J.D. Strontium isotope ratios in streams and the effect of flow rate in relation to weathering in catchments. Catena 1998, 32, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G.; Mensing, T.M. The Transantarctic Mountains. Rocks, Ice, Meteorites and Water; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–832. [Google Scholar]
- Pełechaty, M.; Pukacz, A.; Pełechata, A. Diversity of micro- and macrophyte communities in the context of the habitat conditions of a meromictic lake on Lubuskie Lakeland. Limnol. Rev. 2004, 4, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Pełechata, A.; Pełechaty, M.; Pukacz, A. Complete mixing of a meromictic lake as a result of extreme weather events and its impact on phytoplankton community. In Proceedings of the 23rd Congres of Polish Hydrobiologists, Koszalin, Poland, 8–12 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zieleniewski, W. Fisherman report for waters of circumference I.5.8. In The Fishing Region of the Lubińskie Lake on an Unnamed Watercourse Flowing into the Rzepia River-No. 1 in the Ilanka River Basin in the Lower Oder and Western Catchment Water Region; Polish Fishermans Association: Zielona Góra, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Choiński, A. Outline of Polish Physical Limnology; Adam Mickiewicz University Press: Poznań, Poland, 1995; pp. 1–298. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jańczak, J. Atlas of Polish Lakes; Bogucki Press: Poznań, Poland, 1996; pp. 1–256. [Google Scholar]
- Stupnicka, E. Regional Geology of Poland; University of Warsaw Press: Warsaw, Poland, 2007; pp. 1–346. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Main Office of Geodesy and Cartography. Available online: http://www.gugik.gov.pl/ (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pin, C.; Briot, D.; Bassin, C.; Poitrasson, F. Concomitant separation of strontium and samarium-neodymium for isotopic analysis in silicate samples, based on specific extraction chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 1994, 298, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopieralska, J. Neodymium Isotopic Composition of Conodonts as a Palaeoceanographic Proxy in the Variscan Oceanic System. Ph.D. Thesis, Justus-Liebig-University, Giessen, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pełechata, A.; Pełechaty, M.; Pukacz, A. An attempt to the trophic status assessment of the lakes of Lubuskie Lakeland. Limnol. Rev. 2006, 6, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Pukacz, A.; Pełechaty, M.; Pełechata, A.; Sękowska, N. The influence of winter windstorms on the disorder of meromixia of Lubińskie Lake. In Proceedings of the 14th Polish Limnologic Conference Natural and Anthropogenic Transformations of the Lakes, Szczecin-Stare Drawsko, Poland, 20–23 September 2010. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Boehrer, B.; von Rohden, C.; Schultze, M. Physical features of Meromictic Lakes: Stratification and circulation. In Ecology of Meromictic Lakes; Gulati, R.D., Zadereev, E., Degermendzhy, A.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–405. [Google Scholar]
- Hakala, A. Meromixis as a part of lake evolution—Observations and a revised classification of true meromictic lakes in Finland. Boreal Environ. Res. 2004, 9, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Shand, P.; Darbyshire, D.P.F.; Love, A.J.; Edmunds, W.M. Sr isotopes in natural waters: Applications to source characterisation and water-rock interaction in contrasting landscapes. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczucińska, A. Spatial distribution and hydrochemistry of springs and seepage springs in the Lubuska Upland of western Poland. Hydrol. Res. 2014, 45, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiber, M.; Webb, J.A.; Bennetts, D.A. Strontium isotopes as tracers to delineate aquifer interactions and the influence of rainfall in the basalt plains of southeastern Australia. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.M.; Howarth, R.J.; Bailey, T.R. Strontium isotope stratigraphy: LOWESS version 3: Best fit to the marine Sr-isotope curve for 0-509 Ma and accompanying look-up table for deriving numerical age. J. Geol. 2001, 109, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, P.; Guerrot, C.; Millot, R. Chemical and strontium isotope characterization of rainwater in France: Influence of sources and hydrogeochemical implications. Isot. Environ. Health S 2007, 43, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Han, G. Chemical and strontium isotope characterization of rainwater in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Morohashi, S.; Yasuda, H.; Sakai, M.; Aizawa, S.; Shichi, K.; Morisawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Sanada, M.; et al. Determination of seasonal and regional variation in the provenance of dissolved cations in rain in Japan based on Sr and Pb isotopes. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7409–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, R.F.; Edmond, J.M. Geochemistry of the Amazon, 1. Precipitation chemistry and the marine contribution to the dissolved load at the time of peak discharge. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 9844–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Atmospheric inputs and river transport of dissolved substances. In Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences Conference Dissolved load of rivers and surface water quantity/quality relationships, Hamburg, Germany, 15–27 August 1983; pp. 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood, W.C. Chloride loading in the South Fork of the Shenandoah River, Virginia, U.S.A. Environ. Geol. Water S 1989, 14, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters and Indices | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Surface area | ha | 22.7 |
| Maximum length | m | 1130 |
| Maximum width | m | 270 |
| Mean width | m | 200 |
| Length ratio | - | 4.2 |
| Shoreline length | m | 2950 |
| Shoreline development | - | 1.75 |
| Volume | 103 m3 | 1997.6 |
| Maximum depth | m | 21.6 |
| Mean depth | m | 8.8 |
| Relative depth * | - | 0.0453 |
| Depth ratio | - | 0.41 |
| Exposure ratio | - | 2.6 |
| Parameter | (unit) | 2003 | 2008 | 2017 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | H | E | H | E | H | ||
| SD | (m) | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 2.5 ± 0.9 | 2 ± 0.1 | |||
| Temp. | (°C) | 14.4 ± 10.7 | 4.4 ± 0.1 | 13.4 ± 9.8 | 4.3 ± 0.8 | 15.3 ± 12.7 | 4 ± 0.5 |
| EC | (µS cm−1) | 416 ± 11.3 | 452 ± 19.8 | 442 ± 15.6 | 485 ± 28.3 | 380 ± 7.1 | 460.5 ± 0.7 |
| pH | (mg L−1 ) | 8.4 ± 0.6 | 7.5 ± 0 | 8.6 ± 0.3 | 7.7 ± 0.6 | 8.4 ± 0.2 | 7.2 ± 0 |
| O2 | (mg L−1) | 14 ± 2.2 | 0 ± 0 | 12.2 ± 1.5 | 2.8 ± 3.9 | 8.2 ± 0.6 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Ca2+ | (mg L−1) | 70 ± 8.06 | 76.4 ± 7.07 | 77.3 ± 13.72 | 67.45 ± 0.49 | 74.16 ± 2.76 | 90.26 ± 1.75 |
| Mg2+ | (mg L−1) | 4.3 ± 0 | 5.05 ± 2.19 | 1.91 ± 1.33 | 3.29 ± 0.79 | 3.54 ± 0.15 | 6.81 ± 0.11 |
| Hard. | (dH) | 10.8 ± 1.13 | 12.2 ± 0 | 9.05 ± 1.49 | 10.2 ± 0.14 | 12 ± 0.14 | 12.8 ± 0.14 |
| TP | (mg L−1) | 0.08 ± 0.025 | 0.199 ± 0.106 | 0.088 ± 0.071 | 0.834 ± 0.069 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.998 ± 0.04 |
| TN | (mg L−1) | 1.524 ± 1.561 | 4.357 ± 1.008 | 1.964 ± 0.31 | 4.008 ± 3.029 | 3.812 ± 0.173 | 5.844 ± 0.047 |
| Norg.-N | (mg L−1) | 1.252 ± 1.177 | 3.194 ± 0.504 | 1.335 ± 0.064 | 2.605 ± 1.563 | 3.029 ± 0.033 | 3.804 ± 0.157 |
| NO3-N | (mg L−1) | 0.1 ± 0.141 | 0 ± 0 | 0.199 ± 0.177 | 0.148 ± 0.209 | 0.467 ± 0.195 | 0.656 ± 0.109 |
| NO2-N | (mg L−1) | 0.002 ± 0.003 | 0.004 ± 0.005 | 0.005 ± 0.004 | 0.003 ± 0.004 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0 ± 0 |
| NH4-N | (mg L−1) | 0.17 ± 0.24 | 1.16 ± 0.509 | 0.426 ± 0.555 | 1.253 ± 1.679 | 0.316 ± 0.013 | 1.384 ± 0.218 |
| SRP | (mg L−1) | 0.011 ± 0.016 | 0.127 ± 0.051 | 0.036 ± 0.009 | 0.126 ± 0.096 | 0.089 ± 0.012 | 0.858 ± 0.084 |
| N:P * | 6.8 | 18.5 | 15.8 | 7.8 | 33.9 | 6.0 | |
| TSI | 52.8 | 59.5 | 61 | ||||
| Discharge | Q (dm3 s−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | 15.03 | 12.04 | 02.08 |
| Spring (S1) | 6.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Spring (S2) | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 |
| Spring (S3) | 1.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 |
| Spring (S4) | 1.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| Outflow (O) | 29.0 | 40.0 | 21.0 |
| Component | 87Sr/86Sr | Sr Content (mg L−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Spring | Summer | |
| Lake water-open lake | ||||
| 0 m | 0.710798 ± 10 | 0.710790 ± 10 | 0.137 | 0.124 |
| 4 m | 0.710764 ± 10 | 0.710784 ± 9 | 0.130 | 0.129 |
| 8 m | 0.710770 ± 10 | 0.710748 ± 11 | 0.131 | 0.129 |
| 12 m | 0.710762 ± 10 | 0.710744 ± 8 | 0.131 | 0.128 |
| 16 m | 0.710791 ± 12 | 0.710775 ± 9 | 0.137 | 0.148 |
| 20 m | 0.710741 ± 9 | 0.710776 ± 10 | 0.136 | 0.135 |
| Lake water–bay | ||||
| 0 m | 0.710770 ± 10 | ND | 0.133 | ND |
| 4 m | 0.710771 ± 10 | ND | 0.132 | ND |
| Stream | ||||
| 0.710765 ± 10 | 0.710741 ± 9 | 0.143 | 0.135 | |
| Springs | ||||
| S1 | 0.711851 ± 10 | 0.711710 ± 10 | 0.175 | 0.144 |
| S2 | 0.710746 ± 10 | 0.710525 ± 10 | 0.135 | 0.127 |
| S3 | 0.710463 ± 11 | 0.710412 ± 9 | 0.129 | 0.133 |
| S4 | 0.710813 ± 11 | 0.710844 ± 16 | 0.142 | 0.132 |
| Groundwater | ||||
| P2 | ND | 0.710693 ± 10 | ND | 0.266 |
| P4 | 0.710922 ± 10 | 0.710906 ± 10 | 0.227 | 0.241 |
| Rain | ||||
| 0.708879 ± 11 | ND | ND | ND | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zieliński, M.; Szczucińska, A.; Drożdżyński, M.; Frankowski, M.; Pukacz, A. Water Quality Assessment of a Meromictic Lake Based on Physicochemical Parameters and Strontium Isotopes (87Sr/86Sr) Analysis: A Case Study of Lubińskie Lake (Western Poland). Water 2019, 11, 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112231
Zieliński M, Szczucińska A, Drożdżyński M, Frankowski M, Pukacz A. Water Quality Assessment of a Meromictic Lake Based on Physicochemical Parameters and Strontium Isotopes (87Sr/86Sr) Analysis: A Case Study of Lubińskie Lake (Western Poland). Water. 2019; 11(11):2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112231
Chicago/Turabian StyleZieliński, Mateusz, Anna Szczucińska, Mateusz Drożdżyński, Marcin Frankowski, and Andrzej Pukacz. 2019. "Water Quality Assessment of a Meromictic Lake Based on Physicochemical Parameters and Strontium Isotopes (87Sr/86Sr) Analysis: A Case Study of Lubińskie Lake (Western Poland)" Water 11, no. 11: 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112231
APA StyleZieliński, M., Szczucińska, A., Drożdżyński, M., Frankowski, M., & Pukacz, A. (2019). Water Quality Assessment of a Meromictic Lake Based on Physicochemical Parameters and Strontium Isotopes (87Sr/86Sr) Analysis: A Case Study of Lubińskie Lake (Western Poland). Water, 11(11), 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112231






