Method for Estimating Sediment Mass Movement from Delta Recutting: A Case Study Using Single Beam Sonar in Deer Creek Reservoir
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Nutrient Reclying
1.2.1. Geochemical and Biochemical Interactions
1.2.2. Resuspension and Other Factors
1.3. Study Objectives
2. Study Area
3. Methods
3.1. Sonar Equipment
3.2. Setup
3.3. Study Plan
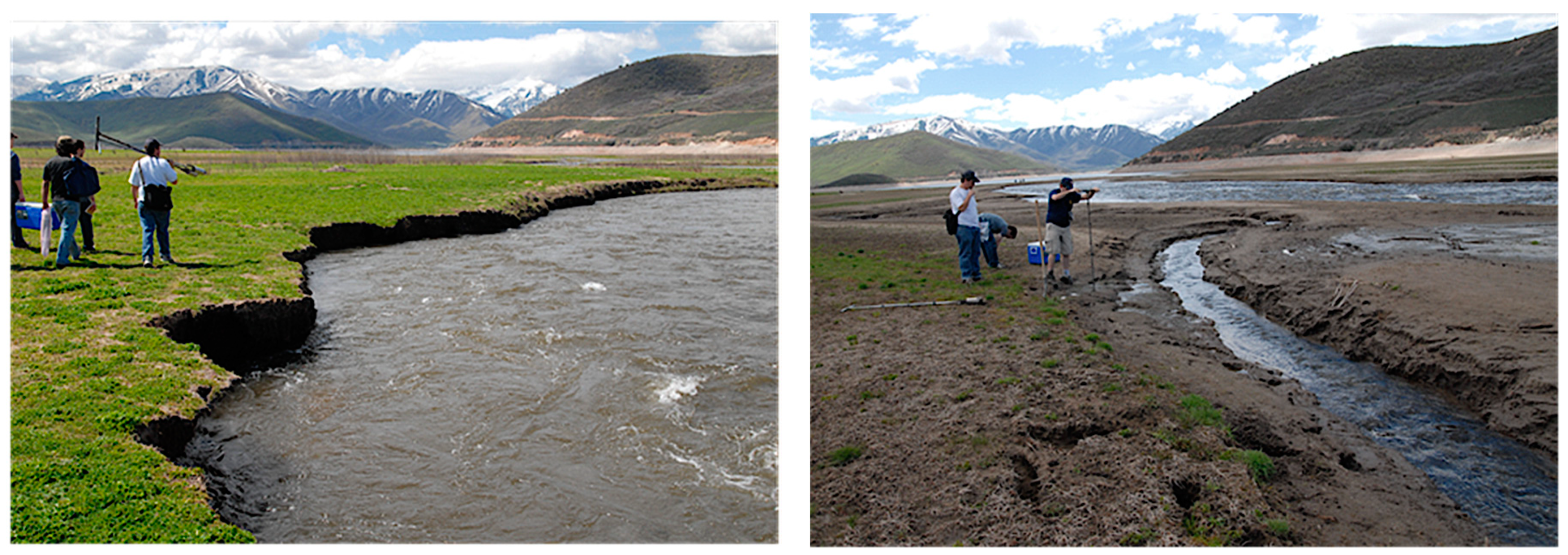
3.4. Field Data Collection
4. Data Processing
5. Discussion
5.1. General Issues
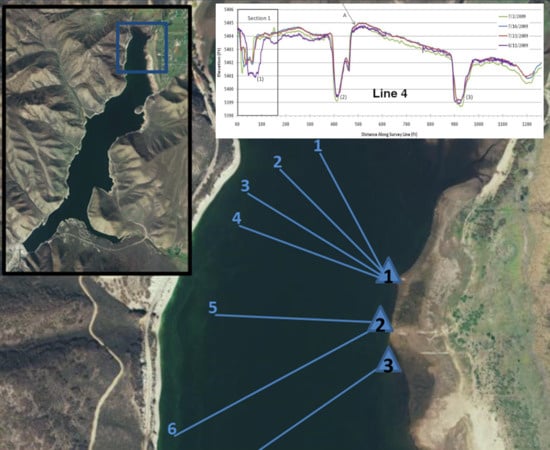
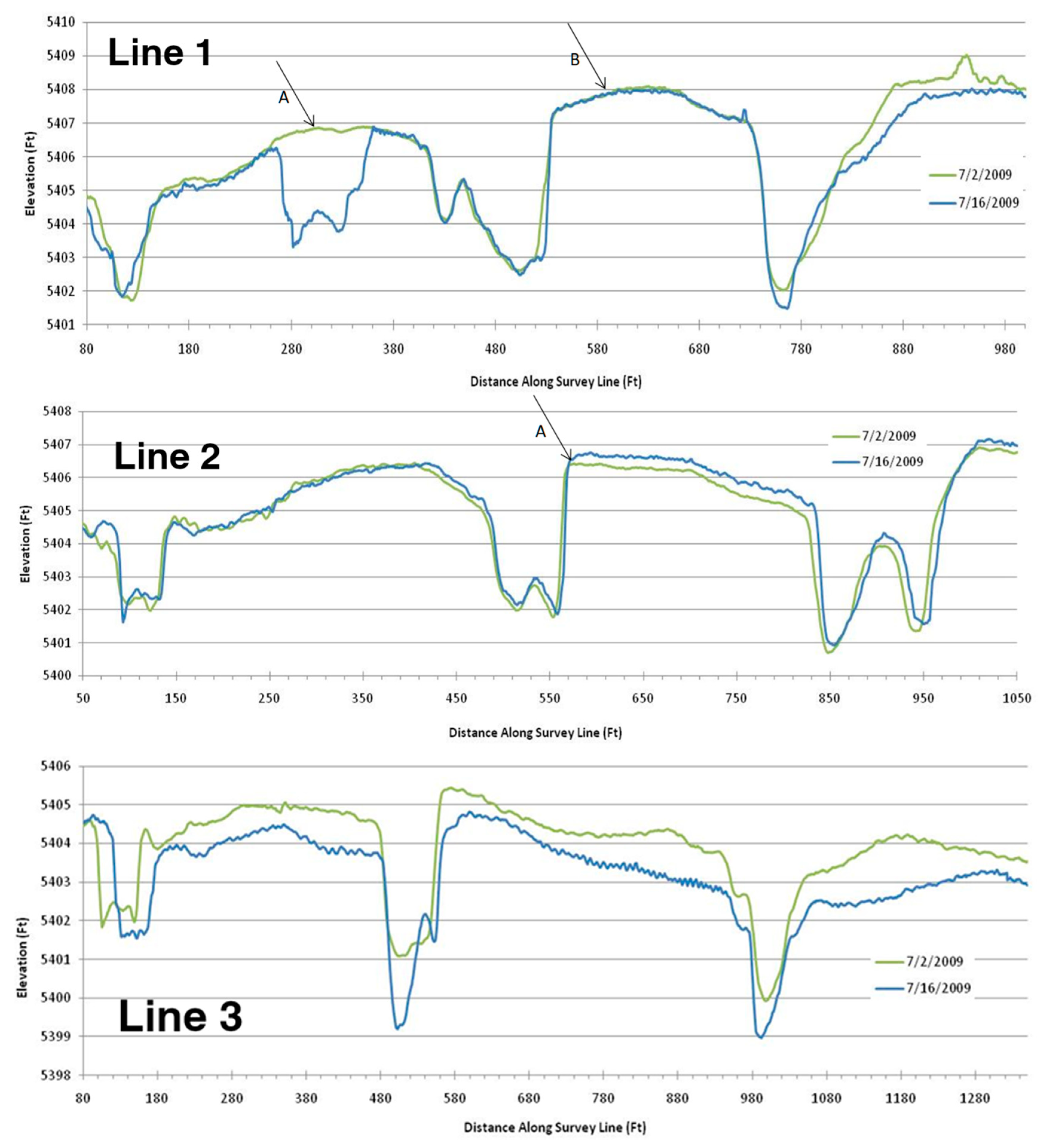
5.2. Discussion Survey Lines 1, 2, and 3
5.3. Discussion Survey Line 4
5.4. Discussion Survey Line 5
5.5. Discussion Survey Line 6
5.6. Discussion Survey Line 7
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakai, Y.; Murase, J.; Sugimoto, A.; Okubo, K.; Nakayama, E. Resuspension of bottom sediment by an internal wave in lake biwa. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2002, 7, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnik, P.M.; Zubenko, I.B. Role of bottom sediments in the secondary pollution of aquatic environments by heavy-metal compounds. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2000, 5, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, T.; Ptacek, C.; Zanini, L. Sediments as a source of nutrients to hypereutrophic marshes of point pelee, ontario, canada. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granéli, W.; Solander, D. Influences of aquatic macrophytes on phosphorus cycling in lakes. Hydrobiologia 1988, 170, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casbeer, W.; Williams, G.; Borup, M. Phosphorus distribution in delta sediments: A unique data set from deer creek reservoir. Hydrology 2018, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hmeidan, H.; Williams, G.; Miller, A. Characterizing total phosphorus in current and geologic utah lake sediments: Implications for water quality management issues. Hydrology 2018, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casbeer, W.C. Phosphorus Fractionation and Distribution Across Delta of Deer Creek Reservoir; Brigham Young University: Provo, UT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer, C.H. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. J. Ecol. 1941, 29, 280–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, C.H. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes: Sections II and IV, Summary and References. J. Ecol. 1942, 30, 147–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnars, A.; Blomqvist, S.; Johansson, P.; Andersson, C. Formation of fe (iii) oxyhydroxide colloids in freshwater and brackish seawater, with incorporation of phosphate and calcium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, V.; Demare, D. Sediment phosphorus and internal phosphate flux in the hydroelectric reservoir of bort-les-orgues, france. In Oceans, Rivers and Lakes: Energy and Substance Transfers at Interfaces; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 349–359. [Google Scholar]
- Tunney, H.; Carton, O.T.; O’Donnell, T.; Fanning, A. Phosphorus Loss from Soil to Water; Teagasc: Carlow, Ireland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gächter, R.; Meyer, J.S.; Mares, A. Contribution of bacteria to release and fixation of phosphorus in lake sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 1542–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, D.; Kling, H.; Schmidt, R.; Prokopowich, J.; Frost, V.; Reid, R.; Capel, M. Eutrophication of lake 227 by addition of phosphate and nitrate: The second, third, and fourth years of enrichment, 1970, 1971, and 1972. J. Fish. Board Can. 1973, 30, 1415–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.; Hesslein, R.; Kipphut, G. Interactions between sediments and overlying waters in an experimentally eutrophied precambrian shield lake. In Interactions Between Sediments and Fresh Water, Proceedings of an International Symposium; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, S.; Stainton, M.; Schindler, D. A radiotracer study of phosphorus cycling in a eutrophic canadian shield lake, lake 227, northwestern ontario. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1986, 43, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gächter, R.; Wehrli, B. Ten years of artificial mixing and oxygenation: No effect on the internal phosphorus loading of two eutrophic lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3659–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gächter, R.; Müller, B. Why the phosphorus retention of lakes does not necessarily depend on the oxygen supply to their sediment surface. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gächter, R.; Meyer, J.S. The Role of Microorganisms in Mobilization and Fixation of Phosphorus in Sediments. In Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on Phosphorus in Sediments; Springer: Zeist, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 103–121. [Google Scholar]
- Hupfer, M.; Gtichter, R.; Ruegger, R.R. Polyphosphate in lake sediments: 31p nmr spectroscopy as a tool for its identification. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.M. Effect of nitrate concentration in lake water on phosphate release from the sediment. Water Res. 1982, 16, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraco, N.; Cole, J.; Likens, G. Sulfate control of phosphorus availability in lakes. Hydrobiologia 1993, 253, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeberg, A. Interactions between benthic phosphorus release and sulfur cycling in lake scharmützelsee (germany). Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 99, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suplee, M.W.; Cotner, J.B. An evaluation of the importance of sulfate reduction and temperature to p fluxes from aerobic-surfaced, lacustrine sediments. Biogeochemistry 2002, 61, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, W.; Nishri, A.; Parparova, R. Factors regulating the flux of phosphate at the sediment—Water interface of a subtropical calcareous lake: A simulation study with intact sediment cores. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 99, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, L.H.; Wood, T.M. Effect of water-column ph on sediment-phosphorus release rate in upper klamath lake, oregon, 2001. Water-Resour. Investig. Rep. 2004, 3, 4271. [Google Scholar]
- Lavery, P.S.; Oldham, C.E.; Ghisalberti, M. The use of fick’s first law for predicting porewater nutrient fluxes under diffusive conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 2435–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, S.; Nausch, G.; Leipe, T. Sedimentary deposition and reflux of phosphorus (p) in the eastern gotland basin and their coupling with p concentrations in the water column. Oceanologia 2005, 47, 663–679. [Google Scholar]
- Søndergaard, M.; Kristensen, P.; Jeppesen, E. Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind-exposed lake arresø, denmark. Hydrobiologia 1992, 228, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, P.; Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E. Resuspension in a shallow eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 1992, 228, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemistö, J.P.; Horppila, J. The contribution of ice cover to sediment resuspension in a shallow temperate lake: Possible effects of climate change on internal nutrient loading. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarra, V.A. Digestive activities of carp as a major contributor to the nutrient loading of lakes. Verhandlungen Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1975, 19, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallepp, G.W. Chironomid influence on phosphorus release in sediment-water microcosms. Ecology 1979, 60, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, C.P.; MacDonald, D.D. Effects of suspended sediments on aquatic ecosystems. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1991, 11, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.R.; Dracup, J.A.; Fogarty, T.J.; Willis, R. Water quality modeling of deep reservoirs. J. (Water Pollut. Control Fed.) 1976, 48, 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Tarela, P.A.; Menendez, A.N. A model to predict reservoir sedimentation. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1999, 4, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.O.; Nearing, M.A. Rare earth element oxides for tracing sediment movement. CATENA 2004, 55, 255–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, W.; Duck, J.M. Sidescan sonar applications in limnoarchaeology. Geoarchaeology 1987, 2, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- HYPACK. Hydrographic Survey Software User Manual; HYPACK: Middletown, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Blondel, P. Automatic mine detection by textural analysis of cots sidescan sonar imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 3115–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.; Trevorrow, M.V. Continuous monitoring of fish in a shallow channel using a fixed horizontal sonar. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 105, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.; Kostaschuk, R.; Villard, P. Quantitative visualization of flow fields associated with alluvial sand dunes: Results from the laboratory and field using ultrasonic and acoustic doppler anemometry. J. Vis. 2001, 4, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSOMAS. Deer Creek Reservoir Drainage, Tmdl Study; DNR, Ed.; Utah Department of Natural Resources: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2002.
- Hansen, C.H.; Williams, G.P.; Adjei, Z.; Barlow, A.; Nelson, E.J.; Miller, A.W. Reservoir water quality monitoring using remote sensing with seasonal models: Case study of five central-utah reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2015, 31, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Swain, N.; Munson, K.; Adjei, Z.; Williams, G.P.; Miller, W. Development of sub-seasonal remote sensing chlorophyll-a detection models. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


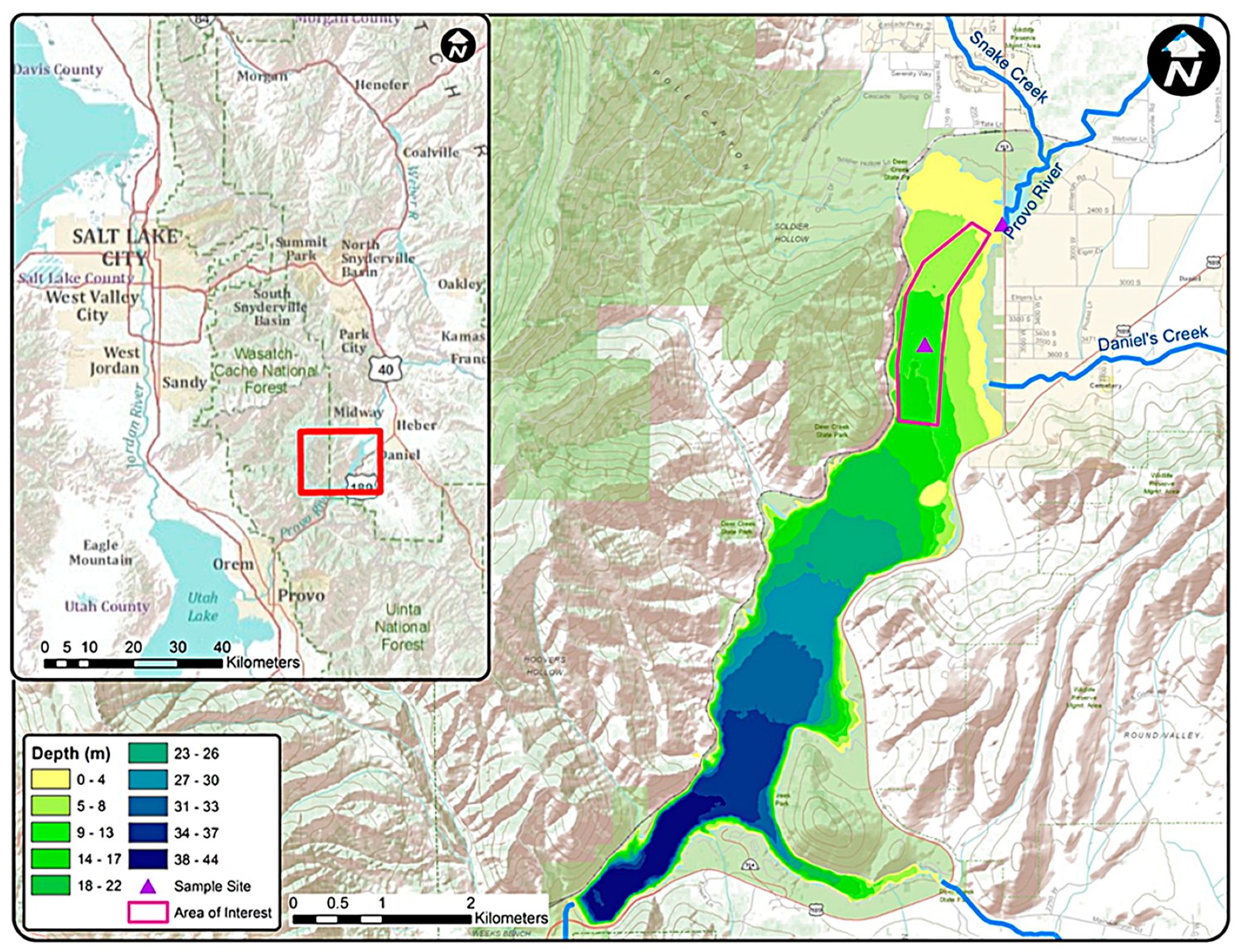
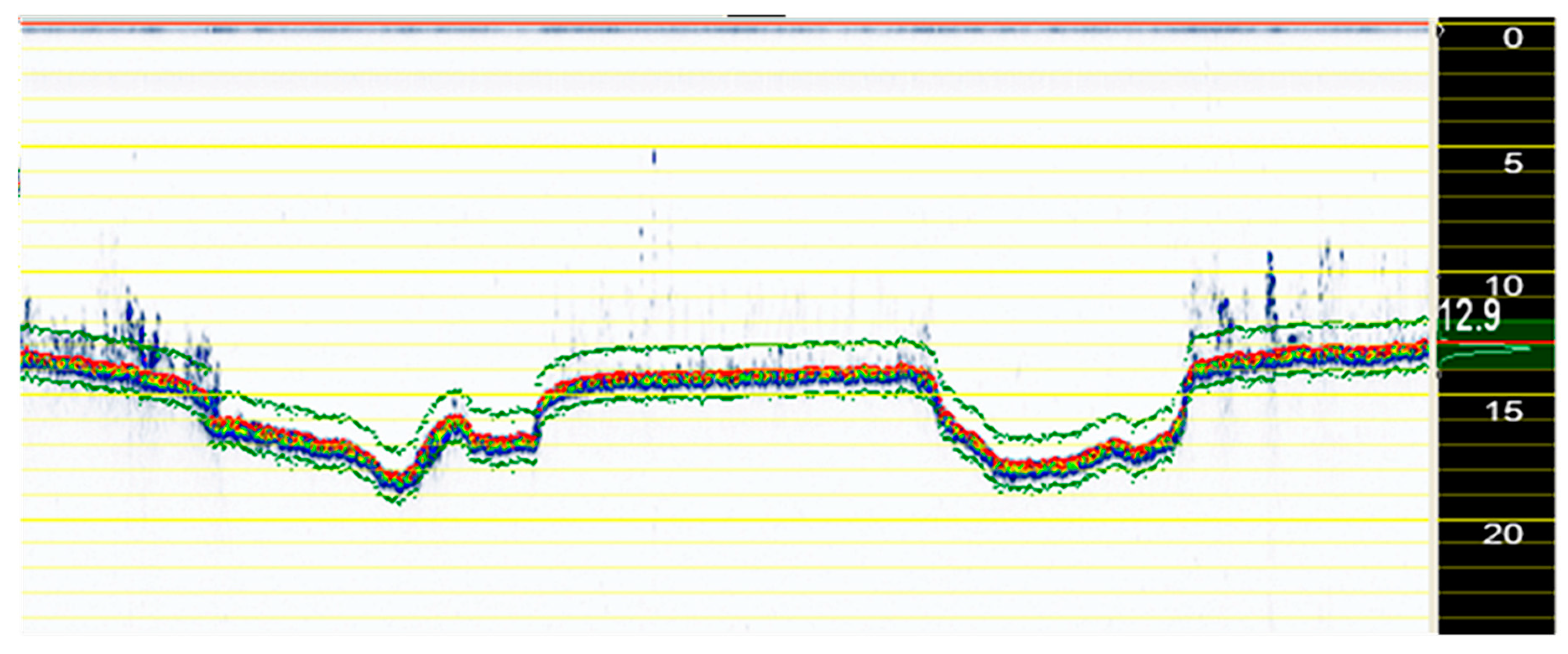
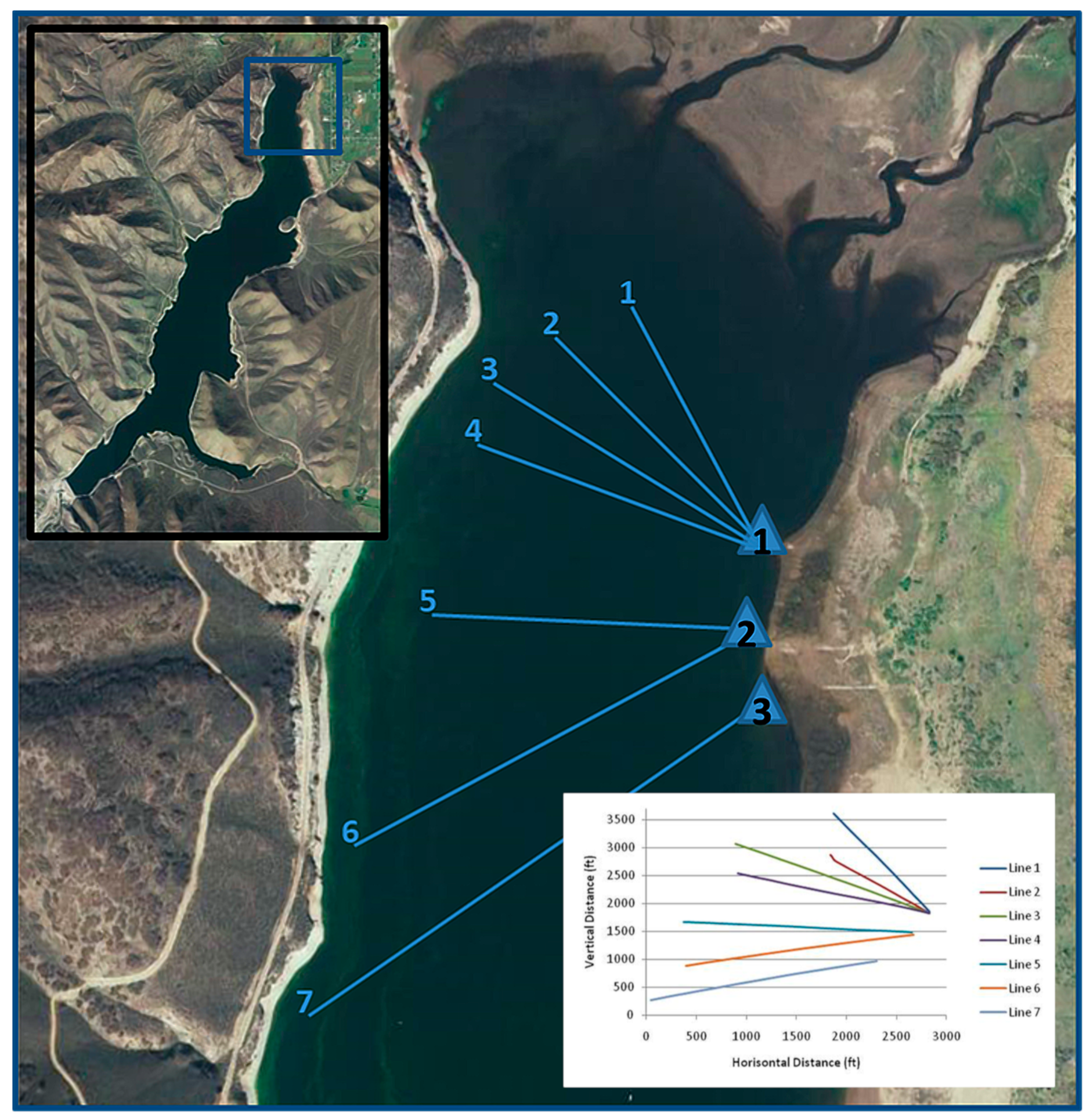




| Line Number | Length m (ft) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 605 (1986) |
| 2 | 435 (1430) |
| 3 | 703 (2308) |
| 4 | 620 (2035) |
| 5 | 697 (2288) |
| 6 | 714 (2344) |
| 7 | 720 (2362) |
| Trip Number | Date | Lines Surveyed | Water Surface Elevation m (Ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30/06/09 | Preliminary survey | 1651.18 (5417.25) |
| 2 | 02/07/09 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ,7 | 1651.10 (5417.01) |
| 3 | 16/07/09 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 | 1650.35 (5414.52) |
| 4 | 23/07/09 | 4, 6 | 1649.74 (5412.53) |
| 5 | 11/08/09 | 4, 5, 6, 7 | 1648.82 (5409.52) |
| 6 | 03/09/09 | 4, 5, 6, 7 | 1648.21 (5407.50) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, G.P.; Walton, A.C. Method for Estimating Sediment Mass Movement from Delta Recutting: A Case Study Using Single Beam Sonar in Deer Creek Reservoir. Water 2019, 11, 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112222
Williams GP, Walton AC. Method for Estimating Sediment Mass Movement from Delta Recutting: A Case Study Using Single Beam Sonar in Deer Creek Reservoir. Water. 2019; 11(11):2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112222
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, Gustavious Paul, and Ashley Childers Walton. 2019. "Method for Estimating Sediment Mass Movement from Delta Recutting: A Case Study Using Single Beam Sonar in Deer Creek Reservoir" Water 11, no. 11: 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112222
APA StyleWilliams, G. P., & Walton, A. C. (2019). Method for Estimating Sediment Mass Movement from Delta Recutting: A Case Study Using Single Beam Sonar in Deer Creek Reservoir. Water, 11(11), 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112222