Analysis of an Ecological Flow Regime during the Ctenopharyngodon Idella Spawning Period Based on Reservoir Operations
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We consider the thermal stratification of reservoirs and analyze the important influence of the hysteresis of the water temperature on the spawning of Ctenopharyngodon idella in habitats.
- A fuzzy logic-based habitat suitability model is established to evaluate the influence of hydraulic factors such as water temperature, velocity, and water depth on the suitability of a Ctenopharyngodon idella habitat.
- By simulating a variety of different reservoir inflow and outflow conditions, the functional relationship between flow and habitat suitability is established, which provides the best management plan for water resources planning and construction.
2. Study Area and Species
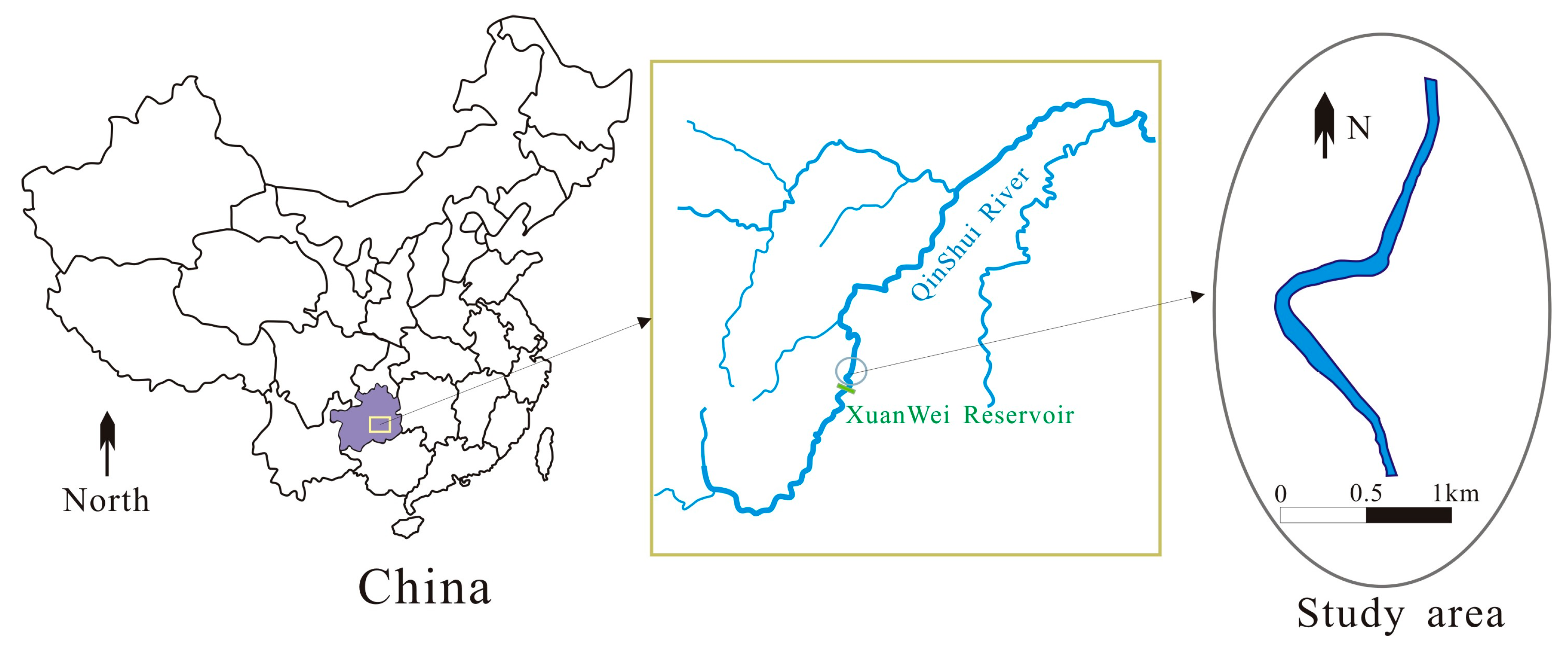
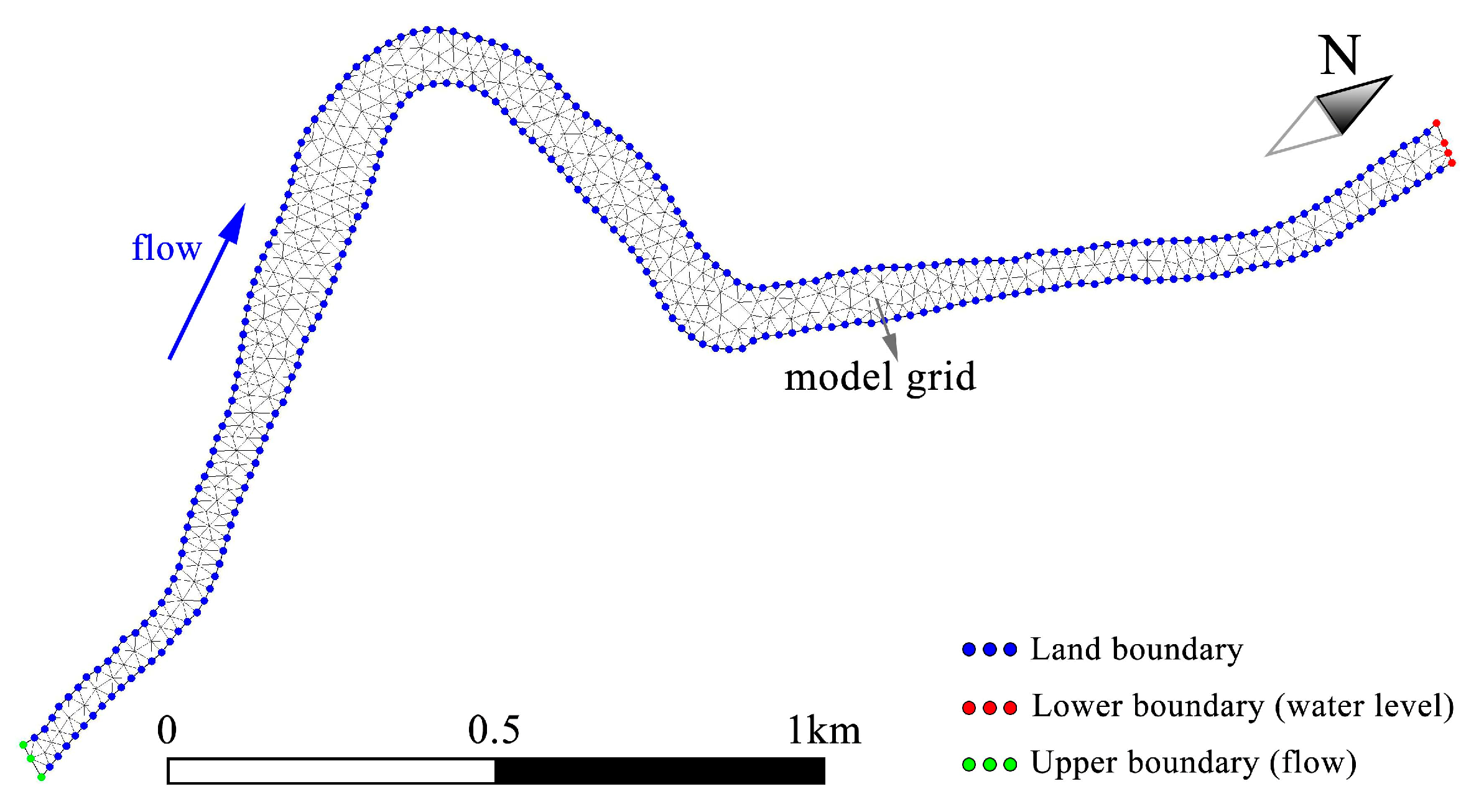
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ctenopharyngodon idella (C. idella)
3. Methods
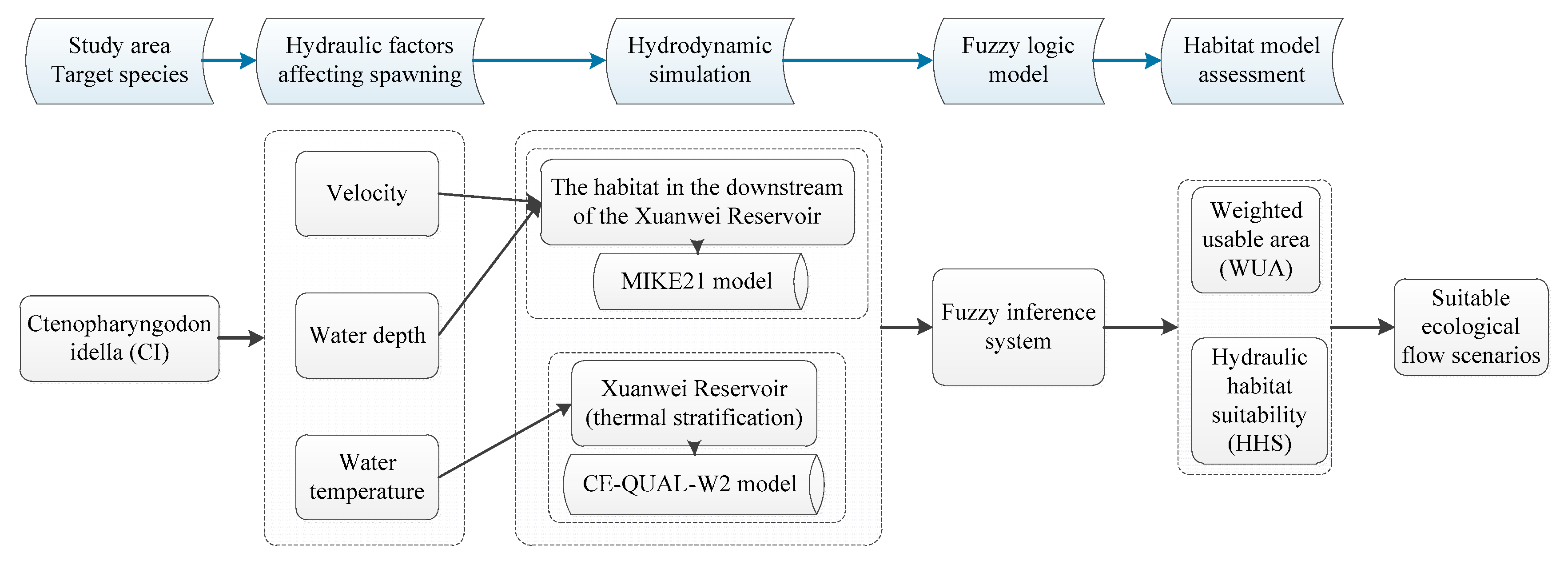
3.1. Model Framework
3.2. Hydrodynamic Simulation
3.2.1. CE-QUAL-W2 Model
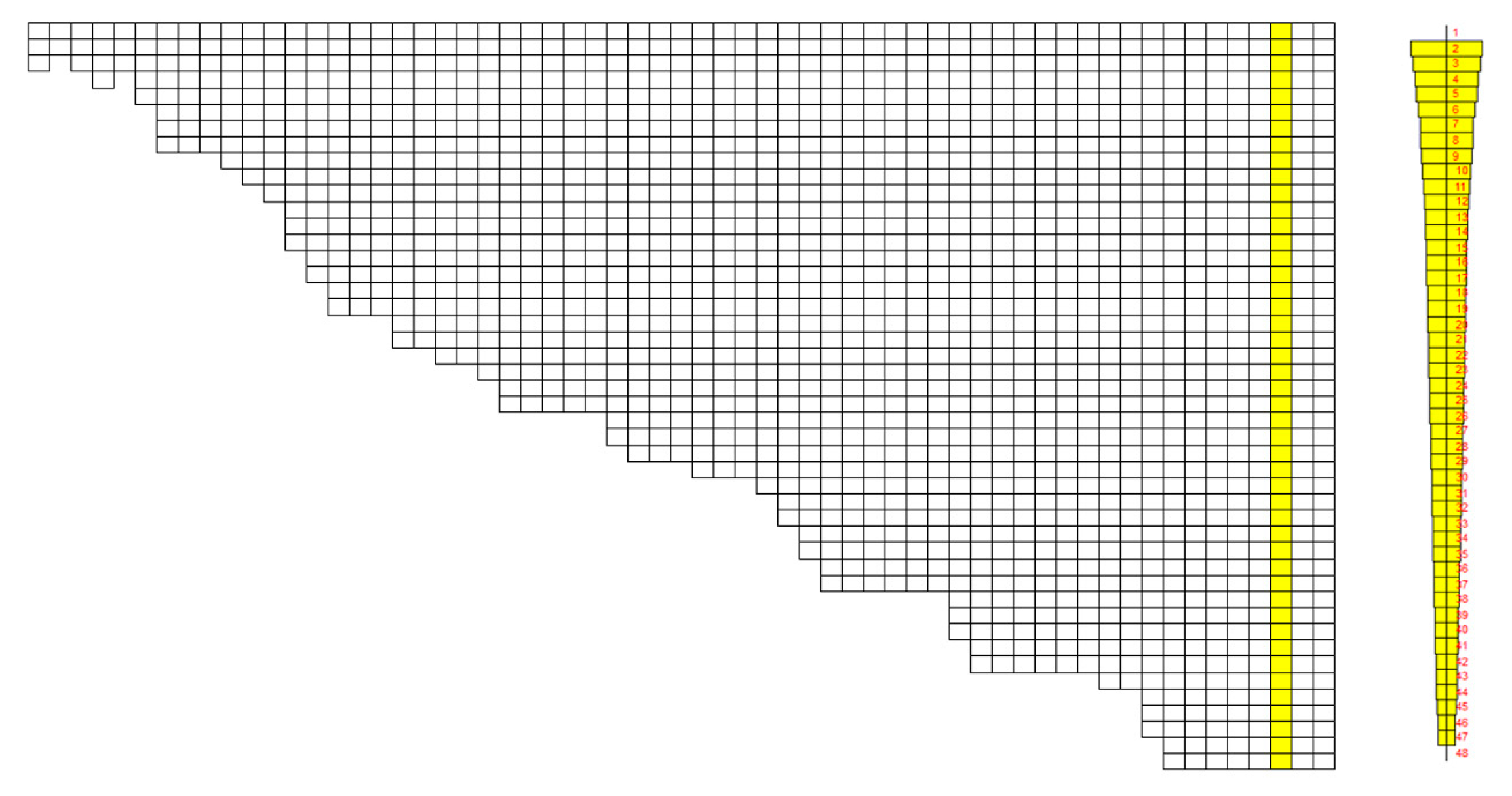
3.2.2. MIKE21 Model
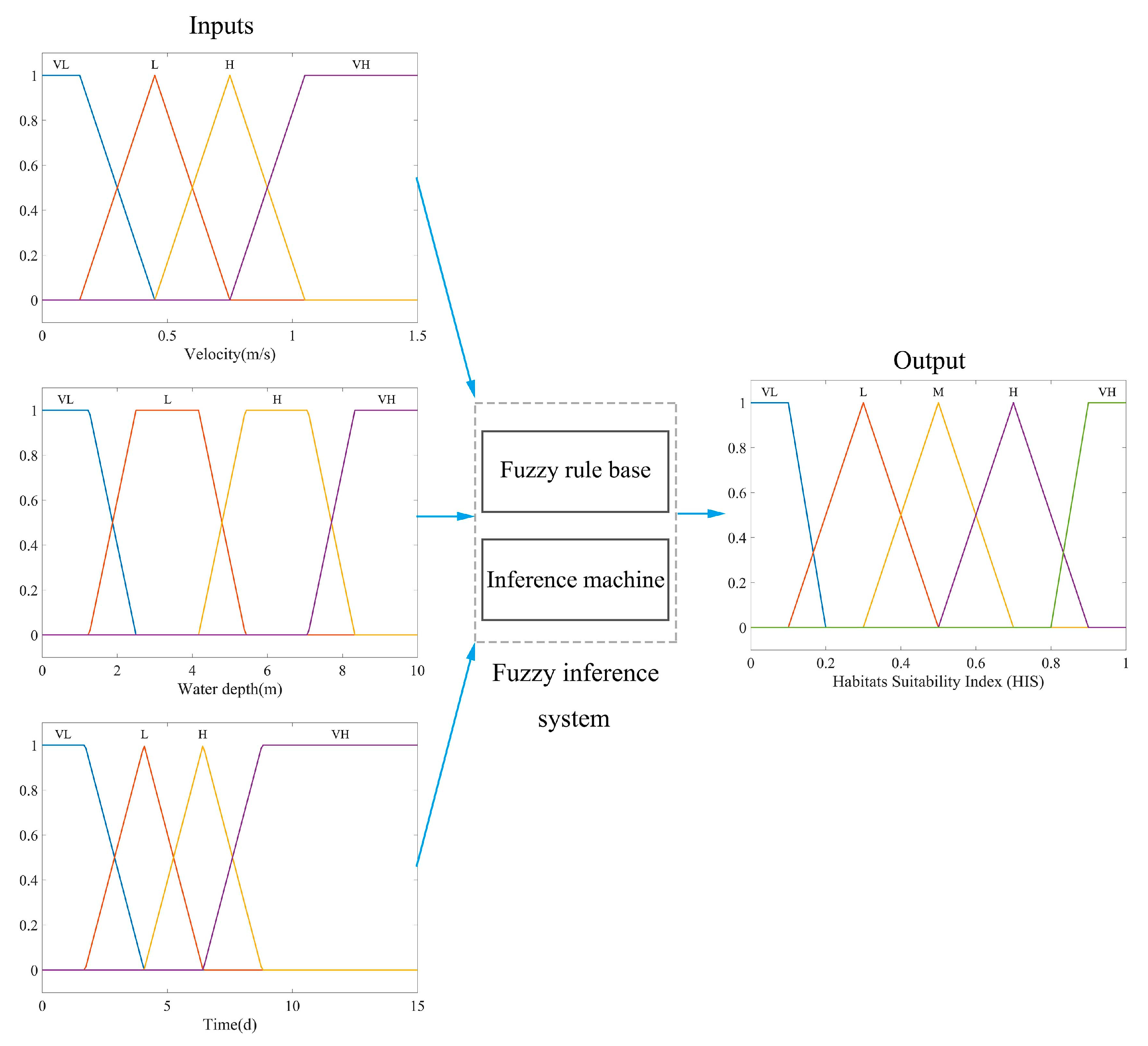
3.3. Fuzzy Logic-Based Habitat Modeling
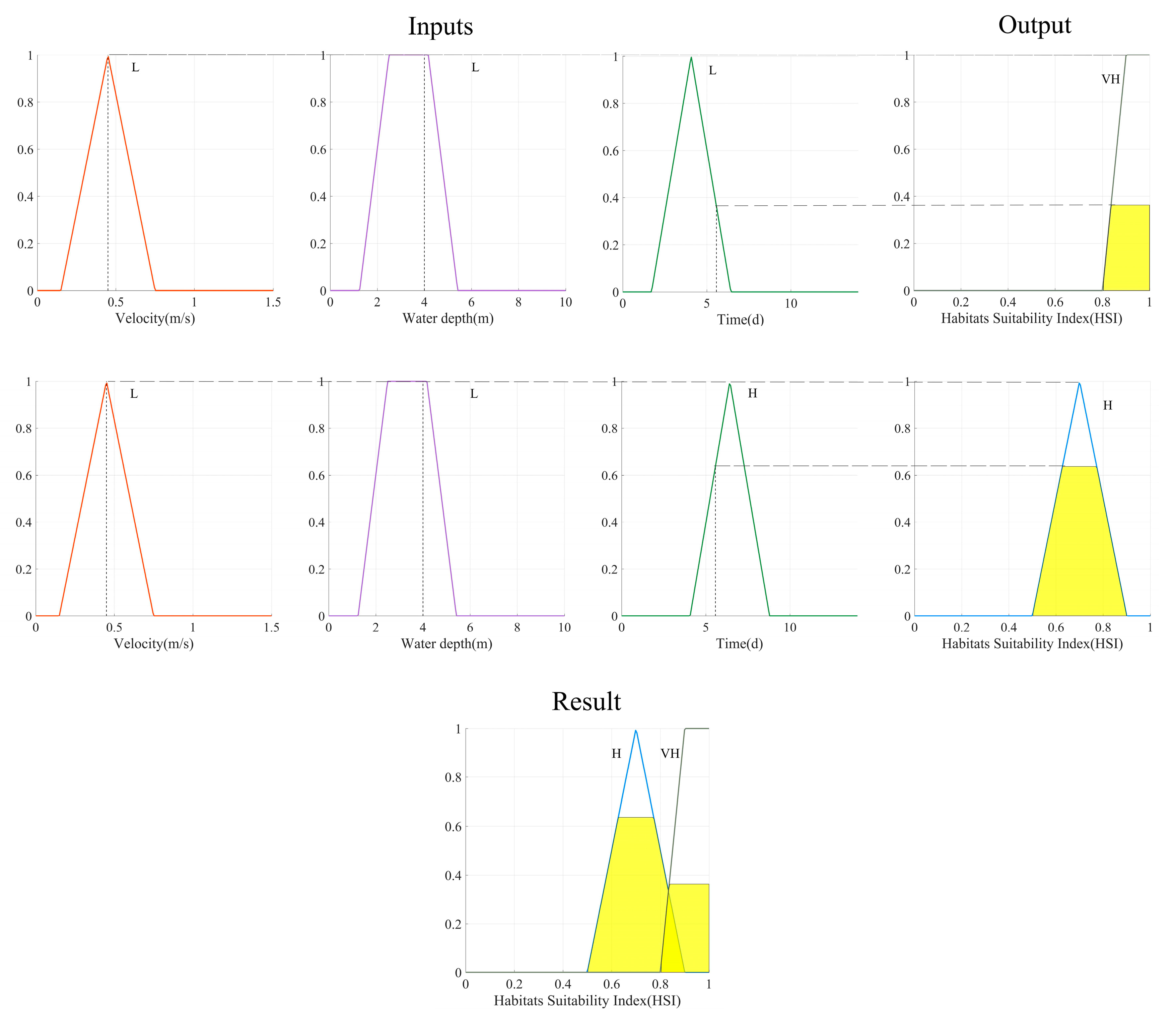
3.3.1. Fuzzification and Defuzzification
- (1)
- Fuzzification
- (2)
- Fuzzy Inference
- (3)
- Defuzzification
3.3.2. Criteria for Assessing Habitat Quality
4. Results and Discussion
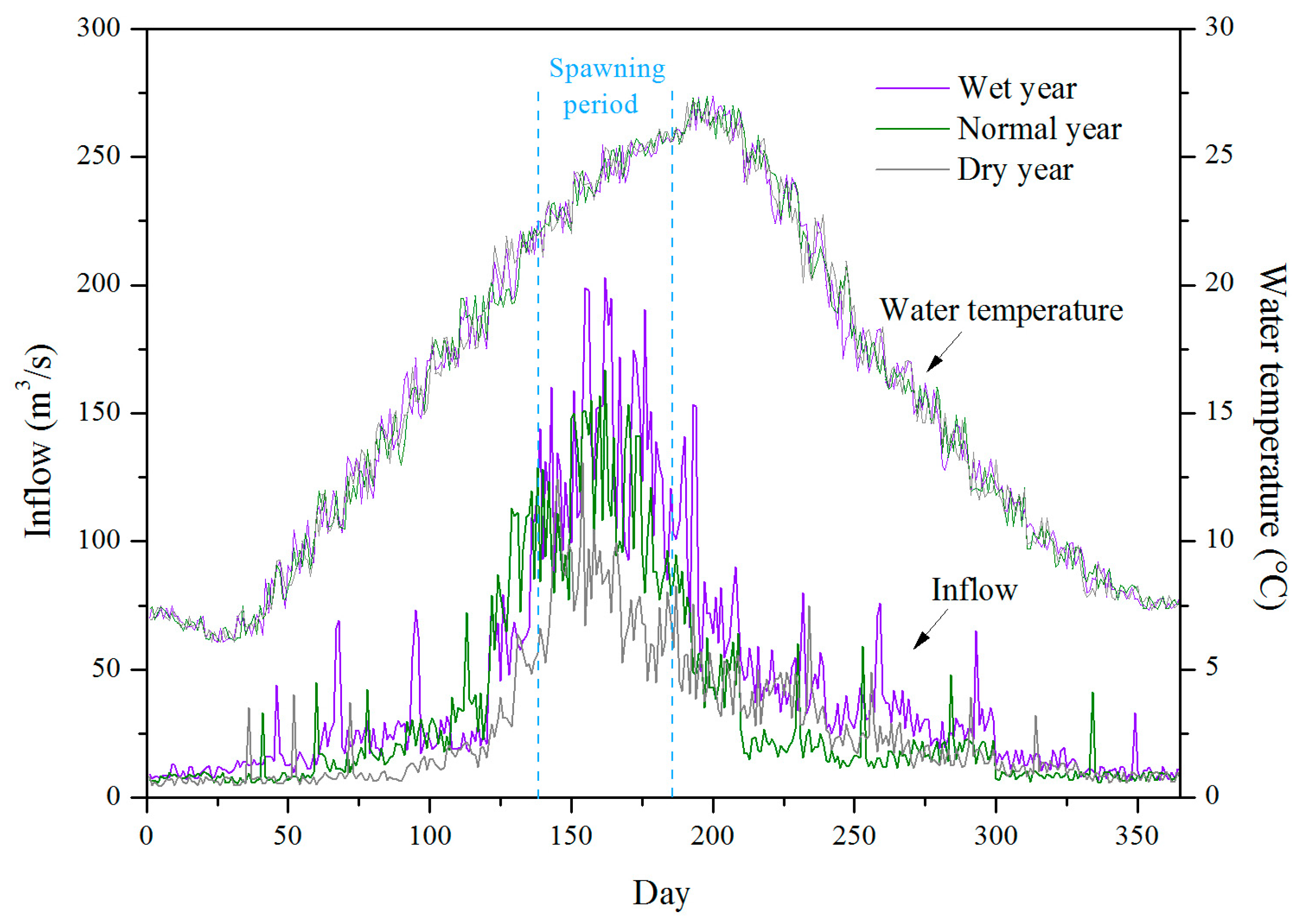
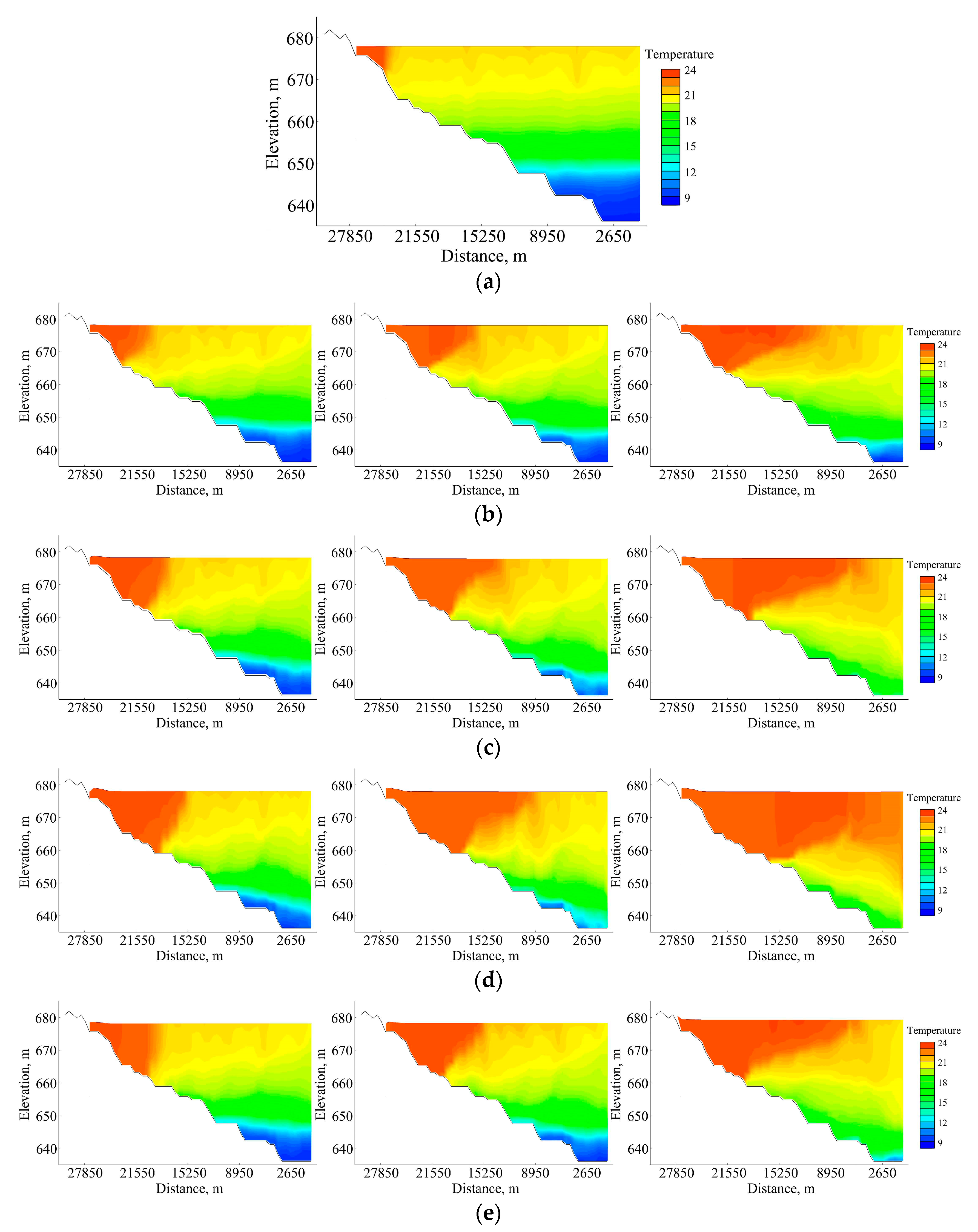
4.1. Result of CE-QUAL-W2 Model Simulation
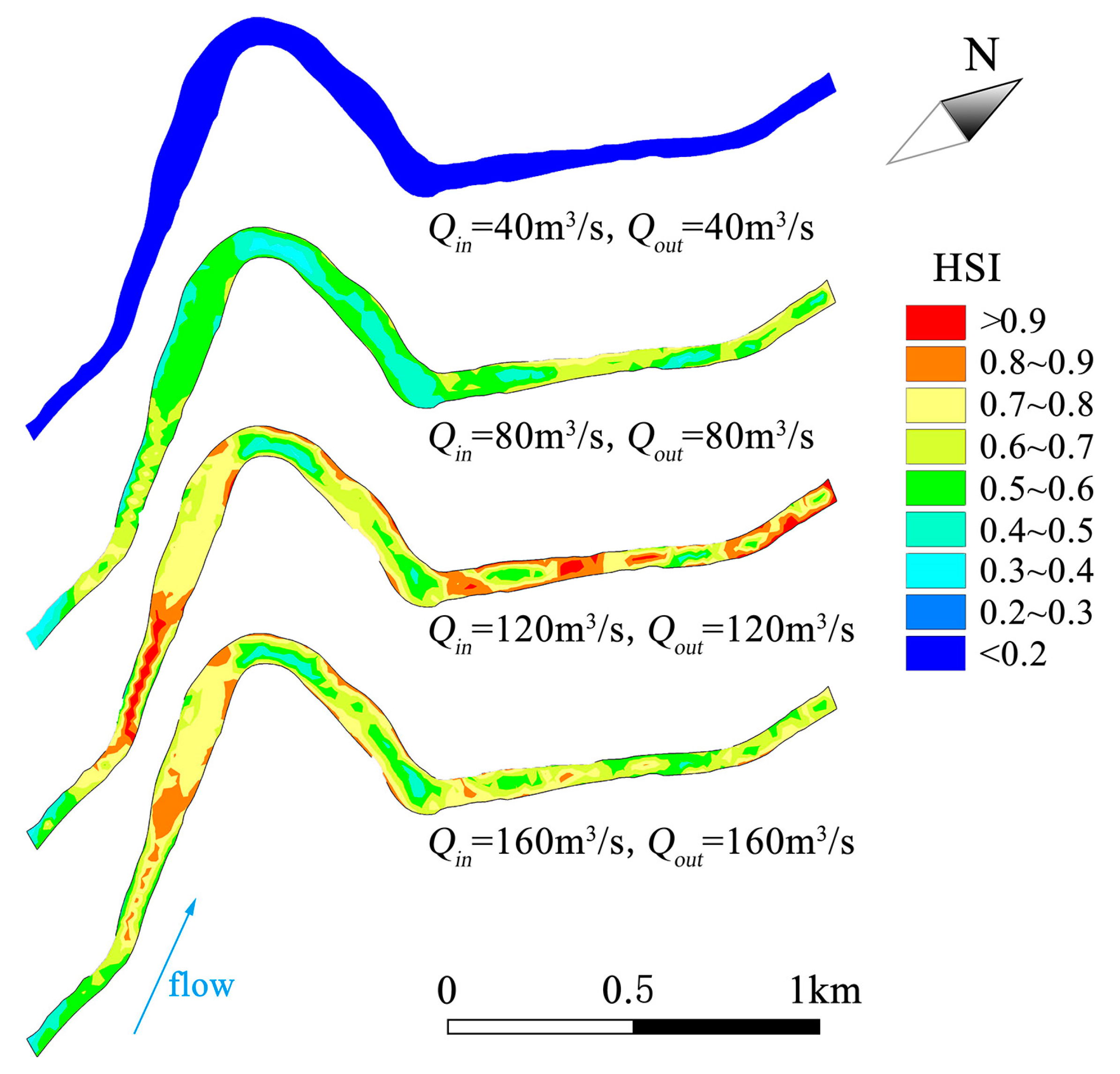
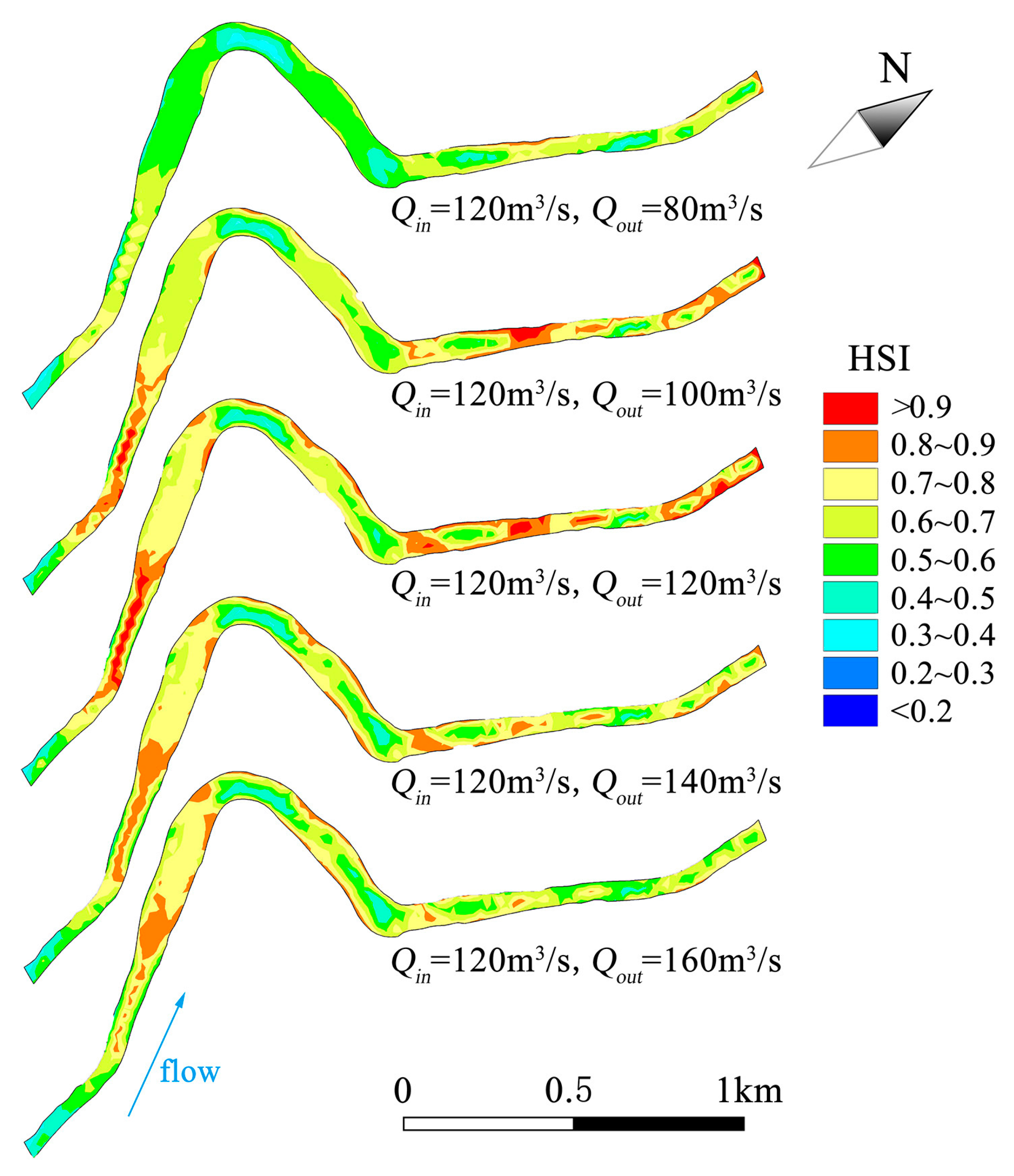
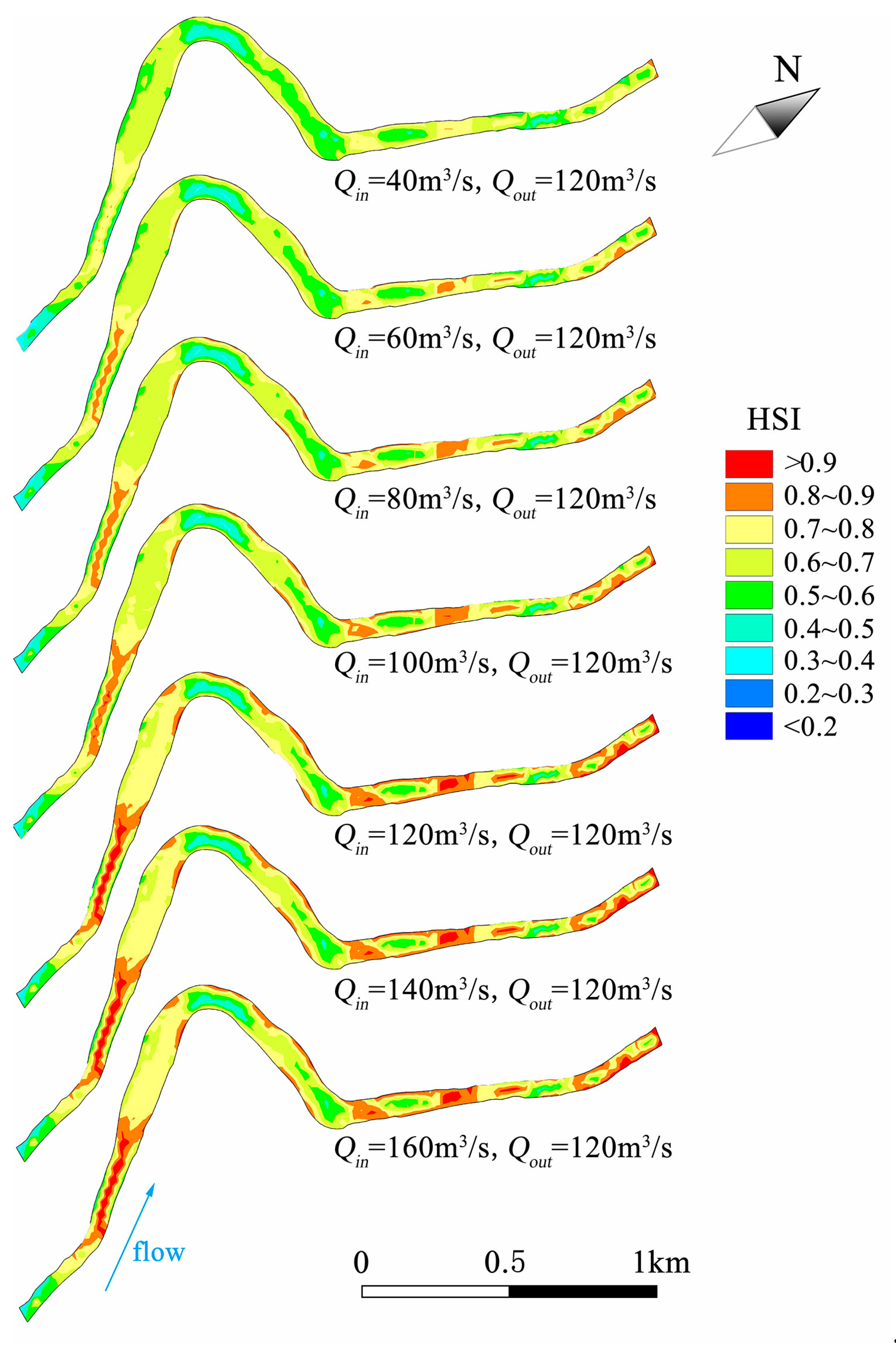
4.2. Result of MIKE21 Model Simulation
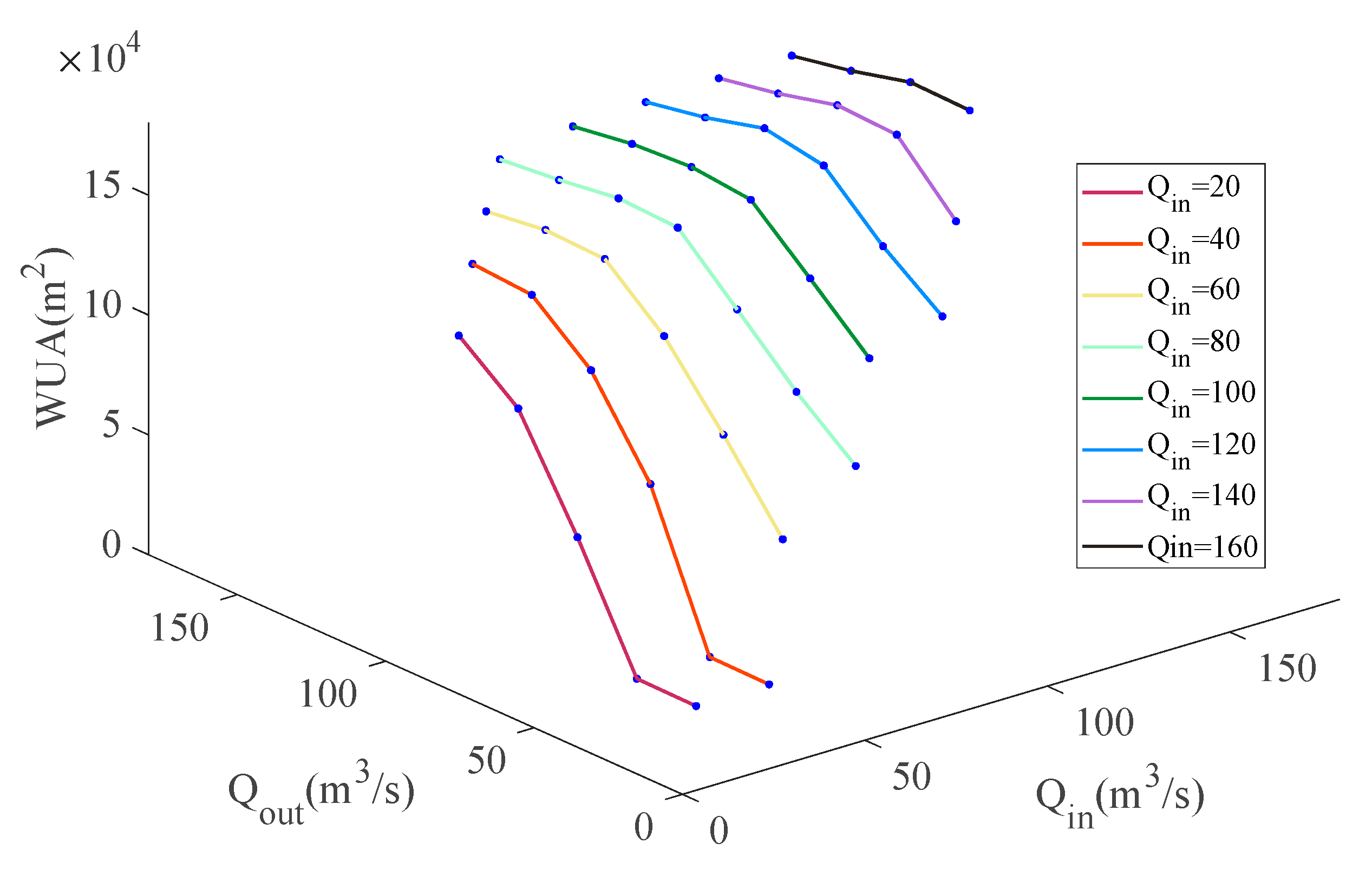
4.3. Suitable Ecological Flow Calculation
4.4. Discussion
4.4.1. Suitable Ecological Flow Discussion
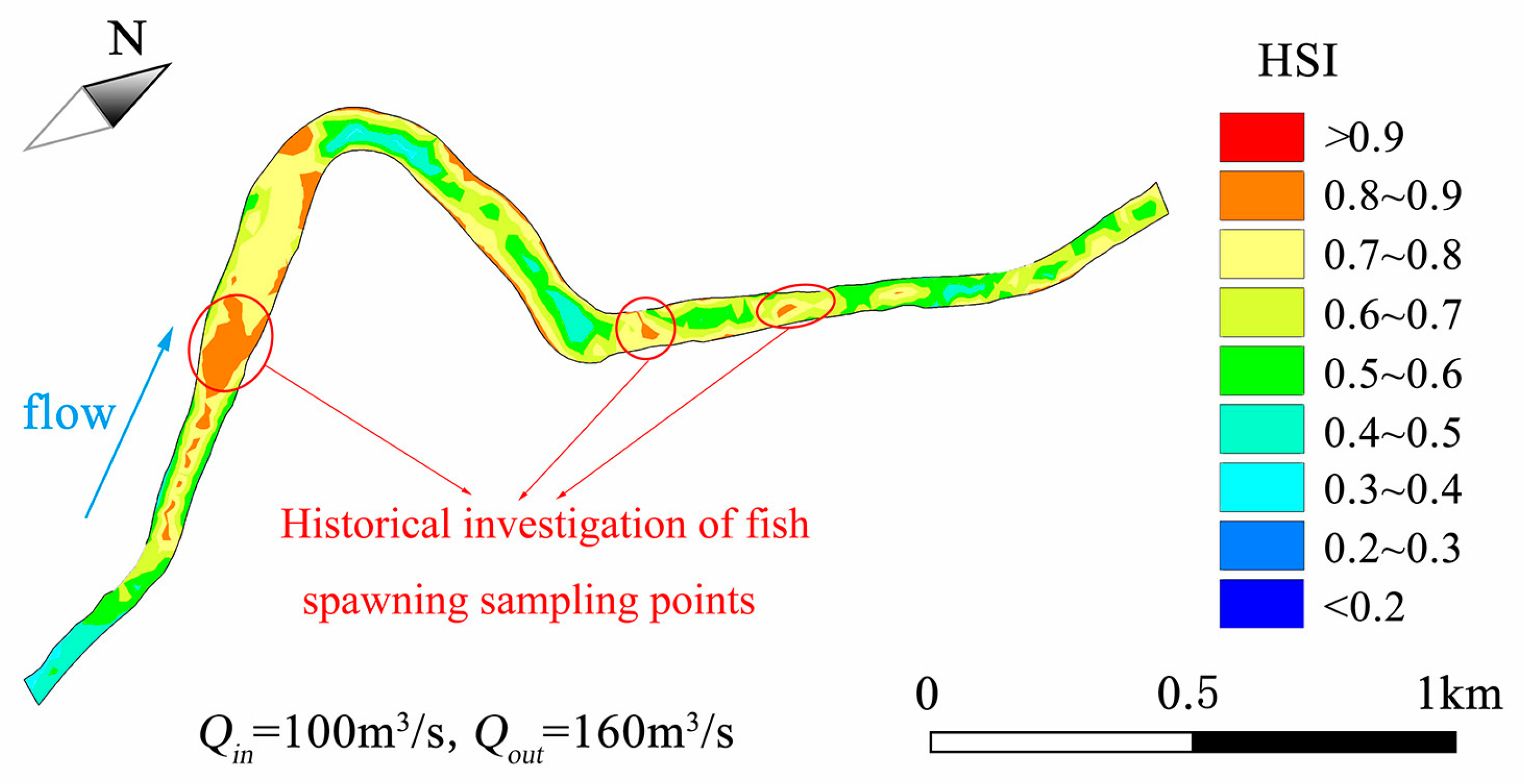
4.4.2. Suitable Spawning Areas Discussion
4.4.3. Future Work
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, L.; Li, X.; Fang, H.; Yin, D.; Si, Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Balancing social, economic and ecological benefits of reservoir operation during the flood season: A case study of the Three Gorges Project, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.T.; Rosewarne, P.J.; Wright, R.M.; Kemp, P.S. The impact of an Archimedes screw hydropower turbine on fish migration in a lowland river. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 118, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, W.M. A two dimensional hydrodynamic and sediment transport model for dam break based on finite volume method with quadtree grid. Appl. Ocean Res. 2011, 33, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, X.; Wen, X.; Fang, G.; Tan, Q.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Effects of damming and climatic change on the eco-hydrological system: A case study in the Yalong River, southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.; Martinez-Lage, J.; Molina, J.; Oscoz, J.; Tobes, I.; Vilches, A. Effects of stress controlled loading of a reservoir on downstream fish populations in a Pyrenean river. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2012, 11, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, H.; Dias, J.H.P.; Perbiche-Neves, G.; Kashiwaqui, E.A.L.; Ramos, I.P. Importance of dam-free tributaries for conserving fish biodiversity in Neotropical reservoirs. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 224, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Niu, W.; Cheng, C. China’s large-scale hydropower system: Operation characteristics, modeling challenge and dimensionality reduction possibilities. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Arhonditsis, G.B.; Gao, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, N.; Dong, F.; Shi, W. How successful are the restoration efforts of China’s lakes and reservoirs? Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, S.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Brucet, S.; Courrat, A.; Poikane, S.; Solimini, A.; Bund, W.; Zampoukas, N.; Hering, D. Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: An almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pander, J.; Geist, J. Ecological indicators for stream restoration success. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 30, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.; Eiler, J.H. Migration patterns of post-spawning Pacific herring in a subarctic sound. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 147, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzen, S.; Maage, A.; Duinker, A.; Julshamn, K.; Iversen, S.A. A baseline study of metals in herring (Clupea harengus) from the Norwegian Sea, with focus on mercury, cadmium, arsenic and lead. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjankar, R.; Tonina, D.; McKean, J.A.; Sohrabi, M.M.; Chen, Q.; Vidergar, D. Dam operations may improve aquatic habitat and offset negative effects of climate change. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Lian, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, S. Impact of intra-annual runoff uniformity and global warming on the thermal regime of a large reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Kong, N. Potential causes of habitat degradation and spawning time delay of the Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Ecol. Inform. 2018, 43, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskidis, I.; Kokkos, N.; Sapounidis, A.; Triantafillidis, S.; Kamidis, N.; Koutrakis, E.; Sylaios, G.K. Ecohydraulic modelling of Nestos River Delta under low flow regimes. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2018, 18, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, V.E.; Railsback, S.; Accolla, C.; Birnir, B.; Bruins, R.J.F.; Ducrot, V.; Galic, N.; Garber, K.; Harvey, B.C.; Jager, H.I.; et al. Predicting impacts of chemicals from organisms to ecosystem service delivery: A case study of endocrine disruptor effects on trout. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, P.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X. Evaluation of ecological instream flow considering hydrological alterations in the Yellow River basin, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 160, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, C.; Xia, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, T. An instream ecological flow method for data-scarce regulated rivers. J. Hydrol. 2011, 398, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Mas, R.; Martínez-Capel, F.; Alcaraz-Hernández, J.D.; Mouton, A.M. Can multilayer perceptron ensembles model the ecological niche of freshwater fish species? Ecol. Model. 2015, 309–310, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hao, G.; Yang, Z.; Liang, P.; Cai, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Zhu, J. Variation analysis of streamflow and ecological flow for the twin rivers of the Miyun Reservoir Basin in northern China from 1963 to 2011. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Lu, D.; Jin, G. Calculation of flow field and analysis of spawning sites for Chinese sturgeon in the downstream of Gezhouba Dam. J. Hydrodyn. 2007, 19, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.; Schneider, M.; Mutz, M.; Haustein, M.; Halle, M.; Seidel, M.; Sieker, H.; Wolter, C.; Hinkelmann, R. Model-based design for restoration of a small urban river. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Z.; Wieprecht, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y. Evaluating the ecological influence of hydraulic projects: A review of aquatic habitat suitability models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Qian, J.; Yu, Y.; Kong, N. An improved habitat model to evaluate the impact of water conservancy projects on Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) spawning sites in the Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 104, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Chen, Y. Assessing three fish species ecological status in Colorado River, Grand Canyon based on physical habitat and population models. Math. Biosci. 2018, 298, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V.; Scannapieco, D.; Zarra, T.; Ricco, D. Ecological status of rivers in preserved areas: Effects of meteorological parameters. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 53, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, A.; Tanim, A.H. A modeling approach to establish environmental flow threshold in ungauged semidiurnal tidal river. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingraff-Hamed, A.; Noack, M.; Greulich, S.; Schwarzwälder, K.; Pauleit, S.; Wantzen, K. Model-Based Evaluation of the Effects of River Discharge Modulations on Physical Fish Habitat Quality. Water 2018, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, I.; Dias, V.; Ferreira, M.T.; Santos, J.M. Univariate functions versus fuzzy logic: Implications for fish habitat modeling. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, Z.; Cai, L.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Chang, J. Effects of upstream and downstream dam operation on the spawning habitat suitability of Coreius guichenoti in the middle reach of the Jinsha River. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, A.M.; Alcaraz-Hernández, J.D.; de Baets, B.; Goethals, P.L.M.; Martínez-Capel, F. Data-driven fuzzy habitat suitability models for brown trout in Spanish Mediterranean rivers. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; de Baets, B.; Mouton, A.M.; Waegeman, W.; Nakajima, J.; Mukai, T.; Hiramatsu, K.; Onikura, N. Effect of model formulation on the optimization of a genetic Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy system for fish habitat suitability evaluation. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, Q.; Tonina, D.; Cai, D. Effects of upstream reservoir regulation on the hydrological regime and fish habitats of the Lijiang River, China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 76, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wieprecht, S.; Tang, C. Comparison of habitat suitability models using different habitat suitability evaluation methods. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lin, T.; Huang, D.; Perng, M.; Chiu, L. An automated system for egg collection, hatching, and transfer of larvae in a freshwater finfish hatchery. Aquaculture 2000, 182, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dong, S.; Wang, F.; Tian, X.; Gao, Q. Respiratory response of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) to temperature changes. Aquaculture 2011, 322, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Niu, W.; Cheng, C. Optimization of hydropower reservoirs operation balancing generation benefit and ecological requirement with parallel multi-objective genetic algorithm. Energy 2018, 153, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, H.; Mo, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Pang, S.; Yin, X. Hierarchical flood operation rules optimization using multi-objective cultured evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Mas, R.; Marcos-Garcia, P.; Lopez-Nicolas, A.; Martínez-García, F.J.; Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Martínez-Capel, F. Combining literature-based and data-driven fuzzy models to predict brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) spawning habitat degradation induced by climate change. Ecol. Model. 2018, 386, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, R.G.; Hamilton, D.P.; Phillips, R.L. Comparison of two 2-dimensional, laterally averaged hydrodynamic model applications to the Swan River Estuary. Math. Comput. Simul. 2000, 51, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, B.; Johnson, B.E. Integration of a benthic sediment diagenesis module into the two dimensional hydrodynamic and water quality model—CE-QUAL-W2. Ecol. Model. 2015, 297, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Liu, J.; Du, X.; Dai, C.; Liu, R. Simulation-based risk analysis of water pollution accidents combining multi-stressors and multi-receptors in a coastal watershed. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.A.; Perrie, W.; Solomon, S.M. Evaluation of two spectral wave models for wave hindcasting in the Mackenzie Delta. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 62, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, J.H.; Tjahyani, D.T.S.; Ekariansyah, A.S.; Tjahjono, H. Fuzzy probability based fault tree analysis to propagate and quantify epistemic uncertainty. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 85, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feng, X.; Pedrycz, W. Extraction of fuzzy rules from fuzzy decision trees: An axiomatic fuzzy sets (AFS) approach. Data Knowl. Eng. 2013, 84, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Broekhoven, E.; Adriaenssens, V.; de Baets, B.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. Fuzzy rule-based macroinvertebrate habitat suitability models for running waters. Ecol. Model. 2006, 198, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S. Consideration of fuzziness: Is it necessary in modelling fish habitat preference of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes)? Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Zheng, T. Evaluation of flow patterns in vertical slot fishways with different slot positions based on a comparison passage experiment for juvenile grass carp. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 133, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šetlíková, I.; Bláha, M.; Edwards-Jonášová, M.; Dvořák, J.; Burianová, K. Diversity of phytophilous macroinvertebrates in polycultures of semi-intensively managed fishponds. Limnologica 2016, 60, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Li, M.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ai, X.; Lin, Z. Effect of temperature on plasma and tissue kinetics of doxycycline in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) after oral administration. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
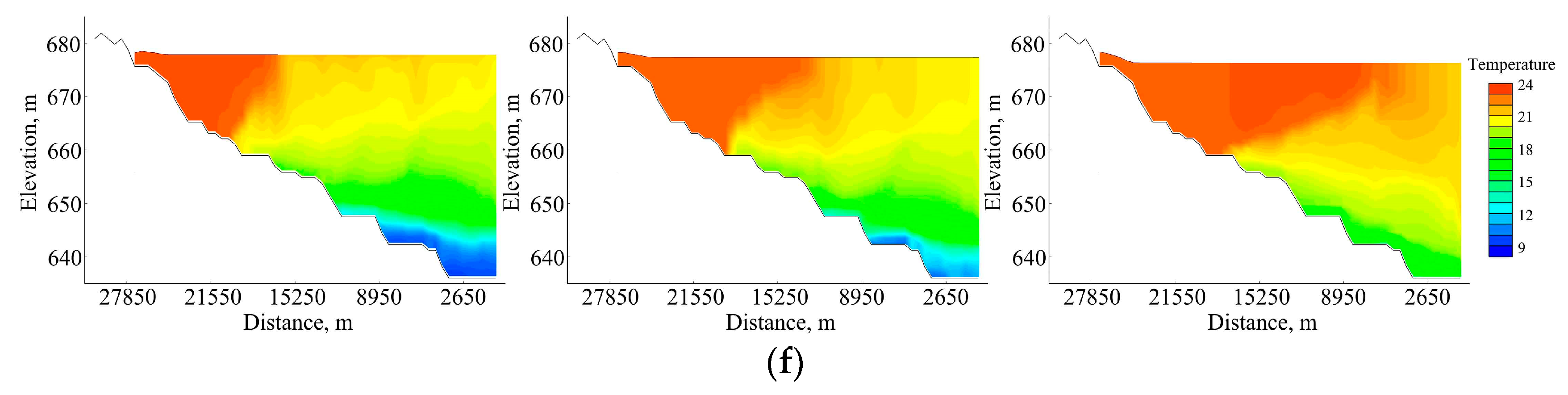
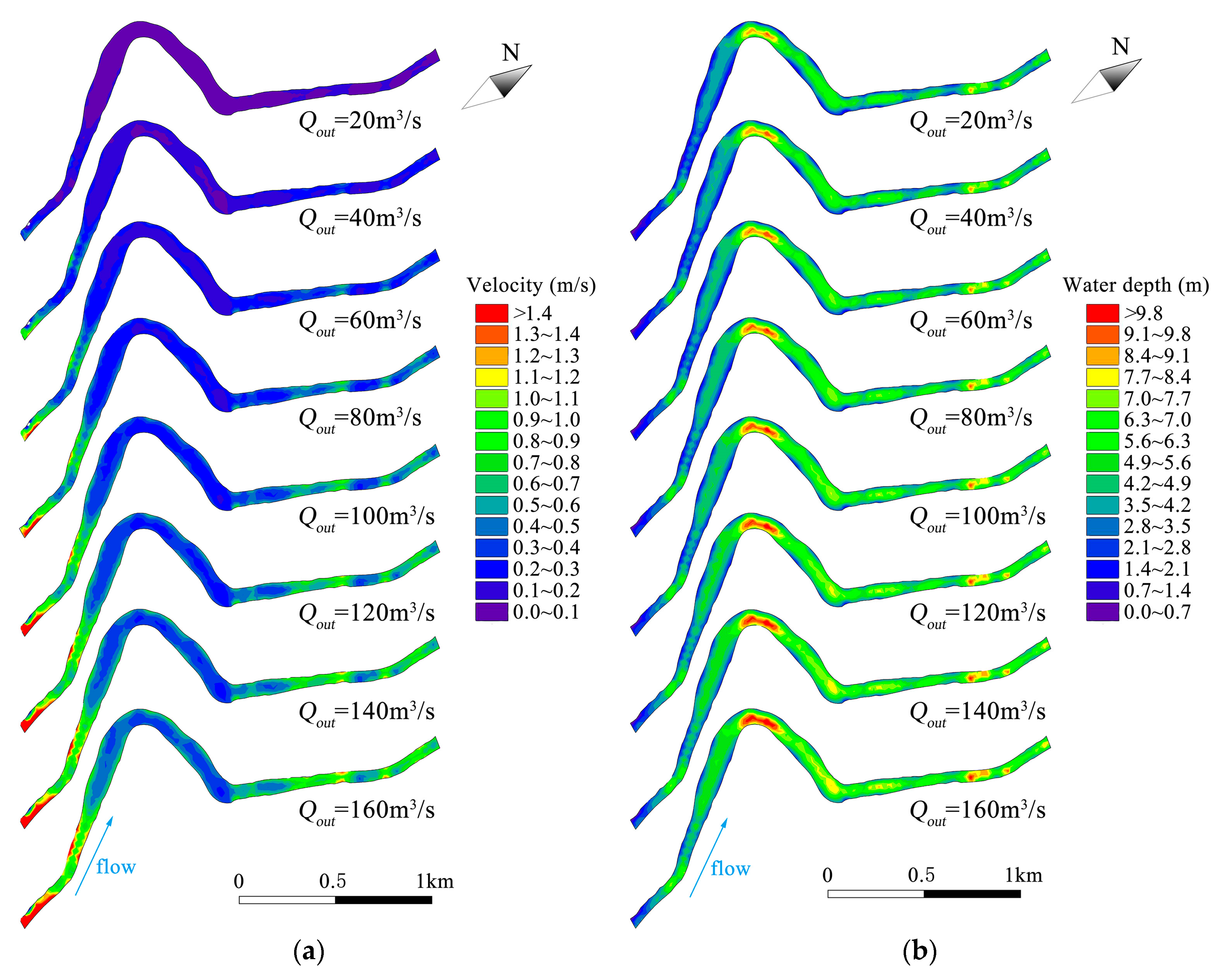
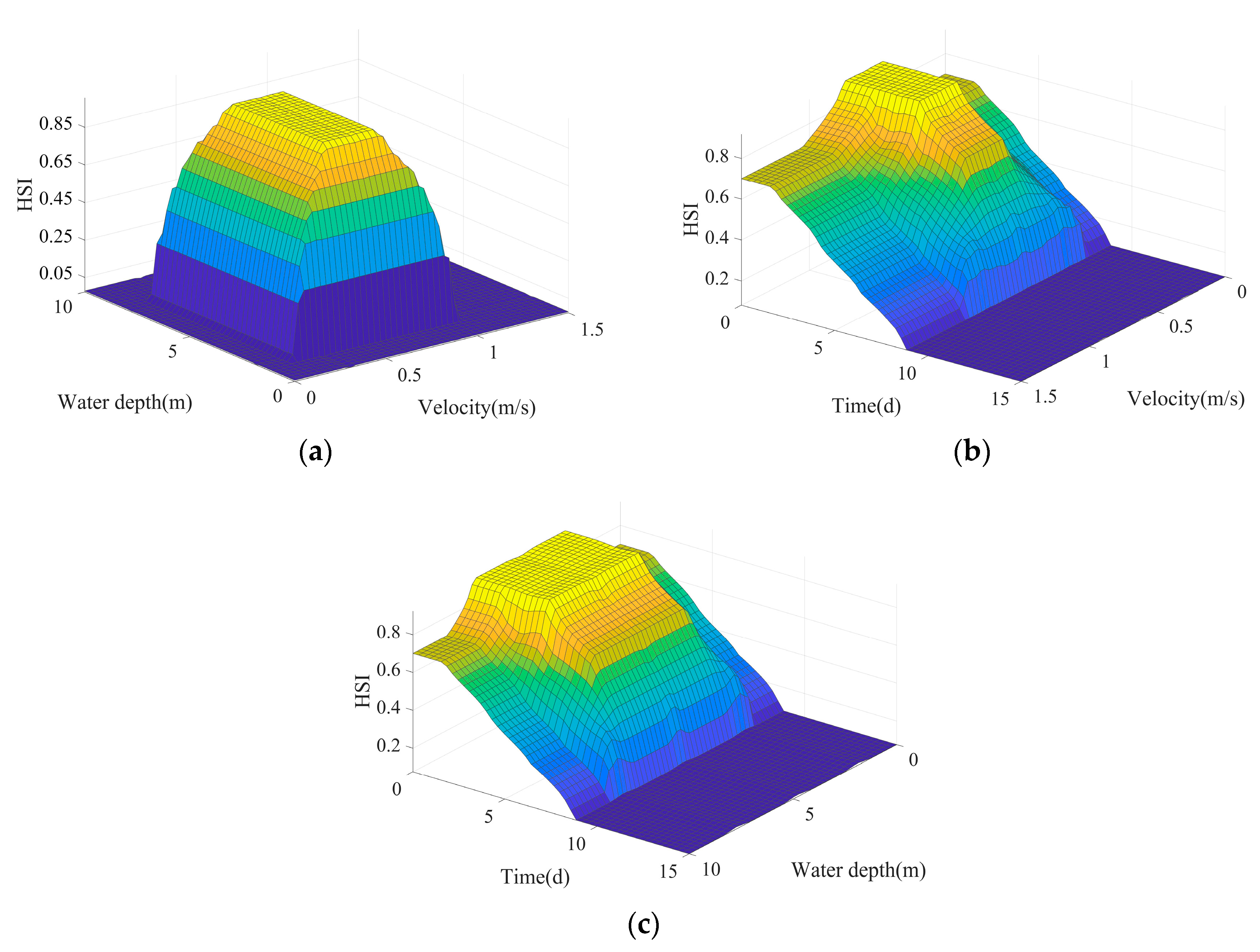
| Velocity | Water Depth | Time | HSI | Velocity | Water Depth | Time | HSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VL | VL | VL | M | VL | VL | L | L |
| L | VL | VL | H | L | VL | L | M |
| H | VL | VL | H | H | VL | L | M |
| VH | VL | VL | M | VH | VL | L | L |
| VL | L | VL | H | VL | L | L | M |
| L | L | VL | VH | L | L | L | VH |
| H | L | VL | VH | H | L | L | VH |
| VH | L | VL | H | VH | L | L | M |
| VL | H | VL | H | VL | H | L | M |
| L | H | VL | VH | L | H | L | VH |
| H | H | VL | VH | H | H | L | VH |
| VH | H | VL | H | VH | H | L | M |
| VL | VH | VL | M | VL | VH | L | L |
| L | VH | VL | H | L | VH | L | M |
| H | VH | VL | H | H | VH | L | M |
| VH | VH | VL | M | VH | VH | L | L |
| VL | VL | H | L | VL | VL | VH | VL |
| L | VL | H | L | L | VL | VH | VL |
| H | VL | H | L | H | VL | VH | VL |
| VH | VL | H | L | VH | VL | VH | VL |
| VL | L | H | L | VL | L | VH | VL |
| L | L | H | H | L | L | VH | L |
| H | L | H | H | H | L | VH | L |
| VH | L | H | L | VH | L | VH | VL |
| VL | H | H | L | VL | H | VH | VL |
| L | H | H | H | L | H | VH | L |
| H | H | H | H | H | H | VH | L |
| VH | H | H | L | VH | H | VH | VL |
| VL | VH | H | L | VL | VH | VH | VL |
| L | VH | H | L | L | VH | VH | VL |
| H | VH | H | L | H | VH | VH | VL |
| VH | VH | H | L | VH | VH | VH | VL |
| Time (day) | Outflow (m3/s) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | ||
| Inflow (m3/s) | 20 | 13 | 10.6 | 8 | 6.4 | 6.2 | / | / | / |
| 40 | 10.8 | 9.8 | 7.2 | 6 | 5.7 | 5.3 | / | / | |
| 60 | / | 7.7 | 6.5 | 5.6 | 5.2 | 4.8 | 4.5 | / | |
| 80 | / | 6.3 | 6 | 5.4 | 4.8 | 4.5 | 4.3 | 4.2 | |
| 100 | / | / | 5.6 | 5 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 4.1 | 4 | |
| 120 | / | / | 4.8 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 4 | 3.9 | 3.8 | |
| 140 | / | / | / | 4.5 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 3.6 | |
| 160 | / | / | / | / | 4 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 3.5 | |
| HHS | Outflow (m3/s) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | ||
| Inflow (m3/s) | 20 | 0.077 | 0.079 | 0.300 | 0.497 | 0.586 | / | / | / |
| 40 | 0.077 | 0.079 | 0.361 | 0.529 | 0.623 | 0.631 | / | / | |
| 60 | / | 0.264 | 0.414 | 0.553 | 0.651 | 0.655 | 0.640 | / | |
| 80 | / | 0.364 | 0.455 | 0.563 | 0.669 | 0.675 | 0.659 | 0.647 | |
| 100 | / | / | 0.478 | 0.581 | 0.681 | 0.693 | 0.686 | 0.669 | |
| 120 | / | / | 0.517 | 0.601 | 0.705 | 0.726 | 0.696 | 0.674 | |
| 140 | / | / | / | 0.608 | 0.723 | 0.729 | 0.700 | 0.678 | |
| 160 | / | / | / | / | 0.728 | 0.731 | 0.702 | 0.680 | |
| WUA (HSI>0.6) (m3) | Outflow (m3/s) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | ||
| Inflow (m3/s) | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27764 | 61698 | / | / | / |
| 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 35069 | 86714 | 99344 | / | / | |
| 60 | / | 0 | 9308 | 42825 | 108387 | 111137 | 103931 | / | |
| 80 | / | 2979 | 14038 | 47581 | 119950 | 119168 | 109860 | 101351 | |
| 100 | / | / | 18432 | 55961 | 124693 | 124188 | 117030 | 106967 | |
| 120 | / | / | 27236 | 69335 | 130415 | 131471 | 118182 | 107612 | |
| 140 | / | / | / | 74387 | 134015 | 132086 | 119230 | 108050 | |
| 160 | / | / | / | / | 135396 | 132667 | 120162 | 108712 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Qin, H.; Pei, S.; Yao, L.; Wen, W.; Yi, L.; Zhou, J.; Tang, L. Analysis of an Ecological Flow Regime during the Ctenopharyngodon Idella Spawning Period Based on Reservoir Operations. Water 2019, 11, 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102034
Li J, Qin H, Pei S, Yao L, Wen W, Yi L, Zhou J, Tang L. Analysis of an Ecological Flow Regime during the Ctenopharyngodon Idella Spawning Period Based on Reservoir Operations. Water. 2019; 11(10):2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102034
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jie, Hui Qin, Shaoqian Pei, Liqiang Yao, Wei Wen, Liang Yi, Jianzhong Zhou, and Lingyun Tang. 2019. "Analysis of an Ecological Flow Regime during the Ctenopharyngodon Idella Spawning Period Based on Reservoir Operations" Water 11, no. 10: 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102034
APA StyleLi, J., Qin, H., Pei, S., Yao, L., Wen, W., Yi, L., Zhou, J., & Tang, L. (2019). Analysis of an Ecological Flow Regime during the Ctenopharyngodon Idella Spawning Period Based on Reservoir Operations. Water, 11(10), 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102034





