The Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Community Composition in an Estuary Reservoir during Spring and Summer Seasons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites and In Situ Measurements
2.2. Physic-Chemical Parameters and Environmental Factors
2.3. Antibiotics Detection and Analysis
2.4. Genome DNA Extraction
2.5. The 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing via (Polymerase Chain Reaction) PCR Amplification
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
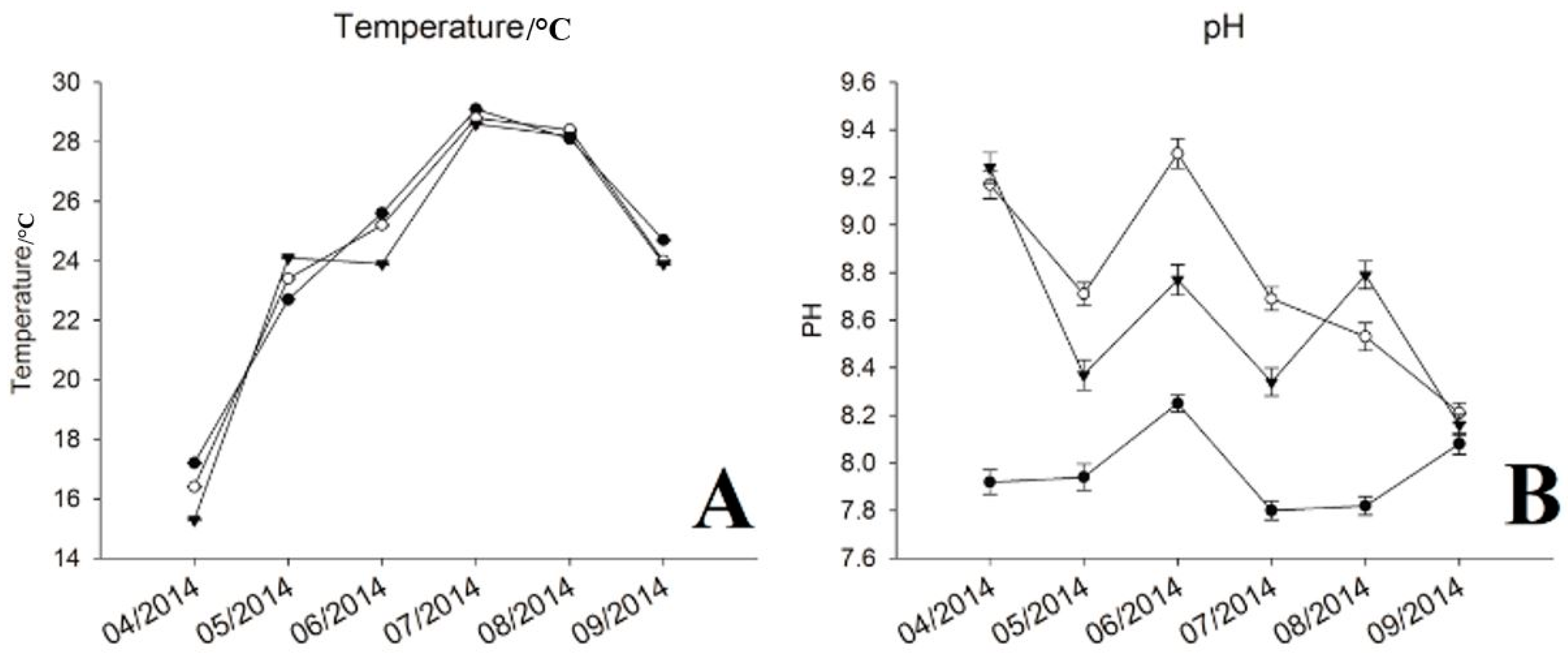
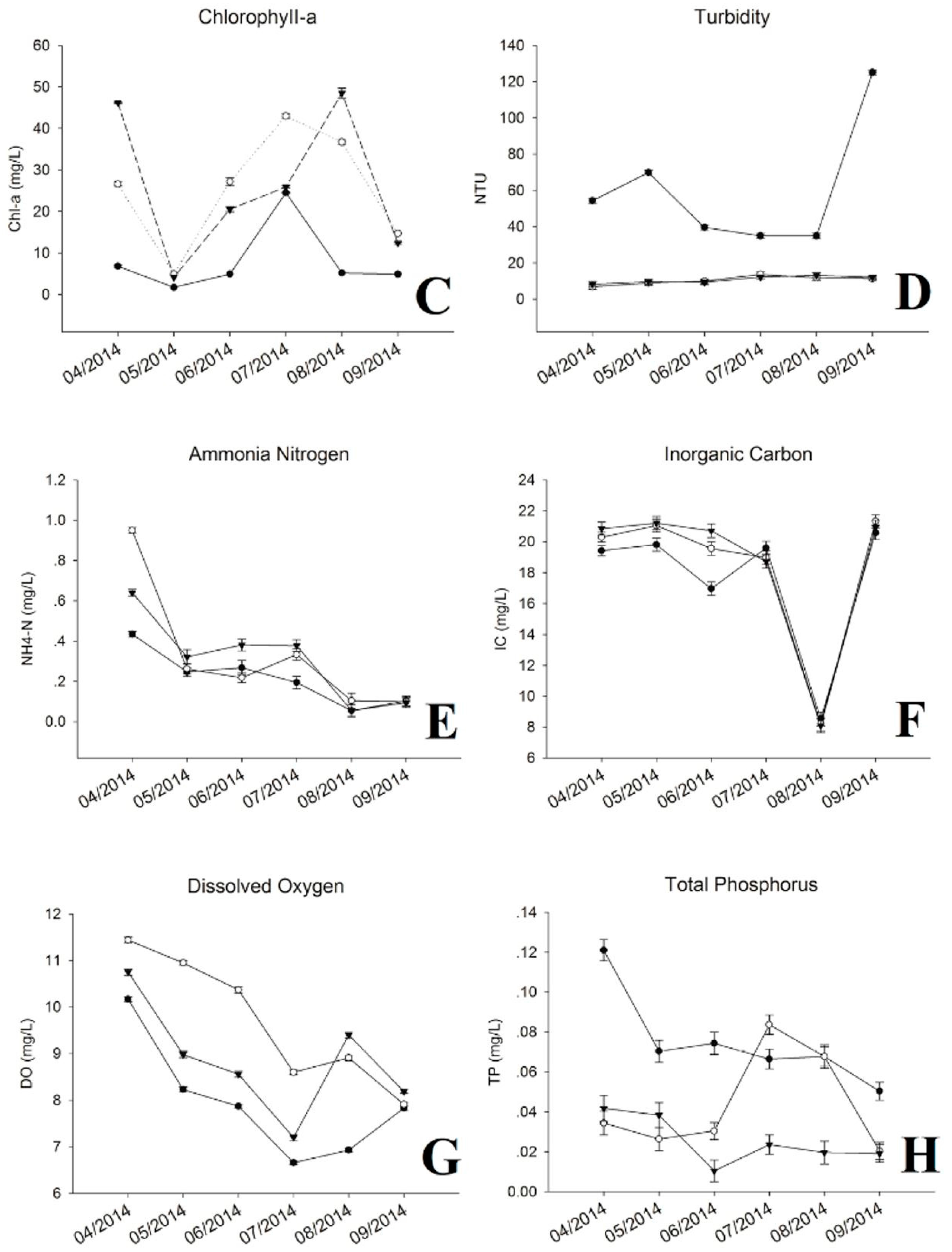
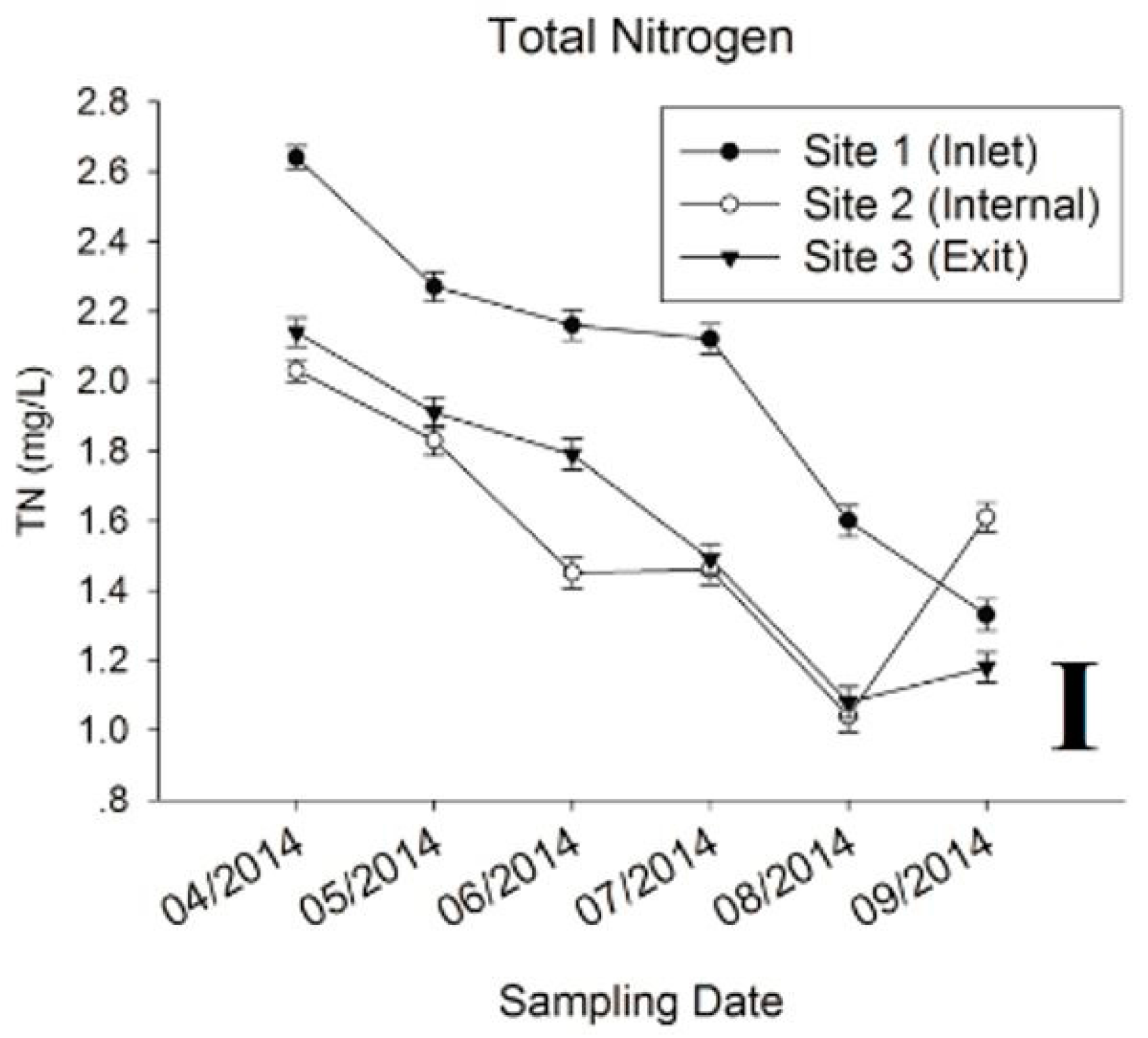
3.1. Physic-Chemical Parameters and Environmental Factor in QCS Reservoir
3.2. Antibiotics in QCS Reservoir
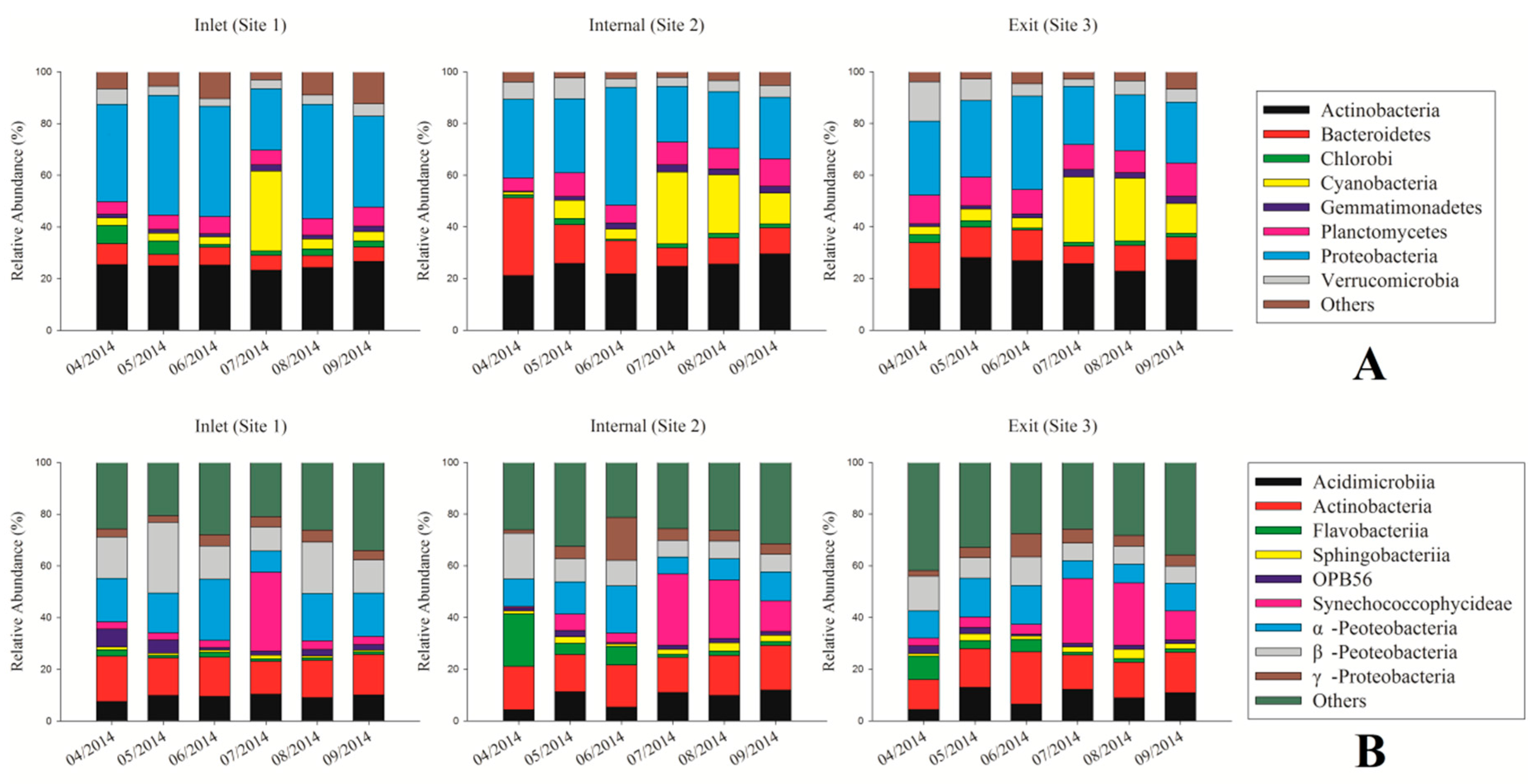
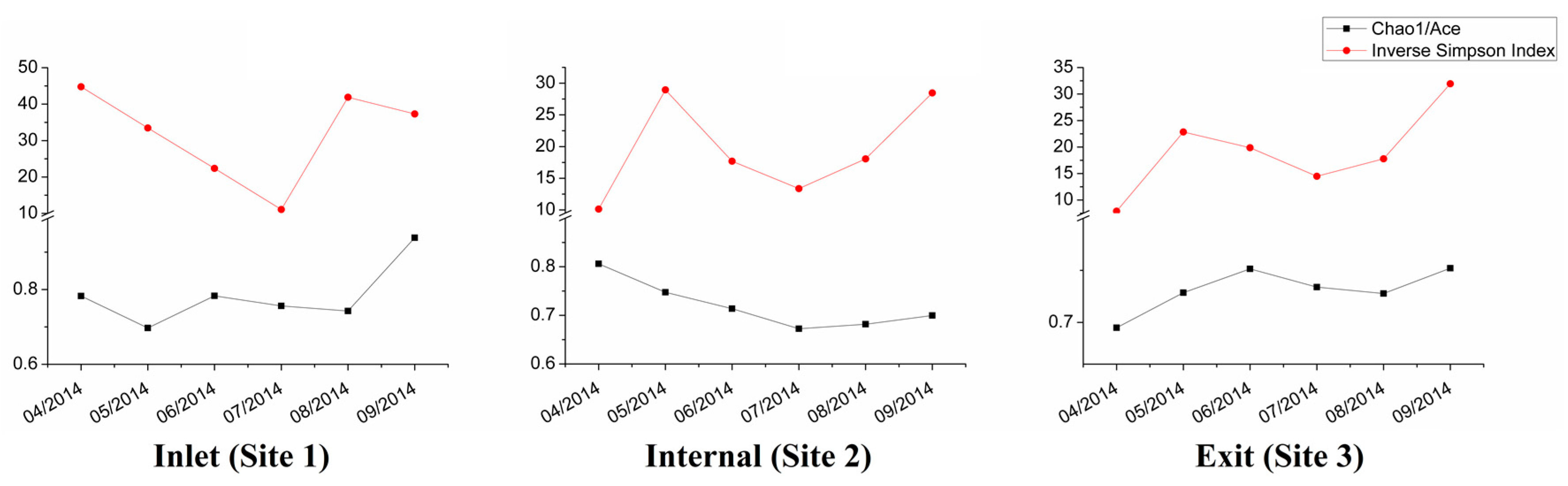
3.3. Dynamic Analysis of Bacterial Community Composition Based on the 16S rRNA Sequencing Data
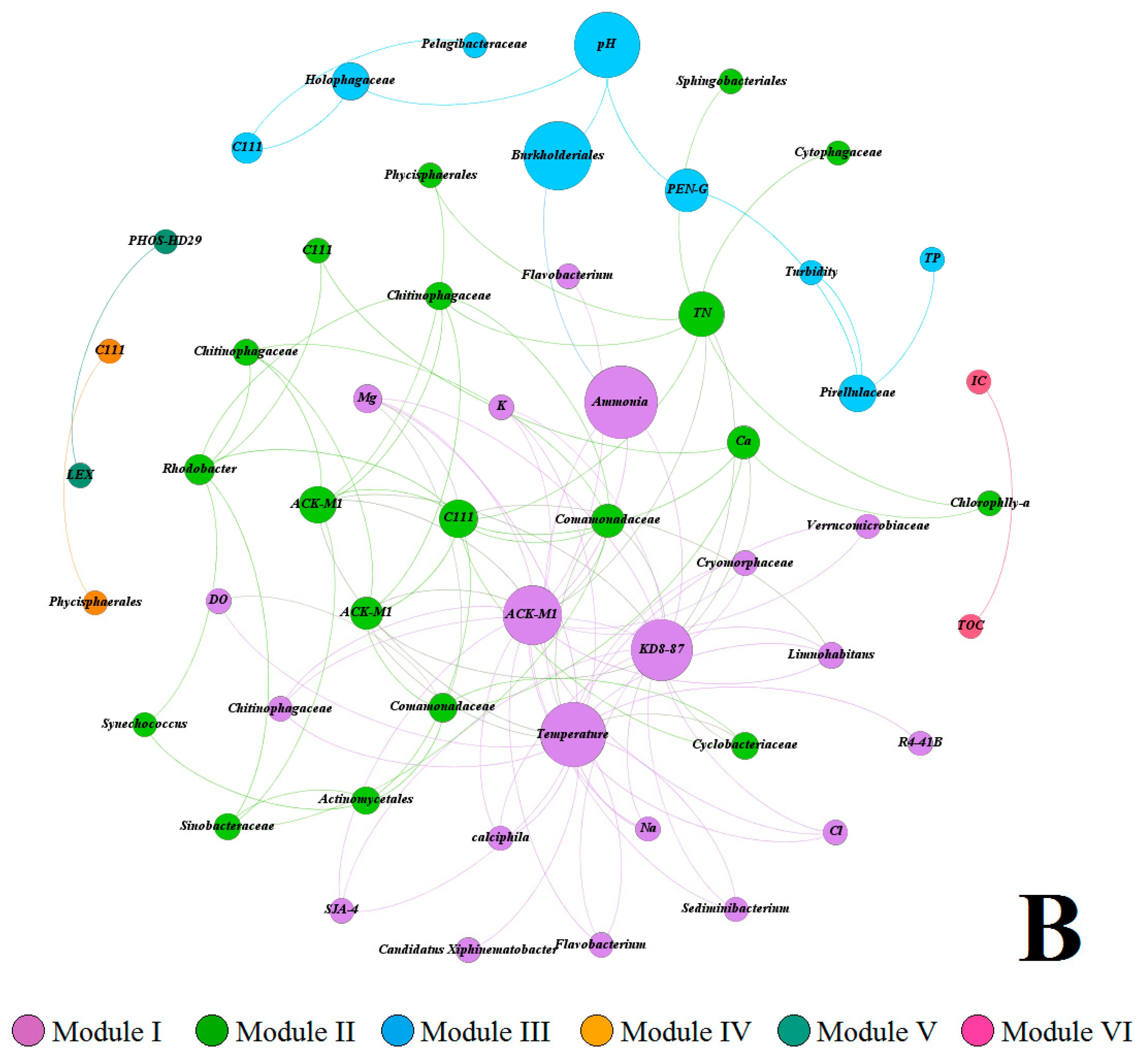
3.4. Covariance Analysis of Bacterial Community Composition and Environmental Variables
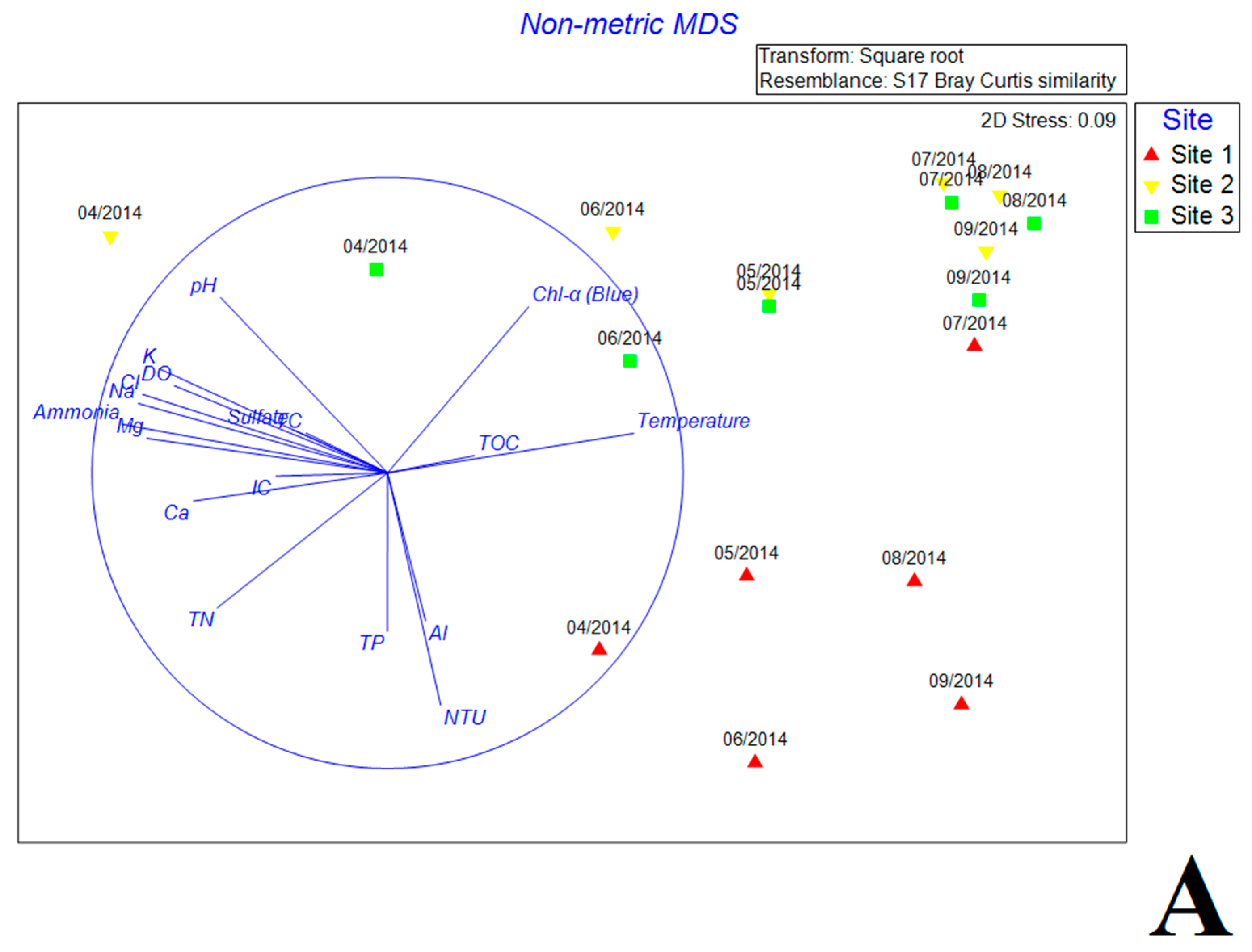
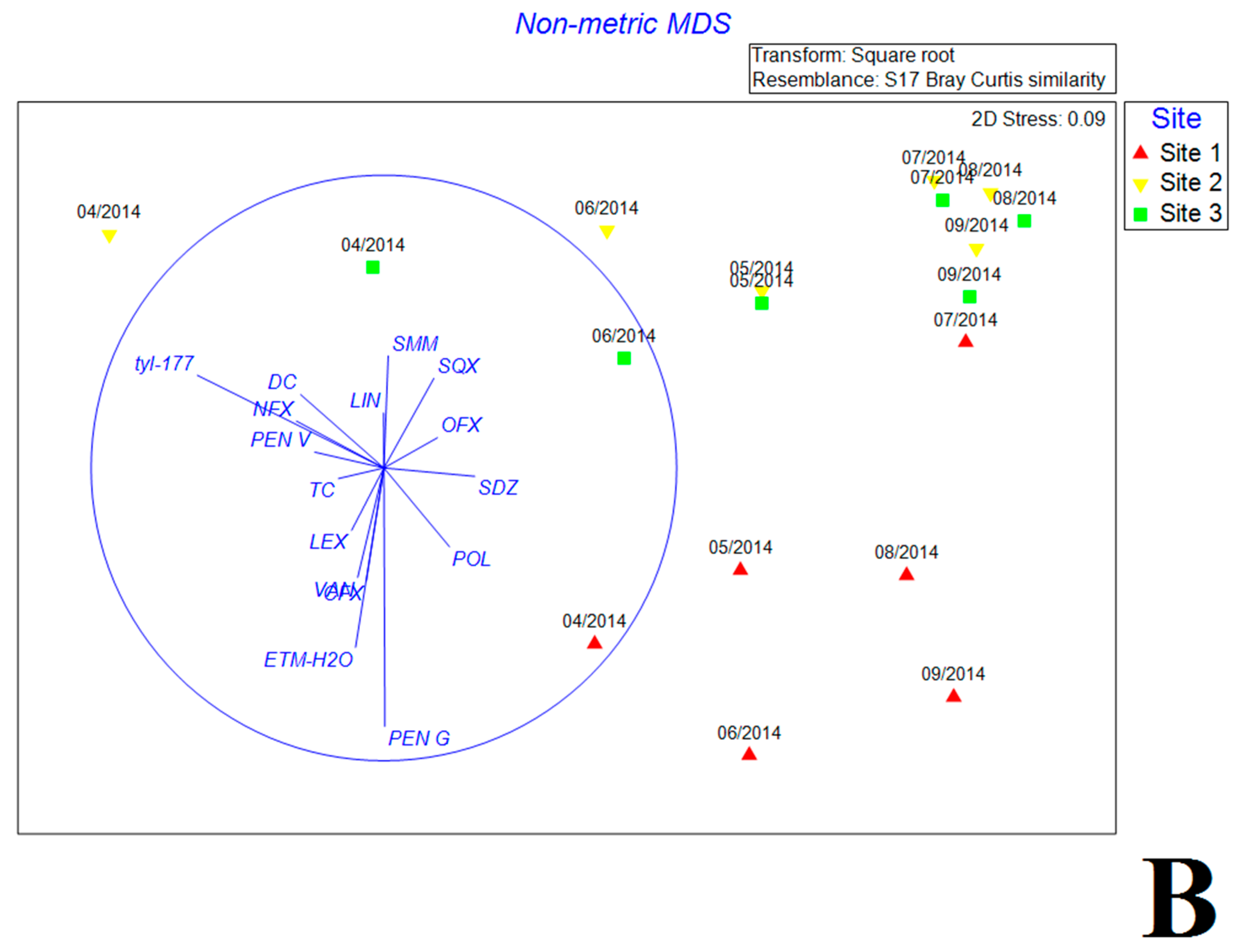
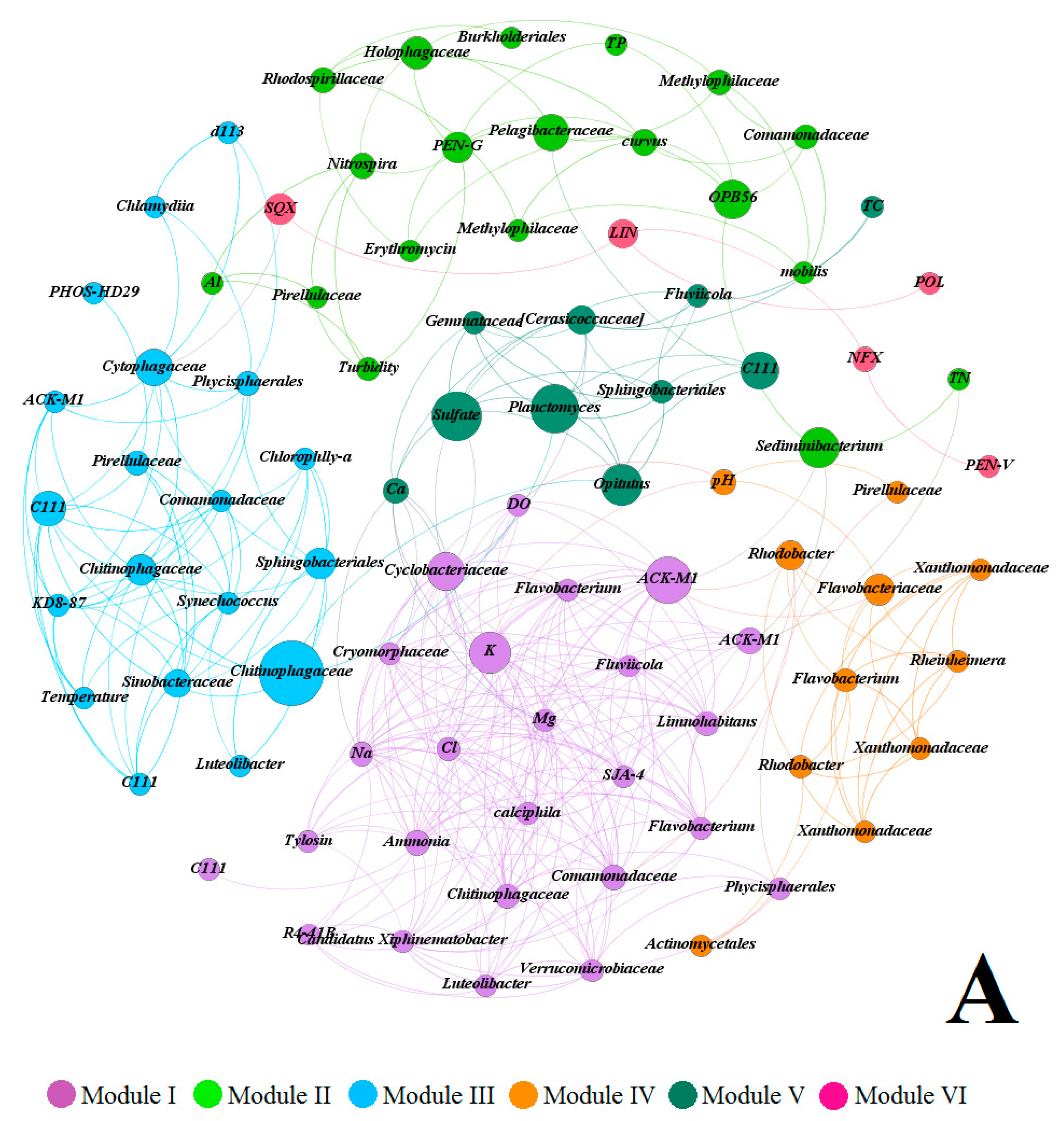
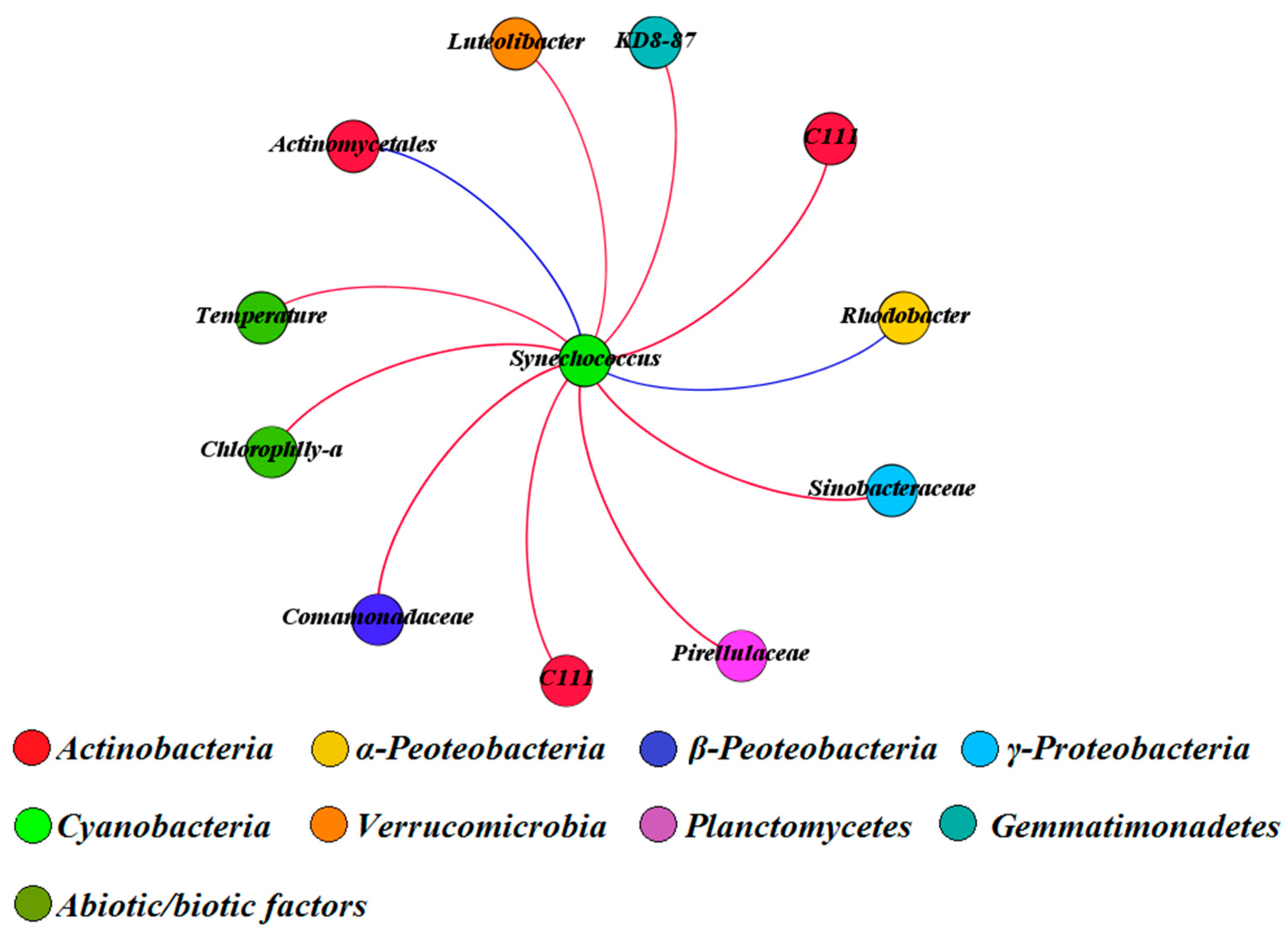
3.5. Multivariate Analysis of Biotic and Abiotic Factors in QCS Reservoir
4. Discussion
4.1. Correlations between Environmental Parameters and Antibiotic Concentrations
4.2. Correlations between Environmental Parameters and Bacterial Community Composition
4.3. Correlations between Antibiotic Concentrations and Bacterial Community Composition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yong, H.J.; Yang, J.S.; Park, K. Changes in Water Quality After the Construction of an Estuary Dam in the Geum River Estuary Dam System, Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 30, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Chen, K.; Kuang, C.; Zhu, D.Z.; He, L.; Mao, X.; Liang, H.; Song, H. Influence of sea level rise on saline water intrusion in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 54, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E.; Abreu, P.C.; Carstensen, J.; Chauvaud, L.; Elmgren, R.; Grall, J.; Greening, H.; Johansson, J.O.; Kahru, M.; Sherwood, E.T. Human Activities and Climate Variability Drive Fast-Paced Change across the World’s Estuarine-Coastal Ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 22, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bound, J.P.; Voulvoulis, N. Pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment—A comparison of risk assessment strategies. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part II. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: A review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 957–995. [Google Scholar]
- Manzetti, S.; Ghisi, R. The environmental release and fate of antibiotics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, B.C.; Baross, J.A.; Simenstad, C.A. Dominance of particle-attached bacteria in the Columbia River estuary, USA. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 14, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieck, A.; Herlemann, D.P.R.; Jürgens, K.; Grossart, H.P. Particle-Associated Differ from Free-Living Bacteria in Surface Waters of the Baltic Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, C.M.; Ward, C.S.; Davis, K.M.; Johnson, Z.I.; Hunt, D.E. Insensitivity of Diverse and Temporally Variable Particle-Associated Microbial Communities to Bulk Seawater Environmental Parameters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3431–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, G.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Yang, X.; Ding, J.; Jiang, Z. Bioconcentration, metabolism, and biomarker responses in freshwater fish Carassius auratus exposed to roxithromycin. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.J.; Hou, J.H.; Kuo, T.F.; Lai, H.T. Toxicity of the veterinary sulfonamide antibiotic sulfamonomethoxine to five aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; He, Y.; Kirumba, G.; Hassan, Y.; Li, J. Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption-release characteristics of the sediment in the Yangtze River estuary reservoir. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 55, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hassan, Y.; George, K. Impact of sulfate and chloride on sediment phosphorus release in the Yangtze Estuary Reservoir, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, H.S.; Wei, C.H.; Deng, Y.; Gao, N.Y. Principal component analysis to assess the composition and fate of impurities in a large river-embedded reservoir: Qingcaosha Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M.; Nie, M.; Shi, H.; Gu, L. Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yan, C.; Yue, H.; Zhou, J. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the surface sediments of the Yangtze Estuary and nearby coastal areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Xie, B.; Yuan, Q.; Xu, W.; Lu, J. Microbial community study in newly established Qingcaosha Reservoir of Shanghai, China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9849–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Jing, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Community dynamics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes in an estuary reservoir. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F. Monitoring and Analysis Methods of Water and Wastewater; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gera, A.; Alcoverro, T.; Mascaró, O.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J. Exploring the utility of Posidonia oceanica chlorophyll fluorescence as an indicator of water quality within the European Water Framework Directive. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berglyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, H.T.; Tan, B.F.; Thompson, J.R.; Gin, Y.H. Relationship of microbiota and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in Planktothricoides-dominated bloom. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4199–4209. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.; Le, T.H.; Goh, S.G.; Liang, L.; Kim, Y.; Rose, J.B.; Yewhoong, K.G. A Comparison of Microbial Water Quality and Diversity for Ballast and Tropical Harbor Waters. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhouse, J.N.; Kinsela, A.S.; Collins, R.N.; Bowling, L.C.; Honeyman, G.L.; Holliday, J.K.; Neilan, B.A. Microbial communities reflect temporal changes in cyanobacterial composition in a shallow ephemeral freshwater lake. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling The False Discovery Rate—A Practical And Powerful Approach To Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. In Proceedings of the Third International Aaai Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Available online: https://gephi.org/publications/gephi-bastian-feb09.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2017).
- Yu, H.; Pm, K.; Sprecher, E.; Trifonov, V.; Gerstein, M. The Importance of Bottlenecks in Protein Networks: Correlation with Gene Essentiality and Expression Dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidhar, T. Antibiotic Pollution in the Environment: A Review. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2015, 43, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Zhang, G.; Zou, S.C.; Li, X.D.; Liu, Y.C. Determination of selected antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waksman, S.A. Microbial Antagonisms and Antibiotic Substances; The Commonwealth Fund: New York, NY, USA, 1947; pp. 1033–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, L.J.; Maruya, K.A.; Snyder, S.A.; Zeng, E.Y. China’s water pollution by persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, D.; Ren, L.; Shi, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y. Concentration and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in the surface water of the Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floehr, T.; Xiao, H.; Scholz-Starke, B.; Ottermanns, R.; Ross-Nickoll, M. Solution by dilution?—A review on the pollution status of the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 6934–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.B.; Jiao, N.Z.; Feng, J.; Shu, Q.L. Research progress on Planctomycetes’ diversity and ecological function in marine environments. Microbiol. China 2014, 41, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Eiler, A.; Olsson, J.A.; Bertilsson, S. Diurnal variations in the auto- and heterotrophic activity of cyanobacterial phycospheres (Gloeotrichia echinulata) and the identity of attached bacteria. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 51, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Fan, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X. Annual periodicity in planktonic bacterial and archaeal community composition of eutrophic Lake Taihu. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, U.; Grossart, H.P.; Amann, R.; Pernthaler, J. Substrate incorporation patterns of bacterioplankton populations in stratified and mixed waters of a humic lake. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 11, 1854–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.E.; Newton, R.J.; Mcmahon, K.D. Evidence for structuring of bacterial community composition by organic carbon source in temperate lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 11, 2463–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, V.O.; Macedo, A.J.; Muxagata, E. Evaluation of antibiotics as a methodological procedure to inhibit free-living and biofilm bacteria in marine zooplankton culture. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias 2016, 88, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cornforth, D.M.; Popat, R.; Mcnally, L.; Gurney, J.; Scottphillips, T.C.; Ivens, A.; Diggle, S.P.; Brown, S.P. Combinatorial quorum sensing allows bacteria to resolve their social and physical environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4280–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, C. Exploiting Quorum Sensing Interfering Strategies in Gram-Negative Bacteria for the Enhancement of Environmental Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, E.; Gothalwal, R. Effect of environmental factors on bacterial quorum sensing. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2014, 60, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kievit, T.R.D.; Iglewski, B.H. Bacterial Quorum Sensing in Pathogenic Relationships. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4839–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcknight, U.S.; Rasmussen, J.J.; Kronvang, B.; Binning, P.J.; Bjerg, P.L. Sources, occurrence and predicted aquatic impact of legacy and contemporary pesticides in streams. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H.; Jin, F. Determination of penicillin G and its degradation products in a penicillin production wastewater treatment plant and the receiving river. Water Res. 2008, 42, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippini, M.; Svercel, M.; Laczko, E.; Kaech, A.; Ziegler, U.; Bagheri, H.C. Fibrella aestuarina gen. nov., sp. nov., a filamentous bacterium of the family Cytophagaceae isolated from a tidal flat, and emended description of the genus Rudanella Weon et al. 2008. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joung, Y.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Lee, B.I.; Ahn, T.S.; Joh, K. Lacihabitans soyangensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cytophagaceae, isolated from a freshwater reservoir. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 3188–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.D. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: Enzymatic degradation and modification. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1451–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijenoort, J.V.; Gutmann, L. Correlation between the structure of the bacterial peptidoglycan monomer unit, the specificity of transpeptidation, and susceptibility to β-lactams. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5028–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuerst, J.A.; Sagulenko, E. Beyond the bacterium: Planctomycetes challenge our concepts of microbial structure and function. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Te, S.H.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H. The Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Community Composition in an Estuary Reservoir during Spring and Summer Seasons. Water 2018, 10, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020154
Xu Z, Jiang Y, Te SH, He Y, Gin KY-H. The Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Community Composition in an Estuary Reservoir during Spring and Summer Seasons. Water. 2018; 10(2):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020154
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zheng, Yue Jiang, Shu Harn Te, Yiliang He, and Karina Yew-Hoong Gin. 2018. "The Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Community Composition in an Estuary Reservoir during Spring and Summer Seasons" Water 10, no. 2: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020154
APA StyleXu, Z., Jiang, Y., Te, S. H., He, Y., & Gin, K. Y.-H. (2018). The Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Community Composition in an Estuary Reservoir during Spring and Summer Seasons. Water, 10(2), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020154




