Enhanced Iron Solubility at Low pH in Global Aerosols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
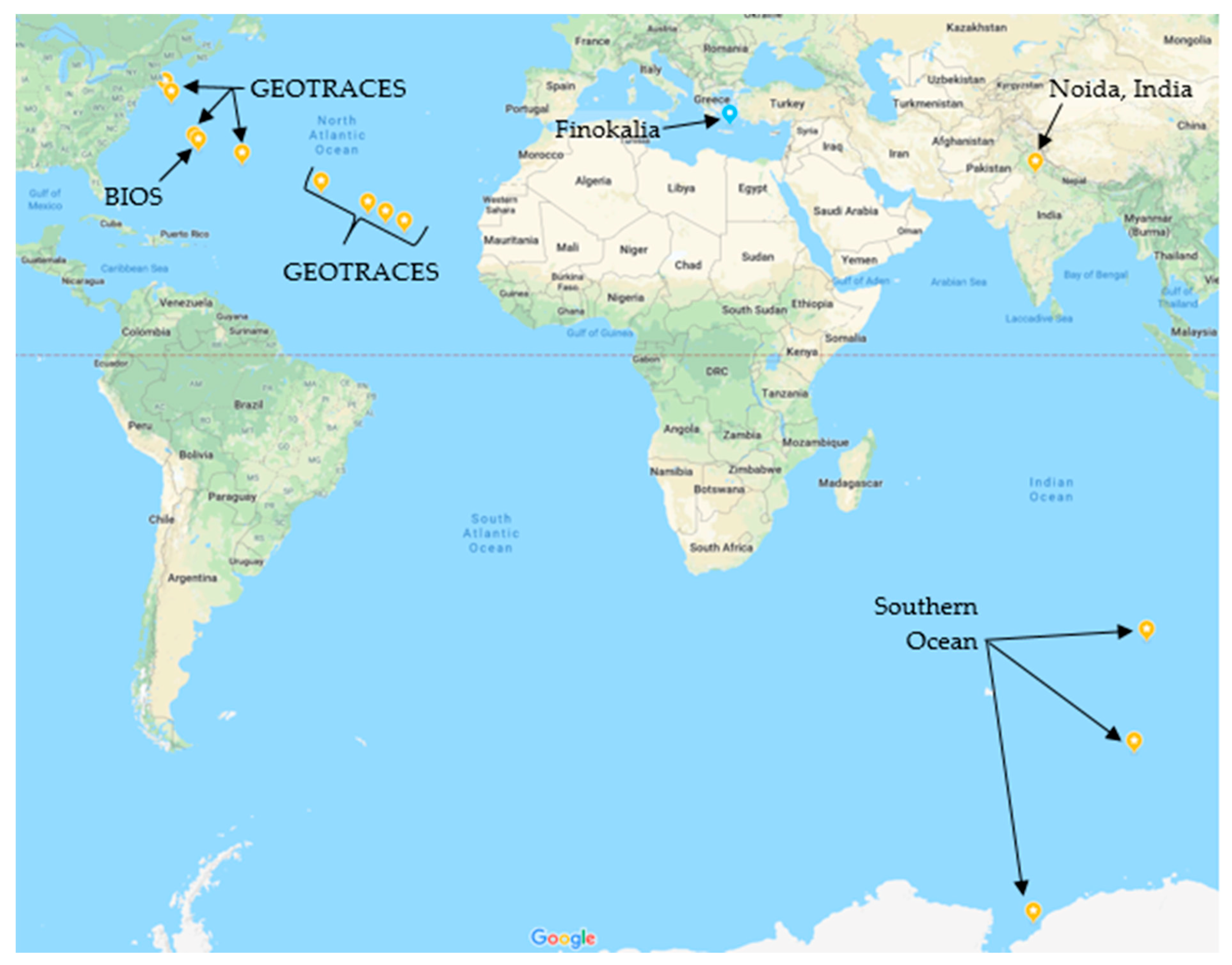
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. HYSPLIT
2.3. Total and Soluble Iron
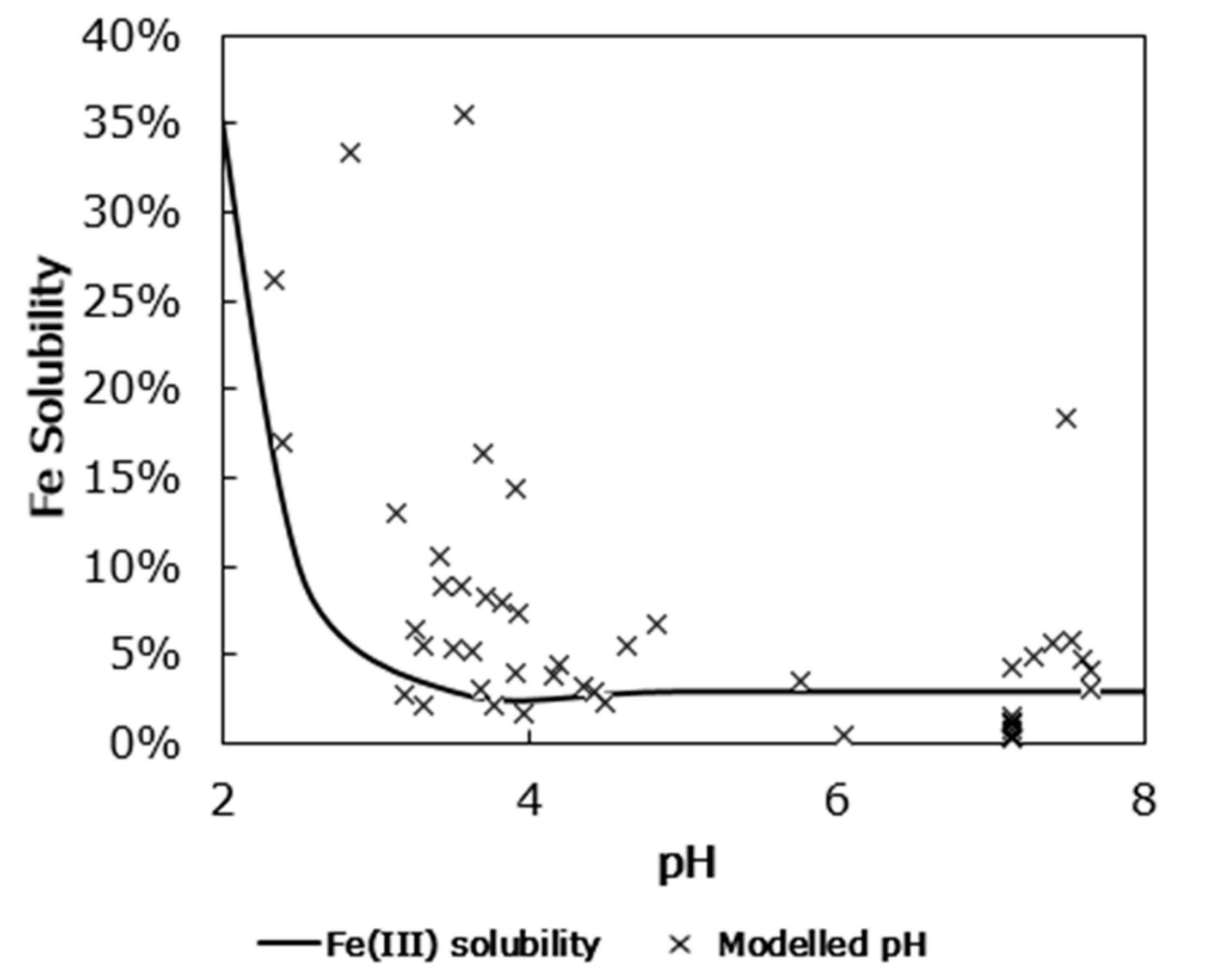
2.4. Soluble Ions and pH Modelling
2.5. Synchrotron Analysis
2.6. Data Reduction and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Iron Solubility
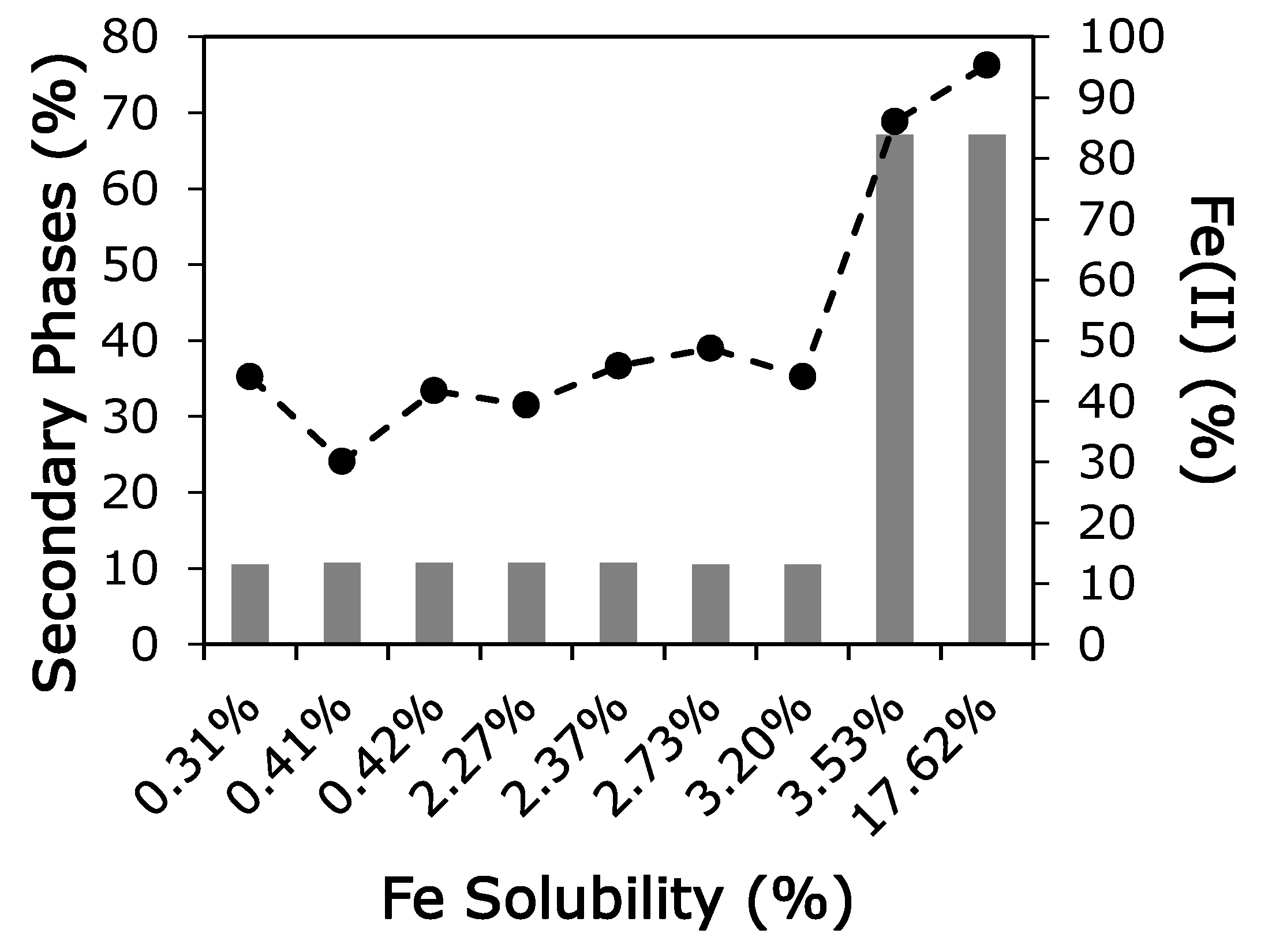
3.2. Oxidation State
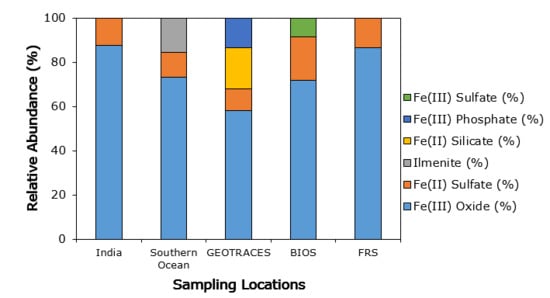
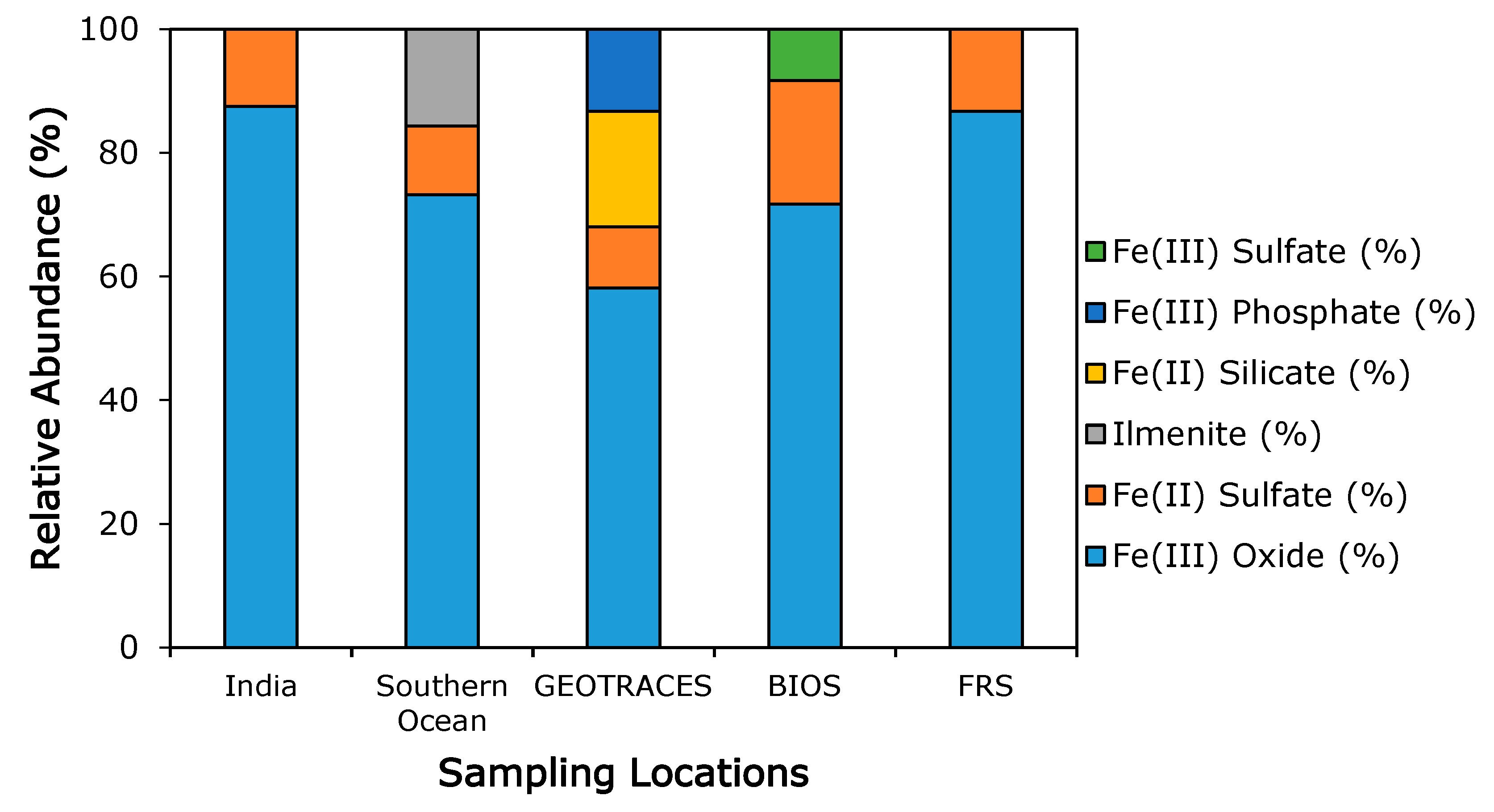
3.3. Iron Mineralogy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schulz, M.; Prospero, J.M.; Baker, A.R.; Dentener, F.J.; Ickes, L.; Liss, P.S.; Mahowald, N.M.; Nickovic, S.; Perez Garcia-Pando, C.; Rodrigeuz, S.; et al. Atmospheric transport and deposition of mineral dust to the ocean: Implications for research needs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10390–10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, P.W.; Mackie, D.S.; Hunter, K.A. Aerosol iron deposition to the surface ocean—Modes of iron supply and biological responses. Mar. Chem. 2010, 120, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H. Glacial-interglacial CO2 change: The iron hypothesis. Paleoceanography 1990, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Yao, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Air pollution–aerosol interactions produce more bioavailable iron for ocean ecosystems. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.M.; Mills, M.M.; Arrigo, K.R.; Berman-Frank, I.; Bopp, L.; Boyd, P.W.; Galbraith, R.; Geider, R.J.; Guieu, C.; Jaccard, S.L.; et al. Processes and patterns of oceanic nutrient limitation. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, J.; Schoemann, V.; Lannuzel, D.; Croot, P.; de Baar, H.; Tison, J.-L. Natural iron fertilization of the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean by continental shelf sources of the Antarctic Peninsula. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coale, K.H.; Johnson, K.S.; Chavez, F.P.; Buesseler, K.O.; Barber, R.T.; Brzezinski, M.A.; Cochlan, W.P.; Millero, F.J.; Falkowski, P.G.; Bauer, J.E.; et al. Southern Ocean iron enrichment experiment: Carbon cycling in high- and low-si waters. Science 2004, 304, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buesseler, K.O.; Andrews, J.E.; Pike, S.M.; Charette, M.A. The effects of iron fertilization on carbon sequestration in the Southern Ocean. Science 2004, 304, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, P.W.; Watson, A.J.; Law, C.S.; Abraham, E.R.; Trull, T.; Murdoch, R.; Bakker, D.C.E.; Bowie, A.R.; Buesseler, K.O.; Chang, H.; et al. A mesoscale phytoplankton bloom in the polar Southern Ocean stimulated by iron fertilization. Nature 2000, 407, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coale, K.H.; Johnson, K.S.; Fitzwater, S.E. A massive phytoplankton bloom induced by an ecosystem-scale iron fertilization experiment in the equitorial Pacific Ocean. Nature 1996, 383, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahowald, N.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Duce, R.A.; Jickells, T.D.; Kubilay, N.; Prospero, J.M.; Tegen, I. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.D.; An, Z.S.; Andersen, K.K.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Cao, J.J.; Boyd, P.W.; Duce, R.A.; Hunter, K.A.; et al. Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate. Science 2005, 308, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Shi, Z. Delivery of anthropogenic bioavailable iron from mineral dust and combustion aerosols to the ocean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolaor, A.; Vallelonga, P.; Cozzi, F.; Gabrielli, P.; Varin, C.; Kehrwald, N.; Zennaro, P.; Boutron, C.F.; Barbante, C. Iron speciation in aerosol dust influences iron bioavailability over glacial-interglacial timescales. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1618–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Nenes, A.; Johnson, M.S.; Meskhidze, N.; Deutsch, C. Acceleration of oxygen decline in the tropical pacific over the past decades by aerosol pollutants. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.R.; Croot, P.L. Atmospheric and marine controls on aerosol iron solubility in seawater. Mar. Chem. 2010, 120, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Yi, Z.; Duce, R.A.; Brown, P.R. Chemistry of iron in marine aerosols. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 1992, 6, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Krom, M.D.; Jickells, T.D.; Bonneville, S.; Carslaw, K.S.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Baker, A.R.; Benning, L.G. Impacts on iron solubility in the mineral dust by processes in the source region and the atmosphere: A review. Aeolian Res. 2012, 5, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journet, E.; Desboeufs, K.V.; Caquineau, S.; Colin, J.L. Mineralogy as a critical factor of dust iron solubility. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Prospero, J.M.; Savoie, D.L.; Millero, F.J.; Zika, R.G.; Saltzman, E.S. Photoreduction of iron(III) in marine mineral aerosol solutions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1993, 98, 9039–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, M.L.I.; Mather, T.A.; Baker, A.R.; De Hoog, J.C.M.; Pyle, D.M. Atmospheric trace metals over the south-west Indian Ocean: Total gaseous mercury, aerosol trace metal concentrations and lead isotope ratios. Mar. Chem. 2010, 121, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhold, J.G.; Kraemer, S.M.; Teutsch, N.; Borer, P.M.; Halliday, A.N.; Kretzschmar, R. Iron isotope fractionation during proton-promoted, ligand-controlled, and reductive dissolution of goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenes, A.; Krom, M.D.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Van Cappellen, P.; Shi, Z.; Bougiatioti, A.; Zarmpas, P.; Herut, B. Atmospheric acidification of mineral aerosols: A source of bioavailable phosphorus for the oceans. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6265–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Krom, M.D.; Bonneville, S.; Benning, L.G. Atmospheric processing outside clouds increases soluble iron in mineral dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Krom, M.D.; Bonneville, S.; Baker, A.R.; Jickells, T.D.; Benning, L.G. Formation of iron nanoparticles and increase in iron reactivity in mineral dust during simulated cloud processing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6592–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cwiertny, D.M.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Hunter, G.J.; Laskin, A.; Scherer, M.M.; Grassian, V.H. Characterization and acid-mobilization study of iron-containing mineral dust source materials. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.J.; Guo, H.; Russell, A.G.; Nenes, A. High aerosol acidity despite declining atmospheric sulfate concentrations over the past 15 years. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Feng, Y. Role of dust alkalinity in acid mobilizaiton of iron. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 9237–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennigan, C.J.; Izumi, J.; Sullivan, A.P.; Weber, R.J.; Nenes, A. A critical evaluation of proxy methods used to estimate the acidity of atmospheric particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2775–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.C.; Guazzotti, S.A.; Sodeman, D.A.; Prather, K.A. Direct observations of the atmospheric processing of Asian mineral dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1213–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, M.; Ingall, E.D.; Lai, B.; Shafer, M.M.; Hays, M.D.; Liu, Z.G.; Russell, A.G.; Weber, R.J. Iron solubility related to particle sulfur content in source emission and ambient fine particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6637–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, P.; Dedik, A.N.; Ensling, J.; Weinbruch, S.; Weber, S.; Sinner, T.; Gutlich, P.; Ortner, H.M. Speciation of iron in atmospheric aerosol samples. J. Aerosol Sci. 1996, 27, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.S.; Landing, W.M.; Resing, J.A.; Lebon, G.T. Aerosol iron and aluminum solubility in the northwest Pacific Ocean: Results from the 2002 IOC cruise. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Lin, Q.; Chen, L.; Lin, H. Spatial and particle size distributions of atmospheric dissolvable iron in aerosols and its input to the Southern Ocean and coastal East Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schindler, P.W. Photochemical dissolution of goethite in acid/oxalate solution. Clays Clay Miner. 1987, 35, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Gao, Y. Characterization of hematite dissolution affected by oxalate coating, kinetics and pH. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides, Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurence and Uses; John Wiley: Hokoken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Winton, V.H.L.; Bowie, A.R.; Edwards, R.; Keywood, M.; Townsend, A.T.; van der Merwe, P.; Bollhofer, A. Fractional iron solubility of atmospheric iron inputs to the Southern Ocean. Mar. Chem. 2015, 177, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majestic, B.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M. Application of synchrotron radiation for measurement of iron red-ox speciation in atmospherically processed aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2475–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittschen, U.E.A.; Meirer, F.; Streli, C.; Wobrauschek, P.; Thiele, J.; Falkenberg, G.; Pepponi, G. Characterization of atmospheric aerosols using synchroton radiation total reflection X-ray fluorescence and Fe K-edge total reflection X-ray fluorescence-X-ray absorption near-edge structure. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2008, 63, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; Kelly, M.; Chen, H.; Chakrabarti, C.L. Evaluation of capillary electrophoresis combined with a BCR sequential extraction for determining distribution of Fe, Zn, Cu, Mn, and Cd in airborne particulate matter. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 498, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.S.; Meskhidze, N. Atmospheric dissolved iron deposition to the global oceans: Effects of oxalate-promoted dissolution, photochemical redox cycling, and dust mineralogy. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2013, 6, 1137–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, A.F.; Feng, Y.; Lai, B.; Landing, W.M.; Shelley, R.U.; Nenes, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Violaki, K.; Ingall, E.D. Influence of atmospheric processes on the solubility and composition of iron in saharan dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6912–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakes, M.; Weber, R.J.; Lai, B.; Russell, A.; Ingall, E.D. Characterization of iron speciation in urban and rural single particles using xanes spectroscopy and micro X-ray fluorescence measurements: Investigating the relationship between speciation and fractional iron solubility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, R.C.; Furutani, H.; Rodel, T.C.; Henn, T.R.; Sprau, P.O.; Laskin, A.; Uematsu, M.; Gilles, M.K. Iron speciation and mixing in single aerosol particles from Asian continental outflows. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Hoffmann, P.; Ensling, J.; Dedik, A.N.; Weinbruch, S.; Miehe, G.; Gutlich, P.; Ortner, H.M. Characterization of iron compounds from urban and rural aerosol sources. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, B.; Sarin, M.; Rengarajan, R. Atmospheric transport of mineral dust from the indo-gangeticplain: Temporal variability, acid processing, and iron solubility. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 3226–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaki, Z.; Oikonomou, K.; Kocak, M.; Kouvarakis, G.; Chaniotaki, A.; Kubilay, N.; Mihalopoulos, N. Atmospheric deposition of inorganic phosphorus in the Levantine Basin, eastern Mediterranean: Spatial and temporal variability and its role in seawater productivity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 1557–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, R.U.; Morton, P.L.; Landing, W.M. Elemental ratios and enrichment factors in aerosols from the US-GEOTRACES North Atlantic transects. Deep Sea Res. Part I Trop. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 116, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. Noaa’s hysplit atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-time environmental applications and display system: Ready. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, L.L. Ferrozine—A new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadko, D.; Landing, W.M.; Shelley, R.U. A novel tracer technique to quantify the atmospheric flux of trace elements to remote ocean regions. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 119, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, P.L.; Landing, W.M.; Hsu, S.C.; Milne, A.; Aguilar-Islas, A.M.; Baker, A.R.; Bowie, A.R.; Buck, C.S.; Gao, Y.; Gichuki, S.; et al. Methods for the sampling and analysis of marine aerosols: Results from the 2008 geotraces aerosol intercalibration experiment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 11, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardouki, H.; Liakakou, H.; Economou, C.; Sciare, J.; Smolik, J.; Zdimal, V.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Ladaridis, M.; Dye, C.; Mihalopoulos, N. Chemical composition of size-resolved atmospheric aerosols in the eastern Mediterranean during summer and winter. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoukis, C.; Nenes, A. Isorropia II: A computationally efficient thermodynamic equilibrium model for K+–Ca2+–Mg2+–NH4+–Na+–SO42–NO3–Cl–H2O aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 4639–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenes, A.; Pandis, S.N.; Pilinis, C. Isorropia: A new thermodynamic equilibrium model for multiphase multicomponent inorganic aerosols. Aquat. Geochem. 1998, 4, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingall, E.; Brandes, J.; Diaz, J.; de Jonge, M.; Paterson, D.; McNulty, I.; Elliott, W.; Northrup, P. Phosphorus k-edge xanes spectroscopy of mineral standards. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2011, 18, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, M.; Farges, F.; Petit, P.E.; Brown, G.E.; Martin, F. Oxidation state and coordination of fe in minerals: An fek-xanes spectroscopic study. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajt, S.; Sutton, S.R.; Delaney, J.S. X-ray microprobe analysis of iron oxidation-states in silicates and oxides using X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 5209–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. Athena, artemis, hephaestus: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using ifeffit. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, M.A.; Lam, P.J. Visualising fe speciation diversity in ocean particulate samples by micro X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy. Environm. Chem. 2014, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingall, E.; Diaz, J.; Longo, A.; Oakes, M.; Finney, L.; Vogt, S.; Lai, B.; Yager, P.L.; Twining, B.S.; Brandes, J. Role of biogenic silica in the removal of iron from antarctic seas. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesterberg, D. Chapter 11—Macroscale chemical properties and X-ray absorption spectroscopy of soil phosphorus. In Developments in Soil Science; Balwant, S., Markus, G., Eds.; Elsevier: New York City, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 34, pp. 313–356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, G.; Yi, Z.; Duce, R.A.; Brown, P.R. Link between iron and sulphur cycles suggested by detection of Fe(n) in remote marine aerosols. Nature 1992, 335, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskhidze, N.; Chameides, W.L.; Nenes, A.; Chen, G. Iron mobilization in mineral dust: Can anthropogenic SO2 emissions affect ocean productivity? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskhidze, N.; Nenes, A.; Conant, W.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Evaluation of a new cloud droplet activation parameterization with in situ data from CRYSTAL-FACE and CSTRIPE. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, E.; Hurab, O.; Rubasinghege, G. Atmospheric processing and iron mobilization of ilmenite: Iron-containing ternary oxide in mineral dust aerosol. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siefert, R.L.; Webb, S.M.; Hoffmann, M.R. Determination of photochemically available iron in ambient aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 10, 14441–14449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siefert, R.L.; Pehkonen, S.O.; Erel, Y.; Hoffmann, M.R. Iron photochemistry of aqueous suspensions of ambient aerosol with added organic acids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3217–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.R.; French, M.; Linge, K.L. Trends in aerosol nutrient solubility along a west-east transect of the saharan dust plume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, B.; Sarin, M.M.; Kumar, A.K. Impact of anthropogenic sources on aerosol iron solubility over the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea. Biogeochemistry 2012, 110, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sarin, M.; Srinivas, B. Aerosol iron solubility over bay of bengal: Role of anthropogenic sources and chemical processing. Mar. Chem. 2010, 121, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Removal of arsenic from contaminated water sources by sorption onto iron-oxide-coated polymeric materials. Water Res. 2002, 26, 5141–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantala, K.; Sthiannopkao, S.; Srinameb, B.O.; Grisdanurak, N.; Kim, K.W.; Han, S. Arsenic adsorption by fe loaded on rh-mcm-41 synthesized from rice husk silica. J. Environ. Eng. ASCE 2012, 138, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchiz, J.; Esparza, P.; Dominguez, S.; Brito, F.; Mederos, A. Solution studies of complexes of iron(III) with iminodiacetic, alkyl-substituted iminodiacetic and nitrilotriacetic acids by potentiometry and cyclic voltammetry. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1999, 291, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.; Melin, V.; Contreras, D.; Moreno, Y.; Mansilla, H.D. Fenton reaction driven by iron ligands. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2013, 58, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Bonneville, S.; Krom, M.D.; Carslaw, K.S.; Jickells, T.D.; Baker, A.R.; Benning, L.G. Iron dissolution kinetics of mineral dust at low pH during simulated atmospheric processing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Higashi, M.; Furukawa, T.; Mitsunobu, S. Change of iron species and iron solubility in Asian dust during the long-range transport from western China to Japan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11237–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, A.F.; Ingall, E.D.; Diaz, J.M.; Oakes, M.; King, L.E.; Nenes, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Violaki, K.; Avila, A.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; et al. P-NEXFS analysis of aerosol phosphorus delivered to the Mediterranean Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4043–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Feng, Y. Iron mobilization in North African Dust. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 6, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolauo, P.; Bougiatioti, A.; Stavroulas, I.; Kouvarakis, G.; Nenes, A.; Weber, R.J.; Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N. Particle water and pH in the eastern Mediterranean: Sources variability and implications for nutrients availability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4579–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xu, L.; Bougiatioti, A.; Cerully, K.M.; Capps, S.L.; Hite, J.R.; Carlton, A.G.; Lee, S.-H.; Bergin, M.H.; Ng, N.L.; et al. Fine-particulate water and pH in the southeastern united states. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5211–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Sedwick, P.N.; Church, T.M. Influence of anthropogenic combustion emissions on the deposition of soluble aerosol iron to the ocean: Empirical estimates for island sites in the North Atlantic. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 3981–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedwick, P.; Sholkovitz, E.R.; Church, T.M. Impact of anthropogenic combustion emissions on the fractional solubility of aerosol iron: Evidence from the Sargasso Sea. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Sedwick, P.N.; Church, T.M.; Baker, A.R.; Powell, C.F. Fractional solubility of aerosol iron: Synthesis of a global-scale data set. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 89, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Russell, A.; Edgerton, E.S. Atmospheric aerosol over two urban–rural pairs in the southeastern United States: Chemical composition and possible sources. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4453–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.R.; Jickells, T.D. Mineral particle size as a control on aerosol iron solubility. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sarin, M. Aerosol iron solubility in a semi-arid region: Temporal trend and impact of anthropogenic sources. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 62, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, A.S.; Shelley, R.U.; Sleighter, R.L.; Abdulla, H.A.N.; Morton, P.L.; Landing, W.M.; Hatcher, P.G. Relationships among aerosol water soluble organic matter, iron and aluminum in European, North African, and Marine air masses from the 2010 US GEOTRACES cruise. Mar. Chem. 2013, 154, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Desboeufs, K.V.; Journet, E. Variability of dust iron solubility in atmospheric waters: Investigation of the role of oxalate organic complexation. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6510–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.B.; Shang, G.F.; Lin, J.; Hu, Y.J.; Hu, Q.Q.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, J.M. Fractional iron solubility of aerosol particles enhanced by biomass burning and ship emissions in Shanghai, East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Furukawa, T.; Kanai, Y.; Uematsu, M.; Zheng, G.; Marcus, M.A. Seasonal changes in Fe species and soluble Fe concentration in the atmosphere in the Northwest Pacific region based on the analysis of aerosols collected in Tsukuba, Japan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7695–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Mahowald, N.M.; Meskhidze, N.; Chen, Y.; Siefert, R.L.; Baker, A.R.; Johansen, A.M. Estimation of iron solubility from observations and a global aerosol model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 , Southern Ocean (S. O.)
, Southern Ocean (S. O.)  , BIOS Saharan air masses
, BIOS Saharan air masses  , BIOS mixed air masses
, BIOS mixed air masses  , BIOS North American air masses
, BIOS North American air masses  , GEOTRACES Saharan air masses
, GEOTRACES Saharan air masses  , GEOTRACES North American air masses
, GEOTRACES North American air masses  , GEOTRACES marine air masses
, GEOTRACES marine air masses  , Finokalia Research Station (FRS) Saharan air masses
, Finokalia Research Station (FRS) Saharan air masses  , and Finokalia Research Station European air masses
, and Finokalia Research Station European air masses  . Generally, samples with the highest total iron have low fractional solubility of iron.
. Generally, samples with the highest total iron have low fractional solubility of iron.
 , Southern Ocean (S. O.)
, Southern Ocean (S. O.)  , BIOS Saharan air masses
, BIOS Saharan air masses  , BIOS mixed air masses
, BIOS mixed air masses  , BIOS North American air masses
, BIOS North American air masses  , GEOTRACES Saharan air masses
, GEOTRACES Saharan air masses  , GEOTRACES North American air masses
, GEOTRACES North American air masses  , GEOTRACES marine air masses
, GEOTRACES marine air masses  , Finokalia Research Station (FRS) Saharan air masses
, Finokalia Research Station (FRS) Saharan air masses  , and Finokalia Research Station European air masses
, and Finokalia Research Station European air masses  . Generally, samples with the highest total iron have low fractional solubility of iron.
. Generally, samples with the highest total iron have low fractional solubility of iron.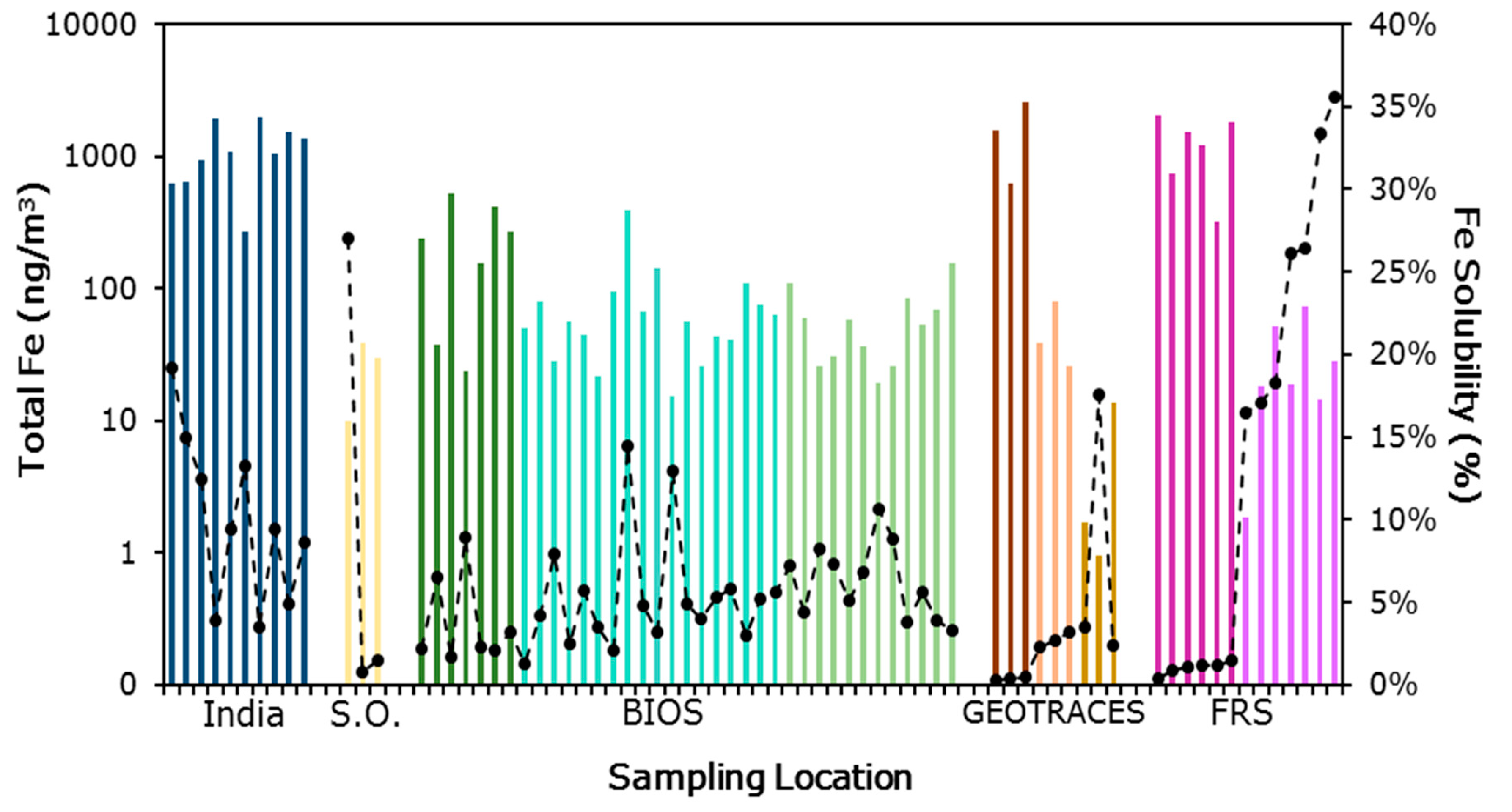
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ingall, E.D.; Feng, Y.; Longo, A.F.; Lai, B.; Shelley, R.U.; Landing, W.M.; Morton, P.L.; Nenes, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Violaki, K.; et al. Enhanced Iron Solubility at Low pH in Global Aerosols. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9050201
Ingall ED, Feng Y, Longo AF, Lai B, Shelley RU, Landing WM, Morton PL, Nenes A, Mihalopoulos N, Violaki K, et al. Enhanced Iron Solubility at Low pH in Global Aerosols. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(5):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9050201
Chicago/Turabian StyleIngall, Ellery D., Yan Feng, Amelia F. Longo, Barry Lai, Rachel U. Shelley, William M. Landing, Peter L. Morton, Athanasios Nenes, Nikolaos Mihalopoulos, Kalliopi Violaki, and et al. 2018. "Enhanced Iron Solubility at Low pH in Global Aerosols" Atmosphere 9, no. 5: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9050201
APA StyleIngall, E. D., Feng, Y., Longo, A. F., Lai, B., Shelley, R. U., Landing, W. M., Morton, P. L., Nenes, A., Mihalopoulos, N., Violaki, K., Gao, Y., Sahai, S., & Castorina, E. (2018). Enhanced Iron Solubility at Low pH in Global Aerosols. Atmosphere, 9(5), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9050201