A Study on Elevated Concentrations of Submicrometer Particles in an Urban Atmosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
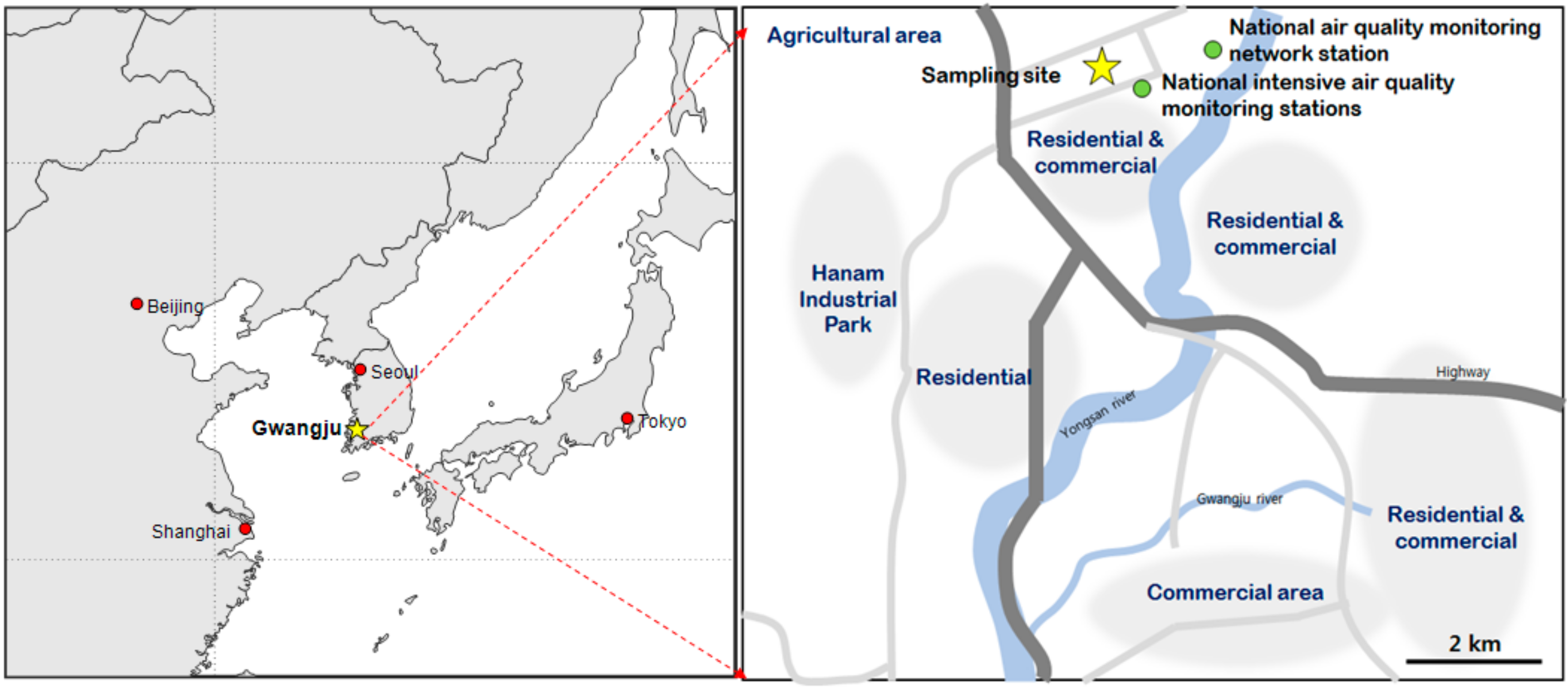
2. Experimental Section
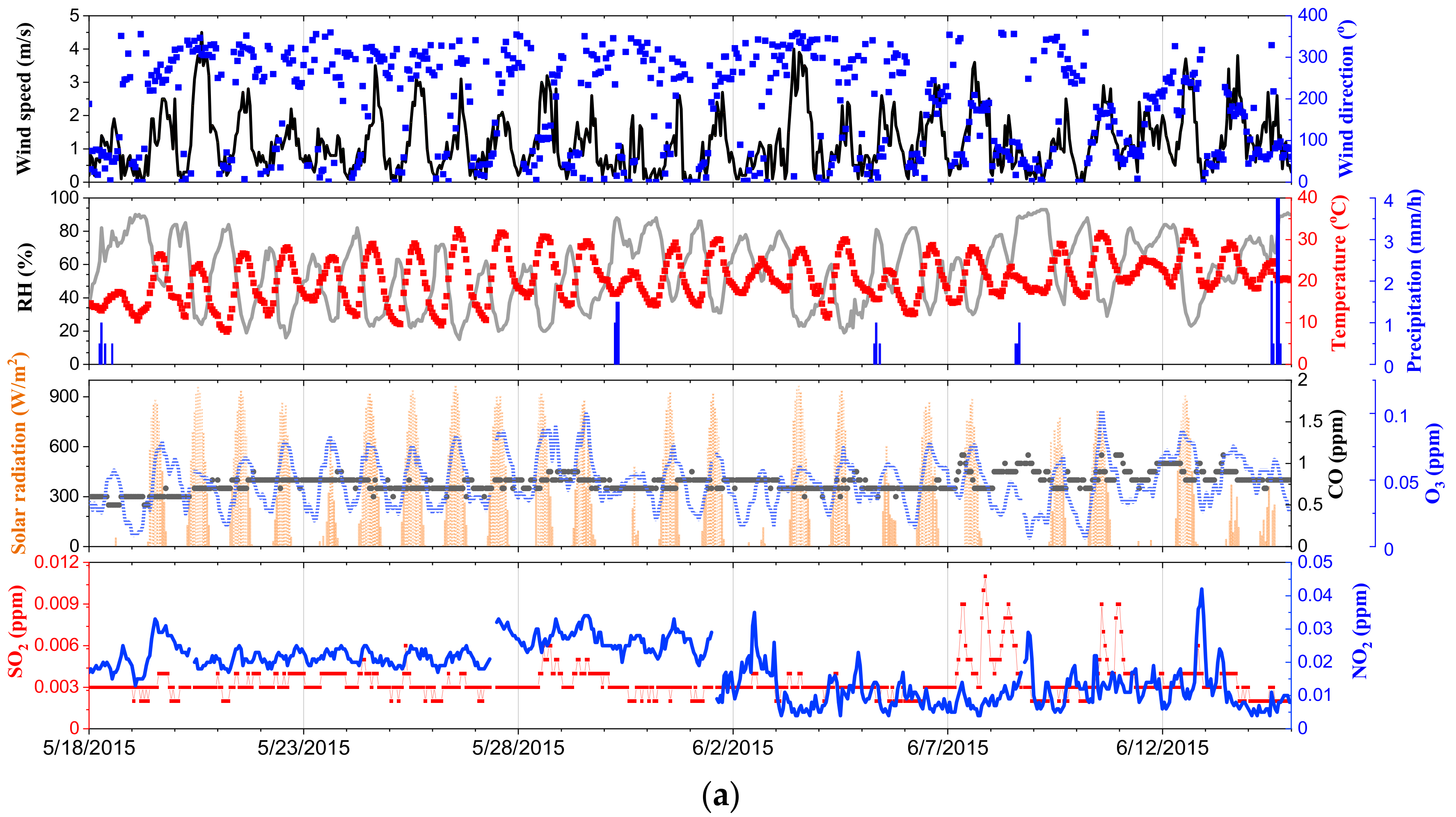
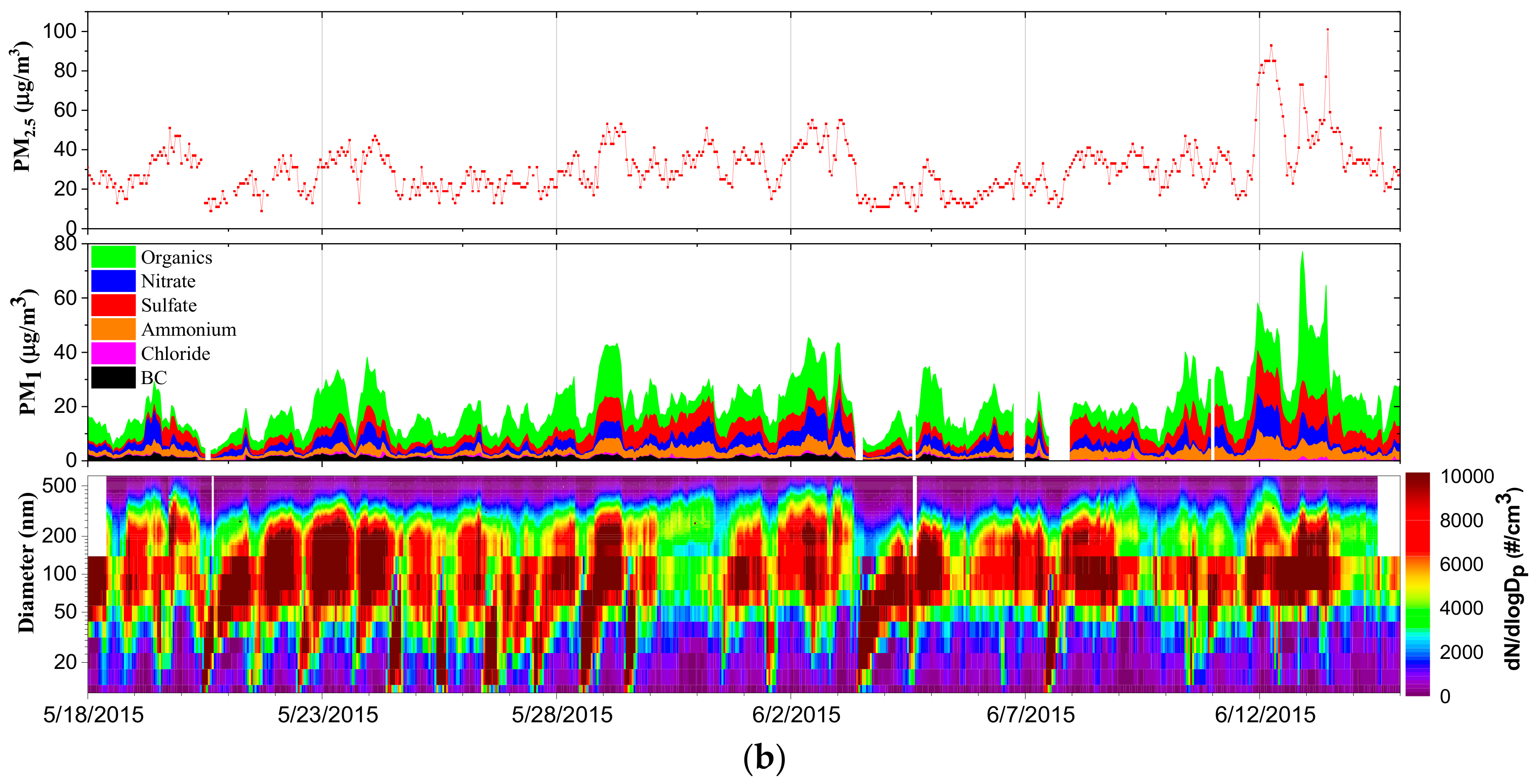
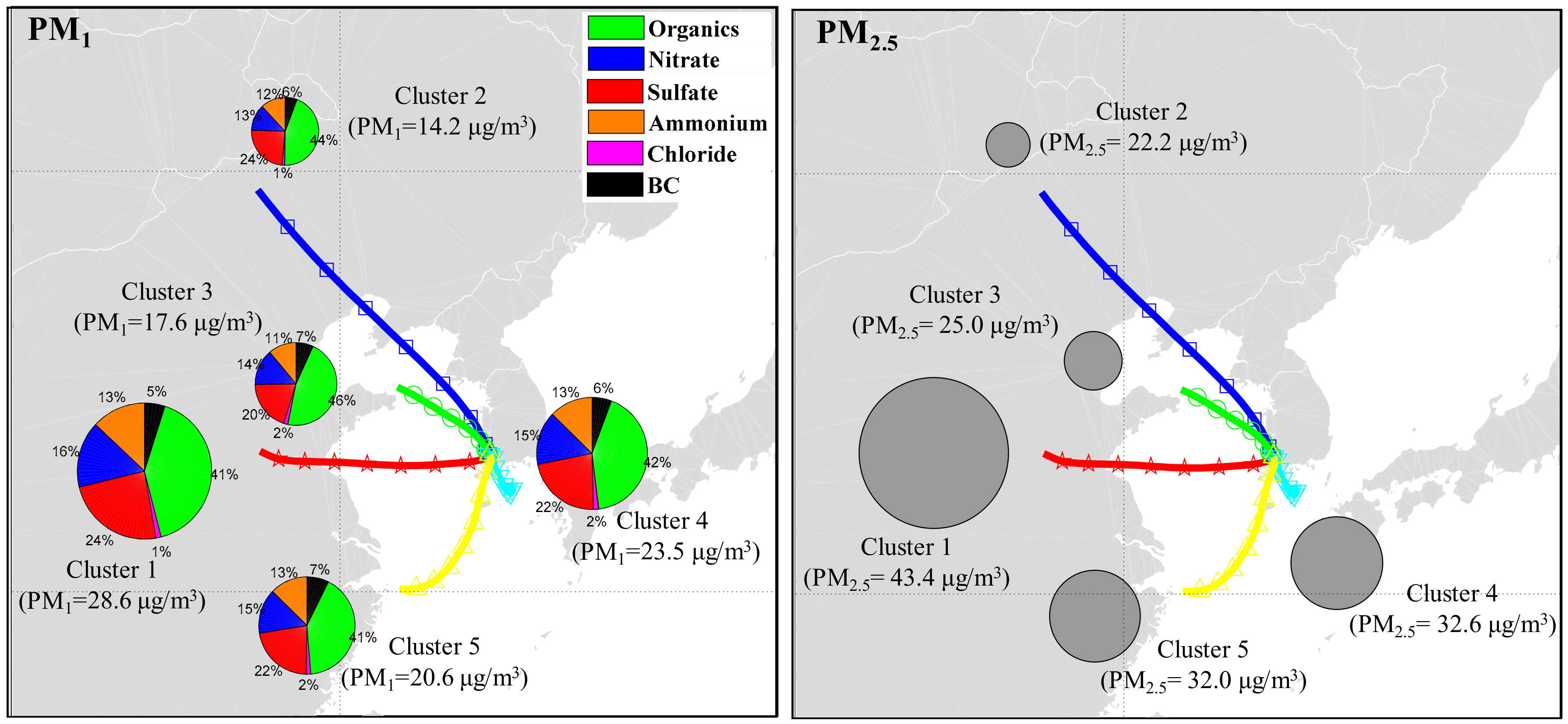
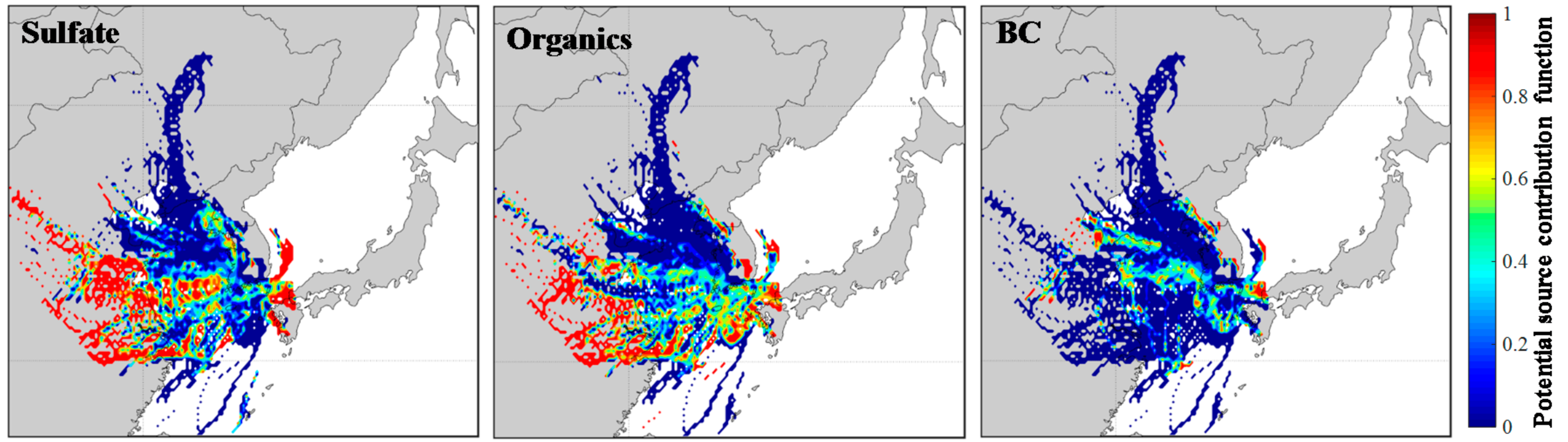
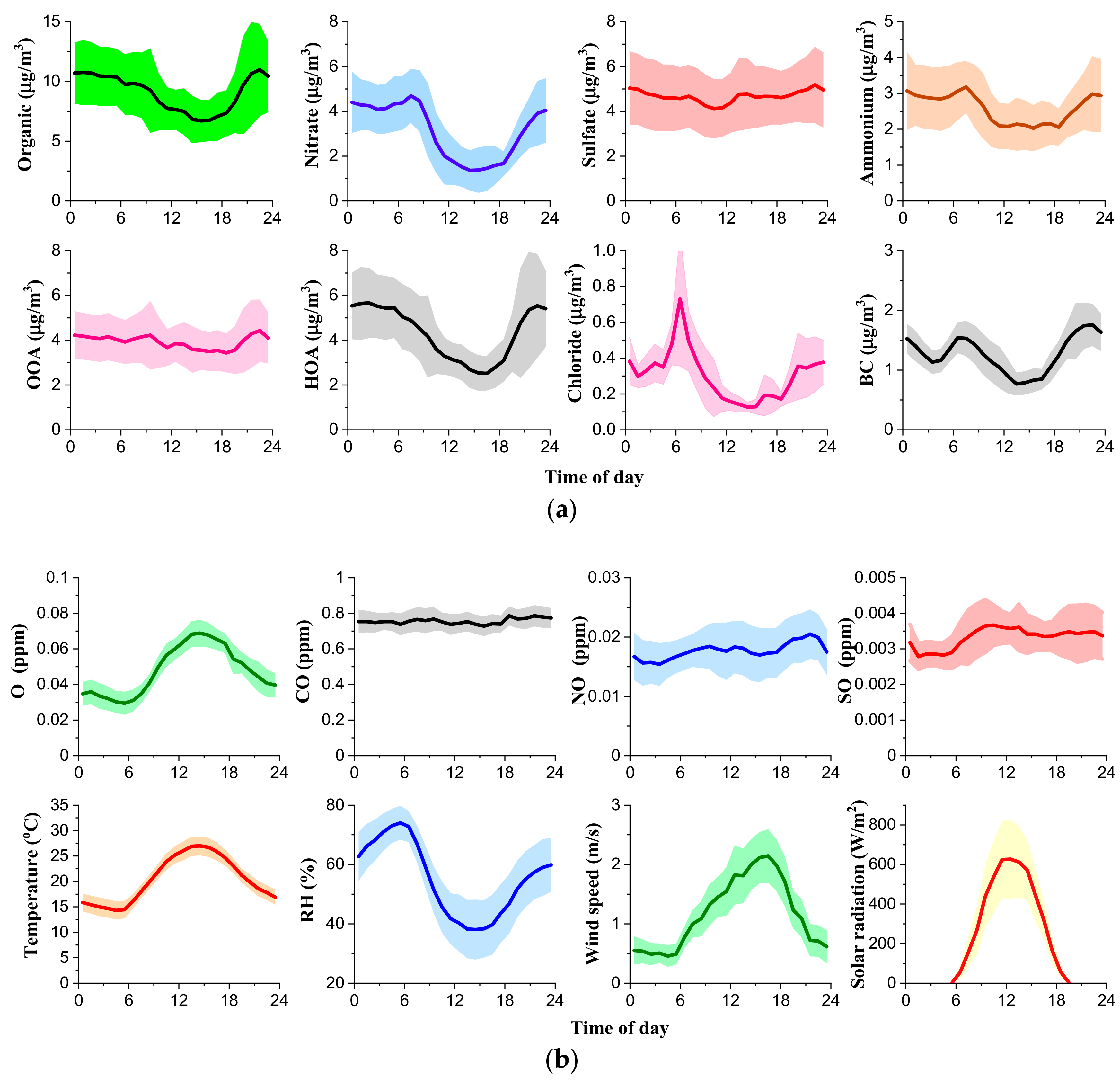
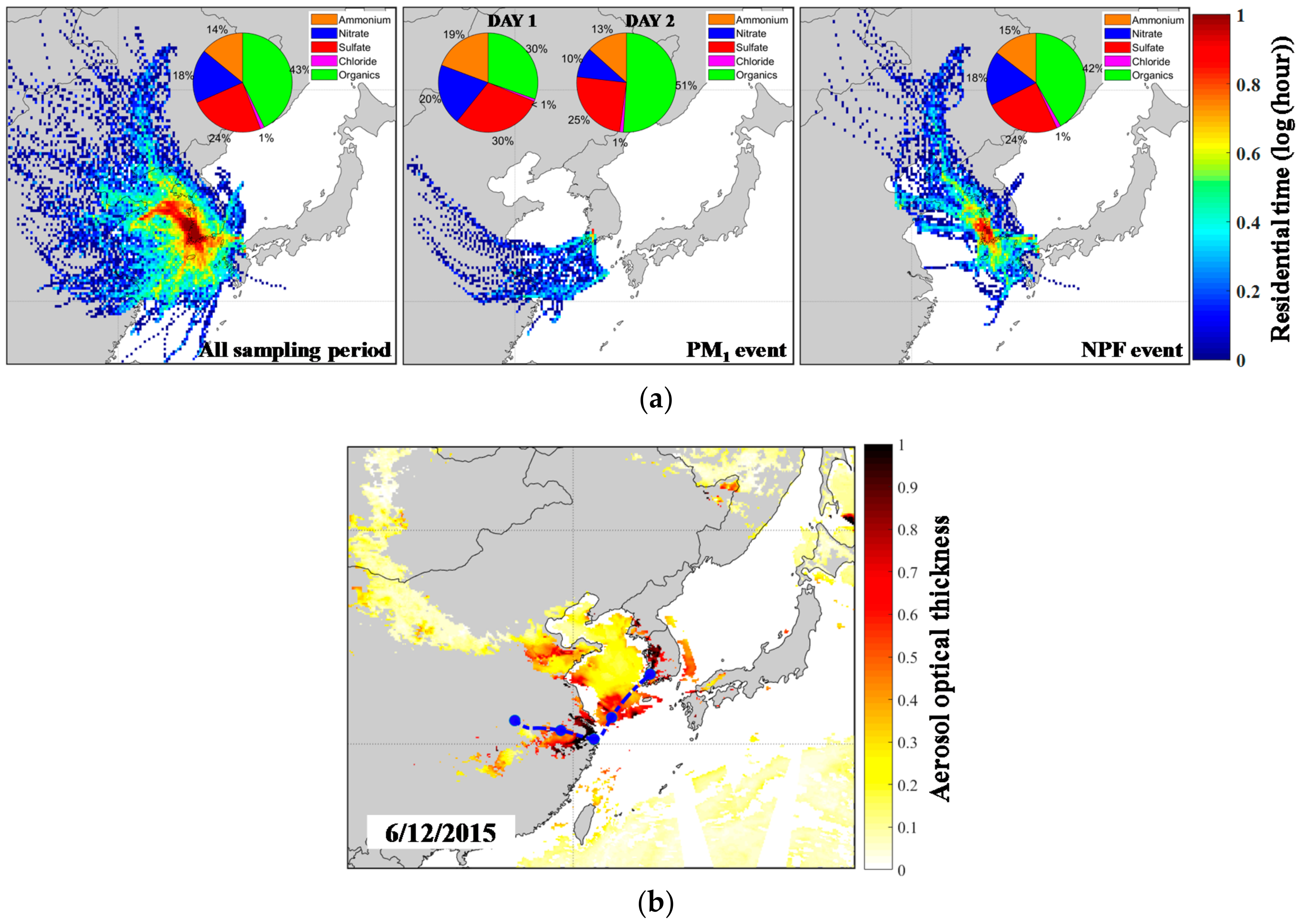
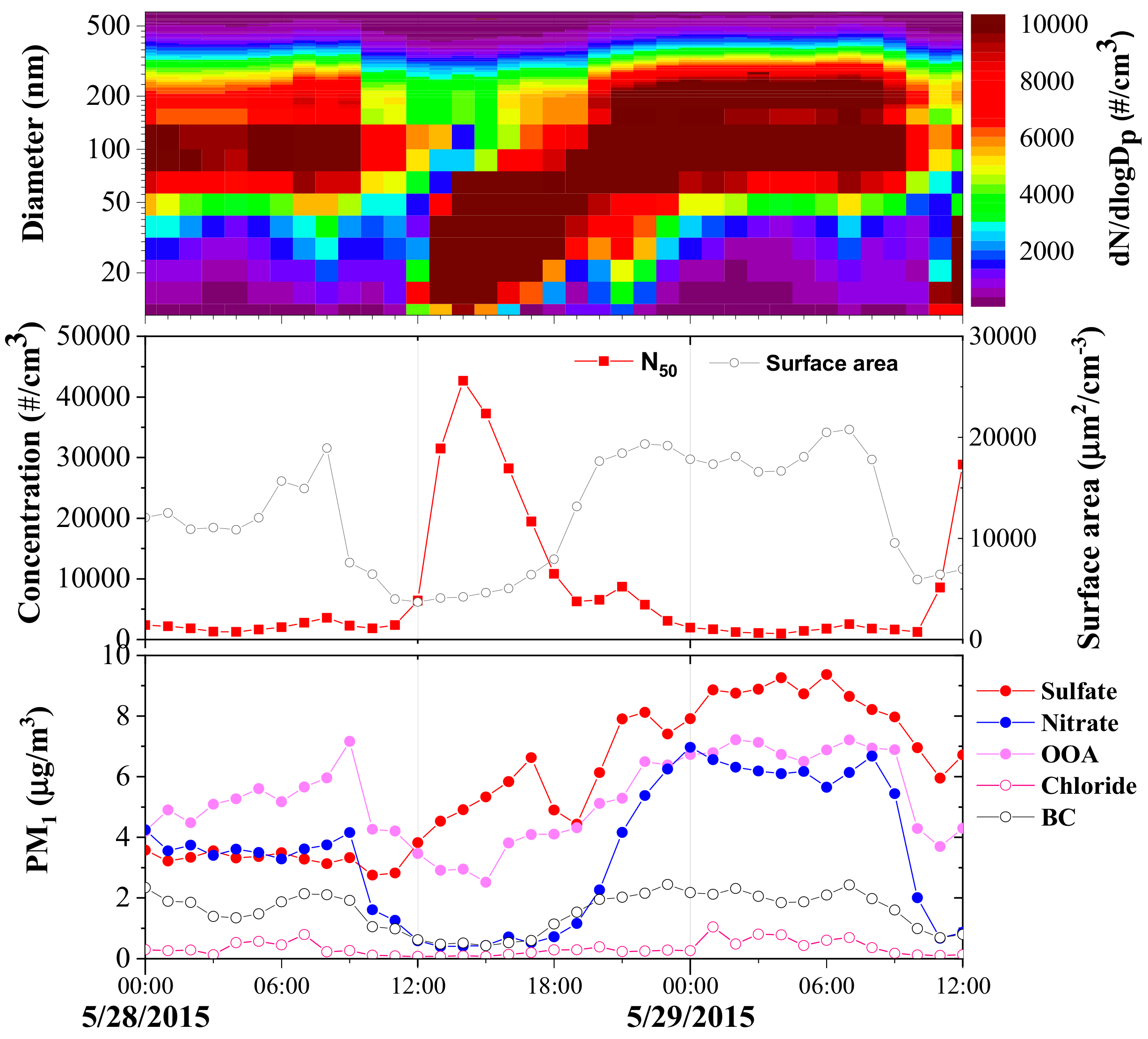
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines That Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassee, F.R.; Heroux, M.E.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Kelly, F.J. Particulate Matter Beyond Mass: Recent Health Evidence on the Role of Fractions, Chemical Constituents and Sources of Emission. Inhal. Toxicol. 2013, 25, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöschl, U. Atmospheric Aerosols: Composition, Transformation, Climate and Health Effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Park, J.Y.; Kwak, J.-H.; Cho, G.N.; Kim, J.-S. Seasonal and Diurnal Variations of Ultrafine Particle Concentration in Urban Gwangju, Korea: Observation of Ultrafine Particle Events. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, S.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, H.J.; Park, K. Ultrafine Particle Events in the Ambient Atmosphere in Korea. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 6, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hu, M.; Zamora, M.L.; Peng, J.; Shang, D.; Zheng, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, Z.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L.; et al. Elucidating Severe Urban Haze Formation in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17373–17378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Park, J.; Kang, M.; Kim, D.; Batmunkh, T.; Bae, M.-S.; Park, K. Chemical Characteristics of Aerosols in Coastal and Urban Ambient Atmospheres. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, Y.J. Tracking Sources of Severe Haze Episodes and Their Physicochemical and Hygroscopic Properties under Asian Continental Outflow: Long-Range Transport Pollution, Postharvest Biomass Burning, and Asian Dust. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D02206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, K.; Cayetano, M.G.; Batmunkh, T.; Kim, Y.J. Optical and Hygroscopic Properties of Long-Range Transported Haze Plumes Observed at Deokjeok Island Off the West Coast of the Korean Peninsula under the Asian Continental Outflows. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 8861–8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yue, D.; Shang, D.; Guo, S.; Sun, J.; Ding, A.; Wang, L.; Jiang, J.; Guo, H.; et al. New Particle Formation in China: Current Knowledge and Further Directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Ren, L.; Kanawade, V.P. New Particle Formation and Growth Mechanisms in Highly Polluted Environments. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2017, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.; Kang, M.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, K.; Park, K. Seasonal Characteristics of Submicrometer Organic Aerosols in Urban Gwangju, Korea Using an Aerosol Mass Spectrometer. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikanto, J.; Spracklen, D.V.; Mann, G.W.; Pickering, S.J.; Carslaw, K.S. Impact of Nucleation on Global Ccn. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8601–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmala, M.; Vehkamäki, H.; Petäjä, T.; Dal Maso, M.; Lauri, A.; Kerminen, V.M.; Birmili, W.; McMurry, P.H. Formation and Growth Rates of Ultrafine Atmospheric Particles: A Review of Observations. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, P.H.; Fink, M.; Sakurai, H.; Stolzenburg, M.R.; Mauldin, R.L.; Smith, J.; Eisele, F.; Moore, K.; Sjostedt, S.; Tanner, D.; et al. A Criterion for New Particle Formation in the Sulfur-Rich Atlanta Atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D22S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Cho, H.J.; Kang, M. Real Time Measurement of Chemical Composition of Submicrometer Aerosols at Urban Gwangju in Korea by Aerosol Mass Spectrometer. Atmos. Enviro. 2012, 62, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, J.T.; Leard, D.C.; Zhang, X.; Davidovits, P.; Smith, K.A.; Kolb, C.E.; Worsnop, D.R. Development of an Aerosol Mass Spectrometer for Size and Composition Analysis of Submicron Particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D.; Jimenez, J.L.; Williams, P.I.; Alfarra, M.R.; Bower, K.N.; Jayne, J.T.; Coe, H.; Worsnop, D.R. Quantitative Sampling Using an Aerodyne Aerosol Mass Spectrometer 1. Techniques of Data Interpretation and Error Analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takegawa, N.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Komazaki, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Jimenez, J.L.; Jayne, J.T.; Worsnop, D.R.; Allan, J.D.; Weber, R.J. Characterization of an Aerodyne Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (Ams): Intercomparison with Other Aerosol Instruments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.L.; Jayne, J.T.; Shi, Q.; Kolb, C.E.; Worsnop, D.R.; Yourshaw, I.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Flagan, R.C.; Zhang, X.; Smith, K.A. Ambient Aerosol Sampling Using the Aerodyne Aerosol Mass Spectrometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, I.; Canagaratna, M.; Zhang, Q.; Worsnop, D.; Jimenez, J. Interpretation of Organic Components from Positive Matrix Factorization of Aerosol Mass Spectrometric Data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2891–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.; Canagaratna, M.; Jimenez, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ulbrich, I.; Worsnop, D. Real-Time Methods for Estimating Organic Component Mass Concentrations from Aerosol Mass Spectrometer Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Ulbrich, I.M.; Ng, N.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Sun, Y. Understanding Atmospheric Organic Aerosols Via Factor Analysis of Aerosol Mass Spectrometry: A Review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3045–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A.; Rosen, H.; Novakov, T. The Aethalometer—an Instrument for the Real-Time Measurement of Optical Absorption by Aerosol Particles. Sci. Total Environ. 1984, 36, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Lin, M.-H. Real-Time Performance of the Microaeth® Ae51 and the Effects of Aerosol Loading on Its Measurement Results at a Traffic Site. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1853–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties Behavior, and Measurement of airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Air Resources Laboratory. Real-Time Environmental Applications and Display System. Available online: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov (accessed on 30 January 2018).
- Ashbaugh, L.L.; Malm, W.C.; Sadeh, W.Z. A Residence Time Probability Analysis of Sulfur Concentrations at Grand Canyon National Park. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1985, 19, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara Begum, B.; Kim, E.; Jeong, C.-H.; Lee, D.-W.; Hopke, P.K. Evaluation of the Potential Source Contribution Function Using the 2002 Quebec Forest Fire Episode. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3719–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Wee, D.; Kim, Y.P.; Lee, J.Y. Development and Application of Three-Dimensional Potential Source Contribution Function (3d-Pscf). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 16946–16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NASA Earth Observations. Available online: https://neo.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 30 January 2018).
- Jimenez, J.; Canagaratna, M.; Donahue, N.; Prevot, A.; Zhang, Q.; Kroll, J.; DeCarlo, P.; Allan, J.; Coe, H.; Ng, N. Evolution of Organic Aerosols in the Atmosphere. Science 2009, 326, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Maso, M.; Kulmala, M.; Riipinen, I.; Wagner, R.; Hussein, T.; Aalto, P.P.; Lehtinen, K.E. Formation and Growth of Fresh Atmospheric Aerosols: Eight Years of Aerosol Size Distribution Data from Smear Ii, Hyytiala, Finland. Boreal Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 323. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Kim, Y.J.; Ogunjobi, K.O.; Hong, C.S. Characteristics of Pm2.5 Species and Long-Range Transport of Air Masses at Taean Background Station, South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High Secondary Aerosol Contribution to Particulate Pollution During Haze Events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Effects of Aerosols on Radiative Forcing and Climate over East Asia with Different So2 Emissions. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.M.; Hobbs, P.V. Atmospheric Science: An Introductory Survey; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006; Volume 92. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, R.; Yang, D.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Hao, J.; Zheng, J.; Jiang, J. Aerosol surface area concentration: A governing factor in new particle formation in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12327–12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Measured Parameters | Instruments | Sampling Period |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 mass concentration a | BAM-1020 (Met One Instruments, USA) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Chemical constituents in PM1 | ||
| Sulfate, Nitrate, Ammonium, Chloride, Organics | AMS (Aerodyne, USA) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| BC | Aethalometer (AE-51, Magee Scientific, USA) | 18 May 2015–7 June 2015 |
| Number size distribution | ||
| 10–420 nm | NanoScan SMPS (3910, TSI, USA) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| 11–608 nm | DMPS (DMA (3081, TSI, USA) and CPC (3022a, TSI, USA) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| 0.3–20 μm | OPC (1.108, Grimm, Germany) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Gases a | ||
| CO | CO analyzer (300E, Teledyne API., USA), | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| SO2 | SO2 Analyzer (100E, Teledyne API., USA) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| NO2 | NOx Analyzer (200E, Teledyne API., USA) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| O3 | O3 Analyzer (400E, Teledyne API., USA) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Meteorological parameters | ||
| Wind speed b | Wind speed sensor (JY-WS161C, Jinyang Industrial, Korea) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Wind direction b | Wind direction sensor (JY100829, Jinyang Industrial, Korea) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Precipitation b | Rain Gauge (JY100097-2, Jinyang Industrial, Korea) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Temperature b | Temperature sensor (JY100829, Jinyang Industrial, Korea) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Relative humidity c | Thermo-hygrometer (HTP-20, Wellbian System, Korea) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Solar radiation c | Pyrheliometer (CMP-21, Kipp & Zonen, Netherlands) | 18 May 2015–14 June 2015 |
| Measured Parameters | Unit | All Sampling Periods | PM1 Event |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | °C | 20.5 ± 5.47 | 23.7 ± 3.84 |
| RH | % | 54.8 ± 20.3 | 58.2 ± 18.3 |
| Wind speed | m/s | 1.2 ± 0.87 | 1.4 ± 0.87 |
| Solar radiation | W/m2 | 334 ± 336 | 170 ± 235 |
| O3 | ppb | 47.6 ± 18.8 | 57.8 ± 16.4 |
| NO2 | ppm | 0.018 ± 0.008 | 0.015 ± 0.009 |
| CO | ppm | 0.76 ± 0.11 | 0.92 ± 0.08 |
| SO2 | ppm | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.004 ± 0.001 |
| PM2.5 | μg/m3 | 30.3 ± 13.5 | 57.8 ± 20.5 |
| PM1 | μg/m3 | 20.8 ± 10.9 | 43.3 ± 12.9 |
| BC | μg/m3 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | N/A |
| Ammonium | μg/m3 | 2.6 ± 1.6 | 5.8 ± 2.0 |
| Nitrate | μg/m3 | 3.2 ± 2.6 | 6.4 ± 3.9 |
| Sulfate | μg/m3 | 4.7 ± 2.9 | 11.1 ± 2.03 |
| Organics | μg/m3 | 9.1 ± 5.5 | 19.4 ± 8.83 |
| OOA | μg/m3 | 3.9 ± 2.2 | 9.0 ± 2.5 |
| HOA | μg/m3 | 4.4 ± 3.2 | 8.8 ± 6.2 |
| N (10 nm–608 nm) | particles/cm3 | 6876 ± 2827 | 7624 ± 2465 |
| N (650 nm–20 μm) | particles/cm3 | 106 ± 109 | 322 ± 264 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, H.-J.; Kang, J.; Kim, D.; Seo, A.; Park, M.; Joo, H.; Park, K. A Study on Elevated Concentrations of Submicrometer Particles in an Urban Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100393
Cho H-J, Kang J, Kim D, Seo A, Park M, Joo H, Park K. A Study on Elevated Concentrations of Submicrometer Particles in an Urban Atmosphere. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(10):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100393
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Hee-Joo, Jia Kang, Dohyeong Kim, Arom Seo, Minhan Park, Hungsoo Joo, and Kihong Park. 2018. "A Study on Elevated Concentrations of Submicrometer Particles in an Urban Atmosphere" Atmosphere 9, no. 10: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100393
APA StyleCho, H.-J., Kang, J., Kim, D., Seo, A., Park, M., Joo, H., & Park, K. (2018). A Study on Elevated Concentrations of Submicrometer Particles in an Urban Atmosphere. Atmosphere, 9(10), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100393






