Turbulence Structure in a Stratocumulus Cloud
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Large-Eddy Simulation
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Boundary and Initial Conditions
2.3. Numerical Discretization
3. Results
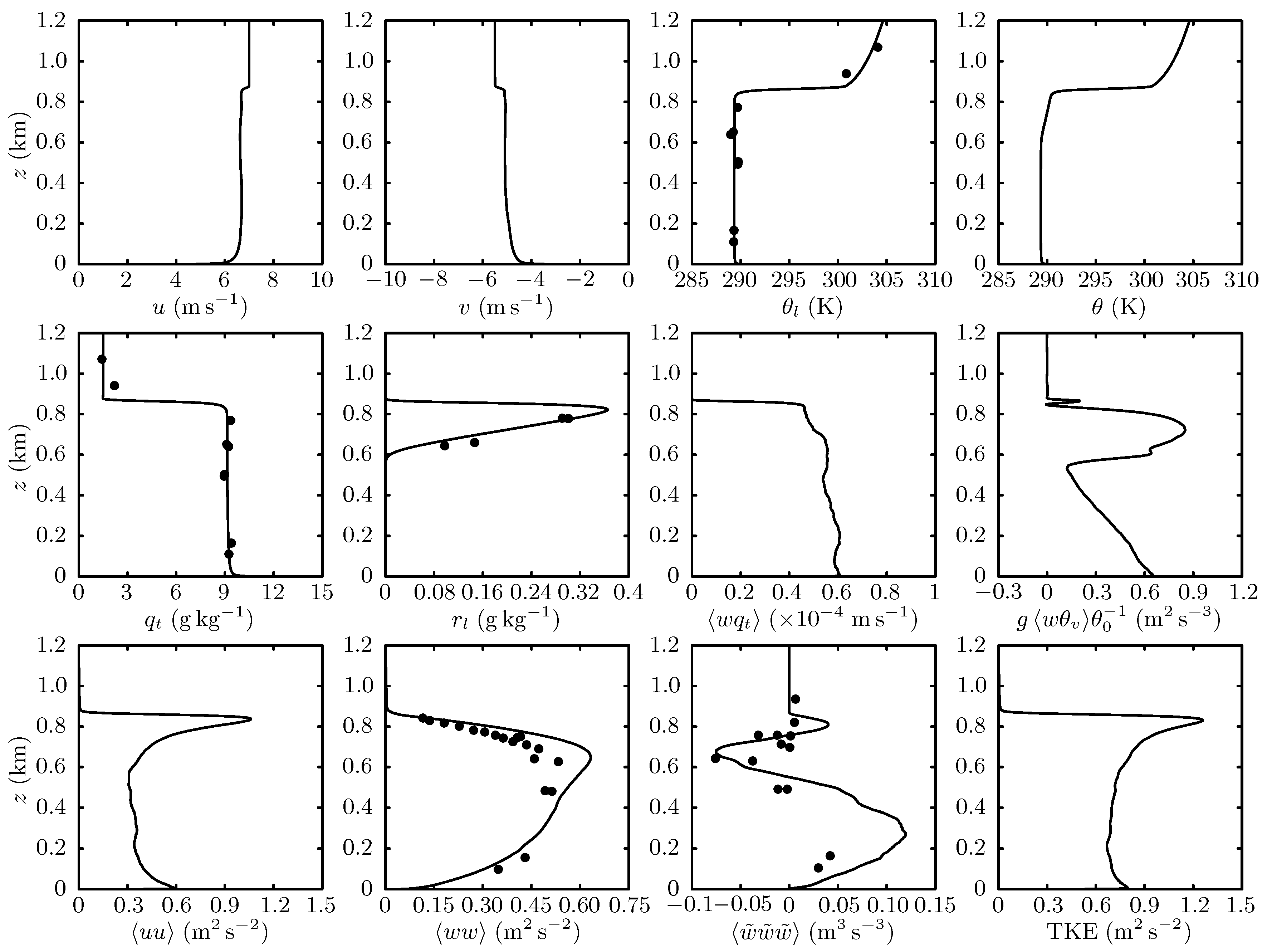
3.1. Boundary Layer Profiles and Validation
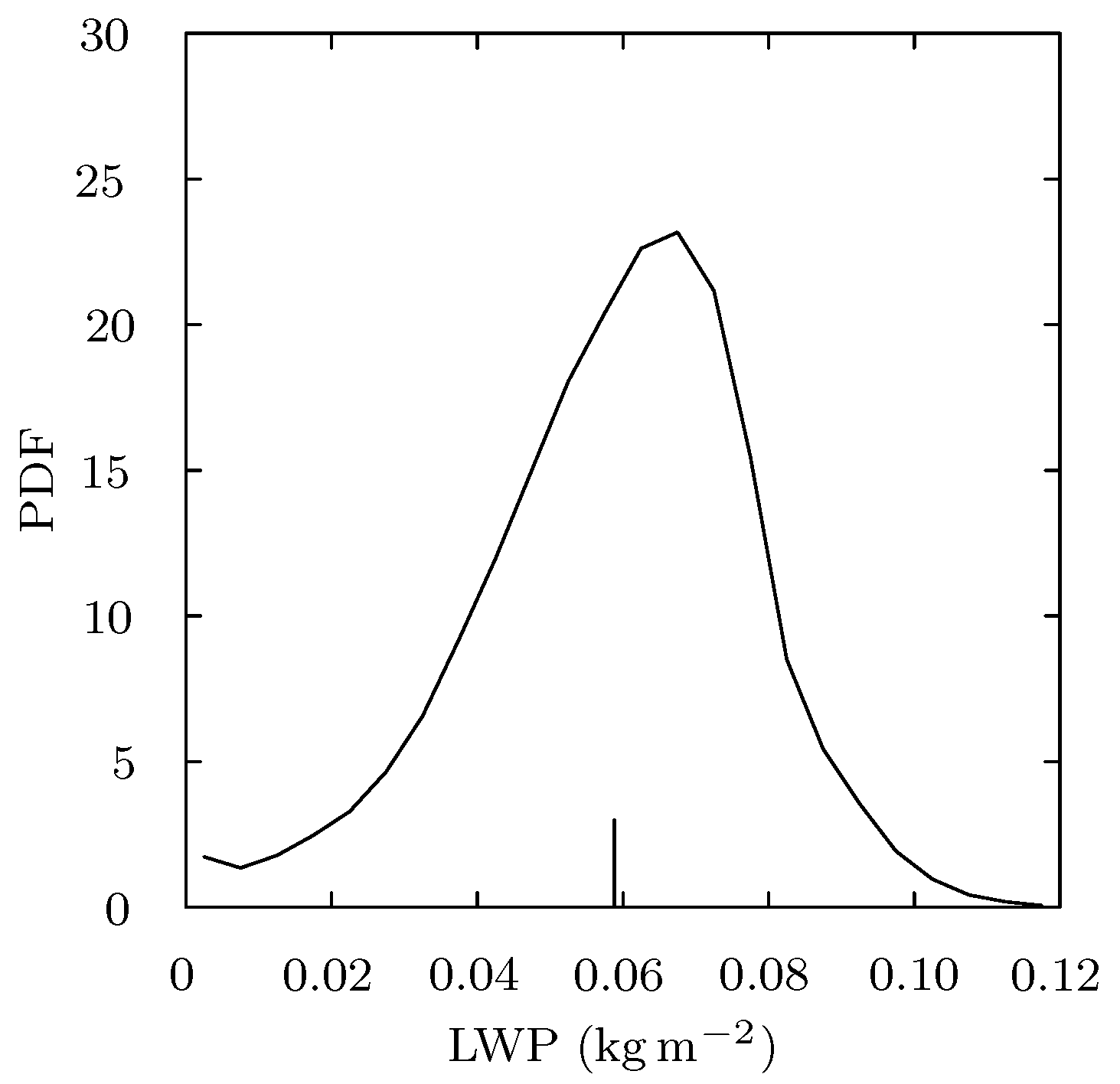
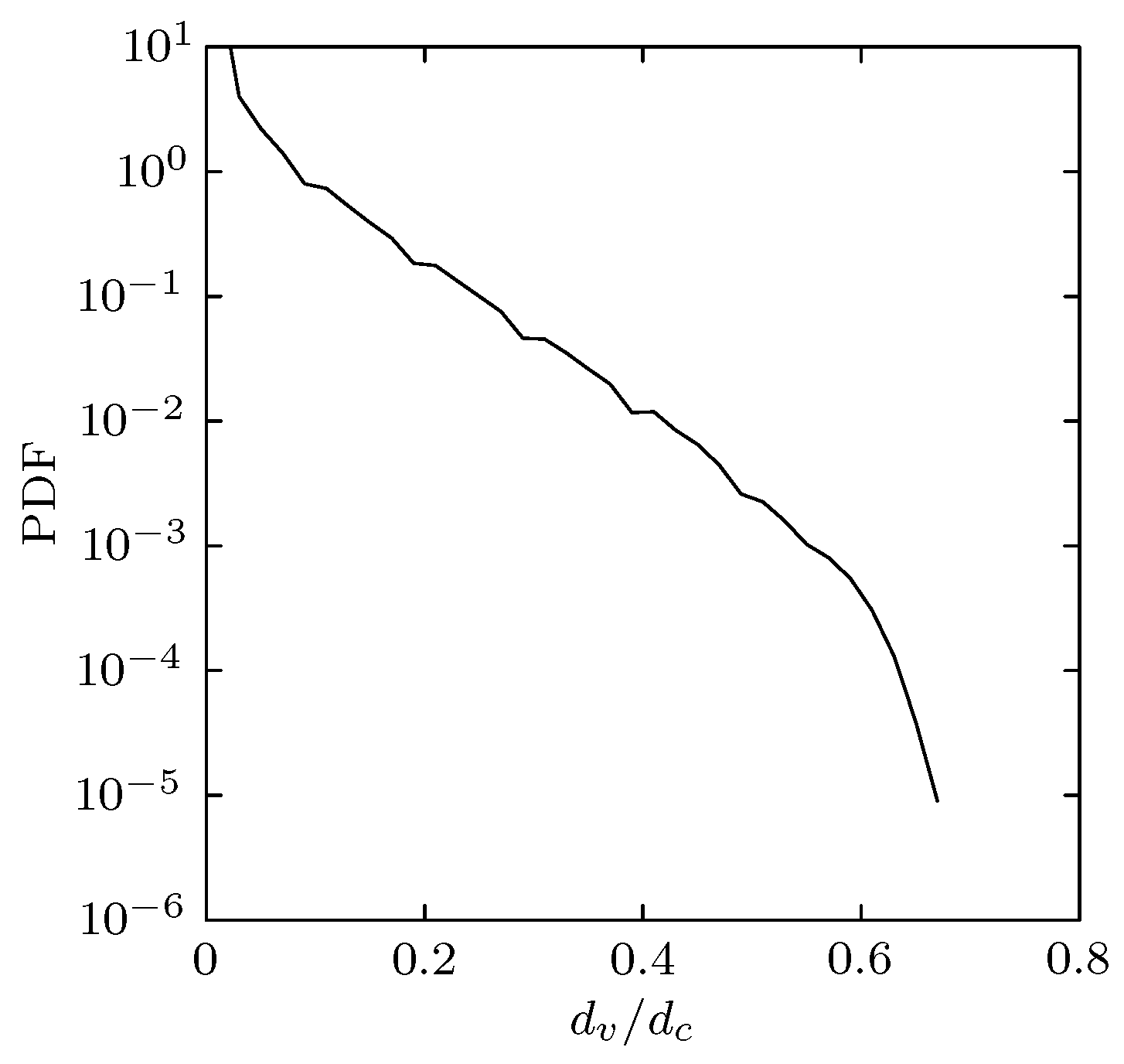
3.2. Cloud Structure
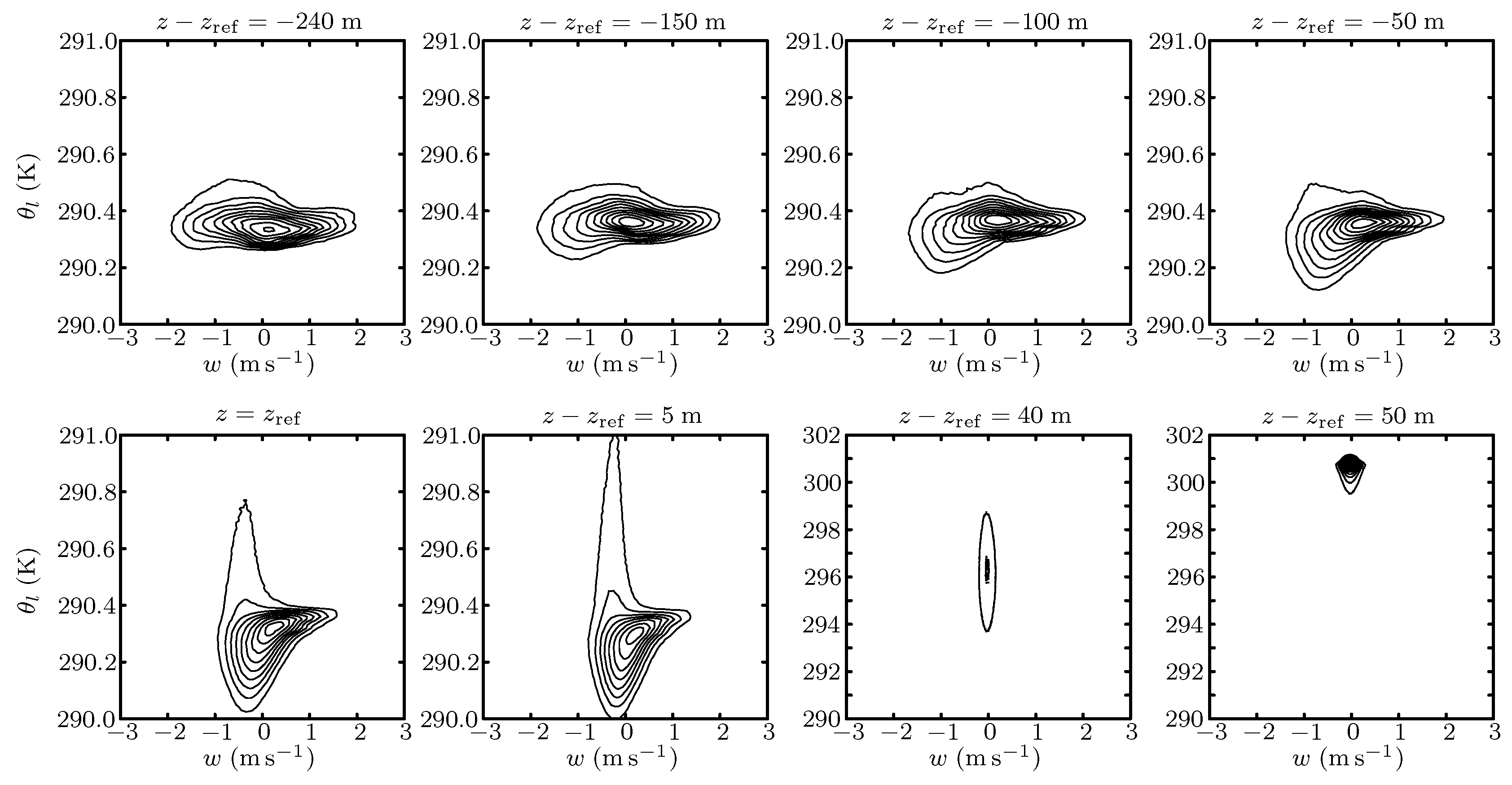
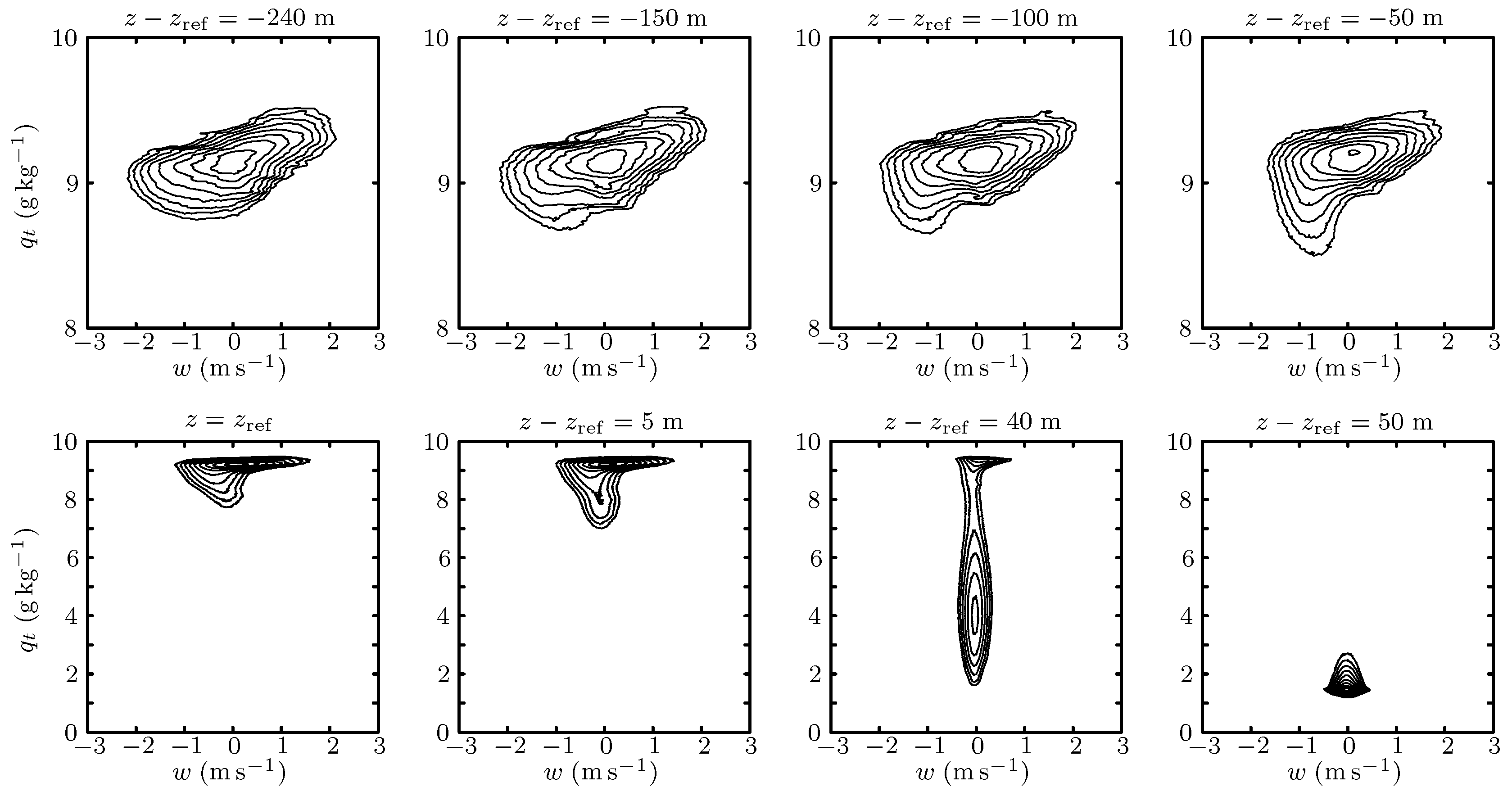
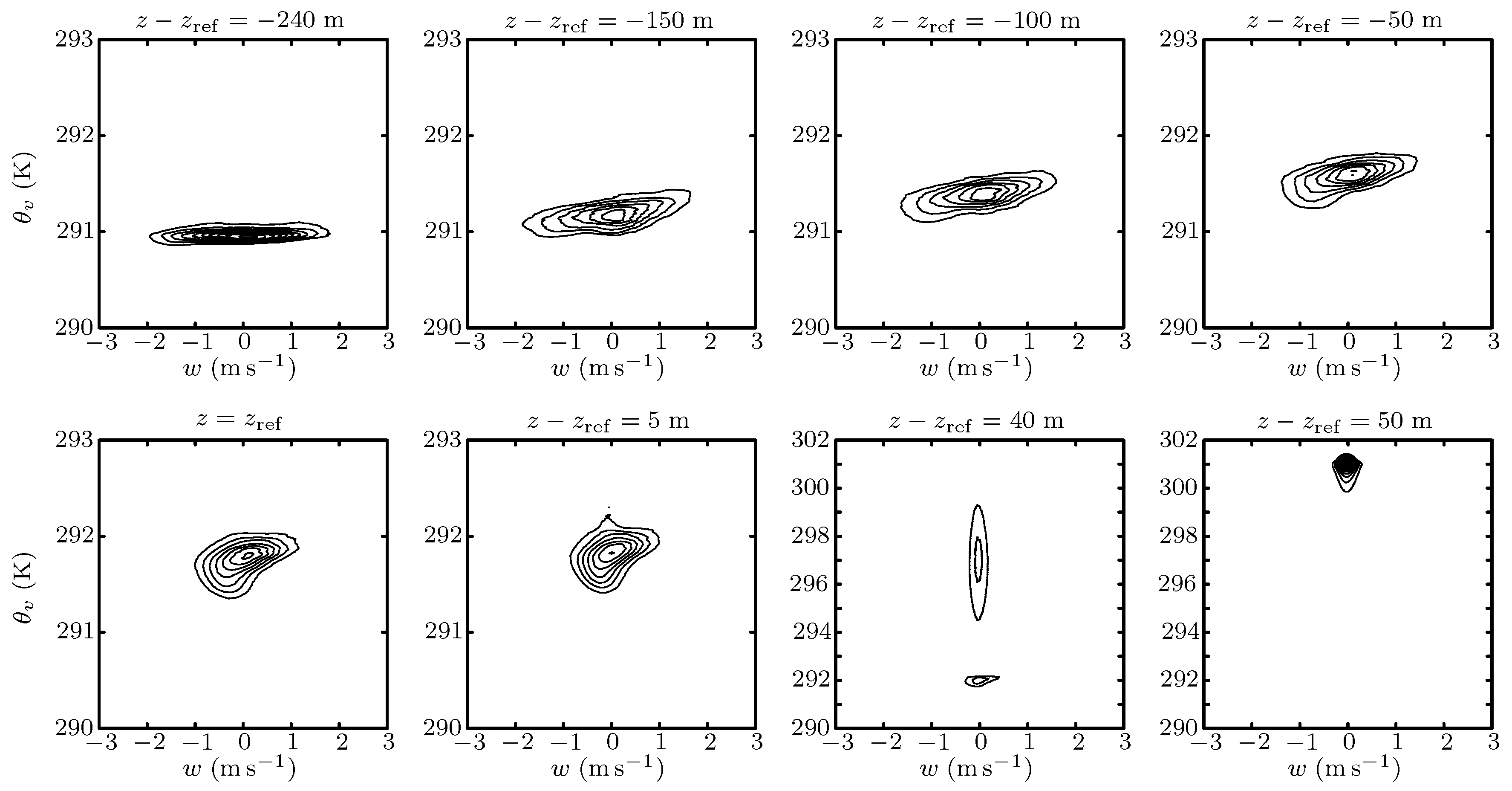
3.3. Joint Probability Density Functions
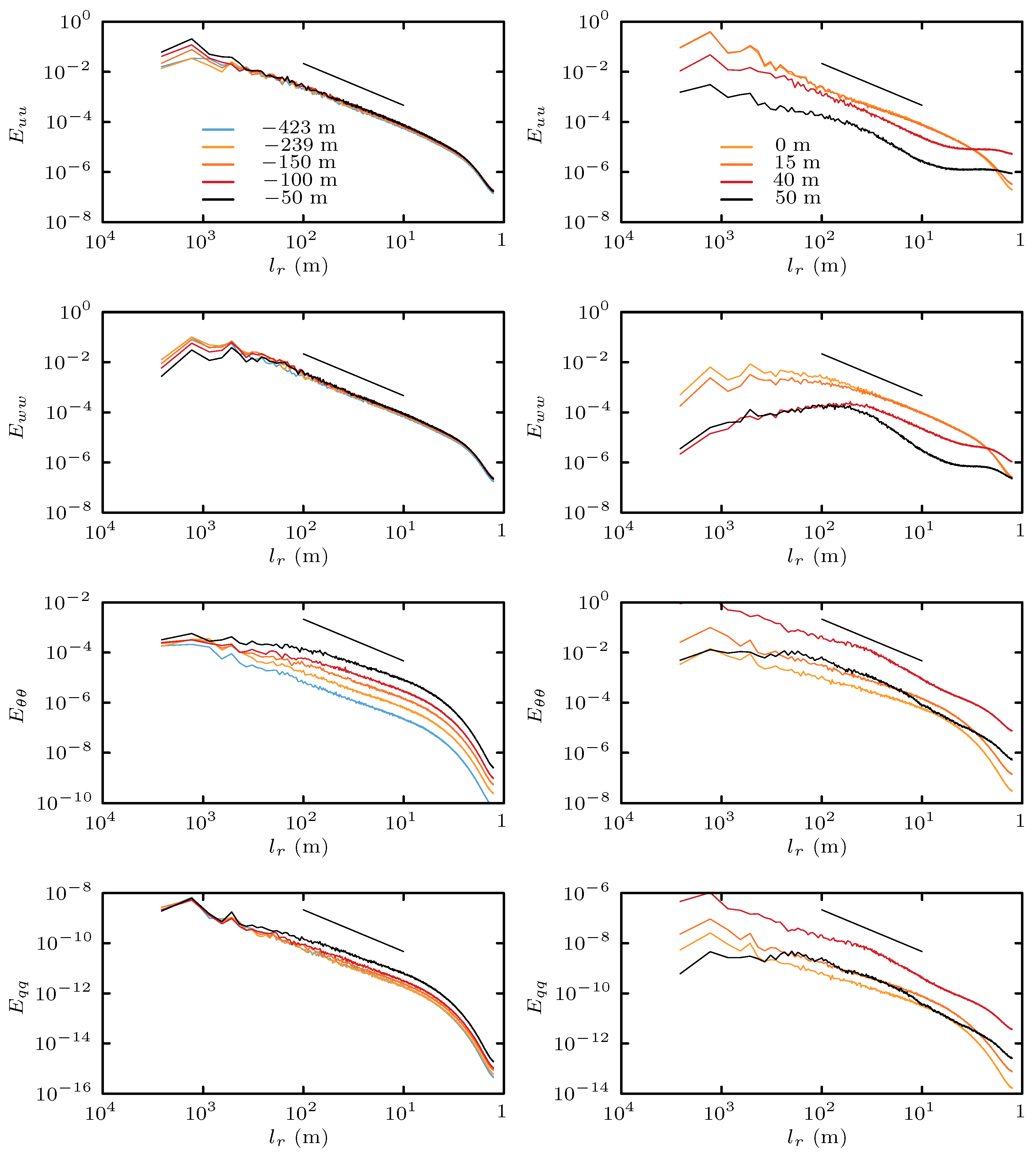
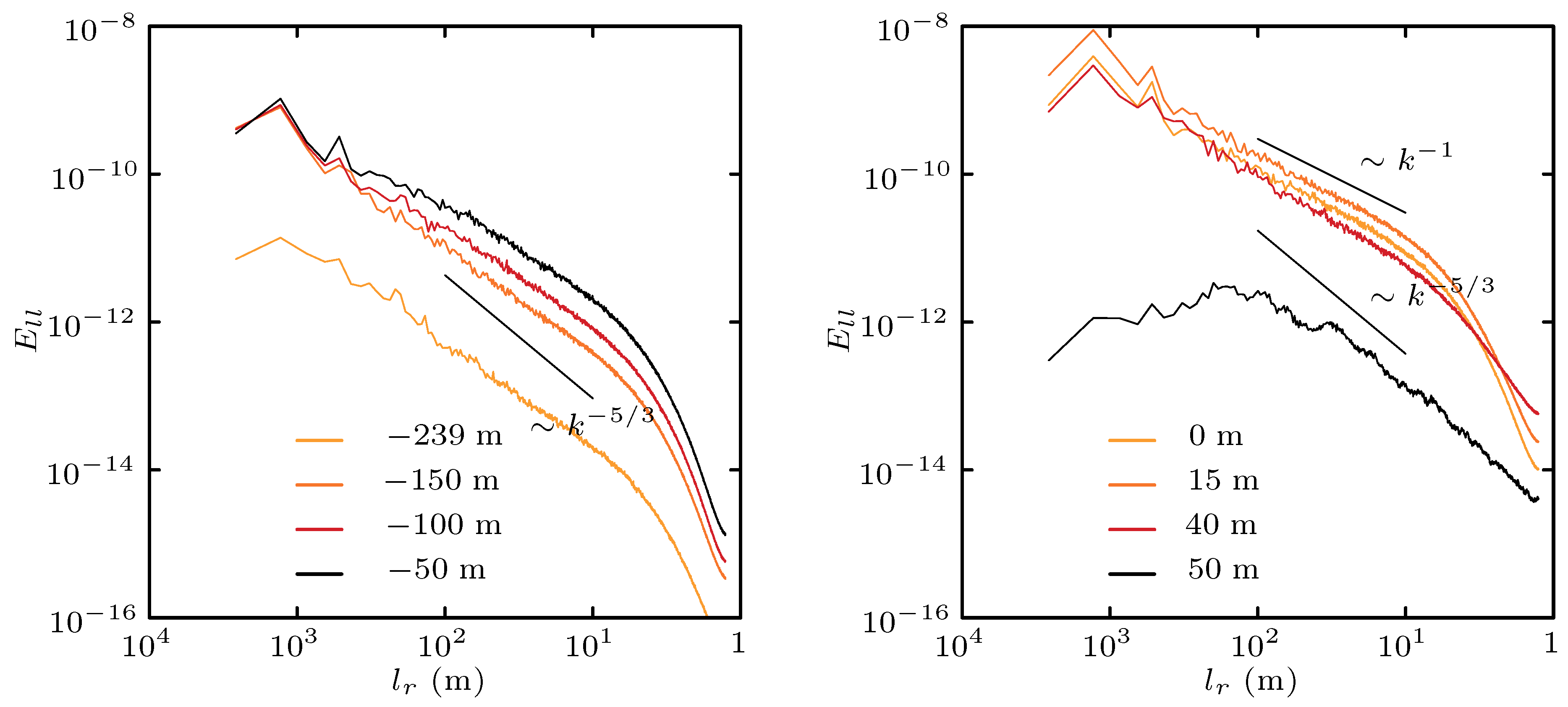
3.4. Spectra
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartmann, D.L.; Ockert-Bell, M.E.; Michelsen, M.L. The effect of cloud type on Earth’s energy balance: Global analysis. J. Clim. 1992, 5, 1281–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretherton, C.S. Convection in stratocumulus-topped atmospheric boundary layers. In The Physics and Parameterization of Moist Atmospheric Convection; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 1997; pp. 127–142. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, B. Atmospheric moist convection. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2005, 33, 605–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R. Stratocumulus clouds. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 2373–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bony, S.; Dufresne, J.L. Marine boundary layer clouds at the heart of tropical cloud feedback uncertainties in climate models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L20806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretherton, C.S. Insights into low-latitude cloud feedbacks from high-resolution models. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2015, 373, 20140415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsushima, Y.; Ringer, M.A.; Koshiro, T.; Kawai, H.; Roehrig, R.; Cole, J.; Watanabe, M.; Yokohata, T.; Bodas-Salcedo, A.; Williams, K.D.; et al. Robustness, uncertainties, and emergent constraints in the radiative responses of stratocumulus cloud regimes to future warming. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 3025–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenschow, D.H.; Paluch, I.R.; Bandy, A.R.; Pearson, R., Jr.; Kawa, S.R.; Weaver, C.J.; Huebert, B.J.; Kay, J.G.; Thornton, D.C.; Driedger, A.R., III. Dynamics and chemistry of marine stratocumulus (DYCOMS) Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 1988, 69, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.; Lenschow, D.H.; Vali, G.; Gerber, H.; Bandy, A.; Blomquist, B.; Brenguier, J.; Bretherton, C.; Burnet, F.; Campos, T.; et al. Dynamics and chemistry of marine stratocumulus—DYCOMS-II. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.; Frick, G.; Malinowski, S.P.; Jonsson, H.; Khelif, D.; Krueger, S.K. Entrainment rates and microphysics in POST stratocumulus. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12-094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plante, J.L.; Ma, Y.F.; Nurowska, K.; Gerber, H.; Khelif, D.; Karpinska, K.; Kopec, M.K.; Kumala, W.; Malinowski, S.P. Physics of Stratocumulus Top (POST): Turbulence characteristics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9711–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.E.; Bell, J.B.; Almgren, A.S.; Beckner, V.E.; Rendleman, C.A. Small-scale processes and entrainment in a stratocumulus marine boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.; Moeng, C.H.; Ackerman, A.S.; Bretherton, C.S.; Chlond, A.; DeRoode, S.; Edwards, J.; Golaz, J.C.; Jiang, H.L.; Khairoutdinov, M.; et al. Evaluation of large-eddy simulations via observations of nocturnal marine stratocumulus. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1443–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.; Matheou, G. Large-eddy simulation of stratified turbulence. Part I: A vortex-based subgrid-scale model. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 1863–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheou, G.; Chung, D. Large-eddy simulation of stratified turbulence. Part II: Application of the stretched-vortex model to the atmospheric boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 4439–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagorinsky, J. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations. I. The basic experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deardorff, J.W. A numerical study of three-dimensional turbulent channel flow at large Reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 1970, 41, 453–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, D.K. The representation of small-scale turbulence in numerical simulation experiments. In IBM Scientific Computing Symposium on Environmental Sciences; IBM: Yorktown Heights, NY, USA, 1967; pp. 195–210. [Google Scholar]
- Deardorff, J. On the magnitude of the subgrid scale eddy coefficient. J. Comput. Phys. 1971, 7, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, A. Energy cascade in large-eddy simulations of turbulent fluid flows. Adv. Geophys. 1974, 18, 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Smagorinsky, J. Some historical remarks on the use of nonlinear viscosities. In Large Eddy Simulation of Complex Engineering and Geophysical Flows; Galperin, B., Orszag, S.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.R. The sensitivity of large-eddy simulations of shallow cumulus convection to resolution and subgrid model. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.; Moeng, C.H.; Sullivan, P.P. Large-eddy simulations-of radiatively driven convection: Sensitivities to the representation of small scales. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 3963–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Phillips, N.A. Scale analysis of deep and shallow convection in the atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1962, 19, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnock, H. Wind stress over a water surface. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1955, 81, 639–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, F.H.; Welch, J.E. Numerical calculation of time-dependent viscous incompressible flow of fluid with free surface. Phys. Fluids 1965, 8, 2182–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, A.; Lamb, V.R. Computational design of the basic dynamical processes of the UCLA general circulation model. In Methods of Computational Physics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; Volume 17, pp. 173–265. [Google Scholar]
- Matheou, G.; Chung, D.; Nuijens, L.; Stevens, B.; Teixeira, J. On the fidelity of large-eddy simulation of shallow precipitating cumulus convection. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 2918–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinishi, Y.; Lund, T.S.; Vasilyev, O.V.; Moin, P. Fully conservative higher order finite difference schemes for incompressible flow. J. Comput. Phys. 1998, 143, 90–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, B.P. A stable and accurate convective modelling procedure based on quadratic upstream interpolation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1979, 19, 59–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheou, G.; Dimotakis, P.E. Scalar excursions in large-eddy simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 2016, 327, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalart, P.R.; Moser, R.D.; Rogers, M.M. Spectral methods for the Navier–Stokes equations with one infinite and two periodic directions. J. Comput. Phys. 1991, 96, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Randall, D.A. Large-eddy simulation of evaporatively driven entrainment in cloud-topped mixed layers. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 1481–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressel, K.G.; Mishra, S.; Schneider, T.; Kaul, C.M.; Tan, Z. Numerics and subgrid-scale modeling in large eddy simulations of stratocumulus clouds. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, M.K.; Malinowski, S.P.; Piotrowski, Z.P. Effects of wind shear and radiative cooling on the stratocumulus-topped boundary layer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 3222–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinita, M.J.; Matheou, G.; Teixeira, J. A joint probability density-based decomposition of turbulence in the atmospheric boundary layer. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S. The structure of radiatively driven convection in stratocumulus. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1989, 115, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.B.; Marshak, A.; Gerber, H.; Wiscombe, W.J. Horizontal structure of marine boundary layer clouds from centimeter to kilometer scales. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 6123–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.; Jensen, J.B.; Davis, A.B.; Marshak, A.; Wiscombe, W.J. Spectral density of cloud liquid water content at high frequencies. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.; Frick, G.; Malinowski, S.P.; Brenguier, J.L.; Burnet, F. Holes and entrainment in stratocumulus. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haman, K.E.; Malinowski, S.P.; Kurowski, M.J.; Gerber, H.; Brenguier, J.L. Small scale mixing processes at the top of a marine stratocumulus—A case study. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 133, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S.; Haman, K.; Kopec, M.; Kumala, W.; Gerber, H. Small-scale turbulent mixing at stratocumulus top observed by means of high resolution airborne temperature and LWC measurements. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 318, 072013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S.P.; Gerber, H.; Plante, J.L.; Kopec, M.K.; Kumala, W.; Nurowska, K.; Chuang, P.Y.; Khelif, D.; Haman, K.E. Physics of Stratocumulus Top (POST): Turbulent mixing across capping inversion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 12171–12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Albrecht, B. The turbulence structure in a continental stratocumulus cloud from millimeter-wavelength radar observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 2417–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheou, G.; Chung, D.; Teixeira, J. Large-eddy simulation of a stratocumulus cloud. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2017, 2, 090509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, J.P. Cloud-top entrainment in stratocumulus clouds. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2017, 49, 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Randall, D.A. Cooling of entrained parcels in a large-eddy simulation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 1118–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haman, K.E. Simple approach to dynamics of entrainment interface layers and cloud holes in stratocumulus clouds. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 135, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.; Taylor, J.P. Liquid water path variability in unbroken marine stratocumulus cloud. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 127, 2635–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lozar, A.; Mellado, J.P. Mixing driven by radiative and evaporative cooling at the stratocumulus top. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 4681–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyngaard, J.C.; Moeng, C.H. Parameterizing turbulent diffusion through the joint probability density. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1992, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Stevens, B. Top-hat representation of turbulence statistics in cloud-topped boundary layers: A large eddy simulation study. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golaz, J.C.; Larson, V.E.; Cotton, W.R. A PDF-based model for boundary layer clouds. Part I: Method and model description. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 3540–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, V.E.; Golaz, J.C. Using probability density functions to derive consistent closure relationships among higher-order moments. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogenschutz, P.A.; Krueger, S.K. A simplified PDF parameterization of subgrid-scale clouds and turbulence for cloud-resolving models. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2013, 5, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.G.; Malinowski, S.P.; Grabowski, W.W. Resolution and domain-size sensitivity in implicit large-eddy simulation of the stratocumulus-topped boundary layer. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2016, 8, 885–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.G.; Ma, Y.F.; Grabowski, W.W.; Malinowski, S.P. Anisotropy of observed and simulated turbulence in marine stratocumulus. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2018, 10, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Malinowski, S.P.; Karpińska, K.; Gerber, H.E.; Kumala, W. Scaling analysis of temperature and liquid water content in the marine boundary layer clouds during POST. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 74, 4075–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheou, G. Numerical discretization and subgrid-scale model effects on large-eddy simulations of a stable boundary layer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 3050–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.; Pullin, D.I. Direct numerical simulation and large-eddy simulation of stationary buoyancy-driven turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 643, 279–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.; Vali, G.; Comstock, K.; Wood, R.; vanZanten, M.C.; Austin, P.H.; Bretherton, C.S.; Lenschow, D.H. Pockets of open cells and drizzle in marine stratocumulus. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2005, 86, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
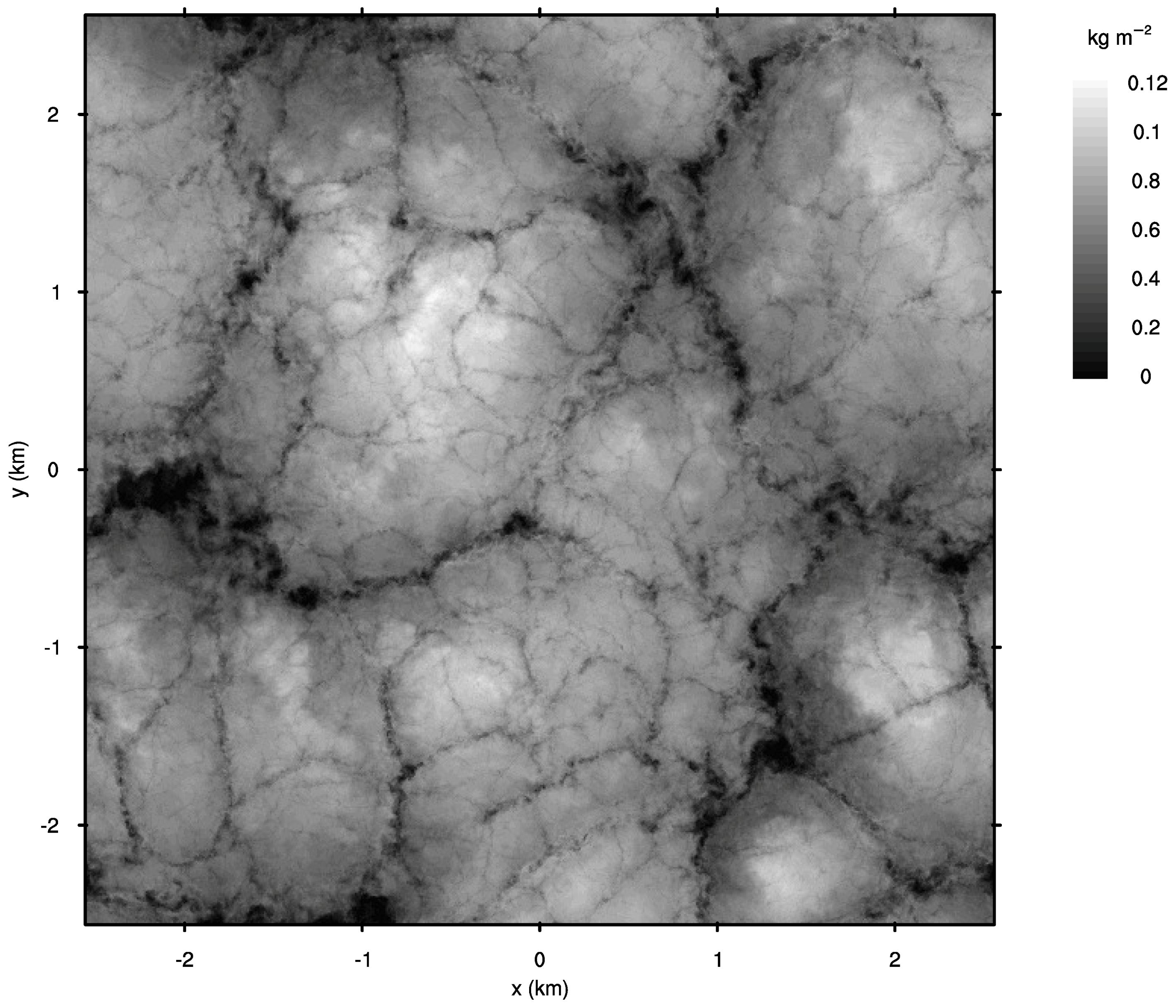


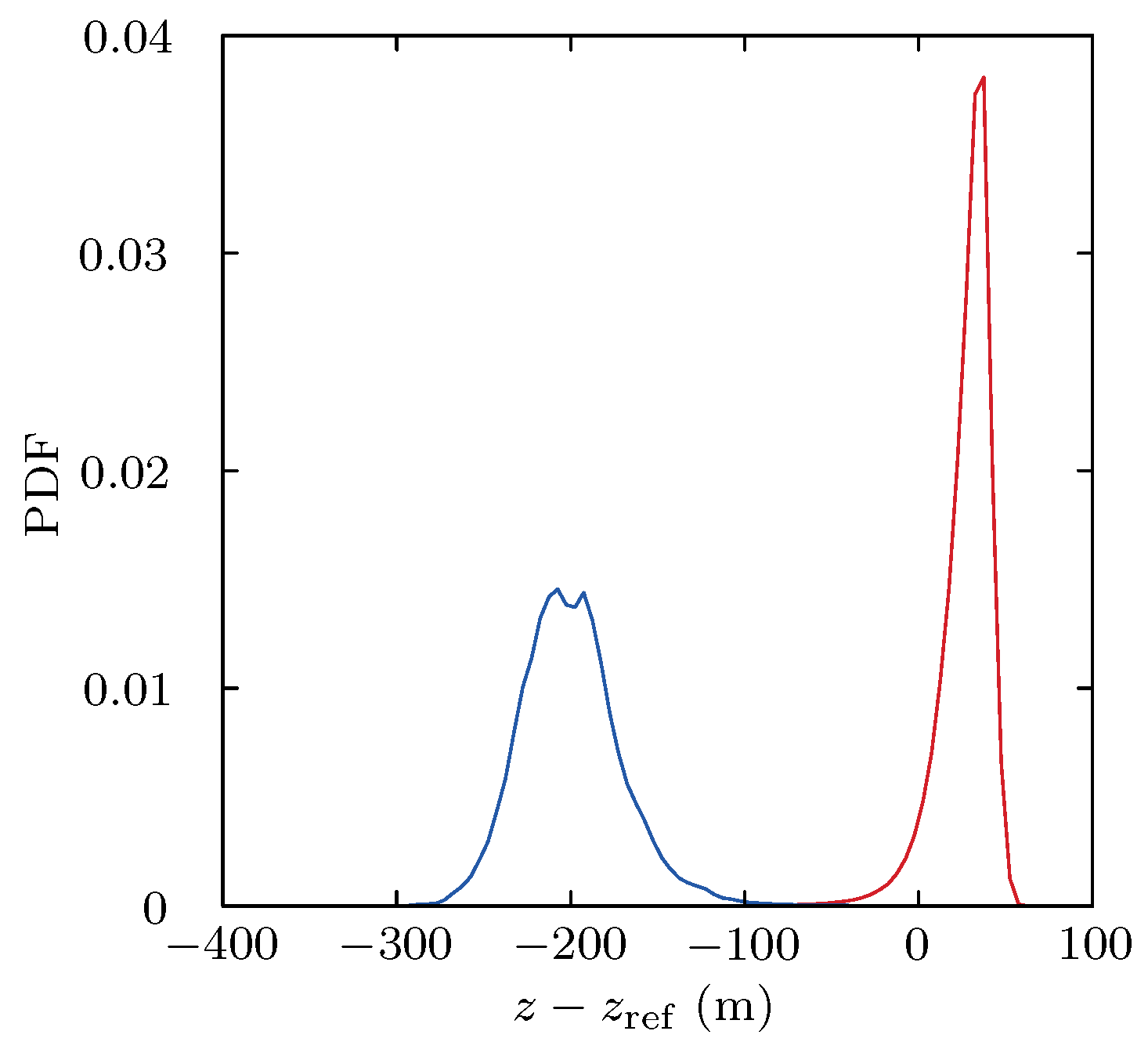

| Mean cloud depth | |
| Height of maximum cloud liquid | |
| Inversion height |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matheou, G. Turbulence Structure in a Stratocumulus Cloud. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100392
Matheou G. Turbulence Structure in a Stratocumulus Cloud. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(10):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100392
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatheou, Georgios. 2018. "Turbulence Structure in a Stratocumulus Cloud" Atmosphere 9, no. 10: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100392
APA StyleMatheou, G. (2018). Turbulence Structure in a Stratocumulus Cloud. Atmosphere, 9(10), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100392





