Sources of Airborne Endotoxins in Ambient Air and Exposure of Nearby Communities—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Endotoxins in Ambient Air
3.1. Endotoxin Concentrations in Urban and Rural Areas
3.2. Temperature
3.3. Size Fractionation
4. Anthropogenic Sources of Endotoxins
4.1. Endotoxins from Composting Facilities
4.2. Endotoxins from Intensive Farming
4.3. Other Endotoxin Sources
4.4. Distribution of Endotoxins from Anthropogenic Sources
4.4.1. Temperature
4.4.2. Sampling Approach
4.4.3. Size Fractions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wouters, I.M.M.; Spaan, S.; Douwes, J.; Doekes, G.; Heederik, D. Overview of Personal Occupational Exposure Levels to Inhalable Dust, Endotoxin, β (1→3)-Glucan and Fungal Extracellular Polysaccharides in the Waste Management Chain. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2005, 50, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawniczek-Walczyk, A.; Gorny, R.L.; Golofit-Szymczak, M.; Niesler, A.; Wlazlo, A. Occupational exposure to airborne microorganisms, endotoxins and beta-glucans in poultry houses at different stages of the production cycle. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2013, 20, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thorn, J.; Beijer, L.; Jonsson, T.; Rylander, R. Measurement Strategies for the Determination of Airborne Bacterial Endotoxin in Sewage Treatment Plants. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2002, 46, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duquenne, P.; Marchand, G.; Duchaine, C. Measurement of endotoxins in bioaerosols at workplace: A critical review of literature and a standardization issue. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2013, 57, 137–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basinas, I.; Sigsgaard, T.; Kromhout, H.; Heederik, D.; Wouters, I.M.; Schlünssen, V. A comprehensive review of levels and determinants of personal exposure to dust and endotoxin in livestock farming. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, L.C.; Vyas, B.; Kanabar, V.; Kemeny, D.M.; O’Connor, B.J. Inhaled endotoxin in healthy human subjects: A dose-related study on systemic effects and peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebers, V.; Brüning, T.; Raulf-Heimsoth, M. Occupational endotoxin-exposure and possible health effects on humans. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2006, 49, 474–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebers, V.; Raulf-Heimsoth, M.; Brüning, T. Health effects due to endotoxin inhalation (review). Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celedón, J.C.; Milton, D.K.; Ramsey, C.D.; Litonjua, A.A.; Ryan, L.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Gold, D.R. Exposure to dust mite allergen and endotoxin in early life and asthma and atopy in childhood. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 76, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Health Risks Associated with Livestock Farms; 2012/27E; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, S.J.; Milton, D.K.; Heederik, D.; Thorne, P.S.; Donham, K.J.; Croteau, E.A.; Kelly, K.M.; Douwes, J.; Lewis, D.; Whitmer, M.; et al. Interlaboratory evaluation of endotoxin analyses in agricultural dusts—Comparison of LAL assay and mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, T.; Yao, M.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Dutta, A.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Hu, M.; et al. Airborne endotoxin in fine particulate matter in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Baumgartner, J.; Zhang, Y.; Schauer, J.J. Source apportionment of Beijing air pollution during a severe winter haze event and associated pro-inflammatory responses in lung epithelial cells. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menetrez, M.Y.; Foarde, K.K.; Esch, R.K.; Schwartz, T.D.; Dean, T.R.; Hays, M.D.; Cho, S.H.; Betancourt, D.A.; Moore, S.A. An evaluation of indoor and outdoor biological particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5476–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tager, I.B.; Lurmann, F.W.; Haight, T.; Alcorn, S.; Penfold, B.; Hammond, K.S. Temporal and spatial patterns of ambient endotoxin concentrations in Fresno, California. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, B.-A.; Müller, W. Airborne Endotoxins and Airborne Gram-Negative Bacteria in a Residential Neighborhood. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 158, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Annelling, L.; Avol, E.; Peters, J.M.; Thorne, P.S. Ambient endotoxin concentrations in PM10 from Southern California. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.; Van Strien, R.; Ehrenstein, V.; Schierl, R.; Küchenhoff, H.; Radon, K. Ambient endotoxin level in an area with intensive livestock production. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2006, 13, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barnig, C.; Reboux, G.; Roussel, S.; Casset, A.; Sohy, C.; Dalphin, J.C.; de Blay, F. Indoor dust and air concentrations of endotoxin in urban and rural environments. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, A.M. Exposure to Airborne Microbial Components in Autumn and Spring during Work at Danish Biofuel Plants. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2006, 50, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.; Bartlett, K.; Graham, M.; Jackson, P. Ambient concentrations of airborne endotoxin in two cities in the interior of British Columbia, Canada. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, M.A.; MacNeill, M.; Kindzierski, W.B.; Wallace, L.; Héroux, M.-È.; Wheeler, A.J. Predictors of coarse particulate matter and associated endotoxin concentrations in residential environments. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza, F.; Jorquera, H.; Heyer, J.; Palma, W.; Edwards, A.M.; Muñoz, M.; Valdivia, G.; Montoya, L.D. Short-term dynamics of indoor and outdoor endotoxin exposure: Case of Santiago, Chile, 2012. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.P.; Tanner, B.D.; Gerba, C.P.; Pepper, I.L. The measurement of aerosolized endotoxin from land application of Class B biosolids in Southeast Arizona. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carty, C.L.; Gehring, U.; Cyrys, J.; Bischof, W.; Heinrich, J. Seasonal variability of endotoxin in ambient fine particulate matter. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.Y.W.; Hui, E.L.C.; Lau, A.P.S. Bioactive and total endotoxins in atmospheric aerosols in the Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degobbi, C.; Lopes, F.D.T.Q.S.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Muñoz, J.E.; Saldiva, P.H.N. Correlation of fungi and endotoxin with PM2.5 and meteorological parameters in atmosphere of Sao Paulo, Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, L.E.; Champion, W.M.; Li, N.; Montoya, L.D. Indoor air quality in Latino homes in Boulder, Colorado. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, J.; Pitza, M.; Bischofb, W.; Krugc, N.; Borm, P. Endotoxin in fine (PM2.5) and coarse (PM2.5–10) particle mass of ambient aerosols. A temporo-spatial analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3659–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallawicha, K.; Lung, S.C.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Wu, C.D.; Chen, T.H.; Tsai, Y.J.; Chao, H.J. Spatiotemporal distributions and land-use regression models of ambient bacteria and endotoxins in the greater Taipei area. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, A.M. Airborne endotoxin in different background environments and seasons. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2006, 13, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morgenstern, V.; Carty, C.L.; Gehring, U.; Cyrys, J.; Bischof, W.; Heinrich, J. Lack of spatial variation of endotoxin in ambient particulate matter across a German metropolitan area. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6931–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.; Merritt, A.S.; Bellander, T. Endotoxins in urban air in Stockholm, Sweden. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversi, D.; Alessandria, L.; Schilirò, T.; Chiadò Piat, S.; Gilli, G. Meteo-climatic conditions influence the contribution of endotoxins to PM10 in an urban polluted environment. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traversi, D.; Alessandria, L.; Schilirò, T.; Gilli, G. Size-fractionated PM10 monitoring in relation to the contribution of endotoxins in different polluted areas. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3515–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, A.J.; Dobbin, N.A.; Lyrette, N.; Wallace, L.; Foto, M.; Mallick, R.; Kearney, J.; Van Ryswyk, K.; Gilbert, N.L.; Harrison, I.; et al. Residential indoor and outdoor coarse particles and associated endotoxin exposures. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7064–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, A.U.; Barnes, F.H.; Charlebois, S.J.; Smith, R.A. Macrophage cytokine response to particles and lipopolysaccharide in vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 49, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, R.; De Berardis, B.; Paoletti, L.; Guastadisegni, C. Inflammatory mediators induced by coarse (PM2.5–10) and fine (PM2.5) urban air particles in RAW 264.7 cells. Toxicology 2003, 183, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monn, C.; Becker, S. Cytotoxicity and induction of proinflammatory cytokines from human monocytes exposed to fine (PM2.5) and coarse particles (PM10–2.5) in outdoor and indoor air. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1999, 155, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schins, R.P.F.; Lightbody, J.H.; Borm, P.J.A.; Shi, T.; Donaldson, K.; Stone, V. Inflammatory effects of coarse and fine particulate matter in relation to chemical and biological constituents. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 195, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukup, J.M.; Becker, S. Human alveolar macrophage responses to air pollution particulates are associated with insoluble components of coarse material, including particulate endotoxin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 171, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankhurst, L.J.; Deacon, L.J.; Liu, J.; Drew, G.H.; Hayes, E.T.; Jackson, S.; Longhurst, P.J.; Longhurst, J.W.S.; Pollard, S.J.T.; Tyrrel, S.F. Spatial variations in airborne microorganism and endotoxin concentrations at green waste composting facilities. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hryhorczuk, D.; Curtis, L.; Scheff, P.; Chung, J.; Rizzo, M.; Lewis, C.; Keys, N.; Moomey, M. Bioaerosol emissions from a suburban yard waste composting facility. Annu. Agric. Environ. Med. 2001, 8, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Sykes, P.; Morris, R.H.K.; Allen, J.A.; Wildsmith, J.D.; Jones, K.P. Workers’ exposure to dust, endotoxin and β-(1–3) glucan at four large-scale composting facilities. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, S.; Alison, B.; Adrian, K.; Brian, C. Bioaerosol Emissions from Waste Composting and the Potential for Workers’ Exposure; Health and Safety Executive: Crown Copyright, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, B.H.; Würtz, H.; Breum, N.O.; Poulsen, O.M. Microorganisms and endotoxin in experimentally generated bioaerosols from composting household waste. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 1997, 4, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.; Kim, I.; Lee, T.; Kim, K.; Kim, D. Effect of temperature on bacterial emissions in composting of swine manure. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.S.; Rylander, R.; Larsson, L. Levels of Gram-negative bacteria, Aspergillus fumigatus, dust, and endotoxin at compost plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Danneberg, G.; Grüneklee, E.; Seitz, M.; Hartung, J.; Driesel, A.J. Microbial and Endotoxin Immissions in the Neighborhood of a Composting Plant. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 1997, 4, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, L.; Pankhurst, L.; Liu, J.; Drew, G.H.; Hayes, E.T.; Jackson, S.; Longhurst, J.; Longhurst, P.; Pollard, S.; Tyrrel, S. Endotoxin emissions from commercial composting activities. Environ. Health 2009, 8, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Lamarre, B.; Butterfield, D.; Tyrrel, S.; Longhurst, P.; Drew, G.; Al-Ashaab, R.; Nelson, A.; Gladding, T.; Simpson, A.; et al. Monitoring Bioaerosol and Odour Emissions from Composting Facilities-WR1121; DEFRA: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Duquenne, P.; Simon, X.; Koehler, V.; Goncalves-Machado, S.; Greff, G.; Nicot, T.; Poirot, P. Documentation of bioaerosol concentrations in an indoor composting facility in France. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pankhurst, L.J.; Deacon, L.J.; Abate, W.; Hayes, E.T.; Drew, G.H.; Longhurst, P.J.; Pollard, S.; Longhurst, J.; Tyrrel, S.F.; et al. Evaluation of inflammatory effects of airborne endotoxin emitted from composting sources. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolvanen, O.; Nykänen, J.; Nivukoski, U.; Himanen, M.; Veijanen, A.; Hänninen, K. Occupational hygiene in a Finnish drum composting plant. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radon, K.; Schulze, A.; Ehrenstein, V.; van Strien, R.T.; Praml, G.; Nowak, D. Environmental exposure to confined animal feeding operations and respiratory health of neighboring residents. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grethe, H. High animal welfare standards in the EU and international trade-How to prevent potential “low animal welfare havens”? Food Policy 2007, 32, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, P.S.; Ansley, A.C.; Perry, S.S. Concentrations of bioaerosols, odors, and hydrogen sulfide inside and downwind from two types of swine livestock operations. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2009, 6, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungan, R.S.; Leytem, A.B. Airborne endotoxin concentrations at a large open-lot dairy in southern Idaho. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungan, R.S.; Leytem, A.B.; Bjorneberg, D.L. Assessment of bioaerosols at a concentrated dairy operation. Aerobiologia 2010, 26, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, J.; Seedorf, J.; Trickl, T.; Gronauer, H. Emission and distribution of airborne particulates from a piggery. In Proceedings of the 9th ISAH International Congress Animal Hygiene, Helsinki, Finland, 17–21 August 1997; pp. 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Jonges, M.; van Leuken, J.; Wouters, I.; Koch, G.; Meijer, A.; Koopmans, M. Wind-Mediated Spread of Low-Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus into the Environment during Outbreaks at Commercial Poultry Farms. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radon, K.; Danuser, B.; Iversen, M.; Monso, E.; Weber, C.; Hartung, J.; Donham, K.J.; Palmgren, U.; Nowak, D. Air contaminants in different european farming environments. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2002, 9, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.C.; Niven, R.M.; Pickering, C.A.; Oldham, L.A.; Fletcher, A.M.; Francis, H.C. Comparative personal exposures to organic dusts and endotoxin. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1999, 43, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz, B.; Skórska, C.; Dutkiewicz, J. Relationship between concentrations of microbiological agents in the air of agricultural settings and occurrence of work-related symptoms in exposed persons. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, E.; Herrmann, R.; Dahling, T.; Brenner, R.; Wright, S.; Clark, P. Evaluation of Airborne Endotoxin Concentrations Associated with Management of a Crop Grown on Applied Biosolids. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.A.; Johnson, J.C.; Reynolds, S.J.; Thorne, P.S.; O’Shaughnessy, P.T. Indoor and outdoor air quality assessment of four wastewater treatment plants. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2006, 3, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Man, H.; Heederik, D.D.J.; Leenen, E.J.T.M.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; Spithoven, J.J.G.; van Knapen, F. Human exposure to endotoxins and fecal indicators originating from water features. Water Res. 2014, 51, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, H.D.; Balfanz, J.; Becker, G.; Lohmeyer, M.; Mathys, W.; Raulf-Heimsoth, M. Bioaerosol exposure during refuse collection: Results of field studies in the real-life situation. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, G.M.; Hjelmroos-Koski, M.; Rotkin-Ellman, M.; Hammond, S.K. Airborne mold and endotoxin concentrations in New Orleans, Louisiana, after flooding, October through November 2005. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang-Yona, N.; Lehahn, Y.; Herut, B.; Burshtein, N.; Rudich, Y. Marine aerosol as a possible source for endotoxins in coastal areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangamma, S.; Patil, R.S.; Mukherji, S. Characterization and proinflammatory response of airborne biological particles from wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3282–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppliger, A.; Hilfiker, S.; Duc, T.V. Influence of seasons and sampling strategy on assessment of bioaerosols in sewage treatment plants in Switzerland. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2005, 49, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez-Rubio, T.; Ramarui, A.; Sommer, J.; Xin, H.; Anderson, J.; Peccia, J. Emission rates and characterization of aerosols produced during the spreading of dewatered class B biosolids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3537–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tendal, K.; Madsen, A. Exposure to airborne microorganisms, hyphal fragments, and pollen in a field of organically grown strawberries. Aerobiologia 2011, 27, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversi, D.; Gorrasi, I.; Bonetta, S.; Leinardi, R.; Pietrangeli, B.; Carraro, E.; Gilli, G. Green job bio-aerosol exposure during anaerobic digestion for biomass energetic valorisation. Environ. Res. 2015, 138, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heederik, D.; Doekes, G.; van Strien, R.; Brunekreef, B. Daily changes of peak expiratory flow and respiratory symptom occurrence around a soy processing factory. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorn, J. Seasonal variations in exposure to microbial cell wall components among household waste collectors. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2001, 45, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-U.; Ryu, S.-H.; Kim, S.-B.; Yoon, C.-S. An assessment of dust, endotoxin, and microorganism exposure during waste collection and sorting. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, G.; Simmons, O.D.; Likirdopulos, C.A.; Worley-Davis, L.; Williams, C.M.; Sobsey, M.D. Endotoxin levels at swine farms using different waste treatment and management technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3442–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjort Bønløkke, J.; Mériaux, A.; Duchaine, C.; Godbout, S.; Cormier, Y. Seasonal variations in work-related health effects in swine farm workers. Annu. Agric. Environ. Med. 2009, 16, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Douwes, J.; Versloot, P.; Hollander, A.; Heederik, D.; Doekes, G.; Douwes, J.; Versloot, P.; Hollander, A.; Heederik, D.; Doekes, G. Influence of various dust sampling and extraction methods on the measurement of airborne endotoxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spaan, S.; Heederik, D.J.J.; Thorne, P.S.; Wouters, I.M. Optimization of airborne endotoxin exposure assessment: Effects of filter type, transport conditions, extraction solutions, and storage of samples and extracts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6134–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchaine, C.; Thorne, P.S.; Mériaux, A.; Grimard, Y.; Whitten, P.; Cormier, Y. Comparison of Endotoxin Exposure Assessment by Bioaerosol Impinger and Filter-Sampling Methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, B.A.; Draz, A.M.; Müller, W. Comparison of filtration and impingement for sampling airborne endotoxin. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujundzic, E.; Hernandez, M.; Miller, S.L. Particle size distributions and concentrations of airborne endotoxin using novel collection methods in homes during the winter and summer seasons. Indoor Air 2006, 16, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, D.J.; Lillquist, D.R.; DeRosso, F.D.; Greene, D.D.; White, G. Side-by-side comparison of three sampling methods for aerosolized endotoxin in a wastewater treatment facility. J. Environ. Health 2004, 67, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, R.F.; Grosser, R.J.; Farrar, D.; Brobst, R.B. Field studies measuring the aerosolization of endotoxin during the land application of Class B biosolids. Aerobiologia 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, R.M.; Soderholm, S.C.; Tillery, M.I. Aerosol sampling efficiency of 37 mm filter cassettes. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1986, 47, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willeke, K.; Lin, X.; Grinshpun, S.A. Improved Aerosol Collection by Combined Impaction and Centrifugal Motion. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1998, 28, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirychuk, S.P.; Reynolds, S.J.; Koehncke, N.K.; Lawson, J.; Willson, P.; Senthilselvan, A.; Marciniuk, D.; Classen, H.L.; Crowe, T.; Just, N.; et al. Endotoxin and dust at respirable and nonrespirable particle sizes are not consistent between cage- and floor-housed poultry operations. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2010, 54, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
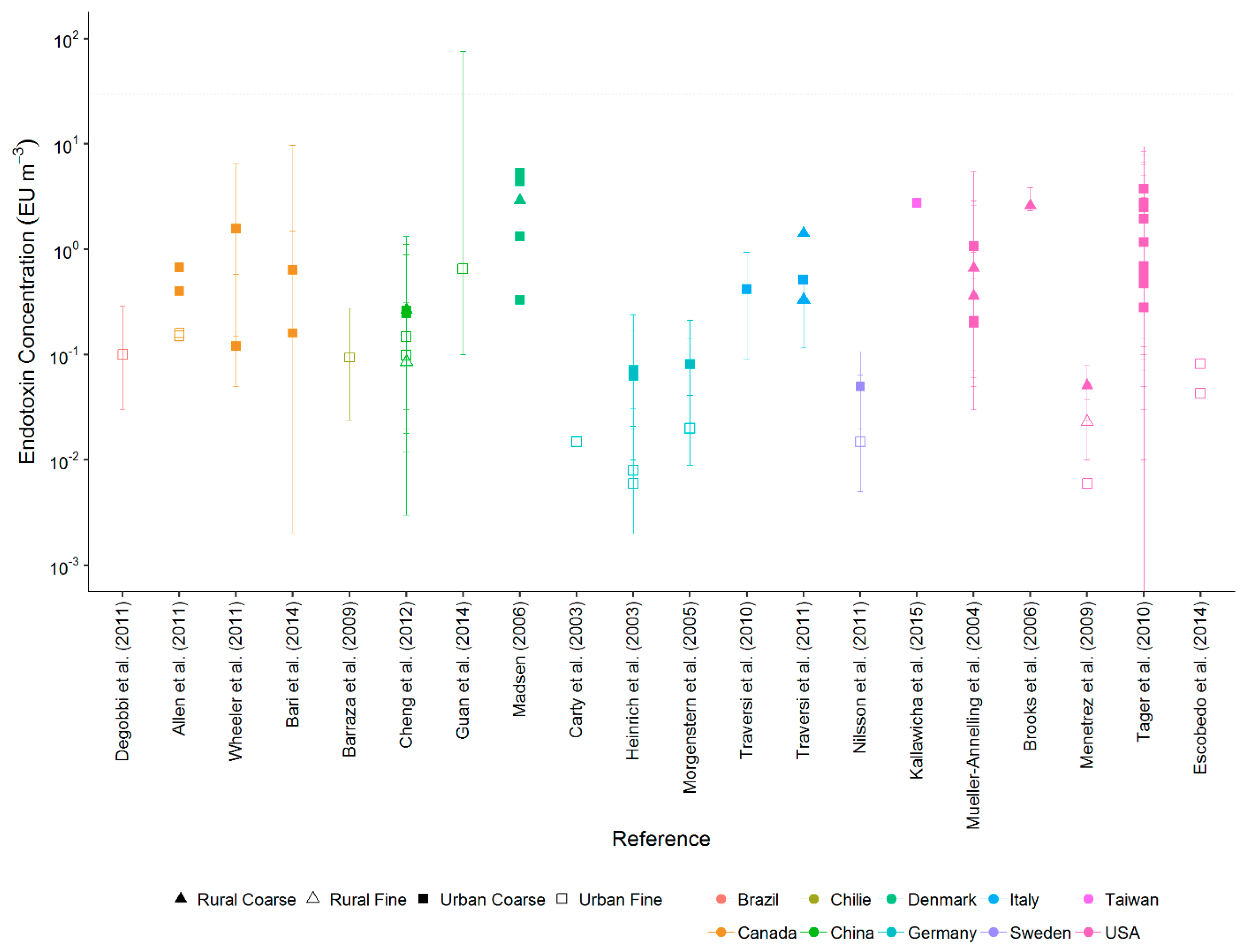

| Country | Environment | Sampling Approach | Season or Months of Measurement | Number of Samples | Flow Rate (L min−1) | Sampling Duration (h) | Mean Endotoxin Concentration (EU m−3) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | Urban | Partisol sampler with glass-fibre filters | All year | 460 | 16.7 | 24 | 0.15–0.67 | Allen et al., 2011 [21] |
| Canada | Urban | Harvard coarse impactor with polyurethane foam | January–August | 242 | 5 | 24 | 0.16–0.64 | Bari et al., 2014 [22] |
| Chile | Urban | Partisol sampler with quartz filters | November–December | 41 | 16.67 | 24 | 0.094 | Barraza et al., 2016 [23] |
| USA | Rural | Impinger | November–December | 41 | 12.5 | 0.17 | 2.6 | Brooks et al., 2006 [24] |
| Germany | Urban | Harvard impactor with 37-mm Teflon filter | All year | 158 | 10 | 42 | 0.015 | Carty et al., 2003 [25] |
| China | Urban and rural | High-volume sampler with quartz filters | All year | 120 | 1130 | 24 | Urban 0.099–0.248 Rural 0.085–0.266 | Cheng et al., 2012 [26] |
| Brazil | Urban | Filter heads with 37-mm polycarbonate filters | April–July | 12 | 10 | 24 | 0.1 | Degobbi et al., 2011 [27] |
| USA | Urban | Tactical air samplers with 47-mm Teflon filters | N/A | 14 | 5 | 24 | 0.04–0.08 | Escobedo et al., 2014 [28] |
| China | Urban | Automatic four-channel sampler with quartz filters | All year | 321 | 16.7 | 23.5 | 0.65 | Guan et al., 2014 [12] |
| Germany | Urban | Graseby Anderson dichotomous samplers with 37-mm Teflon filters | January–June | 84 | 1.671–16.671 | 123–193 | 0.006–0.07 | Heinrich et al., 2003 [29] |
| Taiwan | Urban | Filter heads with 37-mm polycarbonate filters | November–August | 44 | 5 | 24 | 2.75 | Kallawicha et al., 2015 [30] |
| Denmark | Urban and rural | Filter heads with Teflon filters | All year | 168 | 3.5 | 4–6 | Urban 0.33–5.3 Rural 2.9 | Madsen, 2006 [31] |
| USA | Urban and rural | Filter heads or impactors with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) filters | January–May | 33 | 2–16.7 | 10–24 | Urban 0.006 Rural 0.023–0.051 | Menetrez et al., 2009 [14] |
| Germany | Urban | Harvard impactor with 37-mm Teflon filters | All year | 206 | 10 | 42 | 0.02–0.08 | Morgenstern et al., 2005 [32] |
| USA | Urban and rural | High-volume sampler with quartz filters | All year | 99 | 1132 | 24 | Urban 0.2–1.07 Rural 0.36–0.66 | Mueller-Annelling et al., 2004 [17] |
| Sweden | Urban | Harvard impactors with 37-mm Teflon filters | May–September | 40 | 10 | 42 | 0.015–0.05 | Nilsson et al., 2011 [33] |
| USA | Urban | Partisol sampler with 47-mm Teflon filters | All year | N/A | 8.3 | 24 | 0.28–5.7 | Tager et al., 2010 [15] |
| Italy | Urban | High-volume sampler with glass-fibre filters | All year | 116 | 1160 | 24 | 0.42 | Traversi et al., 2010 [34] |
| Italy | Urban and rural | High-volume cascade impactor with glass-fibre filters | Summer | N/A | 1270 | 4 | Urban 0.512 Rural 0.33–1.424 | Traversi et al., 2011 [35] |
| Canada | Urban | Harvard coarse impactor with polyurethane foam | January–March | N/A | 5 | - | 0.12–1.57 | Wheeler et al., 2011 [36] |
| Country | Type of Facility | Sampling Approach | Months of Measurement | Number of Samples | Flow Rate (L·min−1) | Sampling Duration (h) | Distance from Site (m) | Endotoxin Concentration (EU m−3) Mean or Median (min–max) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sweden | In vessel and open windrow; open windrow composting wastewater sludge, household waste and green waste | Filter heads fitted with 2-mm grid and 37-mm cellulose acetate filters | - | 14 | 12 | 1 | - | Onsite 112.6 (10–420) | Clark et al., 1983 [48] |
| Germany | Open windrow and in vessel composting green waste and bio-waste | Stroehlein VC 25 dust sampler with 150-mm quartz filters | - | 5 | - | - | 75–150 | Onsite 207.0 a Upwind 1.6 a Downwind 2.4 a | Danneberg et al., 1997 [49] |
| UK | Open windrow composting green waste | Filter heads with polycarbonate filters | All year | - | 2 | 0.5 | 0–280 | Onsite 1.5–2.3 b Upwind <0.15 b Downwind 0.1–1.2 b | Deacon et al., 2009 [50] |
| UK | Windrow; in vessel; indoor composting biodegradable household waste, food waste, and green waste | Filter heads with polycarbonate filters | All year | 35 | 2 | 1 | 0–525 | Upwind 10.7 (0–62) Downwind 52.7 (0–281) | DEFRA, 2013 [51] |
| France | Indoor composting fermentable household waste and green waste | Filter heads with 37-mm glass-fibre filters | May–June | 3 | 2 | 1.4–3 | 40 | Upwind 105–250 a | Duquenne et al., 2012 [52] |
| USA | Open windrow composting green waste | High-volume particulate sampler with 20 × 25 cm quartz fibre filters | September–November | 18 | 3 | 6–8 | 100–290 | Upwind 1.4 (0.1–3.6) Downwind 1.6 (0.6–4.1) | Hryhorczuk et al., 2001 [43] |
| UK | Open windrow composting green waste | Filter heads with polycarbonate filters | March–December | 115 | 2.2 | 0.5–2 | 100–600 | Onsite (no activity) 4.1 (<0.01–32.0) Upwind 0.15 (<0.01–1.7) Downwind 3.1–116.2 (<0.01–359) | Liu et al., 2011 [53] |
| UK | In vessel; open windrow and in vessel; open windrow; enclosed bays composting food waste and green waste | Filter heads with glass-fibre filters | All year | 117 | 2 | 4 | 25 | Onsite 7.1–121.7 (0.8–4667) Upwind 2.9 (0.6–107) | Sykes et al., 2011 [44] |
| Finland | Indoor in vessel composting biodegradable household waste | Filter heads with glass-fibre filters | All year | 27 | 2 | 1.6–2 | - | Onsite (composting hall) 2340 (0.2–18,000) Onsite (receiving hall) 1900 (60–8200) Onsite (control room) 100 (90.8–870) | Tolvanen et al., 2005 [54] |
| The Netherlands | Indoor composting domestic and green waste | Personal sampling with glass-fibre filters | All year | 205 | 2–3.5 | 7.5–8.3 | - | Onsite 6–1038 (<3–37,043) | Wouters et al., 2006 [1] |
| Country | Type of Farm (Average Number of Animals) | Sampling Approach | Season or Months of Measurement | Number of Samples | Flow Rate (L min−1) | Sampling Duration (h) | Distance from Farm (m) | Endotoxin Concentration (EU m−3) Mean (min–max) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Cattle farm (10,000) | Filter heads with 25-mm polycarbonate filters | June–July | 162 | 2 | 1.25 | 200–1390 | Onsite 19.8–895 Upwind 0.1–144 Downwind 15.8–358 | Dungan et al., 2009 [58] |
| USA | Cattle farm (10,000) | Filter heads with 25-mm polycarbonate filters | All year | 72 | 2 | 2 | 5–200 | Upwind 0.8–140 Downwind 1.6–849 | Dungan et al., 2010 [59] |
| Germany | Swine (1000) | High-volume impactor | - | 3 | 680 | 24 | 50–115 | Upwind 90 Downwind 150–600 | Hartung et al., 1997 [60] |
| The Netherlands | Poultry (4000–18,000) | Filter head with conical inlet and 37-mm Teflon filter | - | 24 | 3.5–50 | 0.3–6 | 7–410 | Downwind 23 (<2–111) | Jonges et al., 2015 [61] |
| Denmark/Germany/ Switzerland | Poultry (2100); pig (~1200) | Personal sampling with 37-mm glass-fibre filters | - | 176 | 3.5 | - | - | Poultry 2575.8 (189.9–16,348) Pig 671.6 (0.1–20,901) | Radon et al., 2002 [62] |
| Germany | Cattle; swine; poultry | Filter heads with 37-mm glass-fibre filters | Winter and Summer | 64 | 3.5 | 24 | - | Winter 3.6 (0.66–19.98) Summer 4.4 (0.66–23.22) | Schulze et al., 2006 [18] |
| USA | Swine | Filter heads with glass-fibre filters | March–November | - | 2 | 4 | 30–160 | Upwind <10 Downwind 30–194 | Thorne et al., 2009 [57] |
| Country | Source | Sampling Approach | Months of Measurement | Number of Samples | Flow Rate (L·min−1) | Sampling Duration (h) | Distance from Site (m) | Endotoxin Concentration (EU·m−3) Mean (min–max) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Application of biosolids to land | Filter heads with 37-mm polycarbonate filters | - | 80 | 4 | - | 10 | Upwind control 7.8 (3.1–11.3) Downwind control 14.5 (6.3–38.1) Upwind application 2.1 (0–7.7) Downwind application 36.0 (24.3–44.8) | Barth et al., 2009 [65] |
| USA | Application of biosolids to land | Impinger | April–June | 125 | 12.5 | 0.2–0.3 | 2–200 | Upwind 2.6 Downwind 33.5–627.3 | Brooks et al., 2006 [24] |
| The Netherlands | Endotoxin from water features | Filter heads with 37-mm glass-fibre filters | June–November | 73 | 3.5 | 3.1–8 | 1–33 | 2.6–61.8 | De Man et al., 2014 [67] |
| India | Wastewater treatment | Impinger | May–June | - | 12.5 | 1–1.5 | - | Onsite 0.8–741 | Gangamma et al., 2011 [71] |
| USA | Wastewater treatment | Filter heads with 37-mm glass-fibre filters | All year | 40 | 2 | 4–5 | - | Onsite 70.9 (35.6–147.8) | Lee et al., 2006 [66] |
| Switzerland | Wastewater treatment | Filter heads with 37-mm polycarbonate filters | All year | 22 | 1.5 | 4 | - | Onsite 8.8–29.8 (1.4–103) | Oppliger et al., 2005 [72] |
| USA | Application of biosolids to land | Impingers | All year | 12 | 12.5 | 0.025–0.75 | - | Onsite 2300 Upwind 3.3 | Paez-Rubio et al., 2007 [73] |
| USA | Bioaerosol exposure after flooding | Filter heads with 37-mm Teflon filters | October–November | - | 10 | 6 | - | 0.6–8.3 | Solomon et al., 2006 [69] |
| Denmark | Strawberry farm | Filter heads with polycarbonate filters | June–August | 12 | 3.5 | 1.3–4.8 | - | 8.9 (2.5–27.8) | Tendal et al., 2011 [74] |
| Italy | Anaerobic digestion of biomass | Multistage impactor with glass-fibre filters | May–June | 12 | 1270 | 4 | - | 12.57–18.9 | Traversi et al., 2015 [75] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rolph, C.A.; Gwyther, C.L.; Tyrrel, S.F.; Nasir, Z.A.; Drew, G.H.; Jackson, S.K.; Khera, S.; Hayes, E.T.; Williams, B.; Bennett, A.; et al. Sources of Airborne Endotoxins in Ambient Air and Exposure of Nearby Communities—A Review. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100375
Rolph CA, Gwyther CL, Tyrrel SF, Nasir ZA, Drew GH, Jackson SK, Khera S, Hayes ET, Williams B, Bennett A, et al. Sources of Airborne Endotoxins in Ambient Air and Exposure of Nearby Communities—A Review. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(10):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100375
Chicago/Turabian StyleRolph, Catherine A., Ceri L. Gwyther, Sean F. Tyrrel, Zaheer A. Nasir, Gillian H. Drew, Simon K. Jackson, Shagun Khera, Enda T. Hayes, Ben Williams, Allan Bennett, and et al. 2018. "Sources of Airborne Endotoxins in Ambient Air and Exposure of Nearby Communities—A Review" Atmosphere 9, no. 10: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100375
APA StyleRolph, C. A., Gwyther, C. L., Tyrrel, S. F., Nasir, Z. A., Drew, G. H., Jackson, S. K., Khera, S., Hayes, E. T., Williams, B., Bennett, A., Collins, S., Walsh, K., Kinnersley, R., & Gladding, T. L. (2018). Sources of Airborne Endotoxins in Ambient Air and Exposure of Nearby Communities—A Review. Atmosphere, 9(10), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100375







