Aerosol Optical Properties over China from RAMS-CMAQ Model Compared with CALIOP Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. RAMS-CMAQ Data
2.1.1. RAMS-CMAQ Model
2.1.2. RAMS-CMAQ 550 nm AOD Calculation
2.2. CALIOP Data
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Analysis
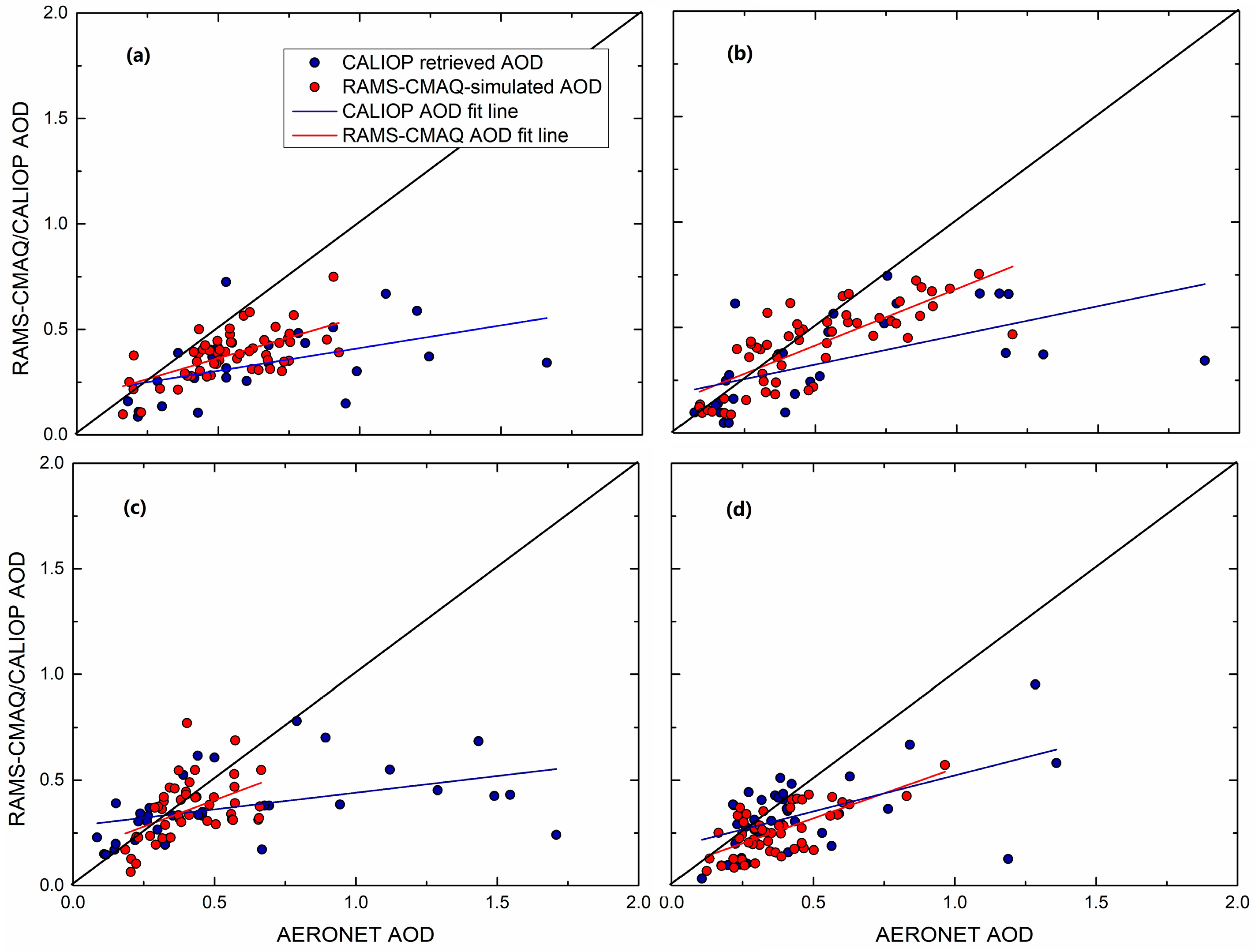
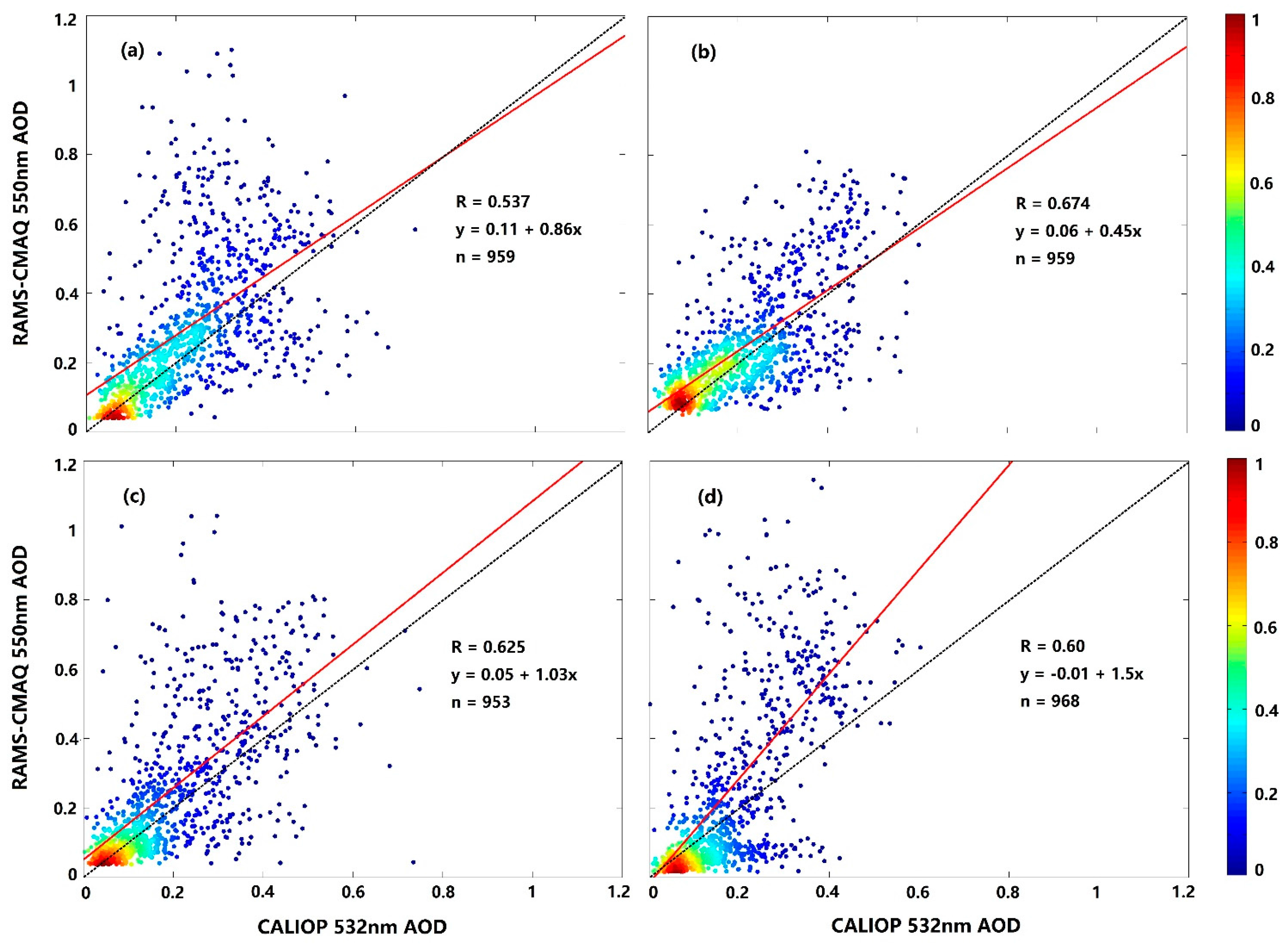
3.1. AOD Validation Using AERONET Data
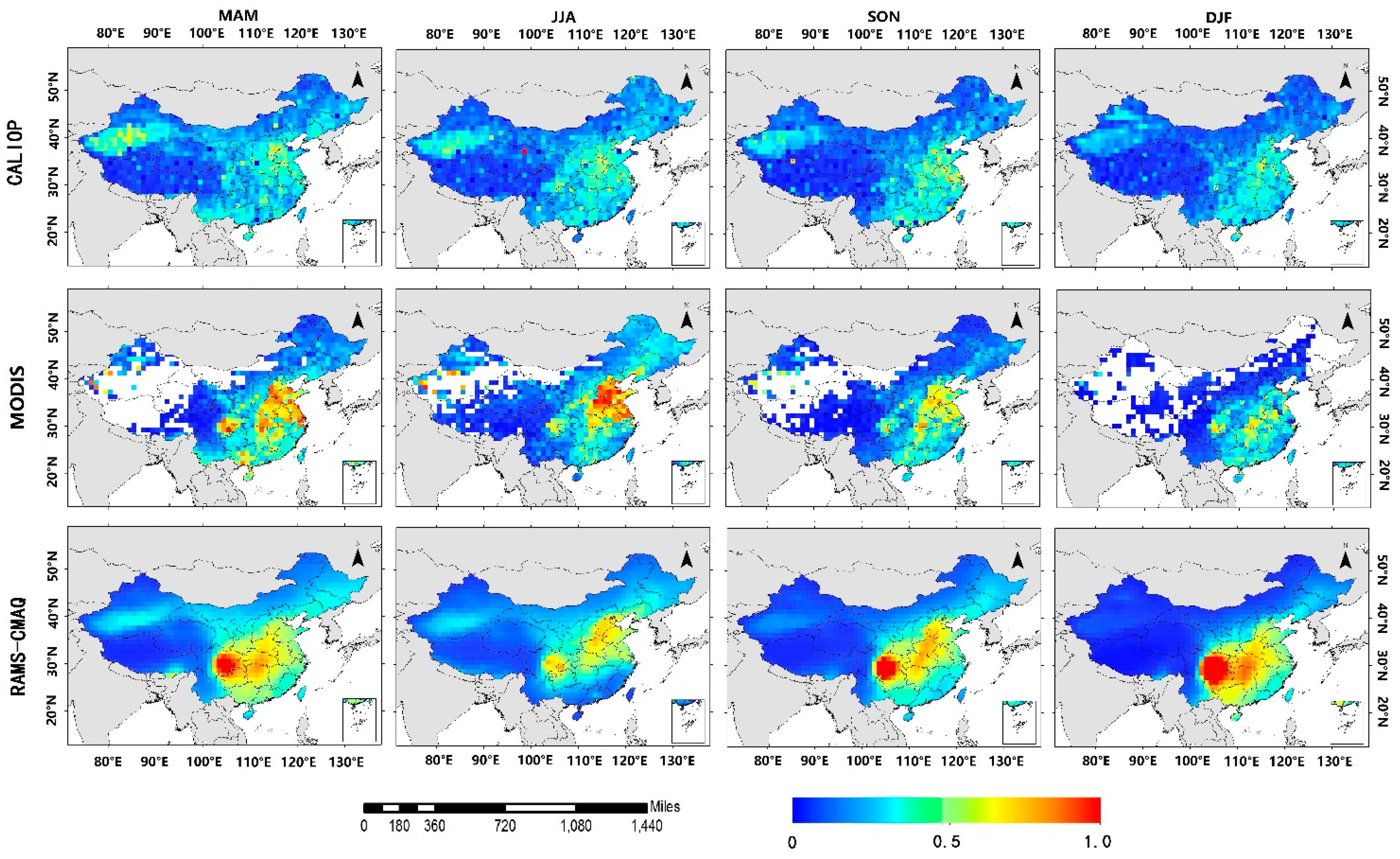
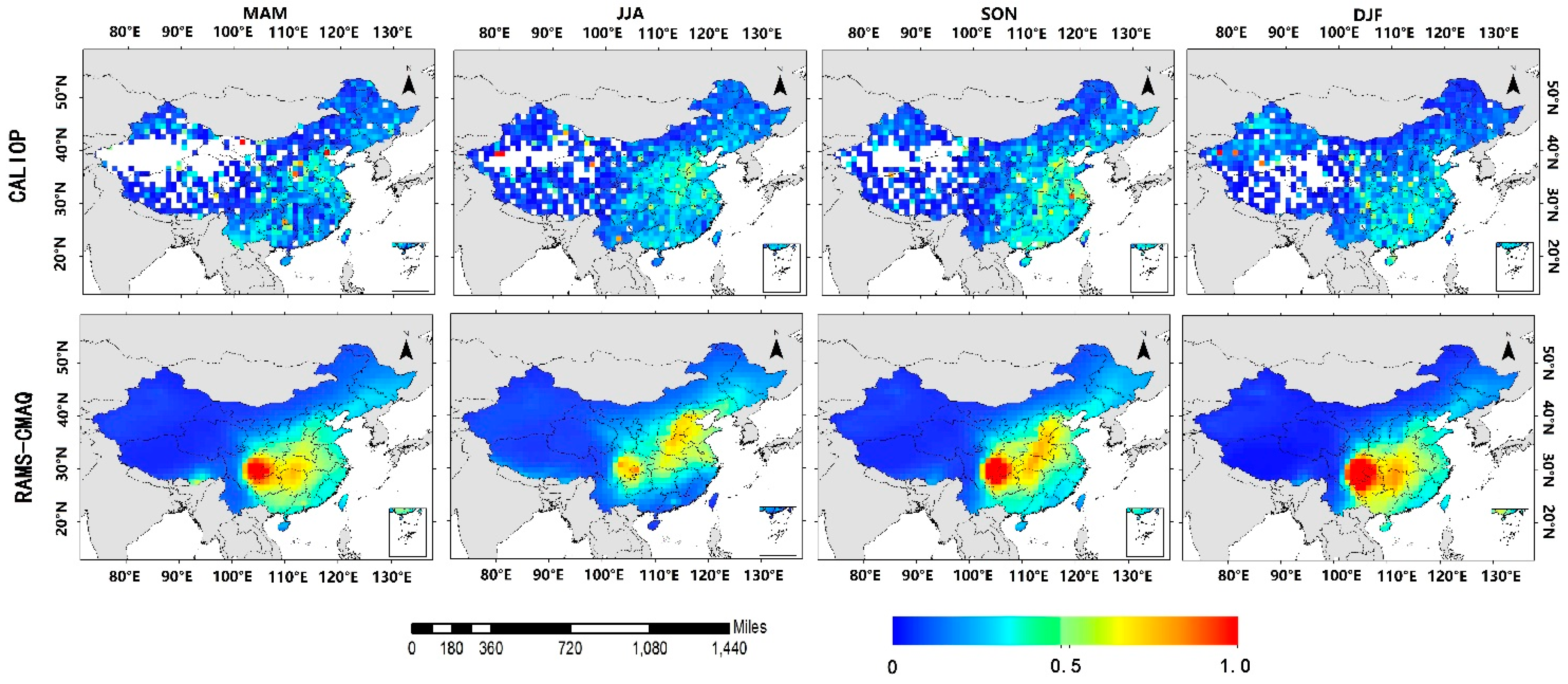
3.2. Spatial Distributions of AODs
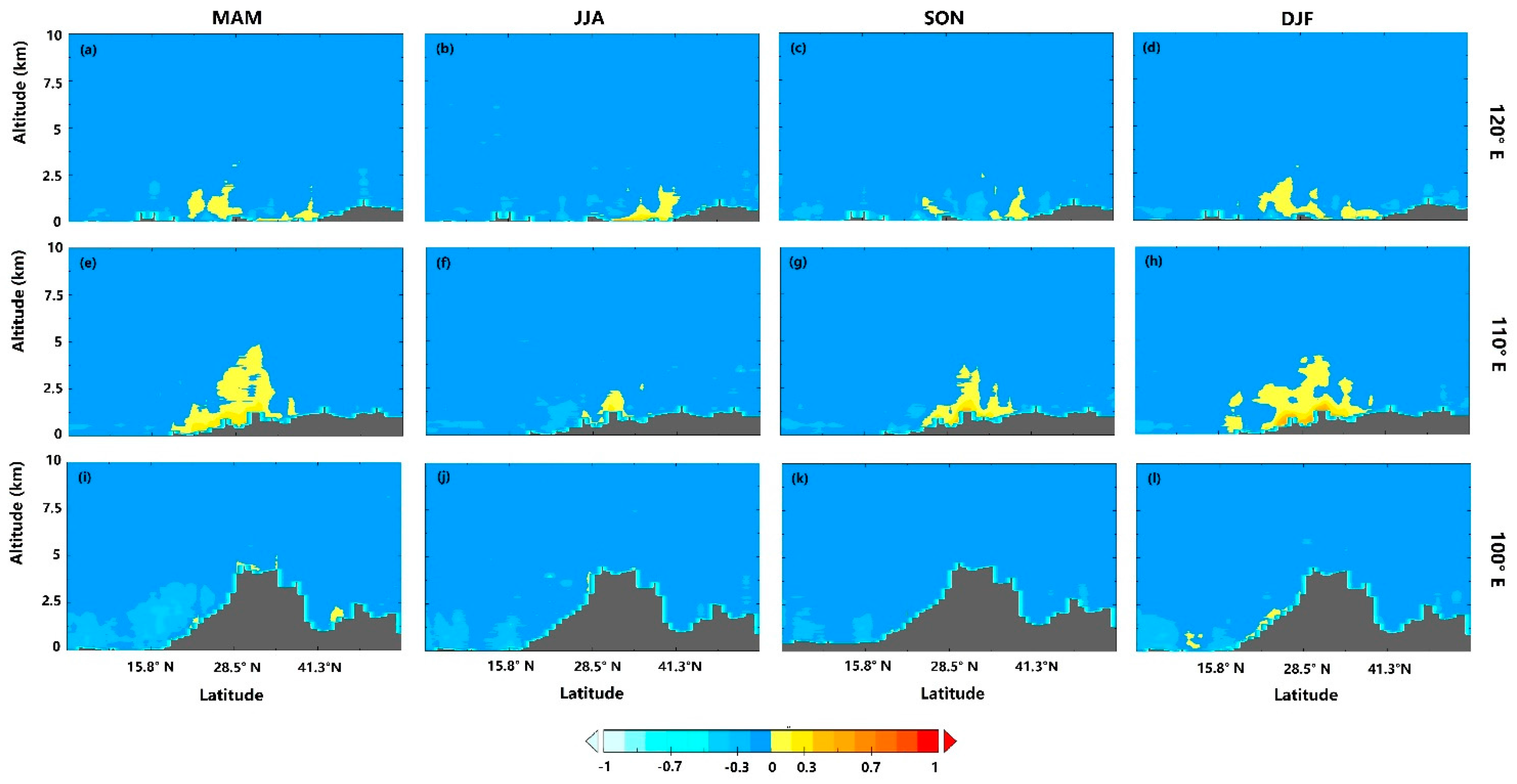
3.3. Vertical Distribution of Extinction Properties
3.3.1. Vertical Extinction Profiles of the Major Cities of China
3.3.2. Cross Sections of the Vertical Aerosol Distribution over China
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, I. Optical properties of aerosols and clouds: The software package opac. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Folini, D.; Schar, C.; Loeb, N.; Dutton, E.G.; Konig-Langlo, G. The global energy balance from a surface perspective. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 3107–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikovsky, A.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Bril, A.; Goloub, P.; Tanre, D.; Pappalardo, G.; Wandinger, U.; Chaikovskaya, L.; Denisov, S.; et al. Lidar-radiometer inversion code (LiRIC) for the retrieval of vertical aerosol properties from combined lidar/radiometer data: Development and distribution in earlinet. Atmos. Measure. Tech. 2016, 9, 1181–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Yin, Y.; Li, P.R.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, R.J.; Cribb, M.; Dong, Z.P.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Ren, G.; et al. Aircraft measurements of the vertical distribution and activation property of aerosol particles over the loess plateau in China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.R.; Tafuro, A.M.; Kinne, S. Dust layer effects on the atmospheric radiative budget and heating rate profiles. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Olmo, F.J.; Aviles-Rodriguez, I.; Navas-Guzman, F.; Perez-Ramirez, D.; Lyamani, H.; Arboledas, L.A. Extreme saharan dust event over the southern iberian peninsula in september 2007: Active and passive remote sensing from surface and satellite. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8453–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The collection 6 modis aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Measure. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on modis deep blue aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Yoon, S.C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.Y. Seasonal and monthly variations of columnar aerosol optical properties over east asia determined from multi-year modis, lidar, and aeronet sun/sky radiometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielonen, T.; Arola, A.; Komppula, M.; Kukkonen, J.; Koskinen, J.; de Leeuw, G.; Lehtinen, K.E.J. Comparison of caliop level 2 aerosol subtypes to aerosol types derived from aeronet inversion data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Chen, B.; Huang, Z.W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Yi, Y.H.; Ayers, J.K. Long-range transport and vertical structure of asian dust from calipso and surface measurements during pacdex. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X. Detection of dust aerosol by combining CALIPSO active lidar and passive IIR measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4241–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kacenelenbogen, M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Redemann, J.; Hoff, R.M.; Rogers, R.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Russell, P.B.; Hostetler, C.A.; Hair, J.W.; Holben, B.N. An accuracy assessment of the caliop/calipso version 2/version 3 daytime aerosol extinction product based on a detailed multi-sensor, multi-platform case study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3981–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.G.; Gao, L.J.; Ge, C.; Xu, Y.P. Simulation of nitrate aerosol concentrations over east asia with the model system RAMS-CMAQ. Tellus. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2007, 59, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, M.G.; Zhu, L.Y.; Xu, L.R. Model analysis of influences of aerosol mixing state upon its optical properties in east asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 30, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zavala, M.; Lei, W.; Tsimpidi, A.P.; Karydis, V.A.; Pandis, S.N.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Molina, L.T. Simulations of organic aerosol concentrations in mexico city using the WRF-chem model during the MCMA-2006/milagro campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3789–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, C.L.; Coe, H.; Jimenez, J.L.; Weber, R.J.; Bahreini, R.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Russell, L.M.; Jolleys, M.; Fu, T.M.; Allan, J.D.; et al. Exploring the vertical profile of atmospheric organic aerosol: Comparing 17 aircraft field campaigns with a global model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12673–12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Schere, K.L. Review of the governing equations, computational algorithms, and other components of the models-3 community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) modeling system. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkowski, F.S.; Shankar, U. The regional particulate matter model.1. Model description and preliminary results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 26191–26209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenes, A.; Pandis, S.N.; Pilinis, C. Continued development and testing of a new thermodynamic aerosol module for urban and regional air quality models. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, G.R.; Sakurai, T.; Streets, D.; Hozumi, Y.; Ueda, H.; Park, S.U.; Fung, C.; Han, Z.; Kajino, M.; Engardt, M.; et al. MICS-Asia II: The model intercomparison study for asia phase II methodology and overview of findings. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3468–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Bond, T.C.; Carmichael, G.R.; Fernandes, S.D.; Fu, Q.; He, D.; Klimont, Z.; Nelson, S.M.; Tsai, N.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; et al. An inventory of gaseous and primary aerosol emissions in Asia in the year 2000. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkovitz, C.M.; Scholtz, M.T.; Pacyna, J.; Tarrason, L.; Dignon, J.; Voldner, E.C.; Spiro, P.A.; Logan, J.A.; Graedel, T.E. Global gridded inventories of anthropogenic emissions of sulfur and nitrogen. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 29239–29253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, J.G.J.; Bouwman, A.F.; Vandermaas, C.W.M.; Berdowski, J.J.M. Emission database for global atmospheric research (EDGAR). Environ. Monit. Assess. 1994, 31, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.W.; Ueda, H.; Matsuda, K.; Zhang, R.J.; Arao, K.; Kanai, Y.; Hasome, H. Model study on particle size segregation and deposition during Asian dust events in March 2002. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.L. A parameterization of sea-salt aerosol source function for sub- and super-micron particles. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, G.G.; Emmons, L.K.; Hess, P.G.; Lamarque, J.F.; Thompson, A.M.; Yorks, J.E. Analysis of the Summer 2004 ozone budget over the United States using Intercontinental Transport Experiment Ozonesonde Network Study (IONS) observations and Model of Ozone and Related Tracers (MOZART-4) simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Mathur, R.; Gilliland, A.B.; Howard, S.C. A comparison of CMAQ-based aerosol properties with improve, MODIS, and aeronet data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, W.C.; Sisler, J.F.; Huffman, D.; Eldred, R.A.; Cahill, T.A. Spatial and seasonal trends in particle concentration and optical extinction in the united-states. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 1347–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; Vane, D.G.; Boain, R.J.; Mace, G.G.; Sassen, K.; Wang, Z.E.; Illingworth, A.J.; O'Connor, E.J.; Rossow, W.B.; Durden, S.L.; et al. The cloudsat mission and the a-train—A new dimension of space-based observations of clouds and precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1771–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Han, Z.W. Aerosol vertical distribution over east China from RIEMS-chem simulation in comparison with calipso measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Winker, D.; Omar, A.; Vaughan, M.; Kar, J.; Trepte, C.; Hu, Y.X.; Schuster, G.; Young, S. Aerosol optical properties above opaque water clouds derived from the caliop version 4 level 1 data. In Proceedings of the 27th International Laser Radar Conference, New York, NY, USA, 5–10 July 2015; Volume 119. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.A.; Vaughan, M.A.; Kuehn, R.E.; Winker, D.M. The retrieval of profiles of particulate extinction from cloud-aerosol lidar and infrared pathfinder satellite observations (CALIPSO) data: Uncertainty and error sensitivity analyses. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 395–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Tackett, J.L.; Getzewich, B.J.; Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.A.; Rogers, R.R. The global 3-d distribution of tropospheric aerosols as characterized by caliop. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3345–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Tackett, J.L.; Giles, D.M.; Kar, J.; Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.A.; Powell, K.A.; Trepte, C.R. Caliop and aeronet aerosol optical depth comparisons: One size fits none. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4748–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Vaughan, M.; Winker, D.; Kittaka, C.; Getzewich, B.; Kuehn, R.; Omar, A.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Hostetler, C. The calipso lidar cloud and aerosol discrimination: Version 2 algorithm and initial assessment of performance. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1198–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulos, N.; Mona, L.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Amiridis, V.; Baars, H.; Binietoglou, I.; Bortoli, D.; D'Amico, G.; Giunta, A.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; et al. Calipso climatological products: Evaluation and suggestions from earlinet. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2341–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.B.; Chin, M.; Winker, D.M.; Omar, A.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Kittaka, C.; Diehl, T. Global view of aerosol vertical distributions from calipso lidar measurements and gocart simulations: Regional and seasonal variations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.S.; Song, C.H.; Han, K.M.; Park, M.E.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.B.; Shimizu, A. A study on the aerosol optical properties over east Asia using a combination of cmaq-simulated aerosol optical properties and remote-sensing data via a data assimilation technique. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12275–12296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Chen, L.F.; Fan, M.; Tao, J.H.; Wang, Z.T.; Yu, C.; Si, Y.D.; Letu, H.; Liu, Y. Estimation of geos-chem and gocart simulated aerosol profiles using calipso observations over the contiguous United States. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 3256–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Shen, X.X.; Gao, W.; Liu, P.D.; Sun, Z.B. Evaluation of CALIPSO aerosol optical depth using AERONET and MODIS data over China. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing and Modeling of Ecosystems for Sustainability XI, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–20 August 2014; Volume 9221. [Google Scholar]
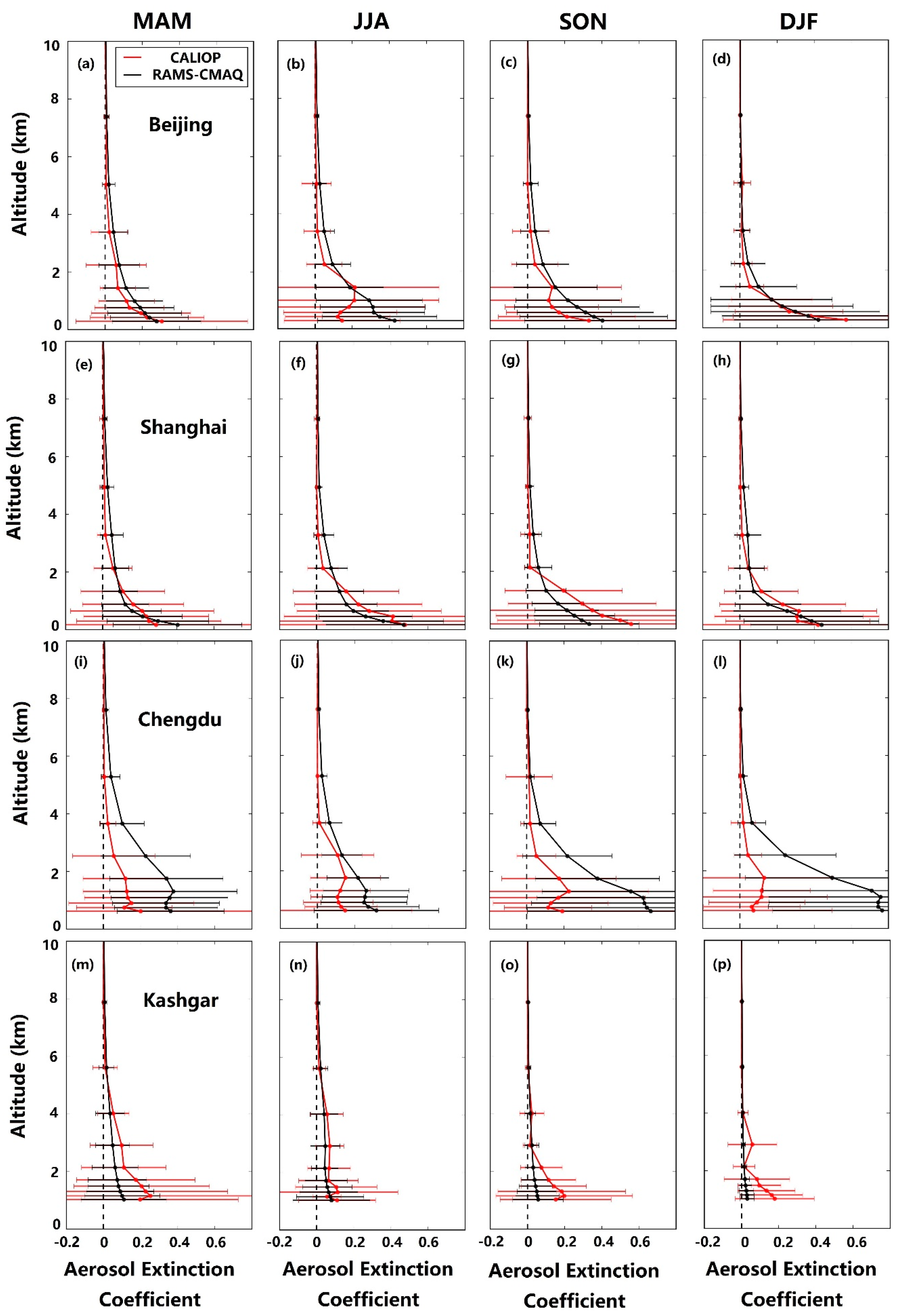
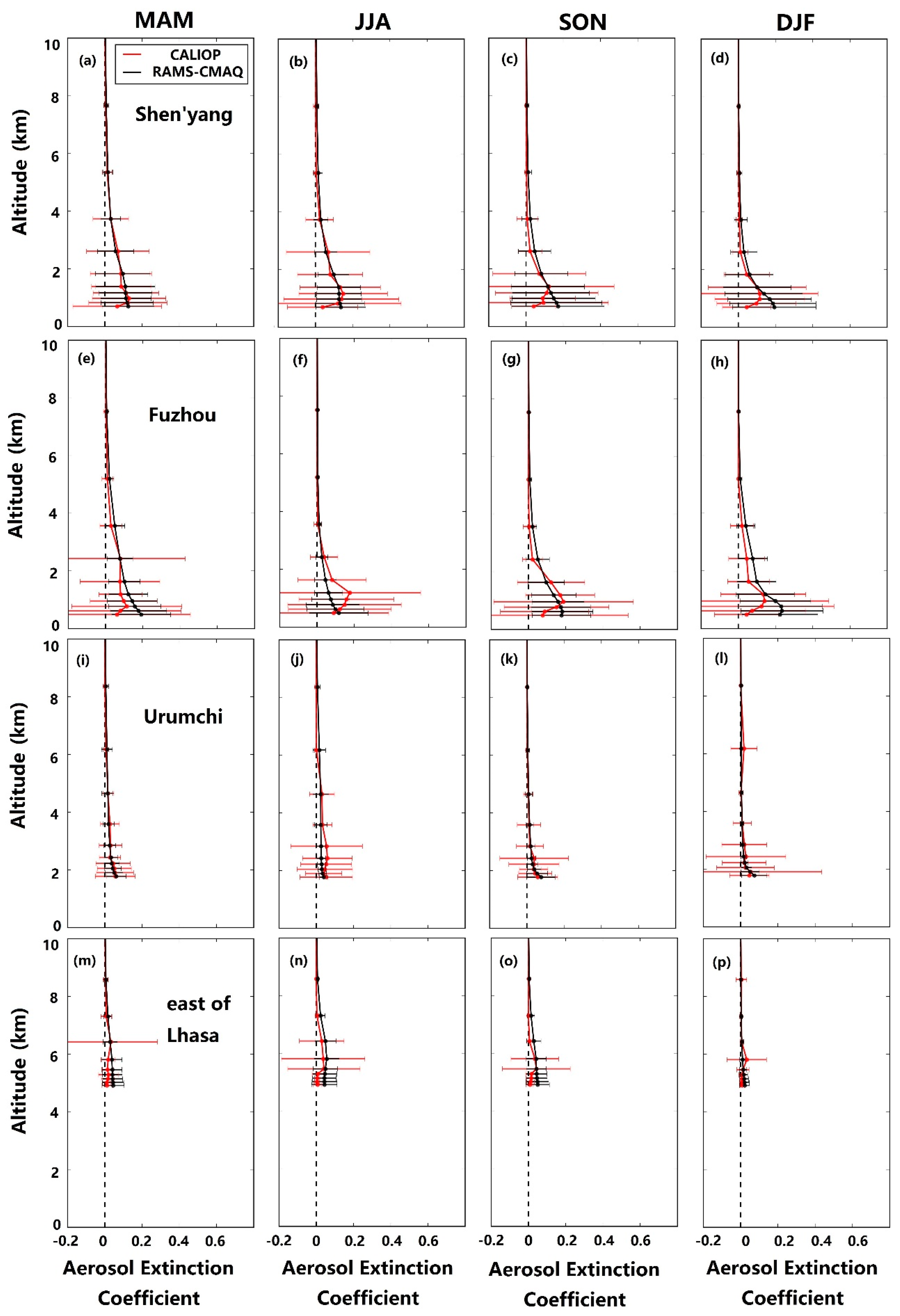
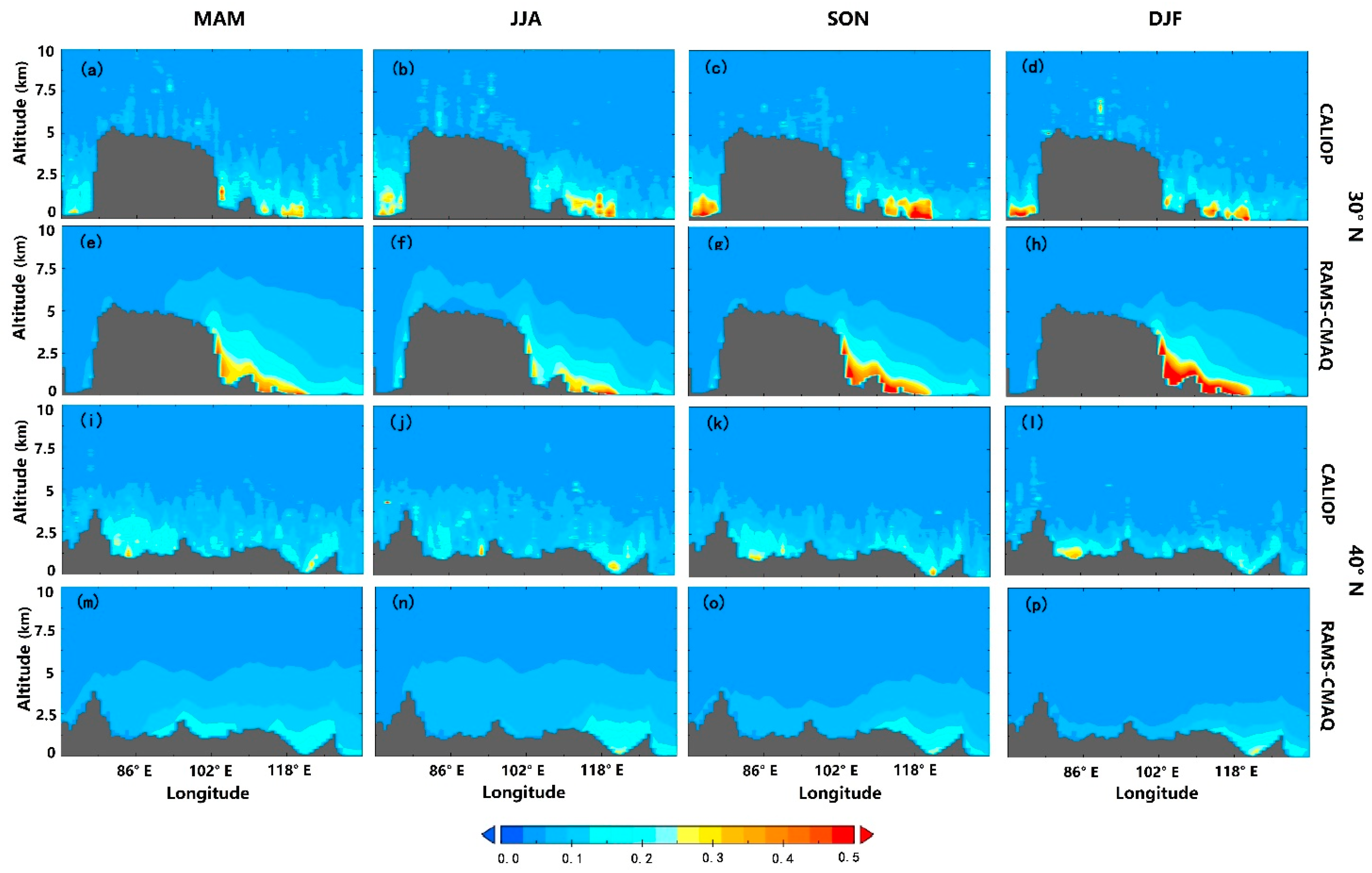

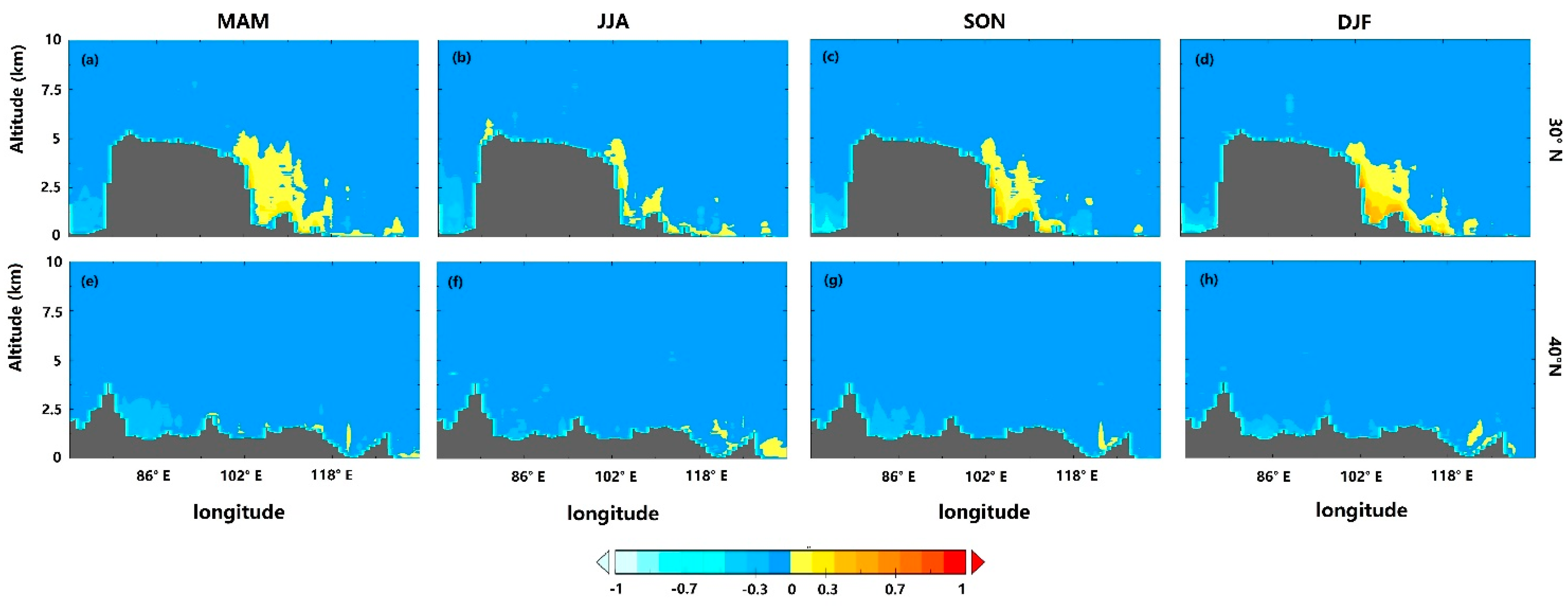
| AERONET Sites | Lat. (° N) | Lon. (° E) | Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 39.977 | 116.381 | 92 |
| Xiang He | 39.754 | 116.962 | 36 |
| Beijing_CAMS | 39.933 | 116.317 | 106 |
| Beijing_RADI | 40.005 | 116.379 | 59 |
| Hong Kong_PolyU | 22.303 | 114.180 | 30 |
| Xu Zhou_CUMT | 34.217 | 117.142 | 59 |
| Hong Kong_Sheung | 22.483 | 114.117 | 40 |
| Time | AERONET vs. | Number of Records | R | RMSE | Mean | Slope | Intercept |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | CALIOP | 124 | 0.50 | 0.04 | 0.3472 | 0.227 ± 0.036 | 0.222 ± 0.024 |
| RAMS-CMAQ | 209 | 0.69 | 0.022 | 0.3528 | 0.512 ± 0.037 | 0.119 ± 0.019 | |
| Spring | CALIOP | 25 | 0.48 | 0.114 | 0.3389 | 0.215 ± 0.085 | 0.196 ± 0.064 |
| RAMS-CMAQ | 56 | 0.62 | 0.054 | 0.3795 | 0.393 ± 0.067 | 0.167 ± 0.038 | |
| Summer | CALIOP | 28 | 0.58 | 0.088 | 0.3401 | 0.277 ± 0.076 | 0.186 ± 0.054 |
| RAMS-CMAQ | 55 | 0.78 | 0.039 | 0.4122 | 0.536 ± 0.060 | 0.147 ± 0.034 | |
| Autumn | CALIOP | 34 | 0.44 | 0.077 | 0.3734 | 0.282 ± 0.041 | 0.158 ± 0.056 |
| RAMS-CMAQ | 46 | 0.47 | 0.033 | 0.3589 | 0.50 ± 0.139 | 0.155 ± 0.060 | |
| Winter | CALIOP | 37 | 0.55 | 0.056 | 0.334 | 0.341 ± 0.087 | 0.181 ± 0.047 |
| RAMS-CMAQ | 52 | 0.68 | 0.046 | 0.2558 | 0.474 ± 0.071 | 0.082 ± 0.029 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, T.; Fan, M.; Tao, J.; Su, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; Han, X.; Chen, L. Aerosol Optical Properties over China from RAMS-CMAQ Model Compared with CALIOP Observations. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100201
Wu T, Fan M, Tao J, Su L, Wang P, Liu D, Li M, Han X, Chen L. Aerosol Optical Properties over China from RAMS-CMAQ Model Compared with CALIOP Observations. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(10):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100201
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Tong, Meng Fan, Jinhua Tao, Lin Su, Ping Wang, Dong Liu, Mingyang Li, Xiao Han, and Liangfu Chen. 2017. "Aerosol Optical Properties over China from RAMS-CMAQ Model Compared with CALIOP Observations" Atmosphere 8, no. 10: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100201
APA StyleWu, T., Fan, M., Tao, J., Su, L., Wang, P., Liu, D., Li, M., Han, X., & Chen, L. (2017). Aerosol Optical Properties over China from RAMS-CMAQ Model Compared with CALIOP Observations. Atmosphere, 8(10), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100201





