Temporal-Spatial Variation of Drought Indicated by SPI and SPEI in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Data and Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Calculation of the SPI and SPEI
Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI)
| Level | Drought Category | SPI, SPEI Values |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Non-drought | 0 ≤ Index |
| 1 | Mild drought | −1.0 < Index < 0 |
| 2 | Moderate drought | −1.5 < Index ≤ −1.0 |
| 3 | Severe drought | −2.0 < Index ≤ −1.5 |
| 4 | Extreme drought | Index ≤ −2.0 |
2.3.2. Drought Evaluation Indicators
Duration and Intensity of Drought Events
Drought Frequency
Drought Station Proportion
2.3.3. Method of Trend Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Variation in the SPI and SPEI
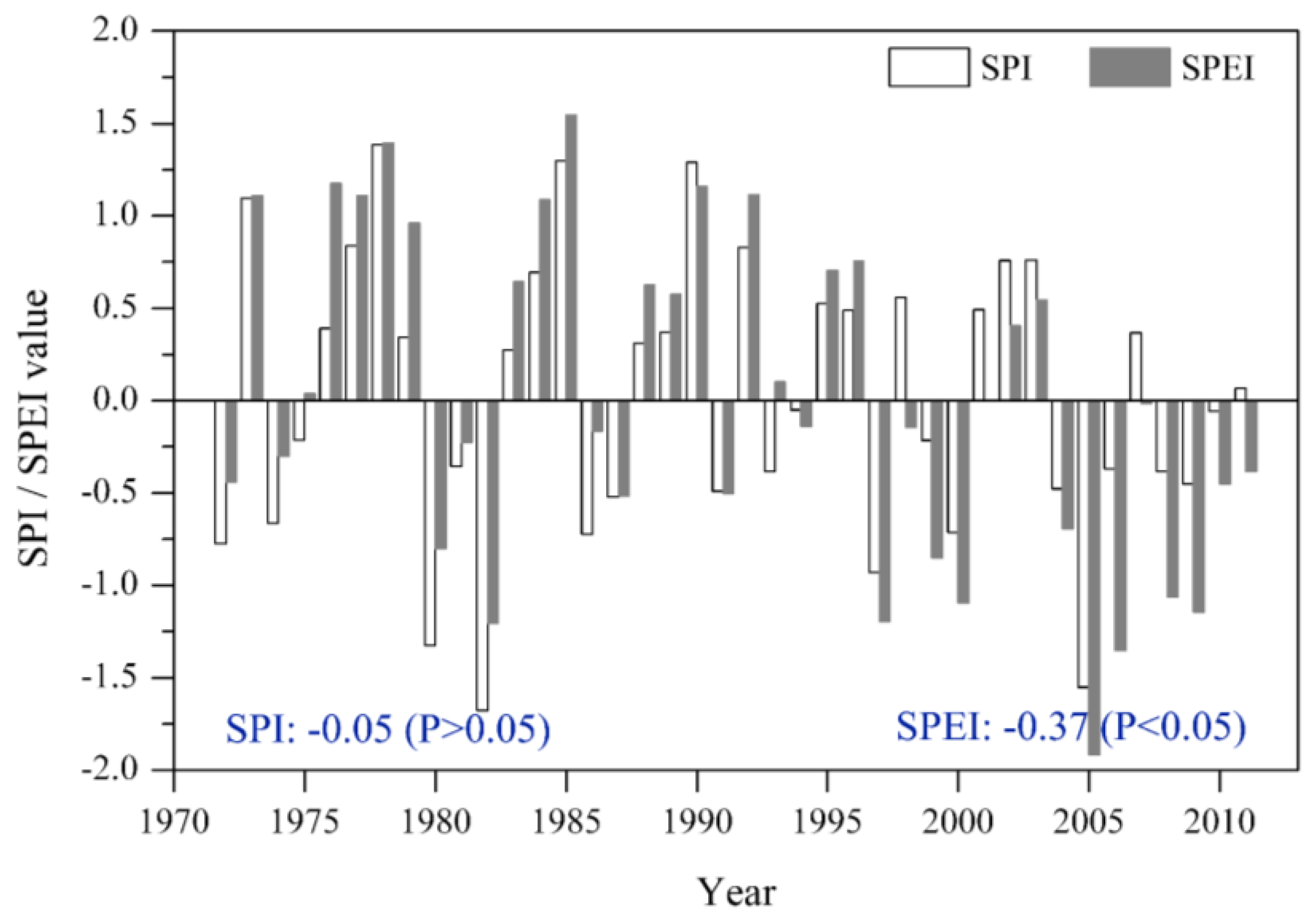
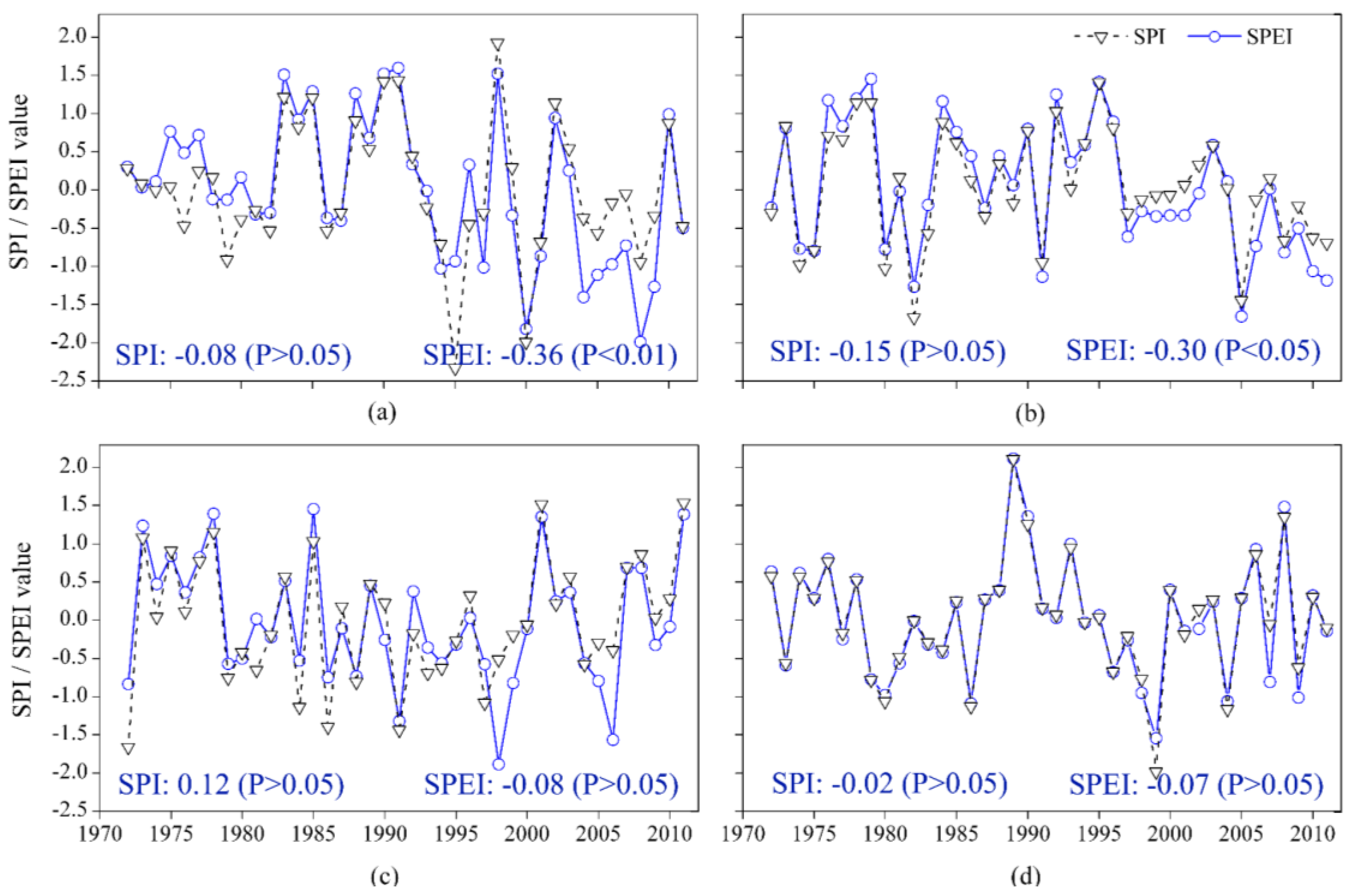
3.1.1. Temporal Variation
3.1.2. Spatial Variation
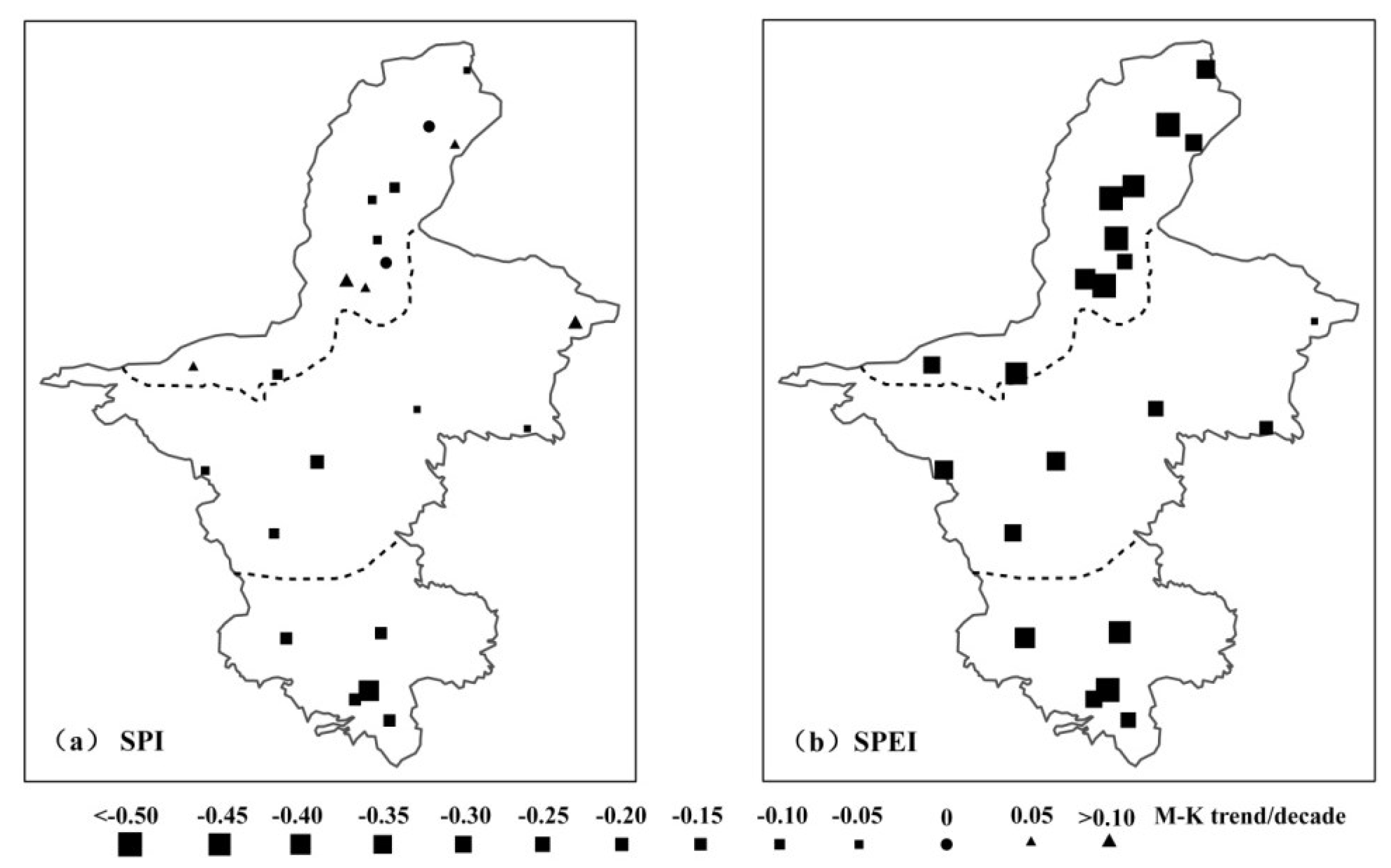
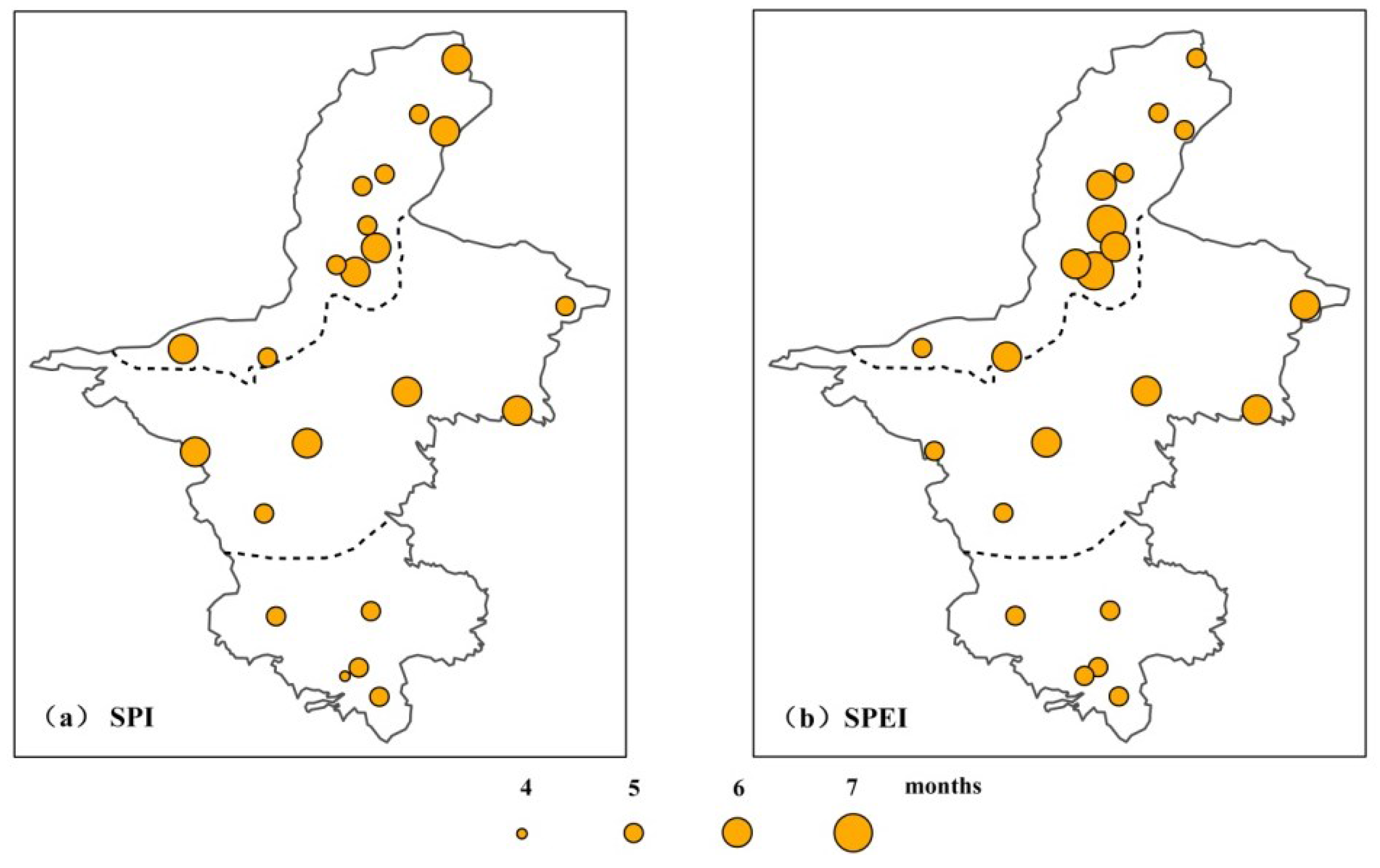
3.2. Drought Duration, Intensity, and Frequency
3.2.1. Duration of Drought Events
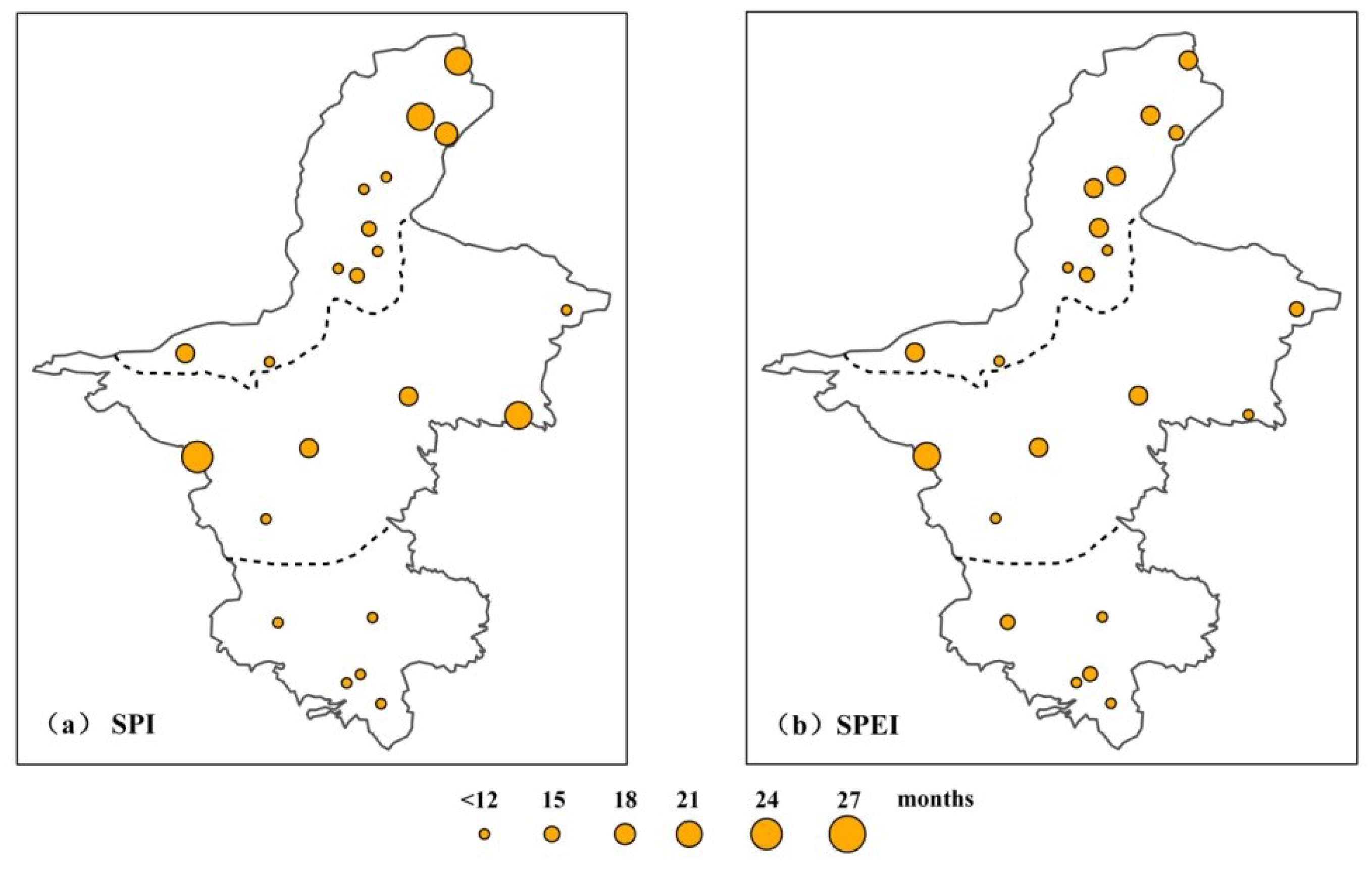
| Drought Indicators | 1972–1991 | 1992–2011 | 1972–2011 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | SPEI | SPI | SPEI | SPI | SPEI | |
| Average drought duration (month) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| Maximum drought duration (month) | 13 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 15 |
| Average drought intensity | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 1.08 | 0.96 | 1.02 |
| Drought frequency (%) | 76.8 | 60.7 | 82.0 | 96.8 | 79.4 | 78.8 |
3.2.2. Intensity of Drought Events
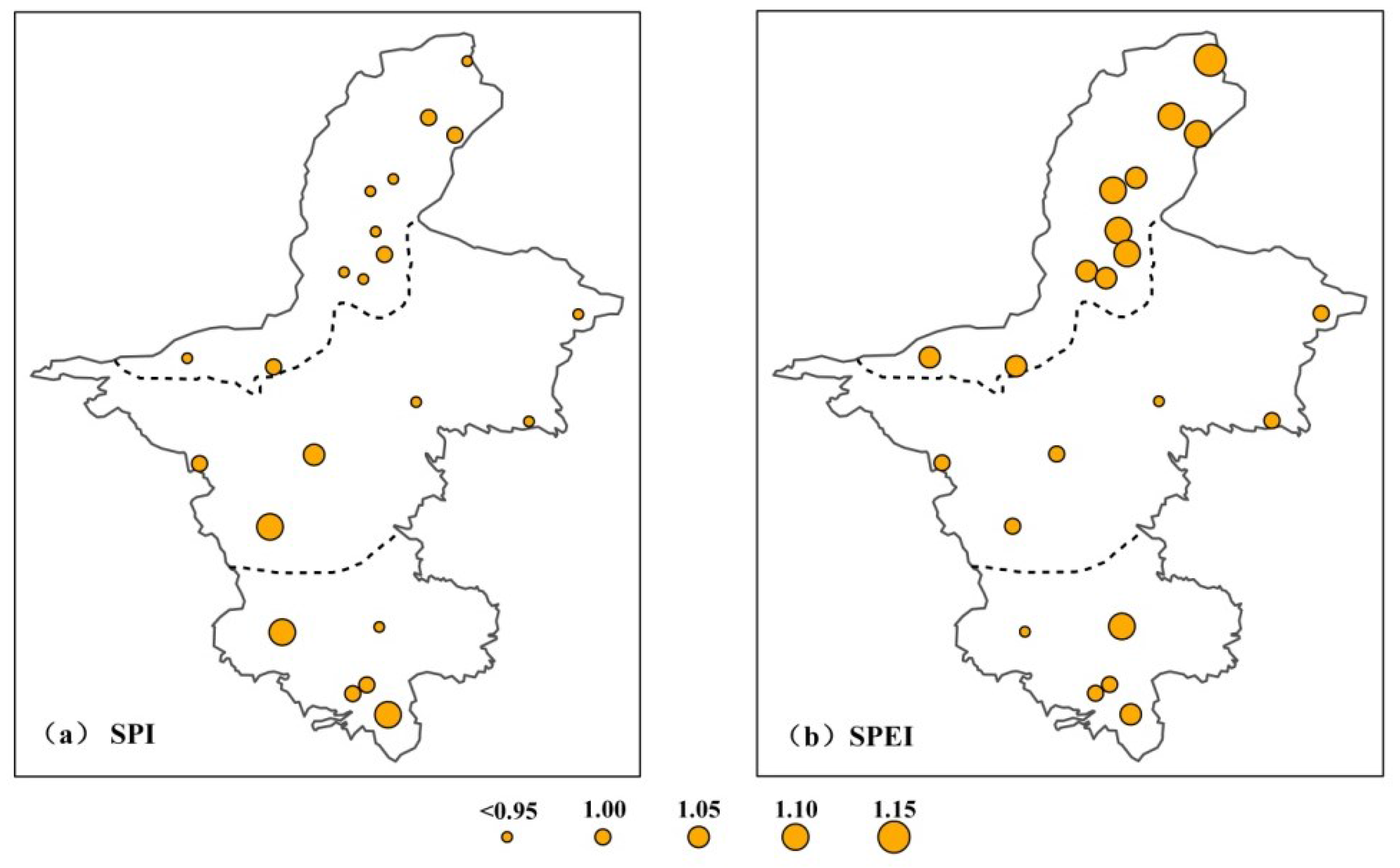
3.2.3. Frequency of Drought Events

3.3. Variation of Drought Station Proportion
| Time | SPI | SPEI | Time | SPI | SPEI | Time | SPI | SPEI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 0.0 | 6.6 | July | 0.0 | 7.0 | Spring | 4.1 | 14.4 ** |
| February | 0.0 | 0.0 | August | 6.5 | 11.4 * | Summer | 3.2 | 8.2 * |
| March | 0.0 | 6.5 | September | 4.0 | 6.5 | Autumn | 0.0 | 4.4 |
| April | 6.5 | 17.6 ** | October | 0.0 | 3.6 | Winter | 0.0 | 5.2 |
| May | 0.0 | 12.2 * | November | 0.0 | 3.5 | Annual | 1.3 | 7.6 ** |
| June | 0.7 | 7.6 | December | 0.0 | 4.8 | - | - | - |
4. Discussion
4.1. Applicability of the SPI and SPEI in Ningxia
4.2. Potential Causal Factors for Drought Variation in Ningxia
| Atmospheric Circulation Index | Summer SPI/SPEI | Drought Station Proportion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | SPEI | SPI | SPEI | |
| EASMI | 0.01 | −0.09 | 0.11 | 0.22 |
| SASMI | 0.10 | 0.05 | −0.06 | 0.03 |
| Atmospheric Circulation Index | Season | SPI/SPEI | Drought Station Proportion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | SPEI | SPI | SPEI | ||
| NAOI | Spring | 0.03 | −0.05 | −0.06 | −0.01 |
| Summer | 0.42 ** | 0.41 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.41 ** | |
| Autumn | 0.18 | 0.26 | −0.13 | −0.16 | |
| Winter | 0.23 | 0.24 | −0.06 | −0.02 | |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interests
References
- Chen, T.; van der Werf, G.R.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Wang, G.; Dolman, A.J. A global analysis of the impact of drought on net primary productivity. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3885–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.Y.; Hong, Y.; Hardy, J.; Sun, Z.H. Examining the influence of river-lake interaction on the drought and water resources in the Poyang Lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.F.; Wu, J.J.; Lei, T.J.; He, B.; Wu, Z.T.; Liu, M.; Mo, X.Y.; Geng, G.P.; Li, X.H.; Zhou, H.K.; et al. Temporal-spatial characteristics of severe drought events and their impact on agriculture on a global scale. Quat. Int. 2014, 349, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Meng, Y.B. An analysis of the drought in Yunnan, China, from a perspective of society drought severity. Nat. Hazards 2013, 67, 431–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology, Boston, MA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–184.
- Sonmez, F.K.; Komuscu, A.U.; Erkan, A.; Turgu, E. An analysis of spatial and temporal dimension of drought vulnerability in Turkey using the Standardized Precipitation Index. Nat. Hazards 2005, 35, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. Comment on “characteristics and trends in various forms of the Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI) during 1900–2008” by Aiguo Dai. J. Geophys. Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; White, R.M., Ed.; U.S. Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, F.N. Droughts of the late 1980s in the United States as derived from NOAA polar-orbiting satellite data. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.R.; Wilhite, D.A. Daily quantification of drought severity and duration. J. Clim. 1996, 5, 1181–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakiris, G.; Pangalou, D.; Vangelis, H. Regional drought assessment based on the Reconnaissance Drought Index (RDI). Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoo, S.H.; Jang, M.W. A decision support system for agricultural drought management using risk assessment. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 10, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Leng, S.; Diao, C.Y. Establishing and assessing the Integrated Surface Drought Index (ISDI) for agricultural drought monitoring in mid-eastern China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2013, 23, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.C.; AghaKouchak, A. Multivariate Standardized Drought Index: A parametric multi-index model. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 57, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.X.; Li, Q.F.; Hayes, M.J.; Svoboda, M.D.; Heim, R.R. Are droughts becoming more frequent or severe in China based on the Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index: 1951–2010? Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.F.; Shi, P.J.; Lei, T.J.; Geng, G.P.; Liu, J.H.; Mo, X.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zhou, H.K.; Wu, J.J. The alleviating trend of drought in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China based on the daily SPEI. Int. J. Climatol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potop, V. Evolution of drought severity and its impact on corn in the Republic of Moldova. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 105, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potop, V.; Mozny, M.; Soukup, J. Drought evolution at various time scales in the lowland regions and their impact on vegetable crops in the Czech Republic. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2012, 156, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.M.; Xin, J.H.; Liu, S.F. China’s regional meteorological disaster loss analysis and evaluation based on grey cluster model. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 1067–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.L. Characteristics, change trend and countermeasures of continuous drought years in China. Adv. Sci. Tech. Water Res. 2010, 30, 75–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.; Xue, C.J.; Ren, Y.Z. Spatio-temporal variability of drought over northern China and its relationships with Indian–Pacific sea surface temperatures. Proc. SPIE 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Yang, Q.G.; Yao, Y.B.; Wei, F.; Shan, H.T. Drought index in summer season of Northwest China. Resour. Sci. 2006, 28, 17–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Qian, Z.H.; Wu, Y.P. Spatiotemporal evolution of the droughts and floods over China. Acta Phys. Sin. 2013, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.K.; Zhang, Q. Preliminary studies on variations in droughts over China during past 50 years. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2008, 19, 679–687. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, R.H.; Xue, H.X.; Li, Q. Effects of drought on ecosystem net primary production in northwestern China. J. Arid L. Res. Environ. 2012, 6, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Tan, D. Anomaly distribution of drought–flood and changing characteristics of arid over eastern Northwest China during 1961–2008. Arid L. Geogr. 2012, 35, 552–558. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.L. Research and application of meteorological drought monitoring indexes in Northwest China. Meteorol. Mon. 2007, 33, 90–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.C.; Xu, Z.X.; Yu, R.H. Spatiotemporal variability of drought and the potential climatological driving factors in the Liao River Basin. Hydrol. Process 2012, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Statistical behaviours of precipitation regimes in China and their links with atmospheric circulation 1960–2005. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Y.; Cai, J.N.; Shao, X.M.; Sha, W.Y. Interdecadal variability of East Asian summer monsoon and its impatc on the climate of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 569–576. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1139–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yin, Z.Y. Spatial and temporal variation of summer precipitation over the eastern Tibetan Plateau and the North Atlantic Oscillation. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 2896–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Duan, K.; Li, M.; Shi, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Impact of the North Atlantic Oscillation on the dipole oscillation of summer precipitation over the central and eastern Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.F.; Zhang, D.D. Relationship between NAO and drought disasters in northwestern China in the last millennium. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.P.; Yang, J.P.; Qin, D.H.; Li, M. Climatic background of persistent drought in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. J. Desert. Res. 2014, 34, 518–526. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.W.; Li, F.X.; Liang, X. Characteristics of drought and its influence to agriculture in Ningxia. Agric. Res. Arid Area 2001, 19, 102–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.S.; Yan, J.P.; Yang, R.; Hu, N.N. Spatial-temporal characteristics of drought and flood disasters under the backgroung of global warming in Ningxia in 1961–2010. J. Desert. Res. 2013, 33, 1552–1559. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Na, L.; Zheng, G.F.; Ren, S.Y.; Xu, J.Q. Relationship of drought with precipitation concentration period and precipitation–concentration degree in Ningxia in spring, summer and fall. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2013, 35, 1015–1021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, P.X.; Cao, L.G.; Gao, Y.; Yong, G.Z. A study on spatial-temporal variation characteristics of drought based on Standardized Precipitation Index in Ningxia Autonomous Region during recent 53 years. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 34, 296–302. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Zheng, G.F.; Li, X.; Li, Z.L.; Yang, J.L.; Feng, J.M. Modification of CI comprehensive meteorological drought index and its application in Ningxia. J. Arid Meteorol. 2013, 31, 561–569. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, G.F.; Wang, S.Y. Analysis of drought disasters-causing factors in Ningxia based on CI index. Plateau Meteorol. 2014, 33, 995–1001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Feng, J.M.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, G.F. A study on drought climate change and its causes. J. Arid L. Res. Environ. 2007, 21, 68–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- China’s Different Province Atlas Series: The Atlas of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; China Cartographic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen–Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorology 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Conway, D.; Wu, Y.J.; Gao, Q.Z.; Rothausen, S.; Xiong, W.; Ju, H.; Lin, E.D. Rural livelihoods and climate variability in Ningxia, Northwest China. Clim. Change 2013, 119, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Ghulam, A.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Nan, P. Evaluation of MODIS derived Perpendicular Drought Index for estimation of surface dryness over northwestern China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.F.; Chen, X.G.; Sun, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.; Na, L. The changes of temperature, precipitation, evaporation and their response to the climate warming. Sci. Meteorol. Sin. 2006, 26, 412–421. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.X.; Li, Q.; Li, J.P. NDVI change and its relationship with climate in Ningxia in the last 25 years. J. Arid L. Res. Environ. 2011, 25, 161–166. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Z.W.; Li, J.P.; Liu, J.; Chang, C.P.; Ding, Y.H.; Wu, G.X. How to measure the strength of the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 4449–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, Q. A unified monsoon index. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Van den Dool, H. Sensitivity of teleconnection patterns to the sign of their primary action center. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 2885–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnston, A.G.; Livezey, R.E. Classification, seasonality and persistence of low-frequency atmospheric circulation patterns. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 1083–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Zeng, Q.C. East Asian Summer Monsoon Index (EASMI). Available online: http://ljp.gcess.cn/dct/page/65577 (accessed on 28 September 2015).
- Li, J.P.; Zeng, Q.C. South Asian Summer Monsoon Index (SASMI). Available online: http://ljp.gcess.cn/dct/page/65576 (accessed on 28 September 2015).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO). Available online: http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/precip/CWlink/pna/nao.shtml. (accessed on 12 December 2005).
- Morid, S.; Smakhtin, V.; Moghaddasi, M. Comparison of seven meteorological indices for drought monitoring in Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damberg, L.; AghaKouchak, A. Global trends and patterns of drought from space. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 117, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, R.G.; Liu, J.T. Drought severity change in china during 1961–2012 indicated by SPI and SPEI. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2437–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, N.B. On the sensitivity of sample-l moments to sample-size. J. Clim. 1994, 7, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. Drought monitoring with multiple time scales. In Proceedings of Ninth Conference on Applied Climatology, Dallas, TX, USA, 15–20 January 1995; pp. 233–236.
- Daneshvar, M.R.M.; Bagherzadeh, A.; Khosravi, M. Assessment of drought hazard impact on wheat cultivation using Standardized Precipitation Index in Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 4463–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.C.; McKee, T.B. Chacteristics of 20th Century Drought in the United States at Multiple Time Scales, 1997. Available online: http://ccc.atmos.colostate.edu/edwards.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2015).
- Almedeij, J. Drought analysis for Kuwait using Standardized Precipitation Index. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornthwaite, C.W. An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geogr. Rev. 1948, 38, 55–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Guo, H.; Yu, F.X. Parameter estimation for 3-parameter log-logistic distribution (LLD3) by Pome. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 1993, 7, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions: With Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- National Drought Mitigation Center (NDMC). Program to Calculate Standardized Precipitation Index. Avaliable online: http://drought.unl.edu/MonitoringTools/DownloadableSPIProgram.aspx (accessed on 15 April 2015).
- Santiago, B.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. SPEI Calculator. Available online: http://digital.csic.es/handle/10261/10002 (accessed on 21 August 2013).
- Banimahd, S.A.; Khalili, D. Factors influencing Markov chains predictability characteristics, utilizing SPI, RDI, EDI and SPEI drought indices in different climatic zones. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3911–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.; Murthy, C.S.; Sai, M.V.R.S.; Roy, P.S. On the use of Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) for drought intensity assessment. Meteorol. Appl. 2009, 16, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.S.; Nagarajan, R. Spatio-temporal drought assessment in Tel river basin using Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and GIS. Geomat. Nat. Haz Risk 2011, 2, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of precipitation and drought data in Serbia over the period 1980–2010. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Hughes, B.; Saunders, M.A. A drought climatology for Europe. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1571–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potop, V.; Boroneant, C.; Mozny, M.; Stepanek, P.; Skalak, P. Observed spatiotemporal characteristics of drought on various time scales over the Czech Republic. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Peters, A.J. Assessing vegetation response to drought in the Northern Great Plains using vegetation and drought indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinoni, J.; Naumann, G.; Carrao, H.; Barbosa, P.; Vogt, J. World drought frequency, duration, and severity for 1951–2010. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2792–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Zheng, X.D.; Lu, F.; Ma, J. Analysis of drought evolvement characteristics based on Standardized Precipitation Index in the Huaihe River Basin. Proced. Eng. 2012, 28, 434–437. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.L.; Xu, C.Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Jiang, T. Observed trends of annual maximum water level and streamflow during past 130 years in the Yangtze River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Merwade, V.; Kam, J.; Thurner, K. Streamflow trends in Indiana: Effects of long term persistence, precipitation and subsurface drains. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Mangin, A.; Hebel, P.; Mallea, P. Detection and estimation trends linked to air quality and mortality on French Riviera over the 1990–2005 period. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storch, H.V. Misuses of statistical analysis in climate research. In Analysis of Climate Variability: Applications of Statistical Techniques; Storch, H.V., Navarra, A., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Berlin Germany, 1995; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Wang, C.Y. Applicability of prewhitening to eliminate the influence of serial correlation on the Mann–Kendall test. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, M.; Onoz, B. To prewhiten or not to prewhiten in trend analysis? Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramopoulos, F.; Rosenzweig, C.; Choudhury, B. Improved ground hydrology calculations for Global Climate Models (GCMs): Soil water movement and evapotranspiration. J. Clim. 1988, 1, 921–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Lopez-Moreno, J.-I.; Beguería, S.; Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; García-Ruiz, J.M.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Revuelto, J.; Trigo, R. Evidence of increasing drought severity caused by temperature rise in southern Europe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Zheng, G.F.; Yang, J.; Li, X. Application of three drought evaluation indices in Ningxia. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 517–524. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Q.H.; Wang, B. Circumglobal teleconnection in the northern hemisphere summer. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3483–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, C.; Yang, J.; Li, M. Temporal-Spatial Variation of Drought Indicated by SPI and SPEI in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1399-1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6101399
Tan C, Yang J, Li M. Temporal-Spatial Variation of Drought Indicated by SPI and SPEI in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(10):1399-1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6101399
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Chunping, Jianping Yang, and Man Li. 2015. "Temporal-Spatial Variation of Drought Indicated by SPI and SPEI in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China" Atmosphere 6, no. 10: 1399-1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6101399
APA StyleTan, C., Yang, J., & Li, M. (2015). Temporal-Spatial Variation of Drought Indicated by SPI and SPEI in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Atmosphere, 6(10), 1399-1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6101399






