Analysis of Flux Contribution Area in a Peatland of the Permafrost Zone in the Greater Khingan Mountains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
3. Observation Methods and Data Processing
4. Flux Footprint Model
4.1. Kormann and Meixner Model
4.2. Kljun Model
4.3. Model Input Parameters
5. Result and Analysis
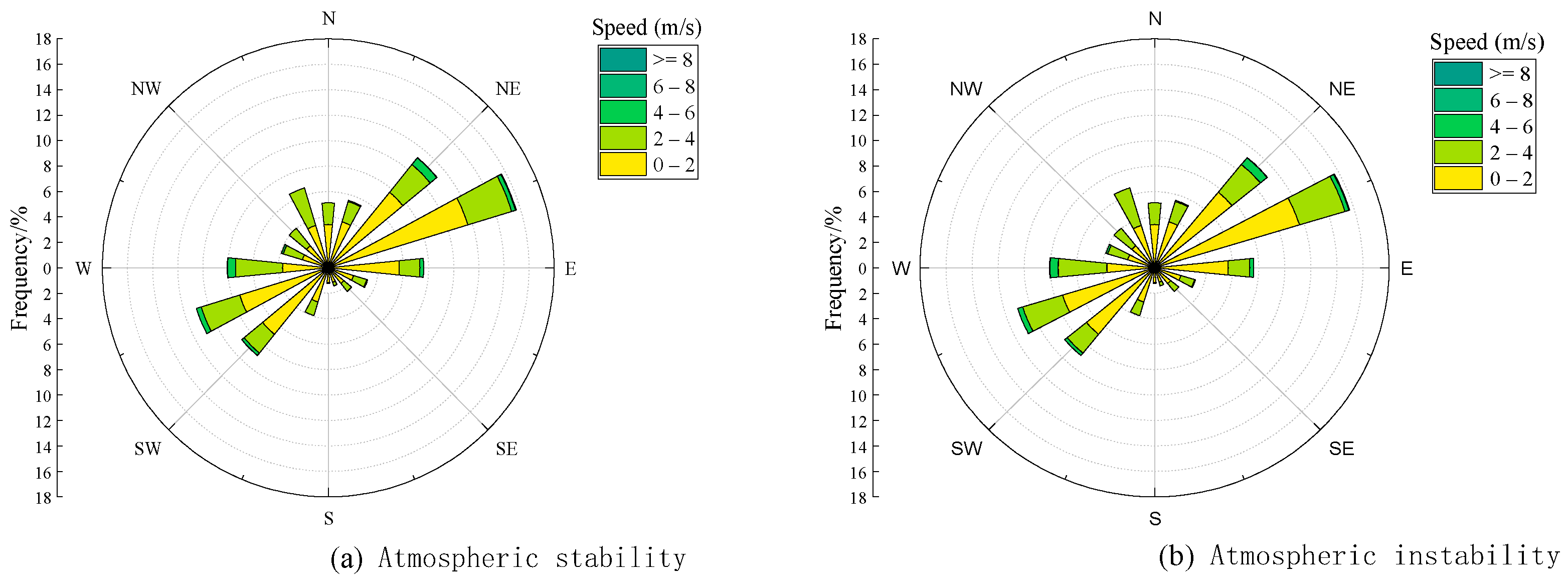
5.1. Wind Direction Characteristics in the Source Region
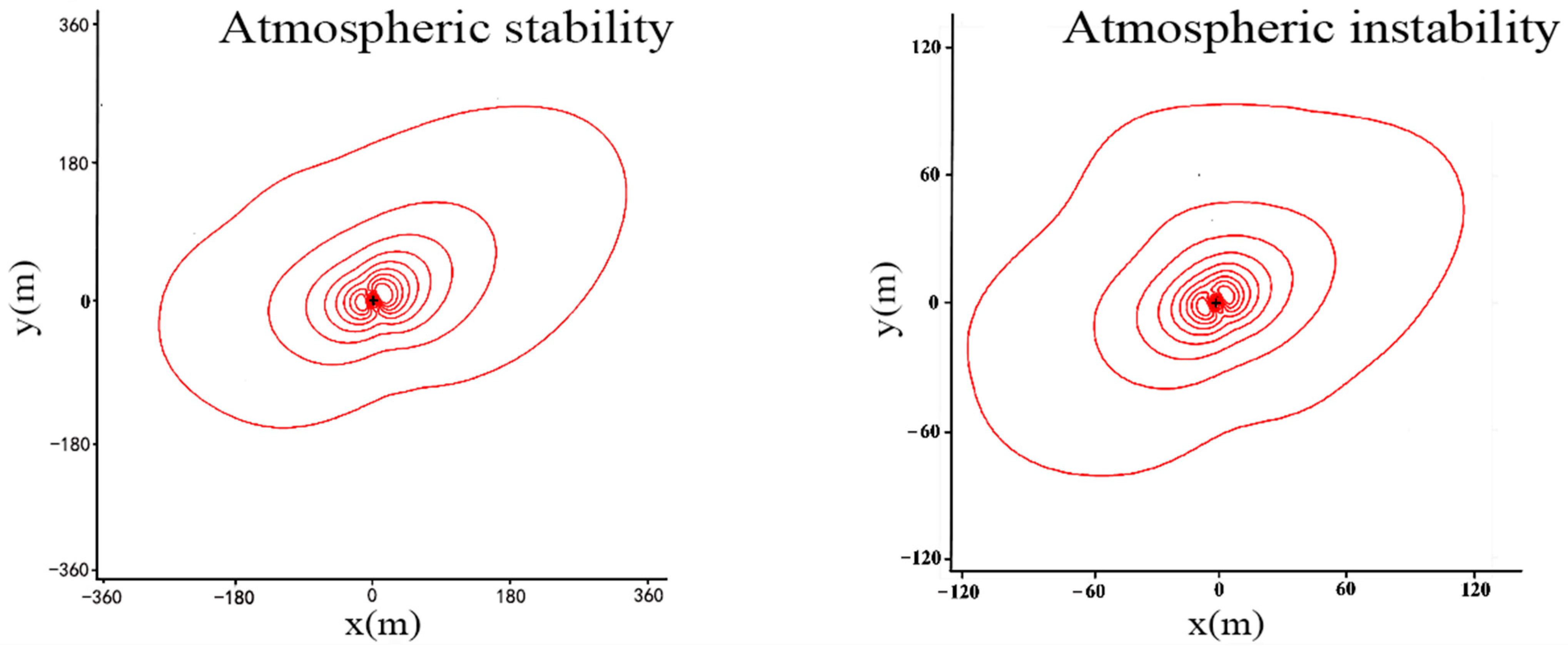
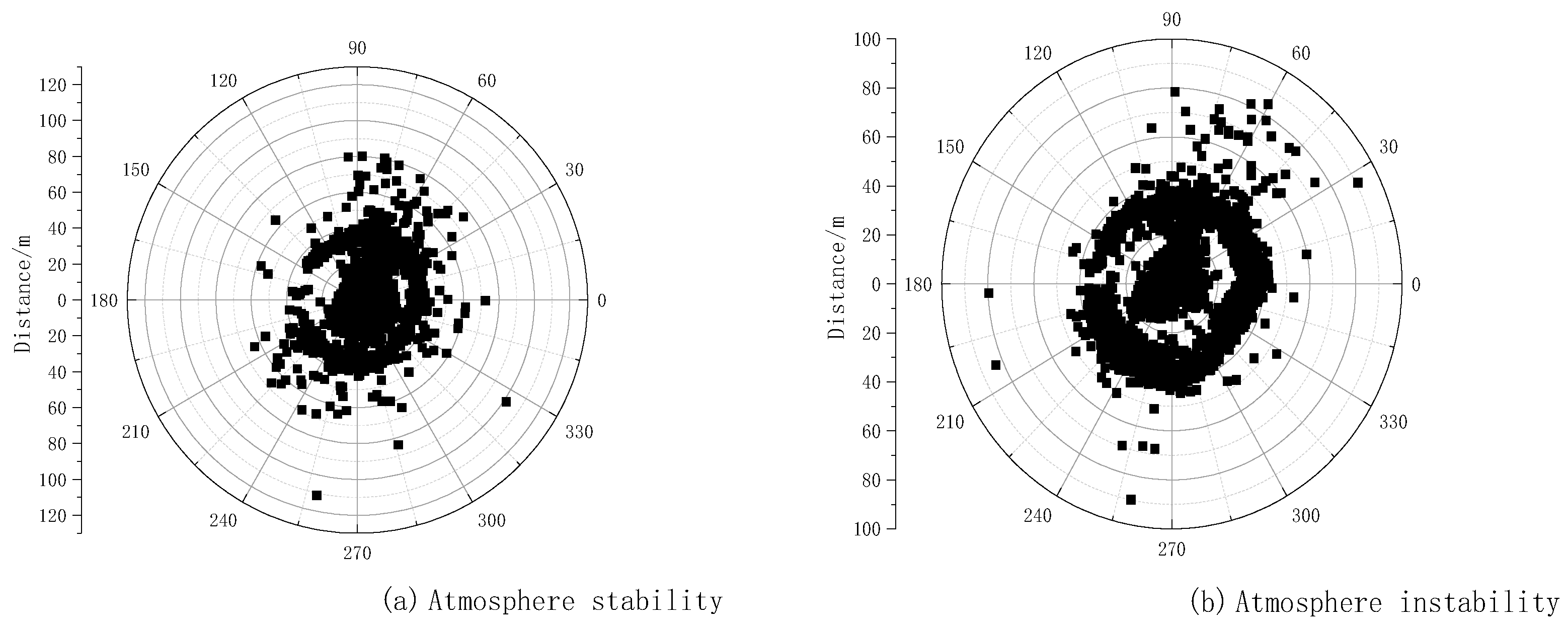
5.2. Overall Distribution Characteristics of Flux Contribution Areas
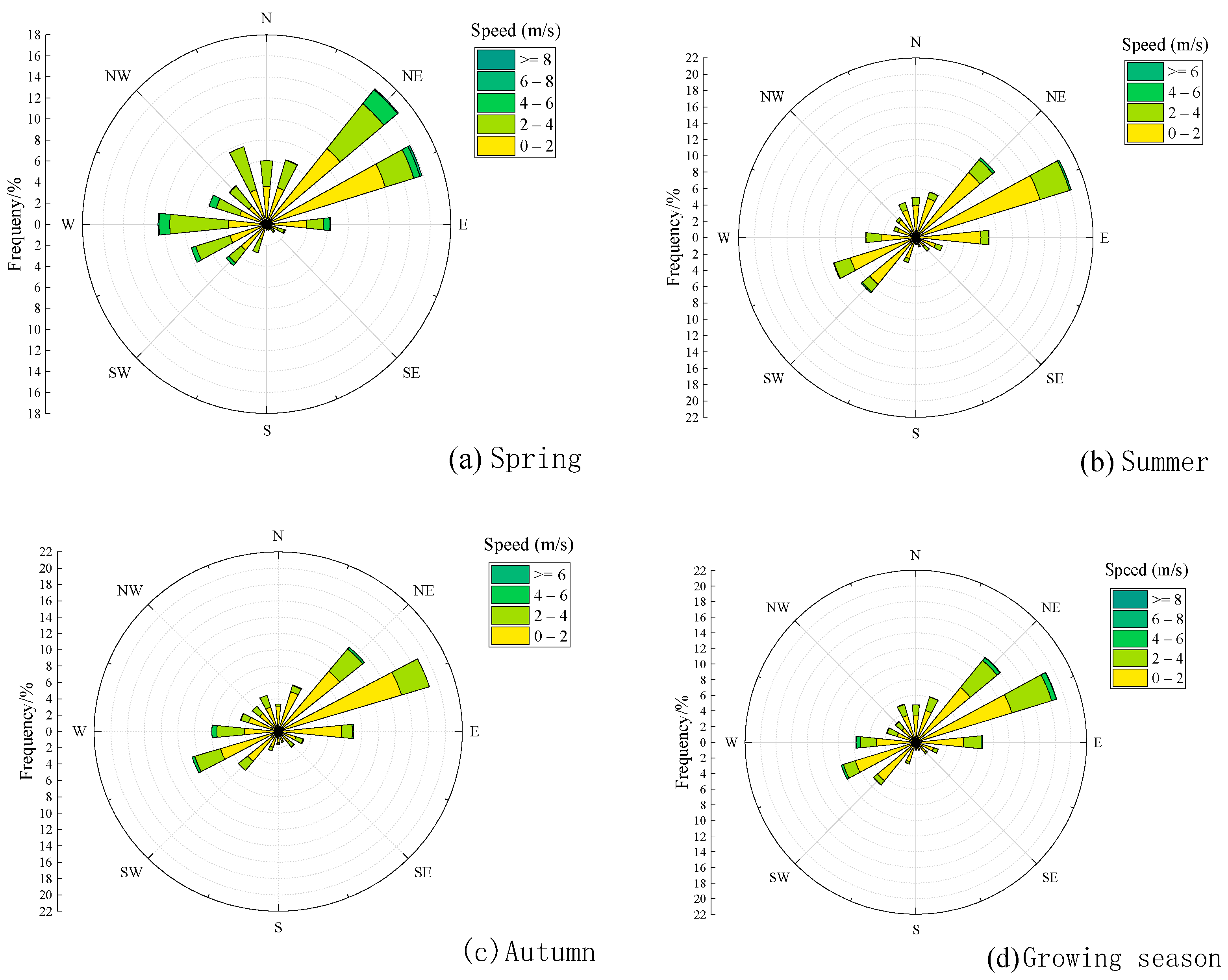
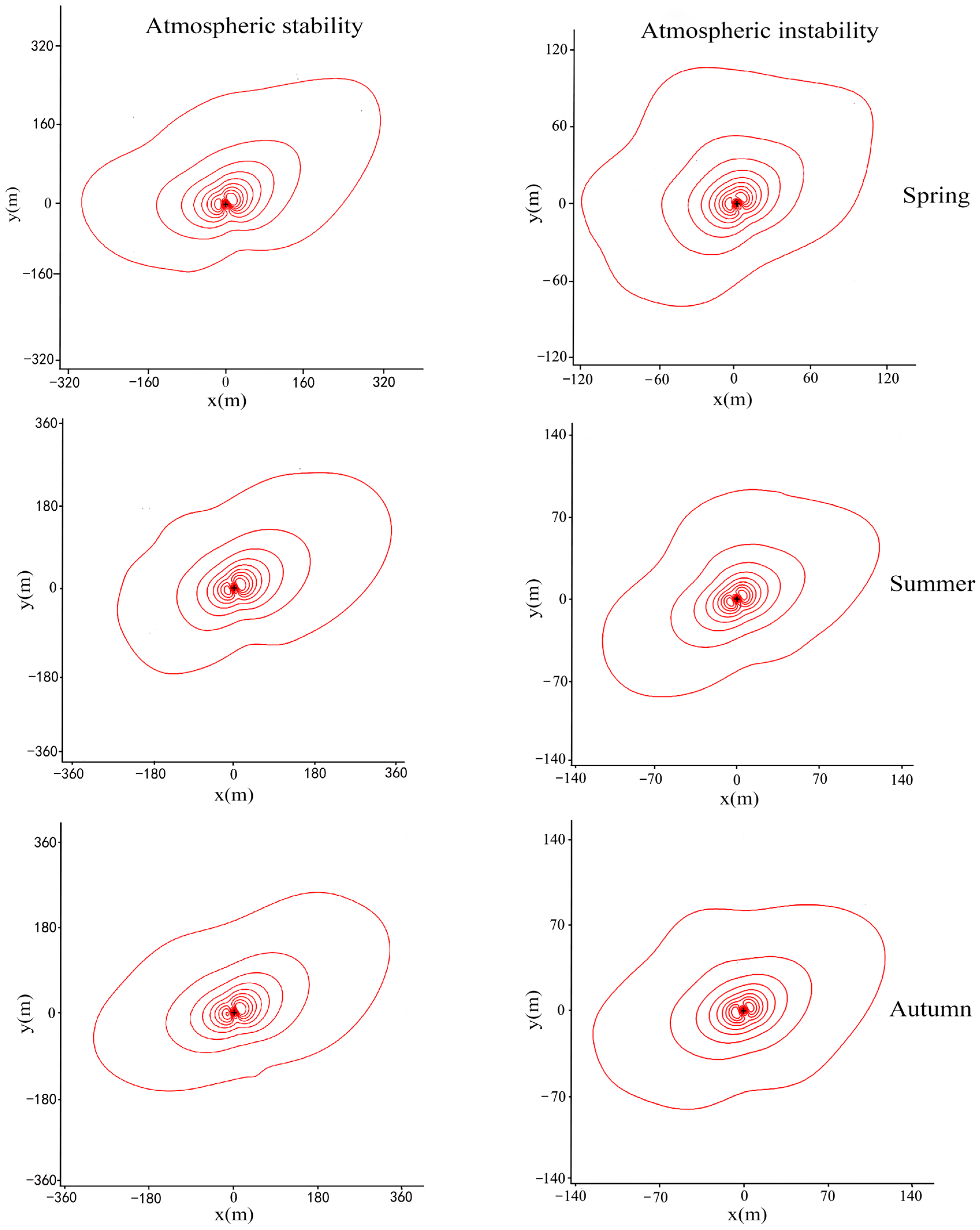
5.3. Seasonal Distribution Characteristics of Flux Contribution Areas
5.4. Flux Contribution Rates of Different Vegetation Types Within the Source Area
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trettin, C.C.; Jurgensen, M.F.; Gale, M.R.; McLaughlin, J.W. Recovery of carbon and nutrient pools in a northern forested wetland 11 years after harvesting and site preparation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twine, T.E.; Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Cook, D.R.; Houser, P.R.; Meyers, T.P.; Prueger, J.H.; Starks, P.J.; Wesely, M.L. Correcting eddy-covariance flux underestimates over a grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 103, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.B.; Hanson, P.J.; Mulholland, P.J.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Wullschleger, S.D. A comparison of methods for determining forest evapotranspiration and its components: Sap-flow, soil water budget, eddy covariance and catchment water balance. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 106, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmond, C.S.B.; King, T.S.; Cropley, F.D.; Nowak, D.J.; Souch, C. Local-scale fluxes of carbon dioxide in urban environments: Methodological challenges and results from Chicago. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 116, S243–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kljun, N.; Calanca, P.; Rotach, M.W.; Schmid, H.P. A simple two-dimensional parameterisation for Flux Footprint Prediction (FFP). Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 3695–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, X.J.; Liang, J.N.; Wang, J. Footprint Analysis for Turbulent Flux Measurements over Complex Terrain on the Loess Plateau of China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 1791, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matustik, J.; Koci, V. What is a footprint? A conceptual analysis of environmental footprint indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanolo, S.; Gabrovšek, F. Estimation of carbon dioxide flux degassing from percolating waters in a karst cave: Case study from Bijambare cave, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Chem. Erde. 2015, 75, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayek, F.; Pandya, R.V.R. Analytical description of particle/droplet-laden turbulent flows. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2003, 29, 329–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesala, T.; Kljun, N.; Rannik, U.; Rinne, J.; Sogachev, A.; Markkanen, T.; Sabelfeld, K.; Foken, T.; Leclerc, M.Y. Flux and concentration footprint modelling: State of the art. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connan, O.; Maro, D.; Hébert, D.; Solier, L.; Ideas, P.C.; Laguionie, P.; St-Amant, N. In situ measurements of tritium evapotranspiration (3 H-ET) flux over grass and soil using the gradient and eddy covariance experimental methods and the FAO-56 model. J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, H.P. Footprint modeling for vegetation atmosphere exchange studies: A review and perspective. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormann, R.; Meixner, F.X. An Analytical Footprint Model for Non-Neutral Stratification. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2001, 99, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Leclerc, M.Y. Forward-in-time and Backward-in-time Dispersion in the Convective Boundary Layer: The Concentration Footprint. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2007, 123, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macalkova, L.; Havrankova, K.; Pavelka, M. Flux footprints in different ecosystems. Glob. ChanGe A Complex ChallenGe 2015, 54, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.S.; Guan, D.X.; Wu, J.L.; Jin, C.J.; Han, S.J. Distribution of footprint and flux source area of the mixed forest of broad-leaved and Korean pine in Changbai Mountain. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2005, 27, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rebmann, C.; Göckede, M.; Foken, T.; Aubinet, M.; Aurela, M.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Buchmann, N.; Carrara, A.; Cescatti, A.; et al. Quality analysis applied on eddy covariance measurements at complex forest sites using footprint modelling. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2005, 80, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogiers, N.; Eugster, W.; Furger, M.; Siegwolf, R. Effect of land management on ecosystem carbon fluxes at a subalpine grassland site in the Swiss Alps. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2005, 80, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutjes, R.W.A.; Vellinga, U.S.; Gioli, B.; Miglietta, F. Dis-aggregation of airborne flux measurements using footprint analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 966–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, T.; Schaaf, C.L.; Kljun, N.; Munger, J.W. Seasonal variation of source contributions to eddy-covariance CO2 measurements in a mixed hardwood-conifer forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 253, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, F. Comparison of Footprint Models of Surface Heat and Water Vapor Fluxes in the Middle and Upper Reaches of Heihe River Basin. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2021, 36, 887–897. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wen, X. Flux Footprint Climatology Estimated by Three Analytical Models over a Subtropical Coniferous Plantation in Southeast China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lu, J.; Feng, M.; Zhuang, J.; Ye, L.; Liu, S.; Fang, W.; Wang, D.; et al. Distribution and characteristics of flux footprint of coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest ecosystem in Fengyang Mountain of Zhejiang, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 7377–7388. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Song, C.; Chen, N.; Qiao, T.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Du, Y. Gas storage of peat in autumn and early winter in permafrost peatland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Song, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Meng, H.; Mao, R. Growing season methane emission from a boreal peatland in the continuous permafrost zone of Northeast China: Effects of active layer depth and vegetation. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 4455–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.X.; Wang, X.W.; Lin, G.G.; Zhang, X.H.; Chen, H.M.; Mao, R. Cryptogams and dwarf evergreen shrubs are vulnerable to nitrogen addition in a boreal permafrost peatland of Northeast China. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2022, 25, e12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, W.; Jia, Z.Z.; Zhu, M.J.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.M. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, Z.; Smith, W. Cloud pattern and water relations in Picea rubens and Abies fraseri, southern Appalachian Mountains, USA. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 162, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.; Pearman, G.; Leuning, R. Correction of flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapour transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieff, J.; Massheder, J.; de Bruin, H.; Elbers, J.; Friborg, T. A system to measure surface fluxes of momentum, sensible heat, water vapour and carbon dioxide. J. Hydrol. 1997, 188, 589–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauder, M.; Foken, T. Quality control of eddy covariance data based on a classification system for flux measurement sites. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 80, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, H.P. Experimental design for flux measurements: Matching scales of observations and fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 87, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljun, N.; Rotach, M.W.; Schmid, H.P. A Three-Dimensional Backward Lagrangian Footprint Model For A Wide Range Of Boundary-Layer Stratifications. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2002, 103, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljun, N.; Kormann, R.; Rotach, M.W.; Meixer, F.X. Comparison of the Langrangian footprint model LPDM-B with an analytical footprint model. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2003, 106, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.D.; Yao, J.; Ling, X.F.; Yan, S.W.; Zhang, F.M.; Lu, Y.Y. Distribution characteristics of flux source of rice-wheat rotation agroecosystem in Huaihe River Basin. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 43, 3113–3120. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.F.; Chen, L.P.; Mo, L.F. Research of Flux footprint of Anji Bamboo forest ecosystems based on the FSAM Model. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2015, 35, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.X.; Li, G.D.; Zhang, X. Flux footprint of winter wheat farmland ecosystem in the North China Plain. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 28, 3663–3674. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.H.; Huang, Y.; Tang, J.W.; Tian, B.; Shen, F.; Wu, P.F.; Yaun, Q.; Zhou, C.; Wang, J.T. Flux footprint analysis of a salt marsh ecosystem in the Jiuduansha Shoals of the Changjiang Estuary. J. East China Norm. Univ. 2021, 2, 42–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, P.H.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, C.L.; Xu, L. A footprint analysis on a desert ecosystem in west China. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Fang, X.R.; Kang, M.C.; Cha, T.G.; Wang, X.P.; Chen, J.Q. Footprint analysis of turbulent flux over a poplar plantation in Northern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 32, 3966–3974. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.J.; Gao, Y.; Guo, H.Q.; Zhao, B. Footprint analysis for carbon Flux in the wetland ecosystem of Chongming Dongtan. J. Fudan Univ. 2008, 3, 374–379+386. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Dang, H.H.; Kong, F.L.; Yue, N.; Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Wei, G.X. Analysis of agro-ecosystem footprint of flux in semi-arid areas. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2015, 23, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar]

| Model | Zm | u* | L | Z0 | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KM | √ | √ | √ | — | — | √ |
| Kljun | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Stability | Wind Direction (°) | Maximum Wind Speed (m·s−1) | Average Wind Speed (m·s−1) | Wind Speed Frequency (%) | Prevailing Wind Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L > 0 | Northeast (0–90°) | 6.1 | 1.2 | 55.7% | Northeast-Southwest Wind |
| Southeast (90–180°) | 6.5 | 1.2 | 8.3% | ||
| Southwest (180–270°) | 5.3 | 1.2 | 18.2% | ||
| Northwest (270–360°) | 6.1 | 1.2 | 17.8% | ||
| L < 0 | Northeast (0–90°) | 7.4 | 1.6 | 39.7% | |
| Southeast (90–180°) | 5.5 | 1.6 | 19.4% | ||
| Southwest (180–270°) | 5.5 | 1.6 | 29.6% | ||
| Northwest (270–360°) | 6.2 | 1.6 | 20.3% |
| Time | Frequency/% | Prevailing Wind Direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast Wind | Southwest Wind | Southeast Wind | Northwest Wind | ||
| Spring | 50 | 19.2 | 5.8 | 25 | Northeast-Southwest Wind |
| Summer | 47.2 | 27.2 | 10.5 | 15.1 | |
| Autumn | 45.6 | 25.1 | 11.1 | 18.2 | |
| Growing season | 46.3 | 24.9 | 9.6 | 19.2 | |
| Ecosystem | Representative Vegetation | Measure Height (m) | P Level (%) | E (m) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest ecosystem | Mixed conifer and broadleaf forest | 40 | 80 | 2717 | [16] |
| Forest ecosystem | Phyllostachys pubescens forest | 25 | 90 | 3500 | [35] |
| Wetland ecosystem | Wetland | 14 | 90 | 836 | [36] |
| Desert ecosystem | Haloxylon ammodendron | 11 | 90 | 670.8 | [37] |
| Agro-ecosystem | Zea mays | 3 | 90 | 155 | [38] |
| Agro-ecosystem | Rice-wheat rotation | 4 | 80 | 158 | [39] |
| Forest ecosystem | Aspen | 37 | 80 | 550 | [40] |
| Wetland ecosystem | Phragmites australis | 5 | 90 | 439 | [41] |
| Agro-ecosystem | Triticum aestivum | 3.5 | 90 | 222 | [42] |
| Wetland ecosystem | peatland | 2.9 | 90 | 390 | The present research |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, Y. Analysis of Flux Contribution Area in a Peatland of the Permafrost Zone in the Greater Khingan Mountains. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040452
Lian J, Sun L, Wang Y, Wang X, Du Y. Analysis of Flux Contribution Area in a Peatland of the Permafrost Zone in the Greater Khingan Mountains. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(4):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040452
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Jizhe, Li Sun, Yongsi Wang, Xianwei Wang, and Yu Du. 2025. "Analysis of Flux Contribution Area in a Peatland of the Permafrost Zone in the Greater Khingan Mountains" Atmosphere 16, no. 4: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040452
APA StyleLian, J., Sun, L., Wang, Y., Wang, X., & Du, Y. (2025). Analysis of Flux Contribution Area in a Peatland of the Permafrost Zone in the Greater Khingan Mountains. Atmosphere, 16(4), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040452






