The Relationship Between Surface Meteorological Variables and Air Pollutants in Simulated Temperature Increase Scenarios in a Medium-Sized Industrial City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
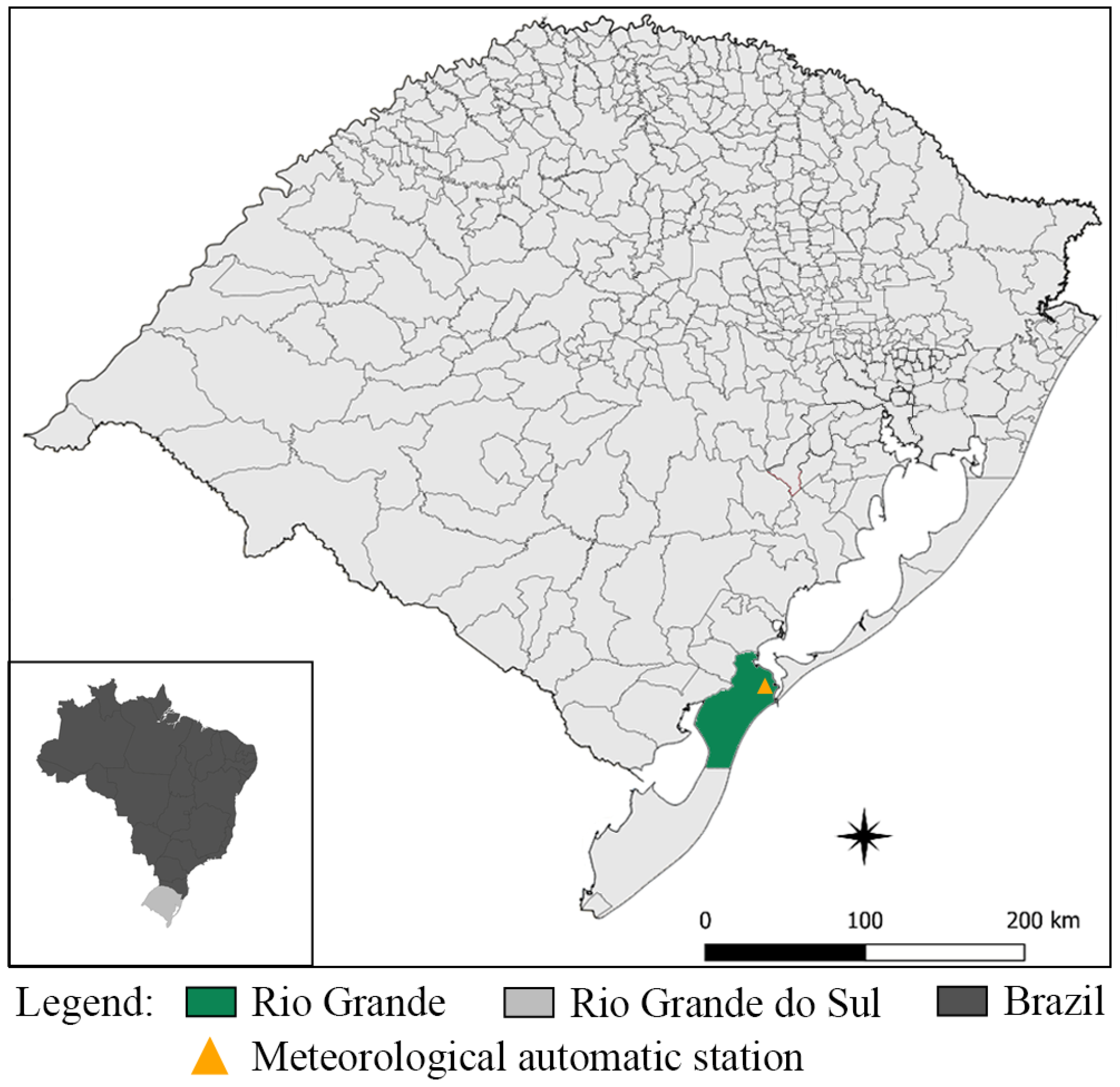
2.1. Study Area
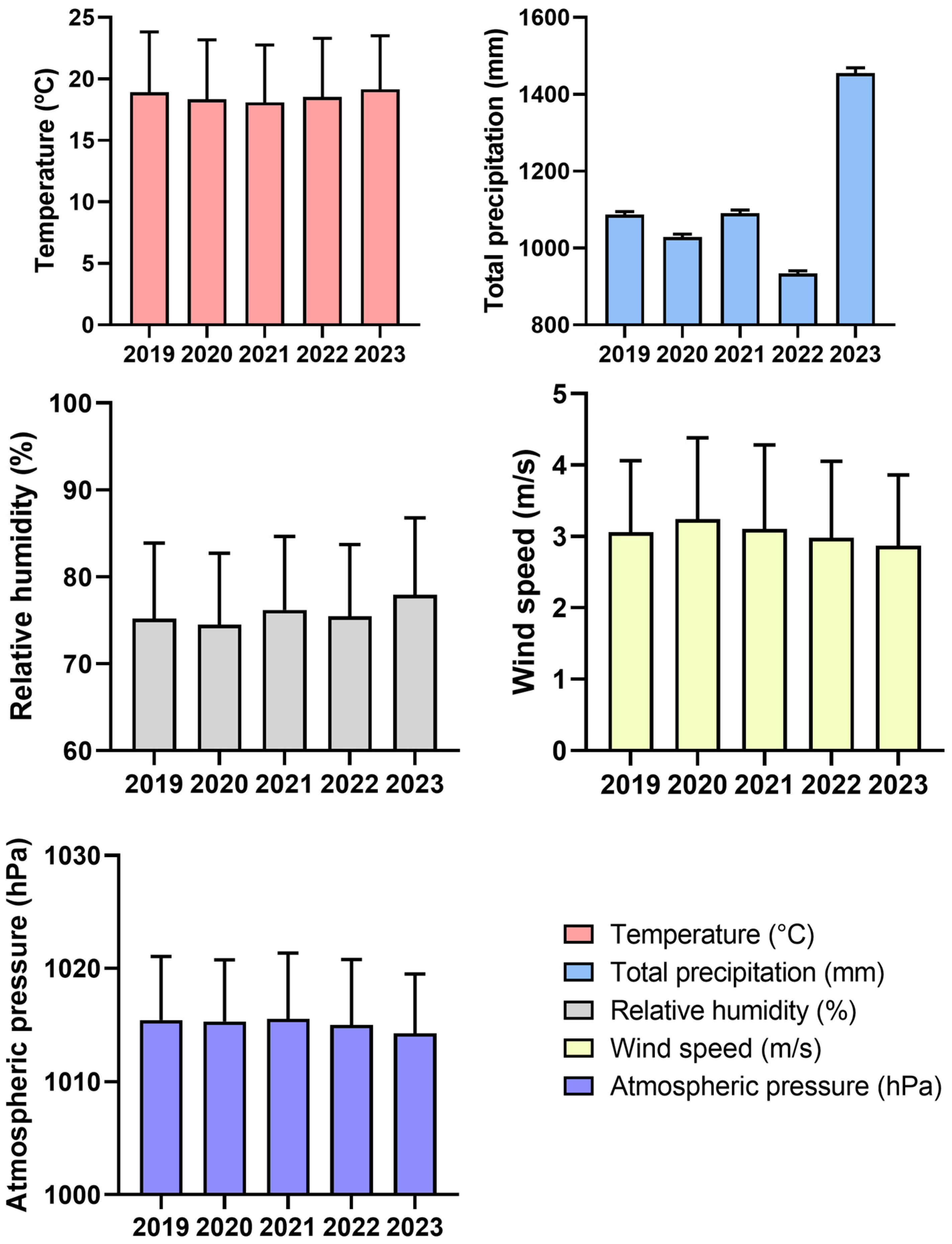
2.2. Data Collection and Monitoring Period
2.2.1. Air Pollutants—O3, PM2.5, and PM10
2.2.2. Meteorological Parameters
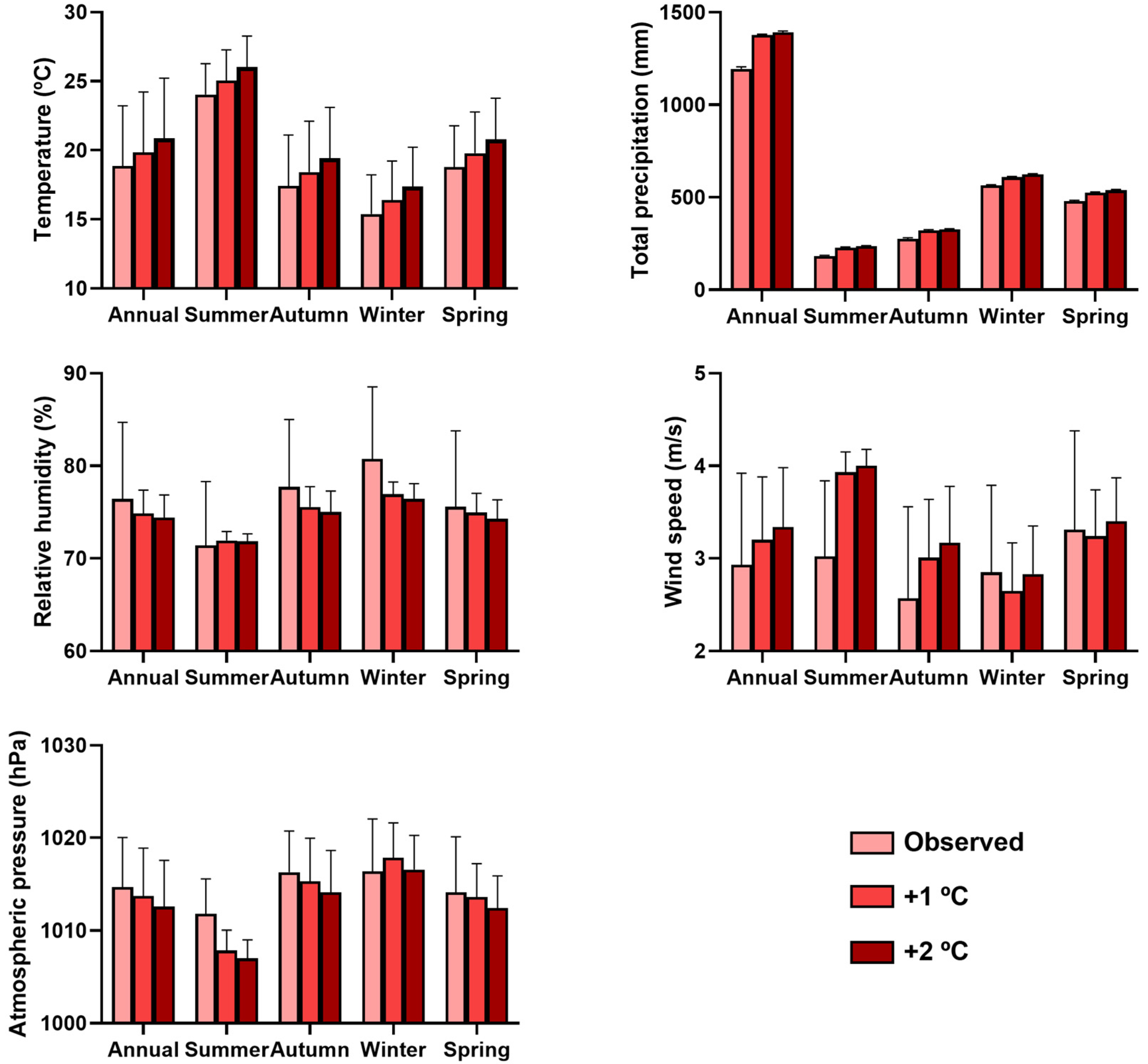
2.3. Scenario Simulations
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; Guillén Bolaños, T.; Bindi, M.; Brown, S.; Camilloni, I.A.; Diedhiou, A.; Djalante, R.; Ebi, K.; et al. The human imperative of stabilizing global climate change at 1.5 C. Science 2019, 365, eaaw6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moura, F.R.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. 2030 Agenda: Discussion on Brazilian priorities facing air pollution and climate change challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 8376–8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Forster, P.M. Estimated human-induced warming from a linear temperature and atmospheric CO2 relationship. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 1222–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, P.; Kota, S.H.; Huang, L. Health effects of climate change through temperature and air pollution. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, H.; Ebi, K.L.; Forsberg, B. The interplay of climate change and air pollution on health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2017, 4, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, D.; Gao, B.; He, B.; Cheng, N.; Xu, B. Understanding meteorological influences on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A temporal and spatial perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5343–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Breitner, S.; Stafoggia, M.; De’Donato, F.; Samoli, E.; Zafeiratou, S.; Katsouyanni, K.; Rao, S.; Palomares, A.D.-L.; Gasparrini, A.; et al. Effect modification of air pollution on the association between heat and mortality in five European countries. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, B.; Khraishah, H.; Althalji, K.; Borchert, W.; Al-Mulla, F.; Koutrakis, P. Connections between air pollution, climate change, and cardiovascular health. Can. J. Cardiol. 2023, 39, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, A.L.; Tella, A.; Baloo, L.; Adebisi, N. A review of the inter-correlation of climate change, air pollution and urban sustainability using novel machine learning algorithms and spatial information science. Urban Clim. 2021, 40, 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, T. A Review of the Interactive Effects of Climate and Air Pollution on Human Health in China. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2024, 11, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tavella, R.A.; Penteado, J.O.; de Lima Brum, R.; da Silva Bonifácio, A.; San Martin, M.C.; Saes-Silva, E.; Brum, A.N.; Buffarini, R.; Filho, W.L.F.C.; Adamatti, D.F.; et al. An exploratory study on the association between air pollution and health problems (ICD-10) with an emphasis on respiratory diseases. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomenko, S.; Cirach, M.; Pereira-Barboza, E.; Mueller, N.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Hoek, G.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Premature mortality due to air pollution in European cities: A health impact assessment. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e121–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badida, P.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Jayaprakash, J. Meta analysis of health effects of ambient air pollution exposure in low-and middle-income countries. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and health impacts of air pollution: A review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S.M.; Balmes, J.R. Systematic review of ozone effects on human lung function, 2013 through 2020. Chest 2022, 161, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hanaoka, T.; Masui, T. Comparison of health and economic impacts of PM2.5 and ozone pollution in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Agrawal, M. A global perspective of fine particulate matter pollution and its health effects. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 244, 5–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominski, F.H.; Branco, J.H.L.; Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; da Silva, M.G.; Andrade, A. Effects of air pollution on health: A mapping review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Garuda, S.; Vogt, U.; Yang, B. Air pollution prediction using machine learning techniques–an approach to replace existing monitoring stations with virtual monitoring stations. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 310, 119987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindiran, G.; Rajamanickam, S.; Kanagarathinam, K.; Hayder, G.; Janardhan, G.; Arunkumar, P.; Arunachalam, S.; AlObaid, A.A.; Warad, I.; Muniasamy, S.K. Impact of air pollutants on climate change and prediction of air quality index using machine learning models. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, C.; Mohomed Jabbar, M.S.; Zaïane, O.; Osornio-Vargas, A. A systematic review of data mining and machine learning for air pollution epidemiology. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdou, A.; El Badisy, I.; Khomsi, K.; Abdala, S.A.; Abdulla, F.; Najmi, H.; Obtel, M.; Belyamani, L.; Ibrahimi, A.; Khalis, M. Interpretable machine learning approaches for forecasting and predicting air pollution: A systematic review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2024, 24, 230151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaev, E.; Ajikeev, B.; Shamyrkanov, U.; Kalnur, K.U.; Maisalbek, K.; Sidle, R.C. Impact of climate change and air pollution forecasting using machine learning techniques in Bishkek. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltare, N.N.; Vahora, S. Air Quality Index prediction using machine learning for Ahmedabad city. Digit. Chem. Eng. 2023, 7, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Lin, T.C.; Yuan, K.Y.; Chiueh, P.T. Spatio-temporal prediction and factor identification of urban air quality using support vector machine. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.C.; Kelani, R.O.; Ahmad, Z.J. Prediction of air pollution index (API) using support vector machine (SVM). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyarini, L.; Purnomo, H.D. Air Quality Prediction Using the Support Vector Machine Algorithm. J. Inf. Syst. Inform. 2024, 6, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, A.N.; de Lima Brum, R.; da Silva Bonifácio, A.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R.; Zhang, L. Impact of temperature increase on air pollutants—A case study in a small city in southern Brazil. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Bonifácio, A.; de Lima Brum, R.; Tavella, R.A.; They, N.H.; Nadaleti, W.C.; Coronas, M.V.; Saes-Silva, E.; Brum, A.N.; Buffarini, R.; Filho, W.L.F.C.; et al. Health impact assessment of air pollutants in simulated temperature scenarios in the largest coal mining region of Brazil. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirlean, N.; Ribeiro Gripp, M.L. Geochemical mapping and environmental indexing of an urban area (Rio Grande, RS). Geochim. Bras. 2018, 32, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE), Brazil. Cidades e Estados do País–Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul. 2022. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/rs/rio-grande/panorama (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Mirlean, N.; Vanz, A.; Baisch, P. Níveis e origem da acidificação das chuvas na região do Rio Grande, RS. Química Nova 2000, 23, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Brum, R.; Penteado, J.O.; Ramires, P.F.; Tavella, R.A.; Honscha, L.C.; da Silva Freitas, L.; de Moura, F.R.; Bonifácio, A.d.S.; da Silva, V.M.; Silva, L.d.S.d.; et al. Southern Air Project-scientific efforts to monitor and measure the impacts of air pollution in southern Brazil. Soc. Impacts 2024, 4, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavella, R.A.; Fernandes, C.L.F.; Penteado, J.O.; De Lima Brum, R.; Florencio Ramires, P.; Coutelle Honscha, L.; Dos Santos, M.; Volcão, L.M.; Muccillo-Baisch, A.L.; Da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Unexpected reduction in ozone levels in a mid-size city during COVID-19 lockdown. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 1801–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavella, R.A.; da Rosa Moraes, N.G.; Aick, C.D.M.; Ramires, P.F.; Pereira, N.; Soares, A.G.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Weekend effect of air pollutants in small and medium-sized cities: The role of policies stringency to COVID-19 containment. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormittag, E.D.M.P.D.A.; Cirqueira, S.S.R.; Wicher, H.; Saldiva, P.H.N. Análise do monitoramento da qualidade do ar no Brasil. Estud. Avançados 2021, 35, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto de Energia e Meio Ambiente (IEMA), Brazil. Dimensionamento da Rede Básica de Monitoramento da Qualidade do Ar no Brasil–Cenários Iniciais. 2021. Available online: https://energiaeambiente.org.br/produto/dimensionamento-da-rede-basica-de-monitoramento-da-qualidade-do-ar-no-brasil-cenarios-iniciais (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Santos, J.E.K.; Tavella, R.A.; de Lima Brum, R.; Ramires, P.F.; da Silva, L.D.S.; Filho, W.L.F.C.; Nadaleti, W.C.; Correa, E.K.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. PM2.5/PM10 ratios in southernmost Brazilian cities and its relation with economic contexts and meteorological factors. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, D.; Faican, G.; Zalakeviciute, R.; Matovelle, C.; Bonilla, S.; Sobrino, J.A. Spatio-temporal evaluation of air pollution using ground-based and satellite data during COVID-19 in Ecuador. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, M.J.; McVey, A.E.; Hegarty, J.D.; Cross, E.S.; Hasenkopf, C.A.; Lynch, R.; Kennelly, E.J.; Onasch, T.B.; Awe, Y.; Sanchez-Triana, E.; et al. Evaluating the use of satellite observations to supplement ground-level air quality data in selected cities in low-and middle-income countries. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA), Brazil. Estabelece Padrões Nacionais de Qualidade do ar e Fornece Diretrizes Para sua Aplicação. Available online: https://conama.mma.gov.br/index.php?option=com_sisconama&view=atonormativo&id=756 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Balogun, A.L.; Tella, A. Modelling and investigating the impacts of climatic variables on ozone concentration in Malaysia using correlation analysis with random forest, decision tree regression, linear regression, and support vector regression. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borhani, F.; Shafiepour Motlagh, M.; Stohl, A.; Rashidi, Y.; Ehsani, A.H. Tropospheric Ozone in Tehran, Iran, during the last 20 years. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 3615–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H. Correlation between surface PM2.5 and O3 in eastern China during 2015–2019: Spatiotemporal variations and meteorological impacts. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 294, 119520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirešová, S.; Guzan, M. Determining the correlation between particulate matter PM10 and meteorological factors. Eng 2022, 3, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhou, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Li, H. Characteristics of ozone pollution and its relationship with meteorological factors in Langfang City. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2021, 11, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Min, B.W. Correlation analysis of atmospheric pollutants and meteorological factors based on environmental big data. Int. J. Contents 2022, 18, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.; Kovač-Andrić, E.; Matasović, B.; Marković, B. Assessment of ozone variations and meteorological influences in west Center of Brazil, from 2004 to 2010. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbo-Bustinza, N.; Belmonte, M.; Jimenez, V.; Montalban, P.; Rivera, M.; Martínez, F.G.; Mohamed, M.M.H.; De La Cruz, A.R.H.; da Costa, K.; López-Gonzales, J.L. A machine learning approach to analyse ozone concentration in metropolitan area of Lima, Peru. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Lichtfouse, E.; Rosenfeld, D.; et al. Large scale control of surface ozone by relative humidity observed during warm seasons in China. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3981–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zender-Świercz, E.; Galiszewska, B.; Telejko, M.; Starzomska, M. The effect of temperature and humidity of air on the concentration of particulate matter-PM2.5 and PM10. Atmos. Res. 2024, 312, 107733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emekwuru, N.; Ejohwomu, O. Temperature, humidity and air pollution relationships during a period of rainy and dry seasons in Lagos, West Africa. Climate 2023, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishali; Verma, G.; Das, R.M. Influence of temperature and relative humidity on PM2.5 concentration over Delhi. MAPAN 2023, 38, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, Q.; Wang, W.; Luo, Y.; Tao, L.; Gao, Q.; Guo, J.; Chen, S.; et al. PM2.5 spatiotemporal variations and the relationship with meteorological factors during 2013-2014 in Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Hong, Y. Temporal and spatial analyses of particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) and its relationship with meteorological parameters over an urban city in northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 198, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, M.; Jafari, A.J.; Gholami, M.; Fanaei, F.; Arfaeinia, H. Association between meteorological parameter and PM2.5 concentration in Karaj, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Health Eng. 2020, 9, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Reboita, M.S.; Kruche, N. Normais climatológicas provisórias de 1991 a 2010 para Rio Grande, RS. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2018, 33, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, Í.S.; da Rosa Silva, T.; Klering, E.; da Silva Lindemann, D.; Maier, É.L.B. Análise da Variabilidade da Temperatura do Ar em Rio Grande–RS (1913-2016). Rev. Bras. Geogr. Física 2022, 15, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
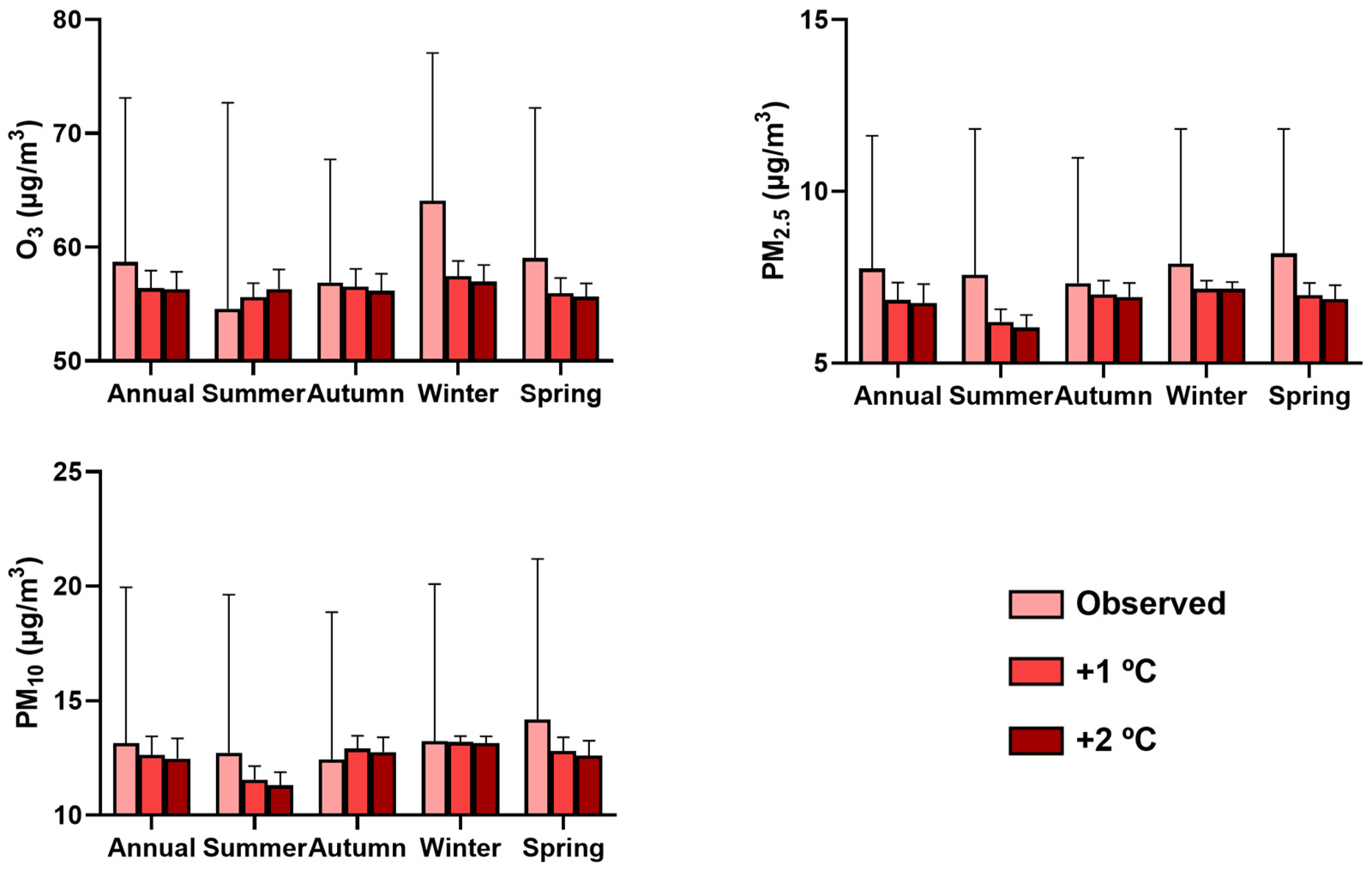
| Parameters | O3 (µg/m3) | PM2.5 (µg/m3) | PM10 (µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (±SD) | 58.69 ± 14.46 | 7.75 ± 3.89 | 13.14 ± 6.84 |
| Median | 58.03 | 7.20 | 11.98 |
| Minimum | 27.69 | 1.11 | 1.50 |
| Maximum | 110.19 | 45.28 | 65.11 |
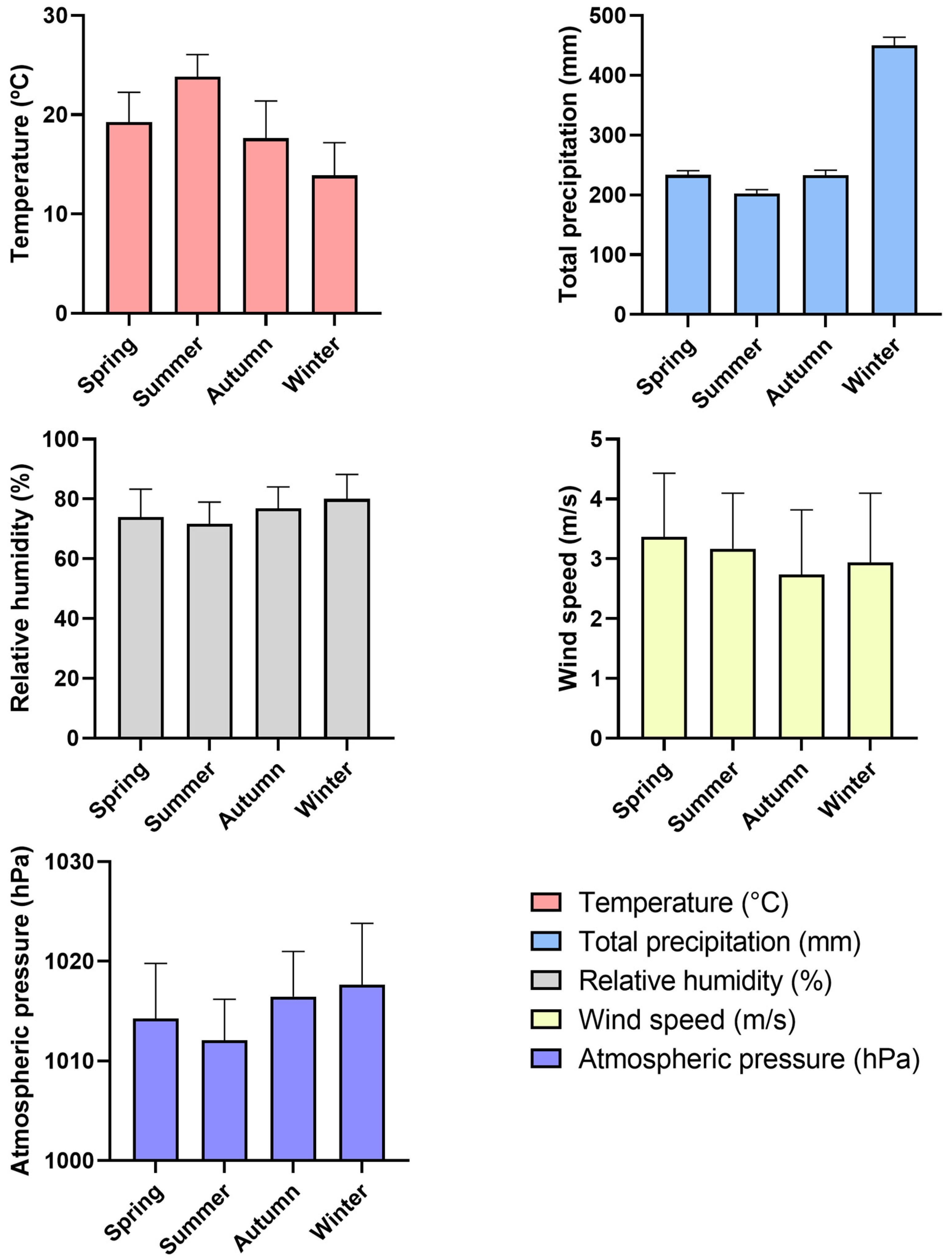
| Season | O3 (µg/m3) | PM2.5 (µg/m3) | PM10 (µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 59.04 ± 13.23 | 8.21 ± 3.64 | 14.18 ± 7.03 |
| Summer | 54.58 ± 18.10 | 7.57 ± 4.25 | 12.73 ± 6.90 |
| Autumn | 56.89 ± 10.85 | 7.32 ± 3.66 | 12.45 ± 6.43 |
| Winter | 64.11 ± 13.06 | 7.90 ± 3.94 | 13.23 ± 6.90 |
| Temperature | Precipitation | Relative Humidity | Wind Speed | Atmospheric Pressure | O3 | PM2.5 | PM10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | −0.16 * | −0.30 * | 0.20 * | −0.53 * | −0.08 | 0.01 | −0.03 | |
| Precipitation | −0.16 * | 0.33 * | 0.06 | −0.17 * | 0.06 | −0.07 | −0.04 | |
| Relative humidity | −0.30 * | 0.33 * | −0.19 * | −0.01 | 0.36 * | 0.12 * | 0.07 | |
| Wind speed | 0.20 * | 0.06 | −0.19 * | −0.17 * | −0.18 * | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| Atmospheric pressure | −0.53 * | 0.17 * | −0.01 | −0.17 * | −0.06 | 0.14 * | 0.21 * | |
| O3 | −0.09 * | 0.06 | 0.36 * | −0.18 * | −0.06 | 0.24 * | 0.17 * | |
| PM2.5 | 0.01 | −0.07 | 0.12 * | 0.01 | 0.14 * | 0.24 * | 0.98 * | |
| PM10 | −0.03 | −0.04 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.21 * | 0.17 * | 0.98 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tavella, R.A.; das Neves, D.F.; Silveira, G.d.O.; Vieira de Azevedo, G.M.G.; Brum, R.d.L.; Bonifácio, A.d.S.; Machado, R.A.; Brum, L.W.; Buffarini, R.; Adamatti, D.F.; et al. The Relationship Between Surface Meteorological Variables and Air Pollutants in Simulated Temperature Increase Scenarios in a Medium-Sized Industrial City. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040363
Tavella RA, das Neves DF, Silveira GdO, Vieira de Azevedo GMG, Brum RdL, Bonifácio AdS, Machado RA, Brum LW, Buffarini R, Adamatti DF, et al. The Relationship Between Surface Meteorological Variables and Air Pollutants in Simulated Temperature Increase Scenarios in a Medium-Sized Industrial City. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(4):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040363
Chicago/Turabian StyleTavella, Ronan Adler, Daniele Feijó das Neves, Gustavo de Oliveira Silveira, Gabriella Mello Gomes Vieira de Azevedo, Rodrigo de Lima Brum, Alicia da Silva Bonifácio, Ricardo Arend Machado, Letícia Willrich Brum, Romina Buffarini, Diana Francisca Adamatti, and et al. 2025. "The Relationship Between Surface Meteorological Variables and Air Pollutants in Simulated Temperature Increase Scenarios in a Medium-Sized Industrial City" Atmosphere 16, no. 4: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040363
APA StyleTavella, R. A., das Neves, D. F., Silveira, G. d. O., Vieira de Azevedo, G. M. G., Brum, R. d. L., Bonifácio, A. d. S., Machado, R. A., Brum, L. W., Buffarini, R., Adamatti, D. F., & da Silva Júnior, F. M. R. (2025). The Relationship Between Surface Meteorological Variables and Air Pollutants in Simulated Temperature Increase Scenarios in a Medium-Sized Industrial City. Atmosphere, 16(4), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040363








