Training a Regulatory Team to Use the Odor Profile Method for Evaluation of Atmospheric Malodors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Panel Description
2.3. Training Activities
2.3.1. Odor Characteristic and Intensity Definition
2.3.2. Triangle Tests
2.3.3. Mixture Evaluation
2.4. Performance Validation
2.5. Statistical Test
3. Results
3.1. Screening by University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test® (UPSIT®)
3.2. Odor References and Triangle Tests
3.3. Odor Perception in Mixtures
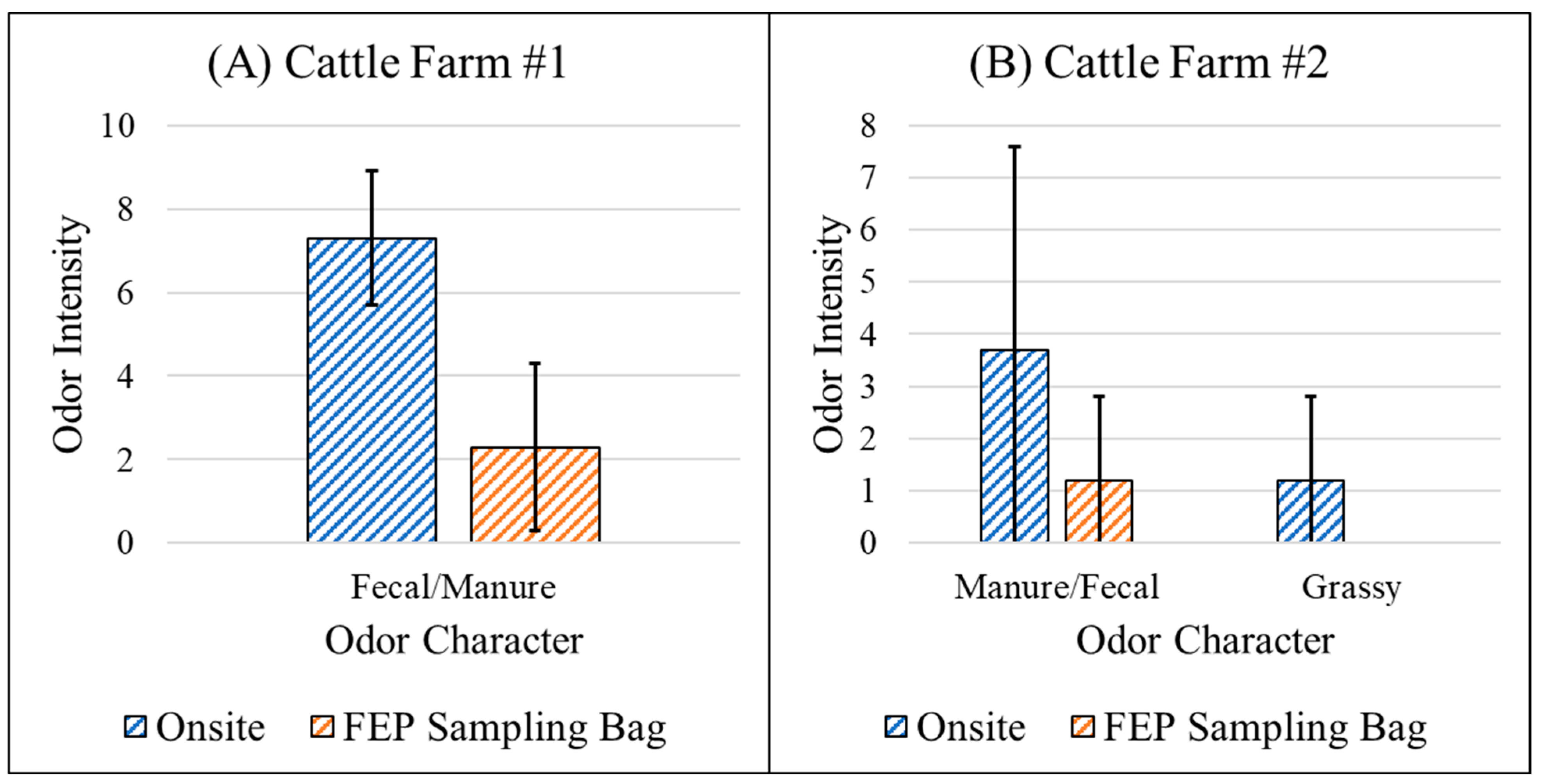
3.4. Performance Validation by the OPM Analysis of Facilities
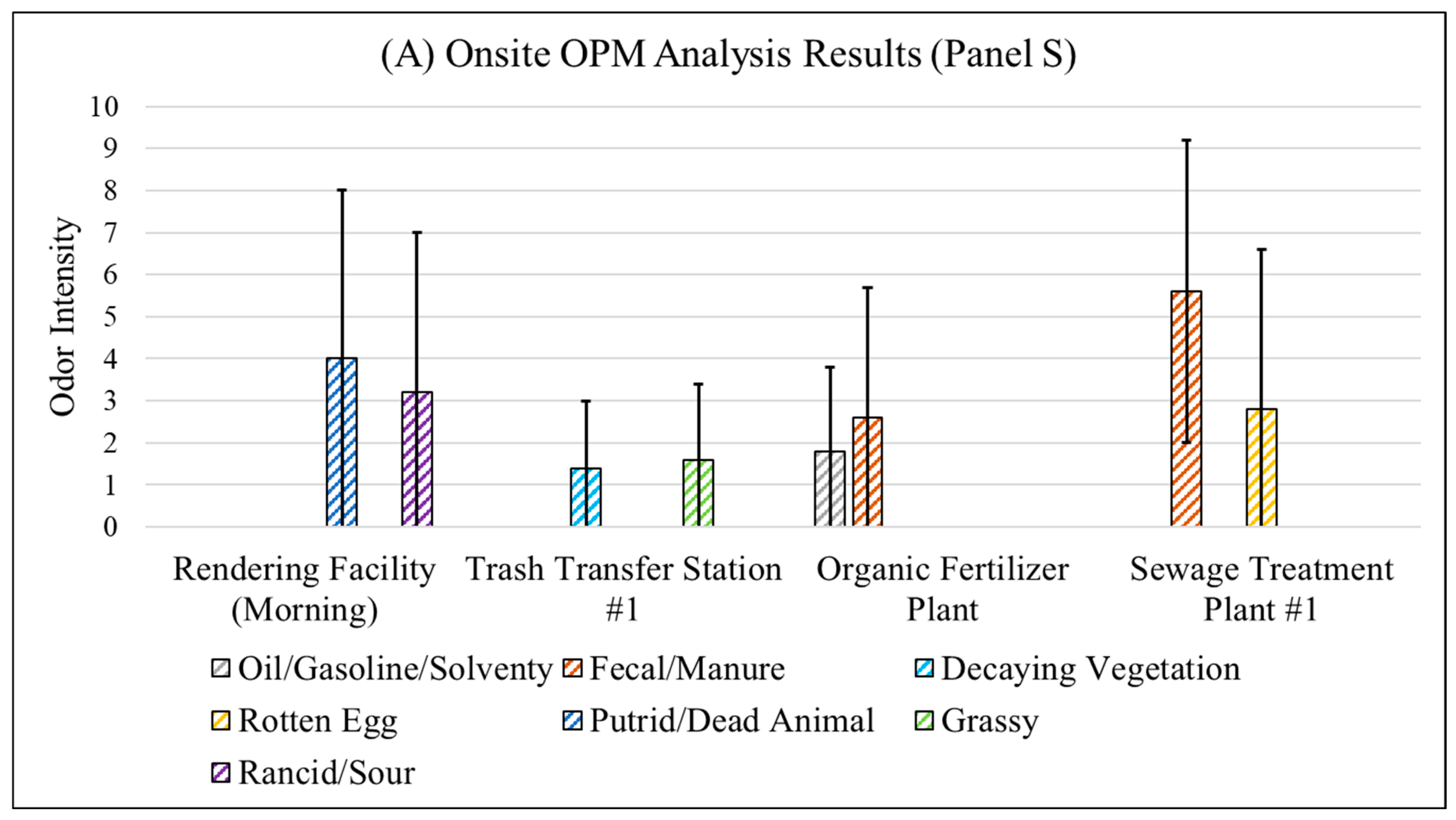
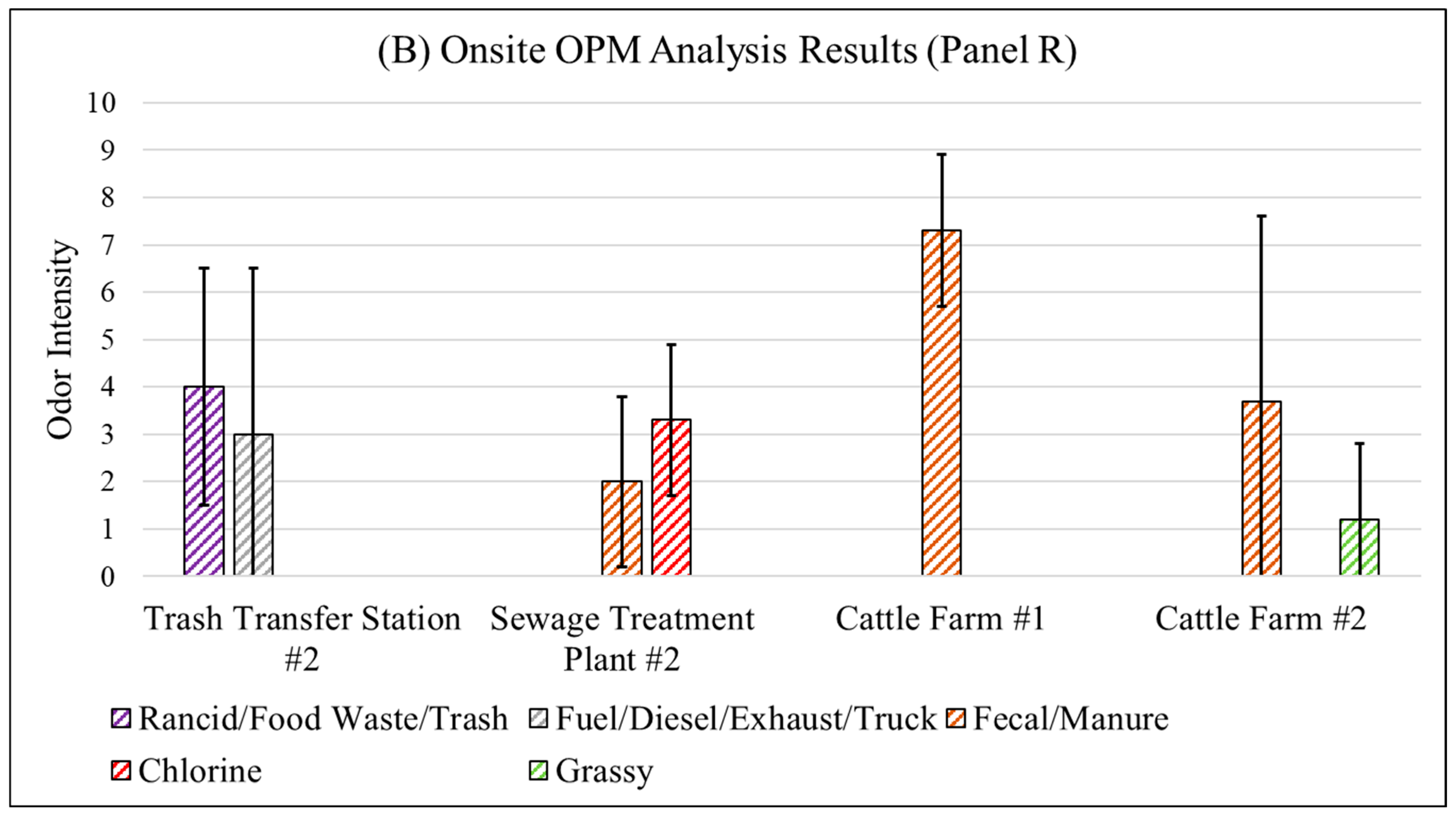
3.4.1. Fenceline Analysis
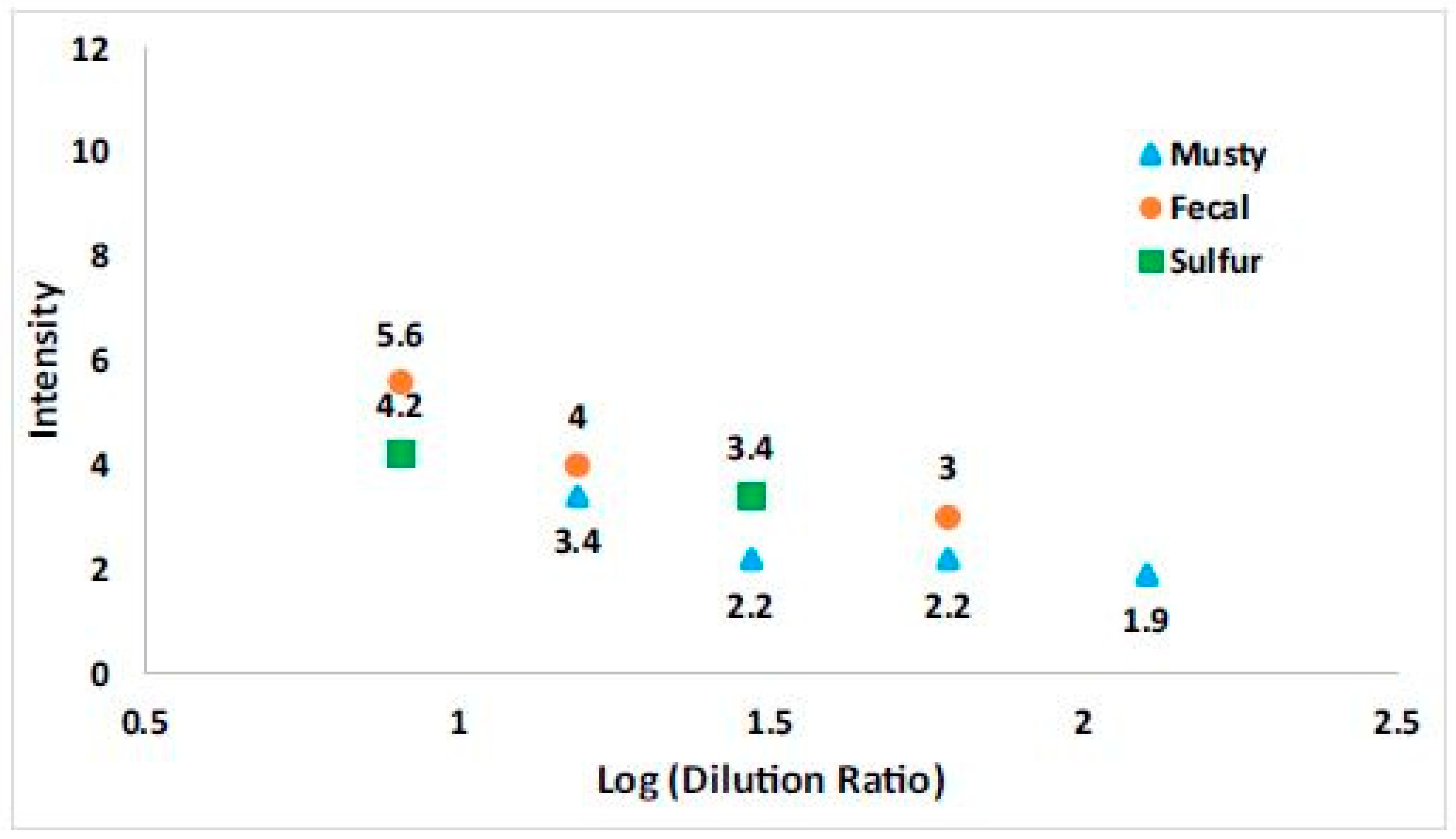
3.4.2. Loss of Sensitivity During Laboratory Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Perception of Odor Mixtures
4.2. High Variance in Individual Odor Intensity Values
4.3. Loss of Sensitivity with Sampling Bag Use
4.4. Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piccardo, M.T.; Geretto, M.; Pulliero, A.; Izzotti, A. Odor emissions: A public health concern for health risk perception. Environ. Res. 2021, 204, 112121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokowa, A.; Diaz, C.; Koziel, J.; Mcginley, M.; Barclay, J.; Schauberger, G.; Guillot, J.-M.; Sneath, R.; Capelli, L.; Zorich, V.; et al. Summary and overview of the odour regulations worldwide. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Designation: E679 – 19; Standard Practice for Determination of Odor and Taste Thresholds by a Forced-Choice Ascending Concentration Series Method of Limits. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.D.; Beaman, A.L.; Winter, P. Olfactometric characterisation of sludge odours. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Vitko, T.G.; Suffet, I.H. A new method for evaluating nuisance of odorants by chemical and sensory analyses and the assessing of masked odors by olfactometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 862, 160905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitko, T.G.; Cowden, S.; Suffet, I.H. Evaluation of bioscrubber and biofilter technologies treating wastewater foul air by a new approach of using odor character, odor intensity, and chemical analyses. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffet, I.; Braithwaite, S.; University of California, Los Angeles. Odor Complaints, Health Impacts and Monitoring Methods. 2019. Available online: https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/sites/default/files/classic/research/apr/past/18rd010.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Brancher, M.; Piringer, M.; Knauder, W.; Wu, C.; Griffiths, K.D.; Schauberger, G. Are empirical equations an appropriate tool to assess separation distances to avoid odour annoyance? Atmosphere 2020, 11, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.M.; Alvarez-Gaitan, J.P.; Stuetz, R.M. Review of the effects of wastewater biosolids stabilization processes on odor emissions. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1515–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 24th ed.; APHA Press: Washington DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Suffet, I.H.; Braithwaite, S.; Zhou, Y.; Bruchet, A. The drinking water taste-and-odour wheel after 30 years. In Taste and Odour in Source and Drinking Water: Causes, Controls, and Consequences; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawko, C.; Verriele, M.; Hucher, N.; Crunaire, S.; Leger, C.; Locoge, N.; Savary, G. A review of environmental odor quantification and qualification methods: The question of objectivity in sensory analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C. Oral referral: On the mislocalization of odours to the mouth. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 50, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechner, G.T. Elemente der Psychophysik; Breitkopf u. Härtel: Leipzig, Germany, 1860; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Suffet, I.H.; Decottignies, V.; Zhou, Y.; Bian, Y.; Vitko, T.G. An evaluation of masking nuisance odors from a source by chemical and sensory analyses. Water Environ. Res. 2023, 95, e10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curren, J.; Hallis, S.A.; Snyder, C.C.L.; Suffet, I.M.H. Identification and quantification of nuisance odors at a trash transfer station. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hallis, S.A.; Vitko, T.; Suffet, I.H. Identification, quantification and treatment of fecal odors released into the air at two wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlingame, G.A. Odor profiling of environmental odors. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffet, I.H.M.; Decottignies, V.; Senante, E.; Bruchet, A. Sensory Assessment and Characterization of Odor Nuisance Emissions during the Composting of Wastewater Biosolids. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Gong, H.; Suffet, I.H. The Use of the Odor Profile Method with an “Odor Patrol” Panel to Evaluate an Odor Impacted Site near a Landfill. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, M. The variation of odor characteristics of wastewater sludge treated by advanced anaerobic digestion (AAD) and the contribution pattern of key odorants. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 840, 156722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curren, J. Characterization of Odor Nuisance, University of California, Los Angeles, 2012. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/characterization-odor-nuisance/docview/1159141549/se-2?accountid=14512 (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; APHA Press: Washington DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Practices for Referencing Suprathreshold Odor Intensity; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curren, J.; Snyder, C.L.; Abraham, S.; Suffet, I.H. Comparison of two standard odor intensity evaluation methods for odor problems in air or water. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 69, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Kingdom. Two Sample T-Test Calculator (Welch’s T-Test). Statskingdom. Available online: https://www.statskingdom.com/150MeanT2uneq.html (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Doty, R.L. The Smell Identification Test: Administration Manual; Sensonics, Incorporated: Schärding, Austria, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y. A Unique Approach of Using the Odor Profile Method and Persistency Curves to Evaluate Odor Nuisance. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5xh2j0sc (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Laing, D.G.; Jinks, A.L. Psychophysical analysis of complex odor mixtures. Chim. Int. J. Chem. 2001, 55, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; An, W.; Cao, N.; Yang, M.; Gu, J.; Zhang, D.; Lu, N. Quantitative method to determine the regional drinking water odorant regulation goals based on odor sensitivity distribution: Illustrated using 2-MIB. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffet, I.H.; Schweitze, L.; Khiari, D. Olfactory and chemical analysis of taste and odor episodes in drinking water supplies. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2004, 3, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlingame, G.A.; Suffet, I.H.; Khiari, D.; Bruchet, A.L. Development of an odor wheel classification scheme for wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
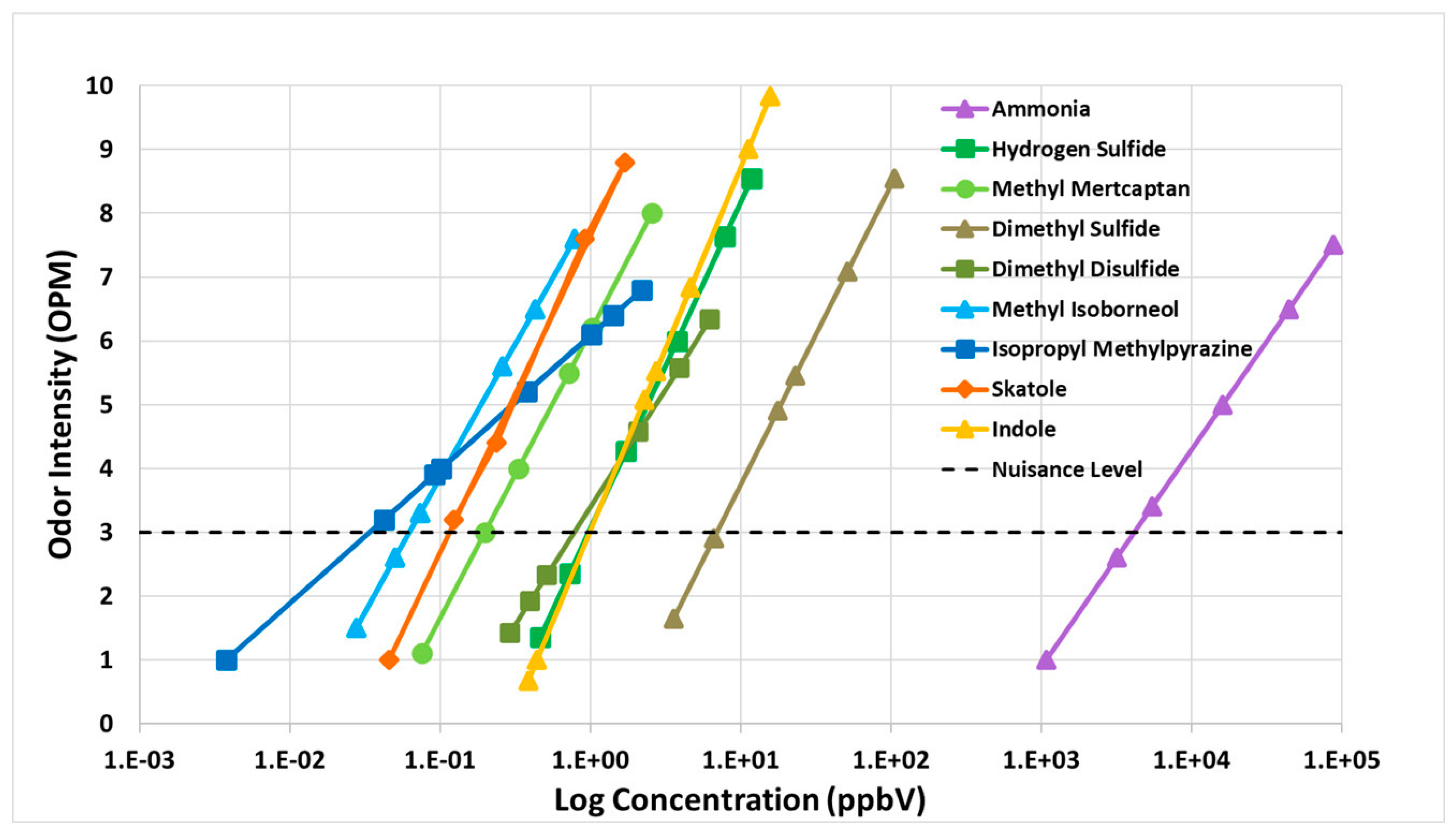
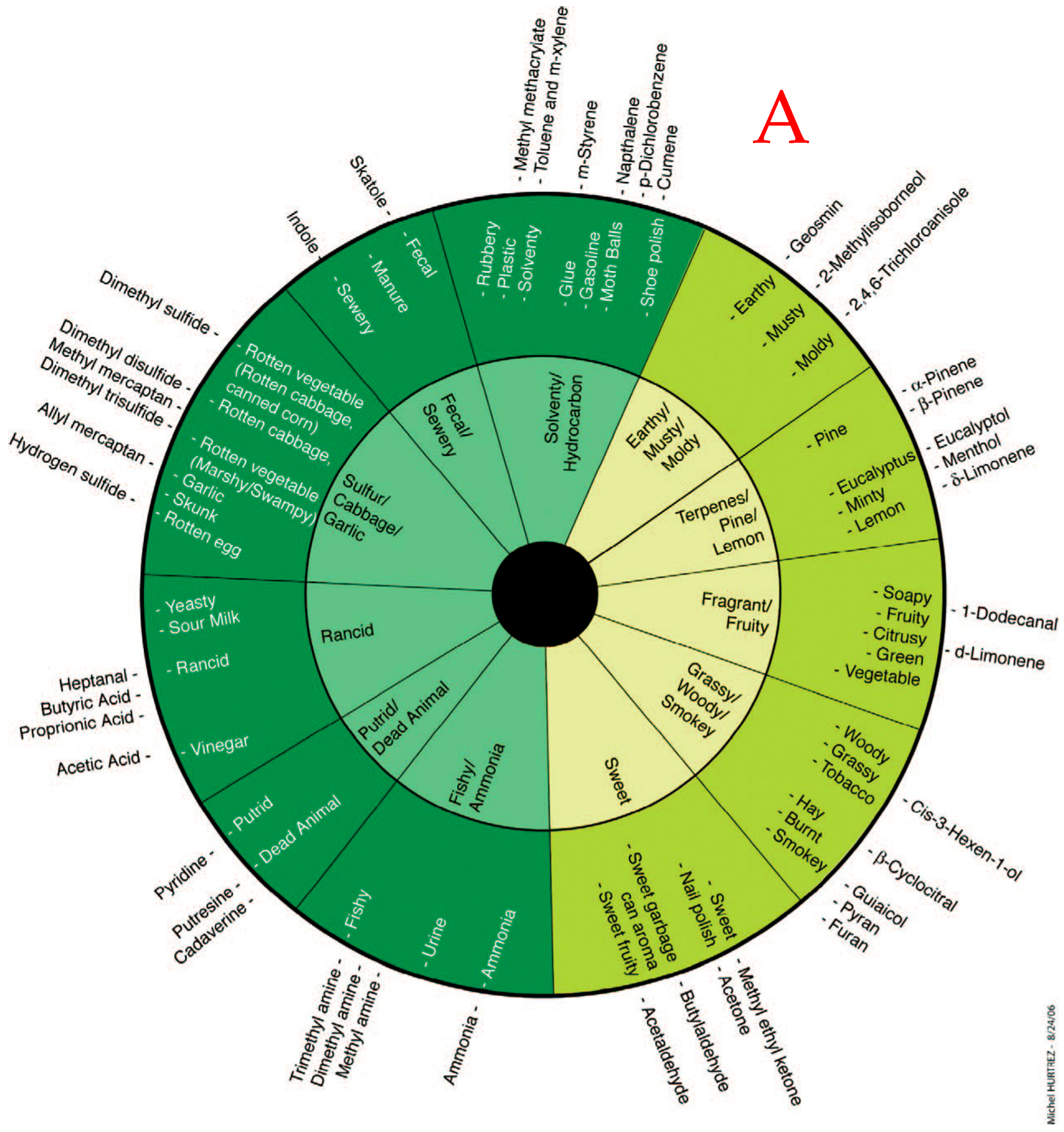





| # | Odorous Compound | Odor Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Indole | Fecal |
| 2 | Cumene | Solvent |
| 3 | MTBE | Sweet Solvent |
| 4 | Geosmin | Earthy |
| 5 | 2-MIB | Musty |
| 6 | cis-3-Hexen-1-ol | Grassy |
| 7 | DMS | Canned Corn |
| 8 | DMDS | Decaying Vegetation |
| 9 | Sodium Sulfide * | Rotten Egg |
| 10 | n-Butyric Acid | Rancid |
| 11 | 1-Butanol | Alcohol |
| 12 | (+)-Limonene | Lemon |
| 13 | MMA | Plastic |
| 14 | Phenol | Medicinal |
| 15 | Ethyl Acetate | Sweet |
| 16 | Guaiacol | Smokey |
| 17 | Methyl Mercaptan | Natural Gas |
| 18 | α-Pinene | Pine |
| 19 | IPMP | Moldy |
| 20 | n-Octane | Hydrocarbon |
| Intensity Value | Odor Strength | Sugar Solution Concentration (%) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Odor Free | 0 | None |
| 1 | Threshold | Not Applicable | Detection Threshold |
| 2 | Very Weak | Not Applicable | Recognition Threshold |
| 3 | Action Level [6] | Not Applicable | The value of 3 is only a threshold for average intensity value, not for individual response. A higher average is expected to be a nuisance problem. |
| 4 | Weak | 5 | None |
| 6 | Weak–Moderate | Not Applicable | None |
| 8 | Moderate | 10 | Uncomfortable to Smell for Extended Periods [5] |
| 10 | Moderate–Strong | Not Applicable | Very Uncomfortable to Smell for Extended Periods [5] |
| 12 | Strong | 12 | Unbearable to Smell Even for Short Periods [5] |
| Test Session | Session A | Session B | Session C | Session D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Name | Sensitivity Test #1 | Sensitivity Test #2 | Differentiation Test #1 | Differentiation Test #2 | Differentiation Test #1 | Differentiation Test #2 | Sensitivity Test (Air) * #1 | Sensitivity Test (Air) * #2 |
| Odor(s) Presented to Panel S | 1 Canned Corn + 2 Odorless | 1 Grassy + 2 Odorless | 1 Rancid + 2 Solventy | 1 Moldy + 2 Grassy | 1 Fecal + 2 Alcohol | 1 Medicinal + 2 Musty | 1 Fecal + 2 Odorless | 1 Canned Corn + 2 Odorless |
| Odor(s) Presented to Panel R | 1 Canned Corn + 2 Odorless | 1 Grassy + 2 Odorless | 1 Rancid + 2 Solventy | 1 Moldy + 2 Grassy | 1 Fecal + 2 Alcohol | 1 Medicinal + 2 Musty | Not Conducted | Not Conducted |
| Test Session | Session #1 | Session #2 | Session #3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixture | 2 Odors | 3 Odors | 4 Odors | 2 Odors | 3 Odors | 4 Odors | 4 Odors (Air) * |
| Odor(s) Presented to Panel S | Fecal, Rancid | Canned Corn, Moldy, Rancid | Pine, Lemon, Earthy, Grassy | Not Conducted | Earthy, Moldy, Fecal | Rotten Egg, Canned Corn, Decaying Vegetation, Rancid | Canned Corn, Lemon Rancid, Fecal |
| Odor(s) Presented to Panel R | Fecal, Rancid | Canned Corn, Moldy, Rancid | Garlic, Earthy, Medicinal, Lemon | Musty, Lemon | Earthy, Moldy, Fecal | Canned Corn, Decaying Vegetation, Fecal, Rancid | Not Conducted |
| Panel | Sample Name | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Panel S | Rendering Facility (Morning) | Trucks carrying dead animals were observed at the entrance. |
| Rendering Facility (Afternoon) | No truck was present. | |
| Trash Transfer Station #1 | None | |
| Organic Fertilizer Plant | None | |
| Landfill | None | |
| Sewage Treatment Plant #1 | None | |
| Panel R | Trash Transfer Station #2 | Trucks carrying trash were observed at the entrance. |
| Sewage Treatment Plant #2 | A truck entered the entrance with unknown load. | |
| Cattle Farm #1 | Cattle were denser and closer to the fenceline compared to cattle farm #2. | |
| Cattle Farm #2 | None |
| Panel | Normosmia Case(s) | Mild Microsmia Case(s) | Moderate Microsmia Case(s) | Severe Microsmia Case(s) | Total Anosmia Case(s) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panel S | 0 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| Panel R | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, Z.; Bader, T.; Lee, L.F.; McDaniels, R.; Suffet, I.H. Training a Regulatory Team to Use the Odor Profile Method for Evaluation of Atmospheric Malodors. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040362
Yin Z, Bader T, Lee LF, McDaniels R, Suffet IH. Training a Regulatory Team to Use the Odor Profile Method for Evaluation of Atmospheric Malodors. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(4):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040362
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Zhihang, Tamara Bader, Lily F. Lee, Regina McDaniels, and Irwin H. (Mel) Suffet. 2025. "Training a Regulatory Team to Use the Odor Profile Method for Evaluation of Atmospheric Malodors" Atmosphere 16, no. 4: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040362
APA StyleYin, Z., Bader, T., Lee, L. F., McDaniels, R., & Suffet, I. H. (2025). Training a Regulatory Team to Use the Odor Profile Method for Evaluation of Atmospheric Malodors. Atmosphere, 16(4), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040362










