Aerodynamic and Dry Deposition Effects of Roadside Trees on NOx Concentration Changes on Roadways and Sidewalks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
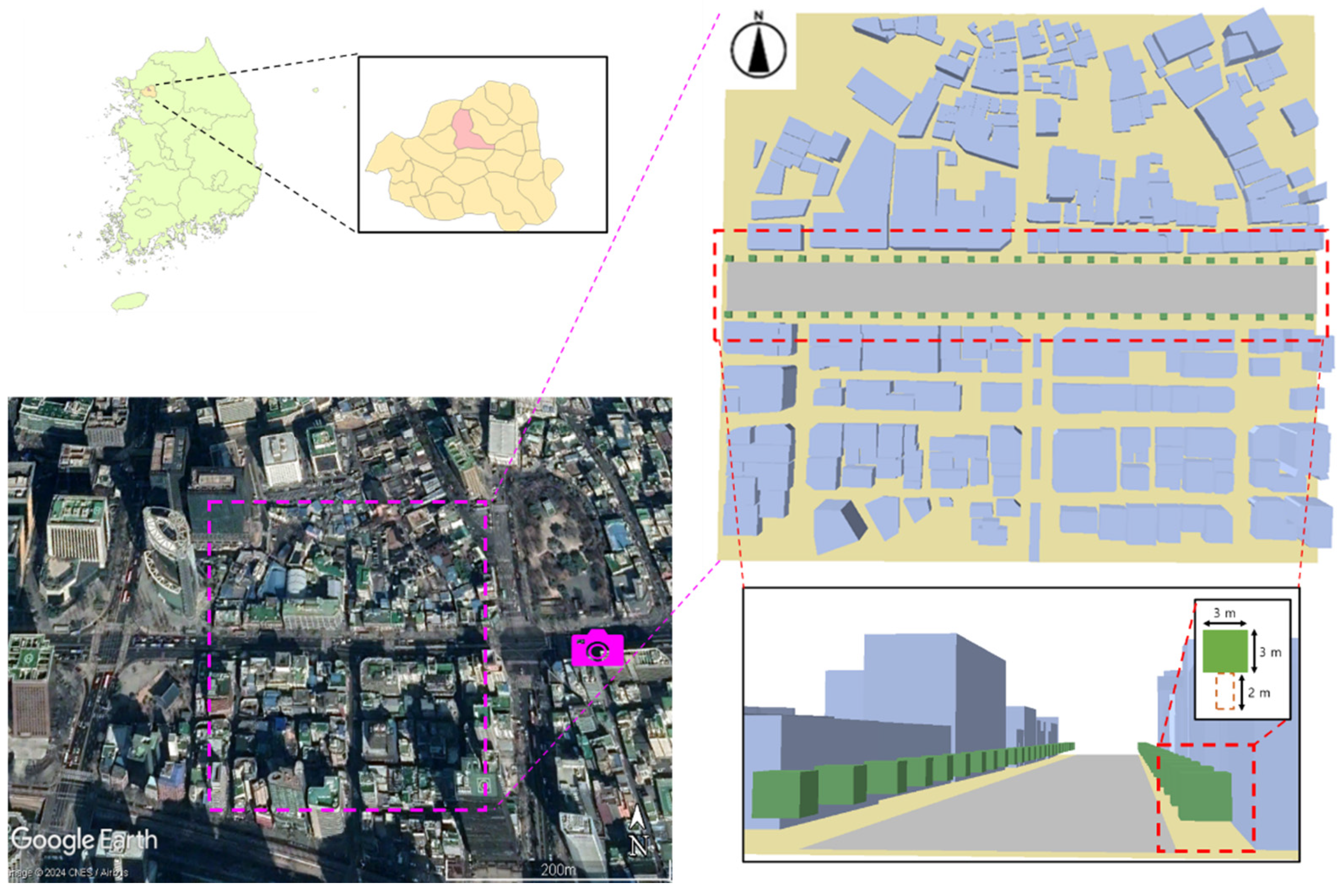
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Measurements
2.3. CFD Model Setup
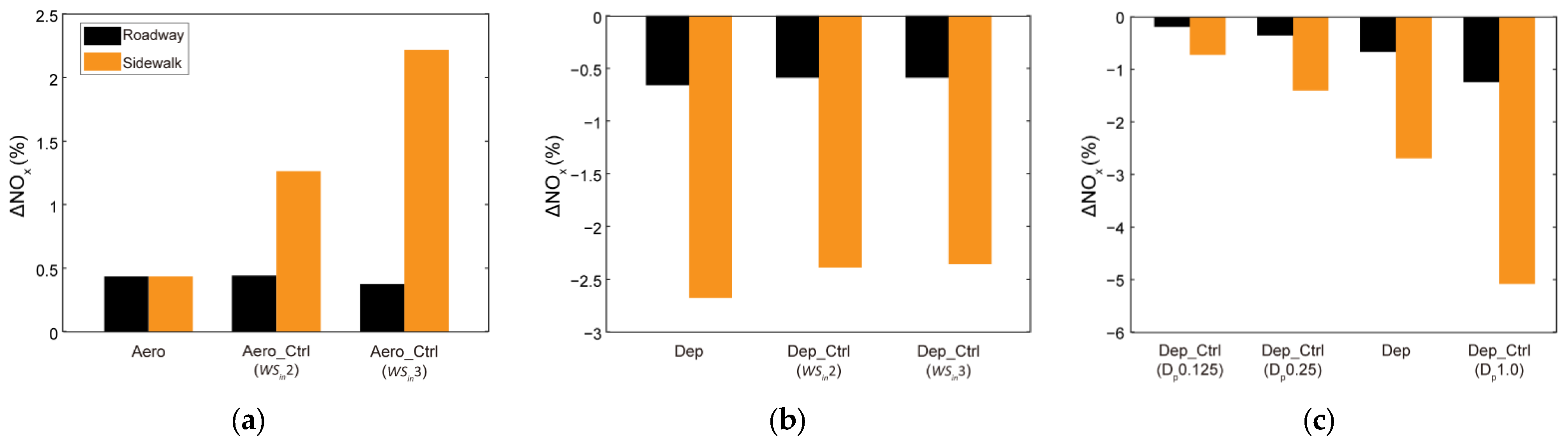
3. Results and Discussion
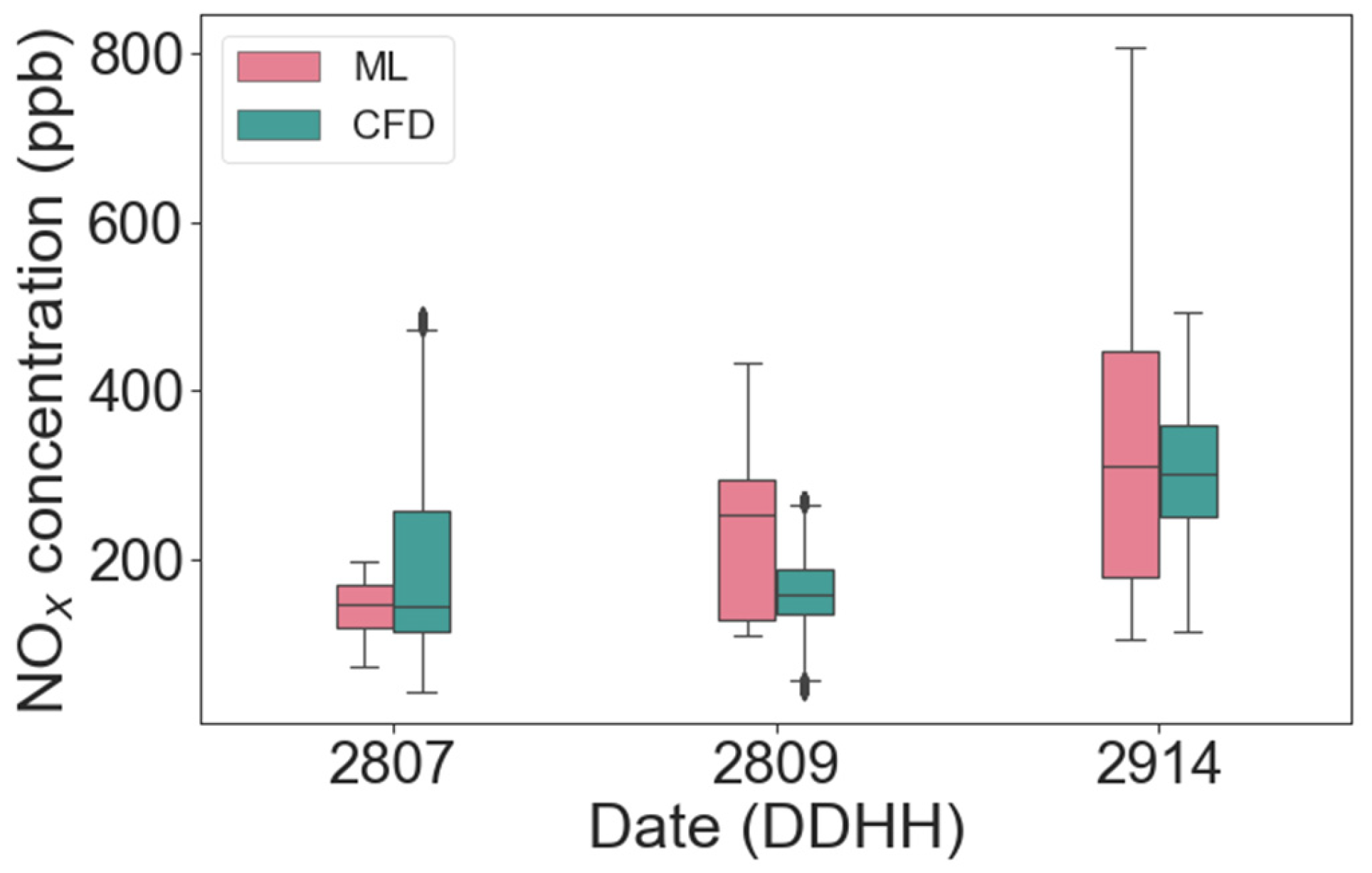
3.1. Validation of CFD Model
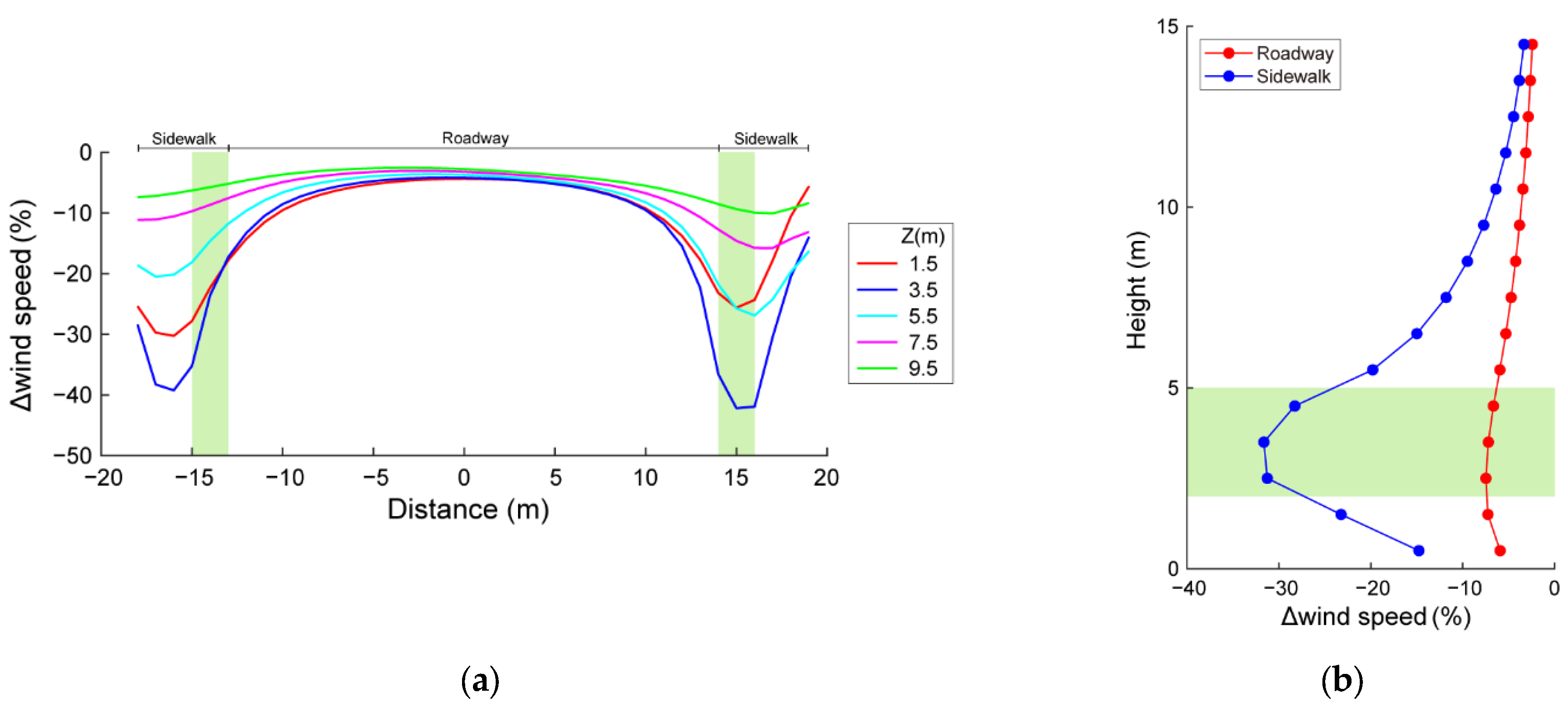
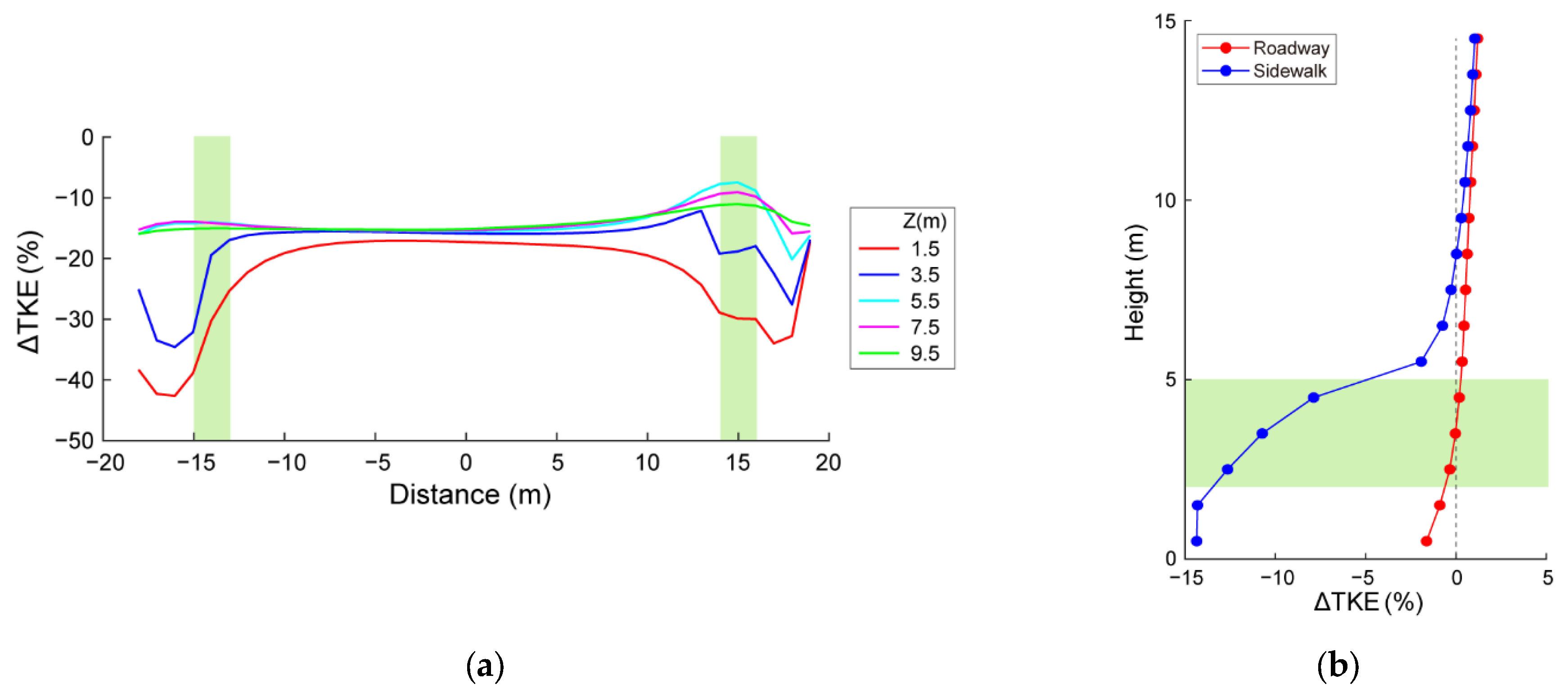
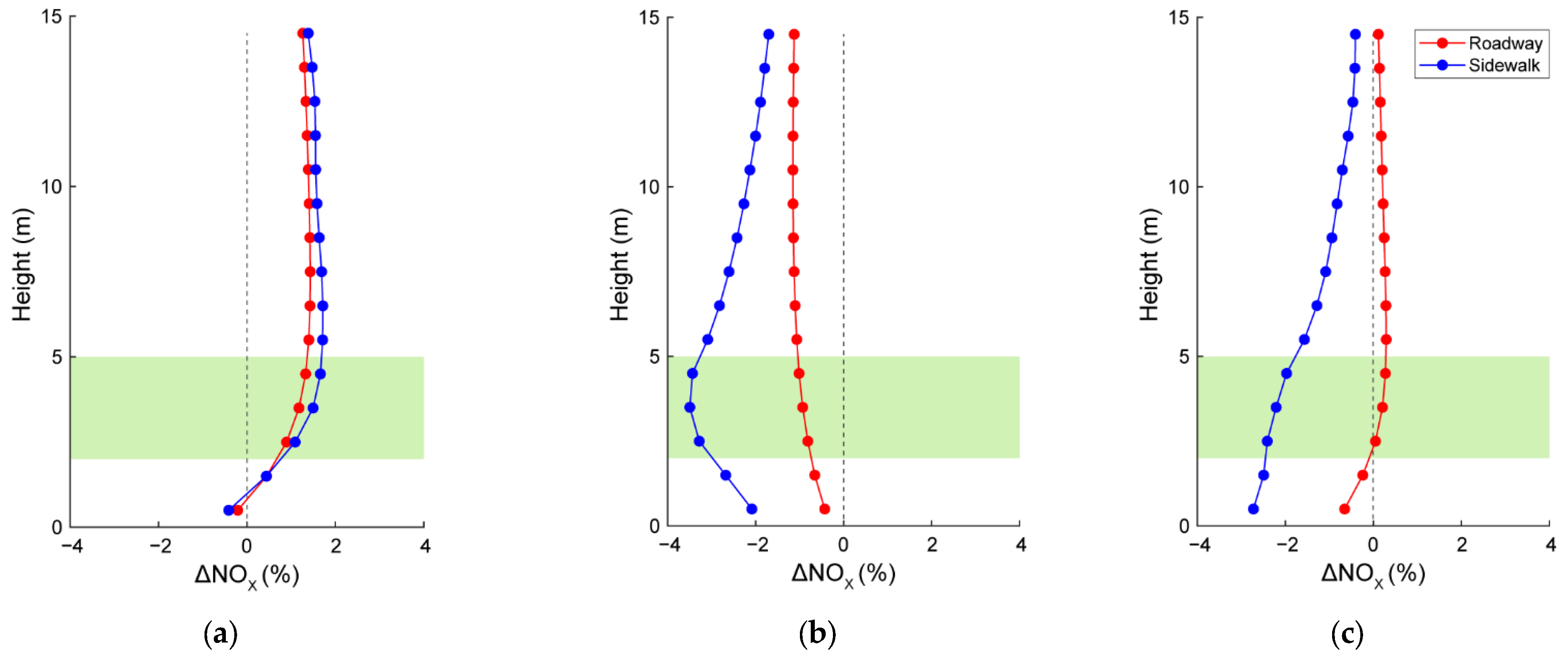
3.2. Effects of Roadside Trees on NOx Concentration Distribution
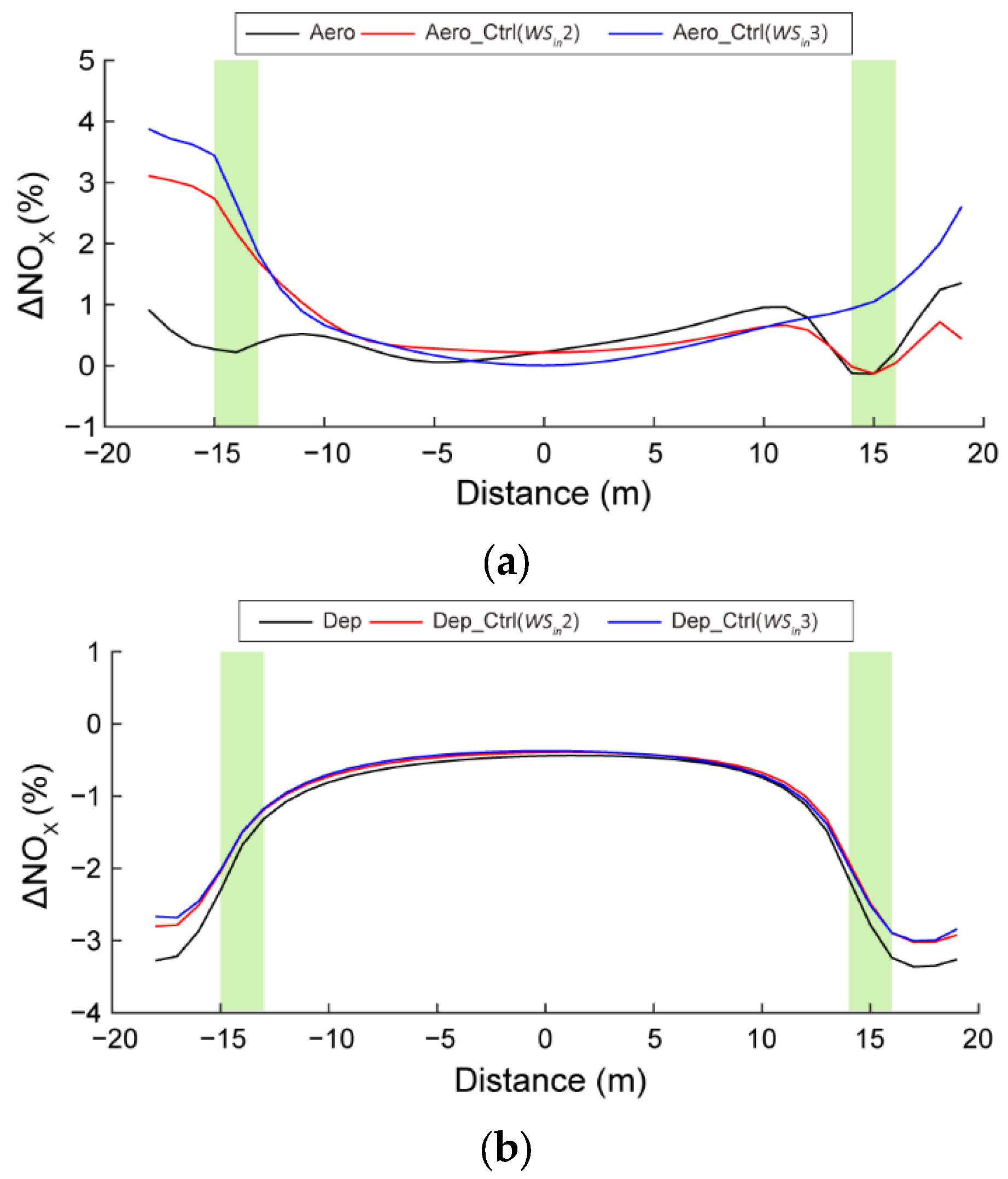
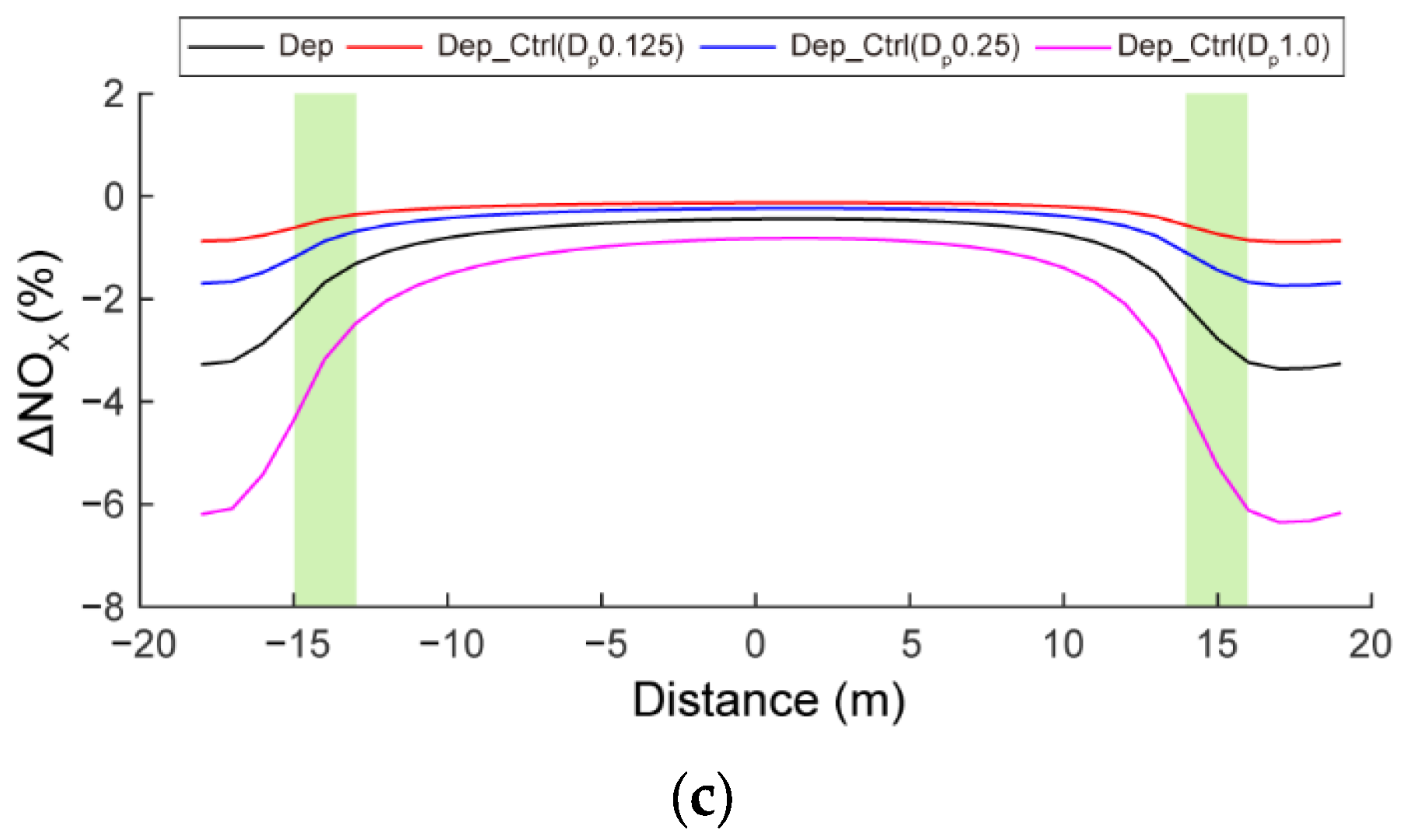
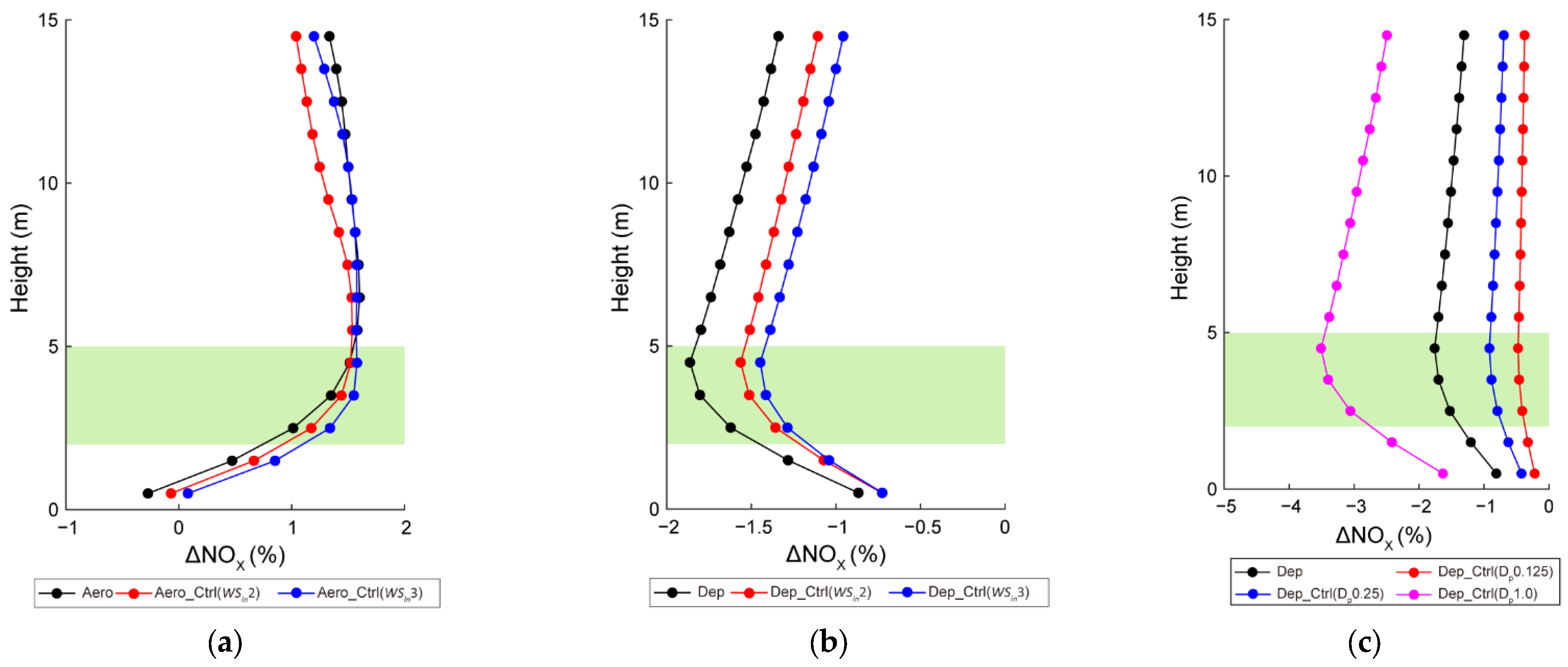
3.3. Sensitivities to Wind Speed and Dry Deposition Velocity
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hang, J.; Li, Y.; Sandberg, M.; Buccolieri, R.; Di Sabatino, S. The influence of building height variability on pollutant dispersion and pedestrian ventilation in idealized high-rise urban areas. Build. Environ. 2012, 56, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zong, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, H. Study on the influence of meteorological conditions and the street side buildings on the pollutant dispersion in the street canyon. Build. Simul. 2016, 9, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, B.; Shi, Y.; Marvin, S.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, G. Air pollution dispersal in high density urban areas: Research on the triadic relation of wind, air pollution, and urban form. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Yu, C.W. Impact Factors on Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion in Urban Street Canyons and Comprehensive Simulations: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 6, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.-S. Impact of building configuration on air quality in street canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4519–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, A.W.M.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Salim, S.M.; Saqr, K.M. A review on the flow structure and pollutant dispersion in urban street canyons for urban planning strategies. Simulation 2014, 90, 892–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ou, C.; Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Gao, P.; Hang, J. Numerical studies of passive and reactive pollutant dispersion in high-density urban models with various building densities and height variations. Build. Environ. 2020, 177, 106916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lei, C.; Liu, C.H.; Perez, P.; Forehead, H.; Kong, S.; Zhou, J.L. A review of strategies for mitigating roadside air pollution in urban street canyons. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, S. Superblocks for the Design of New Cities and Renovation of Existing Ones: Barcelona’s Case. In Integrating Human Health into Urban and Transport Planning; A Framework; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, N.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; Khreis, H.; Cirach, M.; Andrés, D.; Ballester, J.; Bartoll, X.; Daher, C.; Deluca, A.; Echave, C.; et al. Changing the urban design of cities for health: The superblock model. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Gao, Z.; Buccolieri, R.; Zhang, M.; Shen, J. Effect of greening on pollutant dispersion and ventilation at urban street intersections. Build. Environ. 2021, 203, 108075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Juan, Y.H.; Lee, Y.T.; Wen, C.Y.; Yang, A.S. Effects of urban tree planting on thermal comfort and air quality in the street canyon in a subtropical climate. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, N.R.; Han, S.W.; Ko, B. Effects of Green Network Management of Urban Street Trees on Airborne Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.F.; Wen, Y.B.; Chen, H.; Tan, Z.C.; Yao, Y.H.; Zhao, F.Y. Airflow Mitigation and Pollutant Purification in an Idealized Urban Street Canyon with Wind Driven Natural Ventilation: Cooperating and Opposing Effects of Roadside Tree Plantings and Non-Uniform Building Heights. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 92, 104483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, S.; Kurppa, M.; Auvinen, M.; Hellsten, A.; Järvi, L. Large-Eddy Simulation of the Optimal Street-Tree Layout for Pedestrian-Level Aerosol Particle Concentrations—A Case Study from a City-Boulevard. Atmos. Environ. X 2020, 6, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccolieri, R.; Gatto, E.; Manisco, M.; Ippolito, F.; Santiago, J.L.; Gao, Z. Characterization of Urban Greening in a District of Lecce (Southern Italy) for the Analysis of CO2 Storage and Air Pollutant Dispersion. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccolieri, R.; Santiago, J.-L.; Rivas, E.; Sáanchez, B. Reprint of: Review on urban tree modelling in CFD simulations: Aerodynamic, deposition and thermal effects. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 37, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Simeja, D.; Ren, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H. Influence of Urban Road Green Belts on Pedestrian-Level Wind in Height-Asymmetric Street Canyons. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ooka, R.; Kikumoto, H.; Kim, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Flageul, C.; Sartelet, K. Impact of gas dry deposition parameterization on secondary particle formation in an urban canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 333, 120633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Flageul, C.; Maison, A.; Carissimo, B.; Sartelet, K. Impact of trees on gas concentrations and condensables in a 2-D street canyon using CFD coupled to chemistry modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, L.; Karlsson, E.; Jönsson, P. Aspects of Particulate Dry Deposition in the Urban Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.; Andrade, H.; Vaz, T. The cooling effect of green spaces as a contribution to the mitigation of urban heat: A case study in Lisbon. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 2186–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, D.S.; Kang, G.; Yang, M.; Kim, J.J. How trees’ drag and cooling effects influence airflow and temperature distributions around a street canyon. Build. Environ. 2024, 264, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhijith, K.V.; Kumar, P.; Gallagher, J.; McNabola, A.; Baldauf, R.; Pilla, F.; Broderick, B.; Di Sabatino, S.; Pulvirenti, B. Air pollution abatement performances of green infrastructure in open road and built-up street canyon environments—A review. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 162, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, R.; Samson, R.; Alonso, R.; Amorim, J.H.; Cariñanos, P.; Churkina, G.; Fares, S.; Thiec, D.L.; Niinemets, Ü.; Mikkelsen, T.N.; et al. Functional traits of urban trees: Air pollution mitigation potential. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, J.A.; Williams, D.E.; Laing, G.; Kingham, S.; Dirks, K.; Longley, I.; Henshaw, G.S. The influence of vegetation on the horizontal and vertical distribution of pollutants in a street canyon. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanjean, A.P.R.; Gallagher, J.; Monks, P.S.; Leigh, R.J. Ranking current and prospective NO2 pollution mitigation strategies: An environmental and economic modelling investigation in Oxford Street, London. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, G. Leaf Nitrogen Dioxide Uptake Coupling Apoplastic Chemistry, Carbon/Sulfur Assimilation, and Plant Nitrogen Status. Plant Cell Rep. 2010, 29, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, G.M. Atmospheric Deposition of Nutrients and Pollutants in North America: An Ecological Perspective. Ecol. Appl. 1994, 4, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantozzi, F.; Monaci, F.; Blanusa, T.; Bargagli, R. Spatio-temporal variations of ozone and nitrogen dioxide concentrations under urban trees and in a nearby open area. Urban Clim. 2015, 12, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Bai, H.; Gao, H.O. Trees help reduce street-side air pollution: A focus on cyclist and pedestrian exposure risk. Build. Environ. 2023, 229, 109923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hong, B.; Jiang, R.; Yan, S.; Zhou, Y. The Effect of Vegetation Enhancement on Particulate Pollution Reduction: CFD Simulations in an Urban Park. Forests 2019, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, J.-A.E.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Wilson, J.G. Spatial attenuation of ambient particulate matter air pollution within an urbanised native forest patch. Urban For. Urban Green. 2009, 8, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, J.; Han, M.; Li, X.; Xu, R.; Ma, H.; Kumar, P. Understanding the Impacts of Street Greening Patterns and Wind Directions on the Dispersion of Fine Particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.D.; Li, M.Z.; Ren, S.Q.; Wang, M.J.; Cui, P.Y. Impacts of Tree-Planting Pattern and Trunk Height on the Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion inside a Street Canyon. Build. Environ. 2019, 165, 106385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kwak, K.H. Assessing 3-D Spatial Extent of Near-Road Air Pollution around a Signalized Intersection Using Drone Monitoring and WRF-CFD Modeling. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020, 17, 6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Woo, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-B.; Bae, G.-N.; Ma, Y.-I.; Sunwoo, Y.; Baik, J.-J. On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.; Jeong, S.; Park, H.; Park, C.; Kwak, K.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.; Chang, J.S.; Kang, H.; et al. Co-benefit potential of urban CO2 and air quality monitoring: A study on the first mobile campaign and building monitoring experiments in Seoul during the winter. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-C. A spatial distribution analysis and time series change of PM10 in Seoul city. J. KAGIS 2014, 17, 61–69. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- TOPIS. Seoul Transport Operation & Information Service Center. Seoul, Korea. 2020. Available online: https://topis.seoul.go.kr/refRoom/openRefRoom_2.do (accessed on 12 February 2025). (In Korean).
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.-B.; Woo, D.; Bae, G.-N. Influence of wind direction and speed on the transport of particle-bound PAHs in a roadway environment. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Woo, D.; Lee, S.-B.; Bae, G.-N. On-Road Measurements of Ultrafine Particles and Associated Air Pollutants in a Densely Populated Area of Seoul, Korea. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kwak, K.-H.; Lee, J.Y.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, S.-B.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Bae, G.-N.; Oh, I. Spatial Mapping of a Highly Non-Uniform Distribution of Particle-Bound PAH in a Densely Populated Urban Area. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.-J.; Kim, J.-J.; Fernando, H.J.S. A CFD Model for Simulating Urban Flow and Dispersion. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Kim, J.-J. Development of a computational fluid dynamics model adopting a nested grid system: Flow simulations for ideal and real urban settings. Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutar, M.; Oguz, G. Large eddy simulation of wind flow around parallel buildings with varying configurations. Fluid Dyn. Res. 2002, 31, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, D.; Stalder, M.; Rüegsegger, A.; Galli, U.; Brunold, C. Effects of NO₂ and Nitrate on Sulfate Assimilation in Maize. J. Plant Physiol. 1995, 147, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.W. Interaction between SO2 and NO2 and Their Effects on Photosynthetic Properties of Soybean Glycine max. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A Ecol. Biol. 1983, 32, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J. Air Pollution Removal by Chicago’s Urban Forest. In Chicago’s Urban Forest Ecosystem: Results of the Chicago Urban Forest Climate Project; United States Department of Agriculture: Radnor, PA, USA, 1994; pp. 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, P.E.; Maiheu, B.; Vankerkom, J.; Janssen, S. Improving local air quality in cities: To tree or not to tree? Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Olivardia, F.G.; Matsuo, T.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A. Impacts of the Tree Canopy and Chemical Reactions on the Dispersion of Reactive Pollutants in Street Canyons. Atmosphere 2020, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Qin, H.; Lin, B. Prediction of Wind Environment and Indoor/Outdoor Relationships for PM2.5 in Different Building–Tree Grouping Patterns. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.-L.; Buccolieri, R.; Rivas, E.; Sanchez, B.; Martilli, A.; Gatto, E.; Martín, F. On the Impact of Trees on Ventilation in a Real Street in Pamplona, Spain. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.-L.; Rivas, E.; Sanchez, B.; Buccolieri, R.; Martin, F. The Impact of Planting Trees on NOx Concentrations: The Case of the Plaza de la Cruz Neighborhood in Pamplona (Spain). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccolieri, R.; Gromke, C.; Di Sabatino, S.; Ruck, B. Aerodynamic effects of trees on pollutant concentration in street canyons. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5247–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katul, G.G.; Mahrt, L.; Poggi, D.; Sanz, C. One- and two-equation models for canopy turbulence. Bound. -Layer Meteorol. 2004, 113, 81–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Pađen, I.; García-Sánchez, C. Should we care about the level of detail in trees when running urban microscale simulations? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 101, 105143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Air Emission Inventory and Research Center (NAIR). 2019 National Air Pollutant Emissions Inventory; NAIR: Osong, Republic of Korea, 2022. Available online: https://www.air.go.kr (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Jung, S.; Sung, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, I. Experimental Study on the NO2/NOx Ratio from Exhaust of Diesel Vehicles by Chassis Dynamometer. Korean Hydrog. New Energy Soc. 2017, 28, 220–224. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.; Lee, J. Estimating the Effectiveness of Vehicle Emission Regulations for Reducing NOx from Light-Duty Vehicles in Korea Using On-Road Measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Lin, B.; Qin, H. Numerical Investigation on the Coupled Effects of Building-Tree Arrangements on Fine Particulate Matter (PM₂.₅) Dispersion in Housing Blocks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 34, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Li, P.; Yu, S.; Chen, W.; He, X. Does street canyon morphology shape particulate matter reduction capacity by street trees in real urban environments? Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 78, 127762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, B.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, C. Observed Vertical Dispersion Patterns of Particulate Matter in Urban Street Canyons and Dominant Influencing Factors. Forests 2024, 15, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Tian, M.; Gao, Y. Impact of various vegetation configurations on traffic fine particle pollutants in a street canyon for different wind regimes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccolieri, R.; Jeanjean, A.P.; Gatto, E.; Leigh, R.J. The Impact of Trees on Street Ventilation, NOx and PM2.5 Concentrations across Heights in Marylebone Rd Street Canyon, Central London. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccolieri, R.; Jeanjean, A.P.; Buccolieri, R.; Eddy, J.; Monks, P.S.; Leigh, R.J. Air Quality Affected by Trees in Real Street Canyons: The Case of Marylebone Neighbourhood in Central London. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 22, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Morakinyo, T.E.; Lam, Y.F. Study of Traffic-Related Pollutant Removal from Street Canyon with Trees: Dispersion and Deposition Perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21652–21668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesely, M.L.; Hicks, B.B. A Review of the Current Status of Knowledge on Dry Deposition. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2261–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasch, J.M. Measurement of Dry Deposition to Surfaces in Deciduous and Pine Canopies. Environ. Pollut. 1987, 44, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranckx, S.; Vos, P.; Maiheu, B.; Janssen, S. Impact of Trees on Pollutant Dispersion in Street Canyons: A Numerical Study of the Annual Average Effects in Antwerp, Belgium. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.L.; Martilli, A.; Martin, F. On Dry Deposition Modelling of Atmospheric Pollutants on Vegetation at the Microscale: Application to the Impact of Street Vegetation on Air Quality. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2017, 162, 451–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Date (DD-MM-YY) | Time (LST) | Wind Direction (°) | Wind Speed (m·s−1) | Air Temperature (°C) | Surface Temperature (°C) | Emission Rate (ppb·s−1) | Traffic Volume (car·h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28-01-19 | 07:00 | 262 * | 4.4 * | 3.4 * | 2.2 | 11.7 | 4123 |
| 09:00 | 295 * | 3.4 * | −0.7 * | 1.2 | 13.1 | 5147 | |
| 29-01-19 | 14:00 | 71 * | 0.7 * | −0.8 * | 5.5 | 25.9 | 8630 |
| Scenario | Effects of Roadside Trees | Wind Speed (m·s−1) | Dry Deposition Velocity (cm·s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerodynamic Effect | Dry Deposition Effect | |||
| noAero_noDep | X 1 | X | 3 | 0 |
| Aero_Dep | O 2 | O | 0.5 | |
| Aero | O | X | 0 | |
| Dep | X | O | 0.5 | |
| Scenario | Effects of Roadside Trees | Wind Speed (m·s−1) | Dry Deposition Velocity (cm·s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerodynamic Effect | Dry Deposition Effect | |||
| Aero_Ctrl () | O 1 | X | 0 | |
| Dep_Ctrl () | X 2 | O | 0.5 | |
| Aero_Ctrl () | O | X | 0 | |
| Dep_Ctrl () | X | O | 0.5 | |
| Dep_Ctrl (Dp0.125) | X | O | 0.125 | |
| Dep_Ctrl (Dp0.25) | X | O | 0.25 | |
| Dep_Ctrl (Dp1.0) | X | O | 1.0 | |
| Time (DD-MM-HH) | Aerodynamic Effect | Dry Deposition Effect | Aerodynamic Effect + Dry Deposition Effect | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roadway | Sidewalk | Roadway | Sidewalk | Roadway | Sidewalk | |
| 28-01-07 | −0.15 | −0.17 | −0.79 | −2.77 | −0.82 | −3.03 |
| 28-01-09 | 0.46 | 2.09 | −0.59 | −2.60 | −0.11 | −0.53 |
| 29-01-14 | 0.66 | −0.02 | −0.64 | −2.69 | 0.09 | −3.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-U.; Lee, S.-B.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.; Kwak, K.-H. Aerodynamic and Dry Deposition Effects of Roadside Trees on NOx Concentration Changes on Roadways and Sidewalks. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030344
Kim Y-U, Lee S-B, Kim CH, Lee S, Kwak K-H. Aerodynamic and Dry Deposition Effects of Roadside Trees on NOx Concentration Changes on Roadways and Sidewalks. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(3):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030344
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yeon-Uk, Seung-Bok Lee, Chang Hyeok Kim, Seonyeop Lee, and Kyung-Hwan Kwak. 2025. "Aerodynamic and Dry Deposition Effects of Roadside Trees on NOx Concentration Changes on Roadways and Sidewalks" Atmosphere 16, no. 3: 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030344
APA StyleKim, Y.-U., Lee, S.-B., Kim, C. H., Lee, S., & Kwak, K.-H. (2025). Aerodynamic and Dry Deposition Effects of Roadside Trees on NOx Concentration Changes on Roadways and Sidewalks. Atmosphere, 16(3), 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030344










