Abstract
Background: As urbanization progresses, the resulting air pollution has become an increasingly severe public health issue, known to exacerbate respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Recent studies suggest that it may also affect blood coagulation mechanisms. In this study, Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis was used to explore the causal relationship between air pollution and pulmonary embolism (PE). Methods: This study employs MR techniques, using genetic variants associated with air pollution exposure to assess their impact on VTE. Data from large-scale genomic studies, including the UK Biobank and OpenGWAS, were analyzed to explore the relationship between genetic susceptibility to air pollution and the risk of pulmonary embolism. The study also conducted multivariable MR analysis, adjusting for potential confounders such as smoking and BMI. Results: The study finds that long-term exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 significantly increases the risk of pulmonary embolism, with the association for PM2.5 being the most significant. The study also indicates that pollutants like PM2.5–10, NO2, and NOx have a smaller but still notable impact on PE risk. Multivariable MR analysis confirmed the robustness of these results, further highlighting the role of air pollution in thrombosis. Conclusions: In conclusion, this study emphasizes the significant causal relationship between air pollution and PE, providing evidence that pollutants like PM2.5, PM10, and NOx contribute to thrombotic events.
1. Backgrounds
With the acceleration of global industrialization and urbanization, air pollution has become one of the major public health challenges, particularly in large cities, where concentrations of pollutants such as fine particulate matter (PM2.5), coarse particulate matter (PM10), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) continue to rise [1]. Air pollution not only directly harms the respiratory and cardiovascular systems but also affects the blood coagulation process through complex biological mechanisms, thereby increasing the risk of thrombosis. A large population-based prospective cohort study has shown that long-term exposure to environmental air pollutants, particularly, PM2.5, NO2, and NOx, increases the risk of both all-cause and cause-specific mortality [2]. Lifestyle factors significantly influence the relationship between air pollution and mortality. These pollutants, especially PM2.5, due to their tiny particle size, are capable of penetrating deep into the lungs, entering the bloodstream, and triggering systemic inflammatory responses and oxidative stress [3,4].
In recent years, the relationship between air pollution and venous thromboembolism (VTE) has attracted increasing attention. VTE, which includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates and is closely linked to changes in blood coagulation, blood flow, and vascular wall function [5,6]. Studies suggest that air pollutants, particularly PM2.5, PM10, and NO2, may increase the risk of VTE by activating the coagulation system, inducing endothelial damage, and promoting systemic inflammation [3,7]. For instance, a Swedish study found a significant correlation between long-term exposure to PM2.5 and the incidence of VTE [6]. Short-term exposure to air pollution is also considered one of the risk factors for acute pulmonary embolism (PE). Relevant research indicates that short-term exposure to PM10 and NO2 may exacerbate blood coagulation, thereby increasing the risk of pulmonary embolism [3,8]. Furthermore, air pollution may contribute to an increased risk of acute cardiovascular events by promoting inflammation, altering blood rheology, and affecting cardiovascular health [9].
The relationship between air pollution and cardiovascular diseases has been widely studied, particularly the impact of PM2.5 on cardiovascular health. Research has shown that air pollution significantly increases the incidence of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases through mechanisms such as promoting systemic inflammation, increasing blood coagulability, inducing vasoconstriction, and accelerating atherosclerosis [10,11,12]. These mechanisms also apply to venous thromboembolism (VTE), with air pollution having a more pronounced effect on VTE, especially in high-risk populations with underlying conditions such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes [3,13].
Although existing studies indicate a certain association between air pollution and VTE, the results are inconsistent across different studies. This may be attributed to factors such as study design, types of pollutants, duration of exposure, and population differences [9]. Furthermore, epidemiological evidence alone cannot establish a direct causal relationship between air pollution and disease. Therefore, further research is needed, particularly in environments with multi-pollutant exposure, to explore the specific effects of different pollutants on the mechanisms of VTE occurrence and their interactions [13].
To overcome these limitations, this study employs Mendelian randomization (MR), a well-established method for objectively assessing causal relationships at the genetic level. The principle of MR is based on the fact that genetic variation is randomly allocated from parents to offspring at conception. As such, genetic variants are independent of potential confounding environmental exposures. MR can be regarded as similar to a randomized controlled trial (RCT), as it uses genetic variation as the randomization method, ultimately providing causal insights. Moreover, the risk estimated by MR reflects lifetime risk, which is longer than the follow-up period in RCTs.
MR uses genetic variants related to the exposure of interest as instrumental variables to infer the potential causal effect on the outcome [14]. The invariance of the instrumental variable ensures lifelong exposure, mitigating the influence of reverse causality. Additionally, the random allocation of alleles for a given single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) during human gametogenesis maximizes the reduction in potential confounding factors, thereby enhancing the robustness of genetic variation analysis [15].
Therefore, in this study, we conducted a comprehensive two-sample MR analysis to explore the potential impact of five common urban air pollutants—PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and others—on pulmonary embolism (PE) in large cities. Considering the interactions between air pollutants, as well as the possible effects of age, gender, smoking, and BMI on the experimental results, we performed further multivariable MR analysis to account for these potential influences. This approach aims to provide new public health strategies for the prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and to offer scientific evidence for policymaking.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
This study is based on several publicly available databases, which are summarized in Table 1. We used summary statistics from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) that do not access any personal information, focusing on five air pollutants (PM2.5, PM2.5–10, PM10, NO2, and nitrogen oxides) and their association with pulmonary embolism (PE) [16]. Since PE is relatively rare, we selected five datasets from different research institutions. These datasets include cases of PE with and without deep vein thrombosis (DVT), PE patients excluding those with acute pulmonary heart disease, PE patients with or without DVT, and data corrected using Firth and Sparse Data Model (SPA) corrections.

Table 1.
Outcome and exposure GWAS samples used in this study.
The exposures investigated in this study are five air pollutants. The sample size for particulate matter is 423,796, while the sample size for NO2 and nitrogen oxides is 456,380, all of which are from European populations. The number of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) is 9,851,867. The GWAS summary statistics were sourced from MRC-IEU. We selected the top five outcome databases by sample size, three of which are from the UK Biobank, and two from MRC-IEU.
The UK Biobank summarizes genetic data for particulate pollutants from 423,796 European participants, including data from 20 study regions across Europe for PM2.5, PM2.5 absorbance, PM10, and PM2.5–10. This study is based on the ESCAPE project (European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects), in which the land use regression model (LUR) was used to estimate the concentration of particulate pollution at participants’ residential addresses [16]. These datasets are publicly available through MRC-IEU OpenGWAS and MR-Base. This output is derived from the GWAS pipeline using pheasant-derived variables from the UK Biobank. Body mass index (BMI), cigarettes smoked per day, and biological sex (age-adjusted) data were obtained from meta-analyses conducted by MRC-IEU, GSCAN, and other GWAS sources.
2.2. Study Design
This study uses Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization (TSMR) and publicly available datasets to assess the causal relationship between five air pollution-related genetic instrumental variables and pulmonary embolism. Specifically, the study is conducted in three steps. First, to elucidate the potential causal relationships, TSMR analysis is performed using instrumental variables related to air pollution, pairing exposure data with outcome databases to investigate the potential effects of five air pollutants on pulmonary embolism under different circumstances. This study used five similar outcome datasets, four of which share the same research scope. Fisher’s combined probability test was employed to calculate the final associations. Second, to eliminate potential confounders, particularly common confounders like smoking and gender differences, these factors were incorporated into a multivariable Mendelian Randomization (MVMR) framework. This step aims to remove non-specific influences and ensure the reliability of subsequent results. Additionally, as there may be interactions between the five air pollutants, potential interactions were further addressed through multivariable analysis to determine the most robust causal relationship between the pollutants and the disease. The GWAS database IDs used in this study are provided in the table below (Table 1).
2.3. MR Assumptions and Genetic Variant Selection
Mendelian randomization studies [17] rely on three core assumptions: (1) Selection of Instrumental Variables (IVs): Genetic variants chosen as IVs should be strongly associated with the exposure of interest—in this case, five air pollutants. To identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) linked to these pollutants and ensure the accuracy of causal inferences with the five pulmonary embolism datasets, the following steps were undertaken. Initially, a stringent genome-wide significance threshold (p < 5 × 10−⁸) was applied. However, due to a limited number of SNPs meeting this criterion, which hindered robust analysis, the threshold was adjusted to p < 5 × 10−⁶ based on existing literature. This adjustment maintained a balance between inclusivity and statistical rigor. A 10,000 kb window with an LD r2 < 0.001 was set to minimize the influence of residual genetic variation and ensure the independence of IVs, aligning with fundamental MR principles. (2) Independence from Confounders: It is essential that genetic variants used as IVs are not associated with confounding variables. This ensures that observed associations between IVs and outcomes are not distorted by unmeasured confounders. (3) Exclusion of SNPs Associated with Outcomes: SNPs that are directly associated with the outcome (p > 5 × 10−⁵) should be excluded to prevent bias in estimating the causal effect of the exposure on the outcome. By adhering to these criteria, the study aims to identify robust and reliable genetic instruments for air pollutants, facilitating accurate assessments of their causal effects on pulmonary embolism.
2.4. Statistical Methods
Mendelian randomization (MR) [18] models using genetic variations as instrumental variables (IVs) rely on three core assumptions: (1) IV Assumption I (Relevance Assumption): The genetic variation (G) is associated with the exposure (X). (2) IV Assumption II (Independence Assumption): The genetic variation (G) is independent of confounding factors (U). (3) IV Assumption III (Exclusion Restriction Assumption): The genetic variation (G) affects the outcome (Y) only through exposure (X) and not through other pathways. Assumptions II and III together are referred to as independence from pleiotropy.
Due to the inherent biological characteristics of genetic variations, issues such as insufficient representativeness of genetic variations for the exposure and pleiotropy often lead to invalid MR model estimates. Insufficient representativeness of genetic variations typically reduces the statistical power of the MR model, while pleiotropy often leads to biased effect estimates. For Assumption I, the F-statistic is used for evaluation. When F > 10, the relevance assumption is considered to be satisfied, indicating the absence of weak instrument bias [17,19].
2.5. TSMR Analysis
We first performed Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis using the “TwosampleMR” R package [20]. Consistent with most previous studies, we employed the Inverse Variance Weighting (IVW) method [21] as the primary analysis because of its robustness in MR research, allowing for a more accurate determination of causal relationships between various air pollutants and pulmonary embolisms. The IVW method regresses the correlation between SNP-exposure based on the correlation between SNP-outcome, using the inverse of the squared standard error of the SNP-outcome correlation to provide a weighted estimate of the overall causal effect. Additionally, we used other MR methods, including MR-Egger regression [22], weighted median [23], and maximum likelihood, as sensitivity analyses. This multi-method approach ensures the robustness of the results. Statistical analysis was conducted using the TSMR software (version 4.4.1) in the RStudio environment. The threshold for significance was set at p < 0.05, with odds ratios (ORs) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) as the main effect measures.
Furthermore, we employed multivariable Mendelian randomization (MVMR) to account for potential confounders. The MVMR analysis was conducted using the mr_mvivw, mr_mvegger, and mr_mvlasso functions from the “mendelanrandomization” R package. MVMR evaluates the impact of multiple exposures on respiratory diseases, considering potential mediators or confounders [24]. MVMR has been shown to effectively adjust for these effects [25]. We also applied lasso analysis to assess the independent impact on pulmonary embolism, providing conclusions from different perspectives based on the data.
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis
We employed the MR-Egger regression model to test IV Assumption III (exclusion restriction) and ensure the accuracy of the results. The intercept from the MR-Egger regression provides an estimate of the average pleiotropic effect for all SNPs under the InSIDE assumption. If the intercept is significantly different from zero, it suggests the presence of horizontal pleiotropy [26]. Horizontal pleiotropy was tested using the mr_pleiotropy_test function in the “TwoSampleMR” R package. If MR-Egger detects pleiotropy, the MR PRESSO method is used to identify and remove potential outliers. To assess whether any single SNP is driving the causal effect, we performed a leave-one-out analysis. Cochran’s Q statistic was used to test for heterogeneity among SNPs. If the Q statistic p-value is greater than 0.05, it indicates that there is no heterogeneity among the SNPs, and the results do not require adjustment for heterogeneity. If the p-value is less than 0.05, a random-effects model is applied, with the IVW results as the primary reference. Pleiotropy was tested using Egger’s test, and heterogeneity was evaluated using two methods: IVW and MR-Egger. MR-Egger regression was used to estimate the pleiotropic effect and provide a more robust, pleiotropy-corrected causal estimate under the assumption of no measurement error and that instrument strength is independent of direct effects [27]. Additionally, we assessed instrument strength using the following formula:
where R2 represents the explained variance by the selected instrumental variables, N is the sample size of the risk factor database, and k represents the number of instrumental variables. If F < 10, it indicates a higher likelihood of weak instrument bias, suggesting that the association between the instrumental variables and the exposure is weak.
2.7. Analysis Software
All two-sample analyses were performed using the TwoSampleMR (v0.6.9) package in R software (version 4.4.1, R Foundation). Multivariable analyses were conducted using the mendelanrandomization (v0.10.0) package in R software (version 4.4.1, R Foundation).
3. Result
3.1. TSMR Analysis of Air Pollution and Pulmonary Embolism Risk
To assess the causal relationship between common air pollutants (including PM2.5, PM2.5–10, PM10, NO2, and NOX) and respiratory diseases in the European population, we conducted a Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization (TSMR) analysis (results are shown in Supplementary Table S1). First, we calculated the F values for all SNPs using the F-value formula and recorded the maximum and minimum F values (Supplementary Table S1). According to the results, the F values for all SNPs were greater than 10. As illustrated in Figure 1, the main findings using the IVW method indicated a significant relationship between PM2.5 and pulmonary embolism, with or without deep vein thrombosis (OR = 1.008, 95% CI = 1.003–1.014, p = 0.0039). A significant association was also found with pulmonary embolism corrected by Firth and SPA (OR = 1.925, 95% CI = 1.005–3.689, p = 0.0484) and (OR = 1.933, 95% CI = 1.009–3.704, p = 0.0470). However, when analyzing data from the UK Biobank, no significant relationship was observed (OR = 1.0044, 95% CI = 0.999–1.009, p = 0.0554). Additionally, PM2.5 did not show a significant association with pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale (OR = 1.003, 95% CI = 0.998–1.007, p = 0.204). After using the MR-PRESSO method for pleiotropy correction, the results remained unchanged. The scatter plot (Figure 2) and density plot (Figure 3) show strong robustness in these data. In the scatter plot, they show almost the same development trend. The density plot, a newer tool, illustrates the distribution of effect estimates across different Mendelian randomization methods. By comparing the positions of the vertical lines and the density distributions from different methods, we can better understand the consistency of inference and the accuracy of effect size estimates. The remaining forest plot and funnel plot can be found in the Supplementary Materials.
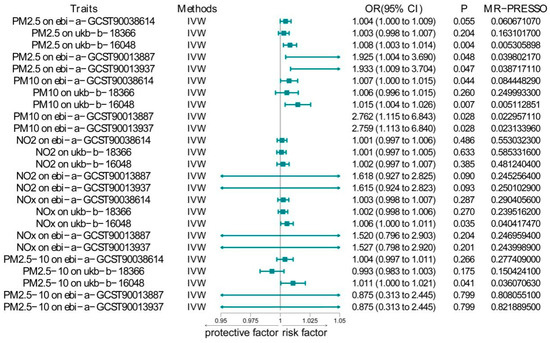
Figure 1.
IVW results between air pollutants and pulmonary embolism.
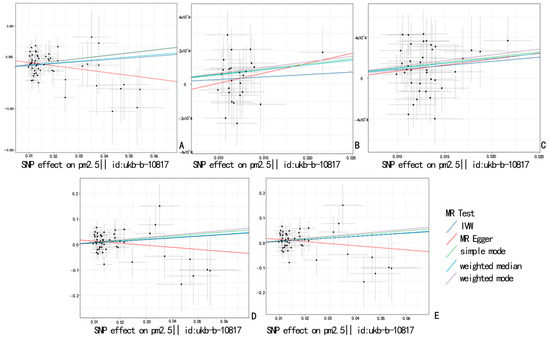
Figure 2.
Scatter plot showing the causal estimate for different MRs of PM2.5 on pulmonary embolism. (A): PM2.5 and pulmonary embolism with or without deep venous thrombosis; (B): PM2.5 and diagnoses—main ICD10: I26.9 pulmonary embolism without mention of acute cor pulmonale; (C): PM2.5 and non-cancer illness code, self-reported: pulmonary embolism +/− dvt; (D): PM2.5 and pulmonary embolism (Firth correction); (E): PM2.5 and pulmonary embolism (SPA correction).
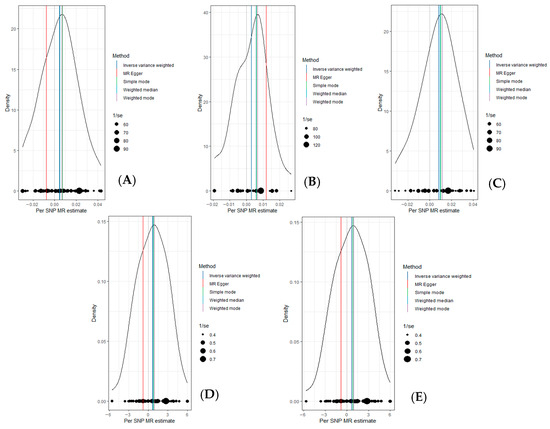
Figure 3.
Density plot showing the causal estimate for different MRs of PM2.5 on pulmonary embolism. (A): PM2.5 and pulmonary embolism with or without deep venous thrombosis; (B): PM2.5 and diagnoses—main ICD10: I26.9 pulmonary embolism without mention of acute cor pulmonale; (C): PM2.5 and non-cancer illness code, self-reported: pulmonary embolism +/− dvt; (D): PM2.5 and pulmonary embolism (Firth correction); (E): PM2.5 and pulmonary embolism (SPA correction).
Compared to PM2.5, the association between PM2.5–10 and pulmonary embolism was significantly weaker. PM2.5–10 showed a significant association only with pulmonary embolism patients from the MRC-IEU Consortium, whether or not they had deep vein thrombosis (OR = 1.011, 95% CI = 1.0004–1.0211, p = 0.0408). No significant correlation was observed with the other four datasets.
Surprisingly, PM10 showed a stronger association with pulmonary embolism than PM2.5–10. When analyzing data from the UK Biobank, a significant relationship was found (OR = 1.007, 95% CI = 1.0002–1.0146, p = 0.0443). Moreover, PM10 showed a significant association with self-reported pulmonary embolism data from the MRC-IEU Consortium (OR = 1.0148, 95% CI = 1.004–1.0256, p = 0.00683). Similar to PM2.5, PM10 was significantly associated with pulmonary embolism corrected by Firth and SPA (OR = 2.762, 95% CI = 1.115–6.843, p = 0.0282) and (OR = 2.759, 95% CI = 1.113–6.840, p = 0.0284). After validating the results with MR-PRESSO, we found that the relationship between PM10 and pulmonary embolism in the UK Biobank weakened (p = 0.0844), while the other analyses showed no significant changes. Through multiple pleiotropy tests, we found that horizontal pleiotropy (Supplementary Table S2) may be present, so we relied on the MR-PRESSO results.
Finally, we combined NO2 and NOX with the five datasets, and only NOX showed a significant association with pulmonary embolism in the MRC-IEU dataset (OR = 1.0056, 95% CI = 1.0004–1.0109, p = 0.0354). Since the MRC-IEU dataset had a different scope of data collection compared to the other four datasets, we applied the Fisher combined probability test to calculate the final p-values between the five pollutants and pulmonary embolism. The results showed significant associations for PM2.5 (p = 0.00031) and PM10 (p = 0.00017) with pulmonary embolism. In contrast, no significant relationships were found between PM2.5–10 (p = 0.26913) and NO2 (p = 0.11458) and pulmonary embolism. Unexpectedly, NOX also showed a significant association with pulmonary embolism (p = 0.04911). However, considering the notable heterogeneity and pleiotropy in this dataset, we corrected it using a random-effects model and MR-PRESSO and recalculated the p-value (p = 0.06378), which indicated no significant association.
3.2. MVMR
After conducting an initial assessment, we performed a multivariable Mendelian randomization (MVMR) analysis. To eliminate potential confounding factors, we adjusted for smoking and gender. The results of the multivariable analysis (Table 2, Supplementary Table S3) were further statistically analyzed using Fisher’s combined probability test. The analysis revealed that PM2.5 had the strongest association with pulmonary embolism (PE) (p = 0.00193), followed by a significant relationship between PM10 and PE (p = 0.0260). Additionally, nitrogen oxides were found to promote the occurrence of pulmonary embolism (p = 0.0320). To further confirm the effect of PM2.5 on PE and minimize the potential interference between air pollutants, we incorporated nitrogen oxides—another pollutant that may affect PE—into the multivariable analysis. Given that obesity is also a significant risk factor for pulmonary embolism, we controlled for BMI. After this adjustment, we found that once the confounding effect of nitrogen oxides on PM2.5 was removed, the association became stronger and more significant.

Table 2.
Multivariable Mendelian randomization results. The results of Fisher’s combined probability test are based on the calculations after removing ukb-b-18366 (pulmonary embolism without mention of acute cor pulmonale).
4. Discussions
Air pollution has long been one of the greatest threats to global environmental and public health. Several common air pollutants, such as fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and toxic gasses like NO2, can enter the bloodstream through the respiratory system, initiating, accelerating, and exacerbating the occurrence of non-communicable diseases [28]. The health risks of air pollution are not limited to its direct impact on the respiratory system but also include far-reaching effects on the cardiovascular, neurological, and other systems. Compared to other cardiovascular diseases, studies on the relationship between air pollution and pulmonary embolism are relatively rare. Pulmonary embolism, as a severe thrombotic disease, is associated with various environmental and lifestyle factors, is difficult to treat, and has a poor prognosis. Existing research shows that air pollutants may influence the blood coagulation system through various mechanisms, such as inducing chronic inflammation, increasing oxidative stress, and other pathways, thereby affecting coagulation mechanisms and increasing the risk of thrombosis.
A meta-analysis by Tang indicates that there is no significant association between exposure to major air pollutants and the risk of venous thromboembolism [29]. However, some studies suggest a significant link between environmental air pollution and pulmonary embolism. For example, Robertson et al. analyzed 74 studies on air pollution and thrombosis formation [30]. However, research on the impact of gaseous pollutants on pulmonary thrombosis is still scarce. Epidemiological studies indicate a certain association between gaseous pollutants (such as NO2, O3, and SO2) and thrombosis formation, although there is considerable inconsistency in the conclusions across these studies.
This study explores the causal relationship between the incidence of pulmonary embolism and air pollutants (PM2.5, PM2.5–10, PM10, NO2, and NOx) by using SNPs associated with these pollutants as exposure variables. Unlike previous studies, we combined multiple identical pulmonary embolism outcome databases and employed two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) and multivariable Mendelian randomization (MVMR) methods to simultaneously investigate the causal relationships between five common air pollutants and the incidence of pulmonary embolism. By utilizing data collected from different consortia and combining Fisher’s combined probability test, we obtained more robust conclusions. This approach takes advantage of a larger patient database and greater diversity in SNP collection, offering a more comprehensive perspective for analyzing pulmonary embolism, a rare disease, and making the conclusions more representative. This method effectively corrects for biases arising from small sample sizes or rare events, enhancing the accuracy and credibility of the analysis, especially in causal inference for rare diseases.
Additionally, our study specifically selected self-reported pulmonary embolism data, which complement cases that may be missing from traditional medical record databases, particularly those who have not received formal medical intervention. These data help reveal the effects of air pollution on mild cases or patients who did not seek medical treatment, providing more sample sources and further improving the analysis of risk factors and genetic backgrounds related to pulmonary embolism. Our findings show a significant positive correlation between PM2.5 and pulmonary embolism, with this association becoming even more pronounced after adjusting for gender, BMI, and nitrogen oxides in the multivariable model. A recent cohort study with 1954 participants found a positive correlation between PM2.5 exposure and the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and venous thromboembolism (VTE), with the association being particularly strong in younger populations (comparing those under 70 years old to those over 70) and those with cancer [13]. These results are consistent with our findings.
Furthermore, existing epidemiological studies have also shown that both short-term and long-term exposure to PM2.5 is significantly associated with the occurrence of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism, possibly through mechanisms such as activation of the inflammatory response, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), endothelial damage, vasoconstriction, and changes in coagulation factors [3]. These biological mechanisms may contribute to the onset and development of pulmonary embolism. However, not all studies support the relationship between PM2.5 exposure and pulmonary embolism. For example, some epidemiological studies suggest that when venous thromboembolism (VTE) is subdivided into specific types, PM2.5 exposure is significantly positively correlated with deep vein thrombosis, but the relationship with pulmonary embolism is not significant.
Compared to other particulate pollutants, research on PM2.5–10 is relatively limited, especially studies exploring its relationship with pulmonary embolism, which are nearly nonexistent. PM2.5–10 is primarily composed of crustal elements, metals in suspended road dust, and organic debris generated by mechanical wear and solid re-suspension. Existing toxicological and controlled human exposure studies suggest that PM2.5–10 adversely affects health through mechanisms such as inducing systemic inflammation, influencing coagulation function, and altering autonomic nervous system tension [31]. A study by Li et al. found that each 50 μg/m3 increase in daily PM2.5–10 exposure was associated with a 23% increased risk of venous thromboembolism [32]. However, our study did not find a statistically significant relationship between PM2.5–10 and venous thromboembolism. Nevertheless, given that our study utilized a large sample size and controlled for confounding factors, it still provides strong evidence for the association between PM2.5–10 and pulmonary embolism, underscoring the necessity of regulatory restrictions on PM2.5–10 concentrations.
Studies on PM10 have already shown that exposure to PM10 can trigger inflammatory responses in the lungs. Animal studies indicate that PM10 exposure significantly increases the concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α [33]. The elevation of these inflammatory markers may exacerbate endothelial injury, further impacting blood coagulation mechanisms. Other research suggests that PM10, by crossing the alveolar epithelium, enters the bloodstream and directly affects endothelial cells, atherosclerotic plaques, and platelets, as well as the formation, structure, and stability of fibrin clots. PM10 exposure may influence blood coagulation through these mechanisms, increasing the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism. These findings are consistent with our results, where both two-sample Mendelian randomization and multivariable Mendelian randomization show a strong association between PM10 and pulmonary embolism.
Although the relationship between PM2.5 and PM10 exposure and pulmonary embolism has been explored in multiple studies, research on other air pollutants, such as NO2 and NOx, remains limited. Most studies on NO2 and NOx focus on their relationship with asthma and the synergistic effect of PM2.5 in increasing lung cancer risk. Recent studies have found that NO2 and O3 may slightly increase the risk of pulmonary embolism, suggesting that sensitivity to air pollutants may vary significantly across different regions and populations. This difference may be closely related to local genetic factors, dietary habits, and lifestyle choices. From a mechanistic perspective, NO2 reacts with pulmonary mucosal fluid to generate oxidants, which in turn trigger inflammation and cellular damage. Animal and cell culture studies also support the relationship between NO2 and inflammation as well as cell damage [34]. Additionally, NO2 may interfere with the cortisol response, weakening its anti-inflammatory effects and thereby exacerbating lung damage [35]. This provides a potential mechanism for the role of NO2 in the occurrence of pulmonary embolism. However, in contrast to previous studies, we found that nitrogen oxides (NOx) show a stronger association with pulmonary embolism than nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Nitrogen oxides appear to have a greater potential to induce pulmonary embolism, which may be due to the presence of certain compounds in nitrogen oxides that are more likely to trigger pulmonary embolism compared to NO2. However, further research is needed to confirm this hypothesis.
Despite the conclusions drawn above, our study has several limitations. First, the participants and controls in the database were all of European descent, which may limit the generalizability of our findings to other racial groups. However, the homogeneity of our participant population helps reduce the risk of confounding due to the mixed use of databases. To expand the applicability of our results, it is essential to validate them in different populations. Second, to ensure sufficient air pollution data, we selected instrumental variables (IVs) with a significance threshold (p < 5 × 10−8) higher than the conventional genome-wide significance level (p < 5 × 10−6). Although we employed various analytical methods to test and adjust for potential biases, this may still result in weaker IVs and potential pleiotropy. Therefore, caution is needed when interpreting these results. Third, our study only focused on five major air pollutants as exposure variables and did not investigate other pollutants that may influence the occurrence of pulmonary embolism, such as nitrous oxide and sulfides, due to limitations in the GWAS database. Finally, there are significant differences between studies in the methods used to assess and report air pollution levels and the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. This inconsistency may lead to measurement errors, limiting the ability to directly compare results across studies. Nonetheless, we believe that despite these limitations, our study still provides important exploratory insights for clinical practice. Finally, the risk factors for pulmonary embolism (PE) include smoking, BMI, physical activity, diet, hormone replacement therapy, and several other factors, but we only adjusted for gender, smoking, and BMI. Future research may need to consider further reducing the impact of other confounding factors, such as socioeconomic status and unhealthy lifestyles, on PE.
From a public health perspective, general practitioners should be aware that elderly individuals and patients with low mobility living in areas with high air pollution exposure are at higher risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) and adjust their clinical practices and preventive recommendations accordingly. Especially in a global context, air pollution remains an increasingly severe public health threat, and urgent measures need to be taken by the international community to address it. Strengthening air pollution control, promoting healthy lifestyles, and integrating public health programs may be more effective than interventions targeting specific pollutants alone. Against this backdrop, raising public awareness of the dangers of air pollution and promoting global cooperation are of utmost importance.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study employed the Mendelian randomization method and Fisher’s combined probability test, providing strong evidence regarding the relationship between five air pollutants and the occurrence of pulmonary embolism. The results show significant causal associations between PM2.5 (p = 0.00031) and PM10 (p = 0.00017) as well as pulmonary embolism, while other air pollutants such as PM2.5–10 (p = 0.26913) did not exhibit a significant causal relationship. Notably, after adjusting for potential confounders, such as smoking, the associations between PM2.5 (p = 0.00193), PM10 (p = 0.0260), and nitrogen oxides (p = 0.0320) with pulmonary embolism remained significant, emphasizing the key role these pollutants may play in the occurrence of pulmonary embolism. This study offers a new perspective on the complex pathogenesis of respiratory diseases from the viewpoint of Mendelian randomization, filling a gap in the existing literature. The findings highlight the urgent need for the development of specific regulatory measures and public health intervention strategies to reduce exposure to harmful air pollutants, particularly for vulnerable groups. Future research should further explore the complex mixtures of air pollution and their evolving patterns, with a focus on the long-term impacts of these pollutants on public health, providing scientific evidence and practical guidance for more effective mitigation strategies and policy formulation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos16040384/s1, Table S1: Causal Estimates of Air Pollution on Pulmonary Embolism from Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization. Table S2: Sensitivity analyses of Mendelian randomization result. Table S3: Results of Multivariable Mendelian Randomization. Figure S1: The forest plots, scatter plots, funnel plots, and density plots of all the analyzed data in the article.
Author Contributions
X.P.: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, and writing—original draft; Y.J.: data curation, visualization, and writing—editing; Z.W.: data curation; X.Z.: writing—review, supervision, and project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Clinical Key Specialty Construction Project, Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Project (grant no. TJYXZDXK-049A), Tianjin Health Science and Technology Clinical Key Specialty Project (grant no. TJWJ2024ZK003) and Tianjin Science and Technology Project (grant no. HH24KYZX0009).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. These data can be found in the UK Biobank and MRC-IEU.
Acknowledgments
We want to acknowledge the participants and investigators of the MRC-IEU study. We would also like to thank the UK Biobank and Open GWAS Database.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lin, C.; Yousefi, S.; Kahoro, E.; Karisani, P.; Liang, D.; Sarnat, J.; Agichtein, E. Detecting Elevated Air Pollution Levels by Monitoring Web Search Queries: Algorithm Development and Validation. JMIR Form. Res. 2022, 6, e23422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liang, H.; Chang, Q.; Lin, F.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Pan, P.; et al. Ambient air pollution, lifestyle, and genetic predisposition on all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A prospective cohort study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 173120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kloog, I.; Zanobetti, A.; Nordio, F.; Coull, B.A.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Schwartz, J. Effects of airborne fine particles (PM2.5) on deep vein thrombosis admissions in the northeastern United States. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gan, Q.; Su, X.; Zhang, S.; Ding, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wu, K. Genetic evidence for the causal effects of air pollution on the risk of respiratory diseases. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nisio, M.; Van Es, N.; Büller, H.R. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Lancet 2016, 388, 3060–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, M.; Xu, Y.; Barregard, L.; Zöller, B.; Molnar, P.; Oudin, A.; Spanne, M.; Engström, G.; Stockfelt, L. Long-term ambient air pollution and venous thromboembolism in a population-based Swedish cohort. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 331, 121841. [Google Scholar]
- Milojevic, A.; Wilkinson, P.; Armstrong, B.; Bhaskaran, K.; Smeeth, L.; Hajat, S. Short-term effects of air pollution on a range of cardiovascular events in England and Wales: Case-crossover analysis of the MINAP database, hospital admissions and mortality. Heart 2014, 100, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Spiezia, L.; Campello, E.; Bon, M.; Maggiolo, S.; Pelizzaro, E.; Simioni, P. Short-term exposure to high levels of air pollution as a risk factor for acute isolated pulmonary embolism. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Brook, R.D.; Franklin, B.; Cascio, W.; Hong, Y.; Howard, G.; Lipsett, M.; Luepker, R.; Mittleman, M.; Samet, J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Expert Panel on Population and Prevention Science of the American Heart Association. Circulation 2004, 109, 2655–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Si, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, F.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Sun, D.; Wang, Z. The Relationship Between PM2.5 and Eight Common Lung Diseases: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Toxics 2024, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunwald, E. Air pollution: Challenges and opportunities for cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1679–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Jing, D.; Liang, H.; Cheng, J.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Lin, F.; Liu, H.; Pan, P.; et al. Association of air pollution, genetic risk, and lifestyle with incident adult-onset asthma: A prospective cohort study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzi, M.; Stafoggia, M.; Michelozzi, P.; Davoli, M.; Forastiere, F.; Solimini, A.G. Long-term exposure to air pollution and risk of venous thromboembolism in a large administrative cohort. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey Smith, G.; Ebrahim, S. ‘Mendelian randomization’: Can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Timpson, N.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Dimou, N.; Langenberg, C.; et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian randomisation (STROBE-MR): Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2021, 375, n2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, P.M.; Brown, M.A.; McCarthy, M.I.; Yang, J. Five Years of GWAS Discovery. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, J.; Holmes, M.V. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birney, E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2022, 12, a041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G.; CRP CHD Genetics Collaboration. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Tilling, K.; Davey Smith, G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007081. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. A causal relationship between childhood obesity and risk of osteoarthritis: Results from a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, E.; Smith, G.D.; Windmeijer, F.; Bowden, J. An examination of multivariable Mendelian randomization in the single-sample and two-sample summary data settings. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 713–727. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, A.R.; Sanderson, E.; Hammerton, G.; Richmond, R.C.; Smith, G.D.; Heron, J.; Taylor, A.E.; Davies, N.M.; Howe, L.D. Mendelian randomisation for mediation analysis: Current methods and challenges for implementation. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 36, 465–478. [Google Scholar]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Smith, G.D.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: The role of the I2 statistic. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss-Ustün, A.; Wolf, J.; Bartram, J.; Clasen, T.; Cumming, O.; Freeman, M.C.; Gordon, B.; Hunter, P.R.; Medlicott, K.; Johnston, R. Burden of disease from inadequate water, sanitation and hygiene for selected adverse health outcomes: An updated analysis with a focus on low- and middle-income countries. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 765–777. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Cheng, Z.-P.; Hu, B.; Liu, J.-D.; Hu, Y. Air pollution and venous thrombosis: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32794. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, S.; Miller, M.R. Ambient air pollution and thrombosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bellavia, A.; Urch, B.; Speck, M.; Brook, R.D.; Scott, J.A.; Albetti, B.; Behbod, B.; North, M.; Valeri, L.; Bertazzi, P.A.; et al. DNA Hypomethylation, Ambient Particulate Matter, and Increased Blood Pressure: Findings From Controlled Human Exposure Experiments. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lu, A.; Si, S.; Zhang, K.; Tang, F.; Yang, F.; Xue, F. Exposure to various ambient air pollutants increases the risk of venous thromboembolism: A cohort study in UK Biobank. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Mills, N.; Macnee, W.; Robinson, S.; Newby, D. Role of inflammation in cardiopulmonary health effects of PM. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 207, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelly, F.J. Oxidative stress: Its role in air pollution and adverse health effects. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 60, 612–616. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, S.E.; Bandoli, G.; Telesca, D.; Su, J.G.; Ritz, B. Chronic exposure to inhaled, traffic-related nitrogen dioxide and a blunted cortisol response in adolescents. Environ. Res. 2018, 163, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).