Occupational and Environmental BTEX Exposure: A Bibliometric Analysis Using Scientific Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
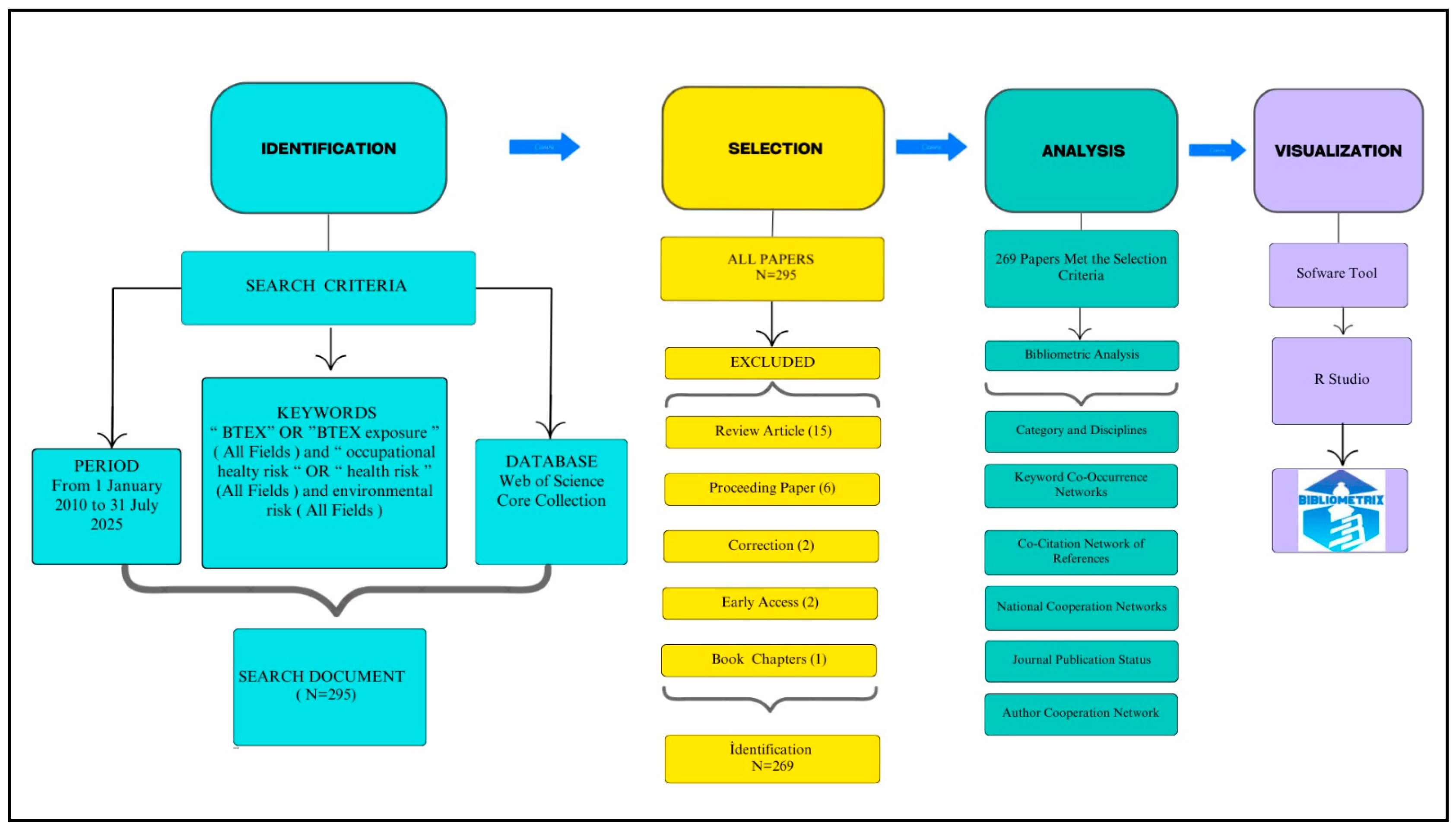
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bibliometric Analysis
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Questions
- What is the annual number of publications on the subject?
- What is the impact of sources (journals) related to the subject?
- What is the distribution of scientific publications on the subject by country, institution, and author?
- What is the citation status of authors and countries?
- What are the relationships between academic institutions, authors, and keywords?
- What is the density of prominent keywords?
- What are the collaboration networks of influential authors, institutions, and countries?
- How have thematic concepts developed and diversified?
- What are the conceptual structure maps of co-occurring keywords?
- What industrial and environmental sources cause BTEX exposure?
- What are the most commonly used analysis methods for assessing BTEX exposure?
- What are the biological monitoring methods for BTEX exposure?
3. Results and Discussion
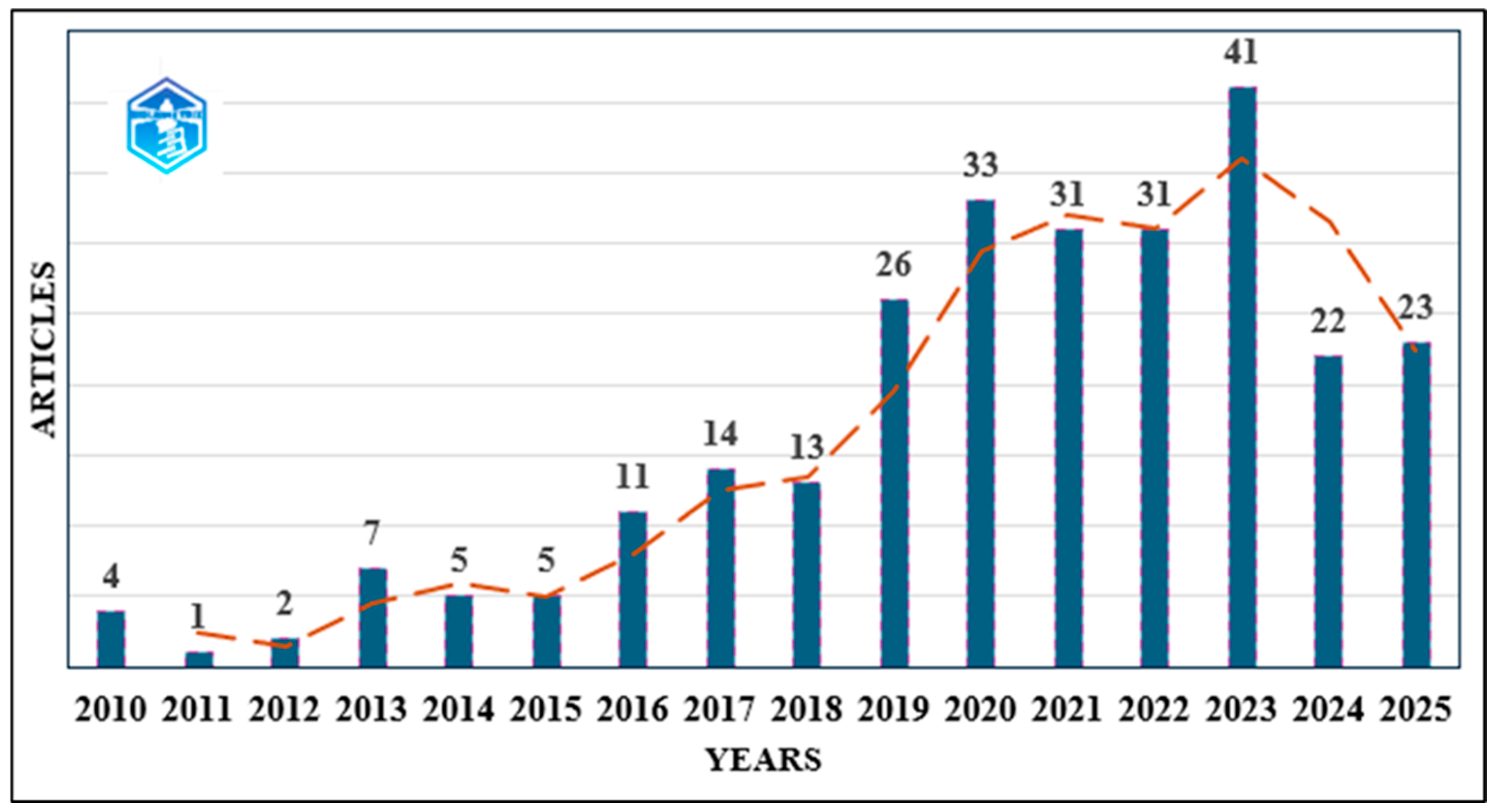
3.1. Number of Scientific Articles Published Annually
- 2010–2015: The annual average output is approximately five articles, with a low and fluctuating output.
- In the period 2016–2022, there was a rapid increase in the number of articles published, accompanied by a significant thematic diversification. On average, approximately 27 articles were published annually.
- 2023–2025: It is evident that there has been a relative stabilization, as evidenced by the publication numbers, which have now stabilized within the 22–23 range.
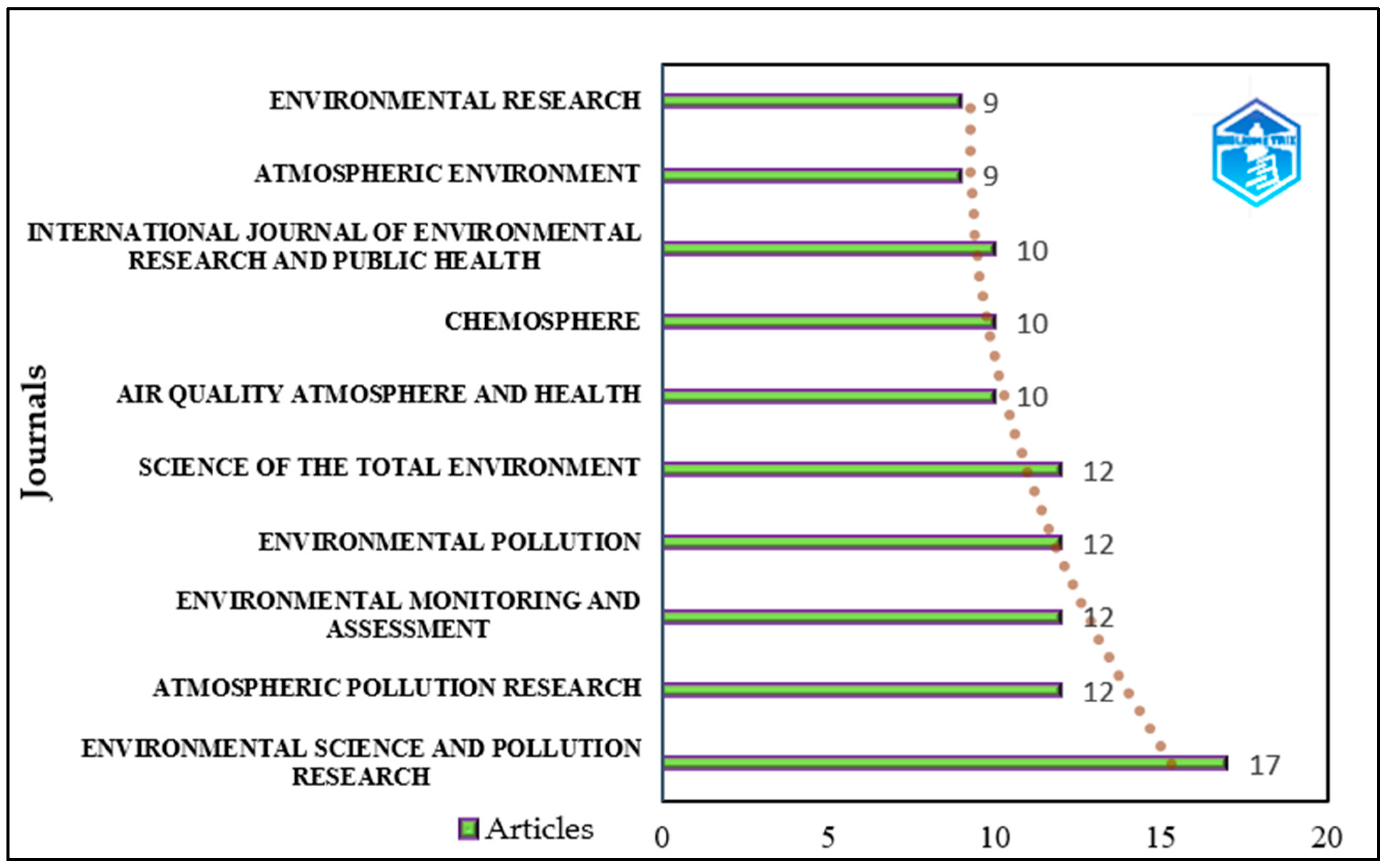
3.2. Journals in Which Scientific Studies Are Published
- The extensive coverage of environmental and health-based dimensions in research,
- The proliferation of interdisciplinary approaches,
- The increase in application and analysis-focused research.
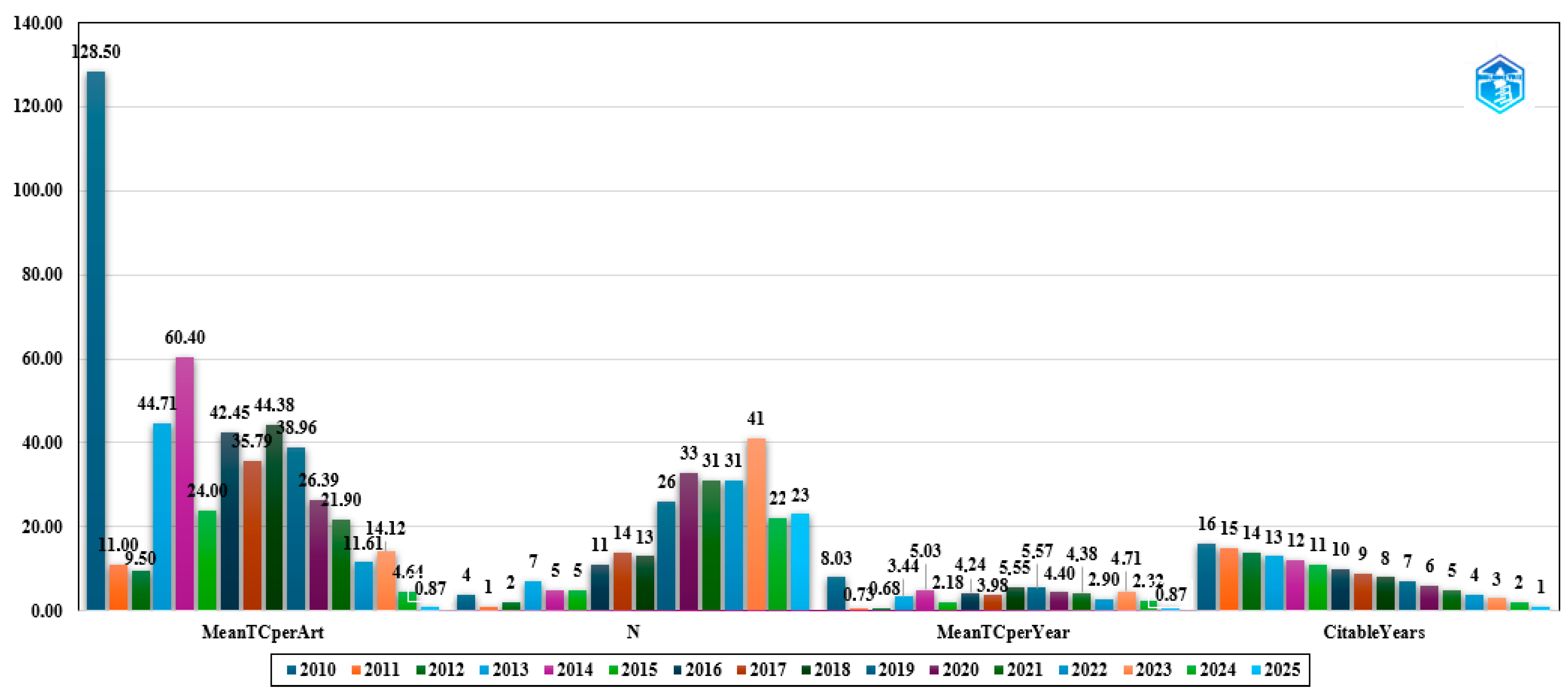
3.3. Citation Performance and Publication Volume of Academic Studies
3.4. Text Mining with Word Clouds and Word Trees
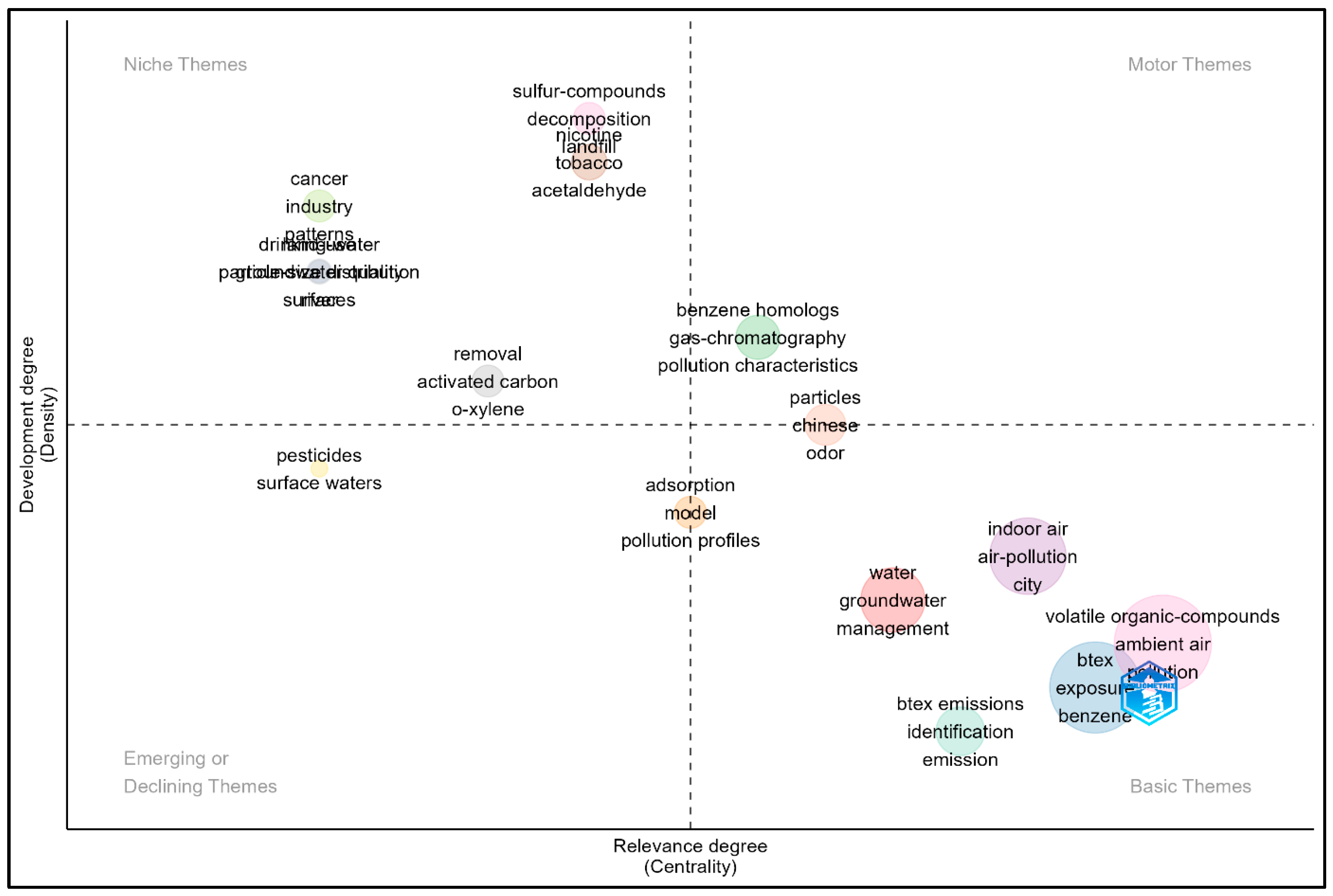
3.5. Thematic Mapping of BTEX Compounds and Their Health Effects
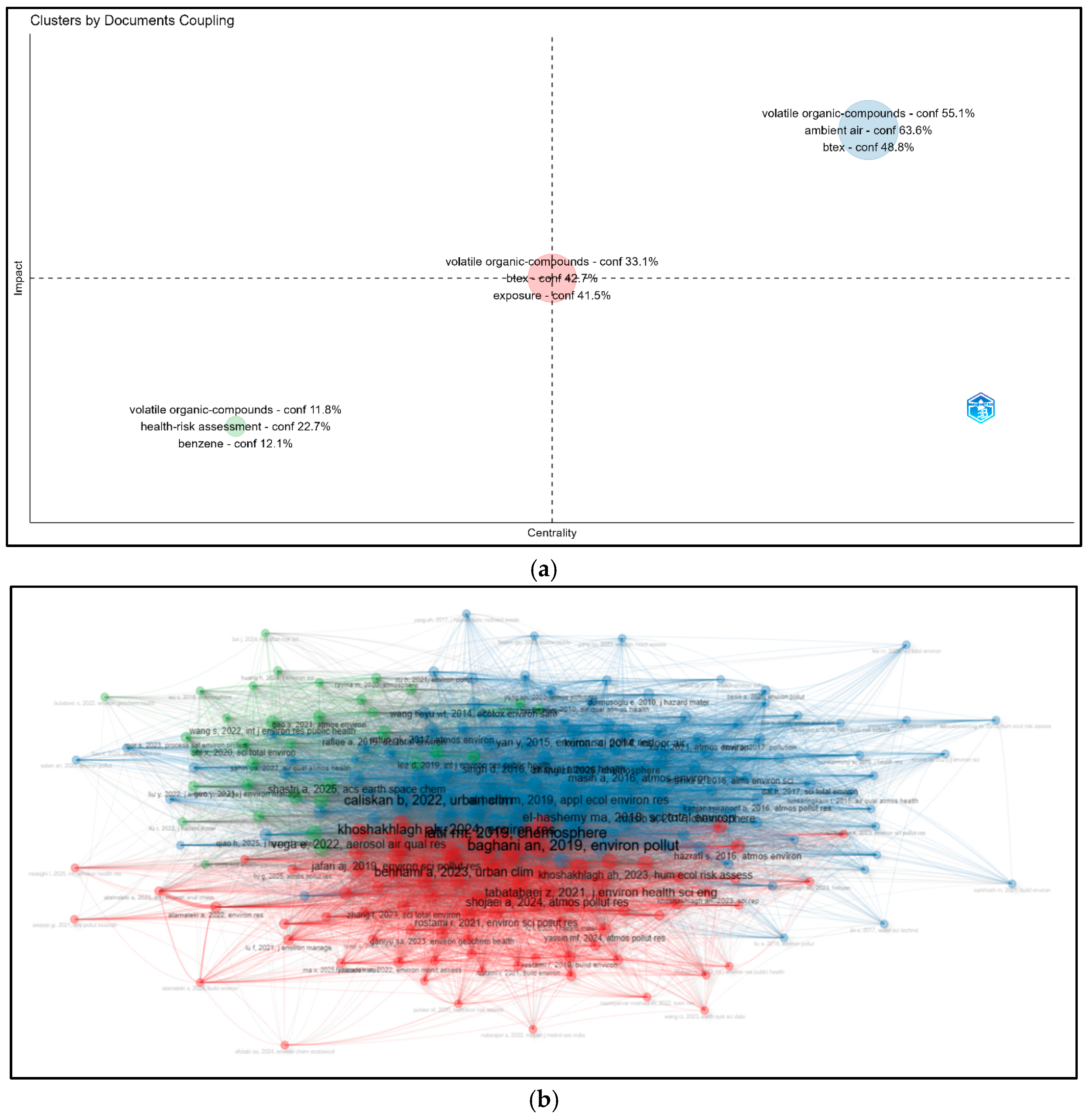
3.6. Coupling-Based Clustering Results
3.6.1. Thematic Cluster Structure and Focus Areas
3.6.2. Centrality and Influence Levels
- Environmental Monitoring and Air Quality Analysis
- Assessment of Health Risks and Occupational Safety and Health Practices
- Analytical Methods and Chemical Characterization
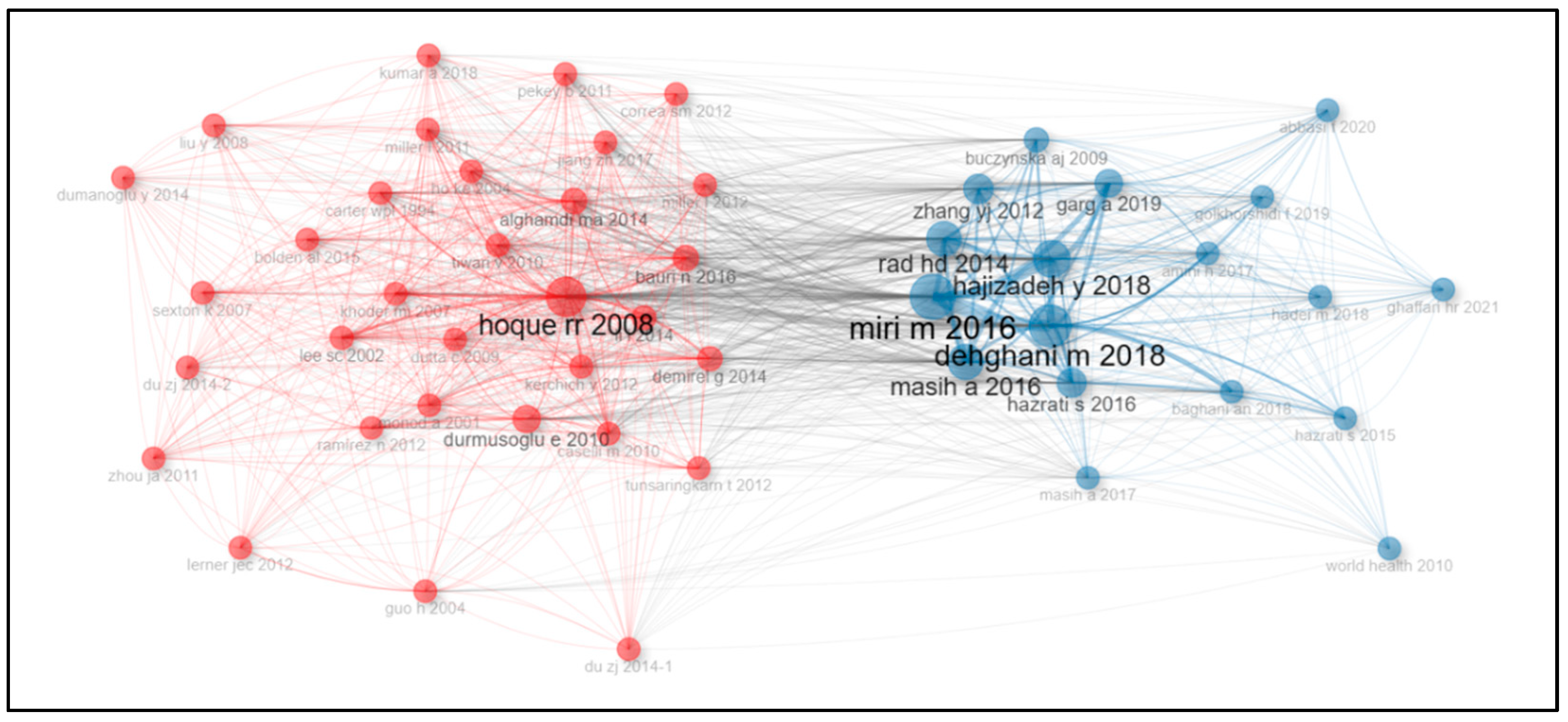
3.7. Co-Citation Network Analysis Results
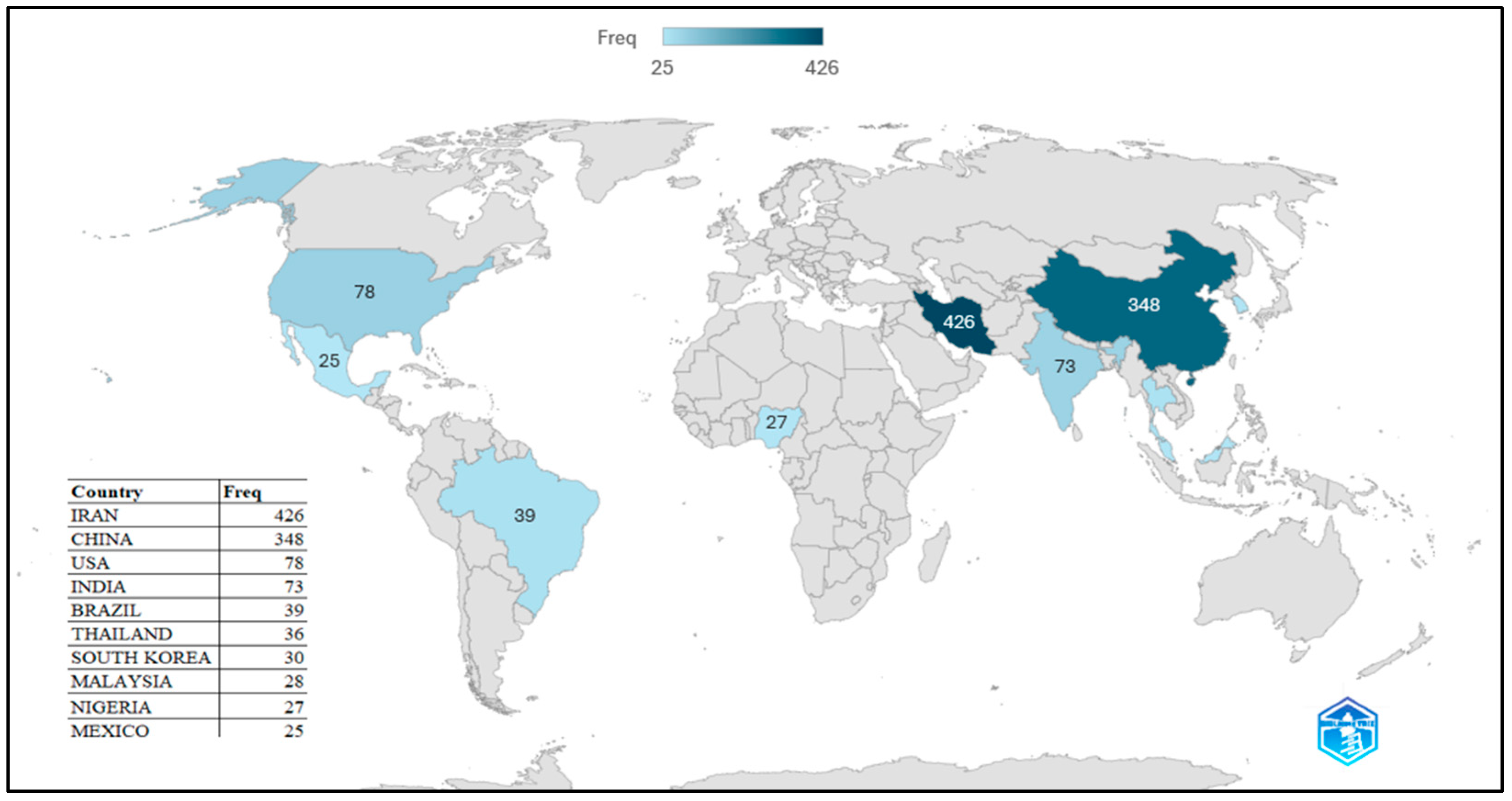
3.8. Countries’ Scientific Studies Analysis Results
3.9. Three-Field Graph Analysis Results
3.10. Average Citation Count and Normalized Contribution Value Analysis Results
3.11. Content Analysis Results Related to BTEX Exposure
3.11.1. Sectoral and Environmental Distribution of BTEX Exposure
3.11.2. Devices, Detectors, and Sampling Methods Used in BTEX Analysis
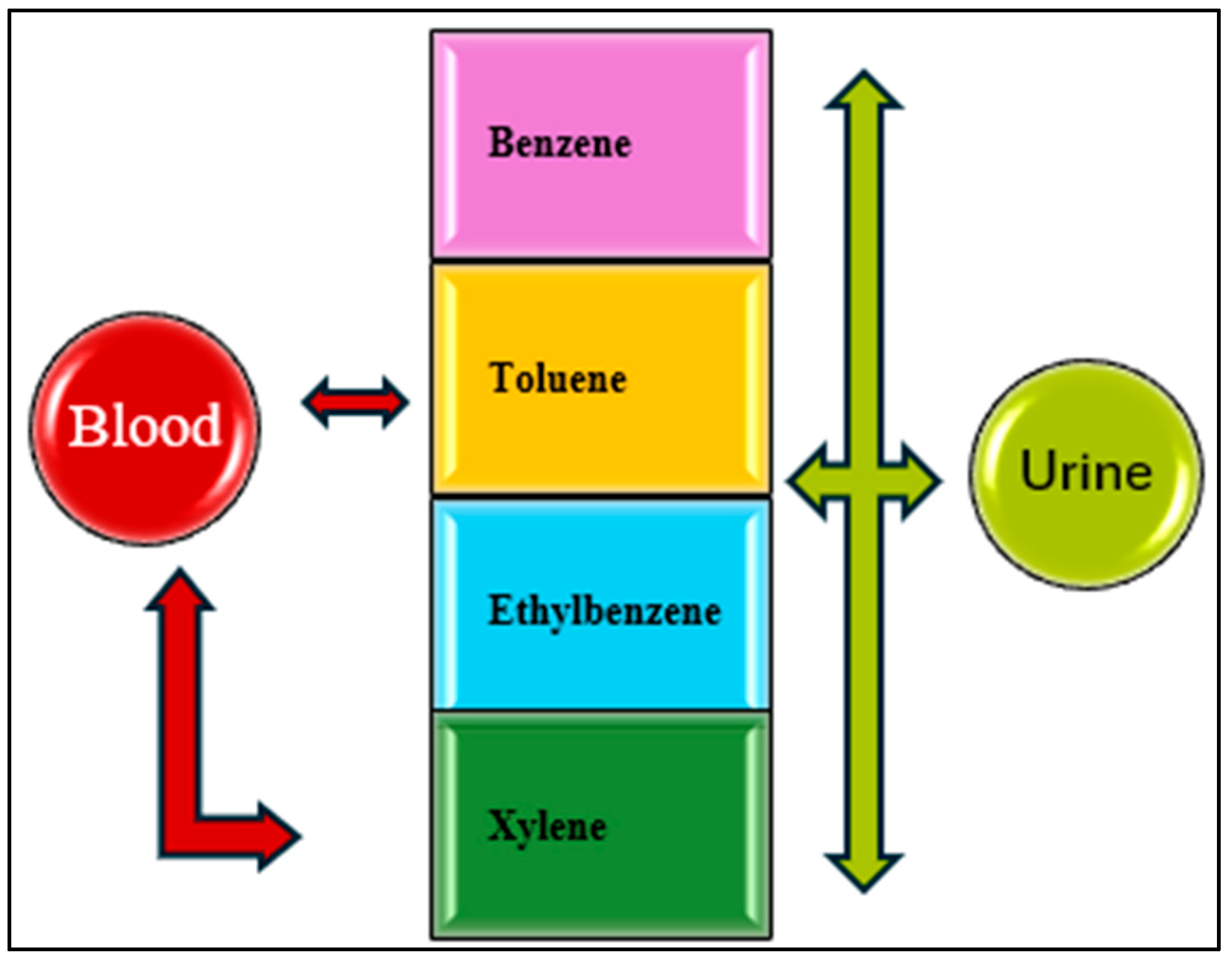
3.11.3. Monitoring BTEX Exposure with Biological Markers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chary, N.S.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R. Determination of volatile organic compounds in drinking and environmental waters. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 32, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmusoglu, E.; Taspinar, F.; Karademir, A. Health risk assessment of BTEX emissions in the landfill environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshakhlagh, A.H.; Yazdanirad, S.; Ducatman, A. Climatic conditions and concentrations of BTEX compounds in atmospheric media. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Sorooshian, A.; Tabatabaee, H.R.; Miri, M.; Baghani, A.N.; Delikhoon, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Rashidi, M. Characteristics and health effects of BTEX in a hot spot for urban pollution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 155, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, Z.; Üzmez, Ö.Ö.; Döğeroğlu, T.; Artun, G.; Gaga, E.O. Atmospheric concentrations of SO2, NO2, ozone and VOCs in Düzce, Turkey using passive air samplers: Sources, spatial and seasonal variations and health risk estimation. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, Z.; Xue-song, F. BTEX in the environment: An update on sources, fate, distribution, pretreatment, analysis, and removal techniques. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, M.; Malekmohammadi, B.; Tajalli, S. Interaction of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene with human’s body: Insights into characteristics, sources and health risks. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, C.J.; Hannigan, J.H.; Bowen, S.E. Effects of inhaled combined Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylenes (BTEX): Toward an environmental exposure model. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 81, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, F.; Lu, W.; Wang, J. Occupational health risk assessment of BTEX in municipal solid waste landfill based on external and internal exposure. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökcan, A.; Demir, G. Industrial Toxic Chemicals and Occupational Health and Safety. In Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Occupational Safety and Health; Çögenli, M.Z., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 85–106. [Google Scholar]
- Friesen, M.C.; Coble, J.B.; Lu, W.; Shu, X.O.; Ji, B.T.; Xue, S.Z.; Portengen, L.; Chow, W.-H.; Gao, Y.-T.; Yang, G.; et al. Combining a job-exposure matrix with exposure measurements to assess occupational exposure to benzene in a population cohort in Shanghai, China. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2012, 56, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.T.; Li, H.; Fu, X.D.; Guo, H.W.; Meng, R.H.; Lu, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H.T. Health risk impacts analysis of fugitive aromatic compounds emissions from the working face of a municipal solid waste landfill in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 97, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muda, I.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Sepahvad, A.; Farhadi, A.; Fadhel Obaid, R.; Taherian, M.; Alali, N.; Chowdhury, S.; Farhadi, M. Associated health risk assessment due to exposure to BTEX compounds in fuel station workers. Rev. Environ. Health 2024, 39, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogliano, V.J.; Baan, R.; Straif, K. Updating IARC’s carcinogenicity assessment of benzene. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2011, 54, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraju, P.; Vijayakumar, Y.; Ramana Reddy, M.V. Room-temperature BTEX sensing characterization of nanostructured ZnO thin films. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2019, 7, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajeh, M.; Zadeh, F.M. Response surface modeling of ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for determination of benzene, toluene and xylenes in water samples: Box–Behnken design. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshakhlagh, A.H.; Askari Majdabadi, M.; Yazdanirad, S.; Carlsen, L. Health risk assessment of exposure to benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX) in a composite manufacturing plant: Monte-Carlo simulations. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2023, 29, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briner, R.B.; Denyer, D. Systematic Review and Evidence Synthesis As a Practice and Scholarship Tool. In The Oxford Handbook of Evidence-Based Management; Rousseau, D.M., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu Avinç, G.; Yıldız, A. A bibliometric and systematic review of scientific publications on metaverse research in architecture: Web of science (WoS). Int. J. Technol. Des. Educ. 2025, 35, 825–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, O.; Kocaman, R.; Kanbach, D.K. How to design bibliometric research: An overview and a framework proposal. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2024, 18, 3333–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, X.; Chen, J.; Yi, C. Visualization Study on Trends and Hotspots in the Field of Urban Air Pollution in Metropolitan Areas and Megacities: A Bibliometric Analysis via Science Mapping. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Soler, R.; Uribe-Toril, J.; Valenciano, J.D.P. Worldwide trends in the scientific production on rural depopulation, a bibliometric analysis using bibliometrix R-tool. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Guo, H.; Qian, K. Deciphering the impact of machine learning on education: Insights from a bibliometric analysis using bibliometrix R-package. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 21995–22022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral-Muñoz, J.A.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Santisteban-Espejo, A.; Cobo, M.J. Software tools for conducting bibliometric analysis in science: An up-to-date review. Prof. De La Inf. 2020, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibliometrix. Biblioshiny for Bibliometrix [Computer Software]. 2025. Available online: https://www.bibliometrix.org/home/index.php/layout/biblioshiny (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Clarivate. Web of Science Core Collection [Database]. 2023. Available online: https://clarivate.com/webofsciencegroup/solutions/web-of-science-core-collection/ (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Pranckutė, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The titans of bibliographic information in today’s academic world. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Chau, K.Y.; Ho, G.T.S.; Yip, H.T.; Tang, Y.M. A bibliometric study on technology usage for occupational safety and health risk assessment in construction industry. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haunschild, R.; Bornmann, L.; Marx, W. Climate change research in view of bibliometrics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslancı, S. Research Inquiry-Based Learning: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sci. Educ. Stud. 2022, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus research: A bibliometric analysis over a 50-year period. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, H.H.A.; Latif, M.T.; Nadzir, M.S.M.; Uning, R.; Khan, M.F.; Kannan, N. Ambient BTEX levels over urban, suburban and rural areas in Malaysia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griivel, L.; Mutschke, P.; Polanco, X. Thematic mapping on bibliographic databases by cluster analysis. Knowl. Organ. 1995, 22, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Aria, M.; Alterisio, A.; Scandurra, A.; Pinelli, C.; D’Aniello, B. The scholar’s best friend: Research trends in dog cognitive and behavioral studies. Anim. Cogn. 2021, 24, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yigit, G.; Engin, O. Ensuring Sustainability with Industry 5.0: A Bibliometric Analysis. Istanb. Aydin Univ. J. Soc. Sci. 2025, 17, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Jing, S.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, L.; Song, W.; Kan, H. VOC characteristics and inhalation health risks in newly renovated residences in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Hanai, Y.; Masunaga, S. Ambient levels of volatile organic compounds in the vicinity of petrochemical industrial area of Yokohama, Japan. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2010, 3, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinedo, J.; Ibáñez, R.; Lijzen, J.P.A.; Irabien, A. Assessment of soil pollution based on total petroleum hydrocarbons and individual oil substances. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 130, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.; Ravindra, K. Municipal solid waste landfills in lower-and middle-income countries: Environmental impacts, challenges and sustainable management practices. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 174, 510–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, S.; Rostami, R.; Farjaminezhad, M.; Fazlzadeh, M. Preliminary assessment of BTEX concentrations in indoor air of residential buildings and atmospheric ambient air in Ardabil, Iran. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 132, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, G. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of benzene homologues in ambient air in the northeastern urban area of Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Li, W.; Yan, L.; Shu, M.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, P.; Cao, W. Assessment of the health risks and odor concentration of volatile compounds from a municipal solid waste landfill in China. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Chai, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Ning, P.; Huang, J.; Tian, S. Interaction of inhalable volatile organic compounds and pulmonary surfactant: Potential hazards of VOCs exposure to lungs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadei, M.; Hopke, P.K.; Rafiee, M.; Rastkari, N.; Yarahmadi, M.; Kermani, M.; Shahsavani, A. Indoor and outdoor concentrations of BTEX and formaldehyde in Tehran, Iran: Effects of building characteristics and health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27423–27437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.M.; Borba, P.F.D.S.; Dos Santos, N.E.; Dos Reis, P.T.B.; Silveira, R.S.; Corrêa, S.M. The relationship between solvent use and BTEX concentrations in occupational environments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, A.; Rostami, R. BTEX concentration and health risk assessment in automobile workshops. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina, M.; Facelli, A.; Zanetti, M. Halocarbon emissions from hazardous waste landfills: Analysis of sources and risks. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, R. Feeding Moral Relations: The Making of Kinship and Nation in Iran. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Anthropology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, R.; Zarei, A.; Saranjam, B.; Ghaffari, H.R.; Hazrati, S.; Poureshg, Y.; Fazlzadeh, M. Exposure and risk assessment of PAHs in indoor air of waterpipe cafés in Ardebil, Iran. Build. Environ. 2019, 155, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edokpolo, B.; Yu, Q.J.; Connell, D. Health risk assessment of ambient air concentrations of benzene, toluene and xylene (BTX) in service station environments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 6354–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadyan, M.; Golafshani, F.Y.; Yousefinejad, R.; Boogaard, P.J.; Heibati, B. Risk assessment of benzene among gas station refueling workers. Feb-Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2016, 25, 3563–3569. [Google Scholar]
- Akal, D.; Yurdakul, S.; Civan, M.Y.; Tuncel, G.; Ersan, H.Y. Sources of volatile organic compounds in a university building. Environ. Forensics 2015, 16, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.H.; Vu, D.C.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Vo, X.T. Volatile organic compounds in primary schools in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam: Characterization and health risk assessment. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolla, R.; Curtis, C.J.; Knight, J. Occupational exposure of diesel station workers to BTEX compounds at a bus depot. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4101–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, X.; Xiong, J. Air quality inside motor vehicles’ cabins: A review. Indoor Built Environ. 2018, 27, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asejeje, G.I.; Ipeaiyeda, A.R.; Onianwa, P.C. Health risk assessment of Ubeji Creek residents’ exposure to BTEX from consumption of locally sourced foods. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2021, 33, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, S.; Chen, D.; Li, G.; Yu, Y.; Fan, R.; An, T. Human exposure to BTEX emitted from a typical e-waste recycling industrial park: External and internal exposure levels, sources, and probabilistic risk implications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Hopke, P.; Hadei, M.; Eslami, A.; Rastkari, N.; Naghdali, Z.; Kermani, M.; Emam, B.; Farhadi, M.; Shahsavani, A. Exposure to BTEX in beauty salons: Biomonitoring, urinary excretion, clinical symptoms, and health risk assessments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badjagbo, K.; Loranger, S.; Moore, S.; Tardif, R.; Sauve, S. BTEX exposures among automobile mechanics and painters and their associated health risks. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2010, 16, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, K.; Singh, B.; Mina, U.; Singh, B.B.; Jain, V.K. Statistical modeling of O3, NOx, CO, PM2.5, VOCs and noise levels in commercial complex and associated health risk assessment in an academic institution. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.P.; Kashyap, P.; Kumar, R.; Pandey, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, K. Cancer and non-cancer health risk assessment associated with exposure to non-methane hydrocarbons among roadside vendors in Delhi, India. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Peng, L.; Cheng, N.; Bai, H.; Mu, L. Health risk assessment of toxic VOCs species for the coal fire well drillers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15132–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Y.; He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Emission characteristics and health risks of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) measured in a typical recycled rubber plant in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Bi, F.; Meng, L.S.; Zhang, X.M.; Mao, J.Y.; Cheng, N.L.; Fang, B.; Yang, Y.; et al. Fast determination of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air using a portable gas chromatography–photoionization detector. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masih, A.; Lall, A.S.; Taneja, A.; Singhvi, R. Exposure levels and health risk assessment of ambient BTX at urban and rural environments of a terai region of northern India. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1678–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, A.; Delgado-Saborit, J.M.; Sly, P.D.; Amiri, H.; Hoseini, M. Lifestyle and occupational factors affecting exposure to BTEX in municipal solid waste composting facility workers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Fan, R.; Wei, F. External exposure to btex, internal biomarker response, and health risk assessment of nonoccupational populations near a coking plant in southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Component | ACGIH TLV (TWA) | OSHA PEL | NIOSH REL | STEL (ACGIH) | STEL (OSHA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | 0.5 ppm (1.6 mg m−3) | 1 ppm (3.2 mg m−3) | 0.1 ppm (0.32 mg m−3) | 2.5 ppm | - |
| Toluene | 20 ppm (75 mg m−3) | 200 ppm (750 mg m−3) | 100 ppm (375 mg m−3) | 150 ppm | - |
| Etilbenzene | 20 ppm (87 mg m−3) | 100 ppm (435 mg m−3) | 100 ppm (435 mg m−3) | 125 ppm | - |
| Xylene | 100 ppm (434 mg m−3) | 100 ppm (435 mg m−3) | 100 ppm (435 mg m−3) | 150 ppm | - |
| Description Main Information About Data | Results |
|---|---|
| Timespan | 2010:2025 |
| Sources (Journals, Books, etc.) | 88 |
| Documents | 269 |
| Annual Growth Rate % | 12.37 |
| Document Average Age | 4.58 |
| Average citations per doc | 23.97 |
| References | 10,160 |
| Document Contents | |
| Keywords Plus (ID) | 702 |
| Author’s Keywords (DE) | 766 |
| Authors | |
| Authors | 1339 |
| Authors of single-authored docs | 3 |
| Author Collaboration | |
| Single-authored docs | 3 |
| Co-Authors per Doc | 6.42 |
| International co-authorships % | 29.74 |
| Document Types | |
| Research article | 269 |
| Authors | Title | TC | TCperYear | NTC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Durmusoglu et al., 2010 [2] | Health risk assessment of BTEX emissions in the landfill environment | 319 | 19.938 | 2.482 |
| Dai et al., 2017 [38] | VOC characteristics and inhalation health risks in newly renovated residences in Shanghai, China | 173 | 19.222 | 4.834 |
| Tiwari et al., 2010 [39] | Ambient levels of volatile organic compounds in the vicinity of petrochemical industrial area of Yokohama, Japan | 152 | 9.5 | 1.183 |
| Pinedo et al., 2013 [40] | Assessment of soil pollution based on total petroleum hydrocarbons and individual oil substances | 139 | 10.692 | 3.109 |
| Davidson et al., 2021 [8] | Effects of inhaled combined Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylenes (BTEX): Toward an environmental exposure model | 132 | 26.4 | 6.018 |
| Mor and Ravindra, 2023 [41] | Municipal solid waste landfills in lower- and middle-income countries: Environmental impacts, challenges and sustainable management practices | 124 | 41.333 | 8.75 |
| Hazrati et al., 2016 [42] | Preliminary assessment of BTEX concentrations in indoor air of residential buildings and atmospheric ambient air in Ardabil, Iran | 112 | 11.2 | 2.638 |
| Li et al., 2014 [43] | Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of benzene homologues in ambient air in the northeastern urban area of Beijing, China | 108 | 9.0 | 1.788 |
| Wu et al., 2018 [44] | Assessment of the health risks and odor concentration of volatile compounds from a municipal solid waste landfill in China | 103 | 12.875 | 2.321 |
| Zhao et al., 2019 [45] | Interaction of inhalable volatile organic compounds and pulmonary surfactant: Potential hazards of VOCs exposure to lung | 102 | 14.571 | 2.618 |
| Industry/Environment | BTEX-Containing Materials | Common Areas of Use/Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Home/Interior [46] | Paint, varnish, cleaning materials | Newly painted walls, carpets, furniture, cleaning products |
| Industry [47,48] | Paint, varnish, coating materials | Production lines, assembly areas, automotive industry, construction sites |
| Waste Facility [49] | Plastic, polymer, waste materials | Waste storage areas, recycling facilities, waste processing areas |
| Hookah Cafes [50,51] | Tobacco products, hookah accessories | Areas where hookah is smoked, sources of tobacco smoke |
| Transportation/Automotive Industry [52,53] | Vehicle interior materials, fuels | Gas stations, vehicle interiors, buses, taxis |
| Educational Institutions [54,55] | Plastic, paint, cleaning supplies | School buildings, classrooms, laboratories |
| Gas Stations [56,57] | Gasoline, diesel, LPG | Fueling areas, pumps, storage areas |
| Food Industry [58] | Packaging materials, cleaning products | Food production facilities, storage areas, restaurants |
| Electronic Waste [59] | E-waste, circuit boards, plastics | Electronic waste recycling facilities, storage areas |
| Beauty Salon [60] | Paint, tobacco products, cleaning supplies | Manicure/pedicure areas, tobacco smoke sources, cleaning products |
| Method Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Gas Chromatography (GC) [62,63] | This method is frequently employed in the separation and detection of volatile organic compounds. |
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) [34,64] | The combination of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is utilized for the determination of the structural composition and quantitative analysis of components. |
| Flame Ionization Detector (FID) [43,65] | The utilization of this method in conjunction with GC is a process of paramount importance in the detection of organic compounds. |
| Gas Chromatography–Photoionization Detector (GC–PID) [66] | GC–PID is a technique that offers rapid analysis capabilities and can be used for both online and offline measurements. |
| Activated Carbon Tube and Pump [67] | Used for collecting and analyzing air samples. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gökcan, A.; Demir, H.H.; Ozdemir, M.; Yasa, H.; Çelikten, H.; Demir, G. Occupational and Environmental BTEX Exposure: A Bibliometric Analysis Using Scientific Mapping. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121353
Gökcan A, Demir HH, Ozdemir M, Yasa H, Çelikten H, Demir G. Occupational and Environmental BTEX Exposure: A Bibliometric Analysis Using Scientific Mapping. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(12):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121353
Chicago/Turabian StyleGökcan, Ahmet, Hacer Handan Demir, Mükerrem Ozdemir, Hüdanur Yasa, Hakan Çelikten, and Göksel Demir. 2025. "Occupational and Environmental BTEX Exposure: A Bibliometric Analysis Using Scientific Mapping" Atmosphere 16, no. 12: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121353
APA StyleGökcan, A., Demir, H. H., Ozdemir, M., Yasa, H., Çelikten, H., & Demir, G. (2025). Occupational and Environmental BTEX Exposure: A Bibliometric Analysis Using Scientific Mapping. Atmosphere, 16(12), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121353







