Abstract
The study was based on 11 years of measurements of ionospheric parameters and atmospheric electric fields reflecting the polarity of lightning discharges and recording return strokes. The response of ionospheric parameters to thunderstorms with lightning discharges of negative and positive polarity under quiet solar and geomagnetic conditions was considered. No changes in the dynamics of ionospheric parameters are observed during thunderstorms with lightning discharges of negative polarity. Variation in the daily course of total electron content and the appearance of wave-like disturbances with a period of 2–5 h are recorded during thunderstorms with lightning discharges of positive polarity. More small-scale disturbances were also detected. Intensification of the sporadic layer was observed in ~70% of the thunderstorm events with positive lightning discharges. A decrease in the height of the sporadic layer Es (h’Es) by 10 km and an increase in the level of radio wave absorption in the D region of the ionosphere were recorded. The experimental results of the study indicate that the polarity of lightning discharges and electromagnetic effects play a decisive role in the process of thunderstorms affecting the ionosphere.
1. Introduction
Radio communication is used by humanity in virtually all areas of its activity. However, its quality is closely linked to the state of the ionosphere, the medium through which radio waves propagate. The performance of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSSs) also depends on the state of the ionospheric conditions. The Earth’s ionosphere, the charged part of the upper atmosphere with a maximum density at 250–350 km altitude, is highly variable. The state of the ionosphere is mainly determined by a combination of phenomena called “space weather”. Ultraviolet and X-ray radiation from the Sun, high-speed solar wind streams, cosmic rays, coronal mass ejections, and the geomagnetic storms they cause all affect the parameters and structure of the ionosphere. However, significant deviations from median values are occasionally observed in ionospheric parameters under completely calm solar and geomagnetic conditions. Changes in ionospheric parameters in these cases are associated with processes in the lower layers of the atmosphere [1]. Among the possible sources capable of modifying the ionosphere are large-scale meteorological phenomena such as thunderstorms, typhoons and atmospheric fronts.
The nighttime ionospheric response during intense thunderstorm events was studied by Lay et al. [2] using Total Electron Content (TEC) data measured by Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers over the Great Plains, USA. These unique observations revealed anomalous TEC variations closely related in time and space to intense thunderstorms. The authors showed that the thunderstorm-induced TEC variation was ~1.4 TECU. It was found that TEC variations near thunderstorms had a higher-frequency composition than variations far from thunderstorms. The authors did not observe any noticeable local TEC variations on thunderstorm-free nights. The authors concluded that thunderstorms were the main source of ionospheric acoustic and gravity waves in the midlatitude region of the USA under consideration.
Ionospheric disturbances in GPS TEC data obtained over Hong Kong during thunderstorms in April 2014 were investigated by Kumar et al. [3]. TEC disturbances were recorded at a distance of ~500 km from the center of lightning activity. The disturbances had periodic structures lasting from several minutes to hundreds of minutes, which coincided with the periods detected in the work of Lay et al. [2]. A noticeable relationship between thunderstorms and wave-like disturbances in the total electron content of the ionosphere was noted by Ogunsua et al. [4], who used GPS TEC data obtained in the West African region in the Congo Basin [4]. The largest deviation of TEC from the average values was ~1.5 TECU. The authors concluded that wave-like disturbances could be the result of the influence of gravitational waves, as suggested by researchers [2,3,4,5,6].
Several studies have shown the effects caused by thunderstorms in the sporadic Es layer. Significant increases and decreases in Es height in mid-latitudes directly above thunderstorms were detected as a result of regular measurements of the ionosphere in Chilton, UK, by Davis et al. [7,8]. The results of Barta et al. [9], in contrast to previous authors, illustrate the disappearance of the Es layer (decrease in electron density within Es) that occurred two hours after the thunderstorm. These results are based on ionospheric observations obtained using ground-based ionosonde observations in Pruhonice (the Czech Republic) and Nagycenk (Hungary) for two active thunderstorms on 20 June 2013 and 30 July 2014. The authors report that geomagnetic conditions during these periods were calm. Significant changes in the critical frequency of the Es layer were observed by Borchevkina et al. [10] during thunderstorm events in Kaliningrad against a background of calm geomagnetic conditions [10,11]. The delay between the ionosphere response and the moment of maximum disturbances in atmospheric parameters was approximately three hours.
Compelling evidence of the influence of various geophysical processes in the troposphere on the ionosphere has been obtained in the works of Pulinets et al. [12,13]. It has been revealed that electromagnetic effects, rather than those related to the propagation of acoustic waves, play a significant role in the process of influencing the ionosphere. Variations in the parameters of the global electric circuit (GEC) play a decisive and important role in this process. The GEC in this case is the connecting link in the transmission of disturbances between the troposphere and the ionosphere. The stable electrodynamic connection between these atmospheric layers manifests itself in the appearance of optical emissions (“sprites” and “blue jets”) above thunderstorm clouds [14], in changes in electrical conductivity, and in an increase in electron concentration in the mesosphere at altitudes where luminescence occurs [15]. Detailed reviews of transient luminous events and their electrodynamic effects can be found in Surkov and Hayakawa [16]. Calculations by Pasko et al. also indicate a possible impact of sprites on the ionosphere [17,18,19].
Experimental observations and theoretical calculations have made it possible to develop mechanisms capable of explaining the interactions detected in the troposphere-ionosphere region. One of them considers the effects of heating and accelerating surrounding electrons by electromagnetic pulses or large quasi-electrostatic fields generated during lightning discharges [17,18,19,20,21]. These processes lead to increased ionization and optical emissions in the atmosphere, affecting the physics, chemistry, and dynamics of the ionosphere.
The runaway breakdown mechanism is currently the most developed and promising theory put forward for explaining discharge initiation in the atmosphere, including high-altitude discharges [22,23]. Lightning discharge occurs at an electric field strength that is an order of magnitude lower than that required for electrical breakdown in natural thunderstorm conditions. The runaway breakdown theory describes the mechanism of avalanche growth of high-energy electrons due to their acceleration in the electric fields of thunderclouds. This mechanism is a decisive factor in creating high conductivity of the medium, ensuring rapid transfer of electric charge and, accordingly, a decrease in the field strength required for breakdown. Runaway electron breakdown is likely a key process underlying high-altitude discharges occurring between thunderclouds and the ionosphere.
At present, a considerable number of studies have been devoted to the impact of thunderstorms on the upper layers of the atmosphere. However, there is insufficient solid experimental evidence of the connection between processes in the Earth’s troposphere and ionosphere during thunderstorm activity. The mechanisms of disturbance penetration from the lower atmosphere into the ionosphere are under discussion. Therefore, further experimental and theoretical studies of ionospheric dynamics under thunderstorm conditions are needed. The aim of this paper is to experimentally study the impact of thunderstorms with lightning discharges of different polarities on ionospheric parameters. The study was based on long-term data from vertical radiosounding of the ionosphere and measurements of the atmospheric electric field.
2. Experimental Facility
Direct parameters characterizing thunderstorm activity are values of the quasi-static electric field, Ez (the vertical component of the atmospheric electric field) and its high-frequency component dE/dt (the time derivative of the electric field associated with return strokes). The main requirements for equipment for studying processes in a thunderstorm atmosphere are a wide range of measurements of quasi-static electric field strength and high time resolution.
The experimental complex “ELIS-TS” (Electric Field and Lightning Detection System at Tien Shan) for measuring atmospheric electric fields in thunderstorm conditions was developed and installed at the high-mountain Tien Shan Cosmic Rays Station (3340 m above sea level, 43°20.0′ N, 76°56.0′ E) in 2005. The complex consists of two detectors: the detector of the quasistatic electric field, Ez, and the detector of the high-frequency component of the electric field. The detector of the atmospheric electric field, Ez component, is an electrostatic fluxmeter (“field mill”) that was designed to measure the vertical component Ez in the range of ±50 kV/m with a sensitivity of 10 V/m.
The detector of the high-frequency component, dE/dt, registers the return stroke in the range of ±600 V/m and, at the moment of the lightning discharge, generates a control signal, i.e., a trigger, for a complex of installations that measures various geophysical parameters. Both measuring systems can work in two modes: “slow” and “fast”. The “slow” mode is intended for recording the measured parameters of the atmosphere in “fair weather” conditions and in the absence of lightning discharges (time resolution 0.05 s). The “fast” mode (time resolution 50 µs) is started by the trigger system due to a signal that comes from a sensor that measures dE/dt when a thunderstorm front approaches. The primary viewing and processing of atmospheric electric field measurements are performed using custom Python-based software, which allows visualization of the recorded data at different time resolutions, provides preliminary analysis, and determines the onset time and duration of thunderstorm events.
Ionosphere observations are carried out at the Institute of the Ionosphere (Almaty; 43.25 N, 76.92 E) on a digital ionosonde PARUS (https://compass.izmiran.ru/ionosphere/parus, accessed on 1 September 2025) connected to a computer, which is designed to collect, store and process ionograms. Information is extracted from ionograms using a semi-automatic method. The ionosonde collects data at 5-min intervals, with a vertical height resolution of approximately 2.5 km, and operates over a frequency range of 0.5–30 MHz. The state of the lower ionosphere was estimated by studying the variations in the minimum reflection frequencies from the ionosphere (fmin) and the critical frequencies of the sporadic layer E (foEs), which were obtained via vertical radio sounding of the ionosphere during the considered thunderstorm events. TEC data were used as an alternative to the foF2 parameter when intense sporadic formations were observed in the E region of the ionosphere. Sporadic formations can screen reflections from the F region. TEC values were obtained from mid-latitude GPS Chum [42.99 N, 74.75 E] and Sele [43.18 N, 77.02 E] database from www.ionolab.org/iriplasonline/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
3. Event Selection for Analysis
This paper examines 125 thunderstorm events with lightning discharges of different polarities at the high-altitude station in the Northern Tien Shan Mountains between 2005 and 2015. A detailed description of the characteristics of thunderstorm activity is presented in [23]. To study the influence of thunderstorm activity on the ionosphere, 50 thunderstorms with numerous lightning discharges to the ground and a response in the high-frequency component of the atmospheric electric field during a return stroke up to ±600 V/m (nearby thunderstorms). The possibility of high-altitude discharges above thunderstorm formations was assessed. Cloud–ionosphere discharges are associated with Mesoscale Convective Systems (MCSs), which are significant in horizontal extent and are not observed above local thunderstorms.
Table 1 includes 20 thunderstorm events from this catalog that were recorded under calm geomagnetic conditions and without the effective influence of solar flares. The specified conditions significantly reduced the number of events for considering the impact of thunderstorm activity on the ionosphere. However, they confirm the results of a study that ~70% of cases of thunderstorm activity are observed after the impact of coronal mass ejections and high-speed sporadic solar wind streams on the Earth’s magnetosphere and atmosphere [24,25]. These thunderstorm events were excluded from the analysis if the criteria for calm geomagnetic conditions were not met.

Table 1.
Storm events recorded under calm heliogeomagnetic conditions.
Geomagnetic field activity was assessed using data from the Dst index (http://wdc.kugi.kyoto-u.ac.jp/, accessed on 1 September 2025) and the daily average planetary Ap index (http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/stp/GEOMAG/, accessed on 1 September 2025). The criterion for calm geomagnetic conditions was a Dst geomagnetic activity index value on the day of thunderstorm activity and on the previous day within ± 20 nT. The symbols in brackets indicate the nature of the thunderstorm discharges (positive (+), negative (−) or mixed (+/−)). The locations of thunderstorm events with positive, negative, and mixed discharges are indicated in the figures by the symbols “↑”, “▼”, and “◆”.
Thunderstorm events lasting at least half an hour with effective lightning discharges that had a significant impact on the quasi-static electric field are highlighted in red in Figures 1, 2, 5, 6, and 7. Information about solar events (flares and their class), CMEs, HSSs, their geo-effectiveness, and the date of their arrival at the Earth’s magnetosphere boundary was obtained from weekly space weather surveys.
Information about solar and space weather conditions, including solar flares (with their class), coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and high-speed solar wind streams (HSSs), as well as their geo-effectiveness and arrival times at the Earth’s magnetosphere, was obtained from the weekly reports of the Space Weather Prediction Center (ftp://ftp.swpc.noaa.gov/pub/warehouse, accessed on 1 September 2025). The effects of thunderstorms on the upper ionosphere are studied using hourly and 15-min values of the critical frequency of the F2 layer (foF2) and the virtual height of the F layer (h’F). The parameter fmin, which is an indicator of changes in absorption in the D-ionosphere, and the parameters of the sporadic layer Es (foEs and h’Es) were used to assess the impact of thunderstorm activity on the lower ionosphere.
The characteristics of ionospheric parameters were examined sequentially during thunderstorms with lightning discharges of negative and positive polarity using methods of statistical processing of experimental data.
4. Results
4.1. Features of Ionospheric Parameters During Thunderstorm Activity with Lightning Discharges of Negative Polarity
Let us consider the changes in ionospheric parameters on 3 September 2008 during the thunderstorm with lightning discharges of negative polarity listed in Table 1. Records of the quasi-static electric field (blue color) and return lightning discharges (green vertical lines) are presented in Figure 1’s upper panel. The record of return lightning discharges (return strokes) is masked by the record of the quasi-static electric field. The quasi-static electric field sharply takes positive values due to the fact that the negative charge, which is transferred to the ground, decreases from above. The peculiarity of lightning discharges in a given thunderstorm is the slow recovery of the quasi-static electric field. It can be connected with features of orography, as well as shielding and amplification of fields by surrounding mountain peaks.
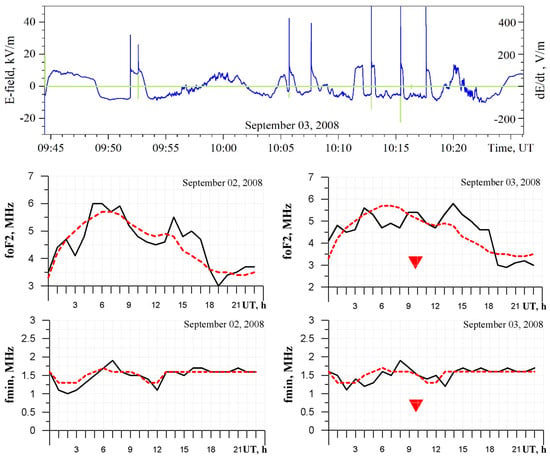
Figure 1.
Variations in the Atmospheric Electric Field during a Thunderstorm with Negative Polarity Lightning Discharges and Associated Ionospheric Responses in foF2 and fmin on 2–3 September 2008. Red triangles (▼) denote negative lightning discharges.
Due to low electron density in the lower ionosphere, effective sounding of electron distribution is difficult; therefore, the effects of ionospheric perturbations during thunderstorm activity are insufficiently studied. We made an attempt to search for such effects in the lower ionosphere during ground-based radiosounding at the ionospheric station Alma-Ata using data on registration of the minimum reflection frequency, fmin, which is an indicator of changes in absorption in the D-region of the ionosphere and parameters of the sporadic layer Es (foEs and h’Es). The state of the upper ionosphere was determined by the dynamics of the critical frequency of the F2 layer (foF2), which is proportional to the maximum electron density in the ionosphere.
The results of registration of ionospheric parameters fmin and foF2 for 2 and 3 September 2008, under quiet geomagnetic conditions are presented in the lower and middle panels of Figure 1. The dotted line represents the median value of these parameters. The position of the thunderstorm with negative discharges is marked in the figures by the symbol “▼”. Changes in the lower ionosphere in this event, judging from the variations in the minimum reflection frequency, fmin, are not observed. The parameter fmin is within the median values both in meteorological calm conditions on 2 September and during the thunderstorm on 3 September. The parameters of the upper layer of the ionosphere F2, foF2, also do not change much. The absence of sporadic formations in the E area is characteristic of this period.
The values of ionospheric parameters during thunderstorm activity with negative discharges in other events considered by us do not differ from the values under quiet geomagnetic conditions. The results of measurements presented in Figure 2 are a confirmation of this conclusion. Two thunderstorms with numerous negative discharges were recorded on 10 August 2010 in quiet geomagnetic conditions, which recovered after the impact of the CME on the Earth’s atmosphere and magnetosphere. The record of the atmospheric electric field during the second thunderstorm (No. 17 in Table 1) is presented in the upper panel of Figure 2. The geomagnetic field activity from the Dst index data for August 2010 is presented in the middle panel of the figure. The lower panel of this figure presents the values of the ionospheric parameter fmin.
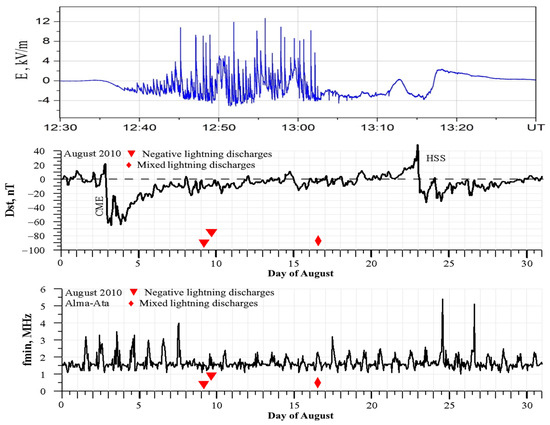
Figure 2.
Variations in the atmospheric electric field (upper panel) during the thunderstorm on 10 August 2010, the geomagnetic activity index (middle panel), and the ionospheric parameter fmin (lower panel) in August 2010. Red triangles (▼) denote negative lightning discharges, and red diamonds (◆) indicate mixed-polarity discharges.
The values of the ionospheric parameter fmin in the figure demonstrate sensitivity to the change in geomagnetic conditions caused by coronal mass ejection and geomagnetic storm. The increase in fmin reflects the increase in the level of electron concentration in the lower ionosphere and the increased absorption of the sounding signal. However, on 9 and 10 August, the values of the Dst index and the ionospheric parameter fmin are restored to the values corresponding to calm geomagnetic conditions. The intense thunderstorm events with negative discharges were not reflected in the ionospheric parameter fmin.
4.2. Features of Ionospheric Parameters During Thunderstorm Activity with Lightning Discharges of Positive Polarity
Positive lightning discharges are typically estimated to constitute ~10% of the total number of discharges. However, according to observations of the polarity of lightning discharges during thunderstorm activity at the high-mountain Tien Shan station, this value exceeds 20%. This is probably a peculiarity of high-mountain thunderstorms [23]. High-mountain discharges directed to the ionosphere are associated exactly with positive lightning discharges during thunderstorm activity. They carry a much larger charge than the negative ones, reaching up to 100 C (coulombs) or more. The electric field is directed toward the Earth and accelerates electrons toward the ionosphere. Above the thunderstorm formations, up to the lower ionosphere, there is an electric field exceeding the minimum breakdown field on fleeing electrons [22,23]. During this period, the possibility of high-altitude discharge (sprites, elves, jets) appears [14]. The observed optical phenomena in the atmosphere above thunderstorm formations due to this process have a very short duration, as well as lightning discharges.
Experimental installations at the high-altitude Tien Shan station for measuring the quasi-static electric field and the high-frequency component, dE/dt (return stroke), have a very high temporal resolution during lightning activity (time resolution 50 μs). The high temporal resolution of detectors allows us to detect the “high-frequency components” of lightning discharge, which in nature we can sometimes observe with the naked eye only as its flicker. Up to 10–20 returning lightning discharges can pass through one visible channel. Figure 3 shows the synchronous recording of the intensity of the quasi-static electric field and its high-frequency component dE/dt (return stroke, vertical green lines) during one positive lightning discharge of the thunderstorm on 15 May 2006. The jump in the quasi-static electric field and the values of the high-frequency components reach the maximum recorded values. We observed mainly positive lightning discharges in this thunderstorm. However, the size of the thunderstorm formation was insignificant and the number of discharges was small, so the development of the cloud-ionosphere discharge is unlikely.
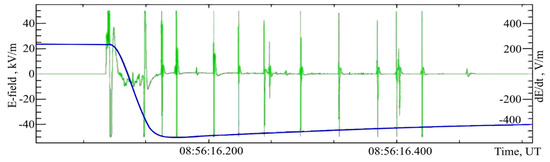
Figure 3.
Synchronous recording of quasi-static electric field strength (blue line) and its high-frequency component dE/dt (green line) during one positive lightning discharge and return strokes.
4.3. Thunderstorm Activity on 10 July 2010
The thunderstorm activity recorded under quiet geomagnetic conditions and without the effective influence of solar flares on the ionosphere on 10 July 2010 is the longest in the list of events in Table 1. It began at the high-mountain Tien Shan station at 07:37, UT, with positive and negative lightning discharges. Thunderstorm activity on this day lasted ~9 h with short breaks, changes in thunderstorm cells and polarity of lightning discharges, precipitation in the form of rain, and very large hail. The formation of high-altitude discharges in such events is the most probable. During the previous three days at the high-altitude Tien-Shan station, high-density cloudiness, fog and precipitation in the form of rain were observed. Part of the record of electric field variations during the thunderstorm front passage on 10 July 2010, through the high-mountain pass, where the experimental complex is located, is presented in Figure 4 with 10-s temporal resolution (upper panel) and with 1-s resolution (lower panel).
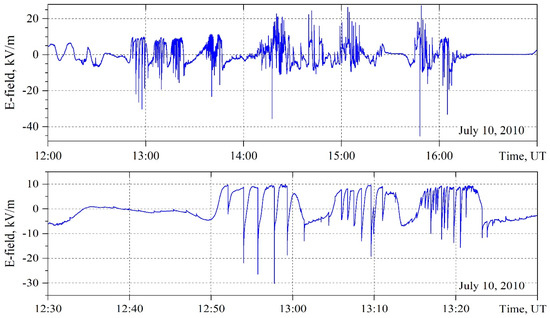
Figure 4.
Atmospheric electric field variations during the thunderstorm on 10 July 2010 at the Tien Shan station shown for two time intervals: 12:00–16:00 UT (top) and 12:30–13:30 UT (bottom).
Three thunderstorm cells with apparent positive lightning discharges and a duration of ~40 min are observed in the upper panel of the figure. Only positive discharges are also observed in the next thunderstorm cell until 13:50, UT. All other thunderstorm cells were accompanied by both positive and negative lightning discharges. The synchronous recording of the quasi-static electric field strength and high-frequency component, dE/dt (return strokes), with millisecond time resolution of the presented positive discharges is similar to the recording in Figure 3.
4.4. Features of Ionospheric Parameters During Thunderstorm Activity on 10 July 2010
Variations in the lower ionosphere parameters (foEs, h’Es) for the period 10–11 July 2010 are shown in Figure 5. A small increase (up to 3 MHz) of fmin values is observed on 10 July relative to the median (dashed red line). The fmin values are within the background level after the passage of the thunderstorm front on 11 July. We believe that the increase in fmin values is determined by the passage of the thunderstorm front through the gorges of the Northern Tien Shan and the high mountain pass, where the experimental facilities are located. The geomagnetic conditions on 10 July were quiet, and solar flares were not observed at all.
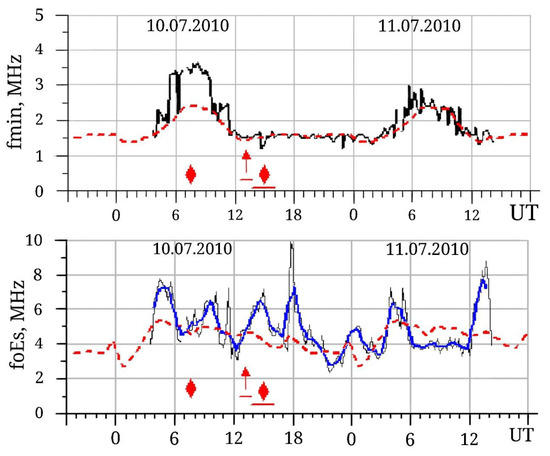
Figure 5.
Variations in fmin, foEs, and Es-layer height (h’Es) on 10–11 July 2010. The black line shows the original data, the red dashed line represents the median, and the blue line indicates the moving average. Red upward arrows (↑) denote positive lightning discharges and red diamonds (◆) indicate mixed-polarity discharges.
Particular attention is drawn to the behavior of the critical frequencies of foEs, which, during the period of intense and prolonged thunderstorm activity, experience distinct quasi-wave variations with a period of ~4 h and peak-to-peak amplitude of ~2 MHz, Figure 5 (middle panel).
During the period of the complex of active thunderstorm events, a noticeable lowering (by ~10 km) of the Es layer height (h’Es) is revealed, as shown in the lower panel of Figure 5. The beginning of the lowering coincides with the passage of the thunderstorm front with numerous effective positive lightning discharges, as shown in Figure 4. The lowered values of the Es (h’Es) height are observed until the end of the thunderstorm activity (~16:20, UT), in which, after a series of thunderstorm cells with positive lightning discharges, thunderstorm cells with mixed lightning discharges (positive and negative) were registered. However, the positive discharges prevailed both in number and in the efficiency of their impact on the atmospheric electric field. Significant enhancement and decrease in Es height at mid-latitudes directly above thunderstorms were also detected from regular measurements of the ionospheric state at Chilton, UK, by Davis et al. [7,8].
Data on ground-based vertical radiosonde of the ionosphere showed significant bursts of the values of critical frequencies of the sporadic Es layer during the period under study. This was the cause of the shielding of the F region by the Es layer. The nature of foF2 variations in this case was not possible to show. However, as an alternative to the foF2 parameter, the TEC plot of Figure 6 was considered.
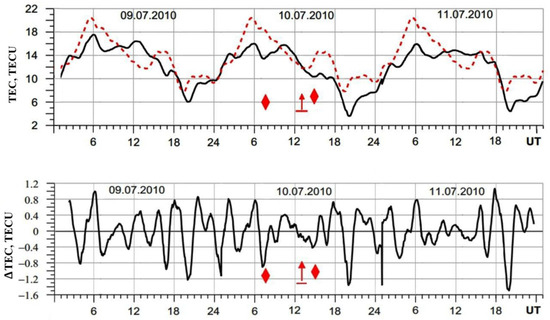
Figure 6.
TEC and ΔTEC variations during 9–11 July 2010, near the Tien Shan station. The upper panel shows the diurnal TEC variations (black solid line) and the reference distribution for a magnetically quiet day (red dashed line), while the lower panel presents the detrended component (ΔTEC), illustrating short-period fluctuations associated with thunderstorm activity. Red symbols mark the times of the observed thunderstorm events.
The upper panel of Figure 6 shows the daily variations of the TEC for the period 9–11 July 2010, including the time of passage of the thunderstorm front through the high-mountain station on 10 July 2010. The position of thunderstorm events on the time axis is shown by the corresponding symbols (events with positive (↑) and mixed (◆) discharges). The dotted line represents the median value of the daily distribution of the electron content in the ionosphere characteristic of the Kazakhstan region under calm meteorological and geomagnetic conditions, Yakovets et al. [26].
The typical diurnal distribution of the electron content in the ionosphere becomes non-typical, with the appearance of a wave-like inhomogeneous structure, not only on the day of thunderstorm activity at the station but also on 9 and 11 July. Apparently, the change in the typical diurnal distribution of TEC in this event is connected with the duration of the thunderstorm front and its activity in the vicinity of the high-mountain station on 9 and 11 July. The variation in the form of the daily TEC in this event is also manifested in the displacement of the noon maximum to later hours.
To identify the perturbed component in the distribution of the TEC, we smoothed the TEC series by a 6th-degree polynomial (dashed line). The perturbed (fluctuating) component in the distribution of total electron content was obtained by calculating the difference between the current and smoothed TEC values. Figure 6, bottom panel, illustrates the smooth, periodic nature of the perturbation with a period of ~3 h and a peak-to-peak amplitude of ~2 TECU on the eve of thunderstorm activity at the high-mountain station, 9 July. However, after the beginning of prolonged thunderstorm activity at the Tien-Shan station on 10 July, an obvious violation of the regularity of the TEC wave structure and a decrease in the period of oscillations to ~60 min are observed. The amplitude of the “peak-to-peak” detected small-scale oscillations amounted to ~1 TECU. These quasi-periodic structures may resemble medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances (MSTIDs). However, in our case, they occurred under magnetically quiet conditions and coincided with thunderstorm activity accompanied by strong positive lightning discharges near the observation site. Similar background TID characteristics under quiet geomagnetic conditions, as well as the methods of their processing, are presented by Andreyev et al. [27].
4.5. Features of Ionospheric Parameters During Thunderstorm Activity on 2–6 August 2005
This period includes four intense events of thunderstorm activity. Three thunderstorms were accompanied only by positive lightning discharges. Negative discharges were observed after a series of positive discharges in one thunderstorm on 5 August. The analysis of meteorological conditions recorded by us at the high-mountainous Tien Shan station during this period showed clear low cloudiness only on 3 August. Cloudiness, rain, thunderstorms and occasionally hail were observed on the other days of the analyzed period. The changes in ionospheric parameters for the analyzed period are presented in Figure 7. A typical summer diurnal variation of the TEC, with a maximum at noon time and a pronounced summer anomaly characteristic of the middle latitudes of the region under consideration, was observed only on 3 August. It is presented by the dotted line on 2, 4 and 5 August 2005 in the figures for TEC values. For other ionospheric parameters, their median values under quiet geomagnetic conditions are presented by the dotted line.
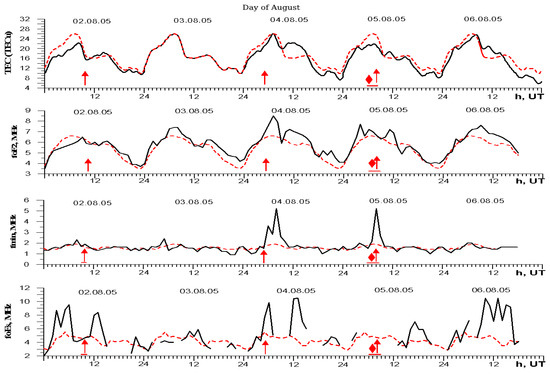
Figure 7.
Variations in ionospheric parameters on 2–6 August 2005. Red upward arrows (↑) denote positive lightning discharges and red diamonds (◆) indicate mixed-polarity discharges.
A violation of the typical pattern of daily distribution of the electron content in the ionosphere is observed on 2, 4–6 August. The modification of the diurnal course of TEC is manifested in the displacement of the noon maximum to later hours and in the smoothing of the summer anomaly. The suppression of the diurnal trend with the appearance of wave-like perturbations is also observed on the day of thunderstorm activity, which was especially manifested on 5 August. The wave-like perturbations continued to be observed for another day after the thunderstorm activity. Variations in the minimum frequency of reflection, fmin, also showed noticeable changes in the state of the lower ionosphere during these periods, especially on 4 and 5 August. The changes are determined by the increased absorption of the sounding signal in the D-region. A noticeable increase in the values of critical frequencies of the Es-layer (increase in the electron content in the sporadic E layer) was also observed during the periods of high thunderstorm activity.
5. Discussion
The experimental results demonstrate that the ionospheric response to thunderstorm activity strongly depends on the polarity of lightning discharges. During thunderstorms with negative discharges, no significant changes in ionospheric parameters were observed, indicating that such discharges do not produce sufficiently strong electric fields or upward-propagating disturbances to affect the ionosphere. In contrast, thunderstorms with positive discharges caused a clear modification of the daily course of TEC and the appearance of quasi-periodic wave structures, likely associated with the propagation of atmospheric gravity waves and quasi-electrostatic fields generated by lightning. The observed lowering of the sporadic Es-layer and the increase in fmin reflect enhanced ionization and absorption in the lower ionosphere. These effects may result from transient electric fields and electromagnetic pulses accompanying positive lightning discharges, which can influence ionospheric conductivity and plasma density at altitudes of 90–120 km.
The obtained results agree with the runaway electron mechanism proposed by Gurevich et al. [22,23], suggesting that strong positive lightning discharges can initiate upward-propagating ionization processes influencing the lower ionosphere. These observations highlight the role of positive lightning as a potential driver of small-scale ionospheric perturbations even under quiet geomagnetic conditions and contribute to a better understanding of troposphere–ionosphere coupling mechanisms.
6. Conclusions
The experimental study of the impact of thunderstorms with lightning discharges of different polarity on the dynamics of ionospheric parameters was conducted using unique long-term measurements of atmospheric electric fields with very high temporal resolution, as well as vertical ionospheric sounding data, under quiet helio-geomagnetic conditions.
The results of the study of the ionosphere state during thunderstorms with lightning discharges of negative polarity showed no changes in the dynamics of ionospheric parameters. Their values in the considered events did not differ from the values under quiet helio-geomagnetic conditions. Different effects were detected in the dynamics of ionospheric parameters during thunderstorms with lightning discharges of positive polarity and also during thunderstorm activity with mixed discharges (positive and negative):
- A change in the regular daily variations of the TEC, typical of the summer season of middle latitudes, is observed, which is manifested in the shift of the noon maximum of the daily variations to later hours and in the smoothing of the effect of the summer anomaly typical of middle latitudes of the northern hemisphere.
- In the background of the diurnal variations in the total electron content, the appearance of wave-like perturbations with an amplitude of ~3–4 TECU and a period of 2–5 h is registered. The period of wave disturbances decreases to 60–120 min during the active phase of thunderstorm activity with effective lightning discharges. The amplitude of the detected small-scale fluctuations of the total electron content for most cases considered in this work is ~1–2 TECU.
- Intensification of the sporadic layer Es (growth of foEs values) was registered, indicating an increase in the level of electron concentration at altitudes of 100–120 km. Intensification of the sporadic layer was observed in ~70% of the events considered. During an intense and prolonged complex of thunderstorm events on 10 July 2010, a decrease in the height of the sporadic layer Es (h’Es) was observed at ~10 km, the duration of which was about 4–5 h. In the events considered by us, there was also an increase in fmin values, which reflects the increase in the level of radio wave absorption in the D-region of the ionosphere.
The obtained experimental results of the study regarding the impact of thunderstorms on the ionosphere prove that the polarity of lightning discharges and electromagnetic effects play a determining role in the process of their impact on the ionosphere.
Author Contributions
V.A. developed the concept, designed and performed the evaluation, carried out the main data analysis, wrote the manuscript, and revised it. V.L. supervised the research work related to atmospheric electric fields and thunderstorm activity, contributed to data processing and analysis, manuscript preparation and revision, and prepared the tables and figures. G.G. supervised the research work related to the ionosphere, provided measurement results, contributed to their interpretation, prepared the tables and figures, and wrote the corresponding section of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the Committee of Science of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan, grant No. AP23489628.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Forbes, J.M.; Palo, S.E.; Zhang, X. Variability of the ionosphere. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2000, 62, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, E.H.; Shao, X.-M.; Carrano, C.S. Variation in total electron content above large thunderstorms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1945–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Singh, R.P. Thunderstorm-/lightning-induced ionospheric perturbation: An observation from equatorial and low-latitude stations around Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 9032–9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsua, B.O.; Srivastava, A.; Bian, J.; Qie, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, R.; Yang, J. Significant Day-time Ionospheric Perturbation by Thunderstorms along the West African and Congo Sector of Equatorial Region. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, E.H.; Shao, X.-M.; Kendrick, A.K.; Carrano, C.S. Ionospheric acoustic and gravity waves associated with midlatitude thunderstorms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 6010–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Liu, H. Generation of large-scale gravity waves and neutral winds in the thermosphere from the dissipation of convectively generated gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, A10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.J.; Johnson, C.G. Lightning-induced intensification of the ionospheric sporadic E layer. Nature 2005, 435, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.J.; Lo, K.-H. An enhancement of the ionospheric sporadic-E layer in response to negative polarity cloud-to-ground lightning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L05815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, V.; Haldoupis, C.; Sátori, G.; Buresova, D.; Chum, J.; Pozoga, M.; Berényi, K.A.; Bór, J.; Popek, M.; Kis, Á.; et al. Searching for effects caused by thunderstorms in midlatitude sporadic E layers. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2017, 161, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchevkina, O.P.; Karpov, I.V.; Karpov, M.I.; Korenkova, N.A.; Vlasov, V.I.; Leshchenko, V.S. Impact of meteorological storms on the E-region of the ionosphere in 2017–2018. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2020, 6, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchevkina, O.P.; Kurdyaeva, Y.A.; Dyakov, Y.A.; Karpov, I.V.; Golubkov, G.V.; Wang, P.K.; Golubkov, M.G. Disturbances of the Thermosphere and the Ionosphere during a Meteorological Storm. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.A.; Khegai, V.V.; Boyarchuk, K.A.; Lomonosov, A.M. The atmospheric electric field as a source of variability in the ionosphere. Phys.-Uspekhi 1998, 168, 582–589. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.A.; Liu, J.-Y. Ionospheric variability unrelated to solar and geomagnetic activity. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 34, 1826–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uman, M.A.; Rakov, V.A. Lightning: Physics and Effects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; p. 850. [Google Scholar]
- Rodger, C.J.; Cho, M.; Clilverd, M.A.; Rycroft, M.J. Lower ionospheric modification by lightning-emp: Simulation of the night ionosphere over the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 2, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surkov, V.V.; Hayakawa, M. Progress in the study of transient luminous and atmospheric events: A review. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 1101–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasko, V.P.; Inan, U.S.; Taranenko, Y.N.; Bell, T.F. Heating, ionization and Upward discharges in the mesosphere due to intense quasi-electrostatic thundercloud fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasko, V.P.; Inan, U.S.; Bell, T.F. Sprites as luminous columns of ionization produced by quasi-electrostatic thundercloud fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.F.; Reising, S.C.; Inan, U.S. Intense continueing currents following positive cloud-to-ground lightning associated with red sprites. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milikh, G.M.; Papadopoulos, K.; Chang, C.L. On the physics of high altitude Lightning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccippio, D.J.; Williams, E.R.; Heckman, S.J.; Lyons, W.A.; Baker, I.T.; Boldi, R. Sprites, ELF transients, and positive ground strokes. Science 1995, 269, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.V.; Milikh, G.M.; Roussel-Dupre, R.A. Runaway electron mechanism of air breakdown and preconditioning during of thunderstorm. Phys. Lett. A. 1992, 165, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.V.; Zybin, K.P. Runaway breakdown and electric discharges in thunderstorms. Phys.-Uspekhi 2001, 171, 1177–1199. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, V.; Lutsenko, V.; Gordiyenko, G.; Kryukov, S. Impact of various disturbance sources on the atmospheric electric field and thunderstorm activity of the Northen Tien-Shan. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, V.I.; Stozhkov, Y.I. Influence of active areas of the Sun on the global thunderstorm activity and weather on Earth. Short Commun. Phys. FIAN 2003, 3, 9–25. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295822261_Influence_of_active_areas_of_sun_on_global_thunderstorm_activity_and_weather_at_the_Earth (accessed on 23 October 2025). (In Russian).
- Yakovets, A.F.; Gordienko, G.I.; Litvinov, Y.G. Midlatitude summer nighttime anomaly in NmF2 according to the data of vertical sounding in Alma-Ata. Geomagn. Aeron. 2015, 55, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreyev, A.; Kapytin, V.; Yakovets, A.; Chsherbulova, Y. A Method for Determining Parameters of Mid-Scale Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances. Sensors 2025, 25, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).