1. Introduction
Traffic emissions currently represent one of the main sources of air pollution in Chinese cities [
1]. In some large and medium-sized cities, motor vehicles contribute to over 30% of nitrogen oxides (NO
X) and over 20% of particulate matter (PM
10 and PM
2.5) [
2,
3]. In response, the Chinese government has consecutively introduced and strengthened multiple policy measures, including “Action Plan for Air Pollution Prevention and Control” and the “Three Year Action Plan for Blue Sky Defense” in 2013, and the “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Law” revised in 2018, which provided a solid legal foundation for the treatment of motor vehicle exhaust emissions [
4,
5]. Meanwhile, emissions of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter related to transportation have a direct impact on human health. Epidemiological studies have linked NO
X exposure to increased risks of asthma, reduced lung function, and other respiratory diseases, while fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is associated with cardiovascular morbidity and premature mortality [
6,
7]. Populations living near major roads are especially vulnerable, and sensitive groups such as children and the elderly are disproportionately affected. These well-documented health impacts underscore the urgency of improving the accuracy and resolution of traffic emission inventories to support evidence-based air quality management and public health protection. Therefore, it is important to accurately and timely characterize vehicle operations and emission profiles for air pollution control and achieving these policy goals.
Current methods for estimating vehicle activity and emissions remain limited in scope and granularity. Traditional emission inventory approaches in China are primarily developed using an aggregated estimation method, calculated as the product of the number of registered vehicles, average annual vehicle kilometers traveled (VKT), and average emission factors within a given jurisdiction [
8]. While the increasing availability of emission data categorized by regulatory standards has gradually enhanced estimation accuracy, this approach remains inadequate for capturing the dynamic variations across regions, time periods, and vehicle categories [
9]. The reliance on static estimates makes it difficult to evaluate local policy effectiveness and to design data-driven control strategies. For example, non-local transit vehicles, especially heavy-duty trucks, are often excluded from traditional regional inventories despite their large impact. Recent high-resolution analyses using full-sample trajectory data revealed that in certain counties, emissions from non-local heavy-duty trucks can exceed those from local vehicles by ~15 times, contributing up to 31% of regional truck emissions [
10]. Additionally, although Portable Emission Measurement Systems (PEMSs) could provide high-frequency and vehicle-specific real-world emission data, their limited spatial coverage and sample size constrain their applicability for city-scale emission management [
11]. Consequently, traditional estimation methods fall short in supporting real-time pollution forecasting and responsive policymaking. There is an urgent need for more dynamic, fine-grained models to support operational management and timely regulatory intervention.
Recent advances in high-resolution traffic modeling can enhance the capture of spatial and temporal variability of traffic flow and associated emissions. These developments are driven by the integration of intelligent transportation systems (ITSs), online mapping platforms, and real-time monitoring, which provide valuable and detailed data [
12,
13,
14,
15]. For example, Li et al. [
16] utilized three machine learning algorithms: Random Forest, Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT), and Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), integrating taxi GPS and multi-source urban data, to conduct high-resolution spatiotemporal analysis of urban road traffic emissions. Similarly, Yang et al. [
17] constructed a machine learning-based model to forecast surface concentrations of NO
2, O
3, and PM
2.5 in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. However, several limitations remain related to data reliability and modeling robustness. ITS-derived data are often fragmented, inconsistently formatted, and lack standardization across regions, leading to uncertainty in emission estimation [
18]. Additionally, inconsistent data formats, incomplete data fusion algorithms, and lack of long-term data acquisition lead to inaccurate big data analysis results [
19,
20]. Moreover, existing methods struggle to capture the stochastic and non-linear nature of urban traffic flow, especially under dynamic conditions such as congestion, weather disruptions, and policy interventions [
21]. Machine learning methods provide powerful tools for traffic and emission modeling because they can capture complex, non-linear interactions between congestion, temporal variation, and traffic flow that are difficult to represent with traditional regression models [
22,
23,
24]. While machine learning has shown potential for capturing these complexities, existing methods often rely on static historical datasets and lack robust practical deployment [
25].
This study aims to build a high-resolution, transient, and accurate traffic monitoring model system through stable data flow. Based on this framework, multiple data sources including dynamic congestion index were gathered to develop a bottom–up spatiotemporal emission inventory. Through data preprocessing and the application of a Random Forest algorithm, vehicle emissions are estimated across the Jinan city at the road-segment level. This study provides a scientific basis for fine-grained assessment of environmental impacts and gives strong data support for real-time traffic emission management.
3. Results
3.1. Performance of Machine Learning
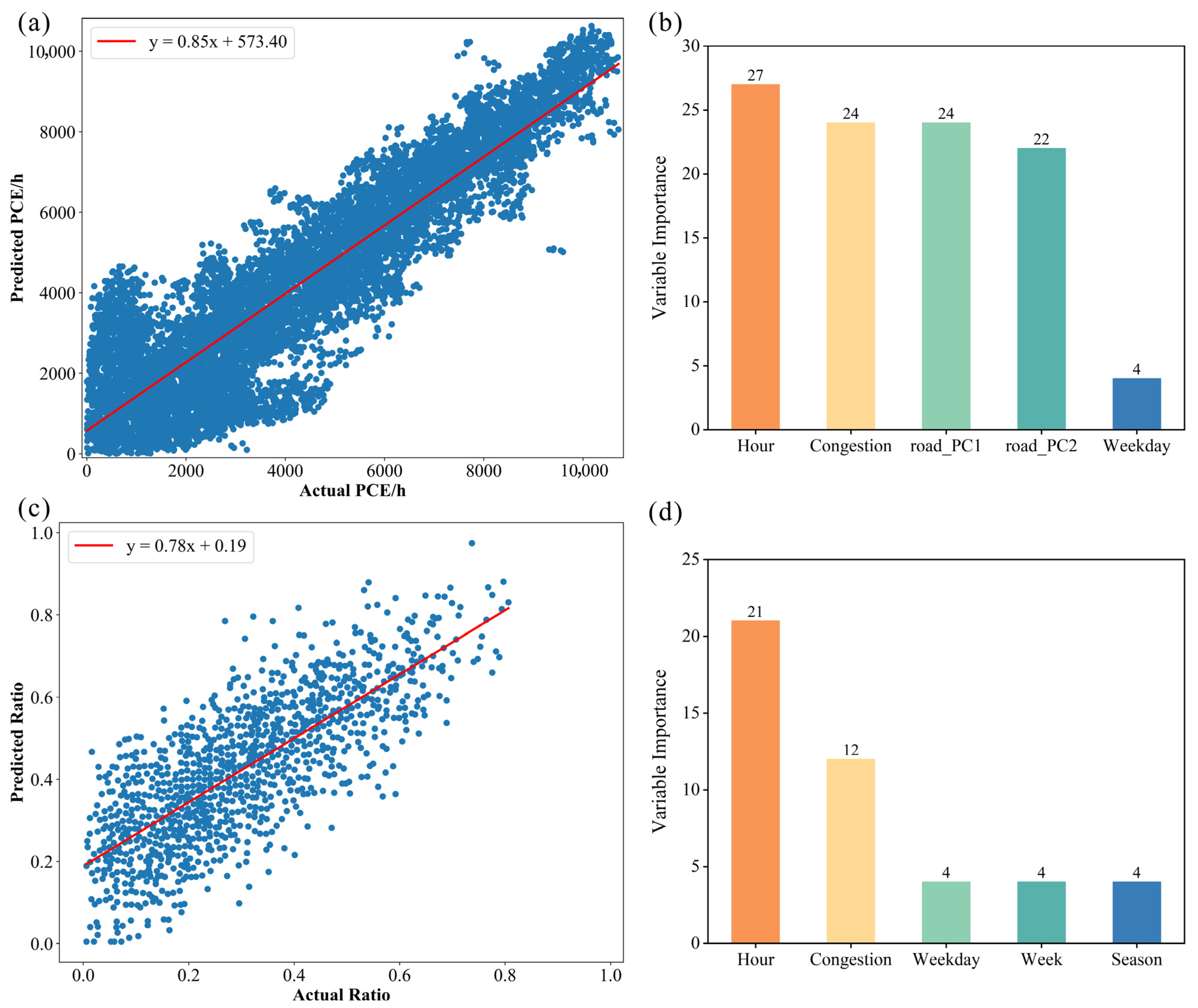
We applied a two-fold validation approach to verify the model, and the validation results are shown in
Figure 2. Fold 1 focused on predicting total traffic flow in PCE units, while Fold 2 aimed to estimate the proportion of passenger cars within total traffic. In Fold 1, the model showed strong performance (R
2 = 0.91), with predictions closely matching observed PCE values (
Figure 2a). The major errors occurred in the low volume end (lower left end in
Figure 2a), which reflect the fact that at the non-congested times—when vehicles operate in a traffic free flow mode—the congestion index is normally set as 1 to 2, thus it cannot reflect the vehicle speed and vehicle traffic flow. This situation normally happens in the evening, and the traffic flow is lower thus has less impacts on vehicle emissions and air quality. In this regard, we do not further iterate the model to avoid overfitting. In Fold 2, the model achieved moderate accuracy in predicting the passenger car share (R
2 = 0.77,
Figure 2c).
Figure 2b shows the top five impactful variables for Fold 1. The first and second principal components of road attributes represent the two features with the highest variance contribution obtained from the principal component analysis (PCA) of road data. The variable “hour” ranked first in importance, highlighting its critical role in capturing temporal dynamics. As a city known for its severe traffic congestion, Jinan exhibits strong time-dependent fluctuations in traffic flow, particularly during peak hours (e.g., 7:00–9:00 and 17:00–19:00). The PCE (Passenger Car Equivalent) essentially reflects traffic load per unit time, and the “hour” variable effectively captures the periodic variations in traffic demand. Furthermore, time-specific traffic control measures implemented in Jinan—such as peak-hour restrictions and odd-even license plate policies—contribute to pronounced differences in vehicle behavior across different times of day, thereby reinforcing the predictive power of this variable. The congestion index ranked second in variable importance, reflecting its strong influence on PCE. As a direct indicator of traffic efficiency and road utilization, congestion plays a critical role in shaping passenger car equivalent values. In Jinan—a city characterized by dense old urban areas, a complex road network, and high traffic volumes—congestion levels exhibit significant variability, especially along arterial roads and expressways. Importantly, congestion is not solely determined by vehicle volume; it is also influenced by signal timing, lane width, and incidental disruptions such as illegal parking or traffic accidents, which further enhance its explanatory power in the model.
Variables derived from road characteristics, such as those represented by principal components (e.g., road_PC1 and road_PC2), capture essential spatial features including land use intensity, road network density, and population distribution within defined buffer zones. The variable “weekday” received the lowest importance score but still contributes meaningful information to the model. Travel behavior in urban areas such as Jinan exhibits clear differences between weekdays and weekends. On weekdays (Monday to Friday), commuting patterns dominate, resulting in pronounced morning and evening peak traffic periods. In contrast, weekends are generally characterized by more discretionary and spatially dispersed travel, leading to different temporal and spatial traffic dynamics. Additionally, several traffic control policies in Jinan—such as license plate-based restrictions implemented on workdays—are explicitly tied to the day of the week. While the influence of “weekday” is less direct than other variables (e.g., hour or congestion), it nonetheless captures systematic variations in traffic demand and regulation that affect PCE.
For Fold 2, time-related variables played a crucial part in the vehicle type distribution (
Figure 2d). The most important variable is also the hour, followed by congestion index and three other time related variables. It is worth noticing that congestion index played important roles in both models. Compared to the Fold 1 model, almost all the important viables besides the road characteristics are time-related variables. This reveals that HDVs running are organized and responses to the dispatching strategy and control policies from the owner and the government regardless the surrounding rode situation.
Based on the model’s tendency to overestimate the PCE ratio, particularly during periods when freight vehicles are more likely to be present, several implications can be drawn regarding traffic regulation and modeling. The dominant role of temporal variables, especially “hour”, suggests that Jinan’s current freight restriction policies, though effective in general, may benefit from more finely tuned temporal and spatial control measures. Real-time or dynamically adjusted freight restrictions, tailored to actual traffic conditions rather than fixed intervals, could improve model calibration and traffic adaptability. Moreover, the model’s bias highlights the need for more detailed data on freight movement, especially during transitional periods around restricted hours. Enhanced vehicle classification data would allow for better differentiation between permitted and restricted freight flows, thereby reducing prediction error and improving model accuracy.
In addition, the integration of traffic policy variables, such as restriction enforcement status or intensity, into the modeling framework, could further enhance predictive performance and enable robust scenario analysis. This would allow transportation planners to evaluate the potential impacts of policy changes before implementation. Finally, in light of the strong time-dependent patterns in traffic composition, policymakers are encouraged to promote off-peak logistics through targeted incentives or dynamic tolling strategies. The development of smart freight routing systems that align with regulatory constraints while minimizing network congestion would support more balanced and sustainable urban traffic management.
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Traffic Flow Distribution
As illustrated in
Figure 3, we analyzed the traffic flow across various road types in Jinan City and identified distinct spatial and temporal patterns for both light and heavy vehicles. We classified the road network into six categories: urban ring expressways, highways, national roads, provincial roads, county roads, and township roads, and recorded vehicle flows hourly over a 24 h period.
As shown in
Figure 3d, the urban ring expressways exhibited concentrated traffic flows, particularly in the central and eastern regions. Light vehicle volumes peaked sharply at 914 vehicles/h around 8:00 a.m., corresponding to morning commuting hours. A secondary evening peak of 789 vehicles/h occurred around 6:00 p.m. In contrast, heavy vehicle volumes remained relatively stable throughout the day, fluctuating slightly around 85 vehicles/h, suggesting the effective implementation of vehicle restrictions during peak periods, in line with Jinan’s traffic control policies. On highways (
Figure 3e), light vehicle traffic reached the highest peak among all road types, at 1306 vehicles/h around 8:00 a.m. Heavy vehicle volumes were also more pronounced than on the urban ring expressways, peaking at 151 vehicles/h, likely due to logistics and freight transport linked to intercity connections. The traffic distribution was geographically more dispersed, covering both urban and suburban fringe areas.
Figure 3f showed that national roads functioned as major transport arteries with substantial light vehicle activity, peaking at 843 vehicles/h in the morning and remaining above 700 vehicles/h through midday. Heavy vehicle flows reached 74 vehicles/h, a moderate level compared to highways, reflecting more flexible freight movement allowed on national roads while still discouraging congestion in central urban areas. Provincial roads, shown in
Figure 3g, exhibited traffic patterns similar to national roads but with slightly lower volumes. Light vehicles peaked at 840 vehicles/h, while heavy vehicles reached 80 vehicles/h. The spatial distribution was more uniform, serving both regional traffic and suburban commuting. These findings aligned with Jinan’s policy goal of decentralizing traffic away from core urban areas. As presented in
Figure 3h, county roads displayed a light vehicle peak of 846 vehicles/h in the morning and 747 vehicles/h in the evening, with a pattern similar to but less intense than highways. Heavy vehicle traffic on county roads peaked at 73.33 vehicles/h, which was notably higher than on some higher-level roads. This trend possibly reflected rural freight movement and agricultural supply transport toward urban centers. Township roads, visualized in
Figure 3i, carried the lowest traffic volumes, with light vehicle peaks at 851.34 vehicles/h and heavy vehicle peaks at 81.32 vehicles/h. Despite modest overall volumes, these roads were densely distributed in rural areas. The relatively strong morning peak suggested growing rural commuting and delivery activity, indicating an increasing role of township roads in supporting regional mobility. Across all road types, light vehicles exhibited a bimodal temporal pattern, with peaks during 7:00–9:00 a.m. and 5:00–7:00 p.m., consistent with commuter travel behavior. In contrast, heavy vehicle traffic remained relatively stable throughout the day, with moderate peaks that avoided rush hours. This trend demonstrated compliance with Jinan’s time-based vehicle restriction policies.
Spatially, heavy vehicle activity appeared more prominent on lower-grade roads, which may have reflected deliberate freight routing strategies intended to minimize congestion and pollution in the urban core. These findings affirmed the effectiveness of Jinan’s differentiated road-use strategy, where expressways and highways prioritized passenger vehicles during peak periods, while lower-grade roads accommodated a larger share of freight transport. Future transportation planning should continue to enhance traffic monitoring and optimize freight corridors to balance transportation efficiency with environmental and livability goals.
The traffic volume of both light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles in Jinan exhibits distinct variation patterns across different days of the week (
Figure A4). Light vehicle traffic volume peaked on Monday (12,753.94 vehicles) and gradually declined over the workweek, reaching a minimum on Thursday (11,858.68 vehicles). This trend suggested a typical commuter-based pattern, in which weekday traffic was largely driven by work and school travel. Throughout the week, light vehicles consistently accounted for over 77% of total traffic volume, with only minor daily variation, highlighting their dominant role in Jinan’s daily mobility. This distribution aligned with the city’s vehicle restriction measures and green commuting policies, which promoted the use of public transit and staggered travel during peak periods, especially on key urban road segments. Heavy vehicle volumes remained relatively steady throughout the week but showed a gradual decrease from Monday (1438 vehicles) to Thursday (1294 vehicles). A moderate increase followed on Friday (1338 vehicles), with slightly lower volumes observed over the weekend. This midweek trough corresponded with freight traffic restrictions implemented on weekdays, which limited the daytime movement of heavy-duty trucks in order to reduce congestion and emissions within the urban core. Despite these restrictions, heavy vehicles consistently represented about 22–23% of the weekly traffic volume, underscoring their essential role in logistics and goods distribution—particularly on peripheral roadways and during nighttime hours. The consistent share of heavy vehicle traffic across the week, despite fluctuations in total vehicle volume, reflected the effectiveness of Jinan’s time-phased traffic control policies. These findings were critical for refining day-specific congestion mitigation strategies, optimizing road network operations, and enhancing the environmental outcomes of differentiated vehicle control policies.
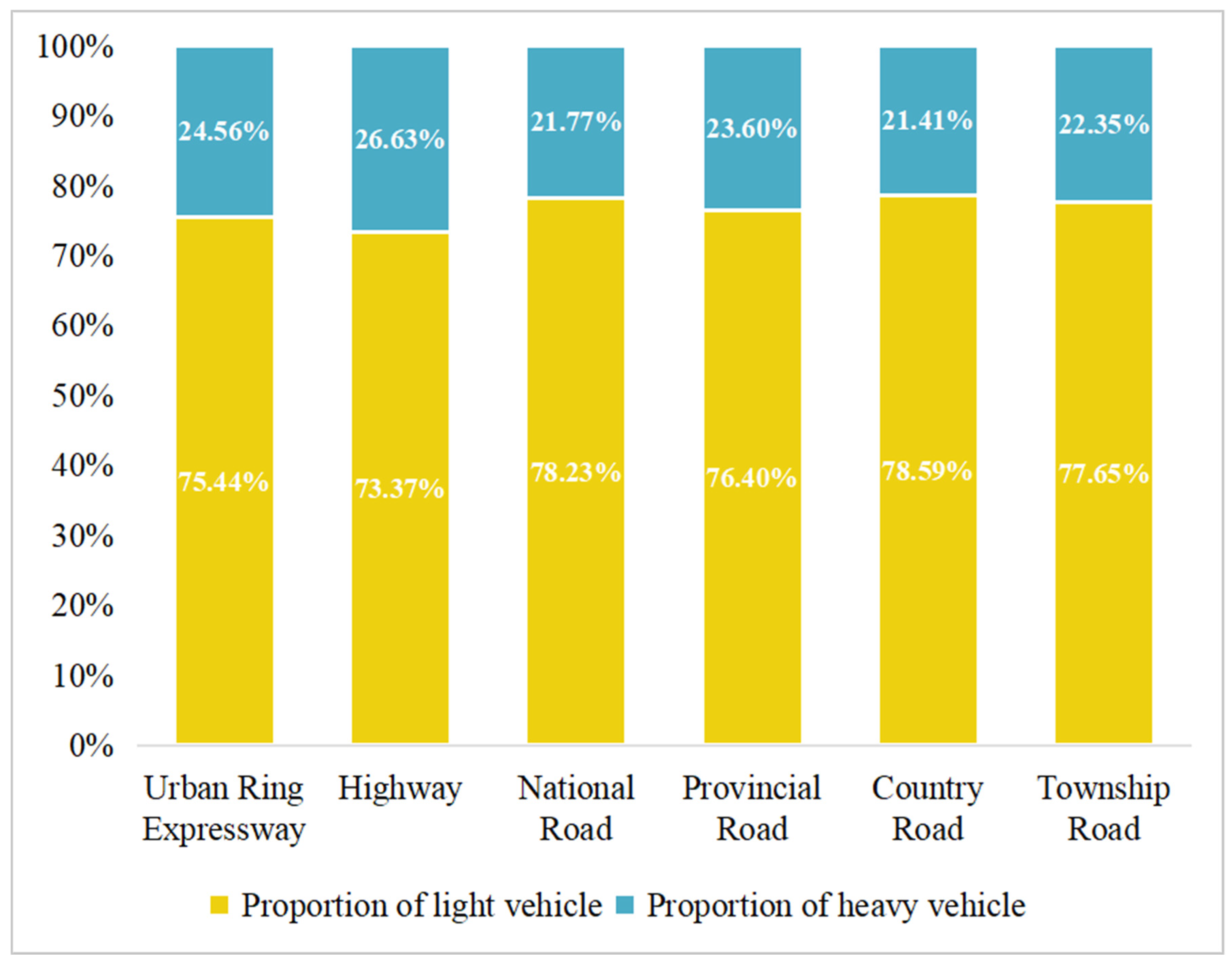
The traffic composition of light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles in Jinan shows slight differences across different road types (
Figure A5). Light vehicles constituted the majority of traffic across all road types, ranging from 73.37% on highways to 78.59% on county roads. Heavy vehicles made up the remaining traffic share, with the highest proportions observed on highways (26.63%) and urban ring expressways (24.56%). These roads functioned as freight-preferred corridors, often situated outside of central traffic restriction zones. This reflected the city’s strategy to redirect truck traffic away from densely populated residential areas. The lower proportions of heavy vehicles on provincial (23.60%), township (22.35%), national (21.77%), and county (21.41%) roads indicated the effectiveness of time-based and zonal freight control policies—such as the “limited hours and areas for truck access” policy—that restricted large freight vehicles during peak hours and within urban districts.
The observed traffic flow distribution across road types supported the effectiveness of Jinan’s hierarchical road network and classification-based traffic policies. By concentrating heavy-duty freight traffic on high-capacity corridors (e.g., highways and expressways) and restricting it on lower-grade roads, the city achieved a balanced spatial allocation that facilitated both economic activity and urban livability. This strategy also aligned with national guidelines on urban freight zoning and vehicle-type planning, which aimed to ensure smoother traffic flow and reduced vehicle emissions in sensitive urban areas. Future transport planning could further reinforce the role of urban ring expressways as freight corridors while strengthening the enforcement of truck access restrictions within the internal urban road system.
3.3. Emission Inventory Results
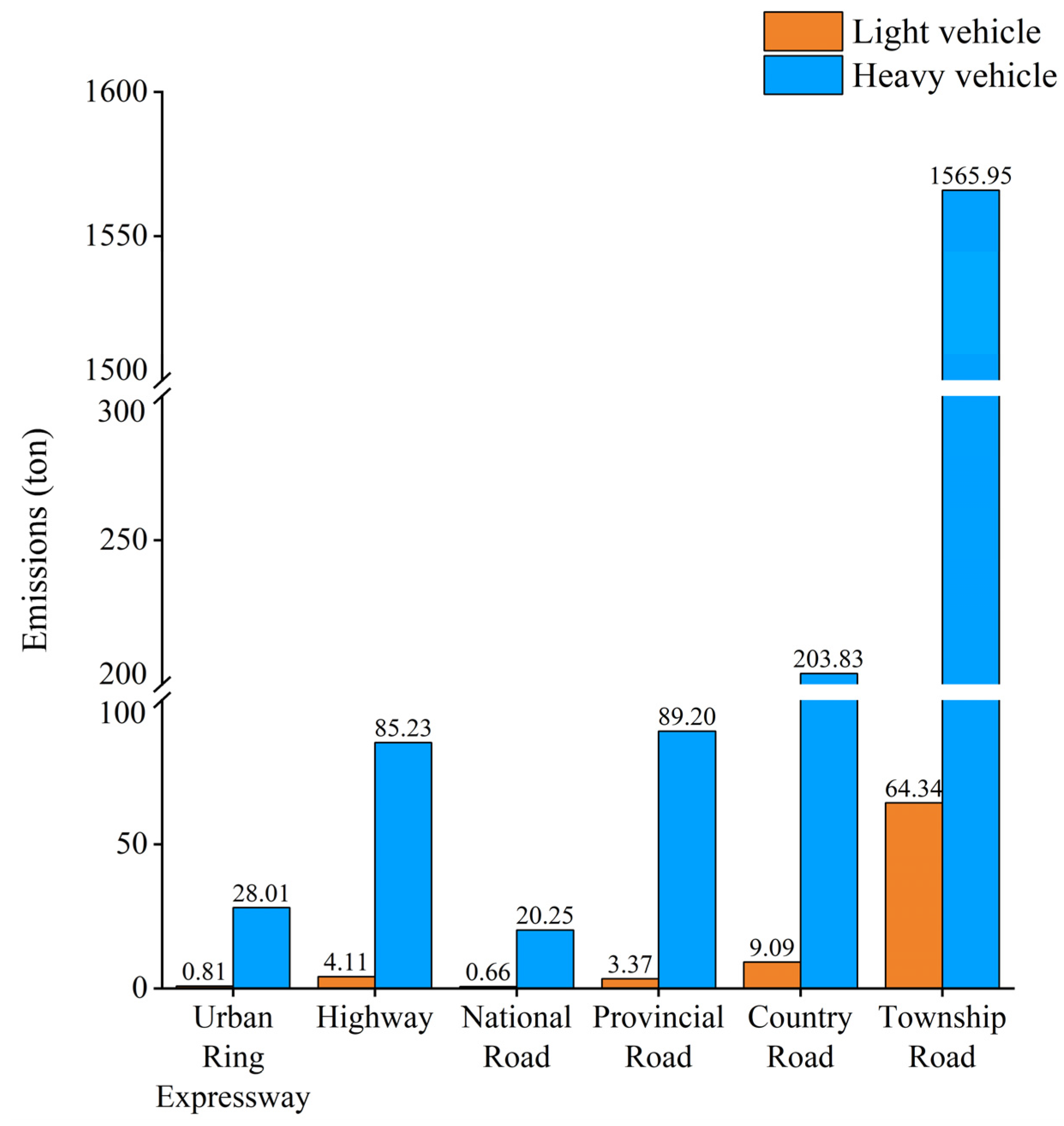
Figure 4 illustrated the spatial distribution of NO
X emissions from light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles across the Jinan metropolitan area, along with the emission quantities classified by road type. NO
X emissions from light-duty vehicles remained relatively low and more evenly distributed across the region. Hotspots primarily appeared in urban centers and along major transportation corridors. Emission levels ranged from 0 to 186.51 kg, with the highest concentrations occurring in areas with dense road networks and intense vehicle activity. In contrast, emissions from heavy-duty vehicles (
Figure 4b) appeared more spatially clustered and showed significantly higher intensities along expressways and freight-dominant corridors. Emission values ranged from 0 to 17,593.37 kg, which indicated that heavy-duty vehicles contributed substantially to overall NO
X emissions, especially in the southern and eastern parts of the study area. Township roads accounted for the highest total NO
X emissions, primarily driven by heavy-duty vehicles, reaching 1565.95 tons, followed by County roads (203.83 tons), provincial roads (89.20 tons) and highways (85.23 tons), as illustrated in
Figure 5. The unexpectedly high contribution of township roads to total NO
X emissions can be explained by several factors. First, township roads constitute the longest cumulative road length in Jinan, which amplifies their aggregate emissions. Second, restrictions on heavy-duty vehicles (HDVs) on expressways and urban ring roads divert a substantial share of freight traffic onto lower-grade township and county roads. Finally, HDVs operating on township roads tend to travel at lower and less stable speeds, which are associated with higher emission factors per kilometer. These combined effects explain why township roads, despite their lower design capacity, surpass highways in total NO
X emissions.
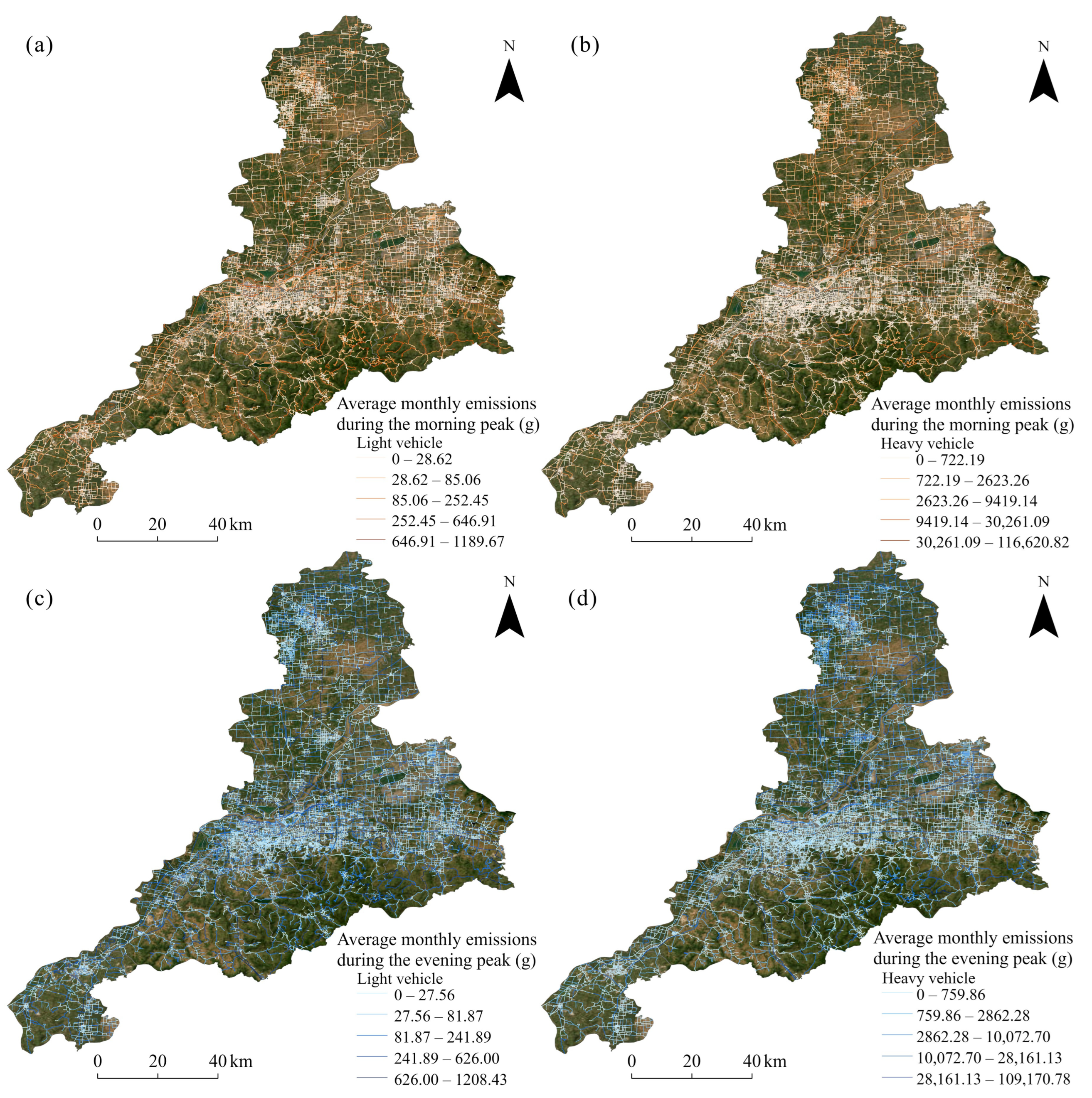
Figure A6 illustrates the spatial distribution of average monthly nitrogen oxide (NO
X) emissions from light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles during the morning and evening peak periods in Jinan. During the morning peak, emissions from light-duty vehicles (
Figure A6a) were relatively widespread but moderate in intensity. The highest emissions, ranging from 545.91 g to 1199.66 g, were concentrated in central urban areas and along major commuting corridors. In contrast, heavy-duty vehicle emissions (
Figure A6b) during the same period were significantly higher and more spatially clustered. Emission hotspots appeared primarily along expressways and key freight routes, particularly in the southern and eastern parts of the city. Maximum values exceeded 17,662.81 g, indicating that heavy-duty traffic contributed substantially to morning NO
X emissions. During the evening peak, emissions from light-duty vehicles (
Figure A6c) showed a broader spatial distribution compared to the morning, with increased intensities both in urban centers and suburban peripheries. Peak values reached up to 1209.44 g, reflecting elevated usage of private vehicles during the evening commute. Heavy-duty vehicle emissions (
Figure A6d) remained high, with values up to 19,097.78 g, and their spatial spread extended into industrial zones and logistics hubs. This suggested that freight transport activity continued actively into the evening hours.
Figure A7 showed the diurnal variation of NO
X emissions from light and heavy vehicles in Jinan. Heavy vehicles consistently contributed the majority of emissions throughout the day. Their emissions began to rise sharply around 6:00, reaching a peak of approximately 210 g during the morning rush hour (7:00–9:00). Afterward, emissions slightly decreased but remained relatively high until the evening. Light vehicle emissions remained low and relatively stable across all hours, with only a slight increase during peak periods. The total emissions pattern closely followed that of heavy vehicles.
The annual NO
X emissions from vehicles in Jinan were estimated to reach approximately 24,000 tons, which is higher than previous estimate of 18,600 tons based on statistic data in 2020 [
29]. It is mainly because statistic data did not account for emissions from non-local transit vehicles, particularly trucks. This study uses dynamic data to capture this important emission contributor, 1.25 times higher when using high-resolution data compared to traditional aggregated estimates. Our results are consistent with those of Deng et al., showing that non-local trucks contribute 31% more pollution [
10].
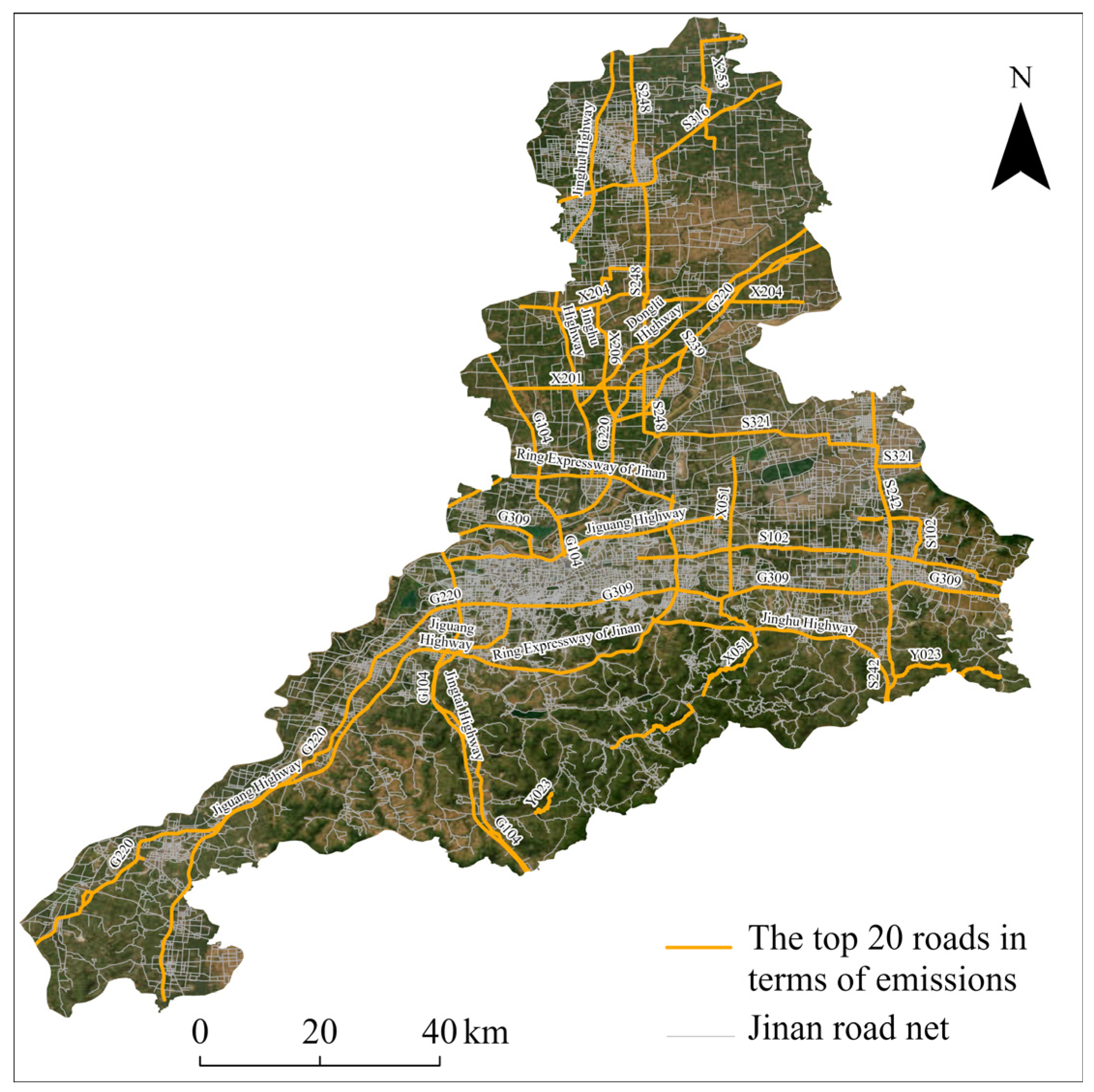
Annual NO
X emissions are particularly prominent along major urban transportation routes such as the Jiguang Highway, G220 National Highway, and S248 Provincial Highway, driven by HDV fleets (
Figure 6). In the southwestern part of Jinan City, Pingyin County stands out as a hotspot for pollution emissions, likely due to transit traffic along the Jiguang Expressway and G220 National Highway, as well as emissions associated with agricultural airport. The top 20 roads with the highest annualized pollution emissions are key arterial routes traversing the city both north–south and east–west, primarily consisting of national highways, provincial highways, and expressways (
Table A7). The concentration of NO
X emissions on the top 20 roads results mainly from several interconnected factors. These routes typically experience high volumes of heavy-duty vehicles. Traffic conditions often involve low and unstable speeds—such as congestion and stop-and-go flow—further increasing per-kilometer emissions. Additionally, the extended length and continuity of these roads accumulate substantial emissions. Finally, freight restrictions on expressways divert trucks to lower-class roads, intensifying local emissions. These findings revealed the spatial heterogeneity of vehicular NO
X emissions and emphasized the dominant role of heavy-duty vehicles and lower-grade road types in regional air pollution in Jinan.
4. Discussion
4.1. Findings and Policy Recommendations
This study aims to develop a methodology that enables near real-time monitoring for urban vehicle emissions, with a high temporal (hourly) and spatial (road segment level) resolution. The method first establishes the digital twin GIS to accurately describe the road characteristics. Based on the GIS, we find a stable token data stream, i.e., the congestion index from the open-source map APP that could be accessed in a 15 min timespan. We then comply with data cleaning mechanisms and Random Forest algorithms to predict the vehicle emissions that cover the whole city with road segment granularity. The model training results are satisfactory both for the comparison of geographic distribution of vehicle emissions and for the trend and statistics of vehicle emissions at specific coordinates and timespans. The results enable accurate descriptions of environmental impacts, thus offering reliable data support for real-time control and management of vehicle emissions. Further, the aggregated results could be used to analyze the vehicle emission trend, thus helping with the development of mid- and long-term vehicle emissions control policy and low-emission zoning.
The proposed framework also has practical implications for near real-time urban management. First, by providing continuously updated traffic emission estimates, it could inform dynamic traffic control strategies, such as adjusting freight vehicle restrictions or deploying congestion mitigation measures at specific times of day. Second, integration with atmospheric dispersion models would enable short-term air quality nowcasting and forecasting, supporting proactive interventions to prevent pollution episodes. Third, the near real-time identification of high-emission corridors can provide actionable intelligence for enforcement, such as establishing checkpoints for heavy-duty vehicle inspections or expanding low-emission zones. Finally, this system could offer valuable decision support for both city-level strategic planning and neighborhood-scale interventions, making it directly relevant for policy implementation and urban governance.
The application of the modeling system in Jinan, a typical big Chinese city, shows a few interesting results. First, by using this completely bottom-up method, we found that the traditional top-down vehicle emission simulation models (vehicle population-based, fuel based, or total activity based) may underestimate vehicle emissions at the city level. This verifies a few scholars’ suspicions regarding incomplete representations in the traditional approach. The reasons are both that the pass-through vehicles are not captured in those top-down models, and that environment-damaging vehicle driving cycles are more commonly found in urban areas.
Township roads contribute the most to total nitrogen oxide emissions. This finding highlights an important policy implication: emission control strategies cannot focus solely on expressways or arterial roads. Township and county roads, which host significant freight activity at lower speeds, emerge as major emission hotspots. Targeted measures such as rerouting policies, speed management, or localized inspection checkpoints may therefore be more effective for reducing emissions in these areas.
The importance of heavy-duty vehicle emission control is further supported in this study. Despite accounting for about 20–30% of traffic flow, HDVs contribute to 70–80% of total vehicle emissions. More importantly, we found that HDV operation follows more regular routes and timing than passenger vehicles, and this high-resolution bottom-up method can effectively catch the operation characteristics of the trucks, thus offering opportunities in truck control. For example, the method could identify the key truck operational corridors with accurate location at a daily level, which gives the chance to control truck emissions through environmental enforcement, and warns the truck owner for traffic control and adjust dispatch operations. Furthermore, the results could also assist the electrification of HDVs by providing suggestions for planning and designing charging infrastructures.
Identifying the hotspots of the top 20 emission roads provides a clear pathway for policy action. Possible interventions include: (i) targeted roadside inspections and emission checks at key entry points to high-emission corridors to remove gross polluters; (ii) time-of-day restrictions or dynamic routing to shift freight movements away from sensitive periods or densely populated areas; (iii) speed management and signal-timing optimization to reduce stop-and-go conditions and lower per-kilometer emissions; (iv) prioritization of retrofitting, replacement, or electrification incentives for HDVs operating predominantly on hotspot corridors; and (v) structural interventions such as dedicated freight bypasses or improved pavement that reduce congestion and improve fuel economy.
4.2. Limitations
Despite the successes in simulating traffic flow in near real-time, there are still several shortfalls in the methodology that need further improvement. Firstly, congestion index alone cannot fully explain traffic volume due to its non-linear relationship with flow. For example, congestion index values of approximately 2.0 may correspond to different traffic volumes in the morning and evening peaks. To address this complexity, the Random Forest model leverages additional temporal predictors (hour of day, day of week, holiday indicators), which enable the model to distinguish such cases and improve predictive accuracy. Feature importance analysis confirms that congestion index and temporal variables are consistently among the top-ranked predictors, jointly accounting for most of the variance explained by the model.
A second limitation concerns the simplified classification of vehicles into only two categories: light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles. Due to current data restrictions, we were unable to obtain detailed vehicle information, including specific categories or usage purposes. As a result, the heterogeneous sub-groups within HDVs—such as buses, medium-duty delivery trucks, and long-haul freight trucks—were aggregated into a single category. This oversimplification may obscure distinct spatial and temporal emission patterns, and could introduce uncertainty in hotspot identification and trend analysis. Future work should aim to incorporate more refined classification when such data become available.
Furthermore, the cross-validation strategy adopted presents another methodological constraint. Although k-fold cross-validation is widely used for model evaluation, applying it directly to traffic flow data may lead to overly optimistic estimates of accuracy because of strong spatiotemporal autocorrelation. In particular, random splitting can assign highly correlated observations—such as consecutive hours on the same road segment, or adjacent road segments observed in the same hour—into both training and testing sets. This leakage of correlated samples reduces the independence of the validation process. While temporal cross-validation or spatial cross-validation would provide stricter and more realistic performance assessments, such approaches were not feasible in the present study due to data and sample size constraints. Future work should incorporate these validation designs to better quantify predictive uncertainty under realistic deployment conditions.
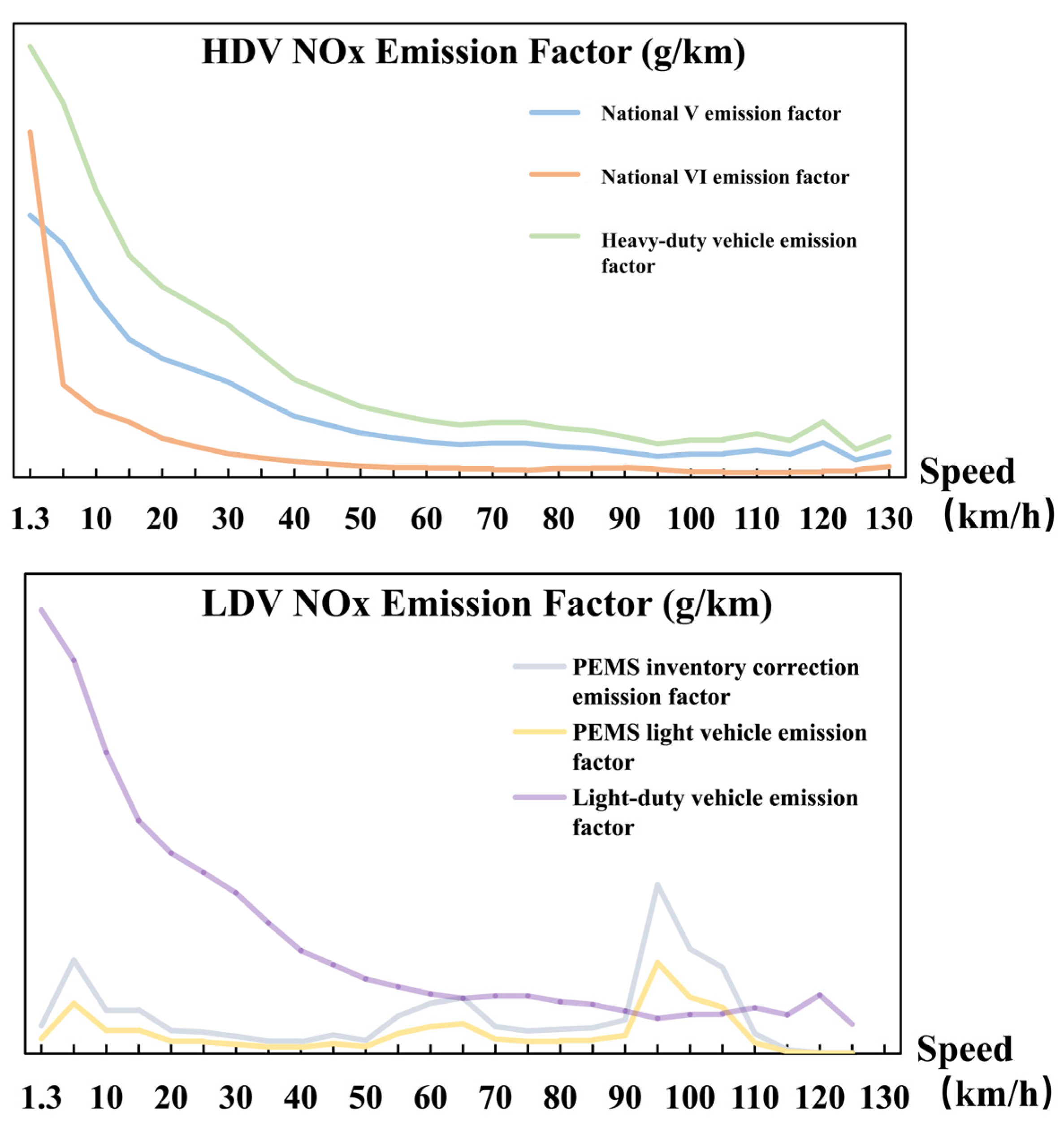
A further limitation of this study is that vehicle emission factors were modeled as a function of speed only, without explicitly accounting for other influencing variables such as ambient temperature, road topography, and vehicle load [
30,
31]. While these factors can significantly affect instantaneous emissions, the necessary high-resolution data were not available for Jinan, and systematic studies quantifying their effects remain relatively scarce. We acknowledge that this simplification may introduce biases in our inventory. Although our focus here is on mobile source NO
X emissions, which are closely tied to vehicle operational states, integrating additional explanatory variables into emission factor models will be an important direction for future research.
Operational deployment remains a necessary step toward validating the proposed methodology within a real intelligent traffic management system. While designed for integration into such platforms, the framework has not yet been implemented or tested in a live operational environment in Jinan. Consequently, its practical efficiency, stability, and scalability under real-world conditions still require thorough evaluation.
It is also important to note that this study focused exclusively on the characterization of vehicle emissions and did not extend to assessing their impacts on ambient air quality and public health—outcomes that represent the ultimate purpose of emission control strategies. Future work should prioritize linking high-resolution emission estimates with air quality monitoring and health impact models. Our long-term goal is to develop an integrated big-data framework that holistically addresses traffic operations, emissions, environmental quality, and public health.
5. Conclusions
This study developed a high-resolution approach for traffic flow prediction and vehicle emission inventory construction by integrating multi-source geospatial data with machine learning techniques. We first built a comprehensive road network framework for Jinan City and employed a two-fold random forest model to predict hourly traffic flows. These predicted flows were then combined with speed-sensitive emission factors to estimate vehicle emissions at a high spatiotemporal resolution. In contrast to traditional static methods reliant on aggregated vehicle population data, our approach not only achieved significantly higher prediction accuracy but also captured transient and non-local emissions that are often missed in conventional inventories. Beyond its methodological advancements, the resulting high-resolution emission inventory offers actionable insights for refined urban governance. It can directly inform traffic management strategies, such as optimizing freight corridors, designating low-emission zones, and guiding infrastructure planning for vehicle electrification. Moreover, as the methodology depends on widely available multi-source traffic data, it is highly scalable and transferable to other Chinese cities and international contexts, thereby providing robust support for integrating traffic emission monitoring into sustainable air quality management and effective regulatory enforcement. This near real-time monitoring framework has the potential to serve not only as a research tool but also as an operational component of smart traffic and environmental management systems, providing a scientific basis for timely and targeted emission reduction policies.
The results demonstrated that temporal variables and the congestion index were the dominant factors influencing traffic flow and vehicle composition prediction. The Fold 1 model achieved strong accuracy under high traffic volume conditions, whereas the Fold 2 model showed systematic biases in freight-intensive periods, where it overestimated the passenger car share. Traffic analysis revealed a pronounced bimodal pattern for light-duty vehicle flows, with distinct morning and evening commuting peaks on ring expressways and highways, while heavy-duty vehicle flows remained relatively stable throughout the day, reflecting the effectiveness of time-based restriction policies. The study also found that heavy vehicle volumes were relatively higher on lower-grade roads, such as county and township roads, despite their limited traffic capacity. Emission estimates further indicated that heavy-duty vehicles, though accounting for a smaller share of total traffic, contributed highly to NOX emissions, with hotspots concentrated along expressways, ring roads, and major freight corridors. Township and county roads also emerged as important contributors due to heavy-duty vehicle freight activity, underscoring the spatial heterogeneity of urban emissions and the policy-driven routing of heavy vehicles toward peripheral areas. These findings underscore the spatial heterogeneity of NOX pollution and highlight the dominant contribution of heavy-duty vehicles and lower-grade roads to regional air pollution. Furthermore, the high-resolution traffic emission inventory developed in this study can be integrated with chemical transport models (e.g., WRF-Chem) to generate dynamic air quality profiles and forecasts, thereby directly linking emission estimates with exposure assessment and policy evaluation.