Air Pollution in Taiyuan City During 2022 to 2024: Status and Influence of Meteorological Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
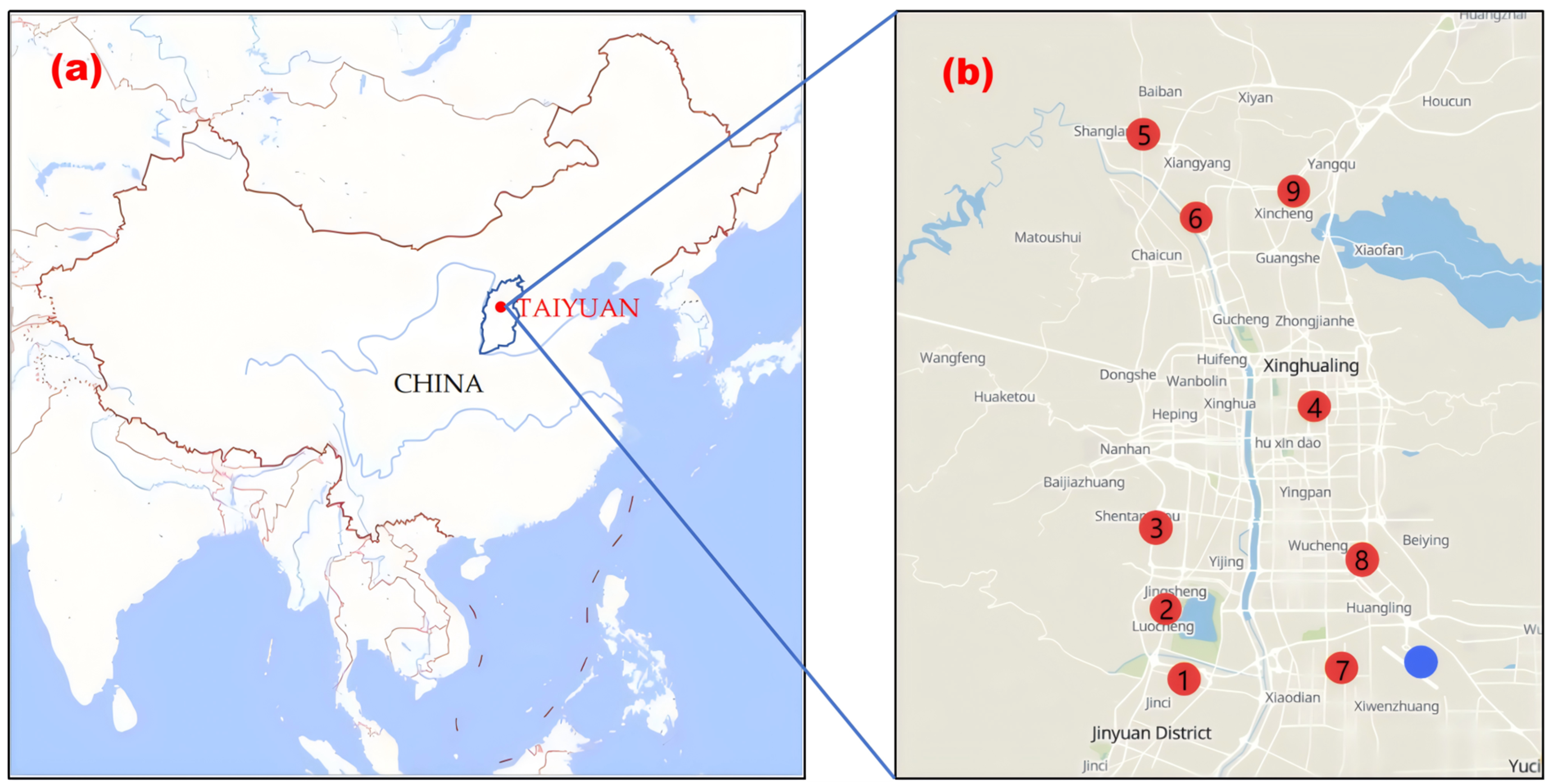
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Meteorological Interpretation
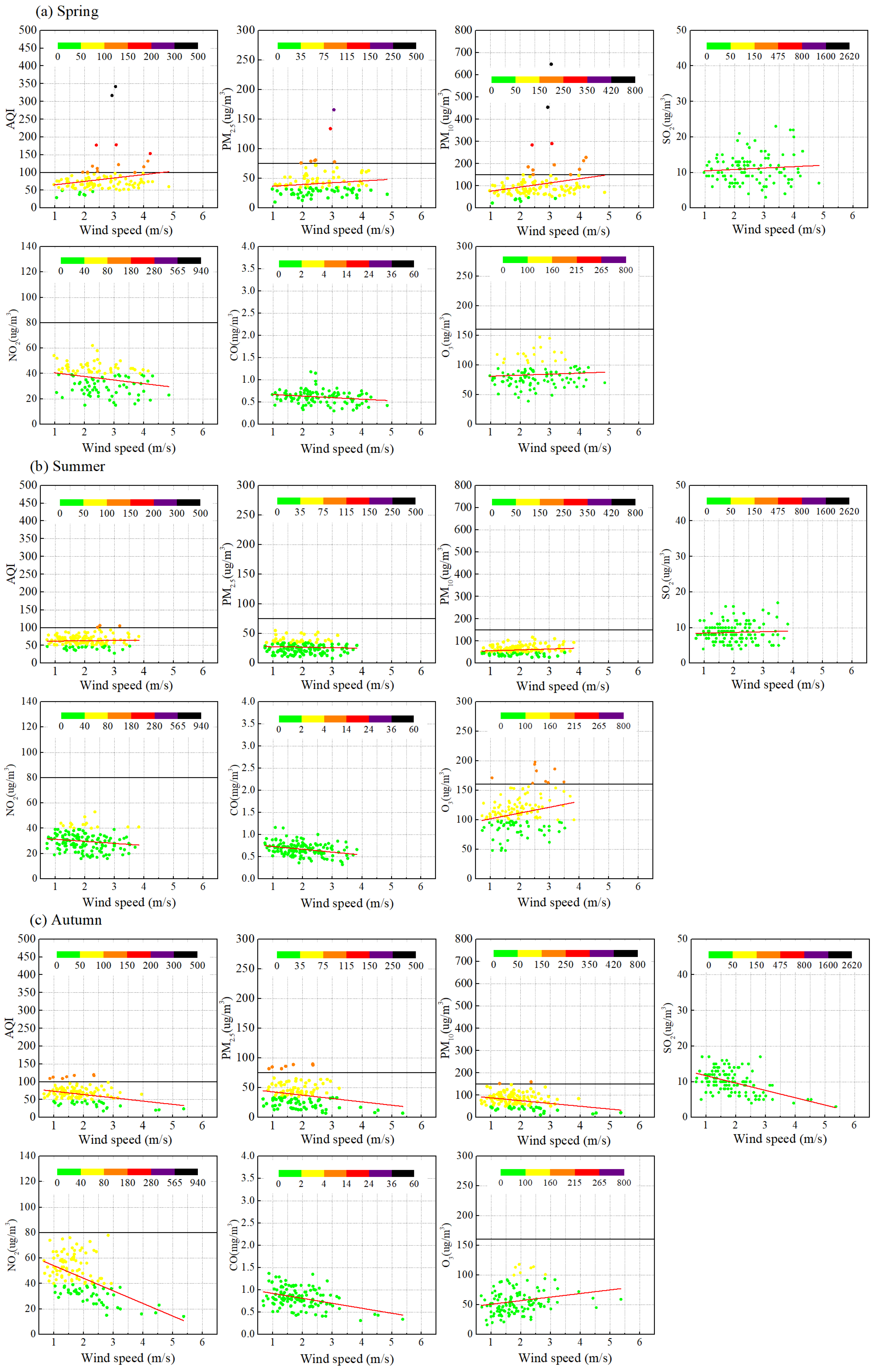
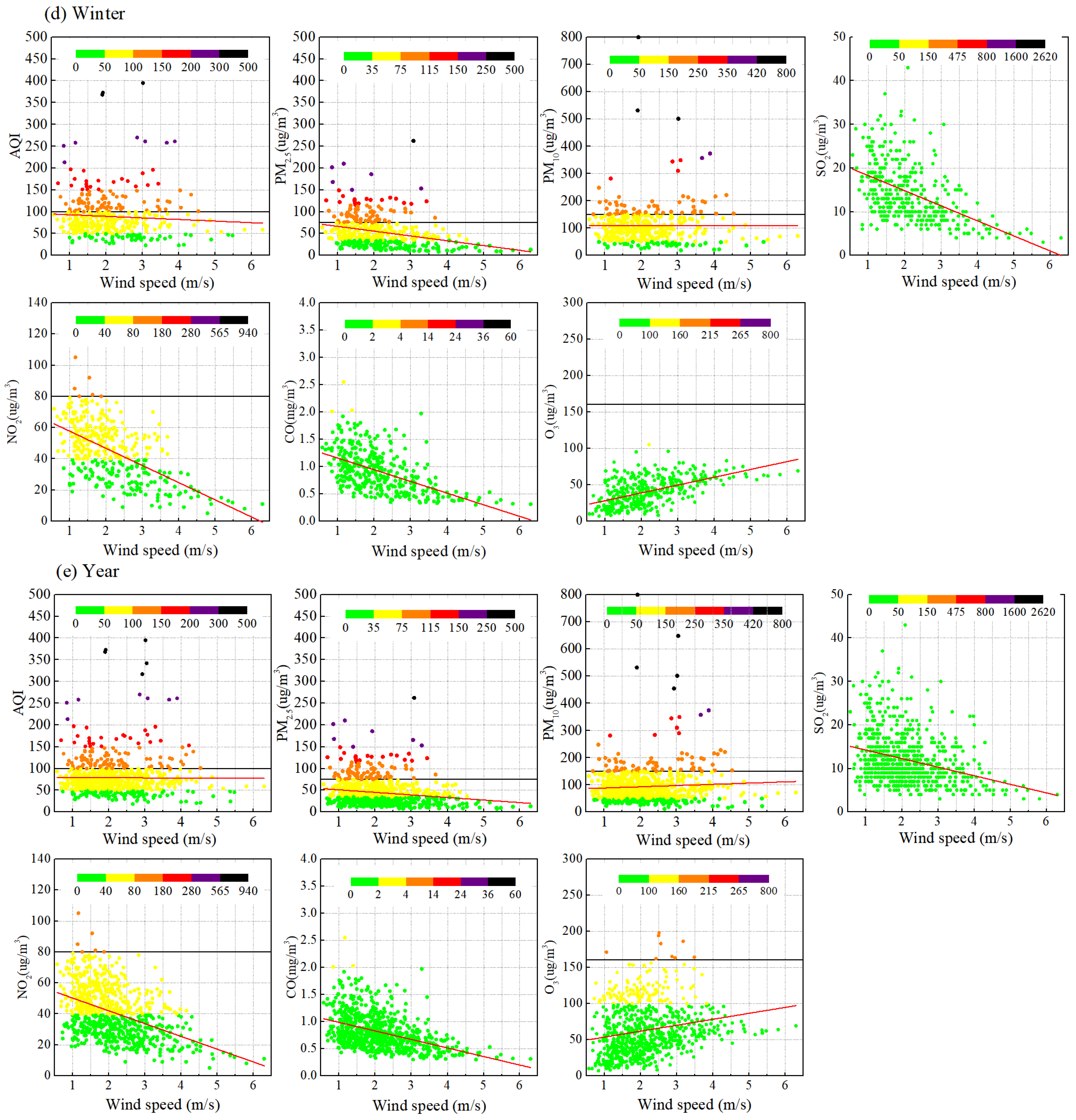
3.1.1. Wind
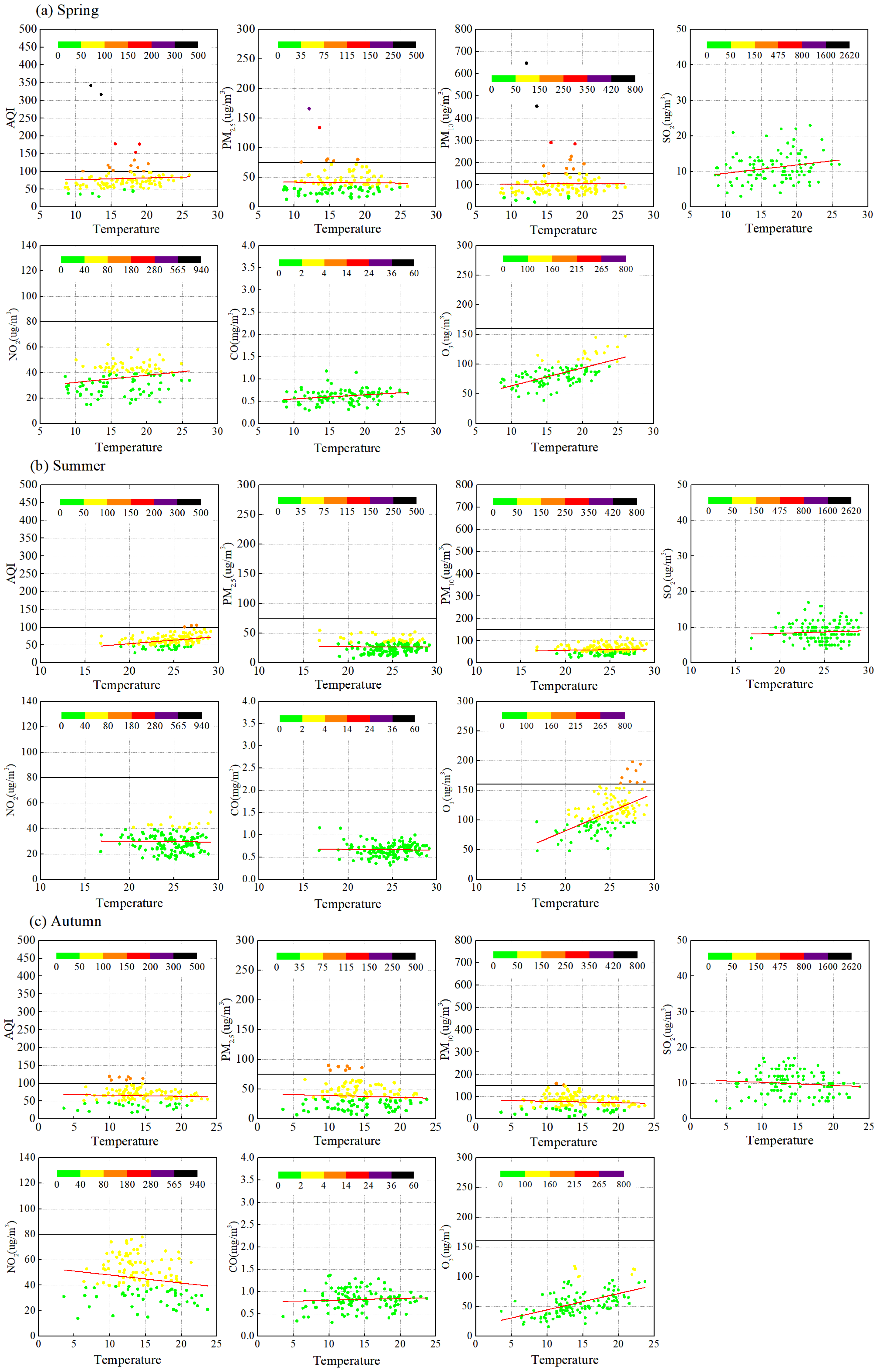
3.1.2. Temperature
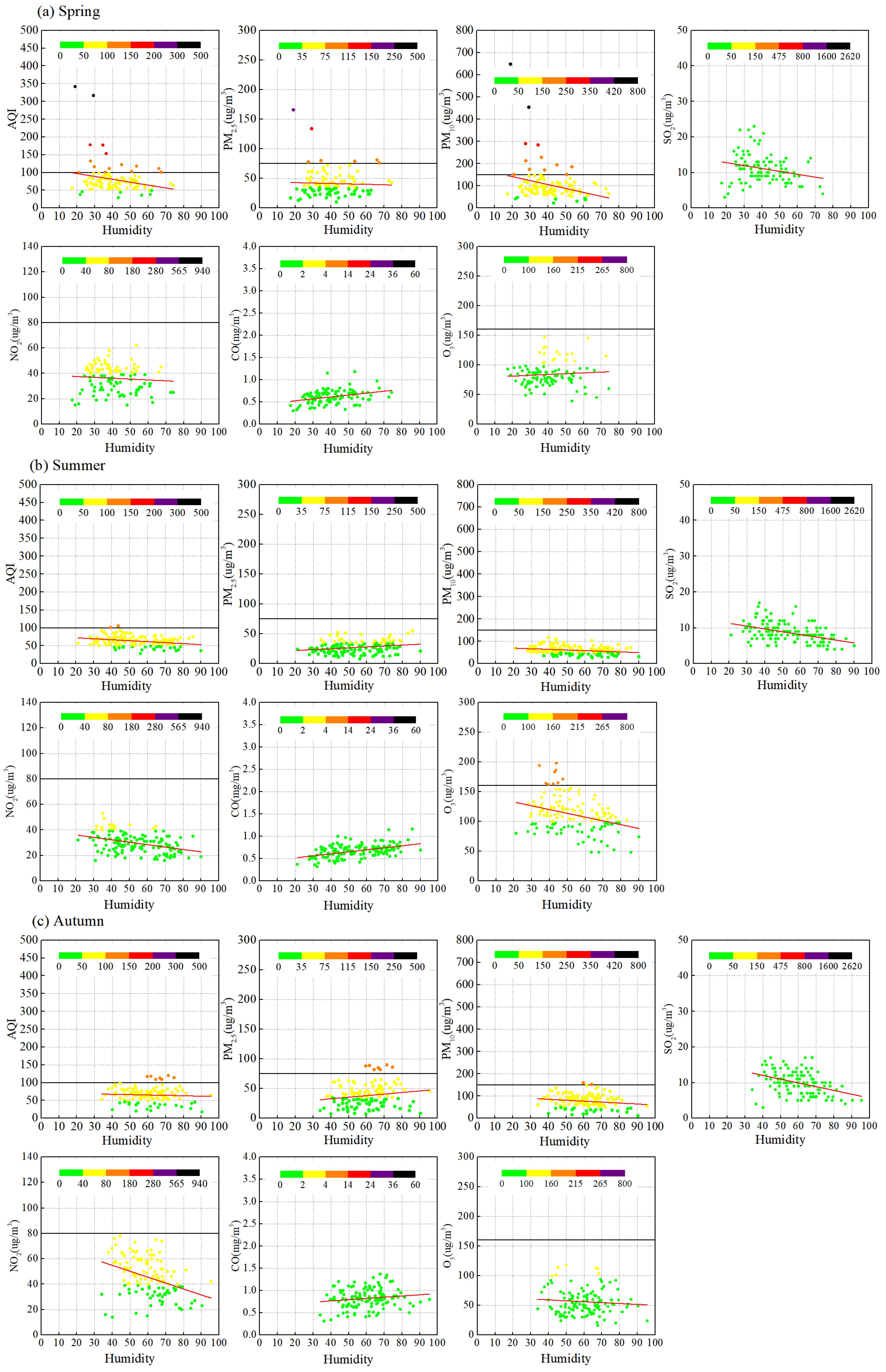
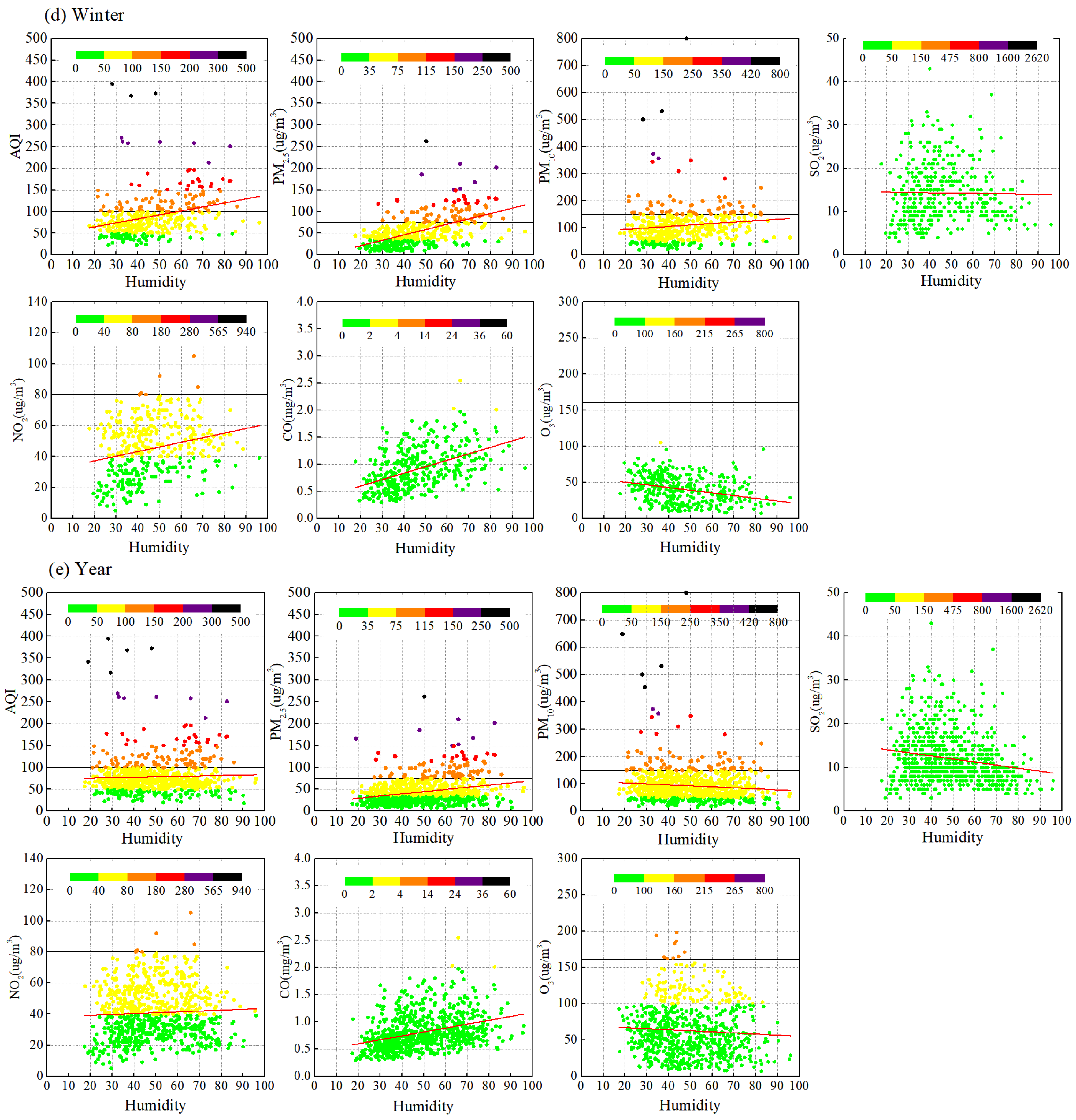
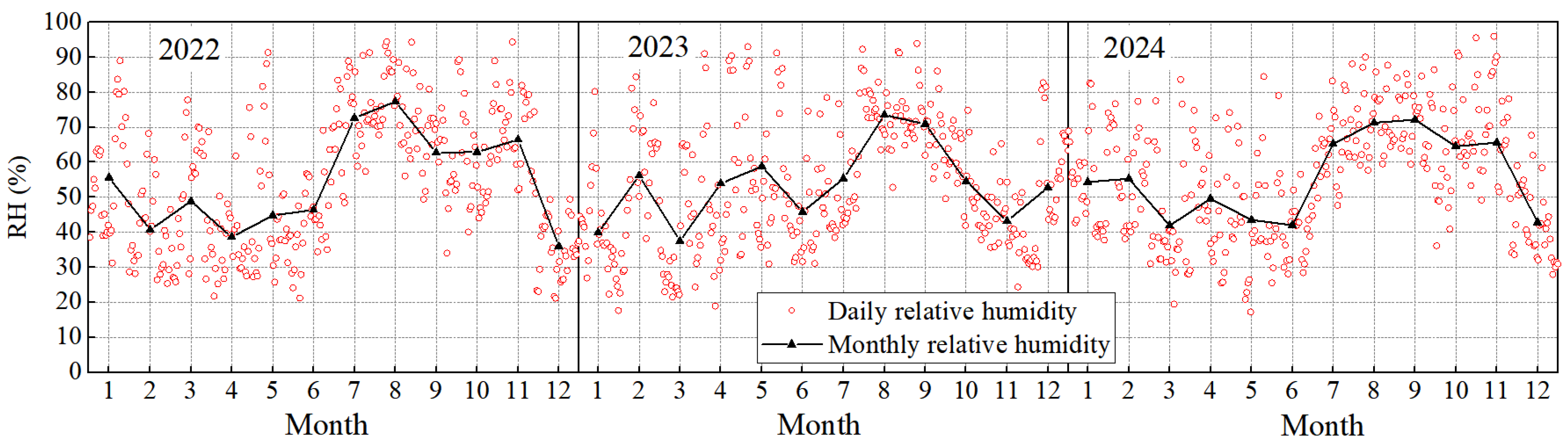
3.1.3. Relative Humidity
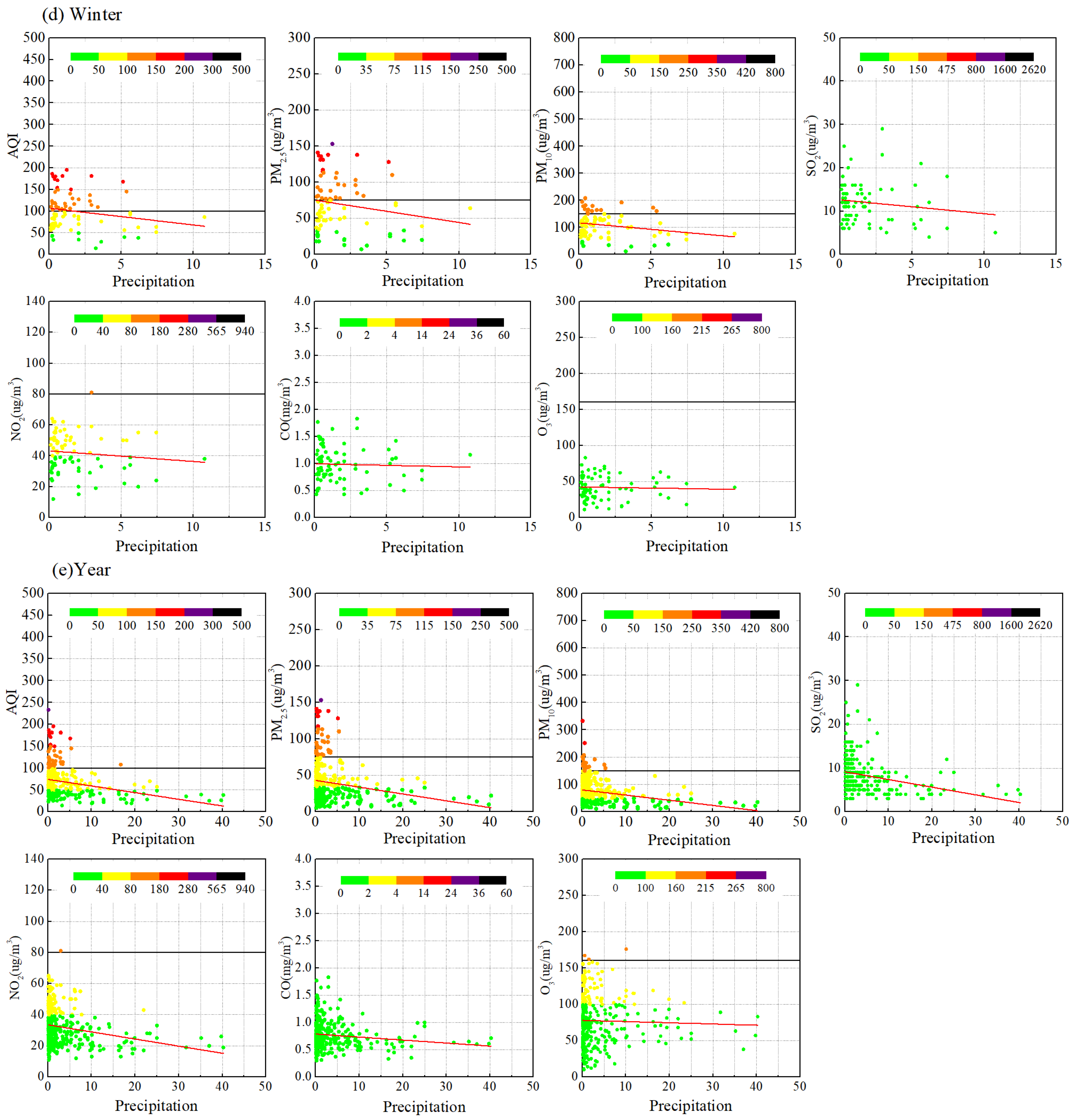
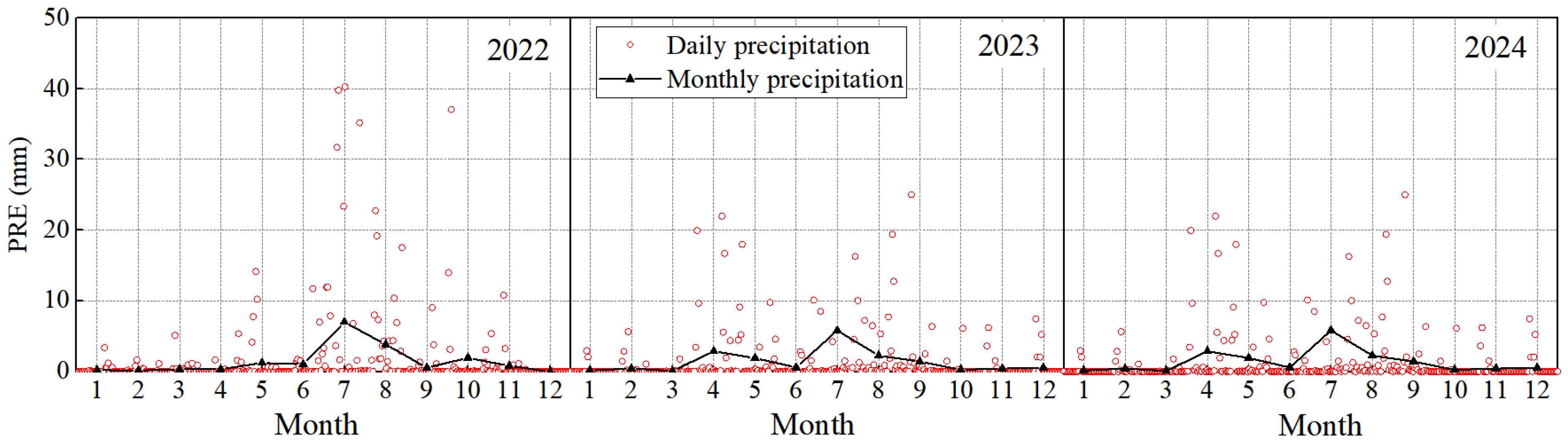
3.1.4. Precipitation
3.2. Variation in Air Quality
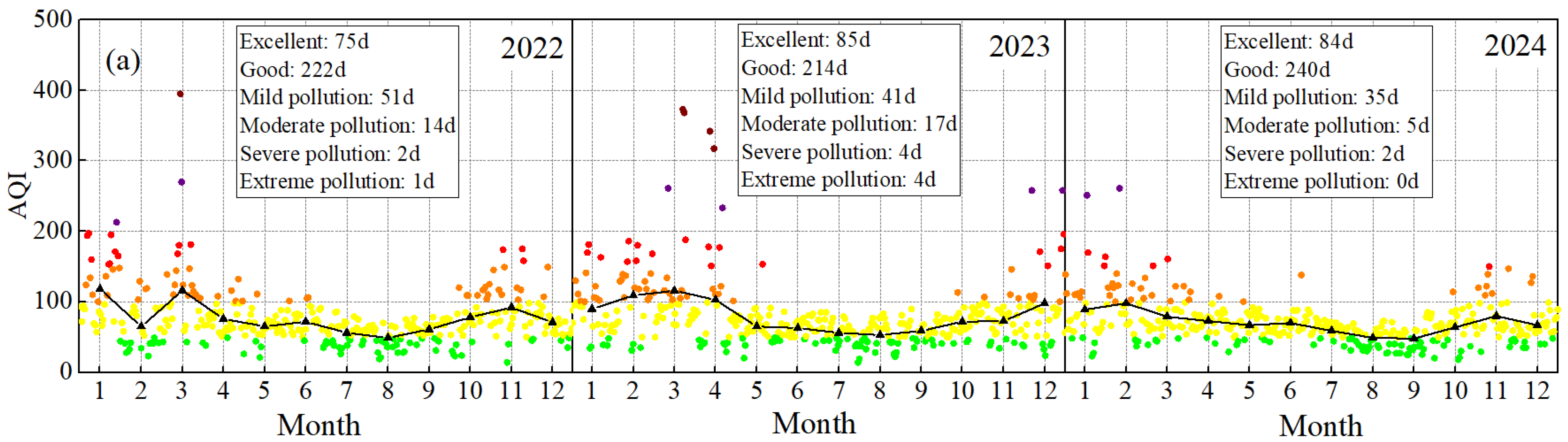
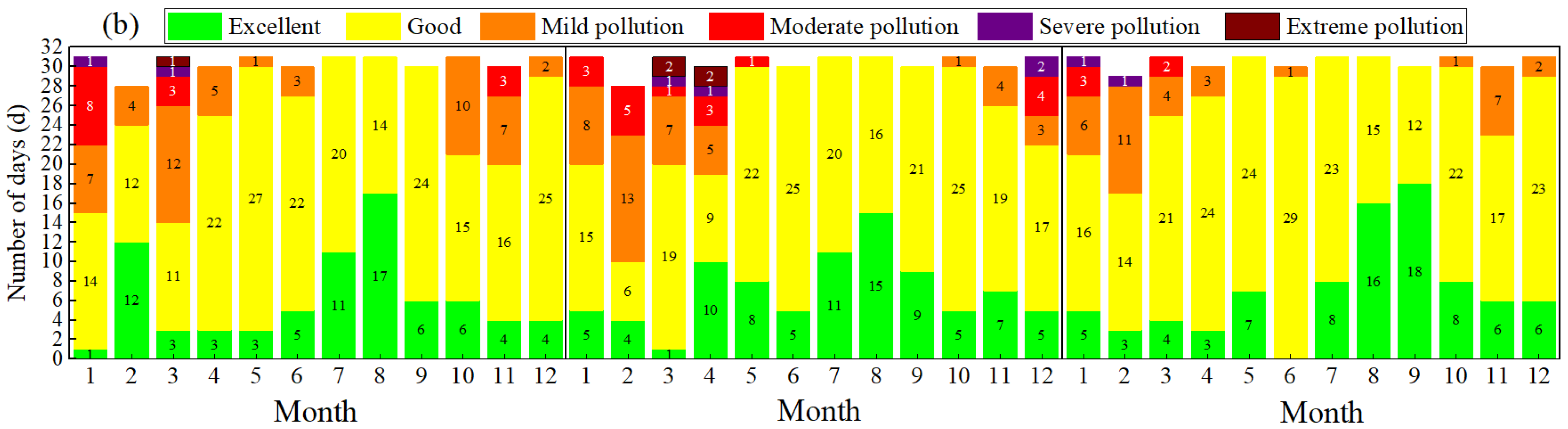
3.2.1. AQI
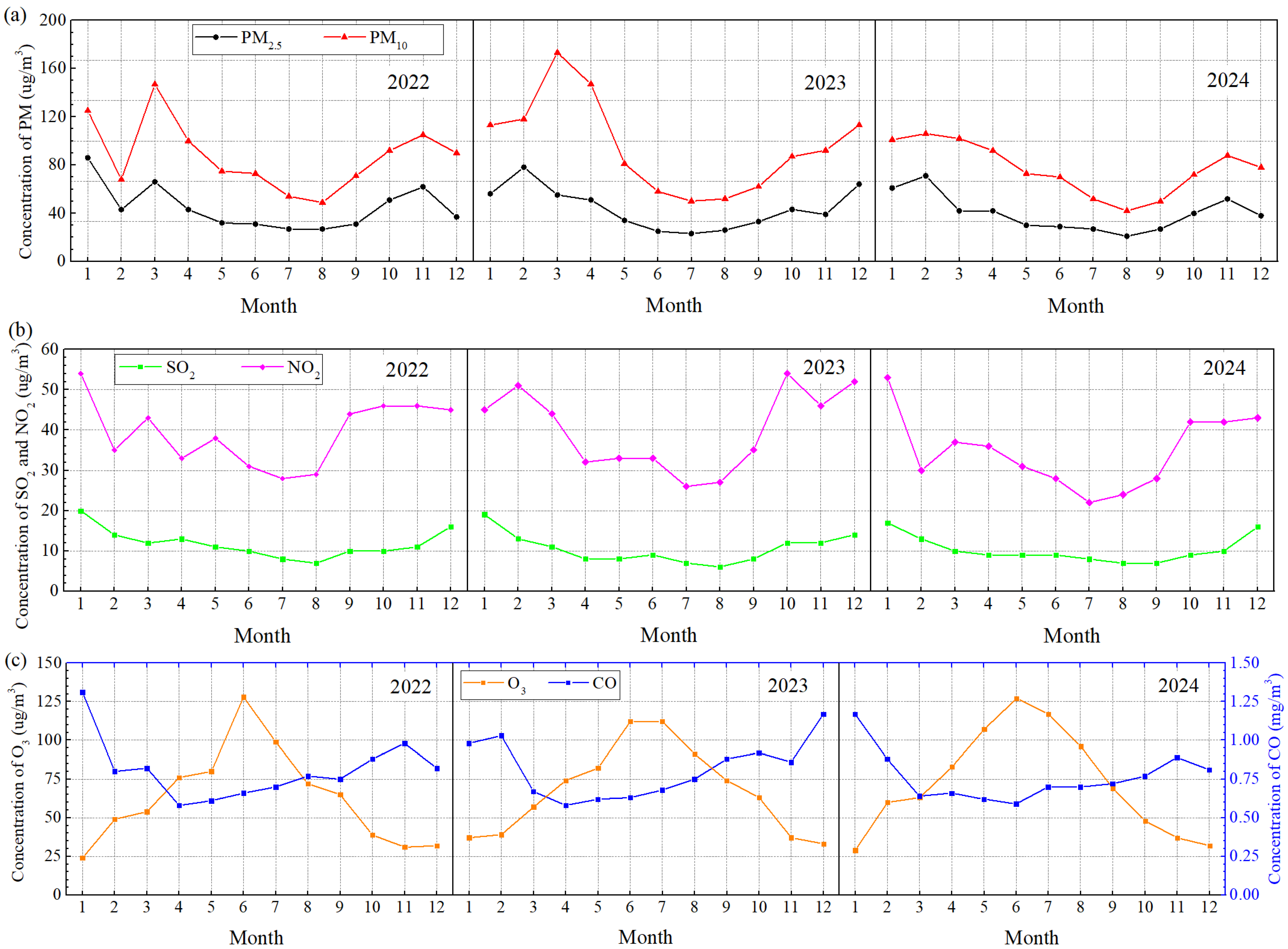
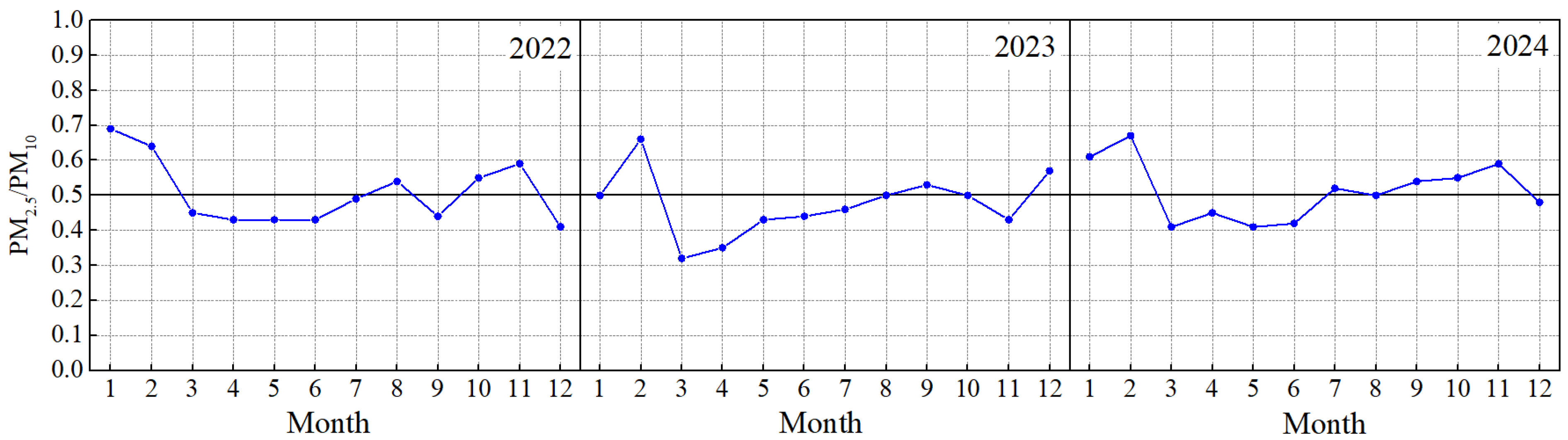
3.2.2. Various Pollutants
- (1)
- PM
- (2)
- SO2
- (3)
- NO2
- (4)
- CO
- (5)
- O3
3.3. Analysis of Factors Affecting Air Quality
3.3.1. Wind Speed
3.3.2. Temperatures
3.3.3. Relative Humidity
3.3.4. Precipitation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Geng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, T.; Zhao, H.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; et al. Drivers of PM2.5 air pollution deaths in China 2002–2017. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strak, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Rodopoulou, S.; Chen, J.; Hoogh, K.; Andersen, Z.J.; Atkinson, R.; Bauwelinck, M.; Bekkevold, T.; Bellander, T.; et al. Long term exposure to low level air pollution and mortality in eight European cohorts within the ELAPSE project: Pooled analysis. BMJ 2021, 374, n1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Braun, D.; Schwartz, J.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Dominici, F. Evaluating the impact of long-term exposure to fine particulate matter on mortality among the elderly. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, K.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yue, X.; Liao, H.; Gu, Y. Meteorology-driven trends in PM2.5 concentrations and related health burden over India. Atmos. Res. 2024, 308, 107548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotrecchiano, N.; Montano, L.; Bonapace, I.M.; Giancarlo, T.; Trucillo, P.; Sofia, D. Comparison process of blood heavy metals absorption linked to measured air quality data in areas with high and low environmental impact. Processes 2022, 10, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.S.; Park, M.S.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Owen, J.S.; Cho, C.R.; Jee, J.B.; Chae, J.H.; Kang, M.S. Meteorological characteristics during periods of greatly reduced PM2.5 concentrations in March 2020 in Seoul. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, D.; Gao, B.; He, B.; Cheng, N.; Xu, B. Understanding meteorological influences on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A temporal and spatial perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5343–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, T.; Song, H.; Lee, J.; Xu, T.; Xing, Y. Effects of meteorological factors and anthropogenic precursors on PM2.5 concentrations in cities in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, S.; Dai, Z.; Yu, L. Comprehensive analyses linking PM2.5 to its precursors and meteorological conditions across regions and time scale in China. Atmos. Pollu. Res. 2025, 16, 102469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; An, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, D.; Gao, Q.; et al. Spatiotemporal variations and influencing factors of PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Cai, J.; Gao, B.; Xu, B.; Dai, S.; He, B.; Xie, X. Detecting the causality influence of individual meteorological factors on local PM2.5 concentration in the Jing-Jin-Ji region. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, N.; Song, W.; Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J.; Cai, X.; Fu, H.; Zhang, M.; Sui, Y.; Sun, H.; et al. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of meteorological impacts on fine particle pollution in winters of cold region in China. Processes 2024, 12, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Ruan, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y. Analysis of atmospheric pollutants and meteorological factors on PM2.5 concentration and temporal variations in Harbin. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Wang, R.; Zhu, J. Influencing factors of PM2.5 and O3 from 2016 to 2020 based on DLNM and WRF-CMAQ. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Dai, Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; Feng, Y. Responses in PM2.5 and its chemical components to typical unfavorable meteorological events in the suburban area of Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hou, L.; Sun, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, N.; Li, R. Characterizing temporal trends and meteorological influences on ozone pollution in Shenyang region (2018–2021). Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2025, 18, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, F.; Gálvez, A.; González, C.M.; Orozco-Alzate, M.; Aristizábal, B.H. Hourly ozone and PM2.5 prediction using meteorological data—Alternatives for cities with limited pollutant information. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, J. Enhancement of atmospheric oxidation capacity induced co-pollution of the O3 and PM2.5 in Lanzhou, northwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Zheng, Q.; Qian, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Y. Feature analysis on air quality in the main urban area of Nanchong city in 2015–2018. Environ. Eng. Res. 2022, 27, 210006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yan, X.; Yao, J.; Zhao, W. Quantifying the scale-dependent relationships of PM2.5 and O3 on meteorological factors and their influencing factors in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and surrounding areas. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S. Relationships between springtime PM2.5, PM10 and O3 pollution and the boundary layer structure in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Miao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Impacts of synoptic forcing and topography on aerosol pollution during winter in Shenyang, Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 262, 105764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, D.; Jandrotia, R.; Varinder, K.; Sharma, S.; Kaushal, J. Air pollution trend in Chandigarh during 2019–2022: Status and influence of meteorological factors. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Zou, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, G. Analysis of PM2.5 concentrations in Heilongjiang Province associated with forest cover and other factors. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Lu, C.; Jiao, P.; Ren, S. Research on air quality in response to meteorological factors based on the Informer model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standard. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Wang, R.; Bei, N.; Hu, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Jiang, Q.; Tie, X.; Li, G. The relationship between the intensified heat waves and deteriorated summertime ozone pollution in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China, during 2013–2017. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, J.; Ramanathan, V. Recent climate and air pollution impacts on Indian agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16319–16324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madronich, S.; Shao, M.; Wilson, S.R.; Solomon, K.R.; Long-streth, J.D.; Tang, X.Y. Changes in air quality and tropospheric composition due to depletion of strato-spheric ozone and interactions with changing climate: Implications for human and environmental health. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; He, Z.; Wang, Z. The characteristics of qir quality changes in Hohhot city in China and their relationship with meteorological and socio-economic factors. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 24, 230274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Indicator | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQI | 0.24 * | −0.02 | −0.24 ** | −0.13 * | −0.05 |
| PM2.5 | 0.13 | −0.05 | −0.15 | −0.33 ** | −0.19 ** |
| PM10 | 0.28 ** | 0.12 | −0.25 ** | −0.07 | −0.00 |
| SO2 | 0.03 | 0.00 | −0.47 ** | −0.53 ** | −0.32 ** |
| NO2 | −0.24 * | −0.20 * | −0.48 ** | −0.54 ** | −0.44 ** |
| CO | −0.16 | −0.28 ** | −0.27 ** | −0.56 ** | −0.46 ** |
| O3 | 0.12 | 0.22 ** | 0.27 ** | 0.55 ** | 0.29 ** |
| Indicator | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQI | 0.32 ** | 0.37 ** | −0.09 | 0.32 ** | −0.11 ** |
| PM2.5 | 0.11 | 0.09 | −0.06 | 0.22 ** | −0.24 ** |
| PM10 | 0.23 * | 0.09 | −0.10 | 0.38 ** | −0.21 ** |
| SO2 | 0.23 * | 0.05 | −0.13 | −0.15 ** | −0.38 ** |
| NO2 | 0.22 * | −0.05 | −0.20 * | 0.15 ** | −0.25 ** |
| CO | 0.30 ** | 0.11 | 0.07 | −0.04 | −0.26 ** |
| O3 | 0.60 ** | 0.56 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.19 ** | 0.76 ** |
| Indicator | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQI | −0.15 | −0.24 ** | −0.05 | 0.37 ** | 0.05 |
| PM2.5 | 0.05 | 0.25 ** | 0.19 * | 0.55 ** | 0.25 ** |
| PM10 | −0.22 * | −0.22 ** | −0.15 | 0.24 ** | −0.05 |
| SO2 | −0.25 * | −0.47 ** | −0.42 ** | 0.06 | −0.19 ** |
| NO2 | −0.11 | −0.38 ** | −0.41 ** | 0.27 ** | 0.06 |
| CO | 0.33 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.14 | 0.52 ** | 0.41 ** |
| O3 | 0.10 | −0.30 ** | −0.00 | −0.33 ** | −0.08 * |
| Indicator | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQI | −0.42 ** | −0.31 ** | −0.18 | −0.06 | −0.26 ** |
| PM2.5 | −0.29 ** | −0.10 | −0.13 | −0.05 | −0.17 ** |
| PM10 | −0.44 ** | −0.23 ** | −0.18 | −0.08 | −0.26 ** |
| SO2 | −0.45 ** | −0.29 ** | −0.29 * | −0.16 | −0.31 ** |
| NO2 | −0.36 ** | −0.12 | −0.07 | −0.05 | −0.20 ** |
| CO | −0.23 ** | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.01 | −0.07 |
| O3 | −0.00 | −0.26 ** | −0.20 | −0.07 | −0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Gao, L. Air Pollution in Taiyuan City During 2022 to 2024: Status and Influence of Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101209
Huang X, Gao L. Air Pollution in Taiyuan City During 2022 to 2024: Status and Influence of Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(10):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101209
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaohui, and Lizhen Gao. 2025. "Air Pollution in Taiyuan City During 2022 to 2024: Status and Influence of Meteorological Factors" Atmosphere 16, no. 10: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101209
APA StyleHuang, X., & Gao, L. (2025). Air Pollution in Taiyuan City During 2022 to 2024: Status and Influence of Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere, 16(10), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101209







