Assessments of Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth for Monitoring Air Quality of the Large Port of Busan, Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. S-NPP/VIIRS Deep Blue Aerosol Optical Depth
2.2. Surface Air-Quality Monitoring Network of the Korea Ministry of Environment
3. Results
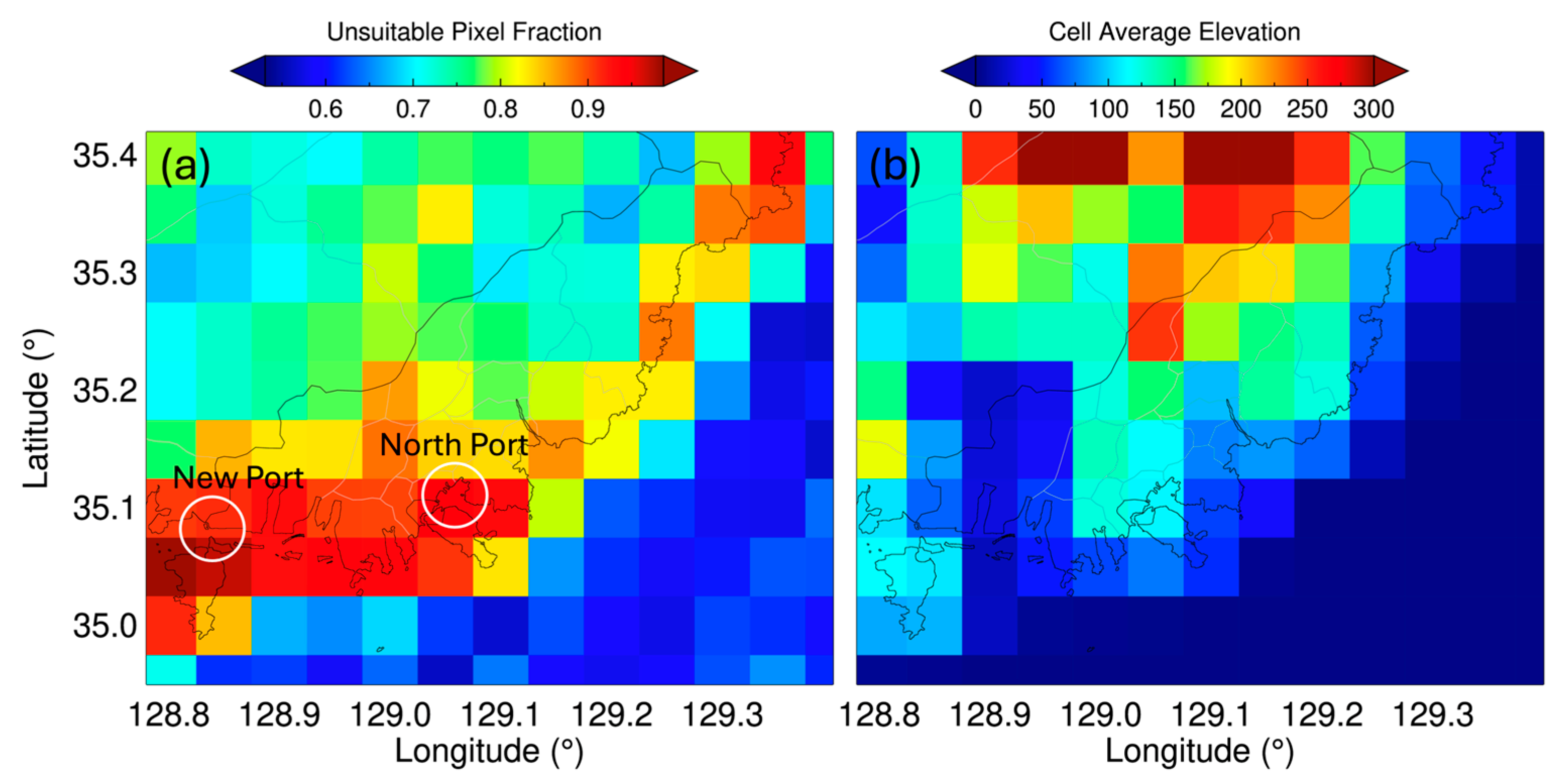
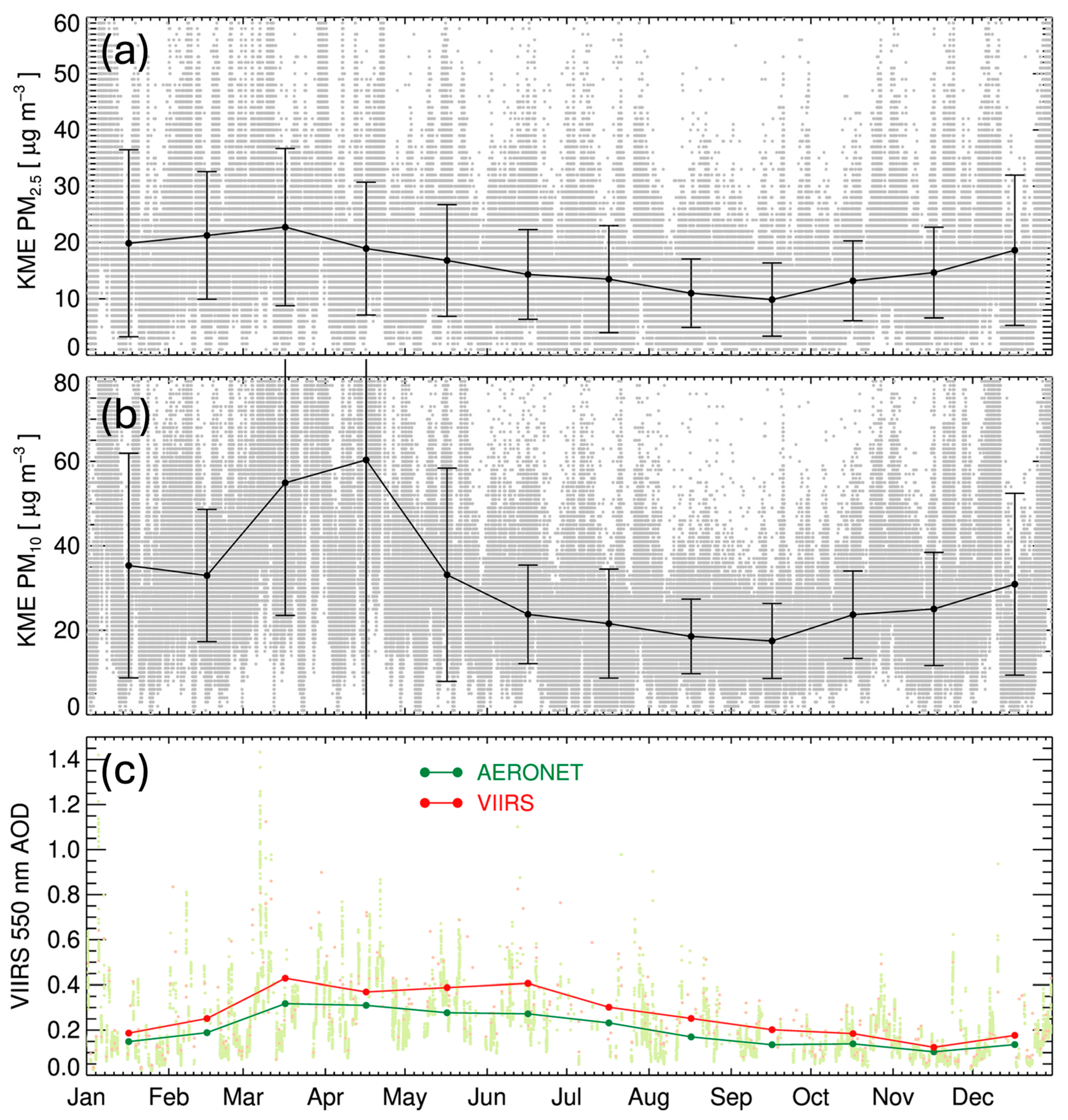
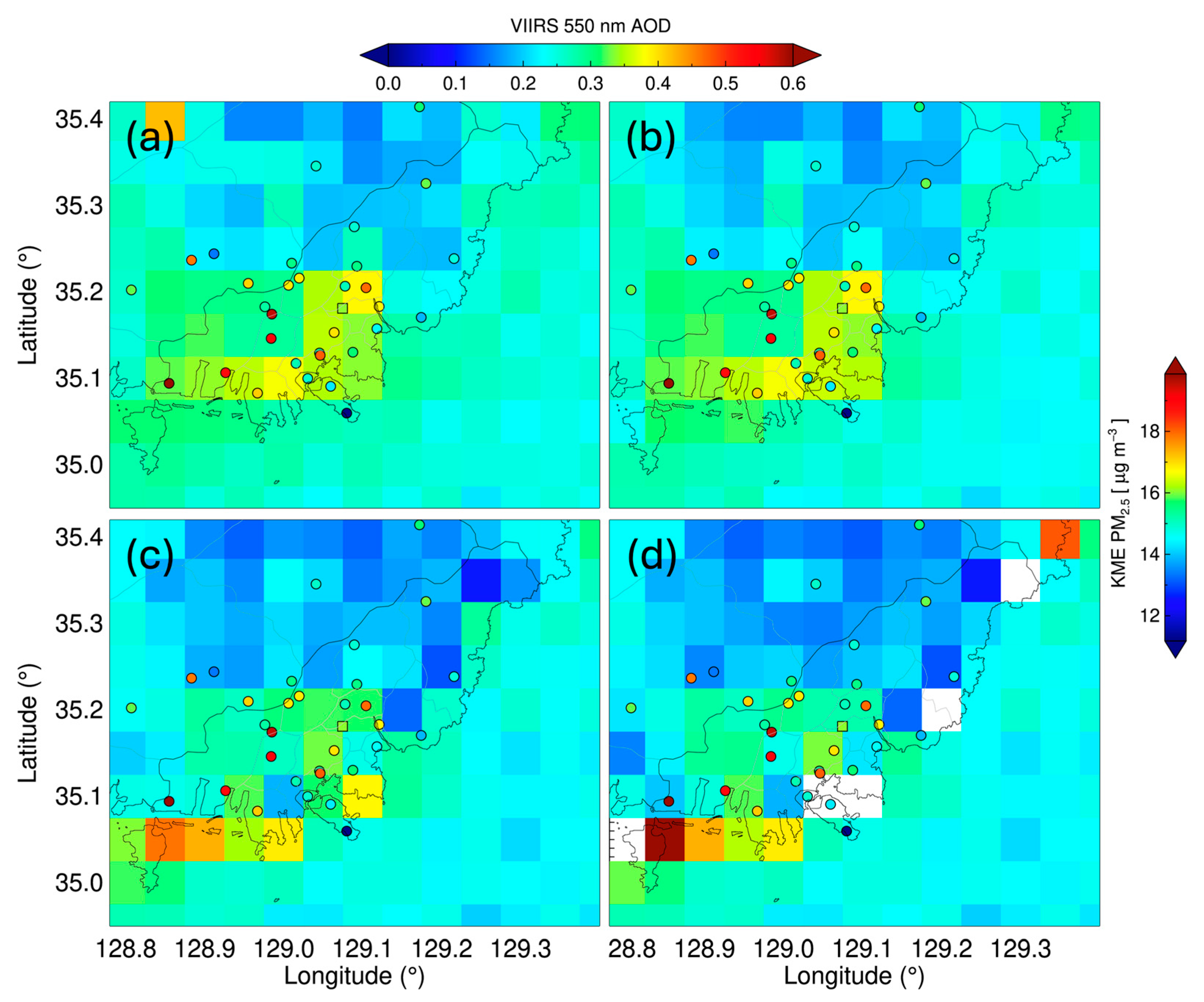
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variabilities of the Aerosols over Busan
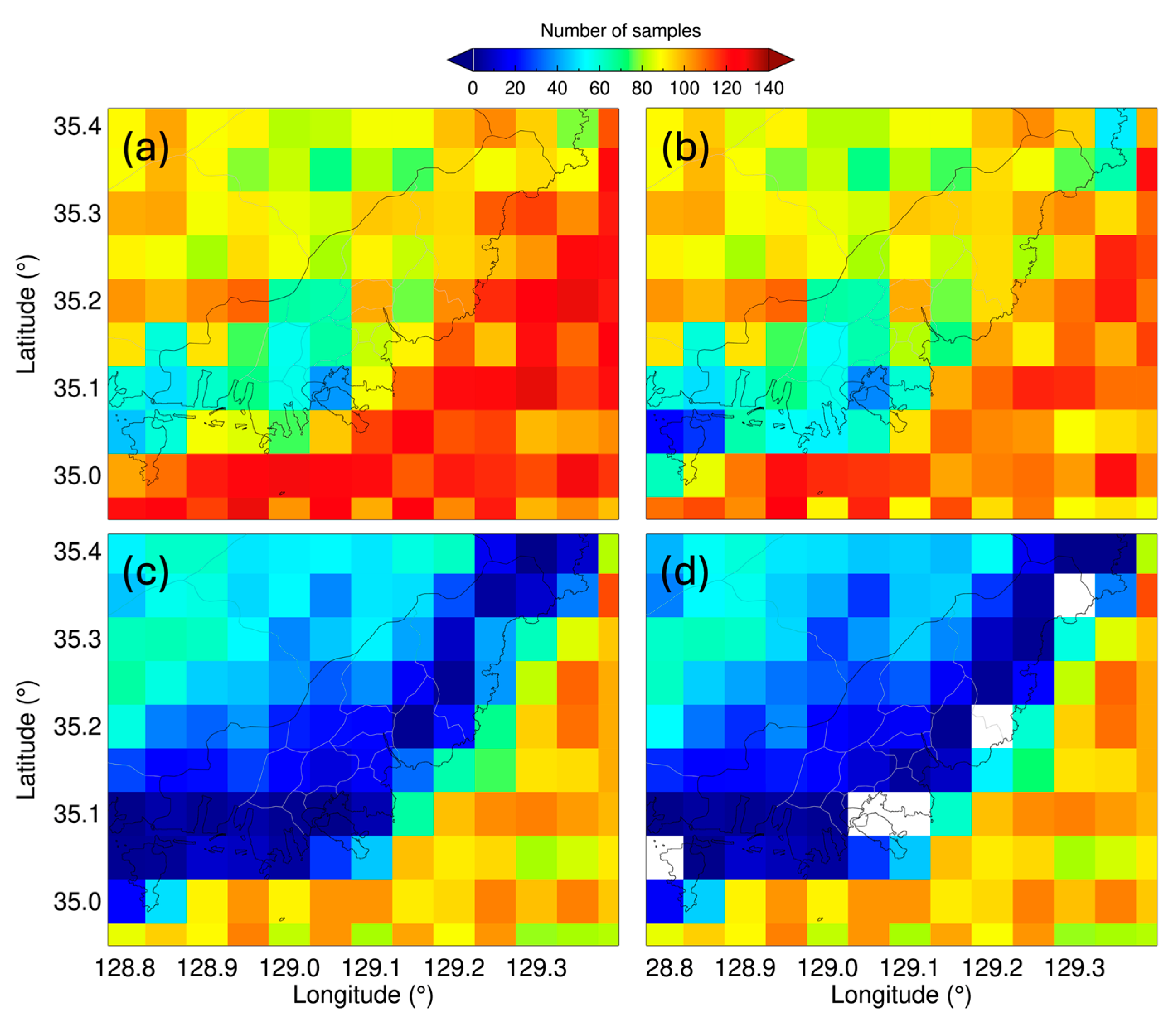
3.2. Sensitivity of the Quality Standard Criteria on the VIIRS AOD
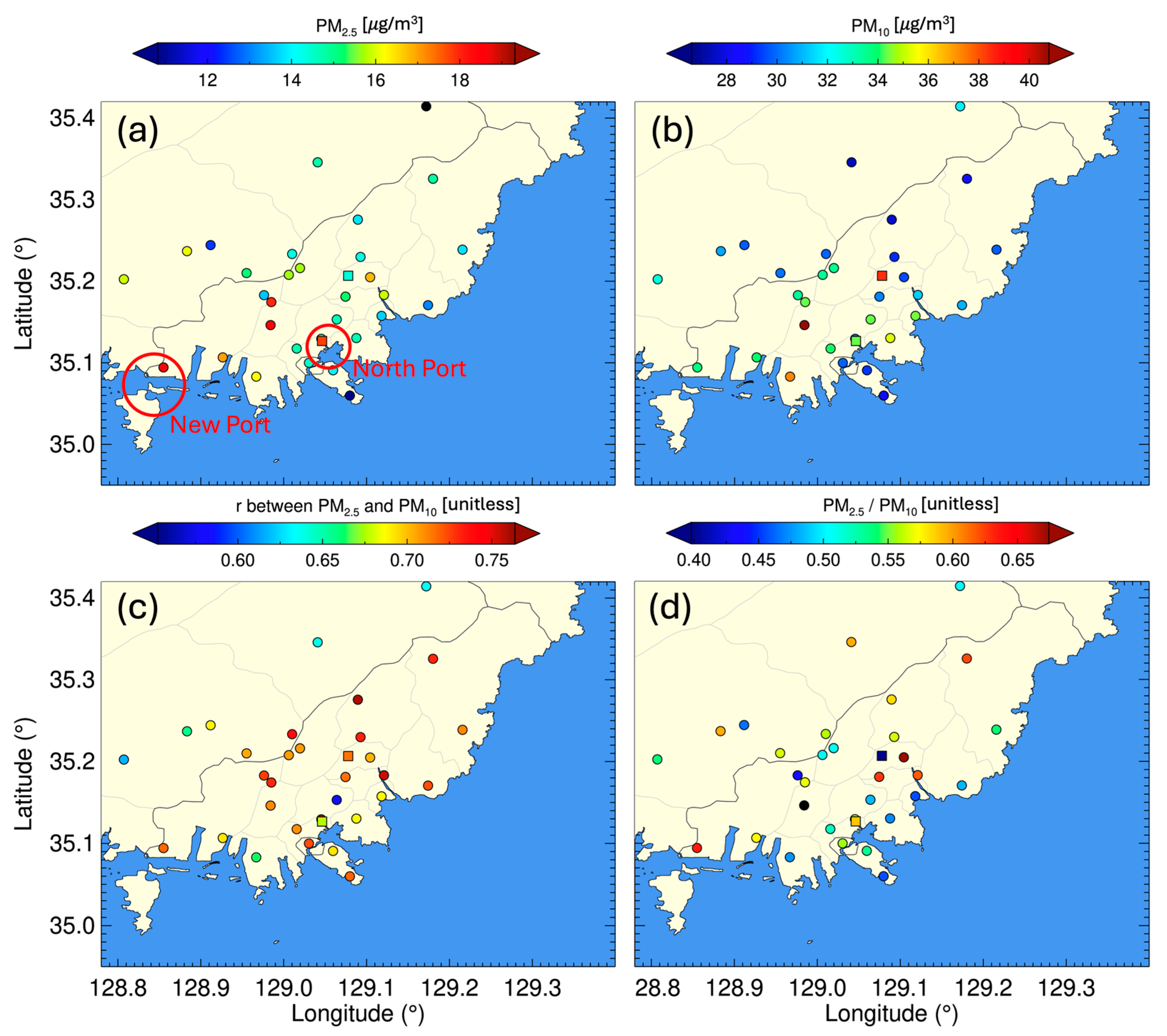
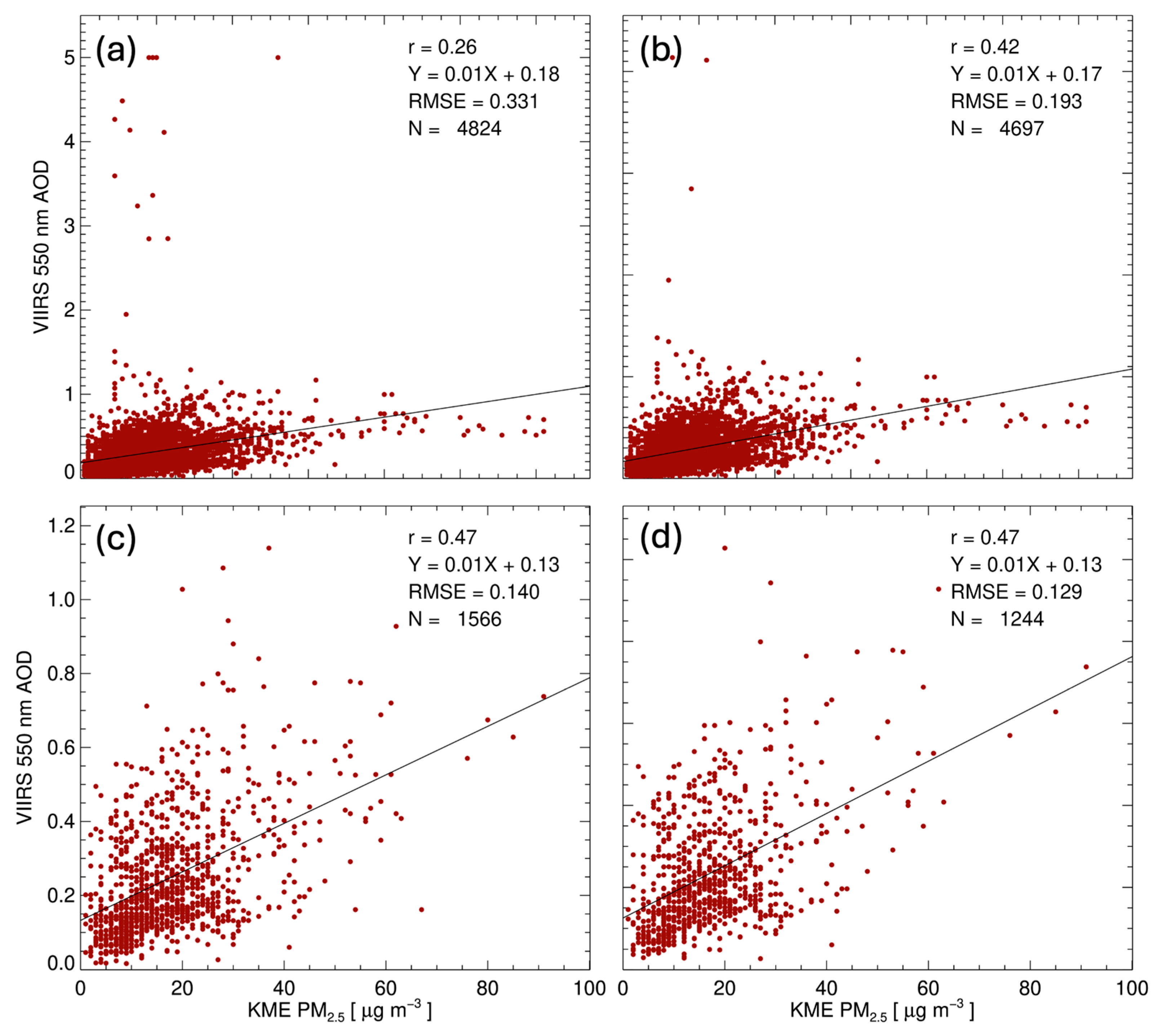
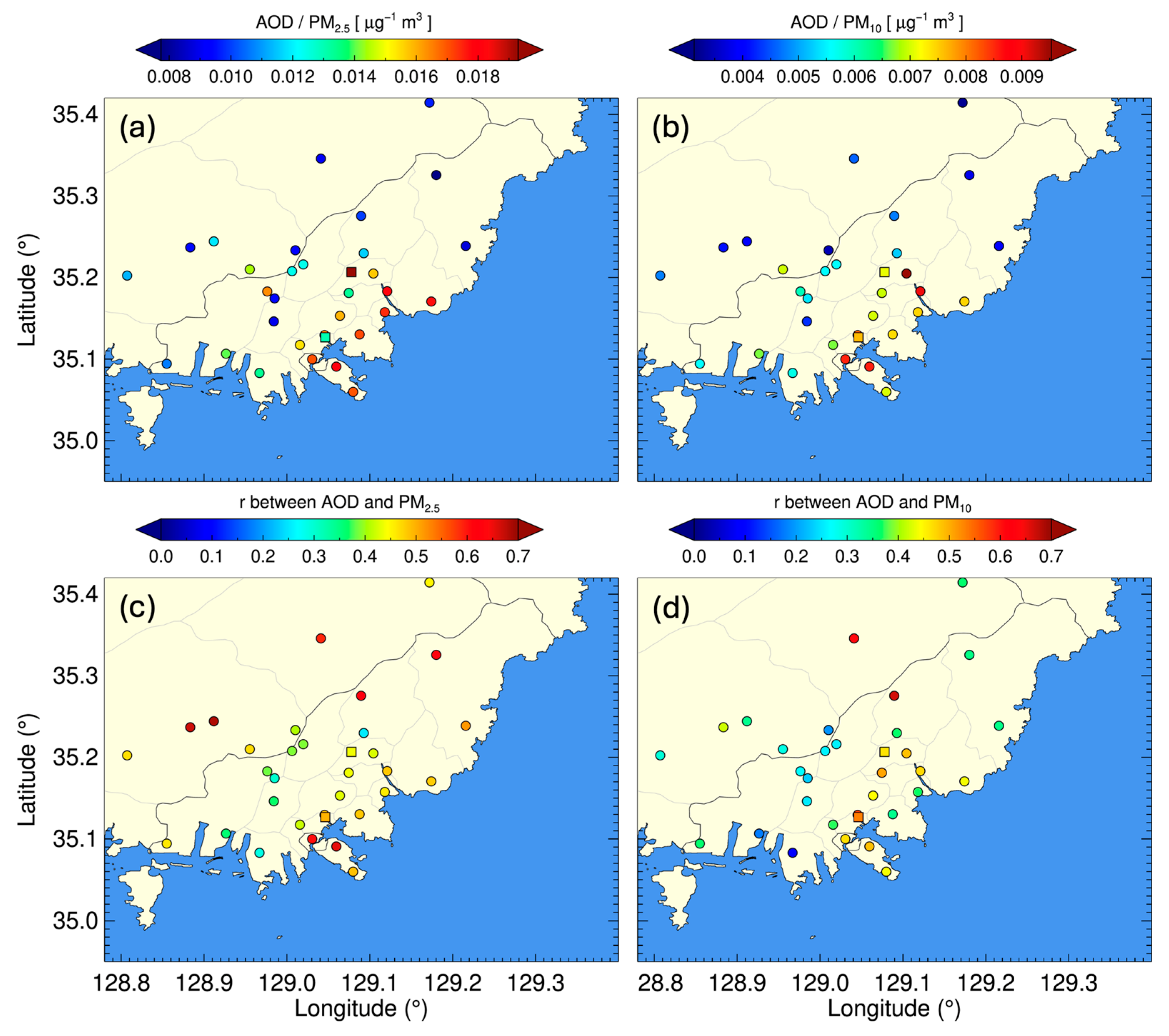
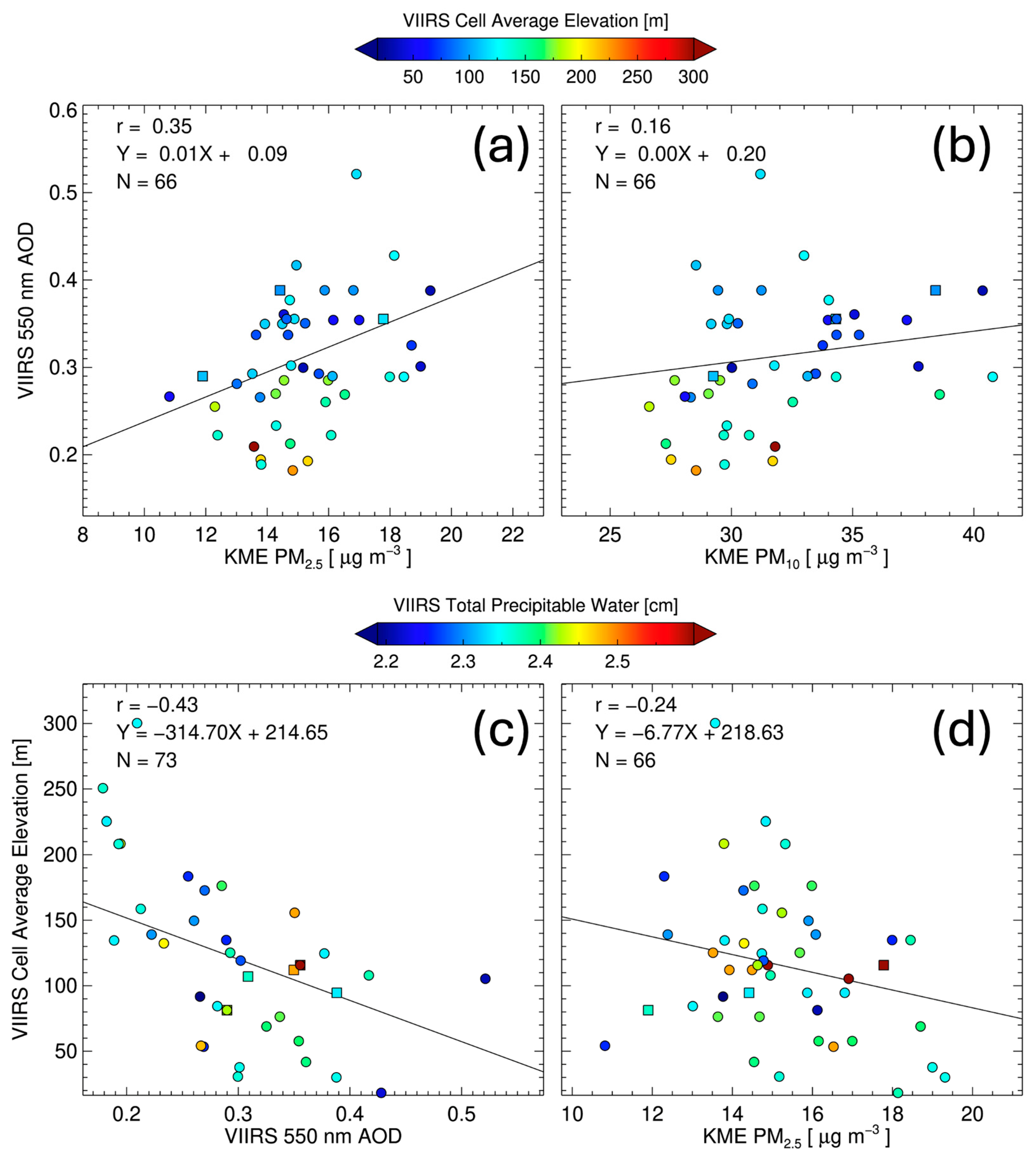
3.3. Relationship Between the AOD and Surface PM Concentrations
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
| APx | ratio of VIIRS AOD to surface PM concentrations |
| C6.1 | Collection 6.1 |
| CAE | cell average elevation |
| DB | Deep Blue |
| DT | Dark Target |
| KME | Korea Ministry of Environment |
| MBE | mean-bias-error |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| PM | particulate matter |
| QA | quality assurance |
| RMSE | root-mean-squared-error |
| SeaWiFS | Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor |
| SIPS | Atmospheres Science Investigator-Led Processing System |
| S-NPP | Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership |
| SOAR | Satellite Ocean Aerosol Retrieval |
| UPF | unsuitable pixel fraction |
| VIIRS | Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer |
References
- Ducruet, C.; Martin, B.P.; Sene, M.A.; Prete, M.L.; Sun, L.; Itoh, H.; Pigné, Y. Ports and their influence on local air pollution and public health: A global analysis. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2024, 915, 170099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, D.; Uibel, S.; Takemura, M.; Klingelhoefer, D.; Groneberg, D.A. Ships, ports and particulate air pollution—An analysis of recent studies. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2011, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Zhu, M.; Chen, S.; Sperling, D. Three steps to a green shipping industry. Nature 2016, 530, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, A.; Kim, D.; An, J.G.; Hyun, S.; Yim, U.H. Shipping-related air pollution at Busan Port: The unceasing threat of black carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, U.; Hong, H. Assessment of tropospheric concentrations of NO2 from the TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 Precursor for the estimation of long-term exposure to surface NO2 over South Korea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Vienneau, D.; Gulliver, J.; Fischer, P.; Briggs, D. A review of land-use regression models to assess spatial variation of outdoor air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7561–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.; Levy, R.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global estimates of ambient fine particulate matter concentrations from satellite-based aerosol optical depth: Development and application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Lee, J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Kim, W.V.; Smirnov, A. Satellite ocean aerosol retrieval (SOAR) algorithm extension to S-NPP VIIRS as part of the “Deep Blue” aerosol project. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 380–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Lee, J.; Sayer, A.M.; Kim, W.; Bettenhausen, C.; Tsay, S.-C. VIIRS Deep Blue aerosol products over land: Extending the EOS long-term aerosol data records. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4026–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Franz, B.A.; McClain, C.R.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Werdell, J.; Shettle, E.P.; Holben, B.N. New aerosol models for the retrieval of aerosol optical thickness and normalized water-leaving radiances from the SeaWiFS and MODIS sensors over coastal regions and open oceans. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5545–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Christopher, S.A. Intercomparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2.5 mass: Implications for air quality studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-P.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Che, H.-Z.; Gong, S.-L.; An, X.; Cao, C.-X.; Guang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, X.-C.; et al. Correlation between PM concentrations and aerosol optical depth in eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5876–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Jeong, U.; Kim, W.; Holben, B.N.; Kim, S.-W.; Song, C.H.; Lim, J.H. Estimation of PM10 concentrations over Seoul using multiple empirical models with AERONET and MODIS data collected during the DRAGON-Asia campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chu, A.; Foster, A. An empirical relationship between PM2.5 and aerosol optical depth in Delhi Metropolitan. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4492–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Yue, L.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The relationships between PM2.5 and aerosol optical depth (AOD) in mainland China: About and behind the spatio-temporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Jacob, D.J.; Brewer, J.F.; Li, K.; Moch, J.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lim, H.; Lee, H.C.; Kuk, S.K.; et al. Relating geostationary satellite measurements of aerosol optical depth (AOD) over East Asia to fine particulate matter (PM2.5): Insights from the KORUS-AQ aircraft campaign and GEOS-Chem model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 16775–16791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, Z. How important is satellite-retrieved aerosol optical depth in deriving surface PM2.5 using machine learning? Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamnes, S.; Baize, R.; Bontempi, P.; Cairns, B.; Chemyakin, E.; Choi, Y.-J.; Chowdhary, J.; Hu, Y.; Jeong, M.; Kang, K.-I.; et al. Simultaneous aerosol and ocean properties from the PolCube CubeSat polarimeter. Front. Remote Sens. 2021, 2, 709040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Holz, R.E.; Lee, J.; Quinn, G.; Veglio, P. Cross-calibration of S-NPP VIIRS moderate-resolution reflective solar bands against MODIS Aqua over dark water scenes. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1425–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.-J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.-C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.-J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS Collection 6 “Deep Blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIER (National Institute of Environmental Research). 2023: Annual Report of Air Quality in Kore; Ministry of the Environment: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wedding, J.B.; Weigand, M.A. An automatic Particle sampler with beta-gauging. J. Air Waste Manag. 1993, 43, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air Korea. Available online: https://www.airkorea.or.kr/eng/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Cabello-Torres, R.J.; Carbo-Bustinza, N.; Romero-Cabello, E.A.; Ureta Tolentino, J.M.; Torres Armas, E.A.; Turpo-Chaparro, J.E.; Canas Rodrigues, P.; López-Gonzales, J.L. An exploratory analysis of PM2.5/PM10 ratio during spring 2016–2018 in Metropolitan Lima. Sci Rep. 2024, 14, 9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, U.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Jung, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, C.H.; Koo, J.H. Estimation of the contributions of long range transported aerosol in East Asia to carbonaceous aerosol and PM concentrations in Seoul, Korea using highly time resolved measurements: A PSCF model approach. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.-S.; Park, S.; Lee, G.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, P.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Physicochemical characteristics and seasonal variations of PM2.5 in urban, industrial, and suburban areas in South Korea. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; de Reus, M.; Krejci, R.; Fischer, H.; Strom, J. Application of the variability-size relationship to atmospheric aerosol studies: Estimating aerosol lifetimes and ages. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2002, 2, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Kuang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhao, R. Joint increase of aerosol scattering efficiency and aerosol hygroscopicity aggravate visibility impairment in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
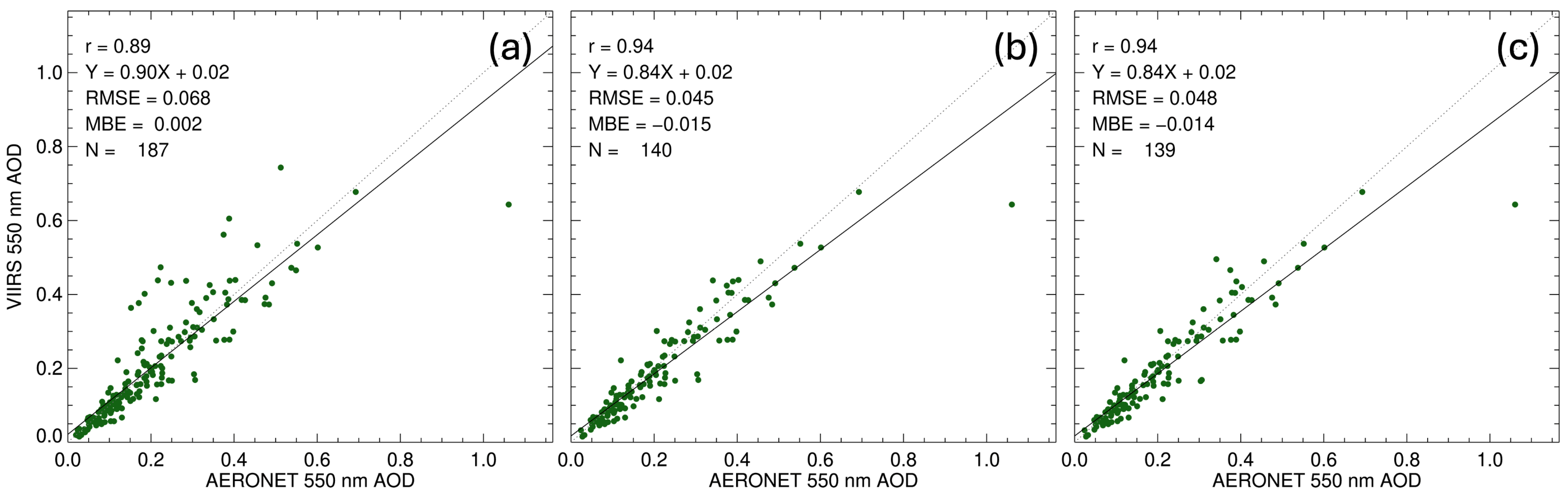
| QA Values | UPF Criteria 1 | Correlation Coefficient | RMSE 2 | MBE 3 | N 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QA ≥ 1 | 0.0 | 0.96 | 0.036 | −0.01 | 64 |
| 0.1 | 0.93 | 0.052 | −0.01 | 97 | |
| 0.2 | 0.93 | 0.052 | −0.01 | 113 | |
| 0.3 | 0.92 | 0.054 | −0.01 | 135 | |
| 0.4 | 0.92 | 0.053 | −0.01 | 149 | |
| 0.5 | 0.92 | 0.054 | −0.01 | 156 | |
| 0.6 | 0.90 | 0.062 | 0.00 | 162 | |
| 0.7 | 0.90 | 0.062 | 0.00 | 172 | |
| 0.8 | 0.89 | 0.069 | 0.00 | 182 | |
| 0.9 | 0.89 | 0.068 | 0.00 | 187 | |
| 1.0 | 0.89 | 0.068 | 0.00 | 187 | |
| QA ≥ 2 | 1.0 | 0.94 | 0.045 | −0.02 | 140 |
| QA = 3 | 1.0 | 0.94 | 0.048 | −0.01 | 139 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, U.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.; Park, S.S. Assessments of Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth for Monitoring Air Quality of the Large Port of Busan, Korea. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101123
Jeong U, Kim S, Lee S, Jung Y, Park SS. Assessments of Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth for Monitoring Air Quality of the Large Port of Busan, Korea. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(10):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101123
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Ukkyo, Serin Kim, Subin Lee, Yeonjin Jung, and Sang Seo Park. 2025. "Assessments of Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth for Monitoring Air Quality of the Large Port of Busan, Korea" Atmosphere 16, no. 10: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101123
APA StyleJeong, U., Kim, S., Lee, S., Jung, Y., & Park, S. S. (2025). Assessments of Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth for Monitoring Air Quality of the Large Port of Busan, Korea. Atmosphere, 16(10), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101123







