Estimation of Ammonia Emission Inventory Using Life Cycle Assessment Based on Livestock Manure Flow: A Case Study of the Manure Management Sector in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- Animal housing;
- (ii)
- Manure storage and treatment facilities;
- (iii)
- Land applications via liquefied fertilizer and compost;
2. Materials and Methods
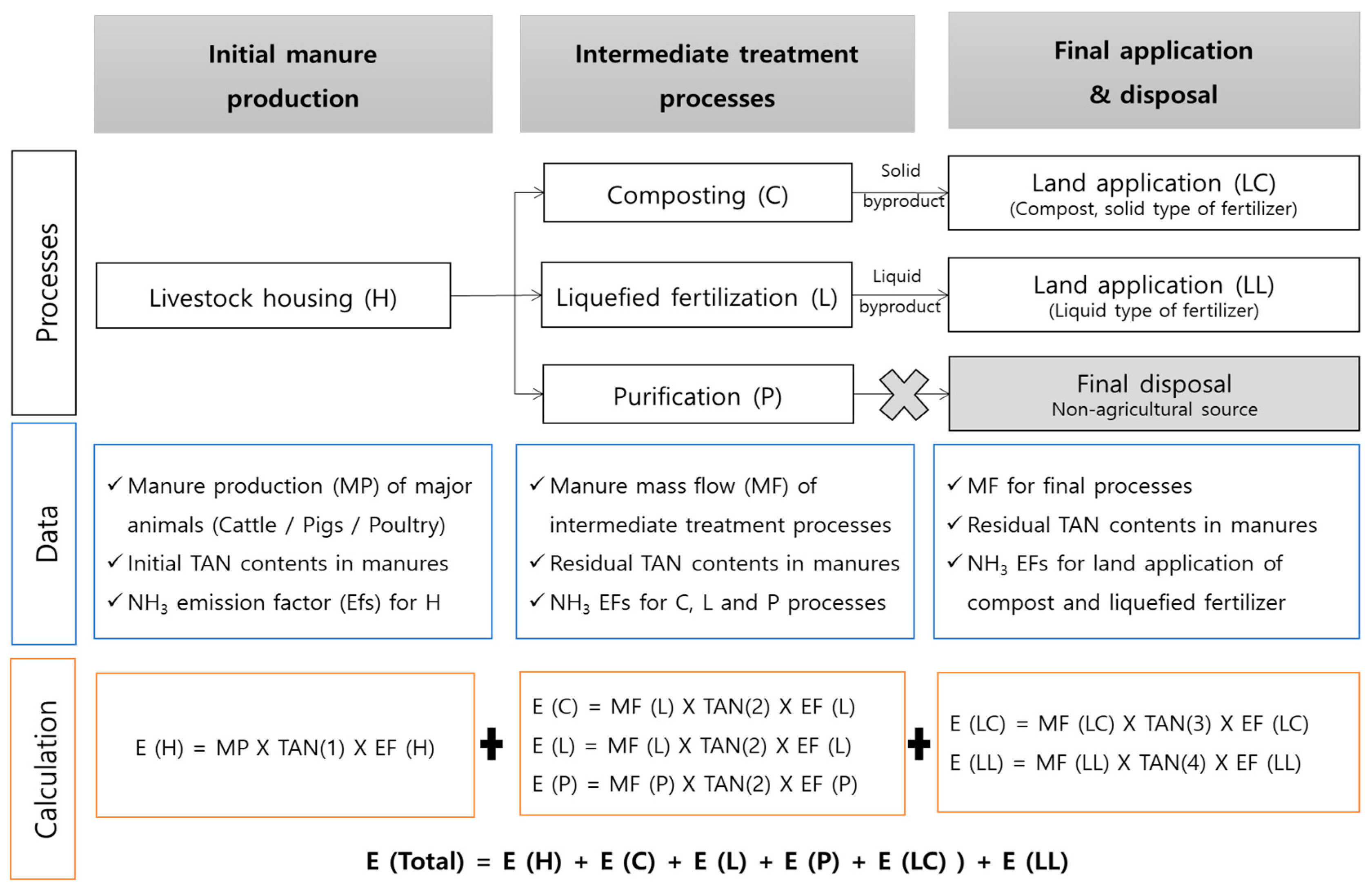
2.1. Various Manure Processes Related to Ammonia Emissions
2.2. Method Comparison
2.3. Calculation of Ammonia Emissions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ammonia Emission by CAPSS 2020
3.2. Manure Mass Flow (MF)
3.3. Initial TAN and Emission Factors
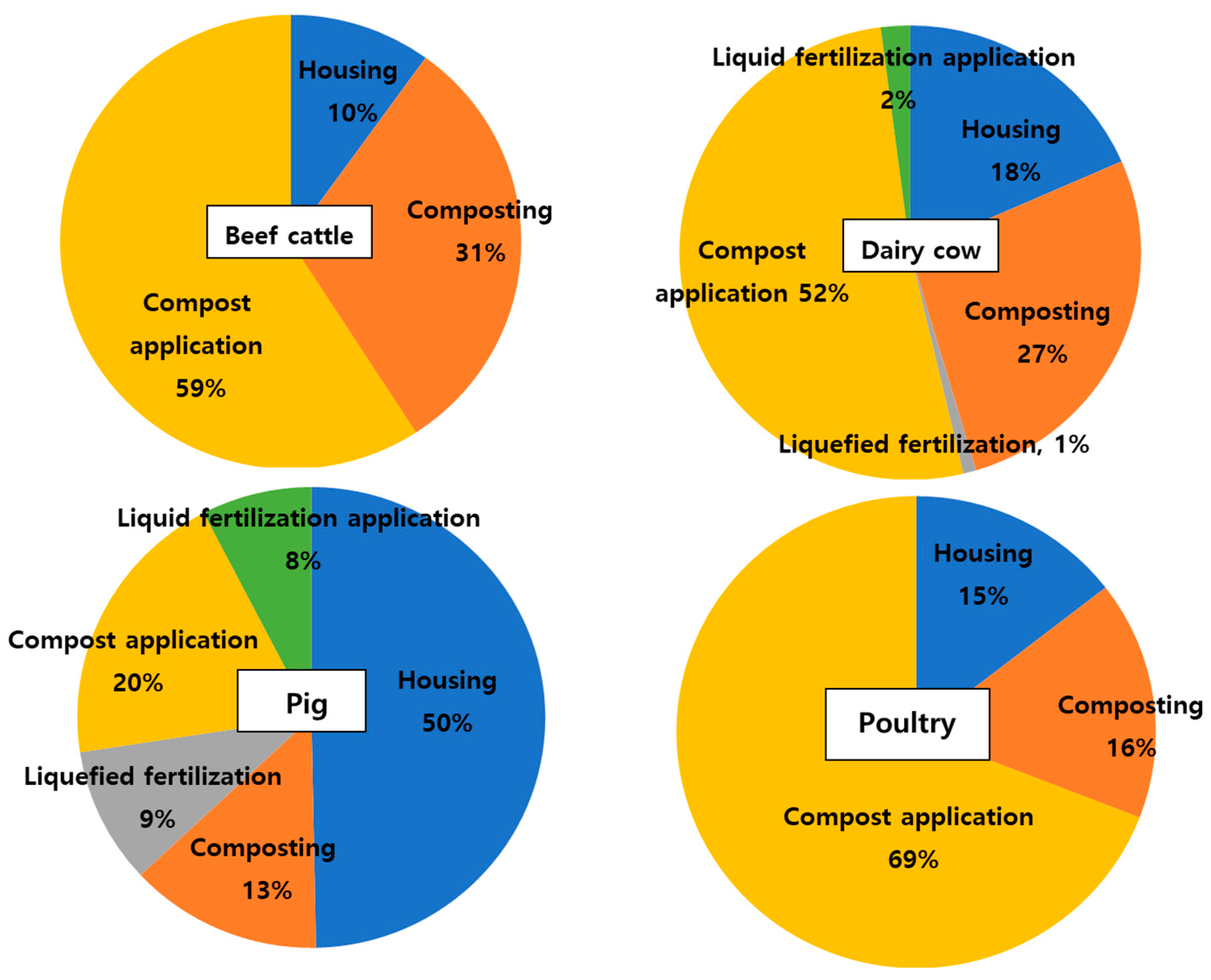
3.4. Estimation of Ammonia Emissions from Four Major Animals
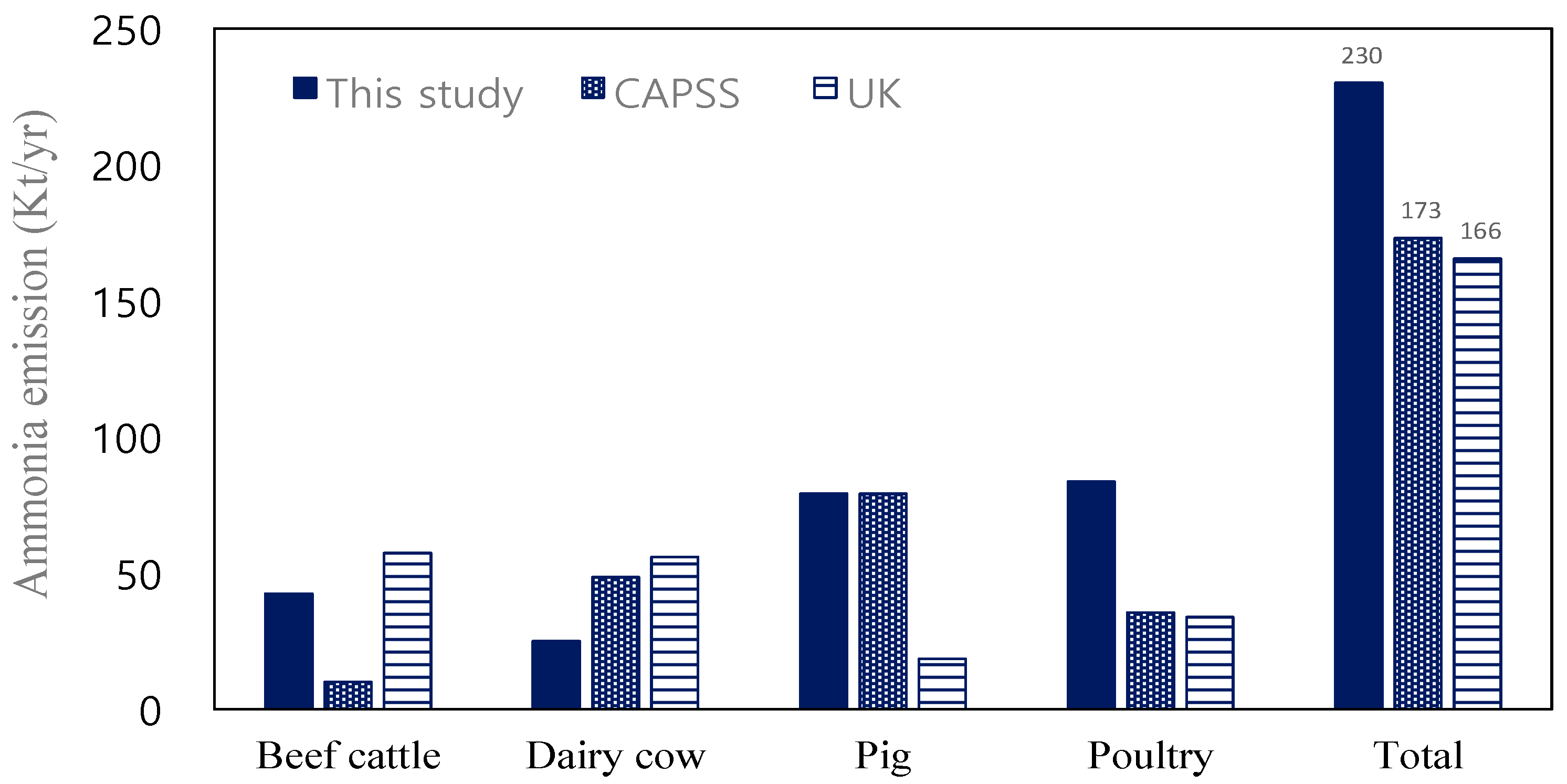
3.5. Comparison of Ammonia Emissions in This Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paria, S.; Pishgar-Komleh, S.H.; Andr, J.A.A. Model Adaptation and Validation for Estimating Methane and Ammonia Emissions from Fattening Pig Houses: Effect of Manure Management System. Animals 2024, 14, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Dinh, P.; Van, D.; Peet-Schwering, C.M.C.; Ogink, N.W.M.; Aarnink, A.J.A. Effect of Diet Composition on Excreta compotion and Ammonia Emissions from Growing-Finishing Pigs. Animals 2022, 14, 964. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, N.; Strader, R.; Davidson, C. Airborne reduced nitrogen: Ammonia emissions from agriculture and other sources. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziru, L.; Weili, L.; Gang, Z. Sources, Variations, and Effects on Air Quality of Atmospheric Ammonia. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2024, 10, 40–53. [Google Scholar]
- William, B.; Viney, P.A.; Paul, A.R. Evaluation and improvement of ammonia emissions inventories. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3873–3883. [Google Scholar]
- National Air Emission Inventory and Research Center (NAlR). National Air Pollutants Emission. 2020. Available online: https://www.air.go.kr (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Misselbrook, T.H.; Gilhespy, S.L. Inventory of Ammonia Emissions from UK Agriculture 2019; Inventory Submission Report: DEPRA Contract SCF0107; UK, 2021. Available online: https://uk-air.defra.gov.uk/assets/documents/reports/cat07/2103191000_UK_Agriculture_Ammonia_Emission_Report_1990-2019.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Meisinger, J.J.; Jokela, W.E. Ammonia Volatilization from Dairy and Poultry Manure. In Managing Nutrients and Pathogens from Animal Agriculture (NARAES-130); Resource, Agriculture and Engineering Service: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.H.; Hussain, N.; Barry, R.H.; Joann, K.W. Ammonia volatilization from manure mixed with biochar. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 102, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.A.; Richard, A. Emission, Dispersion and Local Deposition of Ammonia Volatilized from Farm Buildings and Following the Application of Cattle Slurry to Grassland. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Plymouth, Plymouth, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, H.S.; Ndegwa, P.M.; Wang, X.; Heber, A.J.; Ni, J.Q.; Cortus, E.L.; Ramirez-Dorronsoro, J.C.; Bogan, B.W.; Chai, L. Ammonia and hydrogen sulfide concentrations and emissions for naturally ventilated freestall dairy barns. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, E.C. National Air Pollutant Emission Estimation Manual (II); National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER): Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2008.
- Kim, J.S. National Air Pollutant Emissions Calculation Method Manual (V); National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER): Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2023.
- Jeon, E.C.; Sa, J.H.; Das, P.; Lee, S.R.; Roh, G.H. Flux and Emission factor of ammonia from pig Housing. Environ. Soc. Jt. Conf. 2007, 6D7, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Sa, J.H.; Jeon, E.C. Estimation of Ammonia Flux and Emission Factor from the cattle Housing of Fall and winter. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2010, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.B.; Lee, S.J.; Chang, H.H. Assessment of the Amount of Ammonia Emitted from Hanwoo Loose Barn and Winch-curtain Broiler House. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2013, 47, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Jang, Y.N.; Ha, T.H.; Kwon, K.S.; Jung, M.W. A Study on Ammonia Emission Characteristics in Naturally Ventilated Hanwoo-barn. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 37, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CORINAIR. EMEP/CORINAIR Atmospheric Emission Inventory Guidebook-Second Edition Group 10; CORINAIR: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Battye, R.; Battye, W.; Overcash, C.; Fudge, S. Development and Selection of Ammonia Emission Factors; EPA Contract Number 1994, 68-D3-0034; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- Frederick, K.T.; Mikko, H. A comparative assessment of four methods for estimating ammonia emissions at microclimatic locations in a dairy building. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2010, 54, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, W.B.; Shaw, B.W. Review of ammonia emission factors for United States animal agriculture. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6567–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. 2020 National Emissions Inventory Technical Support Document: Agriculture–Livestock Waste; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Webb, J.; Menzi, H.; Pain, B.F.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Dammgen, U.; Hendriks, H.; Dohler, H. Managing ammonia emissions from livestock production in Europe. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 135, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, S.; Eva, B.; Bart, S.; Peter, D. Validation of Five Gas Analysers for Application in Ammonia Emission Measurements at Livestock Houses According to the VERA Test Protocol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera Test Protocol for Livestock Housing and Management Systems; International VERA Secretariat: Delft, The Netherlands, 2018.
- Misselbrook, T.H.; Gilhespy, S.L.; Carswell, A.M.; Cardens, L.M. Report: Inventory of Ammonia Emissions from UK Agriculture 2021. Inventory Submission Report; DEPRA: Ballston, VA, USA, 21 March 2023; Contract SCF0107. [Google Scholar]
- Demmers TG, M.; Phillips, V.R.; Short, L.S.; Burgess, L.R.; Hoxey, R.P.; Wathes, C.M. Validation of Ventilation Rate Measurement Methods and the Ammonia Emission from Naturally Ventilated Dairy and Beef Buildings in the United Kingdom. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2001, 79, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Koerkamp, P.; Metz, J.H.M.; Uenk, G.H.; Phillips, V.R.; Holden, M.R.; Sneath, R.W.; Short, J.L.; White, R.P.; Hartung, J.; Seedorf, J.; et al. Concentrations and emissions of ammonia in livestock buildings in Northern Europe. J. Agric. Eng. 1998, 70, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palakodeti, A.; Azman, S.; Rossi, B.; Dewil, R.; Appels, L.A. Critical Review of Ammonia Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate of Organic Wastes via Stripping. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, S.d.P.; Raffaele, G.; Stefano, P.; Giovanni, E.; Elena, C.; Marco, B.; Stefania, P. Ammonia Air Stripping from Different Livestock Effluents Prior to and after Anaerobic Digestion. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA). Production and Treatment Types for Livestock Manure; Livestock Environmental Management Institute: Sejong-si, Republic of Korea, 2022; Available online: https://thecce.kr/5008 (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Misselbrook, T.H.; Sutton, M.A.; Scholefield, D.A. Simple process-based model for estimating ammonia emissions from agricultural land after fertilizer applications. Soil Use Manag. 2004, 20, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Farming Statistics Final Crop Areas, Yields, Livestock Populations and Agricultural Workforce; Department for Environment Food & Rural Affairs: Defra, UK, 2019.
- Ministry of Environment (ME). Clean Air Policy Support System (CAPSS); Ministry of Environment (ME): Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2020.
- Korean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). Number of Farmers by Livestock Manures; Korean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS): Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2019.
- Gabriel, A.M.; Aliyu, S.M.; Stephen, A.B. Sustainable Animal Manure Management Strategies and Practices; Intechopen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Livestock and Environment Statistics: Manure and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Global, Regional and Country Trends 1990–2018; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gerard, L.V.; Yong, H.; Oene, O. Society of Chemical Industry, Nitrogen Excretion Factors of Livestock in the European Union: A Review; Intechopen: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.A.; Williams, A.G. Production and management of cattle manure in the UK and implications for land application practice. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32 (Suppl. S1), 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misselbrook, T.H.; Nicholson, F.A.; Chambers, B.J. Predicting ammonia losses following the application of livestock manure to land. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oene, O.; Diti, O.; Gerard, L.V. Nutrient losses from manure management in the European Union. Livestock Sci. 2007, 112, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Sven, G.S.; Webb, J.; Nicholas, D.H. New emission factors for calculation of ammonia volatilization from european livestock manure management Systems. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Owusu-Twum, M.Y.; Kelleghan, D.; Gleasure, G.; Forrestal, P.; Lanigan, G.J.; Richards, K.G.; Krol, D.J. Ammonia emission factors from cattle production systems in Ireland: A review. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 62, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emission Factors by the Number of Herds: Farming Statistics Final Crop Areas, Yields; DEPRA: Ballston, VA, USA, June 2019.


| Korea (CAPSS) | UK | This Study | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia emission (g/yr) | E * = A ** × EF | E = A × EF | E = A × EF |
| Consideration of life cycle analysis (LCA) | - | Manure excretion to final application | Manure excretion to final application |
| Target of EF | Facilities | Manure in individual processes | Manure in individual processes |
| Measurement (Parameter) | Direct measurement (DFC) for each facility (Ammonia emitted from manure) | Nitrogen and TAN in manure (Residual nitrogen in manure) | Nitrogen and TAN in manure (Residual nitrogen in manure) |
| Individual EF | Emission factors of individual facilities (g/yr/head) | Emission factors of individual processes (%) | Emission factors of individual processes (%) |
| Total EF (g/yr/head) | Sum of EFs of individual facilities | Total emission ÷ Heads | Total emission÷ Heads |
| Limitations | Selection of inclusive facility (size/type) Reliability measurement method (DFC) | Statistical data of manure mass flow (DEFRA +) | Statistical data of manure mass flow (MAFRA ++) |
| UK (2019) | Korea (2020) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 Emission (kt/yr) | Animals (Head) | NH3 Emission (kt/yr) | Animals (Head) | |
| Total | 179.10 | 208,844,000 | 181.06 | 215,223,879 |
| Cattle | 113.30 | 9,739,000 | 58.08 | 6,804,051 |
| Sheep | 12.30 | 17,545,000 | 0.23 | 8993 |
| Pigs | 18.50 | 5,078,000 | 79.10 | 11,208,400 |
| Poultry | 33.80 | 176,232,000 | 35.40 | 197,175,910 |
| Horses | 1.20 | 250,000 | 0.14 | 26,525 |
| Treatment | Beef Cattle | Dairy Cows | Pigs | Poultry | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korea 2022 | Individual treatment | Composting | 14,170 | 3607 | 623 | 1575 |
| Liquefied fertilization | 293 | 2507 | ||||
| Purification | 26 | 3370 | ||||
| Community treatment | Composting | 3179 | 655 | 6398 | 7160 | |
| Liquefied fertilization | 3164 | |||||
| Purification | 37 | 3148 | ||||
| Total manure production | 17,349 | 4618 | 19,210 | 8735 | ||
| Community treatment ratio | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.66 | 0.82 | ||
| UK 2019 | Total manure production | 28,310 | 29,950 | 6040 | 4580 | |
| Calculation Procedure | Dairy Cows | Beef Cattle | Pigs | Poultry | References and Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) N excretion per animal (kg/yr/head) | 110 | 55 | 10.6 | 0.57 | Gerard et al., 2015 [36] |
| (2) Animals (head) | 3,223,000 | 6,516,000 | 5,078,000 | 176,232,000 | DEFRA 2019, farming statistics [33] |
| (3) N excretion (kton/yr) | 354.53 | 358.38 | 53.83 | 100.45 | (1) × (2) |
| (4) Manure production (ton/yr) | 28,310,000 | 29,950,000 | 6,040,000 | 4,580,000 | Smith et al., 2016 [39] |
| (5) N excretion (kg/ton-manure) | 12.523 | 11.966 | 8.912 | 21.933 | (3) ÷ (4) |
| (6) % TAN from N excretion (%) | 0.461 | 0.214 | 0.631 | 0.586 | Misselbrook et al., 2004 [32] |
| (7) Initial TAN in housing (kg/ton-manure) | 5.772 | 2.564 | 5.620 | 12.846 | (5) × (6) |
| Housing | Intermediate Treatment Processes | Land Application | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reported EF | Modified | Composting | Liquefied Fertilization | Compost | Liquid Fertilizer | |
| Beef cattle | 12.5 | 7.81 | 26.3 | - | 68.3 | - |
| Dairy cows | 27.7 | 14.23 | 26.3 | 10.6 | 68.3 | 32.4 |
| Pigs | 22.9 | 30.00 | 31.5 | 13.0 | 68.3 | 25.5 |
| Poultry | 10.5 | 8.90 | 11.0 | - | 52.3 | - |
| Stage | Process | Beef Cattle | Dairy Cows | Pigs | Poultry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st stage | Housing | 4221 | 4605 | 39,329 | 12,127 |
| 2nd stage | Composting | 13,039 | 6739 | 10,552 | 13,690 |
| Liquefied fertilization | - | 227 | 7576 | - | |
| 3rd stage | Compost application | 7571 | 12,899 | 15,672 | 21,811 |
| Liquid fertilization application | - | 515 | 6026 | - | |
| Total | 42,384 | 24,985 | 79,154 | 83,577 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-M.; Kim, K.-C.; Kim, M.-W.; Lee, J.-Y.; Joo, H.-S. Estimation of Ammonia Emission Inventory Using Life Cycle Assessment Based on Livestock Manure Flow: A Case Study of the Manure Management Sector in Korea. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080910
Lee H-M, Kim K-C, Kim M-W, Lee J-Y, Joo H-S. Estimation of Ammonia Emission Inventory Using Life Cycle Assessment Based on Livestock Manure Flow: A Case Study of the Manure Management Sector in Korea. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(8):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080910
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hye-Min, Kyoung-Chan Kim, Min-Wook Kim, Ju-Yong Lee, and Hung-Soo Joo. 2024. "Estimation of Ammonia Emission Inventory Using Life Cycle Assessment Based on Livestock Manure Flow: A Case Study of the Manure Management Sector in Korea" Atmosphere 15, no. 8: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080910
APA StyleLee, H.-M., Kim, K.-C., Kim, M.-W., Lee, J.-Y., & Joo, H.-S. (2024). Estimation of Ammonia Emission Inventory Using Life Cycle Assessment Based on Livestock Manure Flow: A Case Study of the Manure Management Sector in Korea. Atmosphere, 15(8), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080910






