Exploring the Spatial Variability of Air Pollution Using Mobile BC Measurements in a Citizen Science Project: A Case Study in Mechelen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. A Citizen Observatory for Air Quality
2.1.1. Instrumentation
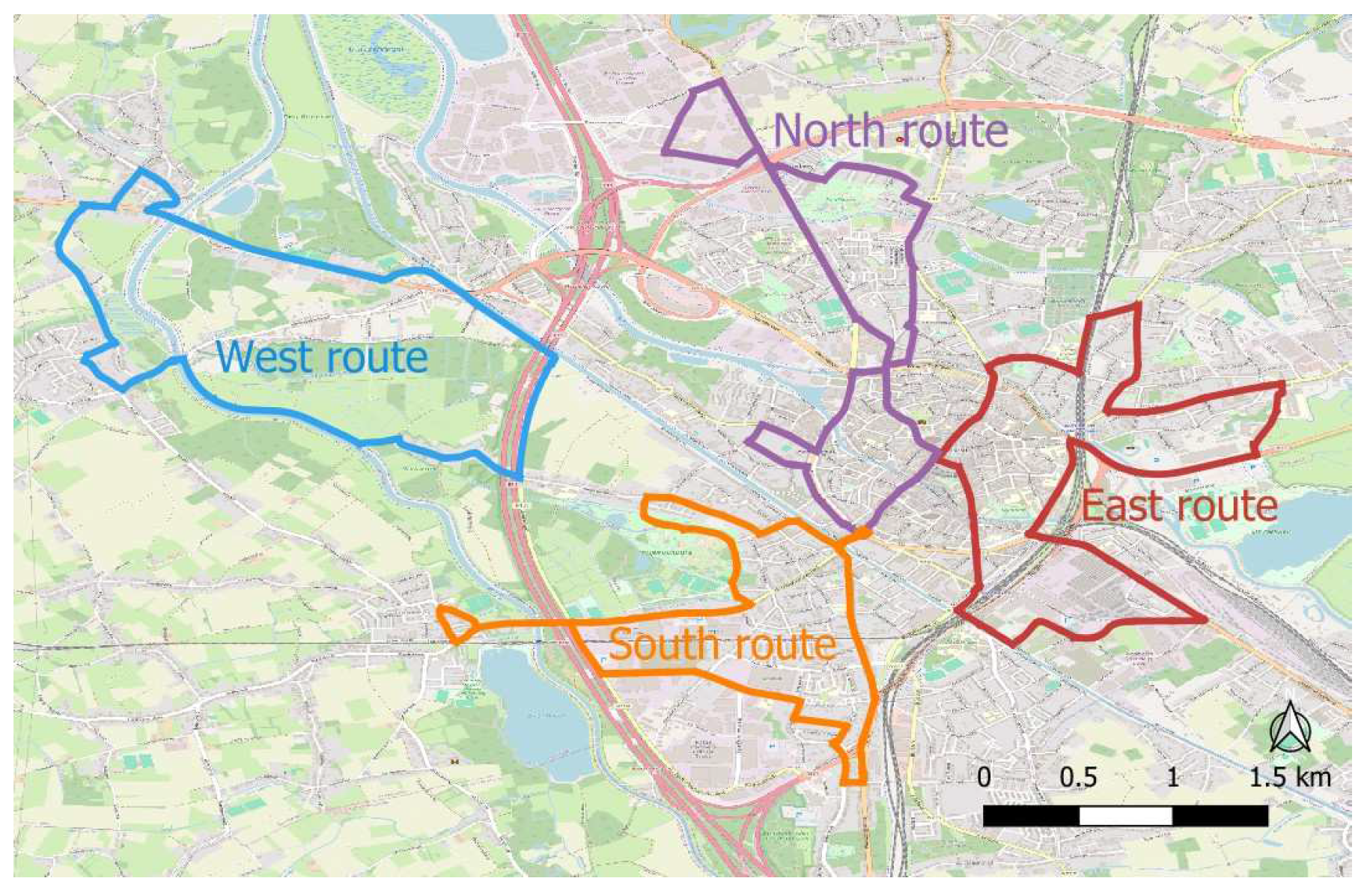
2.1.2. Description of the Measurement Campaign
2.1.3. Collected Dataset
2.1.4. Data Processing
- Input:
- BC data from the four mobile campaigns X = {X1, X2, X3, X4};
- BC data for a virtual traffic station from the reference dataset of the Flemish Environment Agency, Y, for the period October 2017 until October 2018 (including the period from start X1 until end X4).
- Output: Map of the estimated yearly average BC concentration during peak traffic hours from the mobile campaigns.
- Method:
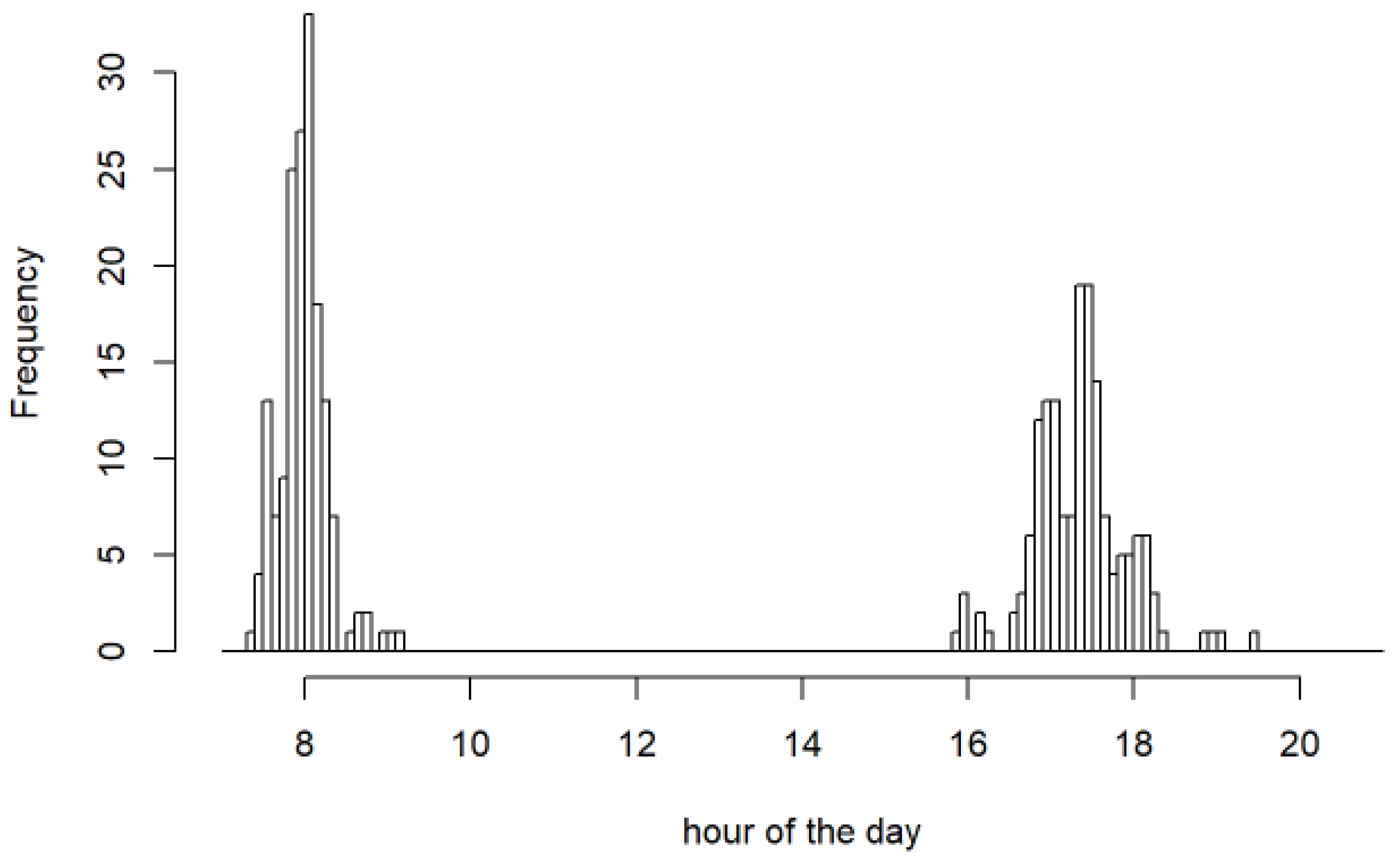
- Subset Y (Ys) for the morning and evening rush hour measurements, in line with the hours of the day of the mobile monitoring (X, see Figure 2);
- Calculate the weekly averages from Ys ( for i = 1,…,52);
- Calculate the averages from Xi ( for i = 1, …, 4);
- Calculate a frequency histogram of in 0.5 µg m−3 bins;
- Obtain the frequency of occurrence of the bins that coincide with ( for i = 1, …, 4, );
- Obtain a weighting ( for i = 1, …, 4) per campaign as
- Apply these weighting factors to estimate the yearly average BC concentration ().
2.2. Air Quality Monitoring Stations and Data
2.3. Model
3. Results
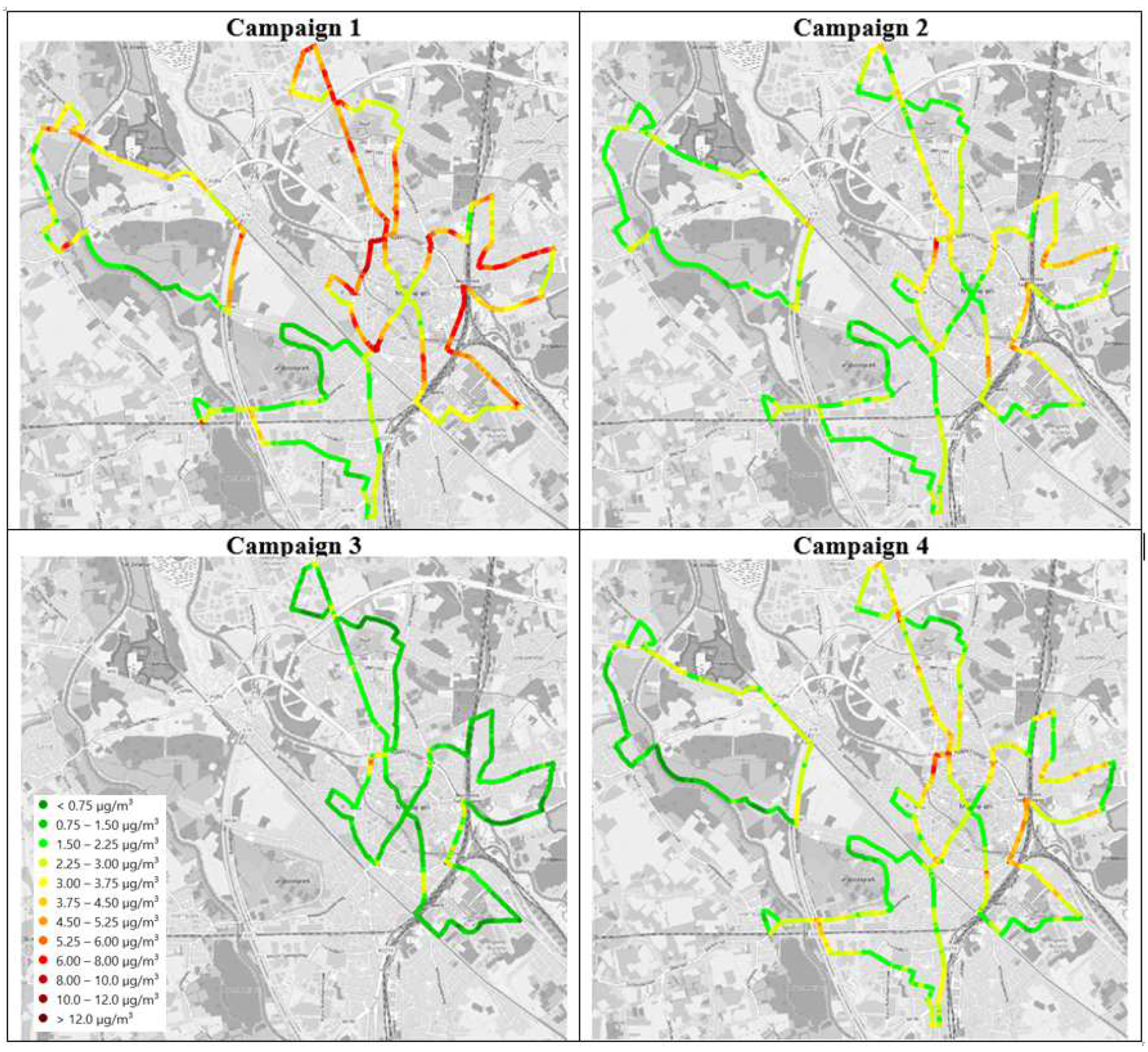
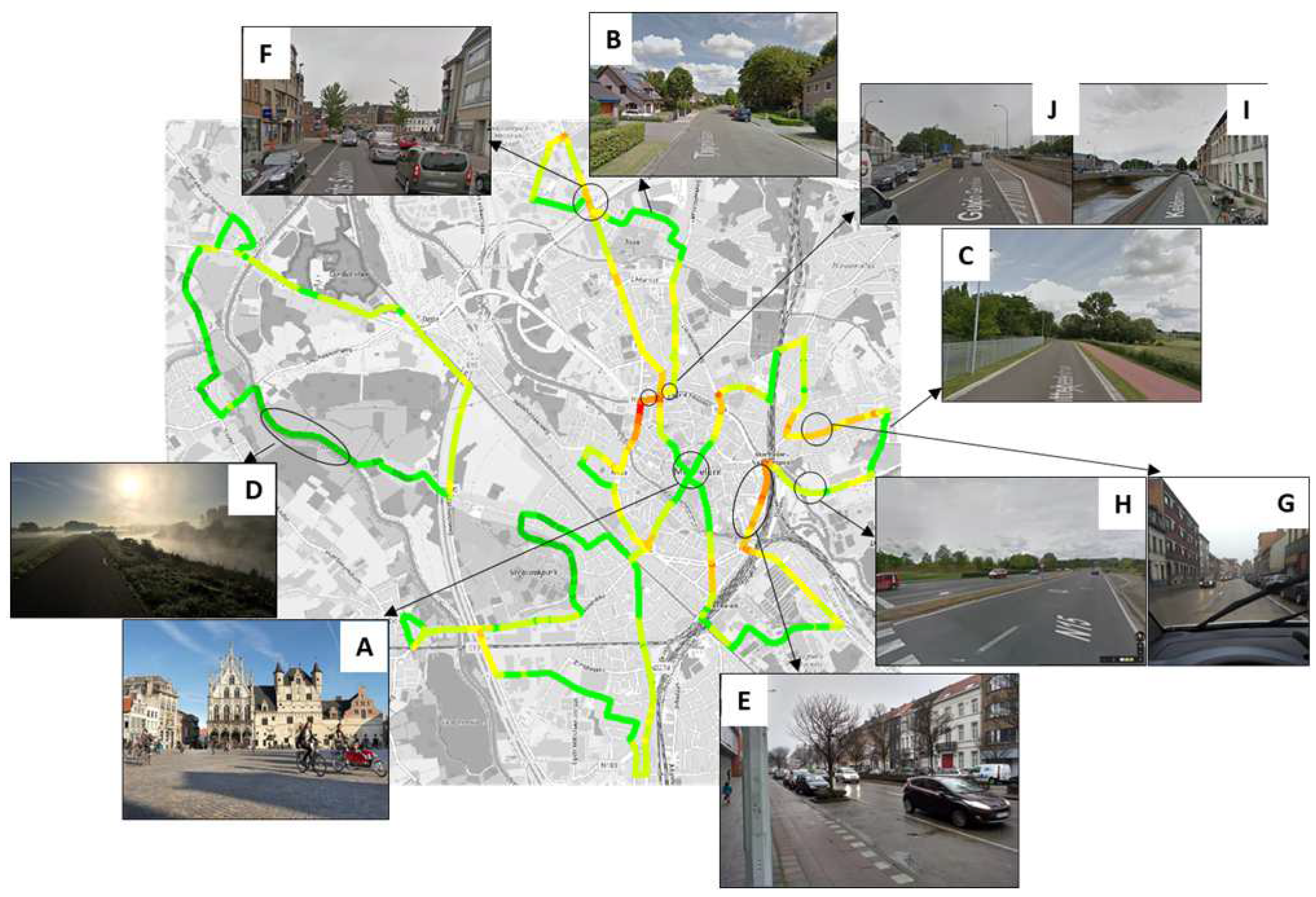
3.1. Black Carbon Concentration Maps
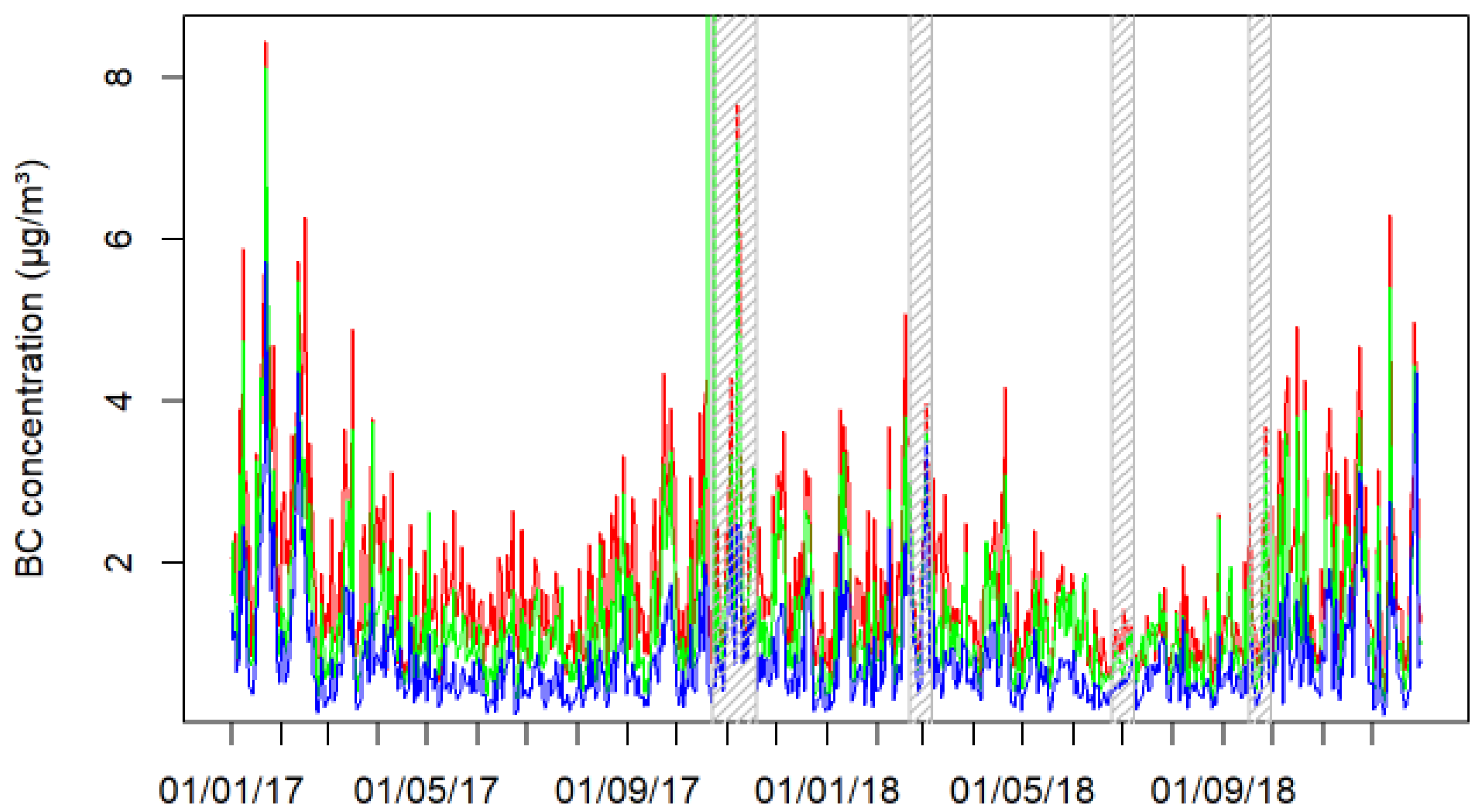
3.2. Black Carbon Concentrations at AQMS
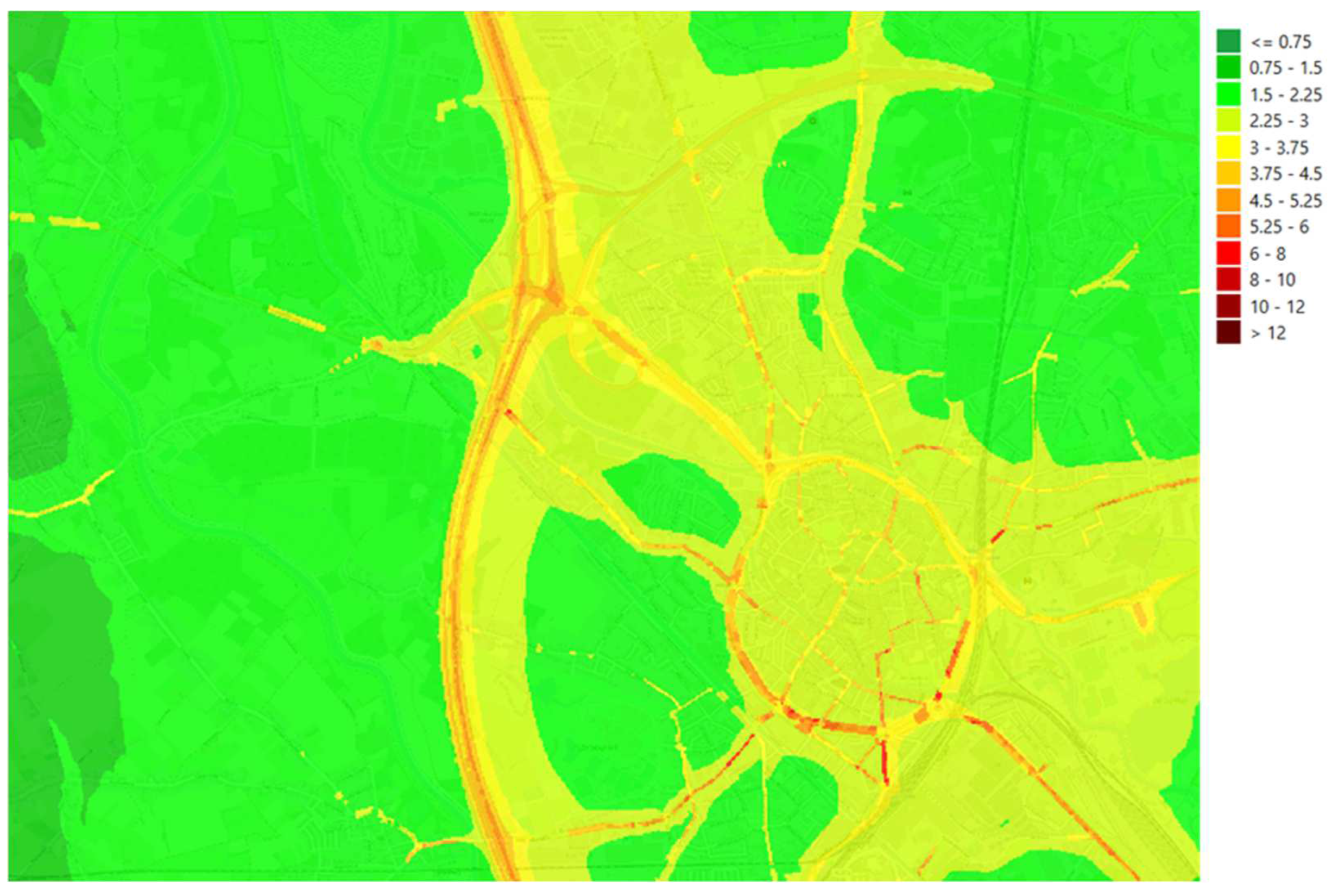
3.3. Aggregated and Rescaled Maps
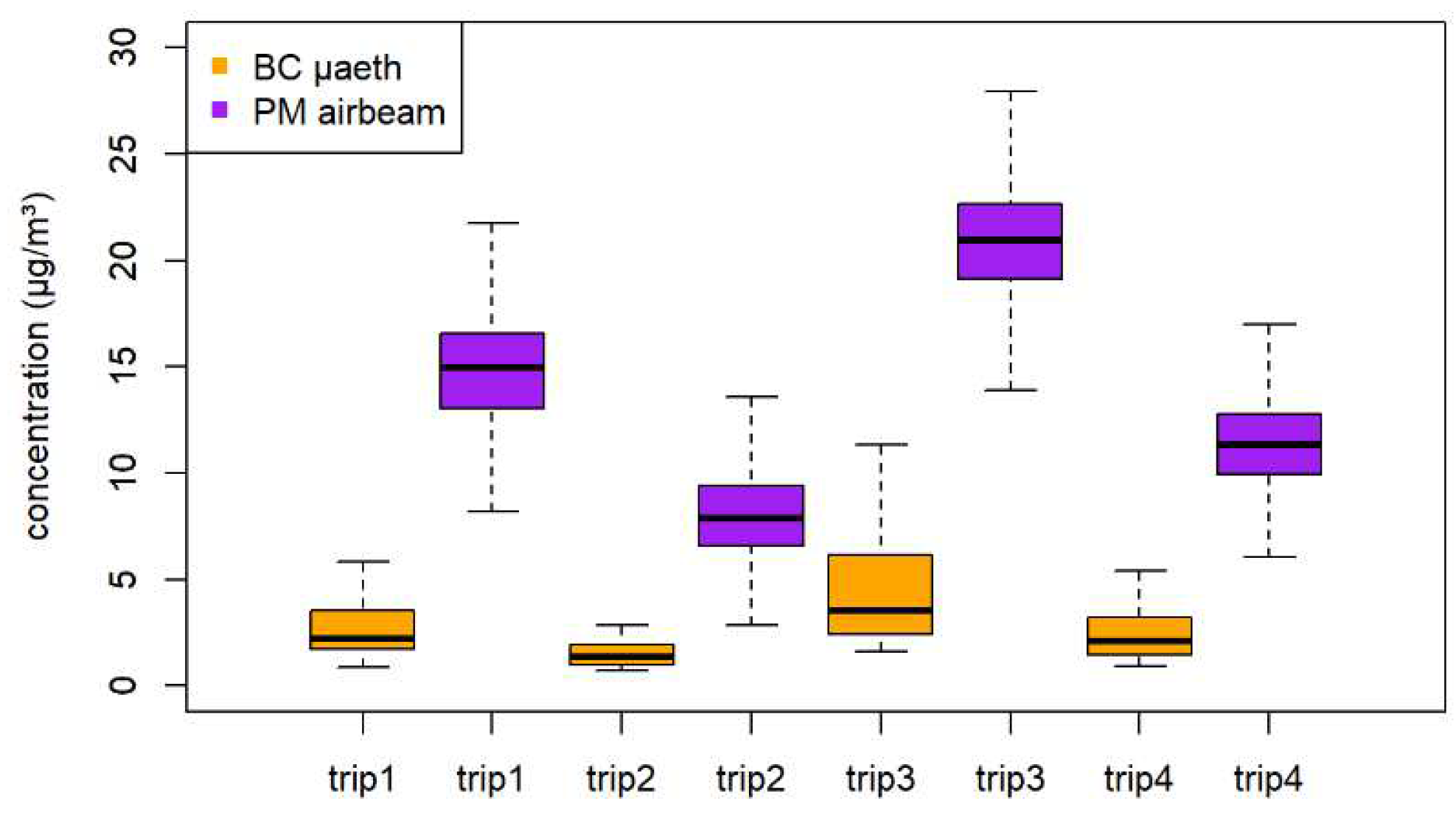
3.4. Comparison with Different Metric and Measurement Technology: BC by AE51 versus PM2.5 by AirBeam
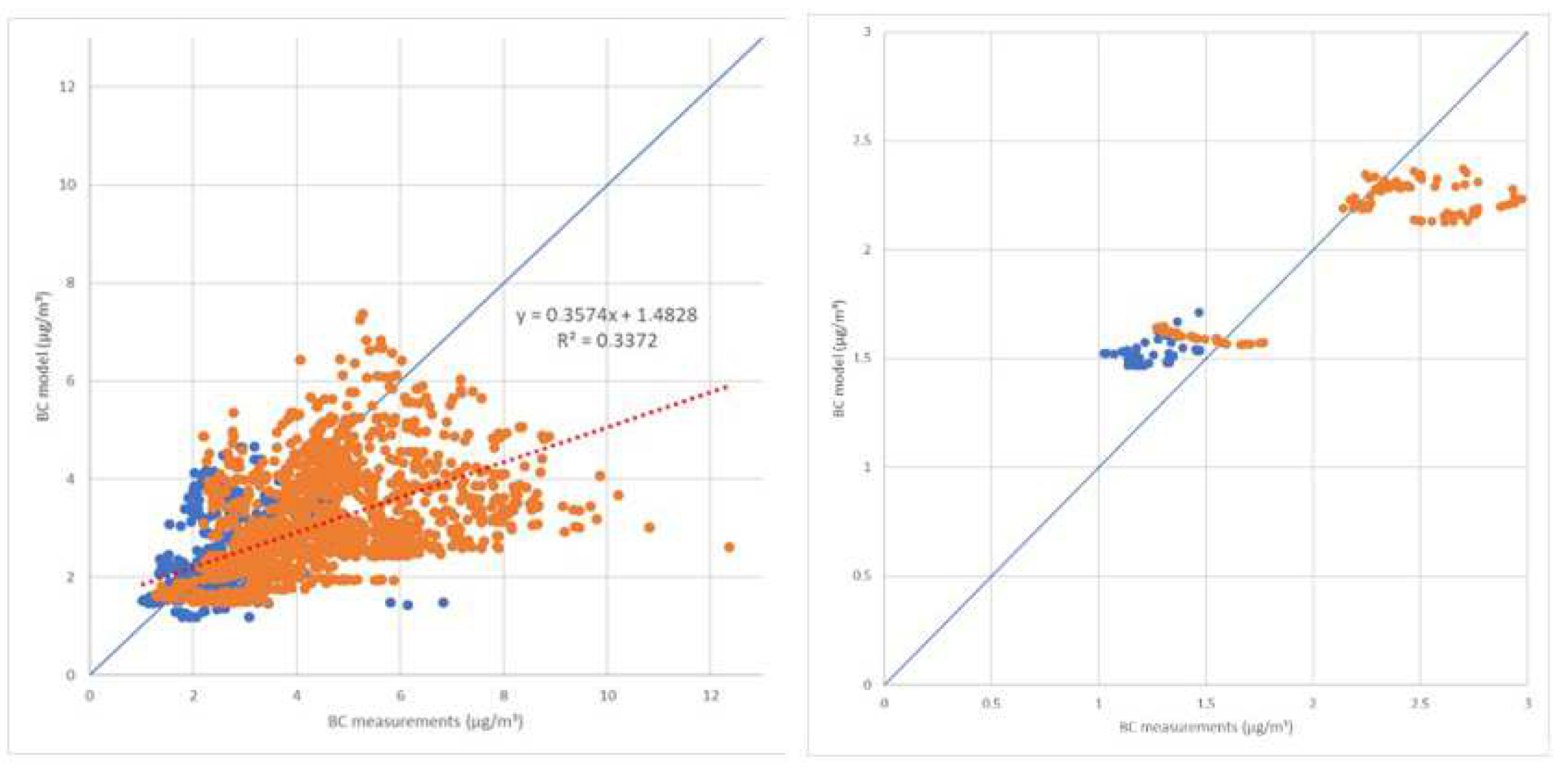
3.5. Comparison with Model Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Different Campaigns
4.2. Rescaling
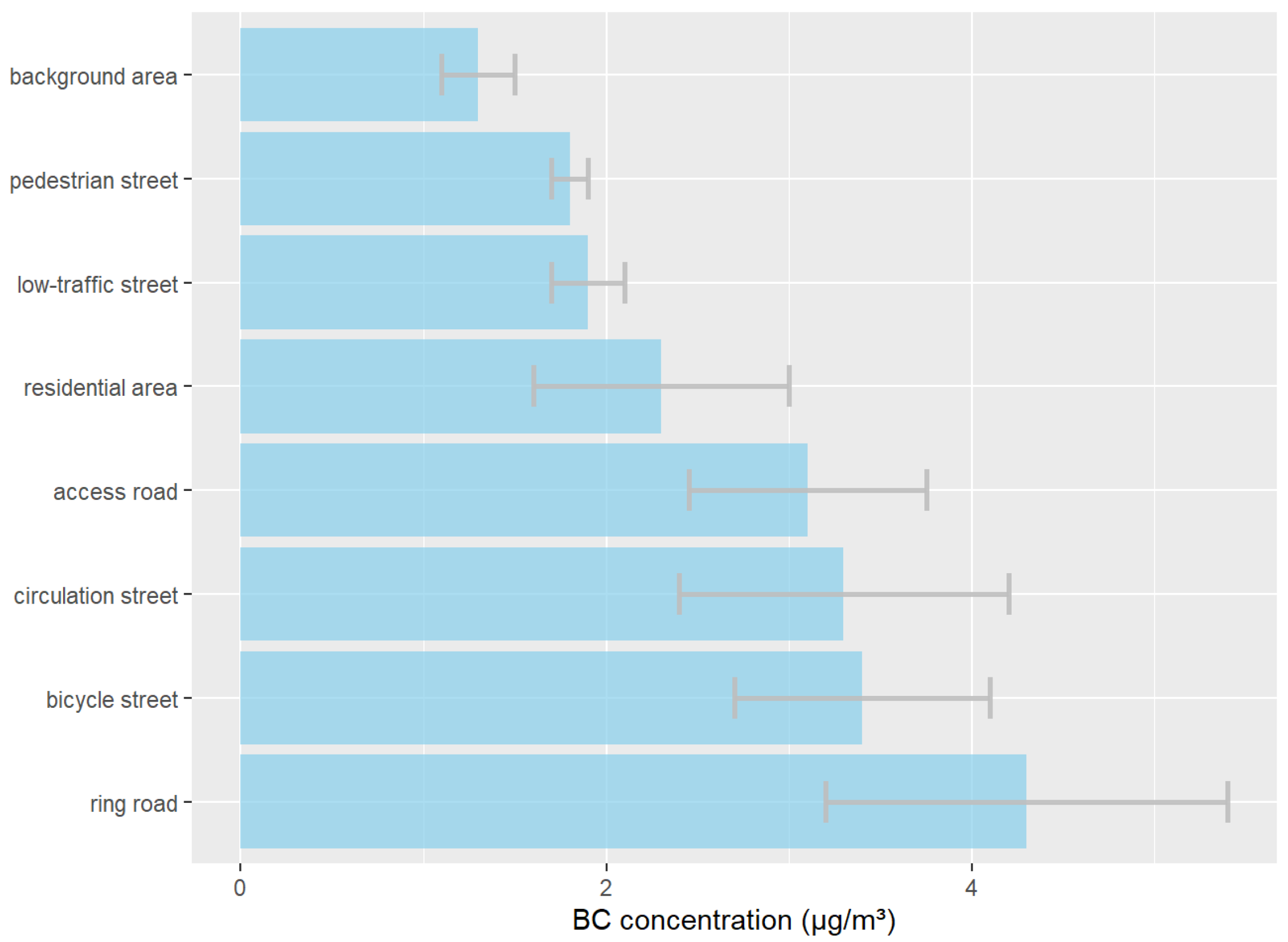
4.3. Interpretation of Results with Respect to Mobility Planning
4.4. Comparison with Model Results
4.5. Mobile Measurements Using airQmap in Citizen Science Projects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conrad, C.C.; Hilchey, K.G. A review of citizen science and community-based environmental monitoring: Issues and opportunities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 176, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, A.; Edwards, P. Validate air pollution sensors. Nat. N. Comment 2016, 535, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Peters, J.; Verwaeren, J.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J.; De Baets, B. Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in urban air quality: Development and validation of a methodology based on an extensive dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.; Laeremans, M.; Orjuela, J.P.; Avila-Palencia, I.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Anaya-Boig, E.; Standaert, A.; De Boever, P.; Nawrot, T.; et al. Wearable Sensors for Personal Monitoring and Estimation of Inhaled Traffic-Related Air Pollution: Evaluation of Methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, J.; Samson, R.; Joosen, S.; Blust, R.; Lenaerts, S. Cyclist exposure to black carbon, ultrafine particles and heavy metals: An experimental study along two commuting routes near Antwerp, Belgium. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.; Van den Bossche, J.; Reggente, M.; Van Poppel, M.; De Baets, B.; Theunis, J. Cyclist exposure to UFP and BC on urban routes in Antwerp, Belgium. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poppel, M.; Peters, J.; Levei, E.A.; Mărmureanu, L.; Moldovan, A.; Hoaghia, M.-A.; Varaticeanu, C.; Van Laer, J. Mobile measurements of black carbon: Comparison of normal traffic with reduced traffic conditions during COVID-19 lock-down. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 297, 119594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, J.S.; Messier, K.P.; Gani, S.; Brauer, M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Lunden, M.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Portier, C.J.; Vermeulen, R.C.H.; Hamburg, S.P. High-Resolution Air Pollution Mapping with Google Street View Cars: Exploiting Big Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6999–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, J.; Panzica La Manna, V.; Ibarrola-Ulzurrun, E.; Peters, J.; Escribano, M.; Van Poppel, M. Opportunistic Mobile Air Quality Mapping using Sensors on Postal Service Vehicles: From Point Clouds to Actionable Insights. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 2, 1232867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messier, K.P.; Chambliss, S.E.; Gani, S.; Alvarez, R.; Brauer, M.; Choi, J.J.; Hamburg, S.P.; Kerckhoffs, J.; LaFranchi, B.; Lunden, M.M.; et al. Mapping Air Pollution with Google Street View Cars: Efficient Approaches with Mobile Monitoring and Land Use Regression. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12563–12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, J.; Hendricx, W.; de Ruiter, H.; van Ratingen, S.; Drukker, D.; Huitema, M.; Schouwenaar, C.; Janssen, G.; van Aken, S.; Smeenk, J.W.; et al. Assessment of PM2.5 Exposure during Cycle Trips in The Netherlands Using Low-Cost Sensors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.N.; Bi, J.; Austin, E.; Larson, T.V.; Marshall, J.D.; Sheppard, L. Impact of mobile monitoring network design on air pollution exposure assessment models. Environ. Sci Technol. 2023, 57, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report to Congress on Black Carbon. Available online: https://19january2017snapshot.epa.gov/www3/airquality/blackcarbon/2012report/fullreport.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Janssen, N.A.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Lanki, T.; Salonen, R.O.; Cassee, F.; Hoek, G.; Fischer, P.; Brunekreef, B.; Krzyzanowski, M. Health Effects of Black Carbon; Technical Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brunekreef, B.; Strak, M.; Chen, J.; Andersen, Z.J.; Atkinson, R.; Bauwelinck, M. Mortality and Morbidity Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Low-Level PM2.5, BC, NO2, and O3, an Analysis of European Cohorts in the ELAPSE Project. Res. Rep. Health Eff. Inst. 2021, 2021, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Rovira, J.; Paredes-Ahumada, J.A.; Barceló-Ordinas, J.M.; García-Vidal, J.; Reche, C.; Sola, Y.; Viana, M. Non-linear models for black carbon exposure modelling using air pollution datasets. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, P.L.; Savadkoohi, M.; Zaidan, M.A.; Niemi, J.V.; Timonen, H.; Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Hussein, T.; Petäjä, T. Constructing transferable and interpretable machine learning models for black carbon concentrations. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerckhoffs, J.; Hoek, G.; Vlaanderen, J.; van Nunen, E.; Messier, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Gulliver, J.; Vermeulen, R. Robustness of intra urban land-use regression models for ultrafine particles and black carbon based on mobile monitoring. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghmans, P.; Bleux, N.; Int Panis, L.; Mishra, V.K.; Torfs, R.; Van Poppel, M. Exposure assessment of a cyclist to PM10 and ultrafine particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.; Int Panis, L.; Van Poppel, M.; Theunis, J.; Wets, G. Personal exposure to Black Carbon in transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; Theunis, J.; Van Poppel, M.; Berghmans, P. Monitoring PM10 and ultrafine particles in urban environments using mobile measurements. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poppel, M.; Peters, J.; Bleux, N. Methodology for setup and data processing of mobile air quality measurements to assess the spatial variability of concentrations in urban environments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.N.; Bi, J.; Austin, E.; Larson, T.V.; Marshall, J.D.; Sheppard, L. Characterization of Annual Average Traffic-Related Air Pollution Concentrations in the Greater Seattle Area from a Year-Long Mobile Monitoring Campaign. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11460–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekoninck, L.; Botteldooren, D.; Int Panis, L.; Hankey, S.; Jain, G.S.K.; Marshall, J. Applicability of a noise-based model to estimate in-traffic exposure to black carbon and particle number concentrations in different cultures. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkhoffs, J.; Hoek, G.; Gehring, U.; Vermeulen, R. Modelling nationwide spatial variation of ultrafine particles based on mobile monitoring. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Languille, B.; Gros, V.; Nicolas, B.; Honoré, C.; Kaufmann, A.; Zeitouni, K. Personal Exposure to Black Carbon, Particulate Matter and Nitrogen Dioxide in the Paris Region Measured by Portable Sensors Worn by Volunteers. Toxics 2022, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apparicio, P.; Carrier, M.; Gelb, J.; Seguin, A.M.; Kingham, S. Cyclists’ exposure to air pollution and road traffic noise in central city neighbourhoods of Montreal. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 57, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jereb, B.; Batkovic, T.; Herman, L.; Sipek, G.; Kovse, S.; Gregoric, A.; Mocnik, G. Exposure to Black Carbon during Bicycle Commuting-Alternative Route Selection. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, S.; Marshall, J.D. On-bicycle exposure to particulate air pollution: Particle number, black carbon, PM2.5, and particle size. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, J.A.; Turek, T.; Van Poppel, M.; Peters, J.; Hofman, J.; Kazak, J.K. Whether cycling around the city is in fact healthy in the light of air quality–Results of black carbon. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 337, 117694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonen, E.O.; Yli-Tuomi, T.; Turunen, A.W.; Taimisto, P.; Pennanen, A.; Vouitsis, I.; Samaras, Z.; Voogt, M.; Keuken, M.; Lanki, T. Particulates and noise exposure during bicycle, bus and car commuting: A study in three European cities. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targino, A.C.; Rodrigues, M.V.C.; Krecl, P.; Cipoli, Y.A.; Ribeiro, J.P.M. Commuter exposure to black carbon particles on diesel buses, on bicycles and on foot: A case study in a Brazilian city. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 25, 1132–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targino, A.C.; Krecl, P.; Danziger, J.E.; Segura, J.F.; Gibson, M.D. Spatial variability of on-bicycle black carbon concentrations in the megacity of Sao Paulo: A pilot study. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targino, A.C.; Gibson, M.D.; Krecl, P.; Rodrigues, M.V.C.; dos Santos, M.M.; Correa, M.D. Hotspots of black carbon and PM2.5 in an urban area and relationships to traffic characteristics. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, R.M.; Galvis, B.; Balachandran, S.; Ramos-Bonilla, J.P.; Sarmiento, O.L.; Gallo-Murcia, S.M.; Contreras, Y. Exposure to fine particulate, black carbon, and particle number concentration in transportation microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 157, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonati, G.; Ozgen, S.; Ripamonti, G.; Signorini, S. Variability of Black Carbon and Ultrafine Particle Concentration on Urban Bike Routes in a Mid-Sized City in the Po Valley (Northern Italy). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehn, U.; Almomani, A. Incentives and barriers for participation in community-based environmental monitoring and information systems: A critical analysis and integration of the literature. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 101, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharesifard, M.; Wehn, U.; van der Zaag, P. Context matters: A baseline analysis of contextual realities for two community-based monitoring initiatives of water and environment in Europe and Africa. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagler, G.S.; Yelverton, T.L.; Vedantham, R.; Hansen, A.D.; Turner, J.R. Postprocessing method to reduce noise while preserving high time resolution in Aethalometer real-time black carbon data. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, B.C.; Delp, W.W. Response to consumer and research grade indoor air quality monitors to residential sources of fine particles. Indoor Air 2018, 28, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, J.; Lazarov, B.; Stroobants, C.; Elst, E.; Smets, I.; Van Poppel, M. Portable Sensors for Dynamic Exposure Assessments in Urban Environments. State Sci. 2024, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; De Baets, B.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J. A spatio-temporal land use regression model to assess street-level exposure to black carbon. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 133, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaarrapport Lucht. Emissies 2000–2016 en Luchtkwaliteit 2017. Available online: https://www.vmm.be/bestanden/VMM-2017-LKT_TW.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Lefebvre, W.; Van Poppel, M.; Maiheu, B.; Janssen, S.; Dons, E. Evaluation of the RIO-IFDM-street canyon model chain. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooyberghs, H.; Lefebvre, W.; Vranckx, S.; Maiheu, B.; Trimpeneers, E.; Vanpoucke, C.; Janssen, S.; Meysman, F.; Fierens, F.; De Craemer, S. Validation and optimization of the ATMO-Street air quality model chain by means of a large-scale citizen-science dataset. Atmos. Environ. Int. J. 2022, 272, 118946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
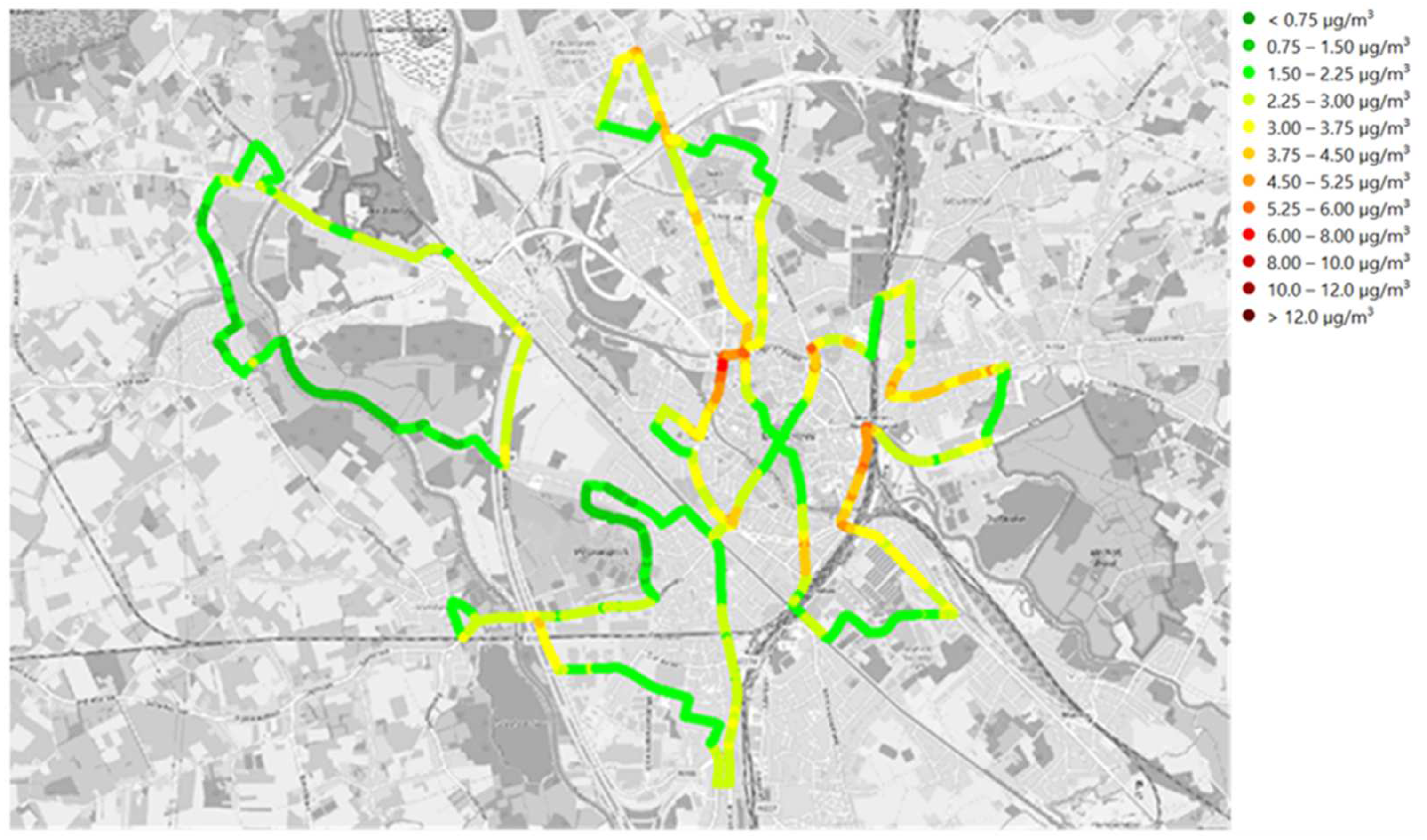
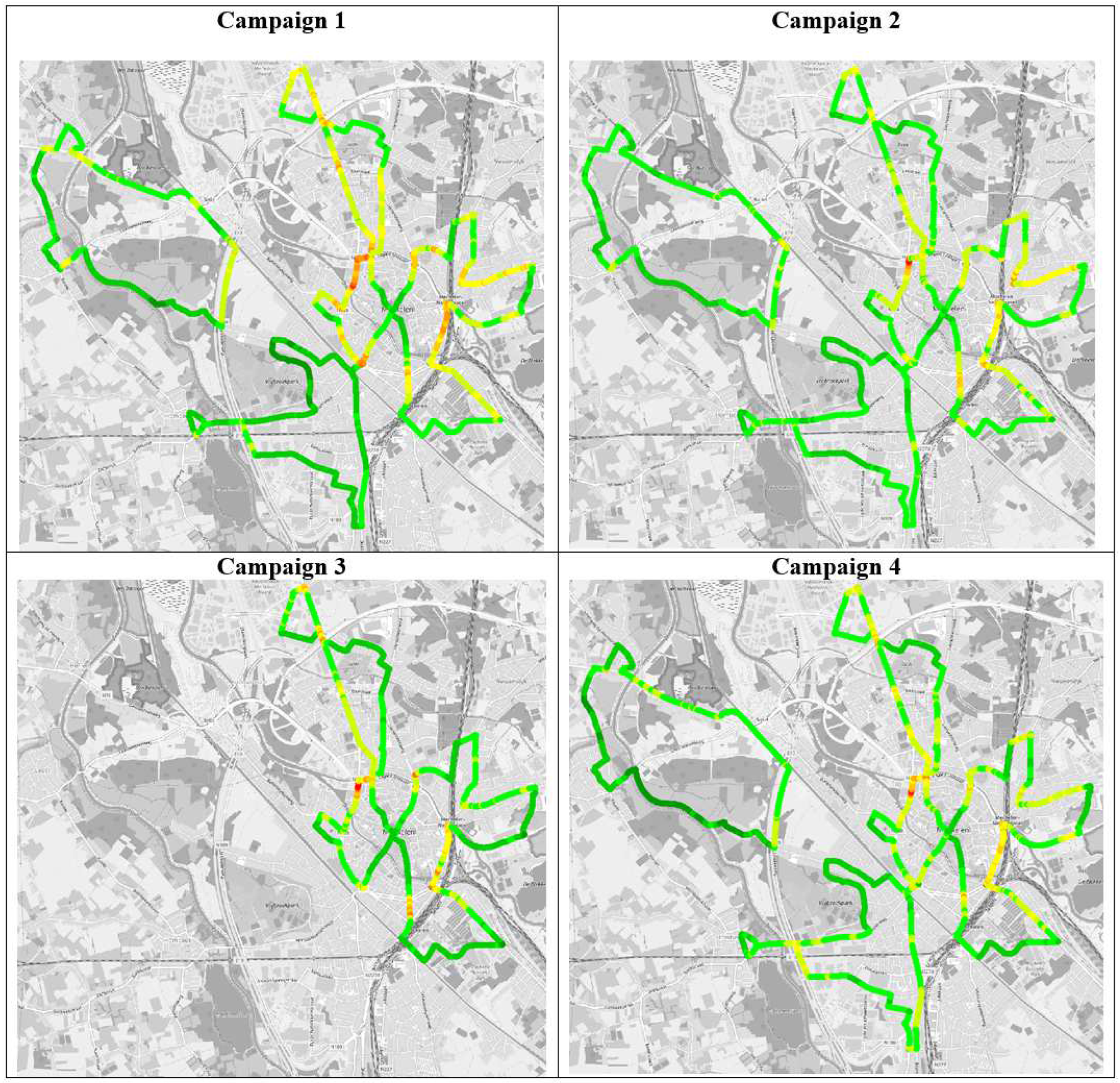
| Campaign 1 Morning/Evening | Campaign 2 Morning/Evening | Campaign 3 Morning/Evening | Campaign 4 Morning/Evening | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | 11/11 | 11/12 | 12/14 | 12/11 |
| East | 11/13 | 13/10 | 12/11 | 12/12 |
| South | 13/14 (a) | 10/9 | - | 11/10 |
| West | 11/13 | 11/11 | - | 12/12 |
| All | 12/13 | 13/12 | 14/14 | 12/12 |
| Concentration (µg m−3) | Rural (R) | Urban Background (UB) | Urban Traffic (UT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Campaign 1 (a) | 1.24 | 2.41 | 3.31 |
| (1.17) | (1.86) | (2.69) | |
| Campaign 2 | 1.30 | 1.83 | 2.41 |
| Campaign 3 | 0.55 | 0.90 | 1.38 |
| Campaign 4 | 0.80 | 1.82 | 2.48 |
| Annual average 2017 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 1.9 |
| Min. | First Qu. | Median | Mean | Third Qu. | Max. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campaign 1 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 12.4 |
| Campaign 2 | 1.3 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 10.5 |
| Campaign 3 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 6.2 |
| Campaign 4 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.1 | 8.3 |
| Ratio (Yearly av./Campaign av.) | R | UB | UT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Campaign 1 | 0.73 | 0.62 | 0.57 |
| Campaign 2 | 0.69 | 0.82 | 0.79 |
| Campaign 3 | 1.64 | 1.66 | 1.38 |
| Campaign 4 | 1.12 | 0.82 | 0.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Poppel, M.; Peters, J.; Vranckx, S.; Van Laer, J.; Hofman, J.; Vandeninden, B.; Vanpoucke, C.; Lefebvre, W. Exploring the Spatial Variability of Air Pollution Using Mobile BC Measurements in a Citizen Science Project: A Case Study in Mechelen. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070757
Van Poppel M, Peters J, Vranckx S, Van Laer J, Hofman J, Vandeninden B, Vanpoucke C, Lefebvre W. Exploring the Spatial Variability of Air Pollution Using Mobile BC Measurements in a Citizen Science Project: A Case Study in Mechelen. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(7):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070757
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Poppel, Martine, Jan Peters, Stijn Vranckx, Jo Van Laer, Jelle Hofman, Bram Vandeninden, Charlotte Vanpoucke, and Wouter Lefebvre. 2024. "Exploring the Spatial Variability of Air Pollution Using Mobile BC Measurements in a Citizen Science Project: A Case Study in Mechelen" Atmosphere 15, no. 7: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070757
APA StyleVan Poppel, M., Peters, J., Vranckx, S., Van Laer, J., Hofman, J., Vandeninden, B., Vanpoucke, C., & Lefebvre, W. (2024). Exploring the Spatial Variability of Air Pollution Using Mobile BC Measurements in a Citizen Science Project: A Case Study in Mechelen. Atmosphere, 15(7), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070757






